In Vitro Trueness and Precision of Intraoral Scanners in a Four-Implant Complete-Arch Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- 1.
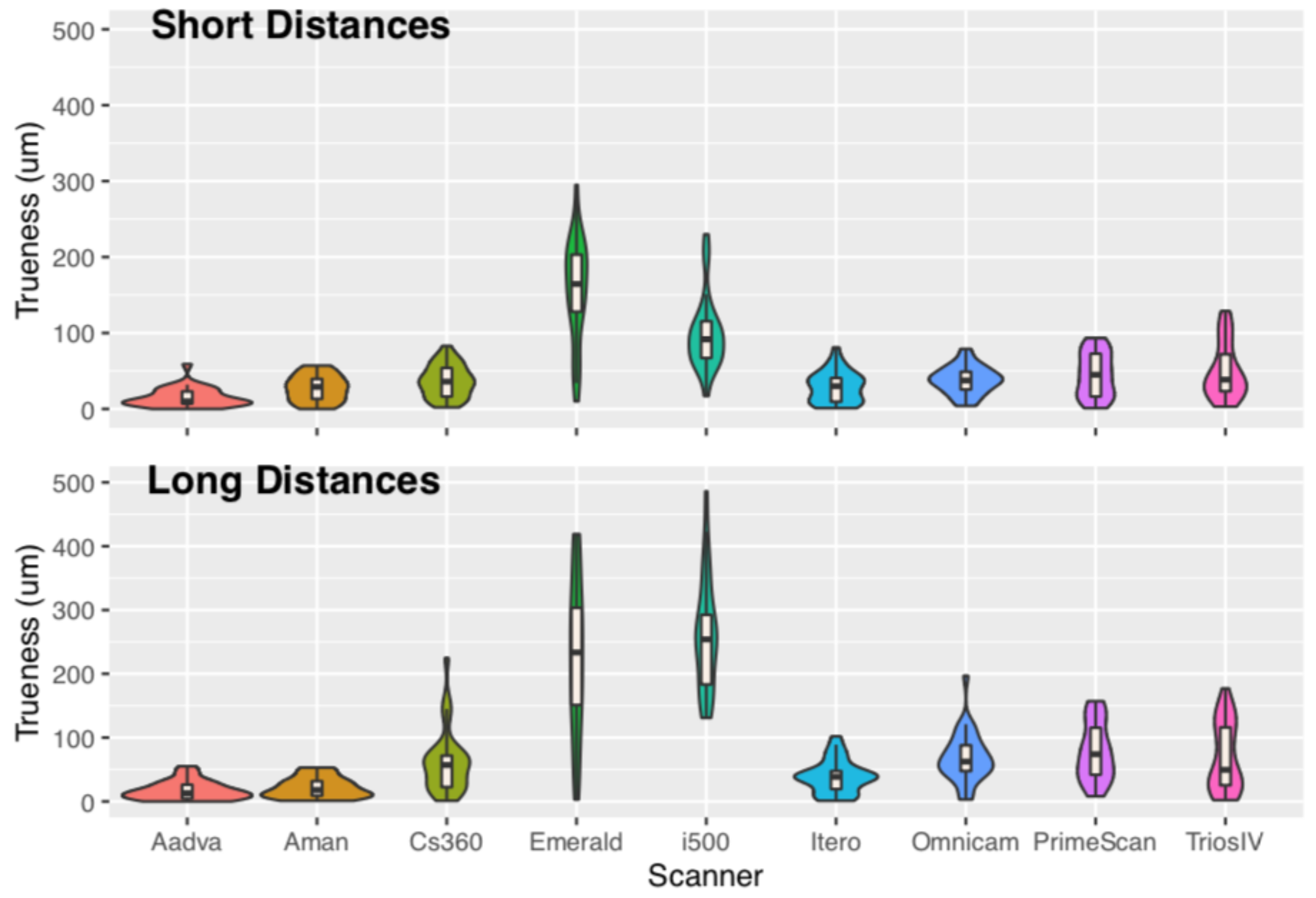
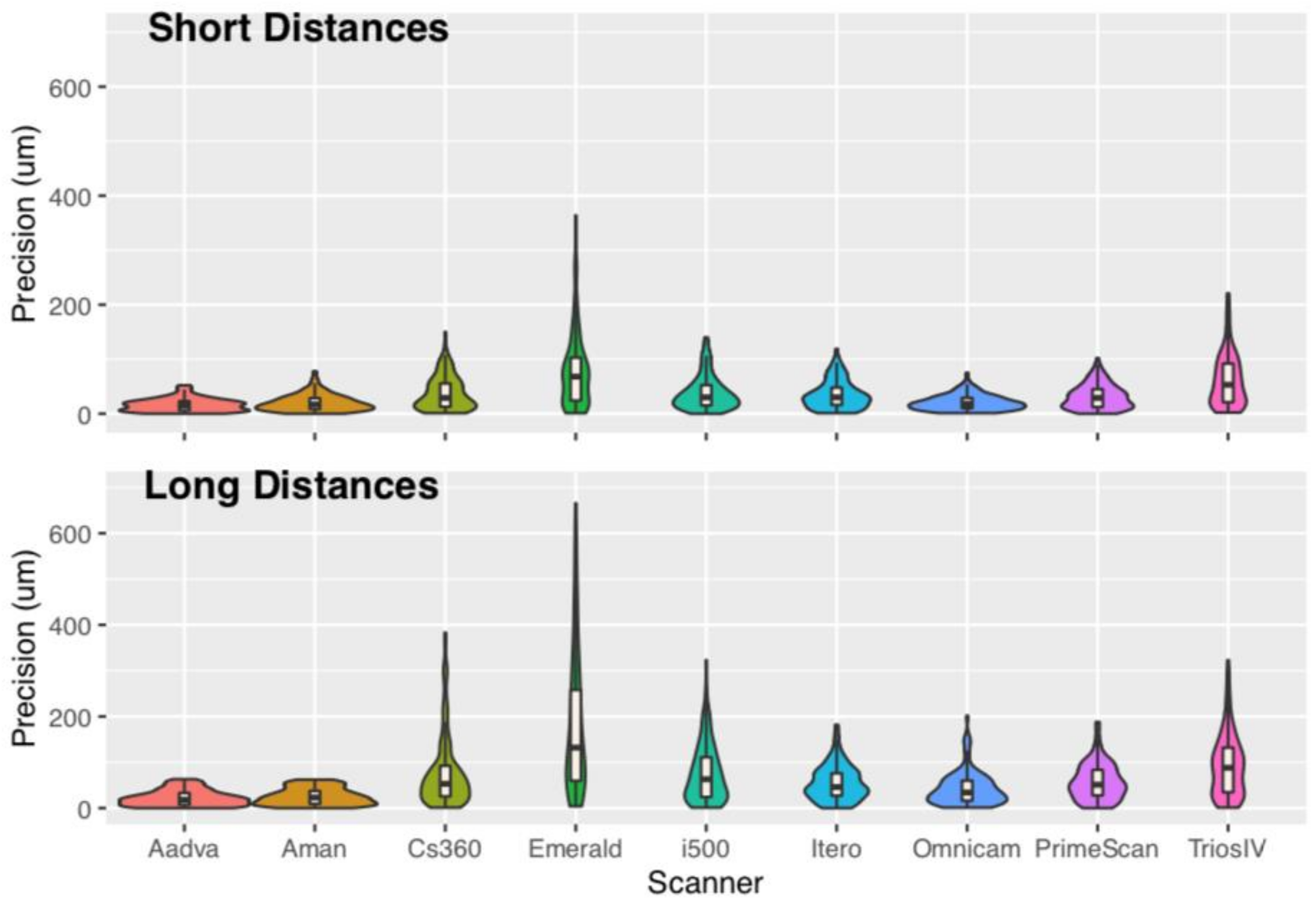
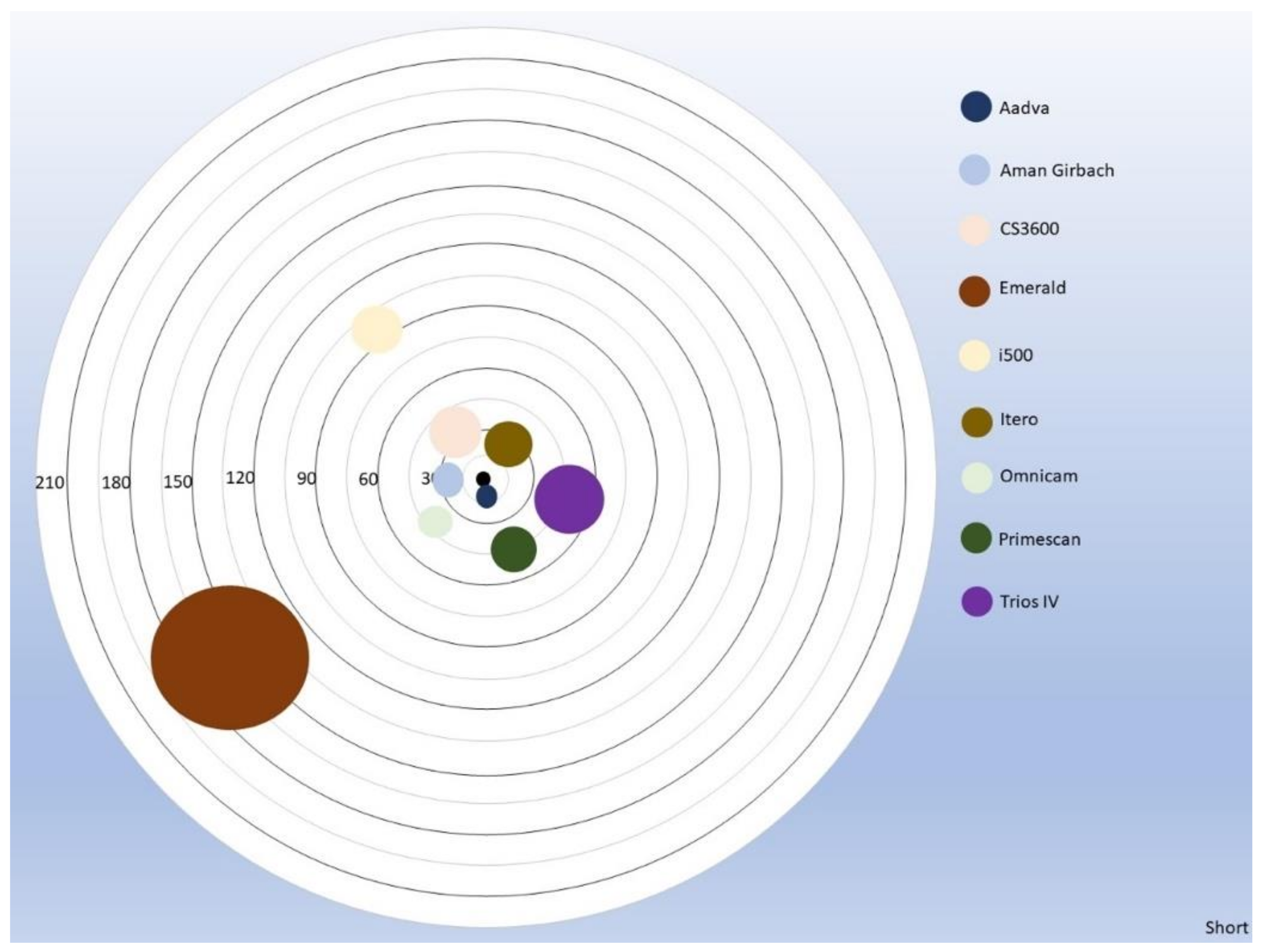
- Laboratory scanners have the best trueness and precision compared to all IOSs for long distances. Only iTero had comparable trueness with one laboratory scanner in short and long distances.
- 2.
- For short distances, CS360, Omnicam, Primescan, and TRIOS 4 had similar trueness to one laboratory scanner. From those, only Omnicam and Primescan had similar precision as the same laboratory scanner.
- 3.
- Most IOSs seem to work better in smaller distances and are less reliable in cross-arch distances.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Joda, T.; Brägger, U. Patient-centered outcomes comparing digital and conventional implant impression procedures: A randomized crossover trial. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2016, 27, 185–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.J.; Macarthur, R.X., IV; Gallucci, G.O. An evaluation of student and clinician perception of digital and conventional implant impressions. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2013, 110, 420–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gjelvold, B.; Chrcanovic, B.R.; Korduner, E.K.; Collin-Bagewitz, I.; Kisch, J. Intraoral digital impression technique compared to conventional impression technique. A randomized clinical trial. J. Prosthodont. 2016, 25, 282–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mangano, F.G.; Admakin, O.; Bonacina, M.; Lerner, H.; Rutkunas, V.; Mangano, C. Trueness of 12 intraoral scanners in the full-arch implant impression: A comparative in vitro study. BMC Oral Health 2020, 20, 263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, R.J.-Y.; Benic, G.I.; Park, J.-M. Trueness of digital intraoral impression in reproducing multiple implant position. PLoS ONE 2019, 19, e0222070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rutkūnas, V.; Gečiauskaitė, A.; Jegelevičius, D.; Vaitiekūnas, M. Accuracy of digital implant impressions with intraoral scanners. A systematic review. Eur. J. Oral Implantol. 2017, 1, 101–120. [Google Scholar]
- ISO 5725-1; Accuracy (Trueness and Precision) of Measurement Methods and Results—Part 1: General Principles and Definitions. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 1994.
- ISO 5725-2; Accuracy (Trueness and Precision) of Measurement Methods and Results—Part 2: Basic Method for the Determination of Repeatability and Reproducibility of a Standard Measurement Method. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 1994.
- Joda, T.; Bragger, U.; Zitzmann, N.U. CAD/CAM implant crowns in a digital workflow: Five-year follow-up of a prospective clinical trial. Clin. Implant Dent. Relat. Res. 2019, 2, 169–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papaspyridakos, P.; Gallucci, G.O.; Chen, C.J.; Hanssen, S.; Naert, I.; Vandenberghe, B. Digital versus conventional implant impressions for edentulous patients: Accuracy outcomes. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2016, 27, 465–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, S.; Weber, H.P.; Finkelman, M.; El Rafie, K.; Kudara, Y.; Papaspyridakos, P. Digital vs. conventional full-arch implant impressions: A comparative study. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2017, 28, 1360–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alikhasi, M.; Siadat, H.; Nasirpour, A.; Hasanzade, M. Three-Dimensional Accuracy of Digital Impression versus Conventional Method: Effect of Implant Angulation and Connection Type. Int. J. Dent. 2018, 4, 3761750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, P.; Herrero-Climent, M.; Díaz-Castro, C.; Ríos-Santos, J.V.; Padrós, R.; Mur, J.G.; Falcão, C. Accuracy of Implant Casts Generated with Conventional and Digital Impressions-An In Vitro Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 27, 1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, M.Y.; Yee, S.H.X.; Wong, K.M.; Tan, Y.H.; Tan, K.B.C. Comparison of Three-Dimensional Accuracy of Digital and Conventional Implant Impressions: Effect of Interimplant Distance in an Edentulous Arch. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implants 2019, 34, 366–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flügge, T.V.; Att, W.; Metzger, M.C.; Nelson, K. Precision of Dental Implant Digitization Using Intraoral Scanners. Int. J. Prosthodont. 2016, 29, 277–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giménez, B.; Özcan, M.; Martínez-Rus, F.; Pradíes, G. Accuracy of a digital impression system based on parallel confocal laser technology for implants with consideration of operator experience and implant angulation and depth. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implants 2014, 29, 853–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangano, F.G.; Veronesi, G.; Hauschild, U.; Mijiritsky, E.; Mangano, C. Trueness and Precision of Four Intraoral Scanners in Oral Implantology: A Comparative in Vitro Study. PLoS ONE 2016, 29, e0163107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imburgia, M.; Logozzo, S.; Hauschild, U.; Veronesi, G.; Mangano, C.; Mangano, F.G. Accuracy of four intraoral scanners in oral implantology: A comparative in vitro study. BMC Oral Health 2017, 17, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sami, T.; Goldstein, G.; Vafiadis, D.; Absher, T. An in vitro 3D evaluation of the accuracy of 4 intraoral optical scanners on a 6-implant model. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2020, 124, 748–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papazoglou, E.; Wee, A.G.; Carr, A.B.; Urban, I.; Margaritis, V. Accuracy of complete-arch implant impression made with occlusal registration material. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2020, 123, 143–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michalakis, K.X.; Asar, N.V.; Kapsampeli, V.; Magkavali-Trikka, P.; Pissiotis, A.L.; Hirayama, H. Delayed linear dimensional changes of five high strength gypsum products used for the fabrication of definitive casts. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2012, 108, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 10360-2; Geometrical Product Specifications (GPS)—Acceptance and Reverification Tests for Coordinate Measuring Machines (CMM)—Part 2: CMMs Used for Measuring Linear Dimensions. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2009.
- ISO 10360-5; Geometrical Product Specifications (GPS)—Acceptance and Reverification Tests for Coordinate Measuring Machines (CMM)—Part 5: CMMs Using Single and Multiple Stylus Contacting Probing Systems. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2010.
- ISO 10360-6:2001; Geometrical Product Specifications (GPS)—Acceptance and Reverification Tests for Coordinate Measuring Machines (CMM)—Part 6: Estimation of Errors in Computing Gaussian Associated Features. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2001.
- BS 7172; Guide to Assessment of Position, Size and Departure from Nominal Form of Geometric Features. British Standards Institution (BSI): London, UK, 1989.
- Bates, D.; Mächler, M.; Bolker, B.; Walker, S. Fitting Linear Mixed-Effects Models Using lme4. J. Stat. Softw. 2015, 67, 1–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenth, R. Emmeans: Estimated Marginal Means, aka Least-Squares Means. R Package Version 1.4.2. 2019. Available online: https://CRAN.Rproject.org/package=emmean (accessed on 3 June 2022).
- Lim, J.H.; Mangal, U.; Nam, N.E.; Choi, S.H.; Shim, J.S.; Kim, J.E. A Comparison of Accuracy of Different Dental Restorative Materials between Intraoral Scanning and Conventional Impression-Taking: An In Vitro Study. Materials 2021, 14, 2060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dutton, E.; Ludlow, M.; Mennito, A.; Kelly, A.; Evans, Z.; Culp, A.; Kessler, R.; Renne, W. The effect different substrates have on the trueness and precision of eight different intraoral scanners. J. Esthet. Restor. Dent. 2020, 32, 204–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, Z.; Yao, X.S.; Yao, H.; Liang, Y.; Liu, T.; Li, Y.; Wang, G.; Lan, S. Measurement of the refractive index of human teeth by optical coherence tomography. J. Biomed. Opt. 2009, 14, 034010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bocklet, C.; Renne, W.; Mennito, A.; Bacro, T.; Latham, J.; Evans, Z.; Ludlow, M.; Kelly, A.; Nash, J. Effect of scan substrates on accuracy of 7 intraoral digital impression systems using human maxilla model. Orthod. Craniofac. Res. 2019, 22, 168–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wulfman, C.; Naveau, A.; Rignon-Bret, C. Digital scanning for complete-arch implant-supported restorations: A systematic review. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2020, 124, 161–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Güth, J.F.; Edelhoff, D.; Schweiger, J.; Keul, C. A new method for the evaluation of the accuracy of full-arch digital impressions in vitro. Clin. Oral Investig. 2016, 20, 1487–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braian, M.; Wennerberg, A. Trueness and precision of 5 intraoral scanners for scanning edentulous and dentate complete-arch mandibular casts: A comparative in vitro study. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2019, 122, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ender, A.; Attin, T.; Mehl, A. In vivo precision of conventional and digital methods of obtaining complete-arch dental impressions. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2016, 115, 313–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehl, A.; Reich, S.; Beuer, F.; Güth, J.F. Accuracy, trueness, and precision—A guideline for the evaluation of these basic values in digital dentistry. Int. J. Comput. Dent. 2021, 24, 341–352. [Google Scholar]
- Revilla-León, M.; Fogarty, R.; Barrington, J.J.; Zandinejad, A.; Özcan, M. Influence of scan body design and digital implant analogs on implant replica position in additively manufactured casts. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2020, 124, 202–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motel, C.; Kirchner, E.; Adler, W.; Wichmann, M.; Matta, R.E. Impact of Different Scan Bodies and Scan Strategies on the Accuracy of Digital Implant Impressions Assessed with an Intraoral Scanner: An In Vitro Study. J. Prosthodont. 2020, 29, 309–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, Y.; Tam, J.M.Y.; Tsoi, J.K.H.; Lam, W.Y.H.; Pow, E.H.N. Reproducibility of laboratory scanning of multiple implants in complete edentulous arch: Effect of scan bodies. J. Dent. 2020, 96, 103329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nulty, A.B. A Comparison of Full Arch Trueness and Precision of Nine Intra-Oral Digital Scanners and Four Lab Digital Scanners. Dent. J. 2021, 9, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, B.-H.; Son, K.; Lee, K.-B. Accuracy of Five Intraoral Scanners and Two Laboratory Scanners for a Complete Arch: A Comparative In Vitro Study. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowak, R.; Wesemann, C.; Robben, J.; Muallah, J.; Bumann, A. An in-vitro study comparing the accuracy of? full-arch casts digitized with desktop scanners. Quintessence Int. 2017, 20, 667–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diker, B.; Tak, Ö. Comparing the accuracy of six intraoral scanners on prepared teeth and effect of scanning sequence. J. Adv. Prosthodont. 2020, 12, 299–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jemt, T. Failures and complications in 391 consecutively inserted fixed prostheses supported by Brånemark implants in edentulous jaws: A study of treatment from the time of prosthesis placement to the first annual checkup. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implants 1991, 6, 270–276. [Google Scholar]
- Orejas-Perez, J.; Gimenez-Gonzalez, B.; Ortiz-Collado, I.; Thuissard, I.J.; Santamaria-Laorden, A. In Vivo Complete-Arch Implant Digital Impressions: Comparison of the Precision of Three Optical Impression Systems. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 3, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alpkılıç, D.Ş.; Değer, S.İ. In Vitro Comparison of the Accuracy of Conventional Impression and Four Intraoral Scanners in Four Different Implant Impression Scenarios. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implants 2022, 37, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knechtle, N.; Wiedemeier, D.; Mehl, A.; Ender, A. Accuracy of digital complete-arch, multi-implant scans made in the edentulous jaw with gingival movement simulation: An in vitro study. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2022, 128, 468–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manazza, F.; La Rocca, S.; Nagni, M.; Chirico, L.; Cattoni, F. A simplified digital workflow for the prosthetic finishing of implant rehabilitations: A case report. J. Biol. Regul. Homeost. Agents 2021, 35 (Suppl. S1), 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kosago, P.; Ungurawasaporn, C.; Kukiattrakoon, B. Comparison of the accuracy between conventional and various digital implant impressions for an implant-supported mandibular complete arch-fixed prosthesis: An in vitro study. J. Prosthodont. 2022, 29, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Name | Manufacturer | Acquisition Technology | Output Files |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aadva | GC Corporation, Tokyo, Japan | High end dual camera system with structured blue led light | open STL or PLY data. |
| ceramill map 600 | Amann Girrbach AG, Koblach, Austria | HD scan via 3D sensor with blue light technology | open STL or PLY data. |
| Cs3600 | Carestream Health, Inc., Rochester, NY, USA | LED light scanner -Active Speed 3D Video | csz (proprietary format), ply and stl (open formats) |
| Emerald | Planmeca Oy, Vantaa, Finland | Red, green and blue lasers- Projected Pattern Triangulation | 3oxz (proprietary format), ply and stl (open formats) |
| i500 | Medit, Seoul, South Korea | 3D in Motion Video Technology | obj, ply and stl (open formats) |
| iTero | Align Technologies Inc., Milpitas, CA, USA | Parallel Confocal Microscopy | 3ds (proprietary format); ply and stl (open formats) |
| Omnicam | Sirona Dental Systems GmbH, Bensheim, Germany | Optical Triangulation and Confocal Microscopy | cs3, sdt, cdt, idt (proprietary format) with possibility to export .stl files (open format) with Cerec Connect® |
| PrimeScan | Sirona Dental Systems GmbH, Bensheim, Germany | High-resolution Sensors and Shortwave Light with Optical High Frequency Contrast Analysis for Dynamic Deep Scan (20 mm) | dxd (proprietary format) with possibility to export .stl files (open format) with Cerec Connect® |
| Trios 4 | 3-Shape A/S, Copenhagen, Denmark | Confocal Microscopy and Ultrafast Optical Scanning | dcm (proprietary format), with possibility to export stl files (open formats) with Trios on Dental Desktop® |
| Response: Abs Difference Trueness | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sum of Squares | df | F Value | p-Value | |
| (Intercept) | 1.670 | 1 | 1414.940 | <0.001 |
| Scanner | 43.686 | 8 | 662.080 | <0.001 |
| Distance Group | 0.0007 | 1 | 0.0804 | 0.777 |
| Scanner: Distance Group | 0.4028 | 8 | 61.041 | <0.001 |
| Residuals | 43.054 | 522 | ||
| Response: Abs Difference Precision | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sum of Squares | df | F Value | p-Value | |
| (Intercept) | 9.0063 | 1 | 775.760 | <0.001 |
| Scanner | 6.9022 | 8 | 74.315 | <0.001 |
| Distance Group | 0.0349 | 1 | 3.010 | 0.083 |
| Scanner: Distance Group | 0.6018 | 8 | 6.479 | <0.001 |
| Residuals | 28.0026 | 2412 | ||
| Scanner | Distance | AbsT Median | AbsT IQR | AbsT Mean (SD) | Statistical Grouping |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aadva | short | 10.0 | 16.0 | 15.0 (13) | A |
| Aman | short | 29.0 | 26.3 | 27.1 (17) | AB |
| Cs3600 | short | 36.0 | 37.8 | 36.5 (21) | B |
| Emerald | short | 164.5 | 75.3 | 157.7 (67) | D |
| i500 | short | 91.5 | 48.5 | 98.5 (48) | C |
| iTero | short | 30.0 | 31.3 | 28.9 (20) | AB |
| Omnicam | short | 37.5 | 23.5 | 38.0 (18) | B |
| Primescan | short | 45.0 | 56.5 | 45.2 (29) | B |
| Trios 4 | short | 38.5 | 48.8 | 49.6 (36) | B |
| Aadva | long | 13.0 | 21.8 | 17.2 (15) | A |
| Aman | long | 18.0 | 22.8 | 21.6 (16) | AB |
| Cs3600 | long | 57.0 | 49.3 | 61.4 (49) | CD |
| Emerald | long | 233.5 | 152.5 | 226.3 (120) | E |
| i500 | long | 254.0 | 109.3 | 259.7 (87) | E |
| iTero | long | 38.5 | 28.3 | 39.0 (26) | BC |
| Omnicam | long | 62.5 | 40.5 | 68.7 (39) | D |
| Primescan | long | 74.0 | 73.8 | 77.4 (45) | D |
| Trios 4 | long | 49.5 | 90.8 | 69.3 (53) | CD |
| Scanner | Distance | AbsT Median | AbsT IQR | AbsT Mean (SD) | Statistical Grouping |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aadva | short | 15.0 | 17.0 | 16.2 (12) | A |
| Aman | short | 17.0 | 20.0 | 20.0 (15) | AB |
| Cs3600 | short | 29.0 | 43.0 | 37.9 (31) | C |
| Emerald | short | 68.0 | 79.0 | 78.2 (67) | D |
| i500 | short | 30.0 | 37.5 | 38.5 (21) | C |
| iTero | short | 30.0 | 32.0 | 35.1 (36) | C |
| Omnicam | short | 18.0 | 19.0 | 20.6 (14) | AB |
| PrimeScan | short | 29.0 | 33.0 | 31.3 (23) | BC |
| Trios 4 | short | 53.0 | 71.0 | 61.5 (48) | D |
| Aadva | long | 18.0 | 26.0 | 22.1 (17) | A |
| Aman | long | 23.0 | 28.5 | 25.4 (18) | A |
| Cs3600 | long | 53.0 | 67.00 | 78.3 (79) | CD |
| Emerald | long | 132.0 | 198.5 | 185.2 (154) | E |
| i500 | long | 63.0 | 87.0 | 75.7 (63) | C |
| iTero | long | 46.0 | 49.0 | 54.8 (38) | BC |
| Omnicam | long | 34.0 | 44.0 | 42.6 (36) | B |
| PrimeScan | long | 51.0 | 56.0 | 57. 4 (40) | BC |
| Trios 4 | long | 88.0 | 97.5 | 93.1 (68) | D |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Spagopoulos, D.; Kaisarlis, G.; Spagopoulou, F.; Halazonetis, D.J.; Güth, J.-F.; Papazoglou, E. In Vitro Trueness and Precision of Intraoral Scanners in a Four-Implant Complete-Arch Model. Dent. J. 2023, 11, 27. https://doi.org/10.3390/dj11010027
Spagopoulos D, Kaisarlis G, Spagopoulou F, Halazonetis DJ, Güth J-F, Papazoglou E. In Vitro Trueness and Precision of Intraoral Scanners in a Four-Implant Complete-Arch Model. Dentistry Journal. 2023; 11(1):27. https://doi.org/10.3390/dj11010027
Chicago/Turabian StyleSpagopoulos, Dimitrios, George Kaisarlis, Foteini Spagopoulou, Demetrios J. Halazonetis, Jan-Frederik Güth, and Efstratios Papazoglou. 2023. "In Vitro Trueness and Precision of Intraoral Scanners in a Four-Implant Complete-Arch Model" Dentistry Journal 11, no. 1: 27. https://doi.org/10.3390/dj11010027
APA StyleSpagopoulos, D., Kaisarlis, G., Spagopoulou, F., Halazonetis, D. J., Güth, J.-F., & Papazoglou, E. (2023). In Vitro Trueness and Precision of Intraoral Scanners in a Four-Implant Complete-Arch Model. Dentistry Journal, 11(1), 27. https://doi.org/10.3390/dj11010027








