Synthesis of a Ru(II) Complex with a Naphthoquinone-Annelated Imidazole Ligand Exhibiting Proton-Responsive Redox and Luminescent Behavior
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
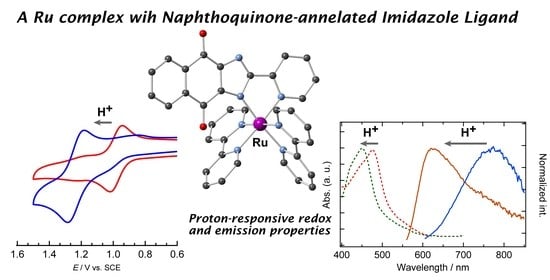
2.1. Structure of [Ru(L)(bpy)2](PF6)·AcOEt·0.5MeOH (1)
2.2. Electrochemistry
2.3. UV-Vis and Emission Spectra
2.4. Effects of Protonation on the Electronic Structure
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Microwave Reaction
3.3. Synthesis of [Ru(L)(bpy)2](PF6).2H2O (1.2H2O).
3.4. X-ray Crystallography
3.5. Physical Measurements
3.6. Cyclic Voltammetry
3.7. DFT Calculations
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cai, W.; Wang, J.; Chu, C.; Chen, W.; Wu, C.; Liu, G. Metal-Organic Framework-Based Stimuli-Responsive Systems for Drug Delivery. Adv. Sci. 2019, 6, 1801526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baroncini, M.; Silvi, S.; Credi, A. Photo- and Redox-Driven Artificial Molecular Motors. Chem. Rev. 2020, 120, 200–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- McConnell, A.J.; Wood, C.S.; Neelakandan, P.P.; Nitschke, J.R. Stimuli-Responsive Metal-Ligand Assemblies. Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 7729–7793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Z.; Yin, Y. Stimuli-Responsive Optical Nanomaterials. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, 1807061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurihara, M.; Nishihara, H. Azo- and Quinone-conjugated Redox Complexes Photo- and Proton-coupled Intramolecular Reactions Based on d-π Interaction. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2002, 226, 125–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mako, T.L.; Racicot, J.M.; Levine, M. Supramolecular Luminescent Sensors. Chem. Rev. 2019, 119, 322–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Sharma, A.; Singh, H.; Suating, P.; Kim, H.S.; Sunwoo, K.; Shim, I.; Gibb, B.C.; Kim, J.S. Revisiting Fluorescent Calixarenes: From Molecular Sensor to Smart Materials. Chem. Rev. 2019, 119, 9657–9721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, J.; Kim, K.; Ogoshi, T.; Yao, W.; Gibb, B.C. The Aqueous Supramolecular Chemistry of Cucurbit[n]urils, Pillar[n]arenes and deep-cavity Cavitands. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2017, 46, 2479–2496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Martinez-Manez, R.; Sancenon, F. Fluorogenic and Chromogenic Chemosensors and Reagents for Anions. Chem. Rev. 2003, 103, 4419–4476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, A.P.; Gunaratne, H.Q.N.; Gunnlaugsson, T.; Huxley, A.J.M.; McCoy, C.P.; Rademacher, J.T.; Rice, T.E. Signaling Recognition Events with Fluorescent Sensors and Switches. Chem. Rev. 1997, 97, 1515–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, F.; Chen, X.; Zhou, F.; Weng, L.-P.; Guo, L.-T.; Chen, M.; Chao, H.; Ji, L.-N. pH Responsive Luminescent Switches of Ruthenium(II) Complexes Containing Two Imidazole Groups: Synthesis, Spectroscopy, Electrochemistry and Theoretical Calculations. Inorg. Chim. Acta 2009, 362, 4960–4966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, H.; Hong, J.; Kim, S.Y.; Choi, I.; Park, M.J. A pH-Responsive Molecular Switch with Tricolor Luminescence. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 704–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, K.; Ohtsu, H.; Wada, T.; Kato, T.; Tanaka, K. Characterization of a Stable Ruthenium Complex with an Oxyl Radical. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 125, 6729–6739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kojima, T.; Hayashi, K.; Matsuda, Y. Structures and Properties of Ruthenium(II) Complexes of Pyridylamine Ligands with Oxygen-Bound Amide Moieties: Regulation of Structures and Proton-Coupled Electron Transfer. Inorg. Chem. 2004, 43, 6793–6804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Pietro, C.; Serroni, S.; Campagna, S.; Gandolfi, M.T.; Ballardini, R.; Fanni, S.; Browne, W.R.; Vos, J.G. Proton Controlled Intramolecular Communication in Dinuclear Ruthenium(II) Polypyridine Complexes. Inorg. Chem. 2002, 41, 2871–2878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Haga, M.; Ano, T.; Kano, K.; Yamabe, S. Proton-induced Switching of Metal-metal Interactions in Dinuclear Ruthenium and Osmium Complexes Bridged by 2,2′-Bis(2-pyridyl)bibenzimidazole. Inorg. Chem. 1991, 30, 3843–3849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huynh, M.H.V.; Meyer, T.J. Proton-Coupled Electron Transfer. Chem. Rev. 2007, 107, 5004–5064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Weinberg, D.R.; Gagliardi, C.J.; Hull, J.F.; Murphy, C.F.; Kent, C.A.; Westlake, B.C.; Paul, A.; Ess, D.H.; McCafferty, D.G.; Meyer, T.J. Proton-Coupled Electron Transfer. Chem. Rev. 2012, 112, 4016–4093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Chen, J.; Xu, B.; Wang, L.; Ma, S.; Dong, Y.; Li, B.; Ye, L.; Tian, W. Remarkable Fluorescence Change Based on the Protonation-deprotonation Control in Organic Crystals. Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 3878–3880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, O. Dynamic Molecular Crystals with Switchable Physical Properties. Nat. Chem. 2016, 8, 644–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gütlich, P.; Gaspar, A.B.; Garcia, Y. Spin State Switching in Iron Coordination Compounds. Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2013, 9, 342–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nihei, M. Molecular Prussian Blue Analogues: From Bulk to Molecules and Low-dimensional Aggregates. Chem. Lett. 2020, 49, 1206–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nihei, M.; Yanai, Y.; Hsu, I.-J.; Sekine, Y.; Oshio, H. A Hydrogen-Bonded Cyanide-Bridged [Co2Fe2] Square Complex Exhibiting a Three-Step Spin Transition. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 591–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sekine, Y.; Nihei, M.; Oshio, H. Dimensionally controlled assembly of an external stimuli-responsive [Co2Fe2] complex into supramolecular hydrogen-bonded networks. Chem. Eur. J. 2017, 23, 5193–5197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Y.-H.; Nihei, M.; Wen, G.-J.; Sun, B.-W.; Oshio, H. Ambient-Temperature Spin-State Switching Achieved by Protonation of the Amino Group in [Fe(H2Bpz2)2(bipy-NH2)]. Inorg. Chem. 2016, 55, 8147–8152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shiga, T.; Saiki, R.; Akiyama, L.; Kumai, R.; Natke, D.; Renz, F.; Cameron, J.; Newton, G.N.; Oshio, H. A Brønsted ligand molecular switch with five accessible states. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 5658–5662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takumi Nakanishi, T.; Hori, Y.; Sato, H.; Wu, S.Q.; Okazawa, A.; Kojima, N.; Yamamoto, T.; Einaga, Y.; Hayami, S.; Horie, Y.; et al. Observation of Proton Transfer Coupled Spin Transition and Trapping of Photoinduced Metastable Proton Transfer State in an Fe(II) Complex. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 14384–14393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueda, A.; Yamada, S.; Isono, T.; Kamo, H.; Nakao, A.; Kumai, R.; Nakao, H.; Murakami, Y.; Yamamoto, K.; Nishio, Y.; et al. Hydrogen-Bond-Dynamics-Based Switching of Conductivity and Magnetism: A Phase Transition Caused by Deuterium and Electron Transfer in a Hydrogen-Bonded Purely Organic Conductor Crystal. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 12184–12192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiga, T.; Kumamaru, R.; Newton, G.N.; Oshio, H. Heteroleptic Iron(II) Complexes with Naphthoquinone-type Ligands. Dalton Trans. 2020, 49, 1485–1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bar, M.; Deb, S.; Paul, A.; Baitalik, S. Stimuli-Responsive Luminescent Bis-Tridentate Ru(II) Complexes toward the Design of Functional Materials. Inorg. Chem. 2018, 57, 12010–12024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, P.; Ganguly, T.; Dasa, S.; Baitalik, S. pH-Responsive colorimetric, emission and redox switches based on Ru(II)-terpyridine complexes. Dalton Trans. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, L.; Moyses, C.A.; Ahlquist, M.S.G.; Sun, L. Highly Efficient and Robust Molecular Ruthenium Catalysts for Water Oxidation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 15584–15588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fujita, E. Photochemical Carbon Dioxide Reduction with Metal Complexes. Coord. Chem. Rev. 1999, 185–186, 373–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mede, T.; Jäger, M.; Schubert, U.S. High-Yielding Syntheses of Multifunctionalized RuII Polypyridyl-Type Sensitizer: Experimental and Computatinal Insight into Coordination. Inorg. Chem. 2019, 58, 9822–9832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.-W.; Chao, H.; Li, H.; Ji, L.-N. Syntheses, Characterization and DNA-binding Studies of Ruthenium(II) Terpyridine Complexes: [Ru(tpy)(PHBI)]2+ and [Ru(tpy)(PHNI)]2+. J. Inorg. Bio. 2003, 93, 247–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Zong, R.; Tseng, H.-W.; Thummel, R.P. Ru(II) Complexes of Tetradentate Ligands Related to 2,9-Di(pyrid-2′-yl)-1,10-phenanthroline. Inorg. Chem. 2008, 47, 990–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.-J.; Chao, H.; Tan, L.-F.; Yuan, Y.-X.; Wei, W.; Ji, L.-N. Interaction of Polypyridyl Ruthenium(II) Complex Containing Asymmetric Ligand with DNA. J. Inorg. Biol. 2005, 99, 530–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mardanya, S.; Mondal, D.; Baitalik, S. Biometallic Ru(II) and Os(II) Complexes Based on a Pyrene-bisimidazole spacer: Synthesis, Photophysics, Electrochemistry and Multisignalling DNA Binding Studies in the Near Infrared Region. Dalton Trans. 2017, 46, 17010–17024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haga, M. Synthesis and Protonation-deprotonation Reactions of Ruthesium(II) Complexes Containing 2,2′-Bibenzimidazole and Reelated Ligands. Inorg. Chim. Acta 1983, 75, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorsche, D.; Rommel, S.A.; Rau, S. Functional Dimming of Pincer-Shaped Bibenziimidazole-Ruthenium(II) Complexes with Improved Anion-Sensitive Luminescence. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2016, 2016, 1503–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parthiban, C.; Ciattini, S.; Chalazziand, L.; Elango, K.P. Colorimetric sensing of anions by Cu(II), Co(II), Ni(II) and Zn(II) complexes of naphthoquinone-imidazole hybrid-Influence of complex formation on selectivity and sensing medium. Sens. Actuators B 2016, 231, 768–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balzani, A.J.V.; Barigelletti, F.; Campagna, S.; Belser, P.; Zelewsky, A. Ru(II) Polypyridine Complexes: Photophysics, Photochemistry, Eletrochemistry, and Chemiluminescence. Coord. Chem. Rev. 1988, 84, 85–277. [Google Scholar]
- Hohloch, S.; Schweinfurth, D.; Sommer, M.G.; Weisser, F.; Deibel, N.; Ehret, F.; Sarkar, B. The Redox Series [Ru(bpy)2(L)]n, n = +3, +2, +1, 0, with L = Bipyridine, “Click” Derived Pyridyl-triazole or Bis-triazole: A Combined Structural, Electrochemical, Spectroelectrochemical and DFT investigation. Dalton Trans. 2014, 43, 4437–4450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sullivan, B.P.; Salmon, T.J.; Meyer, T.J. Mixed Phosphine 2,2′-Bipyridine Complexes of Ruthenium. Inorg. Chem. 1978, 17, 3334–3341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Jin, B. Investigation on Redox Mechanism of 1,4-Naphthoquinone by in situ FT-IR Spectroelectrochemistry. J. Electro. Chem. 2015, 756, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manivannan, R.; Satheshkumar, A.; Elango, K.P. Tuning of the H-bonding Ability of Imidazole N-H Towards the Colorimetric Sensing of Fluoride and Cyanide Ions as Their Sodium Salts in Water. New J. Chem. 2013, 37, 3152–3160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, L.; Zheng, Q.; Chen, Y.; Yang, R.; Yang, Y.; Li, Z.; Meng, X. Design, Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of Novel Naphthoquinone Derivatives as IDO1 Inhibitors. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 157, 423–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, W.; Yan, D. 2-Substituted-1-(2-morpholinoethyl)-1H-naphtho[2,3-d]imidazole-4,9-diones: Design, Synthesis and Antiproliferative Activity. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2018, 28, 2454–2458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G.M. SHELXL-2013. Program for the Refinement of Crystal Structures; University of Göttingen: Göttingen, Germany, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Sheldrick, G.M. SADABS; University of Göttingen: Göttingen, Germany, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Becke, A.D. Density-Functional Thermochemistry. III. The Role of Exact Exchange. J. Chem. Phys. 1993, 98, 5648–5652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Frisch, M.J.; Trucks, G.W.; Schlegel, H.B.; Scuseria, G.E.; Robb, M.A.; Cheeseman, J.R.; Scalmani, G.; Barone, V.; Petersson, G.A.; Nakatsuji, H.; et al. Gaussian 16, Revision A.03; Gaussian Inc.: Wallingford, CT, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Hay, P.J.; Wadt, W.R. Ab Initio Effective Core Potentials for Molecular Calculations. Potentials for K and Au Including the Outermost Core Orbitals. J. Chem. Phys. 1985, 82, 299–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hay, P.J.; Wadt, W.R. Ab Initio Effective Core Potentials for Molecular Calculations. Potentials for the Transition Metal Atoms Sc to Hg. J. Chem. Phys. 1985, 82, 270–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wadt, W.R.; Hay, P.J. Ab Initio Effective Core Potentials for Molecular Calculations. Potentials for Main Group Elements Na to Bi. J. Chem. Phys. 1985, 82, 284–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barone, V.; Cossi, M. Quantum Calculation of Molecular Energies and Energy Gradients in Solution by a Conductor Solvent Model. J. Phys. Chem. A 1998, 102, 1995–2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Compound | [Ru(L)(bpy)2](PF6).AcOEt.0.5MeOH |
|---|---|
| Formula | C40.5H35F6N7O4.5PRu |
| M/g mol–1 | 937.79 |
| Crystal system | Monoclinic |
| Space group | P21/c |
| a/Å | 8.431(3) |
| b/Å | 35.524(14) |
| c/Å | 13.404(5) |
| β/deg. | 99.315(4) |
| Volume/Å3 | 3962(3) |
| Z | 4 |
| T/K | 100(2) |
| ρcalc/g cm–3 | 1.571 |
| μ mm–1 | 0.518 |
| Data/Parameters | 9017/553 |
| Rint | 0.0999 |
| GOF | 1.032 |
| R1 (>2σ(I)) | 0.0773 |
| wR2 (>2σ(I)) | 0.1962 |
| E1/2/V | Ru(II)/Ru(III) | L−/L•2− | bpy/bpy•− | bpy/bpy•− | bpy/bpy•− | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | +0.98 (0.08) | −1.13 (0.08) | −1.53 (0.09) | −1.71 (0.08) | ||
| HL/HL•− | ||||||
| HL | −0.63 (0.16) | |||||
| Ru(II)/Ru(III) | bpy/bpy•− | bpy/bpy•− | bpy/bpy•− | |||
| [Ru(bpy)3]2 + | + 1.25 | −1.36 | −1.52 | −1.76 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shiga, T.; Tachibana, M.; Oshio, H.; Nihei, M. Synthesis of a Ru(II) Complex with a Naphthoquinone-Annelated Imidazole Ligand Exhibiting Proton-Responsive Redox and Luminescent Behavior. Inorganics 2021, 9, 24. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics9040024
Shiga T, Tachibana M, Oshio H, Nihei M. Synthesis of a Ru(II) Complex with a Naphthoquinone-Annelated Imidazole Ligand Exhibiting Proton-Responsive Redox and Luminescent Behavior. Inorganics. 2021; 9(4):24. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics9040024
Chicago/Turabian StyleShiga, Takuya, Minami Tachibana, Hiroki Oshio, and Masayuki Nihei. 2021. "Synthesis of a Ru(II) Complex with a Naphthoquinone-Annelated Imidazole Ligand Exhibiting Proton-Responsive Redox and Luminescent Behavior" Inorganics 9, no. 4: 24. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics9040024
APA StyleShiga, T., Tachibana, M., Oshio, H., & Nihei, M. (2021). Synthesis of a Ru(II) Complex with a Naphthoquinone-Annelated Imidazole Ligand Exhibiting Proton-Responsive Redox and Luminescent Behavior. Inorganics, 9(4), 24. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics9040024