Supramolecular Control of Spin Crossover Phenomena Using Various Amphiphiles
Abstract
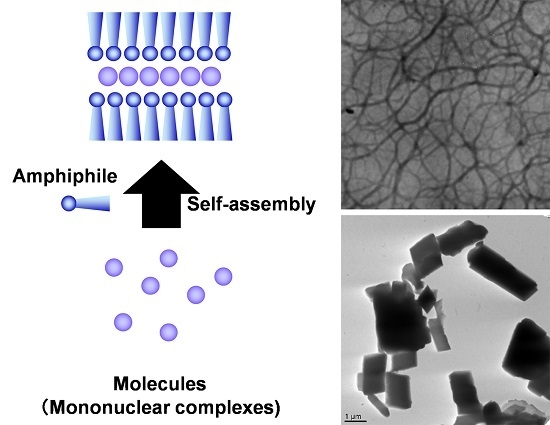
:1. Introduction
2. Self-Assembly of Amphiphilic and Lipophilic FeII 1,2,4-Triazole Complexes
2.1. 4-Alkylated 1,2,4-Triazole Complexes
2.2. 4R-1,2,4-Triazole Complexes with Lipid Amphiphiles
3. Self-Assembly of Metal Complexes with Diblock Copolypeptide Amphiphiles
3.1. Co-Terpyridine Complexes with Diblock Copolypeptide Amphiphiles
3.2. Fe-Complexes with Diblock Copolypeptide Amphiphiles
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gispert, J.R. Coordination Chemistry; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Lippard, S.J.; Berg, J.M. Principles of Bioinorganic Chemistry; University of Science Books: Mill Valley, CA, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Anastassopoulou, J.; Theophanaides, T. The role of metal ions in biological systems and medicine. In Bioinorganic Chemistry: An Inorganic Perspective of Life; Nato Science Series C; Kessissoglou, D.P., Ed.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1995; pp. 209–218. [Google Scholar]
- Anthony, A.; Desiraju, G.R.; Jetti, R.K.R.; Kuduva, S.S.; Madhavi, N.N.L.; Nangia, A.; Thaimattam, R.; Thallad, V.R. Crystal Engineering: Some Further Strategies. Cryst. Eng. 1998, 1, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, D.F.; Wennerström, H. The Colloidal Domain: Where Physics, Chemistry, Biology, and Technology Meet; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, M.N.; Chapman, D. Micelles, Monolayers and Biomembranes; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Lehn, J.M. Toward self-organization and complex matter. Science 2002, 295, 2400–2403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanan, G.S.; Volkmer, D.; Schubert, U.S.; Lehn, J.M.; Baum, G.; Fenske, D. Coordination Arrays: Tetranuclear Cobalt(II) Complexes with [2 × 2]-Grid Structure. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 1997, 36, 1842–1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehn, J.M. Supramolecular polymer chemistry—Scope and perspectives. Polym. Int. 2002, 51, 825–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujita, M.; Yazaki, J.; Ogura, K. Preparation of a macrocyclic polynuclear complex, [(en)Pd(4,4′-bpy)]4(NO3)8 (en = ethylenediamine, bpy = bipyridine), which recognizes an organic molecule in aqueous media. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1990, 112, 5645–5647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondo, M.; Yoshitomi, T.; Seki, K.; Matsuzaka, H.; Kitagawa, S. Three-dimensiona framework with channeling cavities for small molecules: {[M2(4,4′-bpy)3(NO3)4]·xH2O}n (M = Co, Ni, Zn). Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 1997, 36, 1725–1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Eddaoudi, M.; Groy, T.L.; Yaghi, O.M. Establishing microporosity in open metal–organic frameworks: Gas sorption isotherms for Zn(BDC) (BDC = 1,4-benzenedi carboxylate). J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1998, 120, 8571–8572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitesides, G.M.; Mathias, J.P.; Seto, C.T. Molecular self-assembly and nanochemistry: A chemical strategy for the synthesis of nanostructures. Science 1991, 254, 1312–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lehn, J.M. Supramolecular Chemistry: Concept and Perspectives; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Awod, J.L.; Davies, J.E.D.; MacNicol, D.M.; Vögtle, F.; Lehn, J.M. Comprehensive Supramolecular Chemistry; Pergamon: Oxford, UK, 1996; Volume 9. [Google Scholar]
- Whitesides, G.M.; Grzybowski, B. Self-assembly at all scales. Science 2002, 295, 2418–2421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armand, F.; Badoux, C.; Bonville, P.; Ruaudel-Teixier, A.; Kahn, O. Langmuir–Blodgett Films of Spin Transition Iron(II) Metalloorganic Polymers. 1. Iron(II) Complexes of Octadecyl-1,2,4-triazole. Langmuir 1995, 11, 3467–3472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soyer, H.; Dupart, E.; Gómez-García, C.J.; Mingotaud, C.; Delhaès, P. First Magnetic Observation of a Spin Crossover in a Langmuir–Blodgett Film. Adv. Mater. 1999, 11, 382–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soyer, H.; Mingotaud, C.; Boillot, M.L.; Delhaes, P. Spin Crossover of a Langmuir–Blodgett Film Based on an Amphiphilic Iron(II) Complex. Langmuir 1998, 14, 5890–5895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roubeau, O.; Agricole, B.; Clérac, R.; Ravaine, S. Triazole-Based Magnetic Langmuir–Blodgett Films: Paramagnetic to Spin-Crossover Behavior. J. Phys. Chem. B 2004, 108, 15110–15116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurth, D.G.; Lehmann, P.; Schütte, M. A route to hierarchical materials based on complexes of metallosupramolecular polyelectrolytes and amphiphiles. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 5704–5707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shibata, T.; Kimizuka, N.; Kunitake, T. Construction of mesoscopic supramolecular assemblies consisted of hydrophobic triazole derivative and Fe(II) ion. In Proceedings of the 76th CSJ National Meeting, Yokohama, Japan, 28 March 1999; CSJ: Tokyo, Japan, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Fujigaya, T.; Jiang, D.L.; Aida, T. Spin crossover properties of self-assembled iron(II) complexes with alkyl-tethered triazole ligands. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 125, 14690–14691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuroiwa, K.; Oda, N.; Kimizuka, N. Supramolecular solvatochromism. Effect of solvents on the self-assembly and charge transfer absorption characteristics of lipid-packaged, linear mixed valence platinum complexes. Sci. Tech. Adv. Mater. 2006, 7, 629–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuroiwa, K.; Shibata, T.; Takada, A.; Nemoto, N.; Kimizuka, N. Heat-set gel-like networks of lipophilic Co(II) triazole complexes in organic media and their thermochromic structural transitions. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 2016–2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuroiwa, K.; Kimizuka, N. Electrochemically controlled self-assembly of lipophilic FeII 1,2,4-triazole complexes in organic media. Chem. Lett. 2010, 39, 790–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuroiwa, K.; Shibata, T.; Sasaki, S.; Ohba, M.; Takahara, A.; Kunitake, T.; Kimizuka, N. Supramolecular control of spin crossover phenomena in lipophilic Fe(II) 1,2,4-triazole complexes. J. Polym. Sci. A Polym. Chem. 2006, 44, 5192–5202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kume, S.; Kuroiwa, K.; Kimizuka, N. Photo-responsive molecular wires of Fe(II) triazole complexes in organic media and light-induced morphological transformations. Chem. Commun. 2006, 42, 2442–2444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsukizono, H.; Kuroiwa, K.; Kimizuka, N. lipid-packaged linear iron(II) triazole complexes in solution: Controlled spin conversion via solvophobic self-assembly. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 5622–5623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsukizono, H.; Kuroiwa, K.; Kimizuka, N. Self-assembly-directed spin conversion of iron(II) 1,2,4-triazole complexes in solution and their effect on photorelaxation processes of fluorescent counter ions. Chem. Lett. 2008, 37, 446–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuroiwa, K.; Kikuchi, H.; Kimizuka, N. Spin crossover characteristics of nanofibrous FeII-1,2,4-triazole complexes in liquid crystals. Chem. Commun. 2010, 46, 1229–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noguchi, T.; Chikara, C.; Kuroiwa, K.; Kaneko, K.; Kimizuka, N. Controlled morphology and photoreduction characteristics of polyoxometalate(POM)/lipid complexes and the effect of hydrogen bonding at molecular interfaces. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 6455–6457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuroiwa, K.; Kimizuka, N. Self-assembly and functionalization of lipophilic metal–triazole complexes in various media. Polym. J. 2013, 45, 384–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuroiwa, K.; Yoshida, M.; Masaoka, S.; Kaneko, K.; Sakai, K.; Kimizuka, N. Self-assembly of tubular microstructures from mixed-valence metal complexes and their reversible transformation via external stimuli. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 656–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuroiwa, K. Dynamic self-assembly from mixed-valence metal complexes and their reversible transformations by external stimuli. Kobunshi Ronbunshu 2012, 69, 485–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuroiwa, K.; Arie, T.; Sakurai, S.; Hayami, S.; Deming, T.J. Supramolecular control of reverse spin transitions in cobalt(II) terpyridine complexes with diblock copolypeptide amphiphiles. J. Mater. Chem. C 2015, 3, 7779–7783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arie, T.; Otsuka, S.; Maekawa, T.; Takano, R.; Sakurai, S.; Deming, T.J.; Kuroiwa, K. Development of hybrid diblock copolypeptide amphiphile/magnetic metal complexes and their spin crossover with lower-critical-solution-temperature(LCST)-type transition. Polymer 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahn, O.; Martinez, C.J. Spin-transition polymers: From molecular materials toward memory devices. Science 1998, 279, 44–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahn, O. Chemistry and physics of supramolecular magnetic materials. Acc. Chem. Res. 2000, 33, 647–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kahn, O.; Köber, J.; Jay, C. Spin transition molecular materials for displays and data recording. Adv. Mater. 1992, 4, 718–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köber, J.; Codjovi, E.; Kahn, O.; Groliére, F.; Jay, C. A spin transition system with a thermal hysteresis at room temperature. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1993, 115, 9810–9811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haasnoot, J.G. Mononuclear, oligonuclear and polynuclear metal coordination compounds with 1,2,4-triazole derivatives as ligands. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2000, 200–202, 131–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haasnoot, J.G. 1,2,4-Triazoles as ligands for iron(II) high spin-low spin crossovers. In Magnetism: Supramolecular Function; Kahn, O., Ed.; Kluwer Academic Publications: Dordrecht, Netherlands, 1995; pp. 299–321. [Google Scholar]
- Vos, G.; le Fêbre, L.A.; de Graaff, R.A.G.; Haasnoot, J.G.; Reedijk, J. Unique highspin-low-spin transition of the central ion in a linear, trinuclear iron(II) triazole compound. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1983, 105, 1682–1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roubeau, O.; Gomez, M.A.; Balskus, E.; Kolnaar, J.J.A.; Haasnoot, J.G.; Reedijk, J. Spin-transition behaviour in chains of Fe(II) bridged by 4-substituted 1,2,4-triazoles carrying alkyl tails. New J. Chem. 2001, 25, 144–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujigaya, T.; Jiang, D.L.; Aida, T. Spin-crossover dendrimers: Generation numberdependent cooperativity for thermal transition. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 5484–5489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujigaya, T.; Jiang, D.L.; Aida, T. Spin-crossover physical gels: A quick thermoreversible response assisted by dynamic self-organization. Chem. Asian J. 2007, 2, 106–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seredyuk, M.; Gaspar, A.B.; Ksenofontov, V.; Reiman, S.; Galyametdinov, Y.; Haase, W.; Rentschler, E.; Gütlich, P. Room temperature operational thermochromic liquid crystals. Chem. Mater. 2006, 18, 2513–2519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayami., S.; Shigeyoshi, Y.; Akita, M.; Inoue, K.; Kato, K.; Osaka, K.; Takata, M.; Kawajiri, R.; Mitani, R.; Maeda, Y. Reverse spin transition triggered by a structural phase transition. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2005, 44, 4899–4903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayami, S.; Moriyama, R.; Shuto, A.; Maeda, Y.; Ohta, K.; Inoue, K. Spin transition at the mesophase transition temperature in a cobalt(II) compound with branched alkyl chains. Inorg. Chem. 2007, 46, 7692–7694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayami, S.; Murata, K.; Urakami, D.; Kojima, Y.; Akita, M.; Inoue, K. Dynamic structural conversion in a spin-crossover cobalt(II) compound with long alkyl chains. Chem. Commun. 2008, 48, 6510–6512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayami, S.; Kato, K.; Komatsu, Y.; Fuyuhiro, A.; Ohba, M. Unique spin transition and wide thermal hysteresis loop for a cobalt(II) compound with long alkyl chain. Dalton Trans. 2011, 40, 2167–2169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Komatsu, Y.; Kato, K.; Yamamoto, Y.; Kamihata, H.; Lee, Y.H.; Akita, F.; Kawata, S.; Hayami, S. Spin-crossover behaviors based on intermolecular interactions for cobalt(II) complexes with long alkyl chains. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2012, 16, 2769–2775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayami, S.; Nakaya, M.; Ohmagari, H.; Alao, A.S.; Nakamura, M.; Ohtani, R.; Yamaguchi, R.; Kuroda-Sowa, T.; Clegg, J.K. Spin crossover behaviors in solvated cobalt(II) compounds. Dalton Trans. 2015, 44, 9345–9348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pochan, D.J.; Pakstis, L.; Ozbas, B.; Nowak, A.P.; Deming, T.J. SANS and cryo-TEM study of self-assembled diblock copolypeptide hydrogels with rich nano-through microscale morphology. Macromolecules 2002, 35, 5358–5360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novak, A.P.; Breedveld, V.; Pakstis, L.; Ozbas, B.; Pine, D.J.; Pochan, D.; Deming, T.J. Rapidly recovering hydrogel scaffolds from self-assembling diblock copolypeptide amphiphiles. Nature 2002, 417, 424–428. [Google Scholar]
- Holowka, E.P.; Sun, V.Z.; Kamei, D.T.; Deming, T.J. Polyarginine segments in block copolypeptides drive both vesicular assembly and intracellular delivery. Nat. Mater. 2007, 6, 52–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.Y.; Song, B.; Ao, Y.; Nowak, A.P.; Abelowitz, R.B.; Korsak, R.A.; Havton, L.A.; Deming, T.J.; Sofroniew, M.V. Biocompatibility of amphiphilic diblock copolypeptide hydrogels in the central nervous system. Biomaterials 2009, 30, 2881–2898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barth, P.; Schemauss, G.; Specker, H. Complexes of iron (II) with substituted 2-pyridinalphenylimines. Z. Naturforsch 1972, 27, 1149–1154. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, H.H.; Kao, S.P.; Jean, Y.C. The effect of methyl substitution on the spinstate in solid bis(Methylsubstituted 2-pyridinalphenylimine) di(thiocyanato) iron(II). Transit. Met. Chem. 1986, 11, 405–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z. Light-induced excited spin-state trapping of the complex. Transit. Met. Chem. 1996, 21, 472–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Letard, J.F.; Guionneau, P.; Codjovi, E.; Lavastre, O.; Bravic, G.; Chasseau, D.; Kahn, O. Wide thermal hysteresis for the mononuclear spin-crossover compound cis-bis(thiocyanato)bis[N-(20-pyridylmethylene)-4-(phenylethynyl) anilino]iron(II). J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1997, 119, 10861–10862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oso, Y.; Ishida, T. Spin-crossover transition in a mesophase iron(II) thiocyanate complex chelated with 4-hexadecyl-N-(2-pyridylmethylene)aniline. Chem. Lett. 2009, 38, 604–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djukic, B.; Seda, T.; Gorelsky, S.I.; Lough, A.J.; Lemaire, M.T. p-Extended and sixcoordinate iron(II) complexes: Structures, magnetic properties, and the electrochemical synthesis of a conducting iron(II) metallopolymer. Inorg. Chem. 2011, 50, 7334–7343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ksenofontov, V.; Levchenko, G.; Spiering, H.; Gütlich, P.; Letard, J.F.; Bouhedja, Y.; Kahn, O. Spin crossover behavior under pressure of Fe(PM-L)2(NCS)2 compounds with substituted 20-pyridylmethylene 4-anilino ligands. Chem. Phys. Lett. 1998, 294, 545–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chujo, Y.; Tanaka, K. New polymeric materials based on element-blocks. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 2015, 88, 633–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]














© 2017 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kuroiwa, K. Supramolecular Control of Spin Crossover Phenomena Using Various Amphiphiles. Inorganics 2017, 5, 45. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics5030045
Kuroiwa K. Supramolecular Control of Spin Crossover Phenomena Using Various Amphiphiles. Inorganics. 2017; 5(3):45. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics5030045
Chicago/Turabian StyleKuroiwa, Keita. 2017. "Supramolecular Control of Spin Crossover Phenomena Using Various Amphiphiles" Inorganics 5, no. 3: 45. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics5030045
APA StyleKuroiwa, K. (2017). Supramolecular Control of Spin Crossover Phenomena Using Various Amphiphiles. Inorganics, 5(3), 45. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics5030045