Optimization of Electrochemical Performance of LiFePO4/C by Indium Doping and High Temperature Annealing
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. X-ray Diffraction
2.2. Electrical Conductivity
2.3. Morphology and Microstructure
2.4. X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy
2.5. 57Fe Mossbauer Spectroscopy
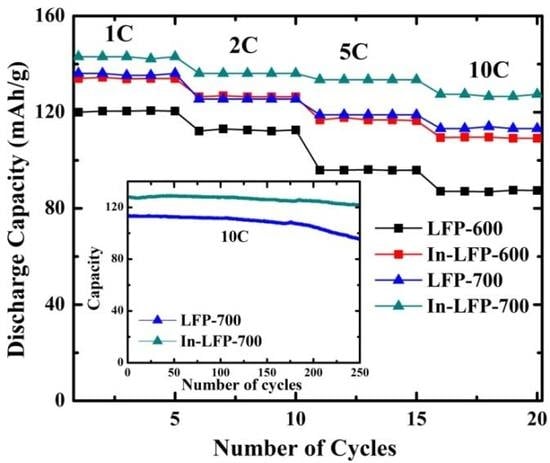
2.6. Electrochemical Measurements
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Synthesis Procedure
3.2. Characterization
3.3. Electrochemical Measurements
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Padhi, A.K.; Nanjundaswamy, K.S.; Goodenough, J.B. Phospho-olivines as Positive-Electrode Materials for Rechargeable Lithium Batteries. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1997, 144, 1188–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, S.; Yoon, C.S.; Cho, J. Synthesis of nanowire and hollow LiFePO4 cathodes for high-performance lithium batteries. Chem. Mater. 2008, 20, 4560–4564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delmas, C.; Maccario, M.; Croguennec, L.; Cras, F.L.; Weill, F. Lithium deintercalation in LiFePO4 nanoparticles via a domino-cascade model. Nat. Mater. 2008, 7, 665–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gibot, P.; Casas-Cabanas, M.; Laffont, L.; Levasseur, S.; Carlach, P.; Hamelet, S.; Tarascon, J.-M.; Masquelier, C. Room-temperature single-phase Li insertion/extraction in nanoscale LixFePO4. Nat. Mater. 2008, 7, 741–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, K.-F.; Tsay, S.-Y.; Hwang, B.-J. Synthesis and characterization of nano-sized LiFePO4 cathode materials prepared by a citric acid-based sol–gel route. J. Mater. Chem. 2004, 14, 2690–2695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.-H.; Goodenough, J.B. High-Rate LiFePO4 Lithium Rechargeable Battery Promoted by Electrochemically Active Polymers. Chem. Mater. 2008, 20, 7237–7241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Dahn, J.R. Reducing carbon in LiFePO4/C composite electrodes to maximize specific energy, volumetric energy, and tap density. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2002, 149, A1184–A1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doeff, M.M.; Wilcox, J.D.; Kostecki, R.; Lau, G. Optimization of carbon coatings on LiFePO4. J. Power Sources 2006, 163, 180–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dominko, R.; Bele, M.; Gaberscek, M.; Remskar, M.; Hanzel, D.; Pejovnik, S.; Jamnik, J. Impact of the Carbon coating thickness on the electrochemical performance of LiFePO4/C composites. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2005, 152, A607–A610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dominko, R.; Bele, M.; Goupil, J.-M.; Gaberscek, M.; Hanzel, D.; Arcon, I.; Jamnik, J. Wired porous cathode materials: A novel concept for synthesis of LiFePO4. Chem. Mater. 2007, 19, 2960–2969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Yin, S.-C.; Nazar, L.F. Approaching theoretical capacity of LiFePO4 at room temperature at high rates. Electrochem. Solid State Lett. 2001, 4, A170–A172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazzi, K.; Mandal, B.P.; Nazri, M.; Naik, V.M.; Garg, V.K.; Oliveira, A.C.; Vaishnava, P.P.; Nazri, G.A.; Naik, R. Effect of Surfactants on the Electrochemical Behavior of LiFePO4 Cathode Material for Lithium Ion Batteries. J. Power Sources 2014, 265, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagemaker, M.; Ellis, B.L.; Lützenkirchen-Hecht, D.; Mulder, F.M.; Nazar, L.F. Proof of Supervalent Doping in Olivine LiFePO4. Chem. Mater. 2008, 20, 6313–6315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, X.; Liang, G.; Wang, L.; Xu, S.; Zhao, X. Effect of Magnesium doping on electronic conductivity and electrochemical properties of LiFePO4. J. Power Sources 2008, 184, 543–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, X.; Huang, K.; Liu, S.; Wang, H.; Wang, H. Preparation and characterization of Na-doped LiFePO4/C composites as cathode materials for lithium-ion batteries. J. Power Sources 2010, 195, 4308–4312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, L.; Zhao, M.; Zhao, X.; Chai, Y. Preparation and electrochemical performance of Gd-doped LiFePO4/C composites. J. Power Sources 2012, 201, 253–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Tang, X.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, M.; Zhai, J. Effects of neodymium aliovalent substitution on the structure and electrochemical performance of LiFePO4. Electrochim. Acta 2010, 55, 5899–5904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, Y.-D.; Fey, G.T.-K.; Kao, H.-M. Physical and electrochemical properties of La-doped LiFePO4/C composites as cathode materials for lithium-ion batteries. J. Solid State Electrochem. 2008, 12, 815–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, S.-Y.; Bloking, J.T.; Chiang, Y.-M. Electronically conductive phospho-olivines as lithium storage electrodes. Nat. Mater. 2002, 1, 123–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Islam, M.S.; Driscoll, D.J.; Fisher, C.A.; Slater, P.R. Atomic-Scale Investigation of Defects, Dopants, and Lithium Transport in the LiFePO4 Olivine-Type Battery Material. Chem. Mater. 2005, 17, 5085–5092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.W.; Park, J.S.; Lee, K.S. Effect of Fe2P on the electron conductivity and electrochemical performance of LiFePO4 synthesized by mechanical alloying using Fe3+ raw material. J. Power Sources 2006, 163, 144–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Y.; Geng, Y.; Yu, J.; Zuo, X. High-capacity cathode for lithium-ion battery from LiFePO4/(C + Fe2P) composite nanofibers by electrospinning. J. Mater. Sci. 2014, 49, 504–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Lu, Y.; Yan, L.; Yang, Z.; Yang, R. Synthesis and effect of forming Fe2P phase on the physics and electrochemical properties of LiFePO4/C materials. J. Power Sources 2006, 160, 570–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herle, P.S.; Ellis, B.; Coombs, N.; Nazar, L.F. Nano-network electronic conduction in iron and nickel olivine phosphates. Nat. Mater. 2004, 3, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rho, Y.-H.; Nazar, L.F.; Perry, L.; Ryan, D. Surface Chemistry of LiFePO4 Studied by Mössbauer and X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy and Its Effect on Electrochemical Properties. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2007, 154, A283–A289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Gao, M.; Zhu, D.; Liu, Y.; Pan, H. Effects of carbon coating and iron phosphides on the electrochemical properties of LiFePO4/C. J. Power Sources 2008, 184, 444–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhindsa, K.; Kumar, A.; Nazri, G.; Naik, V.; Garg, V.; Oliveira, A.; Vaishnava, P.; Zhou, Z.; Naik, R. Enhanced electrochemical performance of LiFePO4/C nanocomposites due to in situ formation of Fe2P impurities. J. Solid State Electrochem. 2016, 20, 2275–2282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, B.; Ceder, G. Battery materials for ultrafast charging and discharging. Nature 2009, 458, 190–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castro, L.; Dedryvere, R.; El Khalifi, M.; Lippens, P.-E.; Bréger, J.; Tessier, C.; Gonbeau, D. The Spin-Polarized Electronic Structure of LiFePO4 and FePO4 Evidenced by in-Lab XPS. J. Phys. Chem. C 2010, 114, 17995–18000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, L.; Dedryvère, R.; Ledeuil, J.-B.; Bréger, J.; Tessier, C.; Gonbeau, D. Aging Mechanisms of LiFePO4//Graphite Cells Studied by XPS: Redox Reaction and Electrode/Electrolyte Interfaces. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2012, 159, A357–A363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, A.; Chung, S.-C.; Hinokuma, K. Optimized LiFePO4 for Lithium Battery Cathodes. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2001, 148, A224–A229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prince, A.; Mylswamy, S.; Chan, T.; Liu, R.; Hannoyer, B.; Jean, M.; Shen, C.; Huang, S.; Lee, J.; Wang, G. Investigation of Fe valence in LiFePO4 by Mössbauer and XANES spectroscopic techniques. Solid State Commun. 2004, 132, 455–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Cao, C.; Li, J. Enhanced electrochemical performance of carbon nanospheres–LiFePO4 composite by PEG based sol–gel synthesis. Electrochim. Acta 2010, 55, 3921–3926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Yang, L.; Chen, Y.; Wang, J.; Bewlay, S.; Liu, H. An investigation of polypyrrole-LiFePO4 composite cathode materials for lithium-ion batteries. Electrochim. Acta 2005, 50, 4649–4654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bard, A.J.; Faulkner, L.R.; Leddy, J.; Zoski, C.G. Electrochemical Methods: Fundamentals and Applications; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1980; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Dhindsa, K.; Mandal, B.P.; Bazzi, K.; Lin, M.; Nazri, M.; Nazri, G.; Naik, V.; Garg, V.; Oliveira, A.; Vaishnava, P.; et al. Enhanced electrochemical performance of graphene modified LiFePO4 cathode material for lithium ion batteries. Solid State Ion. 2013, 253, 94–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Sample | LiFePO4 (wt %) | * Fe2P (wt %) | Li3PO4 (wt %) | Crystallite Size (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LFP-600 * | 97.1 | 0 | 2.9 | 99 |
| In-LFP-600 | 98.6 | 0 | 1.4 | 97 |
| LFP-700 * | 93.2 | 3.6 | 3.2 | 102 |
| In-LFP-700 | 94.6 | 2.2 | 3.2 | 94 |
| Sample | Doublet 1 | Doublet 2 | Doublet 3 | Total | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IS | QS | % | IS | QS | % | IS | QS | % | Fe2P (%) | |
| In-LFP-600 | 1.22 | 2.97 | 92.2 | 0.61 | 0.43 | 7.8 | - | - | - | 7.8 |
| In-LFP-700 | 1.22 | 2.97 | 86.7 | 0.61 | 0.43 | 8.7 | 0.19 | 0.10 | 4.6 | 13.3 |
| Fe2+ | Fe(I) site of Fe2P | Fe(II) site of Fe2P | ||||||||
| Sample | LiFePO4 | Fe2P | Li3PO4 | Capacity (mAh·g−1) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mol % | wt % | mol % | wt % | mol % | wt % | Expected a | Measured at 1 C b | |
| LFP-600 * | 91.5 | 92.8 | 5.1 | 4.7 | 3.4 | 2.5 | 158 | 120 |
| In-LFP-600 | 87.7 | 89.5 | 7.4 | 6.8 | 4.9 | 3.7 | 152 | 134 |
| LFP-700 * | 75.8 | 78.9 | 14.5 | 13.7 | 9.7 | 7.4 | 134 | 136 |
| In-LFP-700 | 79.6 | 82.4 | 12.2 | 11.4 | 8.2 | 6.2 | 140 | 142 |
| Sample | Rct (Ω) | σ (Ω s1/2) | DLi (cm2·s−1) | Io (mA·g−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LFP-600 * | 158 | 142 | 4.5 × 10−14 | 163 |
| In-LFP-600 | 77 | 124 | 6.0 × 10−14 | 334 |
| LFP-700 * | 52 | 83 | 1.3 × 10−13 | 494 |
| In-LFP-700 | 32 | 82 | 1.4 × 10−13 | 802 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kumar, A.; Bashiri, P.; Mandal, B.P.; Dhindsa, K.S.; Bazzi, K.; Dixit, A.; Nazri, M.; Zhou, Z.; Garg, V.K.; Oliveira, A.C.; et al. Optimization of Electrochemical Performance of LiFePO4/C by Indium Doping and High Temperature Annealing. Inorganics 2017, 5, 67. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics5040067
Kumar A, Bashiri P, Mandal BP, Dhindsa KS, Bazzi K, Dixit A, Nazri M, Zhou Z, Garg VK, Oliveira AC, et al. Optimization of Electrochemical Performance of LiFePO4/C by Indium Doping and High Temperature Annealing. Inorganics. 2017; 5(4):67. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics5040067
Chicago/Turabian StyleKumar, Ajay, Parisa Bashiri, Balaji P. Mandal, Kulwinder S. Dhindsa, Khadije Bazzi, Ambesh Dixit, Maryam Nazri, Zhixian Zhou, Vijayendra K. Garg, Aderbal C. Oliveira, and et al. 2017. "Optimization of Electrochemical Performance of LiFePO4/C by Indium Doping and High Temperature Annealing" Inorganics 5, no. 4: 67. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics5040067
APA StyleKumar, A., Bashiri, P., Mandal, B. P., Dhindsa, K. S., Bazzi, K., Dixit, A., Nazri, M., Zhou, Z., Garg, V. K., Oliveira, A. C., Vaishnava, P. P., Naik, V. M., Nazri, G.-A., & Naik, R. (2017). Optimization of Electrochemical Performance of LiFePO4/C by Indium Doping and High Temperature Annealing. Inorganics, 5(4), 67. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics5040067