Omega-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids and the Intestinal Epithelium—A Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Models for Studying the Intestinal Epithelium
3. ω-3 PUFAs and Intestinal Epithelial Fatty Acid Composition
4. ω-3 PUFAs and Intestinal Epithelial Morphology
5. ω-3 PUFAs and Intestinal Permeability
6. ω-3 PUFAs and Intestinal Epithelial Inflammation
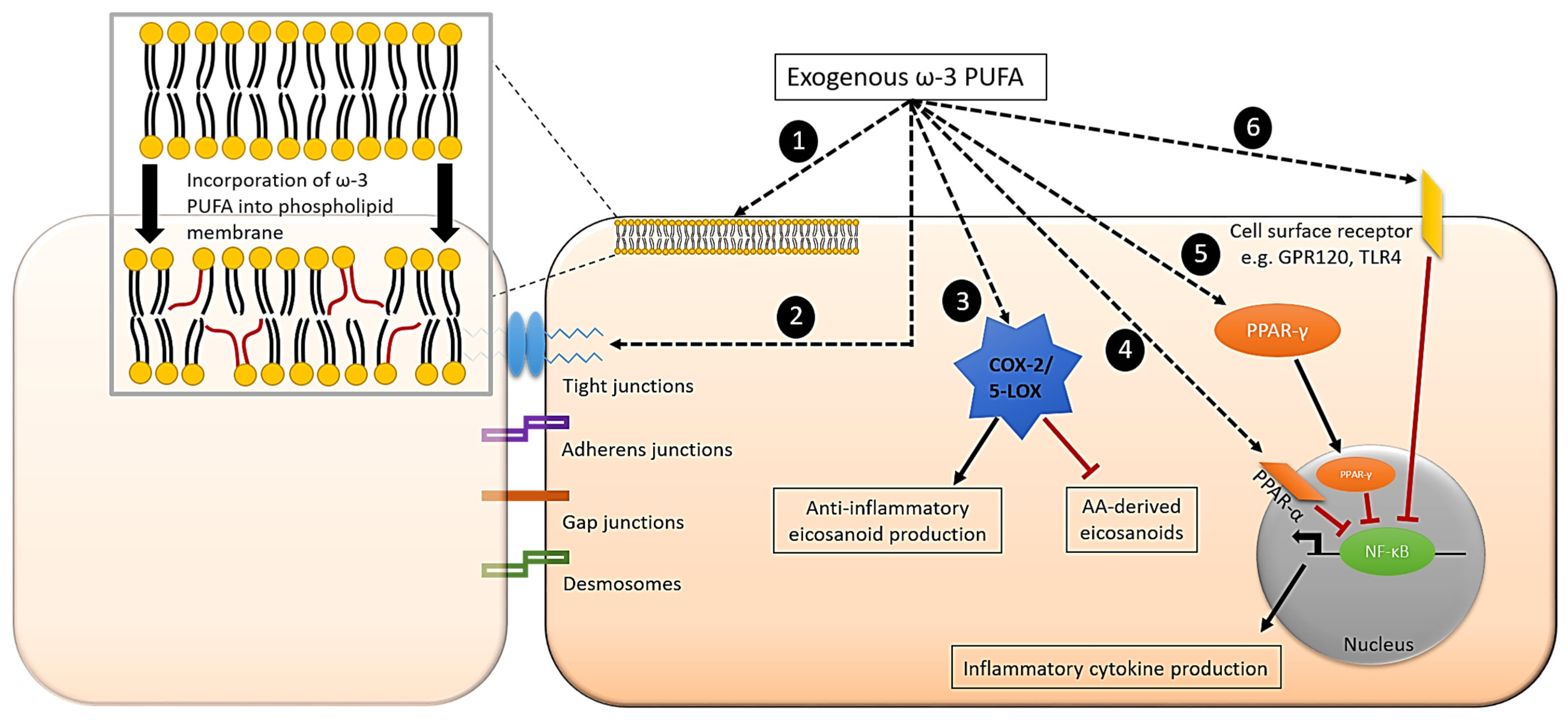
7. Effect of ω-3 PUFAs on Inflammatory Signalling Pathways in Intestinal Epithelial Cells
8. Gut Microbiota, Gut Inflammation, and ω-3 PUFAs
9. ω-3 PUFAs and Human IBD
10. Summary, Concluding Remarks and Limitations of the Literature
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- McCole, D.F.; Barrett, K.E. Varied role of the gut epithelium in mucosal homeostasis. Curr. Opin. Gastroenterol. 2007, 23, 647–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michielan, A.; D’Inca, R. Intestinal permeability in inflammatory bowel disease: Pathogenesis, clinical evaluation, and therapy of leaky gut. Mediat. Inflamm. 2015, 2015, 628157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morrison, D.J.; Preston, T. Formation of short chain fatty acids by the gut microbiota and their impact on human metabolism. Gut Microbes 2016, 7, 189–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, N.; Li, N.; Duan, X.; Niu, H. Interaction between the gut microbiome and mucosal immune system. Milit. Med. Res. 2017, 4, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guillot, X.; Semerano, L.; Saidenberg-Kermanac’h, N.; Falgarone, G.; Boissier, M.-C. Vitamin D and inflammation. Joint Bone Spine 2010, 77, 552–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Souyoul, S.A.; Saussy, K.P.; Lupo, M.P. Nutraceuticals: A review. Dermatol. Ther. 2018, 8, 5–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Tsao, R. Dietary polyphenols, oxidative stress and antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2016, 8, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, J.; McKenzie, C.; Potamitis, M.; Thorburn, A.N.; Mackay, C.R.; Macia, L. The Role of short-chain fatty acids in health and disease. Adv. Immunol. 2014, 121, 91–119. [Google Scholar]
- Wall, R.; Ross, R.P.; Fitzgerald, G.F.; Stanton, C. Fatty acids from fish: The anti-inflammatory potential of long-chain omega-3 fatty acids. Nutr. Rev. 2010, 68, 280–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calder, P.C. Marine omega-3 fatty acids and inflammatory processes: Effects, mechanisms and clinical relevance. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids 2015, 1851, 469–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calder, P.C. Omega-3 fatty acids and inflammatory processes: From molecules to man. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2017, 45, 1105–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Bus, I.; Witkamp, R.; Zuilhof, H.; Albada, B.; Balvers, M. The role of n-3 PUFA-derived fatty acid derivatives and their oxygenated metabolites in the modulation of inflammation. Prostagland. Other Lipid Mediat. 2019, 144, 106351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Innes, J.K.; Calder, P.C. Marine omega-3 (n-3) fatty acids for cardiovascular health: An update for 2020. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miles, E.A.; Calder, P.C. Influence of marine n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids on immune function and a systematic review of their effects on clinical outcomes in rheumatoid arthritis. Brit. J. Nutr. 2012, 107, S171–S184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calder, P.C. Polyunsaturated fatty acids, inflammatory processes and inflammatory bowel diseases. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2008, 52, 885–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahidi, F.; Ambigaipalan, P. Omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids and their health benefits. Ann. Rev. Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 9, 345–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calder, P.C. Is increasing microbiota diversity a novel anti-inflammatory action of marine n-3 fatty acids? J. Nutr. 2019, 149, 1102–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arterburn, L.M.; Hall, E.B.; Oken, H. Distribution, interconversion, and dose response of n-3 fatty acids in humans. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2006, 83, 1467S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derikx, J.P.M.; Luyer, M.D.P.; Heineman, E.; Buurman, W.A. Non-invasive markers of gut wall integrity in health and disease. World J. Gastroenterol. 2010, 16, 5272–5279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cencič, A.; Langerholc, T. Functional cell models of the gut and their applications in food microbiology—A review. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2010, 141, S4–S14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon-Assmann, P.; Turck, N.; Sidhoum-Jenny, M.; Gradwohl, G.; Kedinger, M. In Vitro models of intestinal epithelial cell differentiation. Cell Biol. Toxicol. 2007, 23, 241–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakolish, C.M.; Esch, M.B.; Hickman, J.J.; Shuler, M.L.; Mahler, G.J. Modeling barrier tissues In Vitro: Methods, achievements, and challenges. EBioMed 2016, 5, 30–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosella, O.; Sinclair, A.; Gibson, P.R. Polyunsaturated fatty acids reduce non-receptor-mediated transcellular permeation of protein across a model of intestinal epithelium in vitro. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2000, 15, 626–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, G.; Tang, L.; Yuan, F.; Zhu, W.; Zhang, S.; Liu, Z.; Su, L. Eicosapentaenoic acid enhances heat stress-impaired intestinal epithelial barrier function in Caco-2 cells. Plos ONE 2013, 8, e73571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beguin, P.; Schneider, A.-C.; Mignolet, E.; Schneider, Y.-J.; Larondelle, Y. Polyunsaturated fatty acid metabolism in enterocyte models: T84 cell line vs. Caco-2 cell line. In Vitro Cell Dev. Biol. Anim. 2014, 50, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willemsen, L.E.; Koetsier, M.A.; Balvers, M.; Beermann, C.; Stahl, B.; van Tol, E.A. Polyunsaturated fatty acids support epithelial barrier integrity and reduce IL-4 mediated permeability In Vitro. Eur J. Nutr. 2008, 47, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, M.; Zhao, S.; Xu, G.; Li, J. n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids prevent disruption of epithelial barrier function induced by proinflammatory cytokines. Mol. Immunol. 2008, 45, 1356–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renaville, B.; Mullen, A.; Moloney, F.; Larondelle, Y.; Schneider, Y.J.; Roche, H.M. Eicosapentaenoic acid and 3,10 dithia stearic acid inhibit the desaturation of trans-vaccenic acid into cis-9, trans-11-conjugated linoleic acid through different pathways in Caco-2 and T84 cells. Brit. J. Nutr. 2006, 95, 688–695. [Google Scholar]
- Nieto, N.; Torres, M.I.; Ríos, A.; Gil, A. Dietary polyunsaturated fatty acids improve histological and biochemical alterations in rats with experimental ulcerative colitis. J. Nutr. 2002, 132, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosco, N.; Brahmbhatt, V.; Oliveira, M.; Martin, F.-P.; Lichti, P.; Raymond, F.; Benyacoub, J. Effects of increase in fish oil intake on intestinal eicosanoids and inflammation in a mouse model of colitis. Lipids Health Dis. 2013, 12, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brahmbhatt, V.; Oliveira, M.; Briand, M.; Perrisseau, G.; Schmid, V.B.; Destaillats, F.; Bosco, N. Protective effects of dietary EPA and DHA on ischemia–reperfusion-induced intestinal stress. J. Nutr Biochem. 2013, 24, 104–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reifen, R.; Karlinsky, A.; Stark, A.H.; Berkovich, Z.; Nyska, A. α-Linolenic acid (ALA) is an anti-inflammatory agent in inflammatory bowel disease. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2015, 26, 1632–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, G.; Yuan, F.; Geng, Y.; Qiu, X.; Liu, Z.; Lu, J.; Su, L. Eicosapentaenoic acid enhances heatstroke-impaired intestinal epithelial barrier function in rats. Shock 2015, 44, 348–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hillier, K.; Jewell, R.; Dorrell, L.; Smith, C. Incorporation of fatty acids from fish oil and olive oil into colonic mucosal lipids and effects upon eicosanoid synthesis in inflammatory bowel disease. Gut 1991, 32, 1151–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawthorne, A.; Daneshmend, T.; Hawkey, C.; Belluzzi, A.; Everitt, S.; Holmes, G.; Willars, J.E. Treatment of ulcerative colitis with fish oil supplementation: A prospective 12 month randomised controlled trial. Gut 1992, 33, 922–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudert, C.A.; Weylandt, K.H.; Lu, Y.; Wang, J.; Hong, S.; Dignass, A.; Kang, J.X. Transgenic mice rich in endogenous omega-3 fatty acids are protected from colitis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 11276–11281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilaseca, J.; Salas, A.; Guarner, F.; Rodriguez, R.; Martinez, M.; Malagelada, J. Dietary fish oil reduces progression of chronic inflammatory lesions in a rat model of granulomatous colitis. Gut 1990, 31, 539–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Empey, L.R.; Jewell, L.D.; Garg, M.L.; Thomson, A.B.; Clandinin, M.T.; Fedorak, R.N. Fish oil-enriched diet is mucosal protective against acetic acid-induced colitis in rats. Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 1991, 69, 480–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoda, R.; Matsueda, K.; Yamato, S.; Umeda, N. Therapeutic efficacy of N-3 polyunsaturated fatty acid in experimental Crohn’s disease. J. Gastroenterol. 1995, 30, 98–101. [Google Scholar]
- Yuceyar, H.; Ozutemiz, O.; Huseyinov, A.; Saruc, M.; Alkanat, M.; Bor, S.; Batur, Y. Is administration of n-3 fatty acids by mucosal enema protective against trinitrobenzene-induced colitis in rats? Prostagland Leukotr. Essent. Fat. Acids 1999, 61, 339–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caplan, M.S.; Russell, T.; Xiao, Y.; Amer, M.; Kaup, S.; Jilling, T. Effect of polyunsaturated fatty acid (PUFA) supplementation on intestinal inflammation and necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC) in a neonatal rat model. Ped. Res. 2001, 49, 647–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andoh, A.; Tsujikawa, T.; Ishizuka, I.; Araki, Y.; Sasaki, M.; Koyama, S.; Fujiyama, Y. N-3 fatty acid-rich diet prevents early response of interleukin-6 elevation in trinitrobenzene sulfonic acid-induced enteritis. Int J. Mol. Med. 2003, 12, 721–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, J.; Jilling, T.; Li, D.; Caplan, M.S. Polyunsaturated fatty acid supplementation alters proinflammatory gene expression and reduces the incidence of necrotizing enterocolitis in a neonatal rat model. Ped. Res. 2007, 61, 427–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassan, A.; Ibrahim, A.; Mbodji, K.; Coëffier, M.; Ziegler, F.; Bounoure, F.; Marion-Letellier, R. An α-linolenic acid-rich formula reduces oxidative stress and inflammation by regulating NF-κB in rats with TNBS-induced colitis. J. Nutr. 2010, 140, 1714–1721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, X.; Li, N.; Li, J. The study of n-3 PUFAs protecting the intestinal barrier in rat HS/R model. Lipids Health Dis. 2014, 13, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Shi, P.; Sun, Y.; Sun, J.; Dong, J.N.; Wang, H.G.; Zhu, W.M. DHA protects against experimental colitis in IL-10-deficient mice associated with the modulation of intestinal epithelial barrier function. Brit. J. Nutr. 2015, 114, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chien, Y.-W.; Peng, H.-C.; Chen, Y.-L.; Pai, M.-H.; Wang, H.-Y.; Chuang, H.-L.; Yang, S.C. Different dietary proportions of fish oil regulate inflammatory factors but do not change intestinal tight junction ZO-1 expression in ethanol-fed rats. Mediat. Inflamm. 2017, 2017, 5801768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, J.; Lu, Y.; Zhi, M.; Hu, P.; Wu, W.; Gao, X. Dietary n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids ameliorate Crohn’s disease in rats by modulating the expression of PPAR-γ/NFAT. Mol. Med. Rep. 2017, 16, 8315–8322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charpentier, C.; Chan, R.; Salameh, E.; Mbodji, K.; Ueno, A.; Coëffier, M.; Marion-Letellier, R. Dietary n-3 PUFA may attenuate experimental colitis. Mediat. Inflamm. 2018, 2018, 8430614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haddi, A.; Guendouz, M.; Tabet, S.A.; Mehedi, N.; Kheroua, O.; Saidi, D. Polyunsaturated fatty acids affect intestinal anaphylactic response in BALB/c mice sensitized with β-lactoglobulin. Rev. Française d’Allergol. 2018, 58, 437–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, H.; Zhu, X.; Gong, C.; Liu, H.; Liu, F. Protective effects and mechanisms of omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acid on intestinal injury and macrophage polarization in peritoneal dialysis rats. Nephrology 2019, 24, 1081–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Z.; Dai, Z.; Cao, Y.; Shen, Q.; Zhang, Y. Docosapentaenoic acid (DPA, 22: 5n-3) ameliorates inflammation in an ulcerative colitis model. Food Funct. 2019, 10, 4199–4209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, B.; Moon, K.M.; Kim, C.Y. Tight junction in the intestinal epithelium: Its association with diseases and regulation by phytochemicals. J. Immunol. Res. 2018, 2018, 2645465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lechuga, S.; Ivanov, A.I. Disruption of the epithelial barrier during intestinal inflammation: Quest for new molecules and mechanisms. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Res. 2017, 1864, 1183–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kowalczyk, A.P.; Green, K.J. Structure, function, and regulation of desmosomes. Progr. Mol. Biol. Transl. Sci. 2013, 116, 95–118. [Google Scholar]
- Ulluwishewa, D.; Anderson, R.C.; McNabb, W.C.; Moughan, P.J.; Wells, J.M.; Roy, N.C. Regulation of tight junction permeability by intestinal bacteria and dietary components. J. Nutr. 2011, 141, 769–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunningham, K.E.; Turner, J.R. Myosin light chain kinase: Pulling the strings of epithelial tight junction function. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2012, 1258, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, T. Regulation of the intestinal barrier by nutrients: The role of tight junctions. Anim. Sci. J. 2020, 91, e13357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usami, M.; Muraki, K.; Iwamoto, M.; Ohata, A.; Matsushita, E.; Miki, A. Effect of eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) on tight junction permeability in intestinal monolayer cells. Clin. Nutr. 2001, 20, 351–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usami, M.; Komurasaki, T.; Hanada, A.; Kinoshita, K.; Ohata, A. Effect of gamma-linolenic acid or docosahexaenoic acid on tight junction permeability in intestinal monolayer cells and their mechanism by protein kinase C activation and/or eicosanoid formation. Nutrition 2003, 19, 150–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, K.; Liu, C.; Qin, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhang, J.; Liu, Y. EPA and DHA attenuate deoxynivalenol-induced intestinal porcine epithelial cell injury and protect barrier function integrity by inhibiting necroptosis signaling pathway. FASEB J. 2020, 34, 2483–2496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, H.; Ma, H.; Lu, B.; Wang, J.; Li, Y.; Li, J. Inhibitory effect of dietary n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids to intestinal IL-15 expression is associated with reduction of TCRαβ+ CD8α+ CD8β− intestinal intraepithelial lymphocytes. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2008, 19, 475–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bentley-Hewitt, K.L.; De Guzman, C.E.; Ansell, J.; Mandimika, T.; Narbad, A.; Lund, E.K. Polyunsaturated fatty acids modify expression of TGF-β in a co-culture model ultilising human colorectal cells and human peripheral blood mononuclear cells exposed to Lactobacillus gasseri, Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2014, 116, 505–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marion-Letellier, R.; Butler, M.; Dechelotte, P.; Playford, R.J.; Ghosh, S. Comparison of cytokine modulation by natural peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma ligands with synthetic ligands in intestinal-like Caco-2 cells and human dendritic cells-potential for dietary modulation of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma in intestinal inflammation. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2008, 87, 939–948. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wijendran, V.; Brenna, J.T.; Wang, D.H.; Zhu, W.; Meng, D.; Ganguli, K.; Walker, W.A. Long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids attenuate the IL-1β-induced proinflammatory response in human fetal intestinal epithelial cells. Ped. Res. 2015, 78, 626–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Kwon, M.-J.; Huang, S.; Lee, J.Y.; Fukase, K.; Inohara, N.; Hwang, D.H. Differential modulation of Nods signaling pathways by fatty acids in human colonic epithelial HCT116 cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 11618–11628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vincentini, O.; Quaranta, M.G.; Viora, M.; Agostoni, C.; Silano, M. Docosahexaenoic acid modulates In Vitro the inflammation of celiac disease in intestinal epithelial cells via the inhibition of cPLA(2). Clin. Nutr. 2011, 30, 541–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, R.; Takahashi, N.; Lin, S.; Goto, T.; Murotam, K.; Nakata, R.; Kawada, T. DHA attenuates postprandial hyperlipidemia via activating PPAR alpha in intestinal epithelial cells. J. Lipid Res. 2013, 54, 3258–3268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, P.W.; Stoll, B.J. Necrotising enterocolitis. Lancet 2006, 368, 1271–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofmanová, J.; Vaculová, A.; Kozubík, A. Polyunsaturated fatty acids sensitize human colon adenocarcinoma HT-29 cells to death receptor-mediated apoptosis. Cancer Lett. 2005, 218, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Vogel-van den Bosch, H.M.; Bünger, M.; de Groot, P.J.; Bosch-Vermeulen, H.; Hooiveld, G.J.; Müller, M. PPARalpha-mediated effects of dietary lipids on intestinal barrier gene expression. BMC Genom. 2008, 9, 231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jandhyala, S.M.; Talukdar, R.; Subramanyam, C.; Vuyyuru, H.; Sasikala, M.; Nageshwar Reddy, D. Role of the normal gut microbiota. World J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 21, 8787–8803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, L.C.-H. Microbiota dysbiosis and barrier dysfunction in inflammatory bowel disease and colorectal cancers: Exploring a common ground hypothesis. J. Biomed. Sci 2018, 25, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.-N.; Zhu, J.; Pan, W.-S.; Shen, S.-R.; Shan, W.-G.; Das, U.N. Effects of fish oil with a high content of n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids on mouse gut microbiota. Arch. Med. Res. 2014, 45, 195–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robertson, R.C.; Seira Oriach, C.; Murphy, K.; Moloney, G.M.; Cryan, J.F.; Dinan, T.G.; Stanton, C. Omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids critically regulate behaviour and gut microbiota development in adolescence and adulthood. Brain Behav. Immun. 2017, 59, 21–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djuric, Z.; Bassis, C.M.; Plegue, M.A.; Sen, A.; Turgeon, D.K.; Herman, K.; Ruffin IV, M.T. Increases in colonic bacterial diversity after ω-3 fatty acid supplementation predict decreased colonic prostaglandin E2 concentrations in healthy adults. J. Nutr. 2019, 149, 1170–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coelho, O.G.L.; Cândido, F.G.; Alfenas, R.D.C.G. Dietary fat and gut microbiota: Mechanisms involved in obesity control. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 59, 3045–3053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dourado, E.; Ferro, M.; Sousa Guerreiro, C.; Fonseca, J.E. Diet as a modulator of intestinal microbiota in rheumatoid arthritis. Nutrients 2020, 12, 3504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilag, L.L. Are long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids the link between the immune system and the microbiome towards modulating cancer? Medicines 2018, 5, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costantini, L.; Molinari, R.; Farinon, B.; Merendino, N. Impact of omega-3 fatty acids on the gut microbiota. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shama, S.; Liu, W. Omega-3 fatty acids and gut microbiota: A reciprocal interaction in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2020, 65, 906–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costantini, L.; Merendino, N. Polyunsaturated fatty acids and microbiota relationship: Implications in cancer onset and treatment. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 3490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mozaffari, H.; Daneshzad, E.; Larijani, B.; Bellissimo, N.; Azadbakht, L. Dietary intake of fish, n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids, and risk of inflammatory bowel disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies. Eur. J. Nutr. 2019, 59, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calder, P.C. Fatty acids and immune function: Relevance to inflammatory bowel diseases. Int. Rev. Immunol. 2009, 28, 506–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marton, L.T.; Goulart, R.A.; Carvalho, A.C.A.; Barbalho, S.M. Omega fatty acids and inflammatory bowel diseases: An overview. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacLean, C.H.; Mojica, W.A.; Morton, S.C.; Pencharz, J.; Garland, R.H.; Tu, W.; Shekelle, P. Effects of omega-3 fatty acids on lipids and glycemic control in type II diabetes and the metabolic syndrome and on inflammatory bowel disease, rheumatoid arthritis, renal disease, systemic lupus erythematosus, and osteoporosis: Summary. In AHRQ Evidence Report Summaries; Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality: Rockville, MD, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- MacLean, C.H.; Mojica, W.A.; Newberry, S.J.; Pencharz, J.; Garland, R.H.; Tu, W.; Morton, S.C. Systematic review of the effects of n-3 fatty acids in inflammatory bowel disease. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2005, 82, 611–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, D.; Shah, P.S.; Steinhart, A.H.; Zlotkin, S.; Griffiths, A.M. Maintenance of remission in inflammatory bowel disease using omega-3 fatty acids (fish oil): A systematic review and meta-analyses. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2011, 17, 336–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajabnoor, S.M.; Thorpe, G.; Abdelhamid, A.; Hooper, L. Long-term effects of increasing omega-3, omega-6 and total polyunsaturated fats on inflammatory bowel disease and markers of inflammation: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Eur J. Nutr. 2020, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Reference | Model Used | Condition | ω-3 PUFA(s) Used | Concentration or Dose Used | Duration | Change in Fatty Acid Composition |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell line models | ||||||
| Rosella et al. [23] | Caco-2 cells | Non-stimulated | EPA | 100 μg/mL | 24 h | ↑ Membrane EPA content |
| Renaville et al. [28] | T84/Caco-2 cells | Non-stimulated | EPA | 30 or 300 μM | 3 h or 3 h and 7 days | ↑ Cellular EPA content ↑ Cellular DPA content ↓ Cellular trans-vaccenic acid content ↓ Cellular cis-9, trans-11-conjugated linoleic acid ↓ Cellular oleic acid content |
| Willemsen et al. [26] | T84 cells | IL-4-induced inflammation | ALA | 10 or 100 μM | 96 h | ↑ Phospholipid ALA content |
| EPA | ↑ Phospholipid EPA content | |||||
| DHA | ↑ Phospholipid DHA content | |||||
| Li et al. [27] | T84 cells | TNF-α- and IFN-γ-induced inflammation | EPA | 25–75 μM | 48 h | ↑ Lipid raft EPA content |
| DHA | ↑ Lipid raft DHA content | |||||
| Xiao et al. [24] | Caco-2 cells | Heat stress | EPA | 50 μM | 96 h | ↑ Membrane EPA content |
| DHA | ↑ Membrane DHA content | |||||
| Beguin et al. [25] | T84 cells | Non-stimulated | ALA | 30 μM | 7 days | ↑ Cellular ALA content ↑ Cellular ETE content |
| EPA | ↑ Cellular EPA content ↑ Cellular DPA content | |||||
| DHA | ↑ Cellular DHA content ↓ Cellular DPA content | |||||
| Caco-2 cells | Non-stimulated | ALA | ↑ Cellular ALA content ↑ Cellular ETE content ↑ Cellular EPA content | |||
| EPA | ↑ Cellular EPA content ↑ Cellular DPA content | |||||
| DHA | ↑ Cellular DHA content ↑ Cellular EPA content | |||||
| Rodent models | ||||||
| Nieto et al. [29] | Rats | TNBS colitis | Fish oil | EPA: 4.16% of dietary fatty acids DHA: 3.01% of dietary fatty acids | 7 or 14 days | ↑ Colonic tissue EPA content ↑ Colonic tissue DHA content |
| Bosco et al. [30] | Rag2−/− immunodeficient mice | Adoptive transfer of naïve T-cell-induced colitis | Fish oil | EPA: 3.37 g/100 g diet DHA: 2.10 g/100 g diet | 8 weeks | ↑ Colonic free EPA (7.2-fold) ↑ Colonic free DHA (2.2-fold) ↓ Colonic free arachidonic acid |
| Brahmbhatt et al. [31] | Male Sprague–Dawley rats | Intestinal reperfusion and ischaemia | Fish oil | EPA: 3.00% of dietary fatty acids DHA: 1.98% of dietary fatty acids | 21 days | ↑ Small intestine tissue EPA content ↑ Small intestine tissue DHA content |
| Reifen et al. [32] | Male Wistar rats | TNBS- or DSS-induced colitis | Fish oil | Fish oil: 5% by weight of total diet (EPA: 11.7% of total fatty acids DHA: 15.7% of total fatty acids) | 21 days | ↑ Colonic tissue EPA content ↑ Colonic tissue DHA content |
| Xiao et al. [33] | Male Wistar rats | Heatstroke | EPA | 1 g/kg body weight per day by gavage | 21 days | ↑ Ileal phospholipid EPA content |
| DHA | ↑ Ileal phospholipid DHA content | |||||
| Human studies | ||||||
| Hillier et al. [34] | Human | Inflammatory bowel disease | Fish oil | Fish oil: 18 g/day (3.3 g EPA + 2.2 g DHA/day) | 12 weeks | ↑ Colonic mucosa EPA content ↑ Colonic mucosa DHA content ↓ Colonic mucosa AA content |
| Hawthorne et al. [35] | Human | Inflammatory bowel disease | Fish oil | Fish oil: 20 mL/day (4 g EPA + 1.2 g DHA/day) | 1 year | ↑ Rectal mucosa EPA content |
| Control (No Added ω-3 PUFA) | ALA Treatment | EPA Treatment | DHA Treatment | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell line | T84 | Caco-2 | T84 | Caco-2 | T84 | Caco-2 | T84 | Caco-2 |
| ALA | 4.5 ± 1.2 | 30.1 ± 6.9 | 144.5 ± 0.6 * (32.1) | 414.9 ± 40.1 * (13.8) | 1.4 ± 0.6 (−0.3) | 31.5 ± 4.7 (1.0) | 2.3 ± 1.1 (−0.5) | 41.3 ± 4.2 (1.4) |
| ETE | 0.7 ± 0.4 | 7.0 ± 0.8 | 3.9 ± 0.3 * (5.6) | 83.1 ± 9.3 * (11.9) | 0.3 ± 0.3 (−0.4) | 7.5 ± 0.8 (1.1) | Not detected | 7.5 ± 0.8 (1.1) |
| EPA | 9.5 ± 1.6 | 15.4 ± 1.9 | 8.9 ± 10.2 (−0.9) | 20.7 ± 2.3 * (1.3) | 130.8 ± 11.1 * (13.8) | 257.6 ± 37.2 * (16.7) | 17.0 ± 5.9 (1.8) | 32.3 ± 4.4 * (2.1) |
| n-3 DPA | 5.7 ± 1.2 | 19.9 ± 2.0 | 4.5 ± 1.3 (−0.8) | 21.6 ± 2.1 (1.1) | 10.6 ± 1.4 * (1.9) | 157.4 ± 23.2 * (7.9) | 1.1 ± 0.5 * (−0.2) | 24.9 ± 3.3 (1.3) |
| DHA | 11.8 ± 1.8 | 37.2 ± 4.1 | 9.8 ± 0.7 (−0.8) | 40.8 ± 3.9 (1.1) | 7.4 ± 0.7 (−0.6) | 33.9 ± 4.9 (−0.9) | 114.5 * ± 32.4 (9.7) | 478.3 ± 58.7 * (12.9) |
| Total ω-3 PUFAs | 32.3 ± 6.3 | 72.5 ± 8.1 | 171.6 ± 13.0 * (5.3) | 581.2 ± 8.3 * (8.0) | 150.7 ± 14.2 * (4.7) | 448.9 ± 65.3 * (6.2) | 135.0 ± 39.9 * (4.2) | 535.5 ± 66.4 * (7.4) |
| Reference | Model Used | Condition | ω-3 PUFA(s) Used | Dose Used | Duration | Histological Changes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vilaseca et al. [37] | Male Sprague–Dawley rats | Chronic TNBS colitis | Cod liver digest (providing EPA and DHA) | EPA: 5.95 mg/g diet DHA 6.91 mg/g diet | 50 days | Decreased macroscopic damage (after day 20) Absence of inflammation and ulcerations (day 50) |
| Empey et al. [38] | Male Sprague–Dawley rats | Acetic acid-induced colitis | EPA-enriched fish oil | EPA-enriched fish oil: 10% by weight of total diet | 6 weeks | Improved histology and less macroscopic injury |
| Shoda et al. [39] | Rats | TNBS colitis | Fish oil | Fish oil: 2% by weight of total diet | Not given | Reduced ulcer severity (correlated with decreased plasma LTB4) |
| ALA-rich perilla oil | Perilla oil: 2% by weight of total diet | Decreased colonic weight (correlated with decreased plasma LTB4; ALA > fish oil) | ||||
| Yuceyar et al. [40] | Male Wistar albino rats | TNBS colitis | Fish oil | EPA: 14.4 mg/g diet DHA: 11.6 mg/g diet | 6 weeks (diet) | Improved pathology (decreased number of lesions) |
| 14 days (daily enema) | No effect on macroscopic parameters No effect on pathology | |||||
| Caplan et al. [41] | Neonatal Sprague–Dawley rats | Necrotising enterocolitis | DHA | 23 mg/100 mL formula | 96 h | Improved histological necrotising enterocolitis outcomes |
| Andoh et al. [42] | Male Sprague–Dawley rats | TNBS colitis | ω-3 PUFA-rich liquid diet (providing ALA) | 150 mg/100 kcal | 12 days (followed by 2 days starvation) | Reduced inflammatory damage score |
| Hudert et al. [36] | Transgenic fat-1 mice | DSS colitis | - | Mice have higher colonic EPA, DPA and DHA than controls | - | Increased colon length Decreased severity and thickness of inflammatory infiltrate Decreased epithelial damage |
| Lu et al. [43] | Neonatal Sprague–Dawley rats | Necrotising enterocolitis | DHA | 0.5% of total fatty acids in formula | 72 h | Improved histology |
| Hassan et al. [44] | Male Sprague–Dawley rats | TNBS colitis | ALA | 28.8% of total fatty acids in formula | 14 days | Decreased macroscopic lesions Less neutrophil infiltration No effect on mucosal wall thickness No effect on overall inflammatory score |
| Bosco et al. [30] | Rag2−/− immunodeficient mice | Adoptive transfer of naïve T-cell-induced colitis | Fish oil | EPA: 3.37 g/100 g diet DHA: 2.10 g/100 g diet | 8 weeks | No effect on macroscopic parameters of colitis |
| Li et al. [45] | Male rats | Haemorrhagic shock | Fish oil | Fish oil: 0.2 g/kg body weight | Single intravenous treatment | Less mucosal damage Improved tight junction morphology |
| Reifen et al. [32] | Male Wistar rats | TNBS- or DSS-induced colitis | Sage oil (providing ALA) | Oils: 5% by weight of diet | 21 days | No effect on DSS or TNBS colitis-induced histological changes Increased mucosal inflammation (DSS colitis only) |
| Fish oil | Decreased colon length (DSS colitis only)No effect on TNBS colitis-induced histological changes | |||||
| Zhao et al. [46] | Mice | IL-10 deficiency | DHA | 35.5 mg/kg body weight per day intragastrically | 14 days | Improved histological inflammation score |
| Chien et al. [47] | Male Wistar rats | Chronic ethanol exposure | Fish oil | 7.1 or 16.2 g/kg diet | 8 weeks | No effect on epithelial histological damage |
| Yao et al. [48] | Male Sprague–Dawley rats | TNBS colitis | ω-3 PUFAs (source not specified but presumed to be fish oil) | 20 mg/kg body weight per day intragastrically | 60 days | Decreased disease activity index score Decreased colonic macroscopic damage index score (decreased ulceration) Decreased tissue damage index score (reduced thickening and leukocyte infiltration) |
| Charpentier et al. [49] | Young male Sprague–Dawley rats | TNBS colitis | ω-3 PUFAs (source not specified but presumed to be fish oil) | 6.1 g/kg of diet | 28 days | No effect on colonic weight to length ratio |
| Haddi et al. [50] | Female BALB/c mice | β-lactoglobulin-induced inflammation | Fish oil | 0.6, 1 or 1.5 mL/kg body weight per day by gavage | 15 days | Increased villus height Improved intestinal architecture Improved histological score |
| Tang et al. [51] | Female Sprague–Dawley rats | Peritoneal dialysis | ω-3 PUFAs (source not specified) | 0.5 or 1.5 g/kg body wt per day intragastrically | 28 days | Increased ileal villus length Increased crypt depth/ileal villus length ratio |
| Zheng et al. [52] | Male C57 mice | DSS colitis | DPA | 300 mg/kg body weight per day by gavage | 28 days | Attenuated body weight decrease Decreased disease activity index score Improved gross morphology and pathological inflammatory score Attenuated inflammatory infiltrationAttenuated colon shortening |
| Reference | Model Used | Condition | ω-3 PUFA(s) Used | Concentration or Dose Used | Duration | Changes to Permeability and Related Mechanisms |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell line models | ||||||
| Rosella et al. [23] | Caco-2 cells | Non-stimulated | EPA | 100 μg/mL | 24 h | ↓ Permeability |
| Usami et al. [59] | Caco-2 cells | Non-stimulated | ALA | 50–200 μM | 24 h | ↑ Permeability (dose dependent) |
| EPA | ↑ Permeability (dose dependent) ↓ Electron-dense material at tight junctions and desmosomes (200 μM only) | |||||
| Usami et al. [60] | Caco-2 cells | Non-stimulated | DHA | 10–100 μM | 24 h | ↑ Permeability (dose dependent) |
| Willemsen et al. [26] | T84 cells | IL-4-induced inflammation | ALA | 10 or 100 μM | 48 h | No effect on permeability |
| EPA | ↓ Permeability (100 μM only) | |||||
| DHA | ↓ Permeability (100 μM only) | |||||
| Li et al. [27] | T84 cells | TNF-α- and IFN-γ-induced inflammation | EPA | 25–75 μM | 48 h | ↓ Permeability ↓ Tight junction protein redistribution ↓ Tight junction altered morphology ↓ Occludin and flotillin displacement from lipid rafts |
| DHA | ↓ Permeability ↓ Tight junction protein redistribution ↓ Tight junction altered morphology ↓ Occludin and flotillin displacement from lipid rafts | |||||
| Xiao et al. [24] | Caco-2 cells | Heat stress | EPA | 50 μM | 96 h | ↓ Permeability ↓ Tight junction altered morphology ↓ Tight junction protein redistribution ↑ ZO-1 and occludin protein and mRNA expression |
| DHA | No effect on permeability ↑ ZO-1 and occludin protein and mRNA expression | |||||
| Xiao et al. [61] | IPEC-1 cells | Deoxynivalenol-induced inflammation | EPA | Up to 25 μg/mL | 24–72 h | ↓ Permeability (24 and 48 h) ↓ ZO-1 and claudin redistribution |
| DHA | ↓ Permeability (24 and 48 h) ↓ ZO-1 and claudin redistribution | |||||
| Rodent models | ||||||
| Empey et al. [38] | Male Sprague–Dawley rats | Acetic acid-induced colitis | EPA-enriched fish oil | 10% by weight of total diet | 6 weeks | Protected ileal and colonic absorption |
| Caplan et al. [41] | Neonatal Sprague–Dawley rats | Necrotising enterocolitis | DHA | 23 mg/100 mL formula | 96 h | ↓ Plasma endotoxin level |
| Hudert et al. [36] | Transgenic fat-1 mice | DSS colitis | - | Mice have higher colonic EPA, DPA and DHA | - | ↑ ZO-1 expression (maintained compared to colitis control) |
| Xiao et al. [33] | Male Wistar rats | Heatstroke | EPA | 1 g/kg body weight/day by gavage | 21 days | ↓ Intestinal permeability ↓ Plasma endotoxin and D-lactate levels ↓ Tight junction protein distortion ↑ Tight junction protein expression |
| DHA | ↓ Intestinal permeability ↓ Plasma endotoxin and D-lactate levels ↓ Tight junction protein distortion ↑ Tight junction protein expression | |||||
| Charpentier et al. [49] | Young male Sprague–Dawley rats | TNBS colitis | ω-3 PUFAs (source not specified but presumed to be fish oil) | 6.1 g/kg of diet | 28 days | No effect on claudin-1 protein expression No effect on occludin protein expression No effect on TTF3 protein expression No effect on MUC2 protein expression |
| Chien et al. [47] | Male Wistar rats | Chronic ethanol exposure | Fish oil | 7.1 or 16.2 g/kg diet | 8 weeks | ↓ Plasma endotoxin levels ↑ ZO-1 immunoreactive area in intestinal epithelial tissue (16.2 g/kg/day only) |
| Reference | Model Used | Condition | ω-3 PUFA(s) Used | Dose Used | Duration | Effect on Inflammatory Mediator(s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell line models | ||||||
| Zhao et al. [66] | HCT116 cells | Lauric acid/IE-DAP/MDP-induced inflammation | EPA | 0–20 μM | 20 h | ↓ IL-8 protein (MDP only) |
| DHA | ↓ IL-8 protein (all treatments) | |||||
| Marion-Letellier et al. [64] | Caco-2 cells | IL-1β-induced inflammation | EPA | 0.1–10 μM | 18 h | ↓ IL-6 protein ↓ IL-8 protein |
| DHA | ↓ IL-6 protein ↓ IL-8 protein | |||||
| Vincentini et al. [67] | Caco-2 cells | α-gliadin-induced inflammation | DHA | 2 μM | 24 h | ↓ PGE2 ↓ IL-8 protein |
| Bentley-Hewitt et al. [63] | HT29/HT29-MTX cell co-culture | Non-stimulated | EPA | 50 μM | 12 h | ↑ TGF-β1 mRNA No consistent effect on IL-8 or HSP 72 mRNA |
| DHA | ↑ TGF-β1 mRNA No consistent effect on IL-8 or HSP 72 mRNA | |||||
| Reifen et al. [32] | Caco-2 cells | IL-1β-induced inflammation | Sage oil (providing ALA) | 10 μM | 48 h | ↓ IL-8 protein |
| ALA | ↓ IL-8 protein | |||||
| Wijendran et al. [65] | H4/NEC-IEC/Caco-2 cells | IL-1β-induced inflammation | EPA | 100 μM | 48 h | ↓ IL-8 mRNA and protein (H4 only) ↓ IL-6 mRNA and protein (H4 only) |
| DHA | ↓ IL-8 mRNA and protein ↓ IL-6 mRNA (H4 only) ↓ IL-6 protein (H4 and NEC-IEC) | |||||
| Rodent models | ||||||
| Empey et al. [38] | Rats | Non-stimulated | EPA-enriched fish oil | 10% by weight of total diet | 6 weeks | ↑ PGE2 in colonic dialysate ↑ LTB4 in colonic dialysate |
| Yuceyar et al. [40] | Male Wistar albino rats | TNBS colitis | Fish oil | EPA: 14.4 mg/g diet DHA: 11.6 mg/g diet | 6 weeks (diet) | ↓ Colonic LTB4 ↓ Colonic LTC4 |
| 14 days (daily enema) | ↓ Colonic LTB4 ↓ Colonic LTC4 | |||||
| Andoh et al. [42] | Male Sprague–Dawley rats | TNBS colitis | ω-3 PUFA-rich liquid diet (providing ALA) | 150 mg/100 kcal | 12 days (followed by 2 days starvation) | ↓ Mucosal IL-6 secretion No effect on mucosal TNF-α secretion |
| Hudert et al. [36] | Transgenic fat-1 mice | DSS colitis | - | Mice have higher colonic EPA, DPA and DHA than controls | - | ↑ Mucosal RvE1 ↑ Mucosal RvD3 ↑ Mucosal protectin D1 ↑ Mucosal PGE3 ↑ Mucosal LTB5 No effect on mucosal LTB4 No effect on mucosal PGE2 No effect on mucosal 15-hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid (lipoxin A4 precursor) ↓ Colonic TNF-α mRNA ↓ Colonic IL-1β mRNA ↑ Colonic toll-interacting protein mRNA ↑ Colonic trefoil factor 3 mRNA |
| Wang et al. [62] | Male Lewis rats | Non-stimulated | Fish oil | Fish oil 4% by weight of total diet (EPA: 15.4% of total fatty acids; DHA: 15.1% of total fatty acids) | up to 90 days | ↓ TNF-α mRNA ↓ IFN-γ mRNA ↓ IL-4 mRNA ↓ IL-10 mRNA ↓ IL-15 mRNA and protein No effect on IL-7 mRNA or protein |
| Hassan et al. [44] | Male Sprague–Dawley rats | TNBS colitis | ALA | 28.8% of total fat content of formula | 2 weeks | ↓ TNF-α mRNA and protein ↓ LTB4 No effect on IL-6 expression or secretion No effect on PGE2 |
| Bosco et al. [30] | Rag2−/− immunodeficient mice | Adoptive transfer of naïve T-cell-induced colitis | Fish oil | EPA: 3.37 g/100 g diet DHA: 2.10 g/100 g diet | 8 weeks | ↑ Colonic myeloperoxidase ↑ Colonic IL-1β protein ↑ Colonic IL-12 protein ↑ Colonic keratinocyte-derived chemokine protein ↑ Colonic IL-10 protein ↑ Colonic TNF-α protein ↑ Mucosal PGE3 ↑ Mucosal TXB3 ↑ Mucosal LTB5 ↑ Mucosal 5-HEPE ↑ Mucosal 17,18-EEP ↓ Mucosal PGJ2 ↓ Mucosal 5,6-EET ↓ Mucosal 8,9-EET ↓ Mucosal 14,15-EET No effect on mucosal PGE2 No effect on mucosal TXB2 No effect on mucosal LTB4 |
| Brahmbhatt et al. [31] | Male Sprague–Dawley rats | Intestinal reperfusion and ischaemia | EPA and DHA | EPA: 3.00% of dietary fatty acids DHA: 1.98% of dietary fatty acids | 3 weeks | No effect on cytokine production ↑ TXB3 ↑ 17,18-EEP ↑ 8-iso PGF3α |
| Zhao et al. [46] | Mice | IL-10 deficient | DHA | 35.5 mg/kg body weight per day intragastrically | 2 weeks | ↓ TNF-α protein ↓ IFN-γ protein ↓ IL-17 protein |
| Charpentier et al. [49] | Young male Sprague–Dawley rats | TNBS colitis | ω-3 PUFAs (source not specified but presumed to be fish oil) | 6.1 g/kg of diet | 28 days | ↓ Colonic IL-6 protein ↓ Colonic LTB4 No effect on colonic TNF-α protein |
| Yao et al. [48] | Male Sprague–Dawley rats | TNBS colitis | ω-3 PUFAs (source not specified but presumed to be fish oil) | 20 mg/kg body weight per day intragastrically | 60 days | ↓ Colonic IL-2 mRNA ↓ Colonic IL-4 mRNA |
| Zheng et al. [52] | Male C57 mice | DSS colitis | DPA | 300 mg/kg body weight per day by gavage | 28 days | ↓ Colonic IL-1β mRNA and protein ↓ Colonic IL-6 mRNA and protein ↓ Colonic TNF-α mRNA and protein ↑ Colonic IL-10 mRNA and protein ↓ Colonic PGE2 ↓ Colonic LTB4 |
| Human studies | ||||||
| Hillier et al. [34] | Human | Inflammatory bowel disease | Fish oil | Fish oil: 18 g/day (3.3 g EPA and 2.2 g DHA per day) | 12 weeks | ↓ Colonic mucosa PGE2 ↓ Colonic mucosa TXB2 |
| Reference | Model Used | Condition | ω-3 PUFA(s) Used | Concentration or Dose Used | Duration | Effect on Inflammatory Mechanisms(s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell line models | ||||||
| Hofmanová et al. [70] | HT-29 cells | TNF-α or anti-Fas monoclonal antibody/cycloheximide-induced inflammation | DHA | 20 μM | 48 h | ↑ G0/G1 phase cells ↑ Apoptosis (TNF-α and anti-Fas monoclonal antibody treatments) |
| Renaville et al. [28] | T84/Caco-2 cells | Non-stimulated | EPA | 300 M | 3 h or 3 h and 7 days | No effect on PPAR-α mRNA (both time periods) ↓ Stearoyl CoA desaturase and SREBP-1c mRNA (3 h and 7 days only) |
| Lu et al. [43] | IEC-6 cells | Platelet-activating factor treatment | DHA | 67 μM | 30 min | ↓ TLR4 mRNA ↓ Platelet-activating factor receptor mRNA |
| Zhao et al. [66] | HCT116 cells | Lauric acid/IE-DAP/MDP-induced inflammation | DHA | 0–20 μM | 20 h | ↓ NF-κB activation ↓ IκB degradation |
| EPA | No effect on NF-κB activation No effect on IκB degradation | |||||
| Marion-Letellier et al. [64] | Caco-2 cells | IL-1β-induced inflammation | ALA | 0.1–10 μM | 18 h | No effect on PPAR-γ protein No effect on iNOS protein No effect on IκB protein |
| DHA | ↓ PPAR-γ protein ↓ iNOS protein No effect on IκB protein | |||||
| EPA | ↓ PPAR-γ protein ↓ iNOS protein No effect on IκB protein | |||||
| Vincentini et al. [67] | Caco-2 cells | α-gliadin-induced inflammation | DHA | 2 μM | 24 h | ↓ Cytosolic phospholipase 2 activity ↓ COX-2 protein |
| Kimura et al. [68] | Caco-2 cells | Non-stimulated | DHA | 25 μM | 24 h | ↑ PPAR-α activity ↑ PPAR-γ activity No effect on PPAR-δ activity ↓ Triglyceride and apolipoprotein B secretion |
| EPA | ↑ PPAR-α activity No effect on PPAR-γ activity No effect on PPAR-δ activity | |||||
| Reifen et al. [32] | Caco-2 cells | IL-1β-induced inflammation | Sage oil | 10 μM | 48 h | ↓ COX-2 protein |
| ALA | ↓ COX-2 protein ↓ iNOS protein | |||||
| Wijendran et al. [65] | H4/NEC-IEC/Caco-2 cells | IL-1β-induced inflammation | DHA | 100 μM | 48 h | ↓ NF-κB mRNA ↓ IL-1R1 mRNA |
| EPA | No effect on NF-κB mRNA No effect on IL-1R1 mRNA | |||||
| Rodent models | ||||||
| Yuceyar et al. [40] | Male Wistar albino rats | TNBS colitis | Fish oil | EPA: 14.4 mg/g diet DHA: 11.6 mg/g diet | 6 weeks (diet) | ↓ Myeloperoxidase activity |
| 14 days (daily enema) | No effect on myeloperoxidase activity | |||||
| Caplan et al. [41] | Neonatal Sprague–Dawley rats | Necrotising enterocolitis | DHA | 23 mg/100 mL formula | 96 h | No effect on iNOS protein ↓ Phospholipase A2 protein ↓ Platelet-activating factor receptor protein |
| Hudert et al. [36] | Transgenic fat-1 mice | DSS colitis | - | Mice have higher colonic EPA, DPA and DHA than controls | - | ↓ Colonic NF-κB activity ↓ Colonic iNOS mRNA |
| de Vogel-van den Bosch et al. [71] | 129S1/SvImJ wild-type mice | Non-stimulated | DHA | EPA or DHA: 12.5 g/kg body weight by gavage | 6 h | No effect on regulated long-chain fatty acid uptake, mitochondrial and peroxisomal β-oxidation, ω-oxidation, and metabolism of energy-yielding substrates No effect on regulated oxidative stress mRNAs ↓ Cholesterol uptake transporter (Npc1l1), apical mannose and glucose uptake transporter (Sglt4), and serotonin transporter (Slc6a4) |
| EPA | No effect on regulated long-chain fatty acid uptake, mitochondrial and peroxisomal β-oxidation, ω-oxidation, and metabolism of energy-yielding substrates No effect on regulated oxidative stress mRNAs ↓ Cholesterol uptake transporter (Npc1l1), apical mannose and glucose uptake transporter (Sglt4), and serotonin transporter (Slc6a4) ↑ Cholesterol efflux protein (Abca1) and dopamine transporter (Dat1) | |||||
| Hassan et al. [44] | Male Sprague–Dawley rats | TNBS colitis | ALA | 28.8% of total fat content of formula | 2 weeks | ↓ Colonic iNOS protein ↓ Colonic COX-2 protein ↓ Colonic NF-κB activation No effect on phosphorylation of JNK, P38 and IκB |
| Kimura et al. [68] | Male C57BL/6 mice | PPAR-α deficiency | DHA-rich oil | 60% energy fat diet with1.9% or 3.7% of total fatty acids as DHA (plus some EPA) | 1 week | ↓ Triglyceride secretion (inhibited by PPAR-α deficiency) with 3.7% DHA |
| EPA-rich oil | 3.4% EPA and 1.5% DHA | No effect on triglyceride secretion | ||||
| Reifen et al. [32] | Male Wistar rats | TNBS- or DSS-induced colitis | Fish oil | Fish oil: 5% by weight of total diet (EPA: 11.7% of total fatty acids DHA: 15.7% of total fatty acids) | 3 weeks | ↓ COX-2 mRNA |
| Sage oil | Sage oil: 5% by weight of total diet (ALA: 43.9% of total fatty acids) | ↓ COX-2 mRNA | ||||
| Charpentier et al. [49] | Young male Sprague–Dawley rats | TNBS colitis | ω-3 PUFAs (source not specified but presumed to be fish oil) | 6.1 g/kg of diet | 28 days | ↑ Colonic IL-1A mRNA ↑ Colonic TLR-2 mRNA ↑ Colonic mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 3 mRNA ↓ Colonic iNOS protein ↓ Colonic COX-2 protein |
| Yao et al. [48] | Male Sprague–Dawley rats | TNBS colitis | ω-3 PUFAs (source not specified but presumed to be fish oil) | 20 mg/kg body weight per day intra-gastrically | 60 days | ↓ Colonic nuclear factor of activated T cells mRNA ↑ Colonic PPAR-γ mRNA |
| Zheng et al. [52] | Male C57 mice | DSS colitis | DPA | 300 mg/kg body weight per day by gavage | 28 days | ↓ Colonic myeloperoxidase activity ↓ Colonic COX protein ↓ Colonic 5-LOX protein |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Durkin, L.A.; Childs, C.E.; Calder, P.C. Omega-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids and the Intestinal Epithelium—A Review. Foods 2021, 10, 199. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10010199
Durkin LA, Childs CE, Calder PC. Omega-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids and the Intestinal Epithelium—A Review. Foods. 2021; 10(1):199. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10010199
Chicago/Turabian StyleDurkin, Luke A., Caroline E. Childs, and Philip C. Calder. 2021. "Omega-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids and the Intestinal Epithelium—A Review" Foods 10, no. 1: 199. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10010199
APA StyleDurkin, L. A., Childs, C. E., & Calder, P. C. (2021). Omega-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids and the Intestinal Epithelium—A Review. Foods, 10(1), 199. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10010199





