- Article
Life Cycle Assessment of Phycocyanin Food Colorant Production from Spirulina (Arthrospira platensis) with Biostimulant Waste-Stream Utilization for Soil Carbon Sequestration to Achieve Net Carbon Removal
- Asger Smidt-Jensen,
- Trine Boje Røgild and
- William R. Moomaw
- + 6 authors
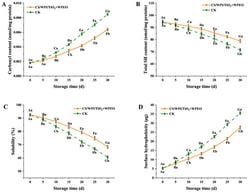
This study introduces a novel approach to producing carbon-negative food ingredients by integrating phycocyanin extraction from Spirulina (Arthrospira platensis) with the application of its residual biomass as a biostimulant for soil organic carbon (SOC) sequestration. A comprehensive life cycle assessment (LCA) was conducted to evaluate the environmental performance of this integrated system, encompassing geothermally powered Spirulina cultivation, phycocyanin extraction, and the use of the waste stream to enhance SOC in degraded Icelandic soils. Although the cultivation and extraction processes are associated with environmental impacts, the SOC sequestration resulting from biostimulant application more than offsets these burdens—yielding a net-carbon-negative natural food colorant under the assumptions applied in this study (−1.60 tCO2-eq per color unit). This work highlights the potential for such ingredients to contribute meaningfully to Scope 3 emission reductions, in line with science-based targets and the GHG Protocol. Traditionally, food pigments have been overlooked in carbon accounting due to their low inclusion rates and perceived minimal contribution to overall product footprints. This study reframes natural colorants as strategic levers for climate action, offering a pathway for food manufacturers to advance decarbonization while transitioning toward more sustainable, bio-based ingredients.
7 February 2026





![Process flow diagram: Flow chart illustrating the integrated process of Spirulina cultivation, phycocyanin extraction, and biostimulant application (highlighted by dashed boxes). Data is drawn from [17,18,19]. * The waste stream acts as a biostimulant when applied in a dilute water-based mixture, this process involves the use of agricultural drones.](https://mdpi-res.com/cdn-cgi/image/w=470,h=317/https://mdpi-res.com/foods/foods-15-00610/article_deploy/html/images/foods-15-00610-g001-550.jpg)