Abstract
Invasive cervical resorption (ICR) is a localized, subepithelial, supra-osseous resorptive process of the tooth. Although there are several predisposing factors associated with ICR, its etiology and pathogenesis are poorly understood. The damage to the protective layer on the external root surface appears to allow for the attachment of clastic cells and initiate the resorptive process, which is confined by the inner protective pericanalar resorption-resistant sheet surrounding the root canal space. The use of cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT) is recommended for the diagnosis and assessment of a resorptive lesion. Based on the thorough evaluation of the size and location of the ICR lesion using CBCT, surgical or nonsurgical treatment can be chosen to address the source of the resorption. This review discusses the current status of knowledge regarding the biology of ICR lesions as well as their external or internal treatment using hydraulic calcium silicate-based materials. Future clinical outcome studies are necessary to evaluate the impact of hydraulic calcium silicate-based materials on the healing of ICR lesions.
1. Introduction
Invasive cervical resorption (ICR) is a pathologic resorptive process that initiates on the external surface of a tooth above alveolar bone crest and gradually replaces mineralized tooth structure with granulomatous fibro-vascular tissue or fibro-osseous tissue. It is a rare disease of which the prevalence ranges from 0.02% to 2.3% [1,2,3], but often leads to tooth loss due to its insidious and asymptomatic nature. The resorptive process of ICR is preceded by the loss of unmineralized precementum layers of the root and characterized by the presence of inflammation and odontoclastic activities below the epithelial attachment of gingiva. Its progression is limited in the extracanal area of the root and rarely invades the root canal space because of the presence of a protective layer surrounding the root canal space [4]. In order to capture the characteristics of this lesion, ICR has been described with various terms such as extracanal invasive resorption [5], supraosseous extracanal invasive resorption [6], external cervical resorption [7], peripheral inflammatory root resorption [8], subepithelial inflammatory resorption [9], and odontoclastoma [10].
Hydraulic calcium silicate-based materials have been recently suggested as a material to restore the resorptive defect of ICR. These materials have shown excellent biocompatibility with osteoinductive, cementoconductive and cementoinductive properties, which may promote the periodontal tissue regeneration or repair [11,12]. They are also known to provide an excellent sealing ability by inducing the formation of hydroxyapatite crystals and chemical bonds with the tooth structure [13]. The antibacterial effects of hydraulic calcium silicate-based materials during the setting reaction have been demonstrated in in vitro studies [14,15]. Despite the generally excellent material characteristics of hydraulic calcium silicate-based materials, not all seem suitable for the management of ICR. There is a growing body of literature concerning the repair of the lesions of ICR with selected hydraulic calcium silicate-based materials, which may allow for the more biocompatible restoration of the resorptive lesions that is conductive to periodontal tissue regeneration around ICR.
2. Literature Search and Scope of Review
Three electronic databases (PubMed, Embase, and Web of Science) were searched to identify relevant studies using appropriate MeSH terms including ‘invasive cervical resorption’, ‘extracanal invasive resorption’, ‘external cervical resorption’, ‘supraosseous extracanal invasive resorption’, ‘peripheral inflammatory root resorption’, ‘subepithelial inflammatory resorption’, ‘odontoclastoma’, ‘bioceramics’, ‘calcium silicate-based material’, ‘biodentine’, ‘mineral trioxide aggregate’, ‘endosequence root repair material’. The inclusion criteria were prospective and retrospective clinical studies, case reports, case series, histological studies, in vitro studies, and review articles that were pertinent to the mechanisms, predisposing factors, diagnosis and classification of ICR, and its management with calcium silicate-based materials. The exclusion criteria were studies based on surveys and studies not relevant to ICR. Of the 152 studies identified from the electronic database search, 59 studies are included for this review. A comprehensive narrative review of ICR was undertaken with relevant studies. The purpose of this study was to review the current knowledge concerning the disease process of ICR and internal and external management of ICR lesions with hydraulic calcium silicate-based materials.
3. Putative Mechanisms of the Disease Process of ICR
Studies on the etiology and pathogenesis of ICR are scarce due to its low prevalence. Two putative mechanisms may be proposed based on the histopathological findings from the ICR lesions [4,16,17]:
Mechanism 1.
Microorganisms are not essential to the initiation of ICR but may be present as secondary invaders to sustain the resorptive process. Following the loss of protective unmineralized tissue (precementum), clastic cells circulating in the subepithelial connective tissue area attach the root surface. The microorganisms from the periodontal pocket that may invade the lesion can stimulate and sustain the inflammatory resorptive process;
Mechanism 2.
Microorganisms are essential to the initiation and perpetuation of ICR. Loss of protective unmineralized tissue (precementum) with concomitant inflammation caused by microorganisms in the periodontal tissue initiates the resorptive process at the cervical tooth structure. Microorganisms in the lesion contribute to the continuation of this resorptive process.
The difference between the mechanisms lies in the role of microorganisms in the initiation of ICR. Recent histological observations seem to support the view that microorganisms are not essential to the initiation of the resorptive process and colonize the lesion at the later phase of the resorption based on the finding that bacteria are identified only at the outer layers of the lesions [16,17]. It is speculated that microorganisms may play a role in promoting the resorptive process by creating a hypoxic microenvironment in the lesion [16,17].
4. Predisposing Factors
The common contributor to ICR in both mechanisms is the loss of protective precementum layers. It is presumed that physical or chemical damage to precementum may increase the likelihood of ICR. Therefore, ICR can be considered a multifactorial disease, the prevalence of which is predisposed by factors associated with the damage to precementum. There are several predisposing factors reported in relation to the loss of the protective layers and ICR. Among these factors, trauma, orthodontic treatment, and periodontal treatment that could cause physical damage to precementum showed strong correlations with ICR [18,19,20,21,22,23]. Heithersay, in the analysis of predisposing factors from 222 patients with 257 ICR teeth, reported that orthodontic treatment (24.1%) was the most common factor, and trauma (15.1%) was the second most common [1]. A recent study by Jeng et al. revealed that dental or orofacial trauma (33.33%) were the most common factors associated with ICR, followed by periodontal treatment (26.98%) and orthodontic treatment (15.87%), based on the observation of 63 ICR teeth from 31 patients [19].
Internal bleaching, identified as a minor predisposing factor (3.9%) of ICR in the study by Heithersay, can cause chemical damage to the precementum layer [1]. It is likely that internal bleaching in the combination of other predisposing factors that cause physical damage to precementum increases the prevalence of ICR. Indeed, 7.4% of ICR teeth had a history of internal bleaching and trauma, and 13.6% showed a history of internal bleaching combined with trauma and/or orthodontic treatment [1]. It is hypothesized that bleaching agents such as 30% hydrogen peroxide penetrate into dentin and denature the organic components of dentin, cementum, and precementum, triggering a foreign body reaction around the cementoenamel junction (CEJ). This type of immune response allows for the recruitment of phagocytes and subsequent attachment of clastic cells, thus initiating the resorptive process via removing the chemically altered tooth structure, recognized as ‘foreign’ by the host immune system. It is noted that heating the bleaching agent to increase the efficiency of bleaching in the thermo-catalytic technique may augment the chemical alteration of tooth structure and promote the risk of ICR [24,25,26,27].
An anatomical defect between enamel and cementum at CEJ, which exposes underlying dentin, may also predispose teeth to ICR [28,29]. This developmental gap at CEJ is more susceptible to clastic activities, and the resorptive process may be initiated without other physical and chemical predisposing factors. The finding that no predisposing factors were identified in 16.4% of ICR teeth in the study by Heithersay [1] might suggest the potential contribution of this anatomical profile at CEJ to the development of ICR. It is presumed that internal bleaching increases the risk of ICR if this developmental defect exists at CEJ. Systemic sclerosis [30], hypercalciuria [31], feline herpes virus type 1 [32], varicella zoster virus [33], hepatitis B virus [34], and bisphosphonates [35] also have been reported to be associated with ICR.
A recent retrospective case-control study showed that the prevalence of ICR was 2.3% based on a 10-year observation of endodontic patients at the university clinic [3]. The disease prevalence of ICR is closely associated with predisposing factors that can cause the loss of the protective layers. Predisposing factors were identified in approximately 78% patients with ICR lesions in this study. Another recent study showed that predisposing factors were detected in 99% of ICR cases [36]. The maxillary anterior teeth were highly affected among all tooth types [3,18,36], implying that mechanical and chemical predisposing factors such as traumatic injuries and internal bleaching could be more frequently associated with this tooth type. No predilection for patients’ age and sex was identified in clinical studies [18,36].
5. Differences in the Pattern of ICR between Vital Teeth and Endodontically Treated Teeth
Why do ICR lesions rarely invade pulp space? It is speculated that there is a protective layer around the root canal space to inhibit the resorptive process, and unmineralized predentin has been thought to function as the protective layer. Mavridou et al., based on their histological analyses of ICR lesions, suggested that predentin and surrounding dentin could function as the protective layer and coined it as ‘pericanalar resorption-resistant sheet (PRRS)’ [17]. The resistance of PRRS to resorption may be attributed to its lower mineral content that inhibits the attachment of clastic cells and normal oxygen tension from blood supply in pulp tissue that attenuates clastic activities [17]. It is hypothesized that hypoxic microenvironments in the inflamed periodontal tissue at the initial phase of ICR promote osteoclastic activities, angiogenesis, and granulomatous tissue formation [37,38,39]. As the resorptive lesion approaches the pulp tissue at the later phase, PRRS, which provides normoxic microenvironments, prevents the lesion from entering the root canal space [17].
There are two notable differences reported in the pattern of ICR lesions between endodontically treated teeth and vital teeth.
- Intensity of resorptionMore extensive resorption is observed in endodontically treated teeth than in vital teeth. This may be because, during endodontic therapy, part of PRRS is damaged mechanically or altered chemically [16]. Moreover, loss of pulp vitality in endodontically treated teeth may create hypoxic microenvironments conducive to continued osteoclastic activities [16,17];
- Presence of osseous tissueIngrowth of osseous tissue in the resorptive defect is more often observed in vital teeth than in endodontically treated teeth [16,17]. Hypoxic conditions induced by pulp tissue extirpation may contribute to the continued growth of granulomatous tissue formation by attenuating osteoblast growth and differentiation [40,41], and stimulating osteoclastic activities [37]. On the other hand, vital teeth maintain normoxic microenvironments around PRRS and allow for the osseous replacement of granulomatous tissue in the resorptive site during normal bone remodeling at the late phase of ICR [17]. Osseous tissue substituted for and integrated into part of PRRS may also function as the protective layer [17].
6. Diagnosis and Assessment of ICR
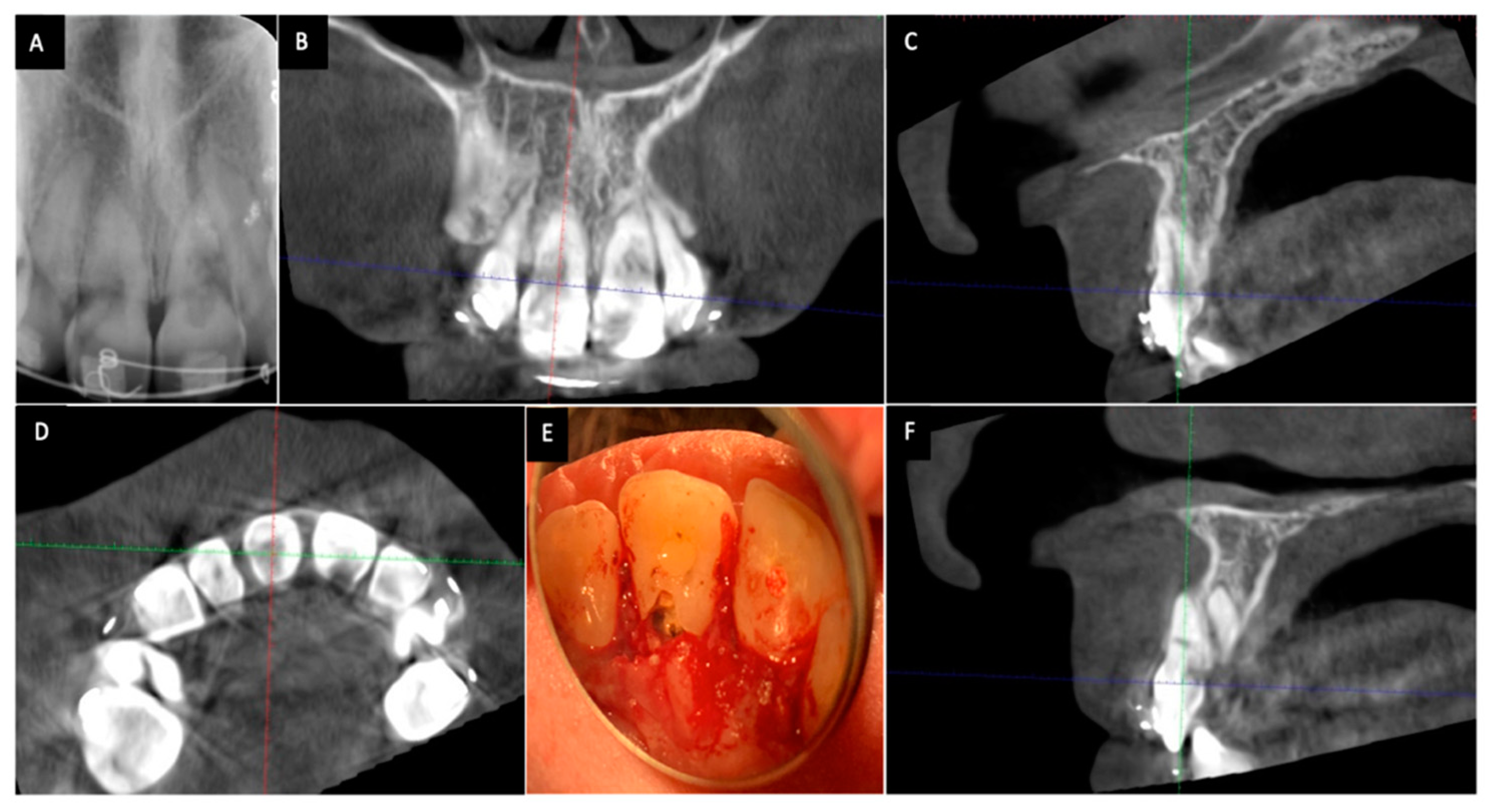
A correct diagnosis and assessment of ICR is an essential prerequisite to its successful treatment. Identification and assessment of ICR lesions heavily rely on radiographic interpretation due to their presence in the subgingival areas. ICR lesions can spread axially, horizontally, and circumferentially as they penetrate into dentin [42]. The sizes and locations of ICR lesions may not be accurately assessed when only two-dimensional radiographs are used (Figure 1). A clinical study by Patel et al. compared the effectiveness of periapical radiographs with that of cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT) in the diagnosis and assessment of ICR [43]. Receiver operating characteristic curve analysis in this study revealed that periapical radiographs had limited performance in the assessment of the size, circumferential spread and locations of the lesions compared with CBCT [43]. Furthermore, periapical radiographs showed significantly lower sensitivity and specificity than CBCT for the detection of ICR lesions [43]. The superiority of CBCT over periapical radiographs for the diagnosis of resorptive defects has also been demonstrated in in vitro studies [44,45,46]. It is highly recommended that CBCT should be used to diagnose and assess the resorptive lesions prior to treatment as stated in American Association of Endodontists/American Association of Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology Joint Position Statement [47] and European Society of Endodontology Position Statement [48] concerning the use of CBCT in Endodontics.
Figure 1.
Cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT) shows a more accurate assessment of invasive cervical resorption (ICR) lesions than two-dimensional radiographs. The size and locations of ICR lesions can be determined with CBCT. (A) Periapical radiograph showing ICR lesions in maxillary right and left incisors; (B) The coronal view of CBCT scan image showing ICR lesions in maxillary right and left incisors;(C) The sagittal view of CBCT scan image (maxillary right incisor); (D) The axial view of CBCT scan image showing the ICR lesion in maxillary right and left incisors; (E) Clinical view of ICR lesions located on the palatal surface of the teeth; (F) The sagittal view of CBCT scan image showing the ICR lesion in maxillary left incisor.
7. Classification of ICR
The classification of ICR lesions has been first developed by Heithersay for the basis of clinical assessment and research purposes [4]. ICR lesions are classified into four categories based on the size and extension of resorptive defects into dentin: Class 1, a small resorptive lesion at the cervical area with superficial penetration into dentin; Class 2, a more invasive resorptive lesion toward the coronal pulp with little or no involvement of radicular dentin; Class 3, a deep cervical resorptive lesion with the extension into the coronal third of radicular dentin; Class 4, an extensive resorptive lesion beyond the coronal third of radicular dentin. Despite the usefulness of this classification, the lesions may not be correctly classified when two-dimensional radiographs were used. Indeed, an ex vivo study by Vaz de Souza et al. showed that examiners had correctly classified 39.7% of cases with periapical radiographs, while approximately 70% cases with CBCT [49]. Moreover, there was a significantly higher intra- and inter-examiner reproducibility associated with CBCT compared to periapical radiographs [49]. To overcome the difficulties in classifying and assessing ICR lesions, Patel et al. have recently devised a three-dimensional classification method using CBCT [50]. This new classification considers three parameters, including the height of ICR lesions, the circumference of the lesions, and proximity of the lesions to root canals [50]. The height of the lesions is scored as supracrestal (1), subcrestal extending into the coronal third of radicular dentin (2), extending into the middle third of radicular dentin (3), and extending into the apical third of radicular dentin (4). The circumference of the lesions is rated as smaller than 90° (A), between 90° and 180° (B), between 180° and 270° (C), and greater than 270° (D). The proximity of the lesions to the root canal is graded as within dentin (d) and pulp involvement (p). The grading value from each parameter is combined to describe the size and extension of an ICR lesion three-dimensionally. This classification system seems to provide a more accurate assessment of the preoperative condition of ICR than the Heithersay classification and may help clinicians to have better treatment planning and management of the lesions.
8. Strategies to Manage ICR Lesions
The management of ICR lesions has focused on removing clastic cells to arrest the resorptive process and proper restoration to maintain a tooth’s structural integrity. Recently, how to reconstitute the periodontal apparatus around the resorption site also has become a new research focus. There are two main strategies proposed based on the method to arrest clastic activities: an external approach and internal approach. The external approach is comprised of surgical and nonsurgical treatment. When the lesion is accessed externally, surgical treatment, including flap surgery, may be necessary if the lesion is located and extended far below the gingival margin. However, external nonsurgical treatment can be performed if the lesion is located at the gingival margin or not extended below the alveolar bone crest. The internal approach is used to access the lesions non-surgically through the endodontic access cavity regardless of the locations of the lesions.
8.1. External Approach
Heithersay first described an external approach, including the topical application of trichloroacetic acid (TCA) to resorptive lesions, curettage of the lesions, endodontic treatment if indicated, and restoration with glass ionomer (GI) [4,51]. This nonsurgical external treatment can be performed on teeth with ICR lesions located above the coronal third of the root, but a surgical technique including periodontal flap surgery is usually performed if the lesions extend below the gingival margin. The surgical external approaches have been more commonly reported than nonsurgical external approaches perhaps due to the extensive size of the lesions at the time of detection. The surgical techniques reported in studies include removal of the resorptive lesions using TCA and/or mechanical debridement and restoration with hydraulic calcium silicate-based materials or glass ionomer cement [51,52,53].
Due to recent advances in materials and instruments, the techniques for the management of ICR lesions should be revisited with the objective of promoting healing processes and regeneration. TCA has been widely used in the management of ICR lesions. It is known to induce coagulation necrosis of the lesions [54], thereby facilitating the removal of the resorptive tissue [51]. However, it is very caustic and induces inflammation in surrounding periodontal tissue. In addition, it can remove hydroxyapatites from the dentin surface to a great extent and will compromise the bonding strength of glass ionomer (GI) [55]. The use of ultrasonic instruments under a surgical microscope may eliminate the need for TCA because it can access small internal resorptive areas without removing a significant amount of tooth structure and safely debride the lesions without irritating periodontal tissue. The use of burs should be minimized to preserve an intact tooth structure around the resorptive lesion.
GI or resin-modified glass ionomer (RMGI) has been advocated as a restorative material for the resorptive defect due to its desirable material properties such as biocompatibility, hydrophilicity, fluoride release, and chemical adhesion to dentin [56,57,58]. The subgingival placement of GI or RMGI also allows for gingival attachment [59,60], but does not induce the regeneration of cementum or bone around the materials. Hydraulic calcium silicate-based materials such as Biodentine (Septodont, Saint-Maur-des-Fossés, France) and Endosequence Root Repair Material (Brasseler, Savannah, GA, USA) have been recently adopted to restore the resorptive cavities. The main advantage of these materials over GI or RMGI is the ability to regenerate cementum, periodontal ligament, and bone [11,12,13]. If the resorptive defect is subgingival or subcrestal and accompanies periodontal tissue destruction, it is preferable to use hydraulic calcium silicate-based materials. Several case reports have been published to support the use of hydraulic calcium silicate-based materials for the restoration of ICR defects [52,53,61,62,63,64,65].
The selection of hydraulic calcium silicate-based materials for restoring ICR defects should be based on their setting time and mechanical properties such as microhardness, bond strength, washout resistance, and compressive strength because ICR defects are located around the mechanically challenging cervical area of a tooth. It is more advantageous to select the materials such as Biodentine or mineral trioxide aggregate (MTA) (ProRoot MTA, Dentsply, York, PA, USA) with a short setting time [66,67] because it allows for better retention with minimal material loss. Other fast setting materials such as Endosequence Root Repair Material-Fast Set Putty may also be considered. Concerning the mechanical properties, Biodentine seems to be a good potential candidate for the restoration of ICR defects [68]. It showed higher surface microhardness compared with GI or RMGI [69]. The push-out bond strength of Biodentine was found to be higher than MTA [70] and was not significantly affected by blood contamination [70] or endodontic irrigants such as sodium hypochlorite and chlorhexidine [71]. It also demonstrated higher washout resistance and compressive strength than MTA [66]. Hydroxyapatite crystal growth at the interface between Biodentine and dentin was confirmed by scanning electron microscopy, suggesting that the seal could improve over time [72]. In addition, it showed significantly less discoloration than MTA, preventing an aesthetic complication in anterior teeth [73]. The chemical composition of ProRoot MTA, Biodentine, and Endosequence Root Repair Material was presented in Table 1 [74,75].

Table 1.
The chemical composition of ProRoot mineral trioxide aggregate (MTA), Biodentine, and Endosequence Root Repair Material.
Orthodontic extrusion can be an alternative to accessing the lesions without surgical interventions [55,76,77]. Intentional replantation has been recently proposed to manage the lesions that are difficult to access [77].
8.2. Internal Approach
It may sound unreasonable to treat ICR lesions internally because the source of resorption (clastic cells and blood supply) originates from and exists on the external surface of teeth, but nonsurgical internal methods to address the lesions by eliminating the source also have been proposed.
Salzano and Tirone successfully treated four cases with Heithersay Class 4 ICR lesions in their case series by using a nonsurgical internal approach [78]. The resorptive granulomatous tissue was mechanically removed through access cavities and root canals and was repaired with MTA or Biodentine following root canal treatment [78]. The survival of the four treated teeth was confirmed to have no relapse of resorption and normal periradicular bone healing at a follow-up varying from four months to 18 months [78]. Similar case reports and case series were reported to have promising outcomes at follow-ups longer than two years [79,80,81]. However, this approach has major shortcomings, including difficulty in removing all resorptive tissue through limited internal access and excessive removal of the tooth structure that may make treated teeth more susceptible to fracture.
Shemesh et al. showed the most conservative method to address Heithersay Class 4 ICR lesions in four maxillary anterior teeth [82]. They used ultrasonically activated sodium hypochlorite irrigation and four-week calcium hydroxide medication to dissolve and necrotize the resorptive tissue without mechanically removing the lesions. The root canals and resorptive defects were filled with gutta percha and sealer only without calcium silicate-based materials [82]. The teeth survived without radiographic progression of resorption at a three-year or five-year follow-up [82].
Another internal method using nonsurgical root canal treatment and obturation with a type of calcium silicate-based cements (calcium-enriched mixture cement) was suggested by Asgary and Nosrat in their case report [83]. A mandibular lateral incisor with a Heithersay Class 4 ICR lesion was endodontically treated in a single visit using chemomechanical instrumentation and filling with the calcium-enriched mixture cement [83]. Normal periapical and periradicular healing with arrested resorption was observed at a two-year follow-up [83]. It was suggested that calcium silicate-based cement placed in the root canal could deactivate clastic cells and arrest the resorptive process by releasing calcium hydroxide. It is presumed that calcium hydroxide used for four weeks prior to root canal filling in the case series by Shemesh et al. [82] may have a therapeutic effect on ICR lesions similar to that of the calcium silicate-based cement in this case report. A case report by Patni et al. used two-week calcium hydroxide medication followed by obturation with Biodentine for the treatment of maxillary lateral incisor with a Class 4 lesion [84]. The tooth was found to be asymptomatic and have periapical healing at a five-year follow-up [84].
A most recent case series suggested that teeth with ICR lesions and normal pulp could be treated by using vital pulp therapy with calcium-enriched mixture cement [85]. Five mandibular molars and one maxillary molar underwent partial pulp excavation to the level of ICR lesions followed by the application of calcium-enriched mixture cement in order to exert the therapeutic effect of the cement near the resorptive lesions [85]. All six teeth treated using vital pulp therapy survived without signs of new resorption at a follow-up period ranging from 12 to 36 months [85]. Alkalinization of the lesions by the sustained release of calcium hydroxide from the cement was thought to arrest clastic activities and promote the healing process [86].
Various internal approaches were proposed to manage ICR lesions [62,78,79,80,81,82,83,84,85]. In general, more extensive resorptive lesions have been managed with internal approaches [78,82,83] because external surgical or nonsurgical approaches require the complete excavation of lesions through the tooth structure that may compromise the long-term survival of treated teeth.
9. Prognosis
There is limited information regarding the outcomes of treatment for ICR lesions due to the scarcity of clinical outcome studies. A majority of studies are case reports and case series [8,20,21,52,53,55,62,63,64,65,78,79,80,81,82,83,84,85], and it may be difficult to predict the prognosis of treated teeth based on those studies because only successful cases tend to be reported. Furthermore, due to the disease rarity, clinical studies may seem difficult to perform.
A clinical study by Heithersay reported the outcomes of the external management of ICR lesions according to his classification of the lesions [51]. The external technique included the use of 90% TCA, curettage, root canal treatment when indicated, and GI restoration for resorptive defects. The outcome was assessed using the success criteria defined as periapical and periradicular healing with no signs of resorption. Based on the analysis of 101 affected teeth in 94 patients with at least three year follow-up period, 100% success was observed for teeth with class 1 and 2 lesions [51]. The success rate was 78% for class 3 lesions, and 2% for class 4 lesions [51]. The reported success rates suggest that the external approach is not advisable for teeth with class 4 lesions. The internal approach using hydraulic calcium silicate-based materials may be indicated for these extensive resorptive defects, although there are only a few successful case reports or case series available [62,78,79,80,81,82,83,84,85].
10. Concluding Remarks
ICR is an aggressive, subepithelial, supra-osseous resorptive process that gradually replaces the unprotective mineralized tooth structure with fibro-vascular tissue and/or fibrous-osseous tissue. The mechanism for ICR resorption is poorly understood, but various dental procedures that cause physical or chemical damages to unmineralized protective layers on the external surface of teeth seem to contribute to the initiation of resorption. Histopathologic analyses revealed the differences in the pattern of ICR between endodontically treated teeth and vital teeth. Due to the presence of PRRS and normoxic microenvironments, less invasive resorption with more fibrous osseous tissue is observed in vital teeth than in endodontically treated teeth. For the diagnosis and assessment of ICR lesions, CBCT is highly recommended because two-dimensional radiographs may underestimate the size of lesions and cannot correctly locate the lesions three-dimensionally. The removal of clastic cells in the resorptive lesions, followed by the restoration of the defect, is the main treatment strategy. Two main approaches have been proposed to address the clastic activities. External approaches have been more commonly used, since they are directed at the complete removal of the source of resorption and better sealing and restoration of the defects with bioactive materials such as hydraulic calcium silicate-based materials. However, the low success rates reported for the management of extensive ICR lesions deter the implementation of the external method and likely warrant a different approach. Internal approaches have been proposed as a new alternative, mainly for the management of the extensive lesions. The internal use of hydraulic calcium silicate-based materials may be suggested to reverse the resorptive process, as reported in case reports and case series. Clinical outcome studies are required to confirm the therapeutic effect of hydraulic calcium silicate-based materials on ICR lesions.
Author Contributions
writing—original draft preparation, O.R., P.W. and S.G.K.; writing—review and editing, S.G.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Heithersay, G.S. Invasive cervical resorption: An analysis of potential predisposing factors. Quintessence Int. 1999, 30, 83–95. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gulsahi, A. Clinical and radiographic appearances of invasive cervical resorption. J. Oral Health Den. Manag. 2014, 13, 934–939. [Google Scholar]
- Irinakis, E.; Aleksejuniene, J.; Shen, Y.; Haapasalo, M. External cervical resorption—A retrospective case-control study. J. Endod. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heithersay, G.S. Invasive cervical resorption. Endod. Top. 2004, 7, 73–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, A.L. External–internal progressive resorption and its non-surgical correction. J. Endod. 1981, 7, 473–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, A.L.; Blakland, L.K. Supra osseous extra-canal invasive resorption. J. Endod. 1987, 13, 348–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, S.; Kanagasingam, S.; Pitt Ford, T. External cervical resorption: A review. J. Endod. 2009, 35, 616–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gold, S.I.; Hasselgren, G. Peripheral inflammatory root resorption. A review of the literature with case reports. J. Clin. Periodontol. 1992, 19, 523–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trope, M. Root resorption of dental and traumatic origin: Classification based on Etiology. Pr. Periodont. Aesthet. Dent. 1998, 10, 515–522. [Google Scholar]
- Fish, E.W. Begnign neoplasia of tooth and bone. Proc. R. Soc. Med. 1941, 34, 427–432. [Google Scholar]
- Parirokh, M.; Torabinejad, M. Mineral trioxide aggregate: A comprehensive literature review—Part III: Clinical applications, drawbacks, and mechanism of action. J. Endod. 2010, 36, 400–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hakki, S.S.; Bozkurt, S.B.; Hakki, E.E.; Belli, S. Effects of mineral trioxide aggregate on cell survival, gene expression associated with mineralized tissues, and biomineralization of cementoblasts. J. Endod. 2009, 35, 513–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prati, C.; Gandolfi, M.G. Calcium silicate bioactive cements: Biological perspectives and clinical applications. Dent. Mater. 2015, 31, 351–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lovato, K.F.; Sedgley, C.M. Antibacterial activity of endosequence root repair material and proroot MTA against clinical isolates of Enterococcus faecalis. J. Endod. 2011, 37, 1542–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sipert, C.R.; Hussne, R.P.; Nishiyama, C.K.; Torres, S.A. In vitro antimicrobial activity of Fill Canal, Sealapex, Mineral Trioxide Aggregate, Portland cement and EndoRez. Int. Endod. J. 2005, 38, 539–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mavridou, A.M.; Hauben, E.; Wevers, M.; Schepers, E.; Bergmans, L.; Lambrechts, P. Understanding external cervical resorption patterns in endodontically treated teeth. Int. Endod. J. 2017, 50, 1116–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mavridou, A.M.; Hauben, E.; Wevers, M.; Schepers, E.; Bergmans, L.; Lambrechts, P. Understanding external cervical resorption in vital teeth. J. Endod. 2016, 42, 1737–1751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heithersay, G.S. Invasive cervical resorption following trauma. Aust. Endod. J. 1999, 25, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeng, P.Y.; Lin, L.D.; Chang, S.H.; Lee, Y.L.; Wang, C.Y.; Jeng, J.H.; Tsai, Y.L. Invasive cervical resorption-distribution, potential predisposing factors, and clinical characteristics. J. Endod. 2020, 46, 475–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Mahony, A.; McNamara, C.; Ireland, A.; Sandy, J.; Puryer, J. Invasive cervical resorption and the oro-facial cleft patient: A review and case series. Br. Dent. J. 2017, 222, 677–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Lo Giudice, G.; Matarese, G.; Lizio, A.; Lo Giudice, R.; Tumedei, M.; Zizzari, V.L.; Tete, S. Invasive cervical resorption: A case series with 3-year follow-up. Int. J. Periodontics Restor. Dent. 2016, 36, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kim, Y.; Lee, C.Y.; Kim, E.; Roh, B.D. Invasive cervical resorption: Treatment challenges. Restor. Dent. Endod. 2012, 37, 228–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Discacciati, J.A.; de Souza, E.L.; Costa, S.C.; Sander, H.H.; Barros, V.M.; Vasconcellos, W.A. Invasive cervical resorption: Etiology, diagnosis, classification and treatment. J. Contemp. Dent. Pr. 2012, 13, 723–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madison, S.; Walton, R. Cervical root resorption following bleaching of endodontically treated teeth. J. Endod. 1990, 16, 570–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, S.; Rotstein, I.; Libfeld, H.; Stabholz, A.; Heling, I. Incidence of external root resorption and esthetic restuls in 58 bleached pulpless teeth. Endod. Dent. Traumatol. 1988, 4, 23–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heithersay, G.S.; Dahlstrom, S.W.; Marin, P.D. Incidence of invasive cervical resorption in bleached root-filled teeth. Aust. Dent. J. 1994, 39, 82–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rotstein, I.; Friedman, S.; Mor, C.; Katznelson, J.; Sommer, M.; Bab, I. Histological characterization of bleaching-induced external root resorption in dogs. J. Endod. 1991, 17, 436–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neuvald, L.; Consolaro, A. Cementoenamel junction; microscopic analysis and external cervical resorption. J. Endod. 2000, 26, 503–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroeder, H.E.; Scherle, W.F. Cemento-enamel junction—Revisted. J. Periodontal. Res. 1988, 23, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arroyo-Bote, S.; Bucchi, C.; Manzanares, M.C. External cervical resorption: A new oral manifestation of systemic sclerosis. J. Endod. 2017, 43, 1740–1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liena-Puy, M.C.; Amengual-Lorenzo, J.; Forner-Navarro, L. Idiopathic external root resorption associated to hypercalciuria. Med. Oral. 2002, 7, 192–199. [Google Scholar]
- Von Arx, T.; Schawalder, P.; Ackermann, M.; Bosshardt, D.D. Human and feline invasive cervical resorption: The missing link?-Presentation of four cases. J. Endod. 2009, 35, 904–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, K.; Schirru, E.; Niazi, S.; Mitchell, P.; Mannocci, F. Multiple apical radiolucencies and external cervical resorption associated with varicella zoster virus: A case report. J. Endod. 2016, 42, 978–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, V.; Chawla, A.; Kaur, A. Multiple idiopathic cervical root resorptions in patients with hepatitis B virus infection. J. Endod. 2018, 44, 1575–1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, S.; Saberi, N. External cervical resorption associated with the use of biosphosphonates: A case series. J. Endod. 2015, 742–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mavridou, A.; Bergmans, L.; Barendregt, D.; Lambrechts, P. Descriptive analysis of factors associated with external cervical resorption. J. Endod. 2017, 43, 1602–1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnett, T.R.; Gibbons, D.C.; Utting, J.C.; Orriss, I.R.; Hoebertz, A.; Rosendaal, M.; Meghji, S. Hypoxia is a major stimulator of osteoclast formation and bone resorption. J. Cell. Physiol. 2003, 196, 2–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mavridou, A.M.; Hikens, P.; Lambrichts, I.; Hauben, E.; Wevers, M.; Bergmans, L.; Lambrechts, P. Is hypoxia related to external cervical resorption? A case report. J. Endod. 2019, 45, 459–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, S.; Mavridou, A.M.; Lambrechts, P.; Saberi, N. External cervical resorption—Part 1: Histopathology, distribution and presentation. Int. Endod. J. 2018, 51, 1205–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Utting, J.C.; Robins, S.P.; Brandao-Burch, A.; Orriss, I.R.; Behar, J.; Arnett, T.R. Hypoxia inhibits the growth, differentiation and bone-forming capacity of rat osteoblasts. Exp. Cell. Res. 2006, 312, 1693–1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnett, T.R. Acidosis, hypoxia and bone. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2010, 503, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunst, V.; Mavridou, A.; Huybrechts, B.; Van Gorp, G.; Bergmans, L.; Lambrechts, P. External cervical resorption: An analysis using cone beam and microfocus computed tomography and scanning electron microscopy. Int. Endod. J. 2013, 46, 877–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, K.; Mannocci, F.; Patel, S. The assessment and management of external cervical resorption with periapical radiographs and cone-beam computed tomography: A clinical study. J. Endod. 2016, 42, 1435–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Creanga, A.G.; Geha, H.; Sankar, V.; Teixeira, F.B.; McMahan, C.A.; Noujeim, M. Accuracy of digital periapical radiography and cone-beam computed tomography in detecting external root resorption. Imaging Sci. Dent. 2015, 45, 153–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Addazio, P.; Campos, C.; Ozcan, M.; Teixeira, H.G.C.; Passoni, R.M.; Carvalho, A.C.P. A comparative study between cone-beam computed tomography and periapical radiographs in the diagnosis of simulated endodontic complications. Int. Endod. J. 2011, 44, 218–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deliga Schroder, A.G.; Westphalen, F.H.; Schroder, J.C.; Fernandes, A.; Westphalen, V.P.D. Accuracy of digital periapical radiography and cone-beam computed tomography for diagnosis of natural and simulated external root resorption. J. Endod. 2018, 44, 1151–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AAE/AAOMR Joint Position Statement. Available online: https://f3f142zs0k2w1kg84k5p9i1o-wpengine.netdna-ssl.com/specialty/wp-content/uploads/sites/2/2017/06/conebeamstatement.pdf (accessed on 1 June 2020).
- Patel, S.; Brown, J.; Semper, M.; Abella, F.; Mannocci, F. European Society of Endodontology position statement: Use of cone beam computed tomography in endodontics: European Society of Endodontology (ESE) developed by. Int. Endod. J. 2019, 52, 1675–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaz de Souza, D.; Schirru, E.; Mannocci, F.; Foschi, F.; Patel, S. External cervical resorption: A comparison of the diagnostic efficacy using 2 different cone-beam computed tomographic units and periapical radiographs. J. Endod. 2017, 43, 121–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, S.; Forschi, F.; Mannocci, F.; Patel, K. External cervical resorption: A three-dimensional classification. Int. Endod. J. 2018, 51, 206–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heithersay, G.S. Treatment of invasive cervical resorption: Analysis of results using topical application of trichloracetic acid, curettage, and restoration. Quintessence Int. 1999, 30, 96–110. [Google Scholar]
- Karunakar, P.; Soloman, R.V.; Anusha, B.; Nagarjun, M. Endodontic management of invasive cervical resorption: Report of two cases. J. Coserv. Dent. 2018, 21, 578–681. [Google Scholar]
- Tsaousoglou, P.; Markou, E.; Efthimiades, N.; Vouros, I. Characteristics and treatment of invasive cervical resorption in vital teeth. A narrative review and a report of two cases. Br. Dent. J. 2017, 222, 423–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heithersay, G.S.; Wilson, D.F. Tissue responses in the rat to trichloracetic acid-an agent used in the treatment of invasive cervical resorption. Aust. Dent. J. 1988, 33, 451–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwartz, R.S.; Robbins, J.W.; Rindler, E. Management of invasive cervical resorption: Observations from three private practices and a report of three cases. J. Endod. 2010, 36, 1721–1730. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tantbirojn, D.; Feigal, R.J.; Ko, C.C.; Versluis, A. Remineralized dentin lesions induced by glass ionomer demonstrate increased resistance to subsequent acid challenge. Quintessence Int. 2006, 37, 273–281. [Google Scholar]
- Hasan, A.M.H.R.; Sidhu, S.K.; Nicholson, J.W. Fluoride release and uptake in enhanced bioactivity glass ionomer cememt (“glass carbomer™”) compared with conventional and resin-modified glass ionomer cements. J. Appl. Oral Sci. 2019, 27, e20180230. [Google Scholar]
- Sidhu, S.K.; Nicholson, J.W. A review of glass-ionomer cements for clinical dentistry. J. Funct. Biomater. 2016, 7, 16. [Google Scholar]
- Santamaria, M.P.; da Silva Feitosa, D.; Nociti, F.H.; Casati, M.Z.; Sallum, A.W.; Sallum, E.A. Cervical restoration and amount of soft tissue coverage achieved by coronally advanced flap. A 2-year-follow-up randomized controlled clinical trial. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2009, 36, 434–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santamaria, M.P.; Ambrosano, G.M.; Casati, M.Z.; Nociti, F.H.; Sallum, A.W., Jr.; Sallum, E.A. Connective tissue graft plus resin-modified glass ionomer restoration for the treatment of gingival recession associated with non-carious cervical lesion: A randomized-controlled clinical trial. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2009, 36, 791–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikhar, A.; Thakur, N.; Patel, A.; Bhede, R.; Ptail, P.; Gupta, S. Management of external invasive cervical resorption tooth with mineral trioxide aggregate: A case report. Case. Rep. Med. 2013, 2013, 139801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eftekhar, L.; Ashraf, H.; Jabbari, S. Management of invasive cervical resorption lesions in a mandibular canine using Biodentine as a restorative material: A case report. Iran. Endod. J. 2017, 12, 386–389. [Google Scholar]
- Karypidou, A.; Chatzinkikolaou, I.D.; Kouros, P.; Koulaouzidou, E.; Econonomides, N. Management of bilateral invasive cervical resorption lesions in maxillary incirosrs using a novel calcium-silicate-based cement: A case report. Quintessence Int. 2016, 47, 637–642. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, S.S.; Kumar, N.S.; Karunakaran, J.V.; Nagendran, S. Management of invasive cervical resorption in a maxillary central incisor. J. Pharm. Bioallied. Sci. 2015, 7, S712–S717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baranwal, A.K. Management of external invasive cervical resorption of tooth with Biodentine: A case report. J. Conserv. Dent. 2016, 19, 296–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grech, L.; Mallia, B.; Camilleri, J. Invesitigation of the physical properties of tricalcium silicate cement-based root-end filling materials. Dent. Mater. 2013, 29, e20–e28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.-J.; Du, T.-F.; Li, H.-B.; Shen, Y.; Mobuchon, C.; Hieawy, A.; Wang, Z.-J.; Yang, Y.; Ma, J.; Haapasalo, M. Physical properties and hydration behavior of a fast-setting bioceramic endodontic material. BMC Oral Health 2016, 16, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malkondu, O.; Karapinar Kaandag, M.; Kazazoglu, E. A review on biodentine, a contemporary dentine replacement and repair material. Biomed. Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 160951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camilleri, J. Investigation of Biodentine as dentine replacement material. J. Dent. 2013, 41, 600–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aggarwal, V.; Singla, M.; Miglani, S.; Kohli, S. Comparative evaluation of push-out bond strength of ProRoot MTA, Biodentine, and MTA plus in furcation perforation repair. J. Conserv. Dent. 2013, 16, 462–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guneser, M.B.; Akbulut, M.B.; Eldeniz, A.U. Effect of various endodontic irrigants on the push-out bond strength of Biodentine and conventional root perforation repair materials. J. Endod. 2013, 39, 380–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gjorgievska, E.S.; Nicholson, J.W.; Apostolska, S.M.; Coleman, N.J.; Booth, S.E.; Slipper, I.J.; Miadenov, M.I. Interfacial properties of three different bioactive dentine substitutes. Microsc. Microanal. 2013, 19, 1450–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valles, M.; Roig, M.; Duran-Sindreu, F.; Martinez, S.; Mercade, M. Color stability of teeth restored with Biodentine: A 6-month in vitro study. J. Endod. 2015, 41, 1157–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaur, M.; Singh, H.; Dhillon, J.S.; Batra, M.; Saini, M. MTA Versus Biodentine: Review of Literature With a Comparative Analysis. J. Clin. Diagn. Res. 2017, 11, ZG01–ZG05. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, J.; Shen, Y.; Stojicic, S.; Haapasalo, M. Biocompatibility of two novel root repair materials. J. Endod. 2011, 37, 793–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smidt, A.; Nuni, E.; Keinan, D. Invasive cervical root resorption: Treatment rationale with an interdisciplinary approach. J. Endod. 2007, 33, 1383–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espona, J.; Roig, E.; Duran-Sindreu, F.; Abella, F.; Machado, M.; Roig, M. Invasive Cervical resorption: Clinical management in the anterior zone. J. Endod. 2018, 44, 1749–1754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salzano, S.; Tirone, F. Conservative nonsurgical treatment of class 4 invasive cervical resorption: A case series. J. Endod. 2015, 41, 1907–1912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baratto-Filho, F.; Limongi, O.; Araujo, C.D.J.R.; Neto, M.D.; Maia, S.M.; Santana, D. Treatment of invasive cervical resorption with MTA: Case report. Aust. Endod. J. 2005, 31, 76–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.B.; Lee, J.H. Use of mineral trioxide aggregrate in the non-surgical repair of perforating invasive cervical resorption. Med. Oral Patol. Oral Cir. Bucal. 2008, 1, E678–E680. [Google Scholar]
- Pace, R.; Giuliani, V.; Pagavino, G. Mineral trioxide aggregate in the treatment of external invasive resorption: A case report. Int. Endod. J. 2008, 41, 258–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shemesh, A.; Ben Itzhak, J.; Solomonov, M. Minimally invasive treatment of class 4 invasive cervical resorption with internal approach: A case series. J. Endod. 2017, 43, 1901–1908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asgary, S.; Nosrat, A. Conservative management of class 4 invasive cervical root resorption using calcium-enriched mixture cement. J. Endod. 2016, 42, 1291–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patni, P.M.; Jain, P.; Jain, S.; Hiremath, H.; Agarwal, R.; Patni, M.J. Internal tunneling resorption associated with invasive cervical resorption. J. Conserv. Dent. 2018, 21, 105–108. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Asgary, S.; Nourzadeh, M.; Verma, P.; Lamar Hicks, M.; Nosrat, A. Vital pulp therapy as a conservative approach for management of invasive cervical resorption: A case series. J. Endod. 2019, 45, 1161–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierce, A. Experimental basis for the management of dental resorption. Endod. Dent. Traumatol. 1989, 5, 255–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).