Journal Description
Dentistry Journal
Dentistry Journal
is an international, peer-reviewed, open access journal on dentistry, published monthly online by MDPI.
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- High Visibility: indexed within Scopus, ESCI (Web of Science), PubMed, PMC, and other databases.
- Journal Rank: JCR - Q1 (Dentistry, Oral Surgery and Medicine) / CiteScore - Q2 (General Dentistry)
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 25.4 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 4.6 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the second half of 2025).
- Recognition of Reviewers: reviewers who provide timely, thorough peer-review reports receive vouchers entitling them to a discount on the APC of their next publication in any MDPI journal, in appreciation of the work done.
Impact Factor:
3.1 (2024);
5-Year Impact Factor:
3.3 (2024)
Latest Articles
Influence of Chemical Composition on the Physical–Mechanical Properties of Some Experimental Titanium Alloys for Dental Implants
Dent. J. 2026, 14(2), 89; https://doi.org/10.3390/dj14020089 (registering DOI) - 3 Feb 2026
Abstract
Background/Objectives: The main objective of optimizing the composition of dental implants is to improve tissue compatibility for enhanced biological/biochemical performance. In this context, research on the development of new titanium alloys in dental implantology considers the careful selection of alloying elements, both in
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: The main objective of optimizing the composition of dental implants is to improve tissue compatibility for enhanced biological/biochemical performance. In this context, research on the development of new titanium alloys in dental implantology considers the careful selection of alloying elements, both in terms of biocompatibility (their lack of toxicity) and their potential to improve the metallurgical processing capacity (thermal and/or thermomechanical), which through controlled microstructural changes lead to the optimal combination of properties for functionality and durability of the implant. The purpose of the research is to study the influence of alloying elements on the phase composition and physical–mechanical properties of experimental titanium alloys. Methods: Four alloys with original chemical compositions were developed, coded in the experiments as follows: Ti1, Ti2, Ti3, Ti4. The characterization of the alloys was carried out by detailed analysis of the chemical composition, phase structure and by testing the physico-mechanical properties (HV hardness, tensile strength, yield strength, elongation, modulus of elasticity), by standardized modern methods. Characterization methods, such as optical microscopy, SEM, EDS and XRD were performed, followed by tensile tests based on ASTM EB/EBM-22 and EN ISO 6892-1-2009 standards. Results: The research results provide information regarding the relationship between the composition and the physico-mechanical properties (Rm, Rp, HV, A, G, E) of the experimental alloys (Ti1–Ti4). Depending on the value level of the properties, these have been highlighted: compositions in which the alloy can be indicated for conditions of intense stress (Ti3), compositions that describe highly ductile alloys, easy to process and adapt to clinical requirements (Ti4), but also alloys compositions characterized by a balanced combination of strength, plasticity/ductility (Ti1, Ti2). Conclusions: Research for the development of new titanium alloys through the optimization of chemical composition has taken into account the requirements regarding the biological/biomechanical compatibility of biomaterials. Analyzed in comparison with Cp-Ti grade 4 and Ti6A4V, the experimental alloys (Ti1–Ti4) can be characterized as follows: The mechanical strength properties (Rm and Rp) are higher than those of pure commercial titanium (Cp-Ti grade 4) for all compositions Ti1–Ti4, but slightly lower than those of alloy Ti6Al4V. The plasticity–ductility properties have values comparable to those of Cp-Ti grade 4 (Ti4 and Ti2 compositions) and Ti6Al4V (Ti1 composition), with one exception, the Ti3 alloy. All four experimental alloys have a lower modulus of elasticity than Cp-Ti grade 4 (102–104 GPa) and Ti6Al4V (113 GPa), commonly used in dental implants. An in-depth analysis, which will also consider information on corrosion behavior and cellular testing, may support the selection of some of the four experimental alloys studied. The research aims to continue the progress to a higher level of testing, through the realization of dental implants (e.g., fatigue, wear, osteointegration capacity, etc.).
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Dental Materials Design and Application)
Open AccessArticle
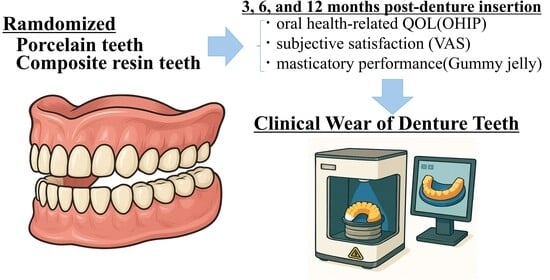
Effects of Composite Resin Teeth Versus Porcelain Teeth in Complete Dentures on Oral Health-Related Quality of Life, Masticatory Function, and Patient Satisfaction: A Randomized Controlled Trial
by
Asuka Kodama, Toshifumi Nogawa, Yoshiyuki Takayama, Kiwamu Sakaguchi and Atsuro Yokoyama
Dent. J. 2026, 14(2), 88; https://doi.org/10.3390/dj14020088 - 3 Feb 2026
Abstract
Background/Objectives: Artificial teeth in complete dentures are classified according to the materials used: porcelain (PO) or composite resin (CR). However, these materials’ effects on function, patient satisfaction, and quality of life (QOL), as well as occlusal wear, remain unclear. We compared PO
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: Artificial teeth in complete dentures are classified according to the materials used: porcelain (PO) or composite resin (CR). However, these materials’ effects on function, patient satisfaction, and quality of life (QOL), as well as occlusal wear, remain unclear. We compared PO and CR complete dentures in edentulous patients by assessing masticatory function, patient satisfaction, and oral health-related QOL at 3, 6, and 12 months post-insertion, as well as occlusal surface morphology owing to material differences. Methods: In this open-label, randomized, single-center, parallel-group study, participants were edentulous patients who visited our hospital and underwent treatment with new complete dentures. The outcomes were oral health-related QOL; subjective satisfaction, assessed using a visual analog scale; and masticatory performance, evaluated with gummy jelly and were assessed at baseline and 3, 6, and 12 months post-denture insertion. Occlusal surface impressions were taken twice, digitized as STL models, superimposed, and analyzed for wear. The Wilcoxon rank-sum test was used to compare between groups. Results: All evaluated items showed improvement. However, no significant differences were observed between the PO and CR groups, including between the amount of wear observed in the two groups. However, the PO group showed a tendency toward less wear. Extended observation may be required to clarify the long-term effects of artificial tooth materials. Conclusions: In the short term, the artificial tooth material did not influence masticatory function, oral health-related QOL, or patient satisfaction.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Dental Materials)
►▼
Show Figures
Graphical abstract
Open AccessSystematic Review
Effects of Oral Probiotics on Streptococcus mutans in Children: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
by
Andrea Caiza-Rennella, Andrea Ordoñez-Balladares, Rosangela Caicedo-Quiroz, Indira Gómez-Capote and Zuilen Jiménez-Quintana
Dent. J. 2026, 14(2), 87; https://doi.org/10.3390/dj14020087 - 3 Feb 2026
Abstract
Background: Early childhood caries is closely associated with oral dysbiosis and the proliferation of Streptococcus mutans. Oral probiotics, particularly Lactobacillus reuteri and Lactobacillus rhamnosus, have been proposed as ecological modulators capable of reducing cariogenic microorganisms. Objective: To evaluate the
[...] Read more.
Background: Early childhood caries is closely associated with oral dysbiosis and the proliferation of Streptococcus mutans. Oral probiotics, particularly Lactobacillus reuteri and Lactobacillus rhamnosus, have been proposed as ecological modulators capable of reducing cariogenic microorganisms. Objective: To evaluate the efficacy of orally administered L. reuteri and L. rhamnosus in reducing salivary S. mutans levels in children aged 6 months to 12 years through a systematic review and meta-analysis. Methods: This review followed the PRISMA 2020 guidelines and was prospectively registered in PROSPERO (CRD420251086304). Searches were conducted in MEDLINE/PubMed, CENTRAL, Embase, Scopus and LILACS without language or date restrictions. Randomized controlled trials administering the target probiotic strains for ≥30 days were included. Risk of bias was assessed using RoB 2, and certainty of evidence using GRADE. Random-effects meta-analyses were performed for continuous and dichotomous outcomes. Results: Six randomized controlled trials were included (N = 1362). Only two trials reported continuous outcomes in comparable log10 CFU/mL format and could therefore be pooled for the continuous meta-analysis. This analysis showed a significant reduction in salivary S. mutans levels (MD = −0.65 log10 CFU/mL; 95% CI: −0.97 to −0.34; p < 0.0001; I2 = 19%), although the pooled estimate was largely driven by one study and should be interpreted cautiously. Four trials contributed to the dichotomous meta-analysis, which showed a non-significant trend toward risk reduction (OR = 0.73; 95% CI: 0.51–1.06; p = 0.10; I2 = 35%). Short-term interventions using high oral-retention formulations demonstrated the most consistent microbiological effects. Conclusions: Oral probiotics may significantly reduce salivary S. mutans in the short-term, especially when delivered through slow-dissolving formulations. However, their effects vary according to strain, vehicle, and intervention duration. Larger, standardized, and longer-term clinical trials are needed to determine the sustainability and clinical relevance of these effects.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Topic Oral Health Management and Disease Treatment)
Open AccessArticle
Does Palatoplasty in Patients with Cleft Palate Really Improve Otitis Media with Effusion?
by
Yosuke Kunitomi, Toshiki Hyodo, Yoshiaki Kitsukawa, Aya Koike, Yasuhiro Tsubura, Yuske Komiyama, Chonji Fukumoto, Takahiro Wakui, Hiroshi Kamioka and Hitoshi Kawamata
Dent. J. 2026, 14(2), 86; https://doi.org/10.3390/dj14020086 - 3 Feb 2026
Abstract
Background: The majority of cleft palate patients have been reported to suffer from otitis media with effusion (OME). The improvement of velopharyngeal function (VPF) after palatoplasty might be evidence for the improvement of the function of the Eustachian tube. The improvement of the
[...] Read more.
Background: The majority of cleft palate patients have been reported to suffer from otitis media with effusion (OME). The improvement of velopharyngeal function (VPF) after palatoplasty might be evidence for the improvement of the function of the Eustachian tube. The improvement of the function of Eustachian tube by palatoplasty has been reported to be effective for the treatment of OME simultaneously with the insertion of a ventilation tube into the tympanic membrane. There are only a few reports that clearly show the association between improvement of VPF and improvement of OME after palatoplasty. In this study, we discussed whether the improvement of VPF after palatoplasty in cleft palate patients with OME improved OME. Methods: Twenty-six patients with cleft palate were included in the study. We retrospectively extracted the information of cleft type, gender, surgical technique, and presence of OME risk factors from electronic medical records. We also investigated the recurrence of OME and the improvement level of VPF at 36 months postoperatively. OME was assessed based on the otolaryngologist’s findings in electronic medical records, with a good prognosis group with no symptom of OME, or a recurrence group with prolonged or recurrent OME. Results: At 36 months after palatoplasty, 19 of 23 patients (82.6%) were in the OME good prognosis group and four (17.4%) were in the OME recurrence group. The rate of patients with recurrent OME did not differ significantly by the degree of improvement of VPF. This study indicated that clear association between other risk factors for OME and OME recurrence could not be shown. Conclusion: We observed that most patients with cleft palate who underwent palatoplasty showed a good prognosis for OME at 36 months after surgery. However, further studies are needed to investigate the impact of different surgical techniques on the improvement of OME and the degree to which VPF improves, as well as the effect of each OME risk factor.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Trends in Orofacial Cleft Research)
Open AccessArticle
The Effect of Adhesive Systems on Shade Matching of Composite Veneer
by
Fadak Al Marar, Raghad Aljarboua, Fatimah M. Alatiyyah, Shahad AlGhamdi, Faraz Ahmed Farooqi, Lama Almuhanna, Rasha AlSheikh and Abdul Samad Khan
Dent. J. 2026, 14(2), 85; https://doi.org/10.3390/dj14020085 - 3 Feb 2026
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Objective: This study aimed to assess the impact of different adhesive systems on the color stability of composite veneers following their exposure to various common beverages. Materials and Methods: A single layer of commercially available adhesives (4th and 7th generations) and two experimental
[...] Read more.
Objective: This study aimed to assess the impact of different adhesive systems on the color stability of composite veneers following their exposure to various common beverages. Materials and Methods: A single layer of commercially available adhesives (4th and 7th generations) and two experimental adhesives based on hydroxyapatite and bioactive glass were applied, followed by composite restoration on incisor typodonts. The typodonts were prepared with depths of 0.3, 0.5, and 0.7 mm at the cervical, middle, and incisal regions, respectively. Samples from each group were immersed in coffee, Cola, and deionized water, and color stability was analyzed on days 1 and 60. One-way and two-way analyses of variance were performed. Results: The interaction between groups and solutions was statistically significant (p = 0.001) across all tooth regions. Coffee and Cola caused significant color changes (p = 0.001). The 4th generation demonstrated better color stability than the 7th generation in the middle and cervical regions (p-values = 0.083 and 0.003, respectively). The findings showed that the bioactive glass-based bonding agent exhibited greater discoloration than the hydroxyapatite-based adhesive (p = 0.001). Conclusions: The composite thicknesses are influenced differently by adhesives with respect to shade matching. Bioactive materials-based adhesives showed more resistance towards color change than commercial adhesives.
Full article
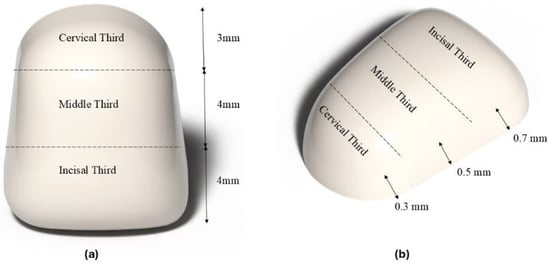
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Discrepancy Between Surface Wear and Subsurface Fatigue Damage in CAD/CAM Composite Crowns: A Comparative Study of Intraoral Scans and Optical Coherence Tomography
by
Julie-Jacqueline Kuhl, Maximiliane Amelie Schlenz, Bernd Wöstmann, Christin Grill, Ralf Brinkmann and Christoph Moos
Dent. J. 2026, 14(2), 84; https://doi.org/10.3390/dj14020084 - 3 Feb 2026
Abstract
Objectives: This study aimed to determine whether surface wear, identified through the superimposition of intraoral scans (IOS), can predict subsurface damage progression detected by optical coherence tomography (OCT) during fatigue testing of computer-aided design/computer-aided manufacturing (CAD/CAM) composite crowns. Methods: Monolithic CAD/CAM composite crowns
[...] Read more.
Objectives: This study aimed to determine whether surface wear, identified through the superimposition of intraoral scans (IOS), can predict subsurface damage progression detected by optical coherence tomography (OCT) during fatigue testing of computer-aided design/computer-aided manufacturing (CAD/CAM) composite crowns. Methods: Monolithic CAD/CAM composite crowns (Brilliant Crios;
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) in Dentistry)
►▼
Show Figures

Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Oral Side Effects of the Most Commonly Prescribed Drugs in Germany
by
Frank Halling, Rainer Lutz and Axel Meisgeier
Dent. J. 2026, 14(2), 83; https://doi.org/10.3390/dj14020083 - 2 Feb 2026
Abstract
Background: The aim of this study is to investigate the potential link between the use of specific medications and oral adverse drug reactions. Methods: The 100 most frequently prescribed drugs in Germany in 2023 were compiled using the “PharMaAnalyst” database. According to the
[...] Read more.
Background: The aim of this study is to investigate the potential link between the use of specific medications and oral adverse drug reactions. Methods: The 100 most frequently prescribed drugs in Germany in 2023 were compiled using the “PharMaAnalyst” database. According to the descriptions of adverse drug reactions (ADRs) in the patient information leaflets the ADRs were selected, analyzed and weighted with scores according to a classification system that distinguishes four groups of ADRs by frequency: ‘very common’ (4), ‘common’ (3), ‘uncommon’ (2) and ‘rare’ (1). The objective was to summarize the scores of the oral ADRs and define the ‘oral side effect score’ (OSES). Results: After accounting for duplication due to various brand names, 49 medications were reviewed. A total of 65% of the medications exhibited oral ADRs. The number of oral ADRs per medication ranged from one to seven. Xerostomia and dysgeusia were the most prevalent oral side effects, accounting for 37% of cases. Overall, 34% of side effects were classified as either ‘very common’ or ‘common’. The medication groups with the highest OSES were antidepressants, antibiotics and analgesics. Of the individual medications, azithromycin, gabapentin and pregabalin exhibited the highest OSES. Conclusions: This study provides a comprehensive overview of oral side effects associated with the 100 most frequently prescribed drugs. Patients with polypharmacy are particularly likely to experience oral side effects such as xerostomia and dysgeusia. Due to their high OSES combinations, antibiotics, analgesics or antidepressants may trigger multiple oral ADRs. It is essential that the medical community is continuously updated on pharmacological knowledge to raise awareness of oral ADRs.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Topic Oral Health Management and Disease Treatment)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Enamel Remineralization Potential of Conventional and Biomimetic Toothpaste Formulations: A Comparative In Vitro Study
by
Cristina-Angela Ghiorghe, Ionuţ Tărăboanţă, Sorin Andrian, Galina Pancu, Corneliu Munteanu, Bogdan Istrate, Fabian Cezar Lupu, Claudia Maxim and Ana Simona Barna
Dent. J. 2026, 14(2), 82; https://doi.org/10.3390/dj14020082 - 2 Feb 2026
Abstract
Background/Objectives: Dental caries remains one of the most prevalent chronic diseases worldwide, making enamel remineralization a key objective in minimally invasive dentistry. This in vitro study compared the remineralization efficacy of five therapeutic toothpastes containing fluoride, NovaMin, CPP-ACP, nano-hydroxyapatite, arginine, and xylitol.
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: Dental caries remains one of the most prevalent chronic diseases worldwide, making enamel remineralization a key objective in minimally invasive dentistry. This in vitro study compared the remineralization efficacy of five therapeutic toothpastes containing fluoride, NovaMin, CPP-ACP, nano-hydroxyapatite, arginine, and xylitol. Methods: Sixty enamel specimens were prepared from extracted human posterior teeth and artificially demineralized. Samples were randomly allocated into six groups (n = 10): one negative control (C1) stored in artificial saliva and five treatment groups (P1–P5). A 28-day remineralization protocol with twice-daily applications was performed. Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDX) were used to assess surface morphology and elemental composition (Ca, P, F, Na, O, Ca/P ratio) at days 1, 14, and 28. Vickers microhardness testing was used to evaluate changes in mechanical properties. Statistical analysis included one-way ANOVA, repeated measures ANOVA, Tukey’s post hoc test, and Kruskal–Wallis where appropriate (α = 0.05). Results: All therapeutic toothpastes produced some increase in mineral content compared to the demineralized control. At day 28, significant intergroup differences were observed for calcium, phosphorus, and fluoride (p < 0.001). The arginine–fluoride formulation (P4) and the NovaMin-based formulation (P3) showed the most consistent increases in Ca and P, with SEM revealing the formation of a continuous, compact surface layer and marked reduction in prismatic porosities. Fluoride-containing toothpastes (P1, P3, P4) showed significant fluoride incorporation (p < 0.001 vs. control). The nano-hydroxyapatite/xylitol prototype (P5) produced a delayed but progressive increase in Ca and P, with partial filling of prismatic spaces. The CPP-ACP-based toothpaste (P2) led to limited changes, with only slight differences vs. control at day 28. Vickers microhardness values increased significantly in groups P1, P3, P4, and P5 (p < 0.05), in agreement with the higher mineral levels found in these samples. Conclusions: Under the present in vitro conditions, toothpastes containing fluoride in combination with NovaMin or arginine, as well as nano-hydroxyapatite/xylitol, demonstrated the highest remineralization potential under the present in vitro conditions, both chemically and mechanically. Xylitol-based formulations without a direct mineral supply showed limited effects. The pH and active composition of the toothpaste strongly influenced enamel remineralization outcomes.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Preventive Dentistry)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessCase Report
Burning Mouth Syndrome as a Central Pain Disorder: A Case Study Demonstrating Response to Occipital Nerve Block Treatment
by
Shachar Zion Shemesh, Paz Kelmer and Lior Ungar
Dent. J. 2026, 14(2), 81; https://doi.org/10.3390/dj14020081 - 2 Feb 2026
Abstract
Background: Burning Mouth Syndrome (BMS) is a chronic orofacial pain condition characterized by a burning sensation in the oral cavity without identifiable lesions. It predominantly affects women (especially postmenopausal) but can occur in men. BMS is considered a multifactorial neuropathic pain disorder involving
[...] Read more.
Background: Burning Mouth Syndrome (BMS) is a chronic orofacial pain condition characterized by a burning sensation in the oral cavity without identifiable lesions. It predominantly affects women (especially postmenopausal) but can occur in men. BMS is considered a multifactorial neuropathic pain disorder involving both peripheral small-fiber neuropathy and central dysregulation, often accompanied by taste alterations (dysgusia) and xerostomia despite normal oral exams. Treatment is challenging, with modest responses to agents like clonazepam, tricyclic antidepressants, or gabapentinoids. Observations: We present a 67-year-old male with recalcitrant primary BMS who showed complete remission temporally associated with occipital nerve blockade, likely affecting central trigeminocervical pathways. Initial therapy with amitriptyline (25 mg) and gabapentin (900 mg/day) yielded ~30% pain relief. Given suspected central sensitization, greater and lesser occipital nerve (GON) blocks were administered in series. After the first, second, and third ON blocks, pain was reduced by ~50%, 80%, and 100%, respectively. Remission persisted at one-year follow-up under continued medications. A mild recurrence (~20% of baseline pain) responded fully to a fourth GON block, maintaining another year of pain-free status. Lessons: This case underscores the complex central mechanisms in BMS and illustrates that modulating central pain circuits via occipital nerve blockade, through trigeminocervical convergence mechanisms, without direct trigeminal intervention. We discuss the diagnostic challenges of BMS, the rationale of occipital neuromodulation, and how this novel therapeutic strategy compares with current literature, supporting the hypothesis of central sensitization in BMS.
Full article
Open AccessSystematic Review
Periodontitis and Oral and Oropharyngeal Cancer Risk: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis with Exploratory Evidence on Tumor-Associated Porphyromonas gingivalis
by
Luis Chauca-Bajaña, Bernarda Andrea Sánchez Arteaga, Andrea Ordóñez Balladares, María Isabel Romero Vasquez, Gustavo Javier Icaza Latorre, Carla Verenice Romo Olvera, Mauro Xavier Zambrano Matamoros and Byron Velásquez Ron
Dent. J. 2026, 14(2), 80; https://doi.org/10.3390/dj14020080 - 2 Feb 2026
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background: Periodontitis is a chronic inflammatory condition characterized by progressive destruction of tooth-supporting tissues and sustained microbial dysbiosis. Increasing evidence suggests that chronic oral inflammation may be associated with oral and oropharyngeal carcinogenesis, although findings across epidemiological and prognostic studies remain heterogeneous. Objective:
[...] Read more.
Background: Periodontitis is a chronic inflammatory condition characterized by progressive destruction of tooth-supporting tissues and sustained microbial dysbiosis. Increasing evidence suggests that chronic oral inflammation may be associated with oral and oropharyngeal carcinogenesis, although findings across epidemiological and prognostic studies remain heterogeneous. Objective: To systematically evaluate the epidemiological association between clinically defined periodontitis and the risk of oral and/or oropharyngeal cancer, and to explore, in a distinct analytical component, the prognostic association between tumor-associated periodontal pathogens, particularly Porphyromonas gingivalis, and survival outcomes in affected patients. Methods: A systematic review and meta-analysis were conducted following PRISMA guidelines and registered in PROSPERO (CRD420251273975). Observational studies evaluating periodontitis and oral/oropharyngeal cancer risk (Arm 1) and prognostic studies assessing tumor-associated periodontal pathogens and survival outcomes (Arm 2) were identified through comprehensive database searches. Random-effects meta-analyses were performed to pool adjusted effect estimates. Risk of bias was assessed using the Newcastle–Ottawa Scale and the QUIPS tool. Results: Six observational studies were included in the epidemiological meta-analysis. Periodontitis was significantly associated with an increased risk of oral and/or oropharyngeal cancer (pooled HR = 2.14; 95% CI: 1.53–2.98), with substantial heterogeneity; trial sequential analysis supported the statistical robustness of this association. In the separate prognostic analysis, three studies evaluating intratumoral Porphyromonas gingivalis were included. A higher presence or expression of P. gingivalis was associated with poorer overall survival (HR = 2.89; 95% CI: 1.93–4.32), with no observed heterogeneity. Sensitivity and influence analyses confirmed the stability of these findings. Conclusions: This systematic review and meta-analysis demonstrate a consistent epidemiological association between periodontitis and an increased risk of oral and/or oropharyngeal cancer. In addition, exploratory prognostic evidence suggests that the presence of Porphyromonas gingivalis within tumor tissue may be associated with adverse survival outcomes. These findings should be interpreted as addressing distinct clinical and microbiological constructs, underscoring the need for further well-designed prospective and mechanistic studies.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessSystematic Review
Artificial Intelligence Models for the Detection and Quantification of Orthodontically Induced Root Resorption Using Cone-Beam Computed Tomography: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
by
Carlos M. Ardila, Eliana Pineda-Vélez and Anny M. Vivares-Builes
Dent. J. 2026, 14(2), 79; https://doi.org/10.3390/dj14020079 - 2 Feb 2026
Abstract
Background/Objectives: Orthodontically induced root resorption (OIRR) is a well-documented but undesired consequence of orthodontic treatment. This systematic review and meta-analysis aimed to assess the diagnostic performance of artificial intelligence (AI) models applied to cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT) for detecting and quantifying OIRR
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: Orthodontically induced root resorption (OIRR) is a well-documented but undesired consequence of orthodontic treatment. This systematic review and meta-analysis aimed to assess the diagnostic performance of artificial intelligence (AI) models applied to cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT) for detecting and quantifying OIRR while evaluating their agreement with manual reference standards and the impact of model architecture, validation design, and quantification strategy. Methods: Comprehensive searches were conducted across PubMed/MEDLINE, Scopus, Web of Science, and EMBASE up to November 2025. Studies were included if they employed AI for OIRR diagnosis using CBCT and reported relevant performance metrics. Following PRISMA guidelines, data were extracted and a random-effect meta-analysis was performed. Subgroup analyses explored the influence of model design and validation. Results: Seven studies were included. Pooled sensitivity from three eligible studies was 0.903 (95% CI: 0.818–0.989), suggesting excellent true positive rates. Specificity ranged from 82% to 98%, and area under the receiver operating characteristic curve values reached up to 0.96 across studies using EfficientNet, U-Net, and other convolutional neural network (CNN)-based architectures. The pooled intraclass correlation coefficient for agreement with manual quantification was 1.000, reflecting near-perfect concordance. Subgroup analyzes showed slightly superior performance in CNN-only models compared to hybrid approaches, and better diagnostic metrics with internal validation. Linear assessments appeared more sensitive to early apical shortening than volumetric methods. Conclusions: AI models applied to CBCT demonstrate excellent diagnostic accuracy and high concordance with expert assessments for OIRR detection. These findings support their potential integration into clinical orthodontic workflows.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Innovations and Trends in Modern Orthodontics)
►▼
Show Figures

Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
The Influence of Filler Morphology and Loading Level on the Properties of Light-Curing Dental Composites
by
Ekaterina Kuznetsova, Yaroslav Meleshkin, Oleg Yanushevich, Natella Krikheli, Elena Mendosa, Marina Bychkova and Pavel Peretyagin
Dent. J. 2026, 14(2), 78; https://doi.org/10.3390/dj14020078 - 2 Feb 2026
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background/Objectives: Light-curing dental resin composites remain limited by high polymerization shrinkage, inadequate wear resistance, and elevated water sorption. The combined influence of filler shape, size, and loading level on mechanical performance and hydrolytic stability remains insufficiently understood. This study aimed to systematically investigate
[...] Read more.
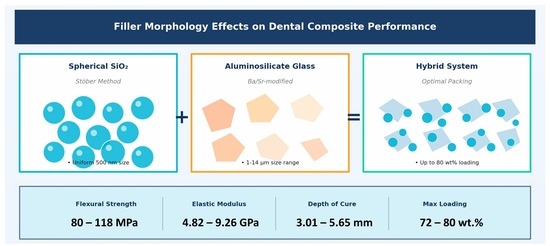
Background/Objectives: Light-curing dental resin composites remain limited by high polymerization shrinkage, inadequate wear resistance, and elevated water sorption. The combined influence of filler shape, size, and loading level on mechanical performance and hydrolytic stability remains insufficiently understood. This study aimed to systematically investigate the effects of filler morphology and particle size distribution on the key properties of dental composites. Methods: Spherical silica (SiO2) nanoparticles (D50 = 0.50 μm) were synthesized via the Stöber method, while irregular aluminosilicate glass was used in coarse (D50 = 3.71 μm) and fine (D50 = 1.98 μm) fractions. Three composite groups were formulated: Group 1 (72 wt.% filler with 0–30% SiO2), Group 2 (maximum filler loading 76–80 wt.% with 10–30% SiO2), and Group 3 (74.5 wt.% filler with varying coarse/fine glass ratios). Flexural strength, flexural modulus, Vickers microhardness, depth of cure, water sorption, and solubility were evaluated according to ISO 4049:2019. Results: Incorporation of spherical SiO2 nanoparticles significantly reduced composite viscosity, enabling maximum filler loading to increase from 72 to 80 wt.%. All composites exceeded ISO requirements for flexural strength (80.54–118.11 MPa), depth of cure (3.01–5.65 mm), water sorption (14.61–22.87 μg/mm3), and solubility (1.20–5.90 μg/mm3). The highest flexural strength (118.11 ± 10.54 MPa) and modulus (9.26 ± 1.12 GPa) were achieved at 78 wt.% filler loading. Bimodal glass systems (50/50 ratio) demonstrated optimal mechanical properties, while higher fine fractions reduced strength. Conclusions: Spherical SiO2 nanoparticles effectively reduce viscosity and enable higher filler loading. The optimal balance between filler loading, particle shape, and size distribution should be tailored to clinical requirements, with high-strength formulations suited for posterior restorations and bimodal formulations for universal applications.
Full article
Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Evaluation of the Color Stability of Multilayer Zirconia After Exposure to Staining Solutions and Artificial Aging
by
Brunilda Koci, Alba Kamberi, Adora Shpati, Olja Tanellari, Balcos Carina and Adela Alushi
Dent. J. 2026, 14(2), 77; https://doi.org/10.3390/dj14020077 - 2 Feb 2026
Abstract
Background/Objectives: Multilayer zirconia restorations can feature a shade gradient or a strength gradient, with layers differing in color or phase composition within the same material. The aim of this in vitro study was to evaluate the color stability in all layers of multilayer
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: Multilayer zirconia restorations can feature a shade gradient or a strength gradient, with layers differing in color or phase composition within the same material. The aim of this in vitro study was to evaluate the color stability in all layers of multilayer zirconia after exposure to staining solutions and artificial aging. Methods: Square-shaped specimens (N = 120) of color A2 were fabricated from 4Y-PSZ and 3Y/4Y-PSZ multilayer zirconia—Katana STML, DD Cube One ML, and Katana YML—and their baseline color values (T0) were measured with a clinical spectrophotometer (VITA Easyshade V). The specimens were randomly divided into four groups (n = 10/gp) and immersed in physiologic solution, 0.2% chlorhexidine gluconate (CHX) mouth rinse, and staining coffee solution. Then, they were measured continuously for 7 (T1), 14 (T2), and 21 days (T3). The last group of specimens underwent accelerated aging in a steam autoclave at 134 °C and 2 bar pressure and measured after 1 (T1), 3 (T2), and 5 h (T3). After the immersion process and artificial aging, discoloration values (ΔE) were calculated using the formula ΔE = [(ΔL*)2 + (Δa*)2 + (Δb*)2]1/2 and analyzed with the SPSS v 23.0 software with a p value < 0.05. Results: All specimens showed significant color differences in the T3 measurements after exposure to coffee and CHX, with the highest ΔE values in the enamel layers. Katana YML showed the most significant differences in ΔE in the cervical layers after exposure to artificial aging. Conclusions: Multilayer zirconia exhibited dependent optical changes, with the enamel layers being the most affected after exposure to staining solutions. Gradient pigmentation and differences in phase composition caused differences in color to the multilayer zirconia layers after exposure to staining solutions and artificial aging.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Advances in Esthetic Dentistry)
►▼
Show Figures
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Impact of Metallurgical and Geometric Features on the Cyclic Fatigue Strength of Reciprocating Endodontic Files
by
Abayomi Omokeji Baruwa, Francisco M. Braz Fernandes and Jorge N. R. Martins
Dent. J. 2026, 14(2), 76; https://doi.org/10.3390/dj14020076 - 2 Feb 2026
Abstract
Background: Nickel–titanium (NiTi) endodontic instruments have undergone significant improvements in heat treatment processing and geometric design, aimed at enhancing flexibility, cutting efficiency, and fatigue strength. Reciprocating motion was introduced to increase cyclic fatigue resistance, which remains the predominant mode of failure in NiTi
[...] Read more.
Background: Nickel–titanium (NiTi) endodontic instruments have undergone significant improvements in heat treatment processing and geometric design, aimed at enhancing flexibility, cutting efficiency, and fatigue strength. Reciprocating motion was introduced to increase cyclic fatigue resistance, which remains the predominant mode of failure in NiTi endodontic file systems. Although these instruments are widely used in both clinical practice and research, few comparative studies have integrated geometric, metallurgical and mechanical evaluations of the most commonly used reciprocating systems. Methods: In the present study, four single-file reciprocating NiTi systems (Reciproc Blue, WaveOne Gold, EdgeOne Fire, and Easy-File Flex) were evaluated for their geometric design, metallurgical composition, and cyclic fatigue strength. Stereomicroscopy and scanning electron microscopy were employed to assess active blade length, spiral configuration, and surface finish, while elemental composition and phase transformation temperatures were analyzed using energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy and differential scanning calorimetry. Ten instruments from each group were tested for cyclic fatigue using a standardized curved stainless-steel canal at room temperature, and the time to fracture was recorded. Fatigue data were statistically analyzed using Mood’s median test, with significance set at p < 0.05. Results: Reciproc Blue exhibited the longest active blade length, highest spiral density, and superior surface finish. R-phase start and finish temperatures were highest in WaveOne Gold and lowest in Easy-File Flex. Reciproc Blue demonstrated the higher cyclic fatigue strength, whereas Easy-File Flex showed the lowest. Conclusions: These findings suggest that the metallurgical and geometric characteristics of the Reciproc Blue file significantly enhance its strength to cyclic fatigue compared with the other instruments evaluated.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Endodontics and Restorative Sciences: 2nd Edition)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Assessment of Dental Students’ and General Dentistry Residents’ Knowledge Regarding the Management of Anaphylactic Shock in the Dental Practice: A Single-Centre Study in Romania
by
Alice Murariu, Elena-Raluca Baciu, Cezara Andreea Onică, Dragoș Nicolae Frățilă, Răzvan Constatin Brânzan, Livia Bobu, Cezar Ilie Foia and Costin Iulian Lupu
Dent. J. 2026, 14(2), 75; https://doi.org/10.3390/dj14020075 - 2 Feb 2026
Abstract
Background/Objectives: Anaphylaxis is a rare occurrence in dental practice, yet when it happens, it demands swift management, as untreated cases can be fatal. The aim of this study is to evaluate the level of knowledge among dental students and residents regarding the
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: Anaphylaxis is a rare occurrence in dental practice, yet when it happens, it demands swift management, as untreated cases can be fatal. The aim of this study is to evaluate the level of knowledge among dental students and residents regarding the symptoms and management of anaphylactic emergencies in dental surgery. Methods: The study involved a sample of 236 students from the 3rd and 5th years, and residents in their 1st and 2nd years of the General Dentistry programme at the Faculty of Dental Medicine in Iași, Romania. The response rate to the invitation was 85.8%. Knowledge was assessed using a self-administered questionnaire consisting of 18 questions organised into three sections, which were tested for internal consistency, yielding a Cronbach’s alpha value of 0.731. Results: Statistically significant differences in the responses provided by the three categories of participants were observed for the following items: management of patients with an allergic background (p = 0.033), factors aggravating allergic predisposition (p = 0.001), the correct dose of epinephrine (p = 0.001), secondary medication (p = 0.001), and the timing of treatment initiation (p = 0.009). Questions where answers indicated moderate to low levels of knowledge (25–50% correct answers) concerned the therapeutic approach for patients with an allergic background, the site of adrenaline administration, and secondary medication. Conclusions: Overall, it can be observed that students demonstrated a high level of knowledge in questions related to the symptomatology of anaphylaxis and the therapeutic management of allergic patients, whereas residents showed better performance in questions addressing the therapeutic management of anaphylaxis. However, significant knowledge gaps were identified across all participant categories, suggesting that there must be periodic supplementary training.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Dental Education: Innovation and Challenge)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
The Intersection of Non-Communicable Chronic Disease and Endodontic Care: A Pilot Retrospective Cross-Sectional Study
by
Fausto Zamparini, Mohamed Mowafy, Andrea Spinelli, Stefano Chersoni, Igor Diemberger, Antonella Polimeni, Maria Giovanna Gandolfi and Carlo Prati
Dent. J. 2026, 14(2), 74; https://doi.org/10.3390/dj14020074 - 2 Feb 2026
Abstract
Objective: To evaluate the prevalence of systemic chronic diseases among patients undergoing endodontic therapy in a University Department of Endodontology and to assess their potential implications for treatment planning and prognosis. Methods: A retrospective cross-sectional study analysis was performed on clinical records of
[...] Read more.
Objective: To evaluate the prevalence of systemic chronic diseases among patients undergoing endodontic therapy in a University Department of Endodontology and to assess their potential implications for treatment planning and prognosis. Methods: A retrospective cross-sectional study analysis was performed on clinical records of patients aged > 18 years treated at the Department of Endodontics, University of Bologna. Data collected included demographic information, presence of chronic systemic diseases, endodontic disease and medication history. Descriptive statistics were used to estimate prevalence rates. Results: More than one third of patients (35%) presented with at least one systemic chronic disease or multiple comorbidities. Cardiovascular diseases (19.8%) were the most prevalent. Polypharmacy was observed in 32% of patients. Patients aged 40 years and older showed a significantly higher prevalence of systemic conditions compared to younger individuals. Conclusions: The study supports the finding that a high percentage of patients undergoing endodontic therapies present systemic chronic diseases, multiple comorbid conditions and polypharmacy. It is important to assess these factors and to customize endodontic treatment and decision-making. These realities are likely to become even more pronounced in the coming years, as global population aging continues apace.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Present Status and Future Directions in Endodontics)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessTechnical Note
Clinical Application of an Oral Liquid Bandage (ORAPLA) for Traumatic and Surgical Oral Mucosal Wounds: A Technical Note
by
Hiroshi Furuta, Atsushi Abe, Shoya Mizuno, Sayaka Furuhashi, Sayumi Hiraguri, Moeko Momokita, Tetsushi Oguma, Atsushi Nakayama and Hiroki Inoue
Dent. J. 2026, 14(2), 73; https://doi.org/10.3390/dj14020073 - 2 Feb 2026
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background/Objectives: Oral mucosal wounds are frequently encountered in daily dental practice and are often difficult to manage because of continuous exposure to saliva, mastication, and mechanical irritation. This technical note describes the clinical practicality of an oral liquid bandage (ORAPLA) as a film-forming
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: Oral mucosal wounds are frequently encountered in daily dental practice and are often difficult to manage because of continuous exposure to saliva, mastication, and mechanical irritation. This technical note describes the clinical practicality of an oral liquid bandage (ORAPLA) as a film-forming protective barrier for traumatic and surgical oral mucosal wounds. Methods: ORAPLA was applied in four clinical scenarios: a traumatic lip bite injury, a postoperative mucosal defect following leukoplakia excision, a biopsy wound for suspected oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC), and aphthous stomatitis. Clinical observations included patient-reported symptom relief, film retention, and the clinical appearance of epithelialization at follow-up (1–2 weeks). Results: In all cases, ORAPLA formed a thin protective film immediately after application and was typically observed to remain on the wound surface for approximately 5–6 h under routine daily activities. Patients reported prompt subjective pain relief, and no adverse events were observed. Epithelialization proceeded without clinically evident secondary infection during the follow-up period. Conclusions: In this small descriptive case series, ORAPLA was feasible to apply, well tolerated, and provided temporary mechanical protection with immediate subjective comfort. Controlled studies using standardized outcome measures are warranted.
Full article

Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Assessing the Efficacy of Artificial Intelligence Platforms in Answering Dental Caries Multiple-Choice Questions: A Comparative Study of ChatGPT and Google Gemini Language Models
by
Amr Ahmed Azhari, Walaa Magdy Ahmed, Abdulaziz Alhamadani, Amal Alfaraj, Min Zhang and Chang-Tien Lu
Dent. J. 2026, 14(2), 72; https://doi.org/10.3390/dj14020072 - 27 Jan 2026
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Objective: This study aimed to compare the accuracy of two large language models (LLMs)—ChatGPT (version 3.5) and Google Gemini (formerly Bard)—in answering dental caries-related multiple-choice questions (MCQs) using a simulated student examination framework across seven examination lengths. Materials and Methods: A
[...] Read more.
Objective: This study aimed to compare the accuracy of two large language models (LLMs)—ChatGPT (version 3.5) and Google Gemini (formerly Bard)—in answering dental caries-related multiple-choice questions (MCQs) using a simulated student examination framework across seven examination lengths. Materials and Methods: A total of 125 validated dental caries MCQs were extracted from Dental Decks and Oxford University Press question banks. Seven examination groups were constructed with varying question counts (25, 35, 45, 55, 65, 75, and 85 questions). For each group, 100 simulations were generated per LLM (ChatGPT and Gemini), resulting in 1400 simulated examinations. Each simulated student received a unique randomized subset of questions. MCQs were answered by each LLM using a standardized prompt to minimize ambiguity. Outcomes included mean score, passing rate (≥60%), and performance differences between LLMs. Statistical analyses included independent t-tests, one-way ANOVA within each LLM, and two-way ANOVA examining interactions between LLM type and question count. Results: Across all seven examination formats, Gemini significantly outperformed ChatGPT (p < 0.001). Gemini achieved higher passing rates and higher mean scores in every examination length. One-way ANOVA revealed significant score variation with increasing exam length for both LLMs (p < 0.05). Two-way ANOVA demonstrated significant main effects of LLM type and question count, with no significant interaction. Randomization had no measurable effect on Gemini performance but influenced ChatGPT scores. Conclusions: Gemini demonstrated superior accuracy and higher passing rates compared to ChatGPT in all simulated examination formats. While both LLMs struggled with complex caries-related content, Gemini provided more reliable performance across question quantities. Educators should exercise caution in relying on LLMs for automated assessment or self-study, and future research should evaluate human–AI hybrid models and LLM performance across broader dental domains.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Assessing the Efficacy of Antibiotic Therapy: A Retrospective Study Comparing 875 mg vs. 500 mg of Amoxicillin/Clavulanic Acid for the Management of Acute Apical Abscesses
by
Tal Capucha, Shaul Lin, Dani Noy, Chaim Ohayon, Mordechai Grupper, Daniel Moreinos, Marc Rothman, Dekel Shilo, Omri Emodi, Adi Rachmiel and Roni Dakar
Dent. J. 2026, 14(2), 71; https://doi.org/10.3390/dj14020071 - 26 Jan 2026
Abstract
Introduction: Antibiotics are routinely prescribed for odontogenic abscesses in emergency departments and dental offices. Augmentin is recommended for moderate to severe dentofacial infections. It is usually prescribed in two popular regimens, namely twice (bid) or three times (tid) per day. The aim
[...] Read more.
Introduction: Antibiotics are routinely prescribed for odontogenic abscesses in emergency departments and dental offices. Augmentin is recommended for moderate to severe dentofacial infections. It is usually prescribed in two popular regimens, namely twice (bid) or three times (tid) per day. The aim of this study was to compare the efficacy of two different formulations of amoxicillin–clavulanate, 875/125 mg bid versus 500/125 mg tid, for the treatment of acute dental apical abscesses with orofacial involvement. Methods: Sixty-one patients with acute apical abscesses were prescribed Augmentin in either an 875/125 mg bid or 500/125 mg tid formulation. The patients were tested for inflammatory markers upon admission and again after 72 h. Results: Although all patients experienced a decrease in inflammatory markers over 72 h of antibiotic therapy, there was a statistically significant greater decrease in white blood cells and neutrophils in the patients receiving the 500/125 mg tid regimen. Conclusions: A 500/125 mg tid Augmentin regimen results in a greater decline in inflammatory markers than 875/125 mg bid over 72 h in the setting of dentofacial infection.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Contemporary Endodontics: Progress and Prospects)
►▼
Show Figures
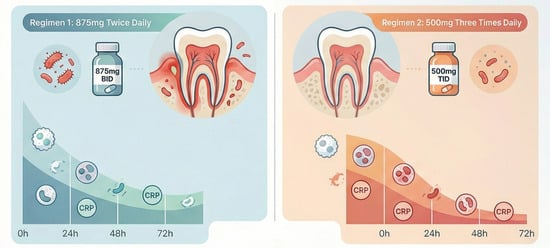
Graphical abstract
Open AccessReview
Systemic Bone Loss and Periodontal Disease: An Updated Review of a Bidirectional Association
by
Abdulkareem A. Alhumaidan and Ahmed Elakel
Dent. J. 2026, 14(1), 70; https://doi.org/10.3390/dj14010070 - 22 Jan 2026
Abstract
Background: Systemic bone loss, particularly osteoporosis, and periodontal disease are highly prevalent chronic conditions that share common risk factors and biological pathways. Increasing evidence suggests a bidirectional relationship between these conditions; however, findings remain heterogeneous and evolving. Objective: This review aims to evaluate
[...] Read more.
Background: Systemic bone loss, particularly osteoporosis, and periodontal disease are highly prevalent chronic conditions that share common risk factors and biological pathways. Increasing evidence suggests a bidirectional relationship between these conditions; however, findings remain heterogeneous and evolving. Objective: This review aims to evaluate and update current evidence on the bidirectional association between systemic bone loss and periodontal disease, with emphasis on underlying mechanisms and clinical implications. Methods: A narrative review of the literature was conducted using major electronic databases, focusing on human studies evaluating the relationship between osteoporosis or systemic bone loss and periodontal disease. Relevant experimental, clinical, and epidemiological studies were included. Results: Most studies support an association between reduced bone mineral density and increased severity of periodontal disease, including greater alveolar bone loss and attachment loss. Conversely, periodontal inflammation may contribute to systemic bone remodeling through inflammatory mediators. However, variability in study design, diagnostic criteria, and confounding factors limits definitive conclusions. Conclusions: Current evidence supports a bidirectional association between systemic bone loss and periodontal disease. Greater interdisciplinary awareness is warranted, and future well-designed longitudinal studies are needed to clarify causality and inform preventive and therapeutic strategies.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Oral Hygiene, Periodontology and Peri-implant Diseases)

Journal Menu
► ▼ Journal Menu-
- Dentistry Journal Home
- Aims & Scope
- Editorial Board
- Reviewer Board
- Topical Advisory Panel
- Instructions for Authors
- Special Issues
- Topics
- Sections & Collections
- Article Processing Charge
- Indexing & Archiving
- Editor’s Choice Articles
- Most Cited & Viewed
- Journal Statistics
- Journal History
- Journal Awards
- Conferences
- Editorial Office
Journal Browser
► ▼ Journal BrowserHighly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics
Topic in
Applied Sciences, Children, Dentistry Journal, JCM
Preventive Dentistry and Public Health
Topic Editors: Denis Bourgeois, Elena BardelliniDeadline: 30 April 2026
Topic in
Biology, JCM, Diagnostics, Dentistry Journal
Assessment of Craniofacial Morphology: Traditional Methods and Innovative Approaches
Topic Editors: Nikolaos Gkantidis, Carlalberta VernaDeadline: 1 June 2026
Topic in
Dentistry Journal, IJMS, JCM, Medicina, Applied Sciences
Oral Health Management and Disease Treatment
Topic Editors: Christos Rahiotis, Felice Lorusso, Sergio Rexhep TariDeadline: 31 July 2026
Topic in
Applied Sciences, Dentistry Journal, Polymers, Applied Biosciences, Bioengineering, Materials
Advances in Biomaterials—2nd Edition
Topic Editors: Satoshi Komasa, Yoshiro Tahara, Tohru Sekino, Hideaki Sato, Yoshiya Hashimoto, Tetsuya AdachiDeadline: 31 December 2026

Conferences
Special Issues
Special Issue in
Dentistry Journal
Endodontics: From Technique to Regeneration
Guest Editor: David E. JaramilloDeadline: 10 February 2026
Special Issue in
Dentistry Journal
Dental Public Health Landscape: Challenges, Technological Innovation and Opportunities in the 21st Century
Guest Editors: Radu Chifor, Aranka Ilea, Anca-Ștefania MesaroșDeadline: 15 February 2026
Special Issue in
Dentistry Journal
Feature Papers in Digital Dentistry
Guest Editors: Luigi Canullo, Maria Menini, Paolo PesceDeadline: 20 February 2026
Special Issue in
Dentistry Journal
Malocclusion: Treatments and Rehabilitation
Guest Editor: Teresa PinhoDeadline: 28 February 2026
Topical Collections
Topical Collection in
Dentistry Journal
Light and Laser Dentistry
Collection Editors: Samir Nammour, Aldo Brugnera Junior
Topical Collection in
Dentistry Journal
Novel Ceramic Materials in Dentistry
Collection Editors: Roberto Sorrentino, Gianrico Spagnuolo
Topical Collection in
Dentistry Journal
Bio-Logic Approaches to Implant Dentistry
Collection Editors: Luigi Canullo, Donato Antonacci, Piero Papi, Francesco Gianfreda, Bianca Di Murro, Carlo Raffone
Topical Collection in
Dentistry Journal
Dental Traumatology and Sport Dentistry
Collection Editor: Enrico Spinas











