Development of Freeze-Thaw Stable Starch through Enzymatic Modification
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Enzymatic Modification of Starch
2.2. Molecular Weight Distribution of Enzyme-Treated Starches
2.3. Side Chain Length Distribution Analysis
2.4. Determination of Starch Water Solubility
2.5. Preparation of Frozen Dough and Bread
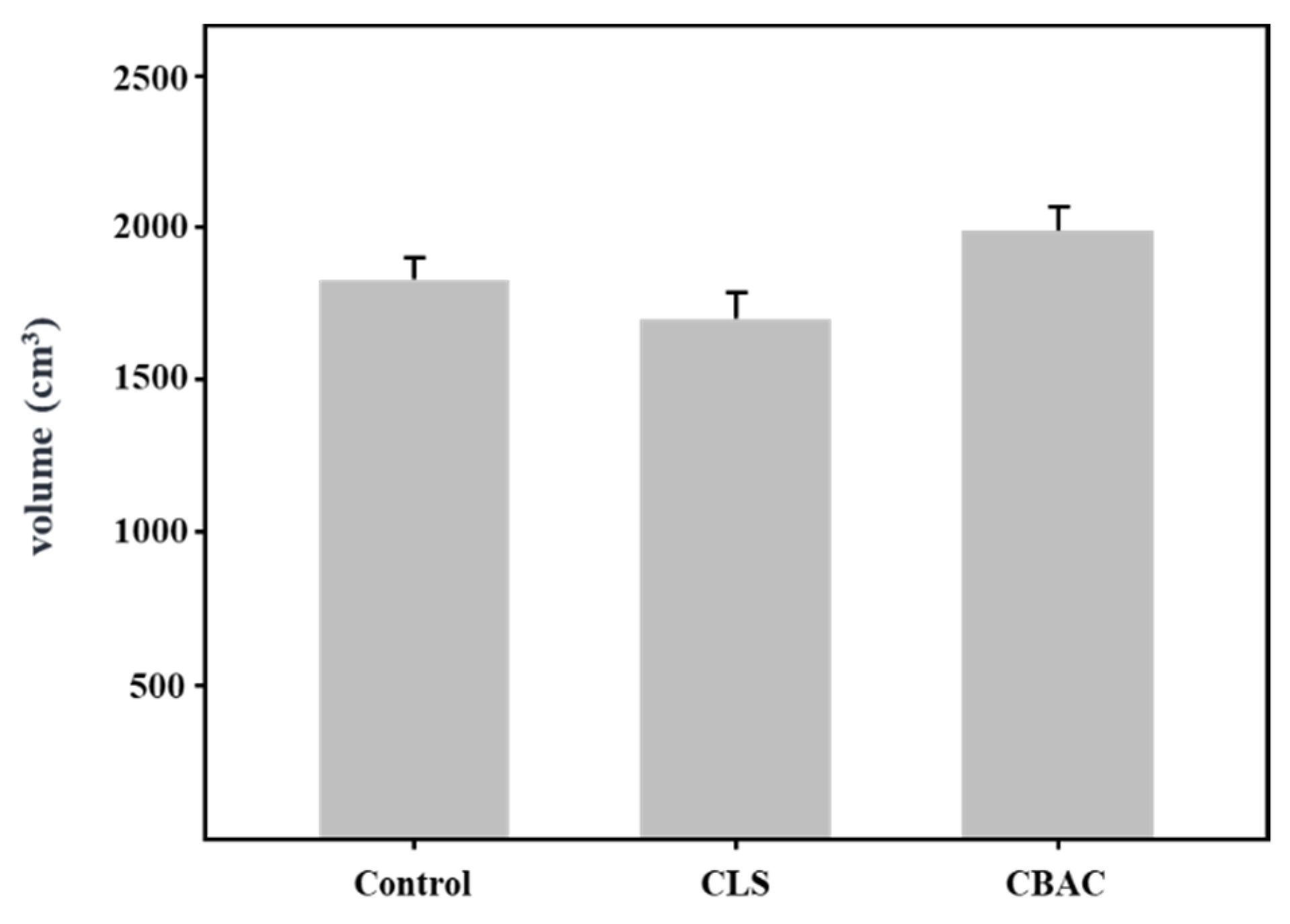
2.6. Bread Loaf Volume
2.7. Texture Profile Analysis (TPA)
2.8. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC) Analysis
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Structural Analysis of Enzyme-Modified Starch
3.2. Solubility of Modified Starch
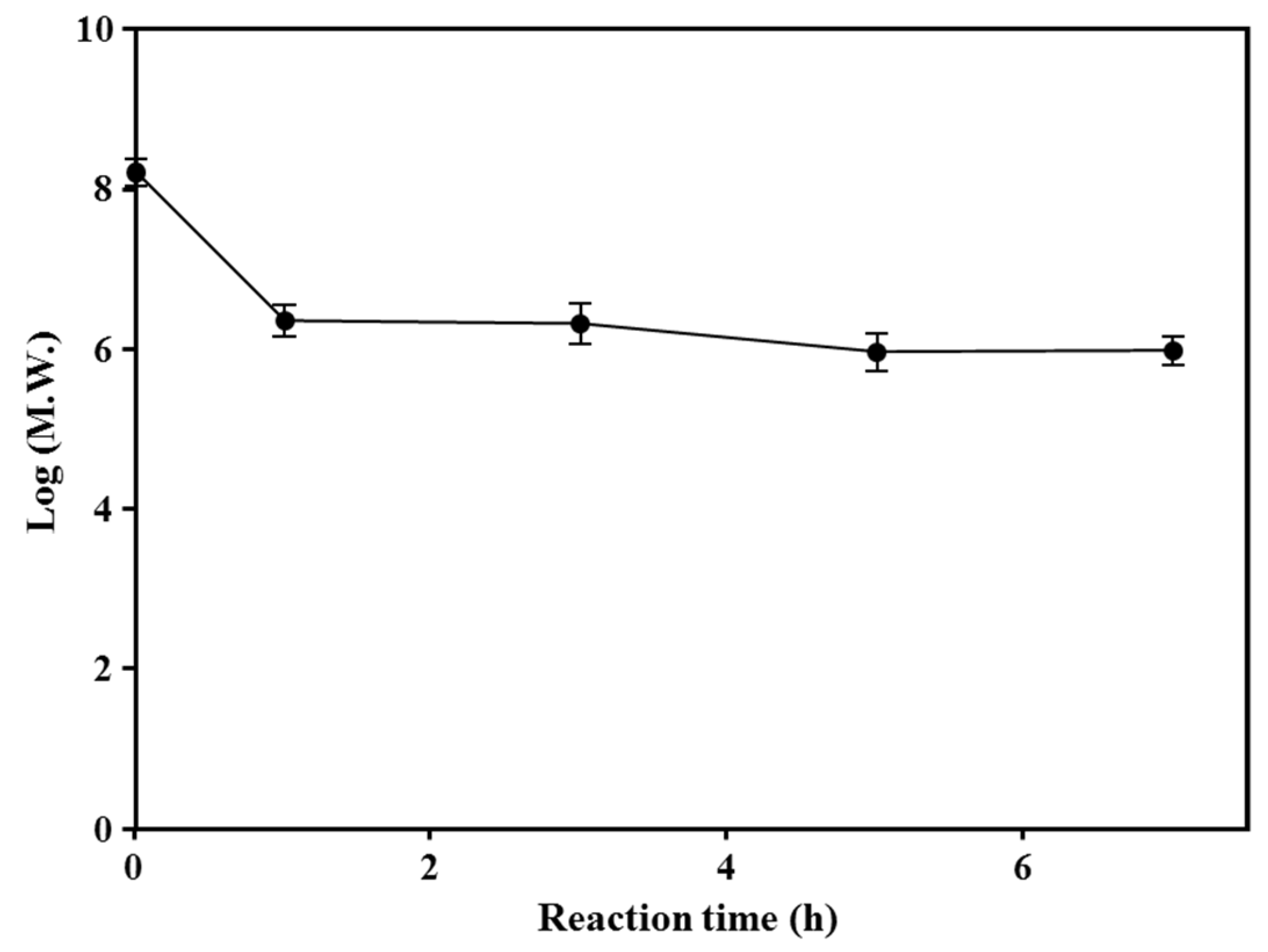
3.3. Molecular Weight Distribution of Enzyme-Treated Starch
3.4. Effects of CBAC on Bread Baking
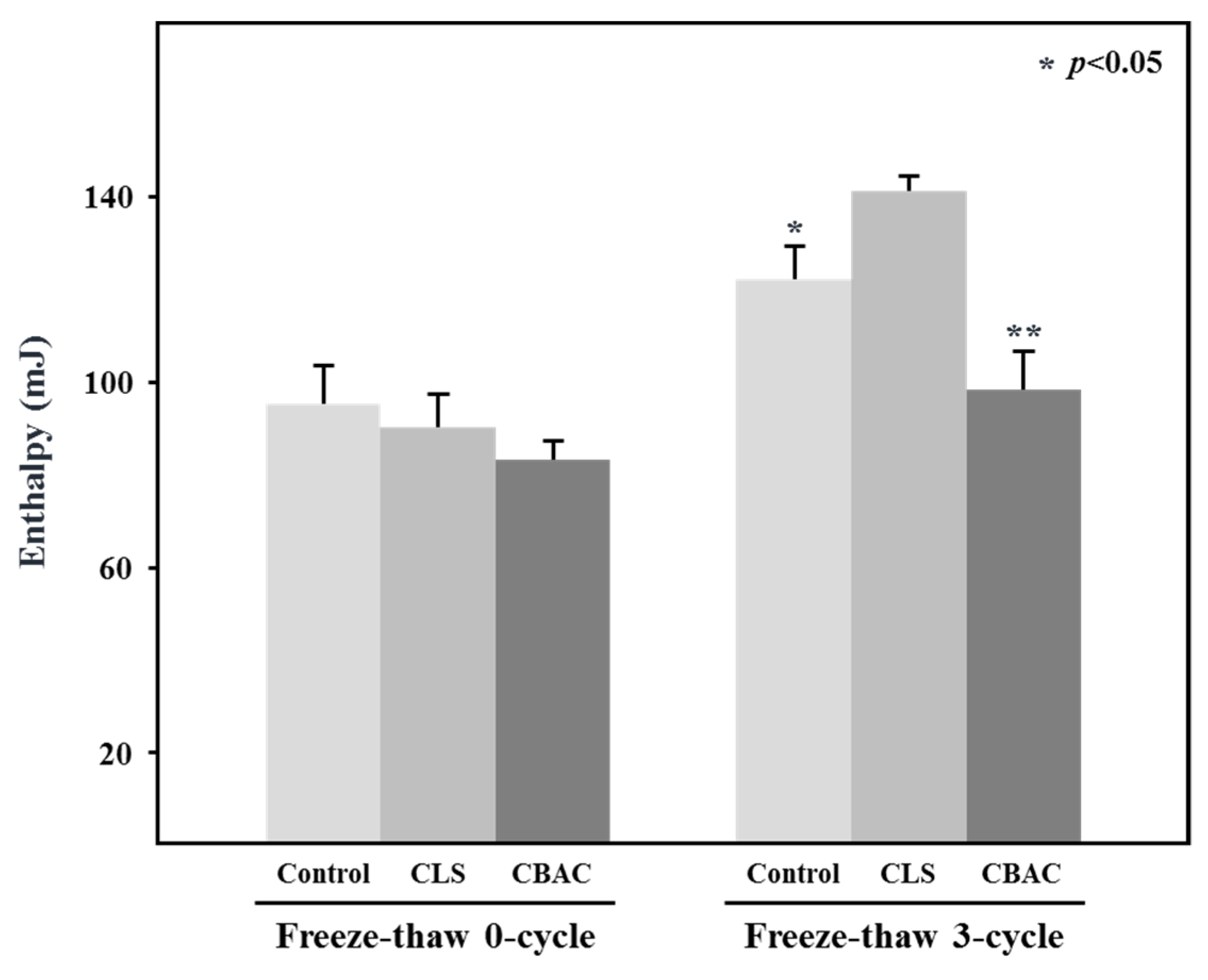
3.5. Freezable Water in Frozen Doughs
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Leray, G.; Oliete, B.; Mezaize, S.; Chevallier, S.; de Lamballerie, M. Effects of freezing and frozen storage conditions on the rheological properties of different formulations of non-yeasted wheat and gluten-free bread dough. J. Food Eng. 2010, 100, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selomulyo, V.O.; Zhou, W. Frozen bread dough: Effects of freezing storage and dough improvers. J. Cereal. Sci. 2007, 45, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanghe, A.; Van Dijck, P.; Dumortier, F.; Teunissen, A.; Hohmann, S.; Thevelein, J.M. Aquaporin expression correlates with freeze tolerance in baker’s yeast, and overexpression improves freeze tolerance in industrial strains. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2002, 68, 5981–5989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hamed, A.; Ragaee, S.; Abdel-Aal, E.M. Effect of β-glucan–rich barley flour fraction on rheology and quality of frozen yeasted dough. J. Food Sci. 2014, 79, E2470–E2479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simmons, A.L.; Smith, K.B.; Vodovotz, Y. Soy ingredients stabilize bread dough during frozen storage. J. Cereal Sci. 2012, 56, 232–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Kweon, M. Formula optimization of ready-to-proof and ready-to-bake frozen dough of sweet bread using response surface methodology. LWT 2021, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, V.; Ragaee, S.M.; Abdel-Aal, E.M. Rheological properties and bread quality of frozen yeast-dough with added wheat fiber. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2017, 97, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Naito, S.; Fukami, S.; Mizokami, Y.; Ishida, N.; Takano, H.; Koizumi, M.; Kano, H. Effect of freeze-thaw cycles on the gluten fibrils and crumb grain structures of breads made from frozen doughs. Cereal Chem. 2004, 81, 80–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya, M.; Langstaff, T.M.; Berzonsky, W.A. Effect of frozen storage and freeze-thaw cycles on the rheological and baking properties of frozen doughs. Food Res. Int. 2003, 36, 365–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Pei, D.; Teng, Y.; Liang, J. Effects of enzymes to improve sensory quality of frozen dough bread and analysis on its mechanism. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 55, 389–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Bail, A.; Grinand, C.; Le Cleach, S.; Martinez, S.; Quilin, E. Influence of storage conditions on frozen French bread dough. J. Food Eng. 1999, 56, 3761–3769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phimolsiripol, Y.; Siripatrawan, U.; Tulyathan, V.; Cleland, D.J. Effects of freezing and temperature fluctuations during frozen storage on frozen dough and bread quality. J. Food Eng. 2008, 84, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosell, C.M.; Gomez, M. Frozen dough and partially baked bread: An update. Food Rev. Int. 2007, 23, 303–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tao, H.; Wang, P.; Wu, F.; Jin, Z.; Xu, X. Particle size distribution of wheat starch granules in relation to baking properties of frozen dough. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 137, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akbarian, M.; Koocheki, A.; Mohebbi, M.; Milani, E. Rheological properties and bread quality of frozen sweet dough with added xanthan and different freezing rate. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 53, 3761–3769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, K.; Chi, C.; She, Z.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, H.; Zhang, H. Understanding how starch constituent in frozen dough following freezing-thawing treatment affected quality of steamed bread. Food Chem. 2021, 366, 130614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berglund, P.T.; Shelton, D.R.; Freeman, T.P. Frozen bread dough ultrastructure as affected by duration of frozen storage and freeze-thaw cycles. Cereal Chem. 1991, 68, 105–107. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, W.; Grant, L.A. Effects of prolonged storage at freezing temperatures on starch and baking quality of frozen doughs. Cereal Chem. 1999, 76, 656–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bárcenas, M.E.; Benedito, C.; Rosell, C.M. Use of hydrocolloids as bread improvers in interrupted baking processwith frozen storage. Food Hydrocoll. 2004, 18, 769–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharadanant, R.; Khan, K. Effect of hydrophilic gums on frozen dough. I. dough quality. Cereal Chem. 2003, 80, 764–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Maeda, T.; Morita, N. Effect of fungal α-amylase on the dough properties and bread quality of wheat flour substituted with polished flours. Food Res. Int. 2006, 39, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mapengo, C.R.; Ray, S.S.; Emmambux, M.N. Pasting properties of hydrothermally treated maize starch with added stearic acid. Food Chem. 2019, 289, 396–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arocas, A.; Sanz, T.; Fiszman, S.M. Clean label starches as thickeners in white sauces. Shearing, heating and freeze/thaw stability. Food Hydrocoll. 2009, 23, 2031–2037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maphalla, T.G.; Emmambux, M.N. Functionality of maize, wheat, teff and cassava starches with stearic acid and xanthan gum. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 136, 970–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Oladele, A.K.; Duodu, K.G.; Emmambux, N.M. Pasting, flow, thermal and molecular properties of maize starch modified with crude phenolic extracts from grape pomace and sorghum bran under alkaline conditions. Food Chem. 2019, 297, 124879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, Y.; Tyl, C. A review on mechanistic aspects of individual versus combined uses of enzymes as clean label-friendly dough conditioners in breads. J. Food Sci. 2021, 86, 1583–1598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eslava-Zomeno, C.; Quiles, A.; Hernando, I. Designing a clean label sponge cake with reduced fat content. J. Food Sci. 2016, 81, C2352–C2359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Roman, L.; Martinez, M.M.; Rosell, C.M.; Gomez, M. Changes in physicochemical properties and in vitro starch digestion of native and extruded maize flours subjected to branching enzyme and maltogenic alpha-amylase treatment. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 101, 326–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, J.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, J.; Han, Q.; Song, L.; Meng, X. Effect of photodynamic treatments on quality and antioxidant properties of fresh-cut potatoes. Food Chem. 2021, 362, 130224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.; Zhou, X. The Overview of Functional Starch. In Functional Starch and Applications in Food; Jin, Z., Ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2018; pp. 1–26. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, H.W.; Jeon, H.Y.; Choi, H.J.; Kim, N.R.; Choung, W.J.; Koo, Y.S.; Ko, D.S.; You, S.; Shim, J.H. Characterization and application of BiLA, a psychrophilic alpha-amylase from Bifidobacterium longum. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 64, 2709–2718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shim, J.H.; Kim, Y.W.; Kim, T.J.; Chae, H.Y.; Park, J.H.; Cha, H.; Kim, J.W.; Kim, Y.R.; Schaefer, T.; Spendler, T.; et al. Improvement of cyclodextrin glucanotransferase as an antistaling enzyme by error-prone PCR. Protein Eng. Des. Sel. 2004, 17, 205–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.K.; Le, Q.T.; Kim, Y.H.; Shim, J.H.; Lee, S.J.; Park, J.H.; Lee, K.P.; Song, S.H.; Auh, J.H.; Lee, S.J.; et al. Enzymatic synthesis and properties of highly branched rice starch amylose and amylopectin cluster. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 126–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukerjea, R.; Slocum, G.; Robyt, J.F. Determination of the maximum water solubility of eight native starches and the solubility of their acidic-methanol and -ethanol modified analogues. Carbohydr. Res. 2007, 342, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukerjea, R.; Robyt, J.F. Isolation, structure, and characterization of the putative soluble amyloses from potato, wheat, and rice starches. Carbohydr. Res. 2010, 345, 449–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jobling, S.A.; Westcott, R.J.; Tayal, A.; Jeffcoat, R.; Schwall, G.P. Production of a freeze-thaw-stable potato starch by antisense inhibition of three starch synthase genes. Nat. Biotechnol. 2002, 20, 295–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, J.; Zeng, X.A.; Buckow, R.; Han, Z. Structural, thermodynamic and digestible properties of maize starches esterified by conventional and dual methods: Differentiation of amylose contents. Food Hydrocoll. 2018, 83, 419–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.Y.; Kim, Y.R.; Park, K.H.; Lee, H.G. Effects of a-glucanotransferase treatment on the thermo-reversibility and freeze-thaw stability of a rice starch gel. Carbohydr. Polym. 2006, 63, 347–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, Y.; Bushuk, W. Studies on frozen doughs. flour quality requirements for bread production from frozen dough. Cereal Chem. 1992, 69, 423–428. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, L.; Xu, D.; Fang, F.; Jin, Z.; Xu, X. Effect of glutathione on wheat dough properties and bread quality. J. Cereal. Sci. 2020, 96, 103116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piccinini, M.; Fois, S.; Secchi, N.; Sanna, M.; Roggio, T.; Catzeddu, P. The Application of NIR FT-Raman spectroscopy to monitor starch retrogradation and crumb firmness in Semolina bread. Food Anal. Methods 2012, 5, 1145–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMichael, P. A global interpretation of the rise of the east asian food import complex. World Dev. 2000, 28, 409–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Starch Sample | Water Solubility (mg/mL) | Relative Solubility |
|---|---|---|
| Corn starch | 12.4 ± 0.00 a,b | 1 |
| CBAC-0.5 h c | 57.6 ± 0.24 | 4.65 |
| CBAC-1 h | 65.5 ± 0.35 | 5.28 |
| CBAC-3 h | 97.6 ± 0.43 | 7.87 |
| CBAC-5 h | 89.4 ± 0.16 | 7.21 |
| CBAC-7 h | 83.4 ± 0.28 | 6.73 |
| Textural Properties | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bread a | Hardness (N) | Springiness | Gumminess (N) | Chewiness (J) |
| Control | 2.52 ± 0.03 | 1.01 ± 0.00 | 1.22 ± 0.08 | 1.23 ± 0.07 |
| CLS | 2.30 ± 0.07 | 1.01 ± 0.00 | 0.83 ± 0.09 | 0.83 ± 0.07 |
| CBAC | 1.59 ± 0.07 | 1.00 ± 0.00 | 0.77 ± 0.03 | 0.77 ± 0.02 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Woo, S.-H.; Kim, J.-S.; Jeong, H.-M.; Shin, Y.-J.; Hong, J.-S.; Choi, H.-D.; Shim, J.-H. Development of Freeze-Thaw Stable Starch through Enzymatic Modification. Foods 2021, 10, 2269. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10102269
Woo S-H, Kim J-S, Jeong H-M, Shin Y-J, Hong J-S, Choi H-D, Shim J-H. Development of Freeze-Thaw Stable Starch through Enzymatic Modification. Foods. 2021; 10(10):2269. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10102269
Chicago/Turabian StyleWoo, Seung-Hye, Ji-Soo Kim, Hyun-Mo Jeong, Yu-Jeong Shin, Jung-Sun Hong, Hee-Don Choi, and Jae-Hoon Shim. 2021. "Development of Freeze-Thaw Stable Starch through Enzymatic Modification" Foods 10, no. 10: 2269. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10102269
APA StyleWoo, S.-H., Kim, J.-S., Jeong, H.-M., Shin, Y.-J., Hong, J.-S., Choi, H.-D., & Shim, J.-H. (2021). Development of Freeze-Thaw Stable Starch through Enzymatic Modification. Foods, 10(10), 2269. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10102269







