Anti-Apoptotic and Anti-Inflammatory Role of Trans ε-Viniferin in a Neuron–Glia Co-Culture Cellular Model of Parkinson’s Disease
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Drugs and Chemicals
2.2. Extractions and Purifications of Polyphenols
2.3. Cell Culture and Treatments
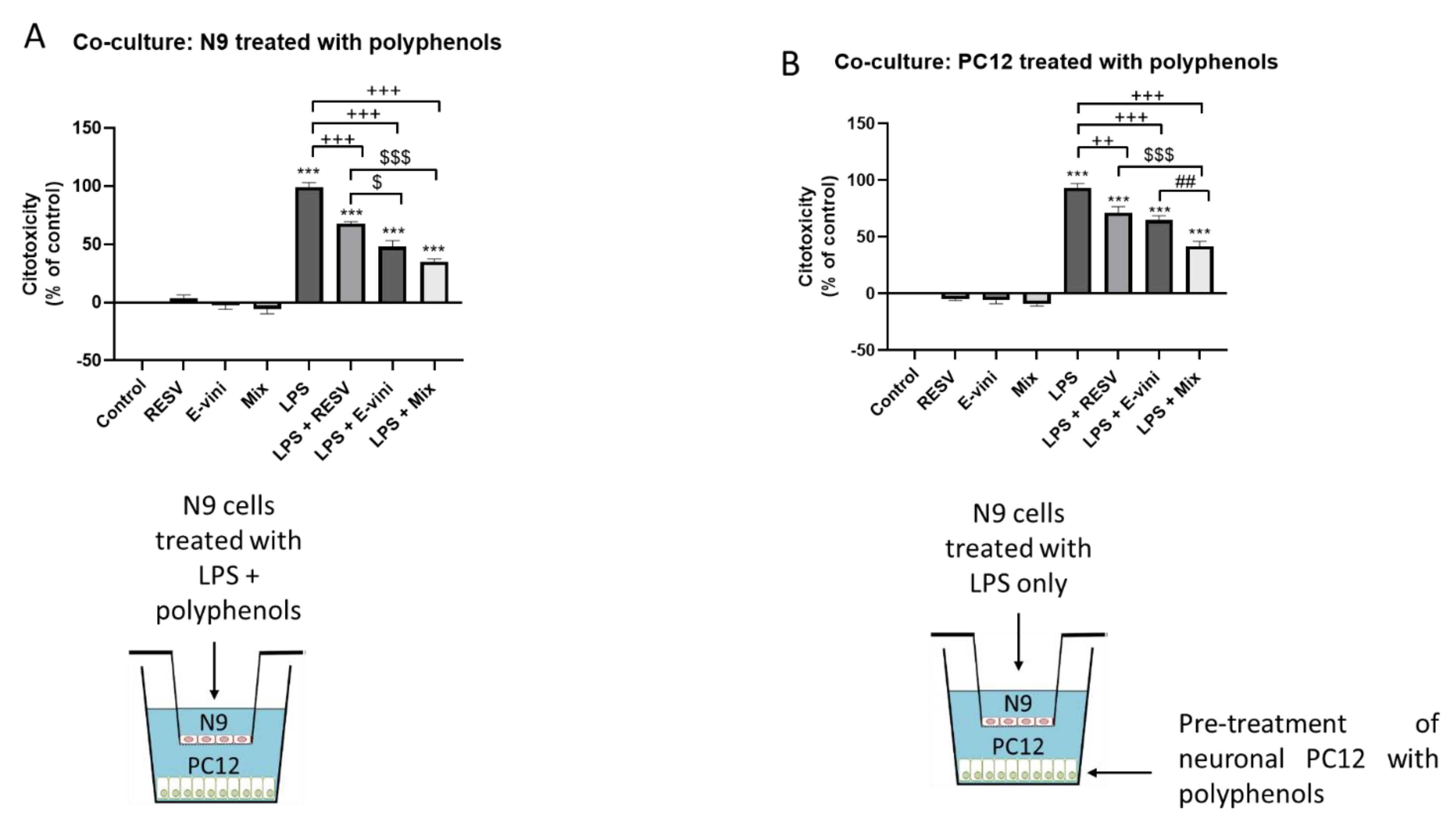
2.4. Neuronal–Glial Co-Culture
2.5. Cytotoxicity Measurements
2.6. MTT Assay
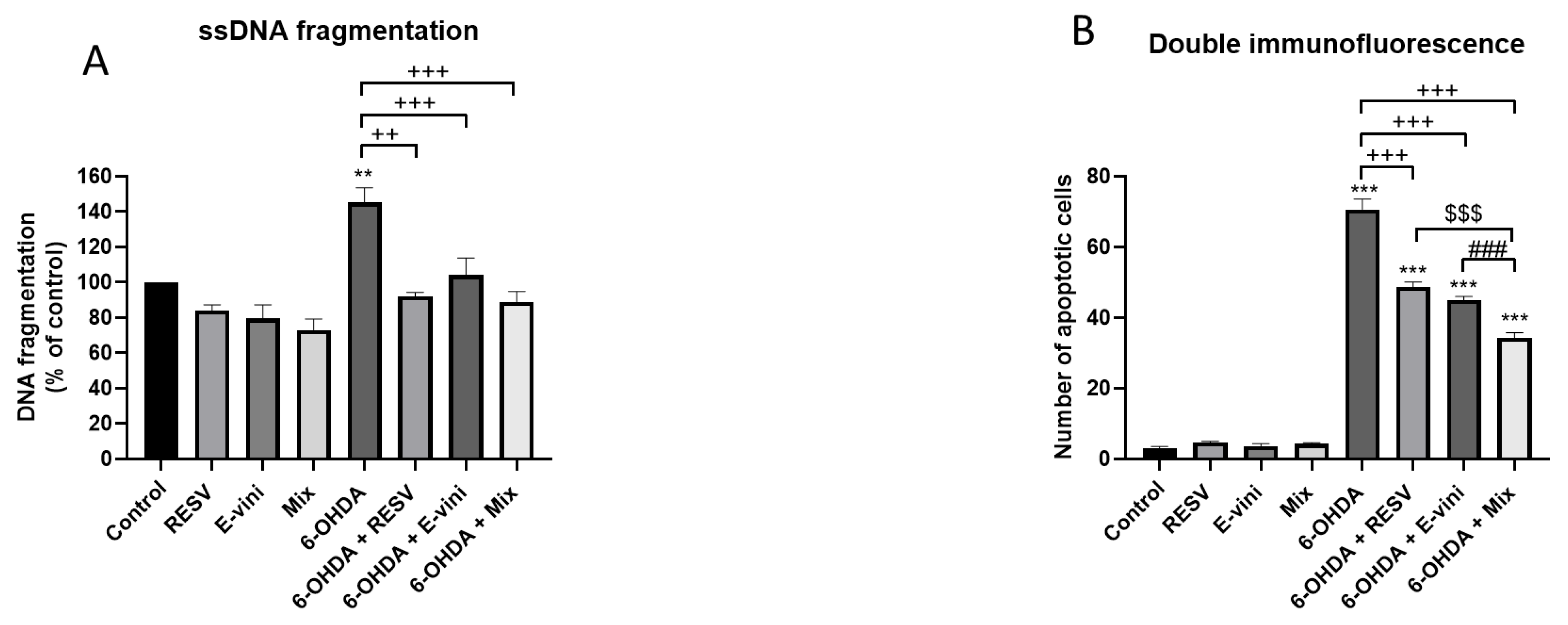
2.7. Apoptosis- Specific DNA Denaturation Detection
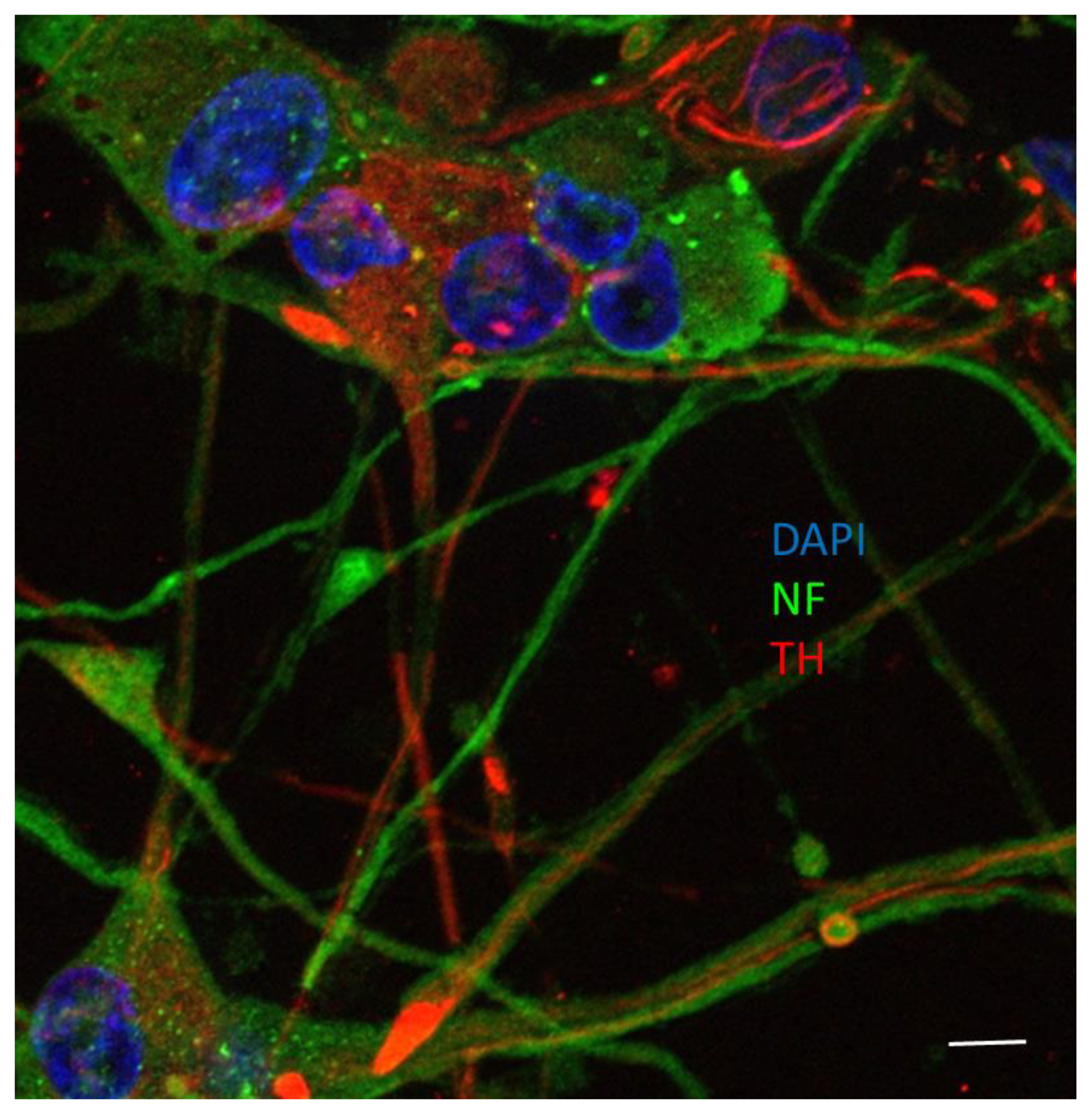
2.8. Immunofluorescent Microscopy
2.9. Electrophoresis and Immunoblot Analysis
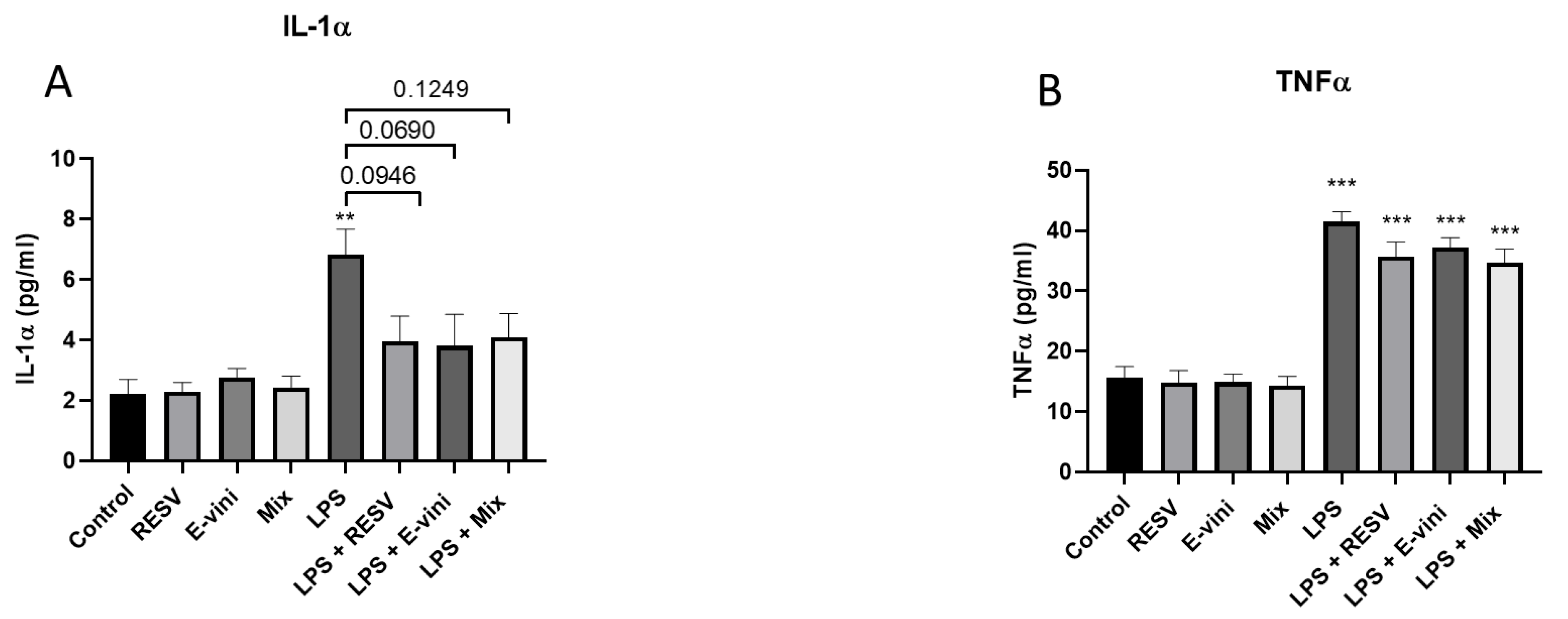
2.10. ELISA
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Viniferin Reduced 6-OHDA-Induced Cytotoxicity and Promoted Cell Survival
3.2. Viniferin Decreased the Rate of Apoptotic Neuronal PC12 Cells
3.3. Viniferin Used Alone or in Combination with Resveratrol Decreased the Cleavage of Caspase-3 and PARP-1 in Neuronal PC12
3.4. Viniferin, Resveratrol and Their Combination Decreased Neuronal PC12 Cytotoxicity Induced by Activated Microglia, in a Co-Culture System
3.5. Viniferin Affected the Secretion of Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines from LPS-Activated N9 Cells
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hornykiewicz, O. The discovery of dopamine deficiency in the parkinsonian brain. J. Neural Transm. Suppl. 2006, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatton, W.G.; Chalmers-Redman, R.; Brown, D.; Tatton, N. Apoptosis in Parkinson’s disease: Signals for neuronal degradation. Ann. Neurol. 2003, 53 (Suppl. 3), S61–S70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiskum, G.; Starkov, A.; Polster, B.M.; Chinopoulos, C. Mitochondrial mechanisms of neural cell death and neuroprotective interventions in Parkinson’s disease. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2003, 991, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sergi, D.; Renaud, J.; Simola, N.; Martinoli, M.G. Diabetes, a Contemporary Risk for Parkinson’s Disease: Epidemiological and Cellular Evidences. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2019, 11, 302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, G. Oxy-radical toxicity in catecholamine neurons. Neurotoxicology 1984, 5, 77–82. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tansey, M.G.; Goldberg, M.S. Neuroinflammation in Parkinson’s disease: Its role in neuronal death and implications for therapeutic intervention. Neurobiol. Dis. 2010, 37, 510–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGeer, P.L.; Itagaki, S.; Boyes, B.E.; McGeer, E.G. Reactive microglia are positive for HLA-DR in the substantia nigra of Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s disease brains. Neurology 1988, 38, 1285–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelders, G.; Baekelandt, V.; Van der P56erren, A. Linking Neuroinflammation and Neurodegeneration in Parkinson’s Disease. J. Immunol. Res. 2018, 2018, 4784268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renaud, J.; Martinoli, M.G. Development of an Insert Co-culture System of Two Cellular Types in the Absence of Cell-Cell Contact. J. Vis. Exp. 2016, e54356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bournival, J.; Plouffe, M.; Renaud, J.; Provencher, C.; Martinoli, M.G. Quercetin and sesamin protect dopaminergic cells from MPP+-induced neuroinflammation in a microglial (N9)-neuronal (PC12) coculture system. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2012, 2012, 921941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bureau, G.; Longpre, F.; Martinoli, M.G. Resveratrol and quercetin, two natural polyphenols, reduce apoptotic neuronal cell death induced by neuroinflammation. J. Neurosci. Res. 2008, 86, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Bing, G. Lipopolysaccharide animal models for Parkinson’s disease. Parkinsons Dis. 2011, 2011, 327089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aquilano, K.; Baldelli, S.; Rotilio, G.; Ciriolo, M.R. Role of nitric oxide synthases in Parkinson’s disease: A review on the antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activity of polyphenols. Neurochem. Res. 2008, 33, 2416–2426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamin, L.L.; Filippi-Chiela, E.C.; Dillenburg-Pilla, P.; Horn, F.; Salbego, C.; Lenz, G. Resveratrol and quercetin cooperate to induce senescence-like growth arrest in C6 rat glioma cells. Cancer Sci. 2009, 100, 1655–1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bournival, J.; Quessy, P.; Martinoli, M.G. Protective effects of resveratrol and quercetin against MPP+-induced oxidative stress act by modulating markers of apoptotic death in dopaminergic neurons. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 2009, 29, 1169–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Khawand, T.; Courtois, A.; Valls, J.; Richard, T.; Krisa, S. A review of dietary stilbenes: Sources and bioavailability. Phytochem. Rev. 2018, 17, 1007–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.; Jin, J.; Cichewicz, R.H.; Hageman, S.A.; Ellis, T.K.; Xiang, L.; Peng, Q.; Jiang, M.; Arbez, N.; Hotaling, K.; et al. trans-(-)-epsilon-Viniferin increases mitochondrial sirtuin 3 (SIRT3), activates AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK), and protects cells in models of Huntington Disease. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 24460–24472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caillaud, M.; Guillard, J.; Richard, D.; Milin, S.; Chassaing, D.; Paccalin, M.; Page, G.; Rioux Bilan, A. Trans epsilon viniferin decreases amyloid deposits and inflammation in a mouse transgenic Alzheimer model. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0212663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vion, E.; Page, G.; Bourdeaud, E.; Paccalin, M.; Guillard, J.; Rioux Bilan, A. Trans epsilon-viniferin is an amyloid-beta disaggregating and anti-inflammatory drug in a mouse primary cellular model of Alzheimer’s disease. Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 2018, 88, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houille, B.; Papon, N.; Boudesocque, L.; Bourdeaud, E.; Besseau, S.; Courdavault, V.; Enguehard-Gueiffier, C.; Delanoue, G.; Guerin, L.; Bouchara, J.P.; et al. Antifungal activity of resveratrol derivatives against Candida species. J. Nat. Prod. 2014, 77, 1658–1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelinas, S.; Martinoli, M.G. Neuroprotective effect of estradiol and phytoestrogens on MPP+-induced cytotoxicity in neuronal PC12 cells. J. Neurosci. Res. 2002, 70, 90–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arel-Dubeau, A.M.; Longpre, F.; Bournival, J.; Tremblay, C.; Demers-Lamarche, J.; Haskova, P.; Attard, E.; Germain, M.; Martinoli, M.G. Cucurbitacin E has neuroprotective properties and autophagic modulating activities on dopaminergic neurons. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2014, 2014, 425496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.Q.; Wang, T.; Pei, Z.; Liu, B.; Hong, J.S. Inhibition of microglial activation by the herbal flavonoid baicalein attenuates inflammation-mediated degeneration of dopaminergic neurons. J. Neural Transm. 2005, 112, 331–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Decker, T.; Lohmann-Matthes, M.L. A quick and simple method for the quantitation of lactate dehydrogenase release in measurements of cellular cytotoxicity and tumor necrosis factor (TNF) activity. J. Immunol. Methods 1988, 115, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frankfurt, O.S.; Krishan, A. Identification of apoptotic cells by formamide-induced dna denaturation in condensed chromatin. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 2001, 49, 369–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renaud, J.; Bournival, J.; Zottig, X.; Martinoli, M.G. Resveratrol protects DAergic PC12 cells from high glucose-induced oxidative stress and apoptosis: Effect on p53 and GRP75 localization. Neurotox. Res. 2014, 25, 110–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carange, J.; Longpre, F.; Daoust, B.; Martinoli, M.G. 24-Epibrassinolide, a Phytosterol from the Brassinosteroid Family, Protects Dopaminergic Cells against MPP-Induced Oxidative Stress and Apoptosis. J. Toxicol. 2011, 2011, 392859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simola, N.; Morelli, M.; Carta, A.R. The 6-hydroxydopamine model of Parkinson’s disease. Neurotox. Res. 2007, 11, 151–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quiroga-Varela, A.; Aguilar, E.; Iglesias, E.; Obeso, J.A.; Marin, C. Short- and long-term effects induced by repeated 6-OHDA intraventricular administration: A new progressive and bilateral rodent model of Parkinson’s disease. Neuroscience 2017, 361, 144–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.W.; Kim, Y.M.; Kang, S.D.; Han, Y.M.; Pae, H.O. Effects of Resveratrol and trans-3,5,4′-Trimethoxystilbene on Glutamate-Induced Cytotoxicity, Heme Oxygenase-1, and Sirtuin 1 in HT22 Neuronal Cells. Biomol. Ther. 2012, 20, 306–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Son, Y.; Byun, S.J.; Pae, H.O. Involvement of heme oxygenase-1 expression in neuroprotection by piceatannol, a natural analog and a metabolite of resveratrol, against glutamate-mediated oxidative injury in HT22 neuronal cells. Amino Acids 2013, 45, 393–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Truong, V.L.; Jun, M.; Jeong, W.S. Role of resveratrol in regulation of cellular defense systems against oxidative stress. Biofactors 2018, 44, 36–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arbo, B.D.; Andre-Miral, C.; Nasre-Nasser, R.G.; Schimith, L.E.; Santos, M.G.; Costa-Silva, D.; Muccillo-Baisch, A.L.; Hort, M.A. Resveratrol Derivatives as Potential Treatments for Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s Disease. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2020, 12, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farkhondeh, T.; Folgado, S.L.; Pourbagher-Shahri, A.M.; Ashrafizadeh, M.; Samarghandian, S. The therapeutic effect of resveratrol: Focusing on the Nrf2 signaling pathway. Biomed. Pharm. 2020, 127, 110234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munialo, C.D.; Naumovski, N.; Sergi, D.; Stewart, D.; Mellor, D.D. Critical evaluation of the extrapolation of data relative to antioxidant function from the laboratory and their implications on food production and human health: A review. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blesa, J.; Trigo-Damas, I.; Quiroga-Varela, A.; Jackson-Lewis, V.R. Oxidative stress and Parkinson’s disease. Front. Neuroanat 2015, 9, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Fan, W.; Wang, H.; Bao, L.; Li, G.; Li, T.; Song, S.; Li, H.; Hao, J.; Sun, J. Resveratrol Protects PC12 Cell against 6-OHDA Damage via CXCR4 Signaling Pathway. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2015, 2015, 730121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Dong, X.; Liu, Z.; Zhu, S.; Liu, H.; Fan, W.; Hu, Y.; Hu, T.; Yu, Y.; Li, Y.; et al. Resveratrol Suppresses Rotenone-induced Neurotoxicity Through Activation of SIRT1/Akt1 Signaling Pathway. Anat. Rec. 2018, 301, 1115–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, N.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, M.; Jin, H.; Nie, J.; Luo, Y.; Zhou, S.; Shi, J.; Jin, F. Resveratrol delays 6-hydroxydopamine-induced apoptosis by activating the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. Exp. Gerontol. 2019, 124, 110653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palle, S.; Neerati, P. Improved neuroprotective effect of resveratrol nanoparticles as evinced by abrogation of rotenone-induced behavioral deficits and oxidative and mitochondrial dysfunctions in rat model of Parkinson’s disease. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharm. 2018, 391, 445–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanchet, J.; Longpre, F.; Bureau, G.; Morissette, M.; DiPaolo, T.; Bronchti, G.; Martinoli, M.G. Resveratrol, a red wine polyphenol, protects dopaminergic neurons in MPTP-treated mice. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2008, 32, 1243–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kupsch, A.; Schmidt, W.; Gizatullina, Z.; Debska-Vielhaber, G.; Voges, J.; Striggow, F.; Panther, P.; Schwegler, H.; Heinze, H.J.; Vielhaber, S.; et al. 6-Hydroxydopamine impairs mitochondrial function in the rat model of Parkinson’s disease: Respirometric, histological, and behavioral analyses. J. Neural Transm. 2014, 121, 1245–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, Q.; Ren, X.; Hu, R.; Yin, X.; Jiang, G.; Pan, Y. Isolation and purification of two antioxidant isomers of resveratrol dimer from the wine grape by counter-current chromatography. J. Sep. Sci. 2016, 39, 2374–2379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, H.Y.; Kim, J.Y.; Lee, H.K.; Ha, D.T.; Song, K.S.; Bae, K.; Seong, Y.H. Leaf and stem of Vitis amurensis and its active components protect against amyloid beta protein (25–35)-induced neurotoxicity. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2010, 33, 1655–1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Ma, Y.; Feng, J. Neuroprotective mechanisms of epsilon-viniferin in a rotenone-induced cell model of Parkinson’s disease: Significance of SIRT3-mediated FOXO3 deacetylation. Neural Regen. Res. 2020, 15, 2143–2153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pino, E.; Amamoto, R.; Zheng, L.; Cacquevel, M.; Sarria, J.C.; Knott, G.W.; Schneider, B.L. FOXO3 determines the accumulation of alpha-synuclein and controls the fate of dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2014, 23, 1435–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gyoneva, S.; Shapiro, L.; Lazo, C.; Garnier-Amblard, E.; Smith, Y.; Miller, G.W.; Traynelis, S.F. Adenosine A2A receptor antagonism reverses inflammation-induced impairment of microglial process extension in a model of Parkinson’s disease. Neurobiol. Dis. 2014, 67, 191–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deleidi, M.; Gasser, T. The role of inflammation in sporadic and familial Parkinson’s disease. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2013, 70, 4259–4273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGeer, P.L.; McGeer, E.G. Inflammation and neurodegeneration in Parkinson’s disease. Parkinsonism Relat. Disord. 2004, 10 (Suppl. 1), S3–S7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castano, A.; Herrera, A.J.; Cano, J.; Machado, A. Lipopolysaccharide intranigral injection induces inflammatory reaction and damage in nigrostriatal dopaminergic system. J. Neurochem. 1998, 70, 1584–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera, A.J.; Castano, A.; Venero, J.L.; Cano, J.; Machado, A. The single intranigral injection of LPS as a new model for studying the selective effects of inflammatory reactions on dopaminergic system. Neurobiol. Dis. 2000, 7, 429–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Bi, W.; Xiao, S.; Lan, X.; Cheng, X.; Zhang, J.; Lu, D.; Wei, W.; Wang, Y.; Li, H.; et al. Neuroinflammation induced by lipopolysaccharide causes cognitive impairment in mice. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 5790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simpson, D.S.A.; Oliver, P.L. ROS Generation in Microglia: Understanding Oxidative Stress and Inflammation in Neurodegenerative Disease. Antioxidants 2020, 743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wardyn, J.D.; Ponsford, A.H.; Sanderson, C.M. Dissecting molecular cross-talk between Nrf2 and NF-kappaB response pathways. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2015, 43, 621–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ha, D.T.; Long, P.T.; Hien, T.T.; Tuan, D.T.; An, N.T.T.; Khoi, N.M.; Van Oanh, H.; Hung, T.M. Anti-inflammatory effect of oligostilbenoids from Vitis heyneana in LPS-stimulated RAW 264.7 macrophages via suppressing the NF-kappaB activation. Chem. Cent. J. 2018, 12, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, R.; Maier, O. Interrelation of oxidative stress and inflammation in neurodegenerative disease: Role of TNF. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2015, 2015, 610813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bournival, J.; Francoeur, M.A.; Renaud, J.; Martinoli, M.G. Quercetin and sesamin protect neuronal PC12 cells from high-glucose-induced oxidation, nitrosative stress, and apoptosis. Rejuvenation Res. 2012, 15, 322–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sergi, D.; Gélinas, A.; Beaulieu, J.; Renaud, J.; Tardif-Pellerin, E.; Guillard, J.; Martinoli, M.-G. Anti-Apoptotic and Anti-Inflammatory Role of Trans ε-Viniferin in a Neuron–Glia Co-Culture Cellular Model of Parkinson’s Disease. Foods 2021, 10, 586. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10030586
Sergi D, Gélinas A, Beaulieu J, Renaud J, Tardif-Pellerin E, Guillard J, Martinoli M-G. Anti-Apoptotic and Anti-Inflammatory Role of Trans ε-Viniferin in a Neuron–Glia Co-Culture Cellular Model of Parkinson’s Disease. Foods. 2021; 10(3):586. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10030586
Chicago/Turabian StyleSergi, Domenico, Alex Gélinas, Jimmy Beaulieu, Justine Renaud, Emilie Tardif-Pellerin, Jérôme Guillard, and Maria-Grazia Martinoli. 2021. "Anti-Apoptotic and Anti-Inflammatory Role of Trans ε-Viniferin in a Neuron–Glia Co-Culture Cellular Model of Parkinson’s Disease" Foods 10, no. 3: 586. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10030586
APA StyleSergi, D., Gélinas, A., Beaulieu, J., Renaud, J., Tardif-Pellerin, E., Guillard, J., & Martinoli, M.-G. (2021). Anti-Apoptotic and Anti-Inflammatory Role of Trans ε-Viniferin in a Neuron–Glia Co-Culture Cellular Model of Parkinson’s Disease. Foods, 10(3), 586. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10030586




