Microbiota of Chicken Breast and Thigh Fillets Stored under Different Refrigeration Temperatures Assessed by Next-Generation Sequencing
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chicken Cuts Provision and Storage
2.2. Microbiological Analyses and pH Measurement
2.3. Total Bacterial DNA Extraction
2.4. Microbiome Analysis through Next Generation Sequencing (NGS)
2.5. Statistics and Multivariate Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Microbial Evolution and pH Values
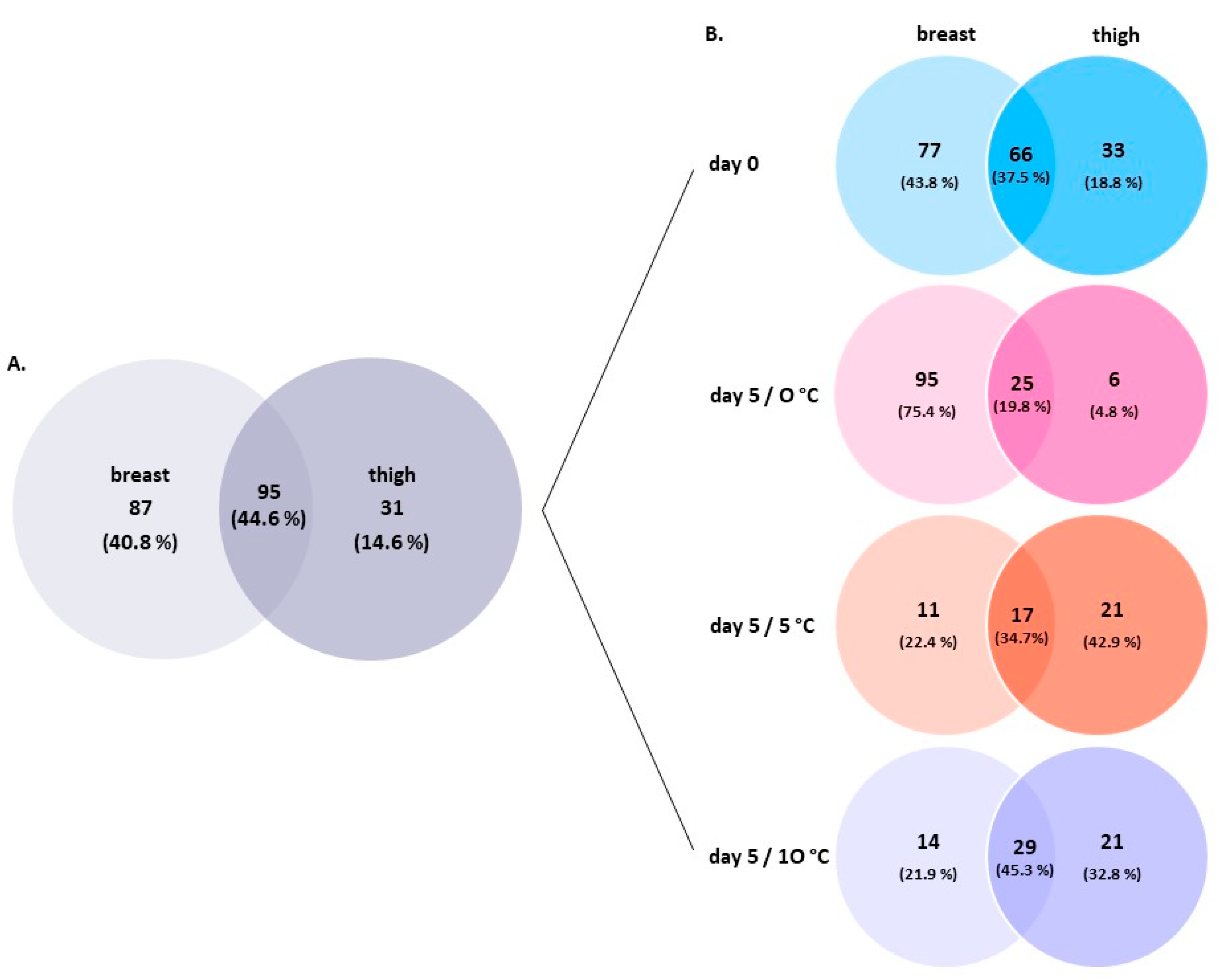
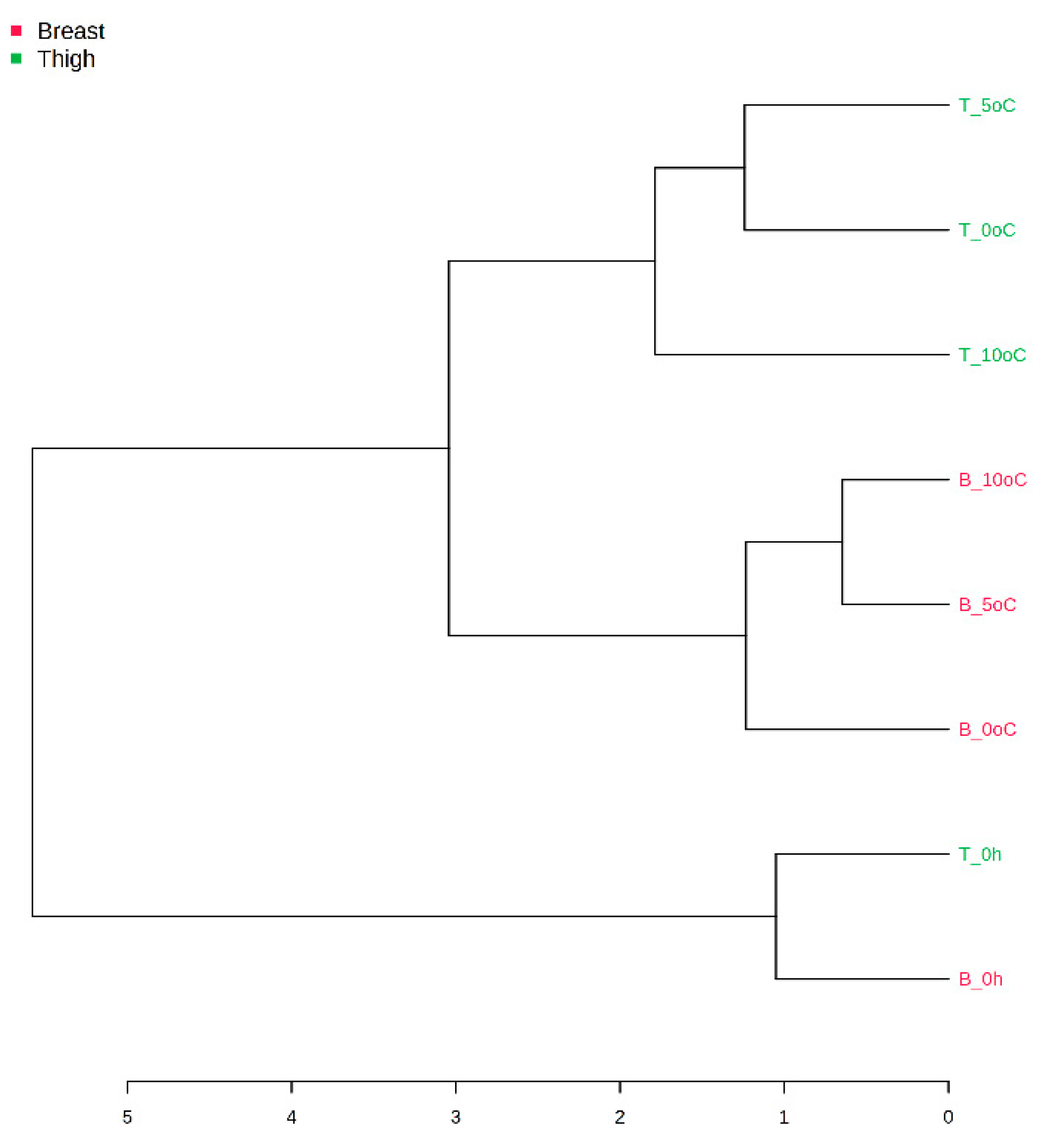
3.2. Amplicon Sequencing of the 16S rRNA Gene of Breast and Thigh Fillets
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- OECD; FAO. OECD-FAO Agricultural Outlook 2020–2029; OECD: Rome, Italy, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marangoni, F.; Corsello, G.; Cricelli, C.; Ferrara, N.; Ghiselli, A.; Lucchin, L.; Poli, A. Role of poultry meat in a balanced diet aimed at maintaining health and wellbeing: An Italian consensus document. Food Nutr. Res. 2015, 59, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- González, N.; Marquès, M.; Nadal, M.; Domingo, J.L. Meat consumption: Which are the current global risks? A review of recent (2010–2020) evidences. Food Res. Int. 2020, 137, 104391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbut, S. The Science of Poultry and Meat Processing; Self-Published Online Book; University of Guelph: Guelph, ON, Canada, 2015; Available online: www.poultryandmeatprocessing.com (accessed on 15 March 2021).
- Odeyemi, O.A.; Alegbeleye, O.O.; Strateva, M.; Stratev, D. Understanding spoilage microbial community and spoilage mechanisms in foods of animal origin. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2020, 19, 311–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cobos, Á.; Díaz, O. Chemical Composition of Meat and Meat Products. In Handbook of Food Chemistry; Cheung, P., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; pp. 471–510. Available online: http://doi-org-443.webvpn.fjmu.edu.cn/10.1007/978-3-642-41609-5_6-1 (accessed on 15 March 2021).
- Rouger, A.; Tresse, O.; Zagorec, M. Bacterial contaminants of poultry meat: Sources, species, and dynamics. Microorganisms 2017, 5, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gill, C.O. Intrinsic bacteria in meat. J. Appl. Bacteriol. 1979, 47, 367–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jay, J.M. Fresh meats and poultry. In Modern Food Microbiology; Jay, J.M., Ed.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2000; pp. 59–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nychas, G.J.E.; Skandamis, P.N.; Tassou, C.C.; Koutsoumanis, K.P. Meat spoilage during distribution. Meat Sci. 2008, 78, 77–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nychas, G.J.E.; Panagou, E.Z.; Mohareb, F. Novel approaches for food safety management and communication. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2016, 12, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rukchon, C.; Nopwinyuwong, A.; Trevanich, S.; Jinkarn, T.; Suppakul, P. Development of a food spoilage indicator for monitoring freshness of skinless chicken breast. Talanta 2014, 130, 547–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaillou, S.; Chaulot-Talmon, A.; Caekebeke, H.; Cardinal, M.; Christieans, S.; Denis, C.; Hélène Desmonts, M.; Dousset, X.; Feurer, C.; Hamon, E.; et al. Origin and ecological selection of core and food-specific bacterial communities associated with meat and seafood spoilage. ISME J. 2015, 9, 1105–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Doulgeraki, A.I.; Ercolini, D.; Villani, F.; Nychas, G.J.E. Spoilage microbiota associated to the storage of raw meat in different conditions. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2012, 157, 130–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remenant, B.; Jaffrès, E.; Dousset, X.; Pilet, M.F.; Zagorec, M. Bacterial spoilers of food: Behavior, fitness and functional properties. Food Microbiol. 2015, 45, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishangulyyev, R.; Kim, S.; Lee, S.H. Understanding food loss and waste-why are we losing and wasting food? Foods 2019, 8, 297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stanbridge, L.H.; Davies, A.R. The Microbiology of chill stored meat. In The Microbiology of Meat and Poultry; Board, R.J., Davies, A.R., Eds.; Springer: Colfax County, NM, USA, 1998; pp. 174–219. [Google Scholar]
- Hugenholtz, P.; Goebel, B.M.; Pace, N.R. Impact of culture-independent studies on the emerging phylogenetic view of bacterial diversity. J. Bacteriol. 1998, 180, 4765–4774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Davey, H.M. Life, death, and in-between: Meanings and methods in microbiology. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 77, 5571–5576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Amann, R.I.; Ludwig, W.; Schleiferand, K.-H. Phylogenetic identification and in situ detection of individual microbial cells without cultivation. Microbiol. Rev. 1995, 59, 143–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cocolin, L.; Alessandria, V.; Dolci, P.; Gorra, R.; Rantsiou, K. Culture independent methods to assess the diversity and dynamics of microbiota during food fermentation. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2013, 167, 29–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loman, N.J.; Pallen, M.J. Twenty years of bacterial genome sequencing. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2015, 13, 787–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kchouk, M.; Gibrat, J.F.; Elloumi, M. Generations of sequencing technologies: From first to next generation. Biol. Med. 2017, 09, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mayo, B.; Rachid, C.; Alegria, A.; Leite, A.; Peixoto, R.; Delgado, S. Impact of next generation sequencing techniques in food microbiology. Curr. Genom. 2014, 15, 293–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Borda-Molina, D.; Seifert, J.; Camarinha-Silva, A. Current perspectives of the chicken gastrointestinal tract and its microbiome. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2018, 16, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rychlik, I. Composition and function of chicken gut microbiota. Animals 2020, 10, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Duquenoy, A.; Ania, M.; Boucher, N.; Reynier, F.; Boucinha, L.; Andreoni, C.; Thomas, V. Caecal microbiota compositions from 7-day-old chicks reared in high-performance and low-performance industrial farms and systematic culturomics to select strains with anti-Campylobacter activity. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0237541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.J.; Cho, S.; La, T.M.; Lee, H.J.; Lee, J.B.; Park, S.Y.; Song, C.S.; Choi, I.S.; Lee, S.W. Comparison of microbiota in the cloaca, colon, and magnum of layer chicken. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0237108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Marzooqi, W.; Al-Maskari, Z.; Al-Kharousi, K.; Johnson, E.H.; El Tahir, Y. Diversity of intestinal bacterial microbiota of indigenous and commercial strains of chickens using 16S rDNA-based analysis. Animals 2020, 10, 391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, S.H.; Fegan, N.; Kocharunchitt, C.; Bowman, J.P.; Duffy, L.L. Changes of the bacterial community diversity on chicken carcasses through an Australian poultry processing line. Food Microbiol. 2020, 86, 103350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Handley, J.A.; Park, S.H.; Kim, S.A.; Ricke, S.C. Microbiome profiles of commercial broilers through evisceration and immersion chilling during poultry slaughter and the identification of potential indicator microorganisms. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ae Kim, S.; Hong Park, S.; In Lee, S.; Owens, C.M.; Ricke, S.C. Assessment of chicken carcass microbiome responses during processing in the presence of commercial antimicrobials using a next generation sequencing approach. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oakley, B.B.; Morales, C.A.; Line, J.; Berrang, M.E.; Meinersmann, R.J.; Tillman, G.E.; Wise, M.G.; Siragusa, G.R.; Hiett, K.L.; Seal, B.S. The poultry-associated microbiome: Network analysis and farm-to-fork characterizations. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e57190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lauritsen, C.V.; Kjeldgaard, J.; Ingmer, H.; Bisgaard, M.; Christensen, H. Microbiota encompassing putative spoilage bacteria in retail packaged broiler meat and commercial broiler abattoir. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2019, 300, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, S.I.; Choi, J.; Daeschel, D.Z.; Park, S.H. Microbiome characterization of poultry products based on the poultry part and production label. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2019, 366, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higgins, D.; Pal, C.; Sulaiman, I.M.; Jia, C.; Zerwekh, T.; Dowd, S.E.; Banerjee, P. Application of high-throughput pyrosequencing in the analysis of microbiota of food commodities procured from small and large retail outlets in a U.S. metropolitan area—A pilot study. Food Res. Int. 2018, 105, 29–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.E.; Lee, J.J.; Lee, M.J.; Kim, B.S. Analysis of microbiome in raw chicken meat from butcher shops and packaged products in South Korea to detect the potential risk of foodborne illness. Food Res. Int. 2019, 122, 517–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Mann, D.A.; Zhang, S.; Qi, Y.; Meinersmann, R.J.; Deng, X. Microbiome-informed food safety and quality: Longitudinal consistency and cross-sectional distinctiveness of retail chicken breast microbiomes. mSystems 2020, 5, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, J.; Huang, X.; Song, L.; Hou, B.; Qiao, M.; Zhang, P.; Zhao, Q.; Zhang, B.; Liu, F. Effect of storage temperature on bacterial diversity in chicken skin. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2019, 126, 854–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rouger, A.; Moriceau, N.; Prévost, H.; Remenant, B.; Zagorec, M. Diversity of bacterial communities in French chicken cuts stored under modified atmosphere packaging. Food Microbiol. 2018, 70, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Qin, X.; Li, X.; Wang, X.; Gao, H.; Zhang, C. Changes in the microbial communities of air- and water-chilled yellow-feathered broilers during storage at 2 °C. Food Microbiol. 2020, 87, 103390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.S.; Kwon, M.; Heo, S.; Kim, M.G.; Kim, G.B. Characterization of the biodiversity of the spoilage microbiota in chicken meat using next generation sequencing and culture dependent approach. Korean J. Food Sci. Anim. Resour. 2017, 37, 535–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gougouli, M.; Koutsoumanis, K.P. Risk Assessment of Fungal Spoilage: A Case Study of Aspergillus Niger on Yogurt. Food Microbiol. 2017, 65, 264–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutchison, M.L.; Walters, L.D.; Avery, S.M.; Reid, C.A.; Wilson, D.; Howell, M.; Johnston, A.M.; Buncic, S.A. A comparison of wet-dry swabbing and excision sampling methods for microbiological testing of bovine, porcine, and ovine carcasses at red meat slaughterhouses. J. Food Prot. 2005, 68, 2155–2162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pepperell, R.; Reid, C.A.; Solano, S.N.; Hutchison, M.L.; Walters, L.D.; Johnston, A.M.; Buncic, S. Experimental comparison of excision and swabbing microbiological sampling methods for carcasses. J. Food Prot. 2005, 68, 2163–2168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spyrelli, E.D.; Stamatiou, A.; Tassou, C.C.; Nychas, G.J.E.; Doulgeraki, A.I. Microbiological and metagenomic analysis to assess the effect of container material on the microbiota of Feta cheese during ripening. Fermentation 2020, 6, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gromski, P.S.; Muhamadali, H.; Ellis, D.I.; Xu, Y.; Correa, E.; Turner, M.L.; Goodacre, R. A tutorial review: Metabolomics and partial least squares-discriminant analysis—A marriage of convenience or a shotgun wedding. Anal. Chim. Acta 2015, 879, 10–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, J.; Wishart, D.S. Web-based inference of biological patterns, functions and pathways from metabolomic data using MetaboAnalyst. Nat. Protoc. 2011, 6, 743–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, J.; Wishart, D.S.; Xia, J. Using MetaboAnalyst 4.0 for Comprehensive and Integrative Metabolomics Data Analysis. Curr. Protoc. Bioinforma. 2019, 68, 1–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveros, J.C. An Interactive Tool for Comparing Lists with Venn’s Diagrams. Published Online 2007. Available online: https://bioinfogp.cnb.csic.es/tools/venny/index.html (accessed on 15 March 2021).
- Chmiel, M.; Hać-Szymańczuk, E.; Adamczak, L.; Pietrzak, D.; Florowski, T.; Cegiełka, A. Quality changes of chicken breast meat packaged in a normal and in a modified atmosphere. J. Appl. Poult. Res. 2018, 27, 349–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spyrelli, E.D.; Doulgeraki, A.I.; Argyri, A.A.; Tassou, C.C.; Panagou, E.Z.; George-John, E.N. Implementation of multispectral imaging (MSI) for microbiological quality assessment of poultry products. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lytou, A.; Panagou, E.Z.; Nychas, G.J.E. Development of a predictive model for the growth kinetics of aerobic microbial population on pomegranate marinated chicken breast fillets under isothermal and dynamic temperature conditions. Food Microbiol. 2016, 55, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakouri, A.; Nychas, G.J.E. Storage of poultry meat under modified atmospheres or vacuum packs: Possible role of microbial metabolites as indicator of spoilage. J. Appl. Bacteriol. 1994, 76, 163–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samapundo, S.; de Baenst, I.; Aerts, M.; Cnockaert, M.; Devlieghere, F.; Van Damme, P. Tracking the sources of psychrotrophic bacteria contaminating chicken cuts during processing. Food Microbiol. 2019, 81, 40–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lytou, A.E.; Panagou, E.Z.; Nychas, G.J.E. Effect of different marinating conditions on the evolution of spoilage microbiota and metabolomic profile of chicken breast fillets. Food Microbiol. 2017, 66, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balamatsia, C.C.; Patsias, A.; Kontominas, M.G.; Savvaidis, I.N. Possible role of volatile amines as quality-indicating metabolites in modified atmosphere-packaged chicken fillets: Correlation with microbiological and sensory attributes. Food Chem. 2007, 104, 1622–1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nychas, G.J.E.; Board, R.G. Entertoxin B production and physicochemical changes in extracts from different turkey muscles during the growth of Staphylococcus aureus S-6. Food Microbiol. 1991, 8, 105–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jian, C.; Luukkonen, P.; Yki-Järvinen, H.; Salonen, A.; Korpela, K. Quantitative PCR provides a simple and accessible method for quantitative microbiota profiling. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0227285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Johnson, J.S.; Spakowicz, D.J.; Hong, B.Y.; Petersen, L.M.; Demkowicz, P.; Chen, L.; Leopold, S.R.; Hanson, B.M.; Agresta, H.O.; Gerstein, M.; et al. Evaluation of 16S rRNA gene sequencing for species and strain-level microbiome analysis. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, N.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, Q.; Gu, Q.; Chen, M.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, X.; Zhang, J. High-throughput sequencing analysis of bacterial community composition and quality characteristics in refrigerated pork during storage. Food Microbiol. 2019, 83, 86–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, Q.; Li, D.; Liu, X.; Luo, Y. Changes in the microbial communities of air-packaged and vacuum-packaged common carp (Cyprinus carpio) stored at 4 °C. Food Microbiol. 2015, 52, 197–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.Y.; Xiao, X.; Wang, H.H.; Zhang, Q.Y.; Zou, Y.F. Characterization of the bacterial community of braised chicken, a specialty poultry product in China. Poult. Sci. 2019, 98, 1055–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soriano-Santos, J. Chemical composition and nutritional content of raw poultry meat. In Handbook of Poultry Science and Technology; Guerrero-Legarreta, I., Ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2010; Volume 1, pp. 467–491. [Google Scholar]
- Casaburi, A.; Piombino, P.; Nychas, G.J.; Villani, F.; Ercolini, D. Bacterial populations and the volatilome associated to meat spoilage. Food Microbiol. 2015, 45, 83–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caldera, L.; Franzetti, L.; Van Coillie, E.; De Vos, P.; Stragier, P.; De Block, J.; Heyndrickx, M. Identification, enzymatic spoilage characterization and proteolytic activity quantification of Pseudomonas spp. isolated from different foods. Food Microbiol. 2016, 54, 142–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales, P.A.; Aguirre, J.S.; Troncoso, M.R.; Figueroa, G.O. Phenotypic and genotypic characterization of Pseudomonas spp. present in spoiled poultry fillets sold in retail settings. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 73, 609–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnaut-Rollier, I.; De Zutter, L.; Van Hoof, J. Identities of the Pseudomonas spp. in flora from chilled chicken. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 1999, 48, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ercolini, D.; Russo, F.; Blaiotta, G.; Pepe, O.; Mauriello, G.; Villani, F. Simultaneous detection of Pseudomonas fragi, P. lundensis, and P. putida from meat by use of a multiplex PCR assay targeting the carA gene. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 2354–2359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stellato, G.; Utter, D.R.; Voorhis, A.; De Angelis, M.; Murat Eren, A.; Ercolini, D. A few Pseudomonas oligotypes dominate in the meat and dairy processing environment. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Geornaras, I.; Kunene, N.F.; Von Holy, A.; Hastings, J.W. Amplified fragment length polymorphism fingerprinting of Pseudomonas strains from a poultry processing plant. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1999, 65, 3828–3833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Doulgeraki, A.I.; Nychas, G. Monitoring the succession of the biota grown on a selective medium for pseudomonads during storage of minced beef with molecular-based methods. Food Microbiol. 2013, 34, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ercolini, D.; Russo, F.; Torrieri, E.; Masi, P.; Villani, F. Changes in the spoilage-related microbiota of beef during refrigerated storage under different packaging conditions. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 72, 4663–4671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nieminen, T.T.; Dalgaard, P.; Björkroth, J. Volatile organic compounds and Photobacterium phosphoreum associated with spoilage of modified-atmosphere-packaged raw pork. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2016, 218, 86–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Höll, L.; Hilgarth, M.; Geissler, A.J.; Behr, J.; Vogel, R.F. Prediction of in situ metabolism of photobacteria in modified atmosphere packaged poultry meat using metatranscriptomic data. Microbiol. Res. 2019, 222, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pennacchia, C.; Ercolini, D.; Villani, F. Spoilage-related microbiota associated with chilled beef stored in air or vacuum pack. Food Microbiol. 2011, 28, 84–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoops, J.; Ruyters, S.; Busschaert, P.; Spaepen, R.; Verreth, C.; Claes, J.; Lievens, B.; Van Campenhout, L. Bacterial community dynamics during cold storage of minced meat packaged under modified atmosphere and supplemented with different preservatives. Food Microbiol. 2015, 48, 192–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuertes-Perez, S.; Hauschild, P.; Hilgarth, M.; Vogel, R.F. Biodiversity of Photobacterium spp. isolated from meats. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilgarth, M.; Fuertes-Pèrez, S.; Ehrmann, M.; Vogel, R.F. An adapted isolation procedure reveals Photobacterium spp. as common spoilers on modified atmosphere packaged meats. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2018, 66, 262–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.; Che, Y.; Qi, Y.; Liang, P.; Song, C. High-throughput sequencing of viable microbial communities in raw pork subjected to a fast cooling process. J. Food Sci. 2017, 82, 145–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Labella, A.M.; Arahal, D.R.; Castro, D.; Lemos, M.L.; Borrego, J.J. Revisiting the genus Photobacterium: Taxonomy, ecology and pathogenesis. Int. Microbiol. 2017, 20, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalgaard, P.; Mejlholm, O.; Christiansen, T.J.; Huss, H.H. Importance of Photobacterium phosphoreum in relation to spoilage of modified atmosphere-packed fish products. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 1997, 24, 373–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalgaard, P.; Munoz, L.G.; Mejlholm, O. Specific inhibition of Photobacterium phosphoreum extends the shelf life of modified-atmosphere-packed cod fillets. J. Food Prot. 1998, 61, 1191–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuuliala, L.; Al Hage, Y.; Ioannidis, A.G.; Sader, M.; Kerckhof, F.M.; Vanderroost, M.; Boon, N.; De Baets, B.; De Meulenaer, B.; Ragaert, P.; et al. Microbiological, chemical and sensory spoilage analysis of raw Atlantic cod (Gadus morhua) stored under modified atmospheres. Food Microbiol. 2018, 70, 232–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hilgarth, M.; Fuertes, S.; Ehrmann, M.; Vogel, R.F. Photobacterium carnosum sp. nov., isolated from spoiled modified atmosphere packaged poultry meat. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 2018, 41, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betts, G. Other spoilage bacteria. In Food Spoilage Microorganisms; de W Blackburn, C., Ed.; Woodhead Publishing Limited: Cambridge, UK, 2006; pp. 668–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stellato, G.; La Storia, A.; De Filippis, F.; Borriello, G.; Villani, F.; Ercolini, D. Overlap of spoilage-associated microbiota between meat and the meat processing environment in small-scale and large-scale retail distributions. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 82, 4045–4054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gill, C.O.; Newton, K.G. The ecology of bacterial spoilage of fresh meat at chill temperatures. Meat Sci. 1978, 2, 207–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gennari, M.; Parini, M.; Volpon, D.; Serio, M. Isolation and characterization by conventional methods and genetic transformation of Psychrobacter and Acinetobacter from fresh and spoiled meat, milk and cheese. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 1992, 15, 61–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, L.M.; Merquior, V.L.C. The Prokaryotes: The family Moraxellaceae. In The Prokaryotes: Gammaproteobacteria; Rosenberg, E., DeLong, E.F., Lory, S., Stackebrandt, E., Thompson, F., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; pp. 254–263. [Google Scholar]
- Rossau, R.; Van Landschoot, A.; Gillis, M.; De Ley, J. Taxonomy of Moraxellaceae fam. nov., a new bacterial family to accommodate the genera Moraxella, Acinetobacter, and Psychrobacter and related organisms. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 1991, 41, 310–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hantsis-Zacharov, E.; Halpern, M. Culturable psychrotrophic bacterial communities in raw milk and their proteolytic and lipolytic traits. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 7162–7168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Teider, P.I.; Ribeiro, J.C.; Ossugui, E.H.; Tamanini, R.; Ribeiro, J.; Santos, G.A.; Alfieri, A.A.; Beloti, V. Pseudomonas spp. and other psychrotrophic microorganisms in inspected and non-inspected Brazilian Minas Frescal cheese: Proteolytic, lipolytic and AprX production potential. Pesqui. Vet. Bras. 2019, 39, 807–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Y.; Zhu, J.; Ye, X.; Yang, Y. Spoilage potential characterization of Shewanella and Pseudomonas isolated from spoiled large yellow croaker (Pseudosciaena crocea). Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2016, 64, 86–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, S.M.; Fletcher, D.L.; Cox, N.A. Spoilage bacteria of fresh broiler chicken carcasses. Poult. Sci. 1995, 74, 2041–2047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ercolini, D.; Ferrocino, I.; Nasi, A.; Ndagijimana, M.; Vernocchi, P.; La Storia, A.; Laghi, L.; Mauriello, G.; Guerzoni, M.E.; Villani, F. Monitoring of microbial metabolites and bacterial diversity in beef stored under different packaging londitions. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 77, 7372–7381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Doulgeraki, A.I.; Paramithiotis, S.; Kagkli, D.M.; Nychas, G.J.E. Lactic acid bacteria population dynamics during minced beef storage under aerobic or modified atmosphere packaging conditions. Food Microbiol. 2010, 27, 1028–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Papadopoulou, O.; Panagou, E.Z.; Tassou, C.C.; Nychas, G.J.E. Contribution of Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy data on the quantitative determination of minced pork meat spoilage. Food Res. Int. 2011, 44, 3264–3271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argyri, A.A.; Papadopoulou, O.S.; Sourri, P.; Chorianopoulos, N.; Tassou, C.C. Quality and safety of fresh chicken fillets after high pressure processing: Survival of indigenous Brochothrix thermosphacta and inoculated Listeria monocytogenes. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Papadopoulou, O.S.; Doulgeraki, A.I.; Botta, C.; Cocolin, L.; Nychas, G.J.E. Genotypic characterization of Brochothrix thermosphacta isolated during storage of minced pork under aerobic or modified atmosphere packaging conditions. Meat Sci. 2012, 92, 735–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holley, R.A. Brochothrix. In Encyclopedia of Food Microbiology, 2nd ed.; Batt, C.A., Tortorello, M.L., Eds.; Elsevier Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2014; pp. 331–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nychas, G.J.E.; Drosinos, E.H. Meat and Poultry: Spoilage of Meat. In Encyclopedia of Food Microbiology, 2nd ed.; Batt, C.A., Tortorello, M.L., Eds.; Elsevier Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2014; pp. 514–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramees, T.P.; Dhama, K.; Karthik, K.; Rathore, R.S.; Kumar, A.; Saminathan, M.; Tiwari, R.; Malik, Y.S.; Singh, R.K. Arcobacter: An emerging food-borne zoonotic pathogen, its public health concerns and advances in diagnosis and control—A comprehensive review. Vet. Q. 2017, 37, 136–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wesley, I.V. Helicobacter and Arcobacter: Potential human foodborne pathogens? Trends Food Sci. Technol. 1997, 8, 293–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahlen, S.D. Serratia infections: From military experiments to current practice. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2011, 24, 755–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hugo, C.J.; Bruun, B.; Jooste, P.J. The Genera Empedobacter and Myroides. In The Prokaryotes; Dworkin, M., Falkow, S., Rosenberg, E., Schleifer, K.H., Stackebrandt, E., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2006; pp. 630–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.Y.; Wang, H.H.; Han, Y.W.; Xing, T.; Ye, K.P.; Xu, X.L.; Zhou, G.H. Evaluation of the spoilage potential of bacteria isolated from chilled chicken in vitro and in situ. Food Microbiol. 2017, 63, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azwai, S.M.; Alfallani, E.A.; Abolghait, S.K.; Garbaj, A.M.; Naas, H.T.; Moawad, A.A.; Gammoudi, F.T.; Rayes, H.M.; Barbieri, I.; Eldaghayes, I.M. Isolation and molecular identification of Vibrio spp. by sequencing of 16s rDNA from seafood, meat and meat products in Libya. Open Vet. J. 2016, 6, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sawabe, T.; Hayashi, K.; Moriwaki, J.; Thompson, F.L.; Swings, J.; Potin, P.; Christen, R.; Ezura, Y. Vibrio gallicus sp. nov., isolated from the gut of the French abalone Haliotis tuberculata. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2004, 54, 843–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dourou, D.; Spyrelli, E.D.; Doulgeraki, A.I.; Argyri, A.A.; Grounta, A.; Nychas, G.-J.E.; Chorianopoulos, N.G.; Tassou, C.C. Microbiota of Chicken Breast and Thigh Fillets Stored under Different Refrigeration Temperatures Assessed by Next-Generation Sequencing. Foods 2021, 10, 765. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10040765
Dourou D, Spyrelli ED, Doulgeraki AI, Argyri AA, Grounta A, Nychas G-JE, Chorianopoulos NG, Tassou CC. Microbiota of Chicken Breast and Thigh Fillets Stored under Different Refrigeration Temperatures Assessed by Next-Generation Sequencing. Foods. 2021; 10(4):765. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10040765
Chicago/Turabian StyleDourou, Dimitra, Evgenia D. Spyrelli, Agapi I. Doulgeraki, Anthoula A. Argyri, Athena Grounta, George-John E. Nychas, Nikos G. Chorianopoulos, and Chrysoula C. Tassou. 2021. "Microbiota of Chicken Breast and Thigh Fillets Stored under Different Refrigeration Temperatures Assessed by Next-Generation Sequencing" Foods 10, no. 4: 765. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10040765
APA StyleDourou, D., Spyrelli, E. D., Doulgeraki, A. I., Argyri, A. A., Grounta, A., Nychas, G.-J. E., Chorianopoulos, N. G., & Tassou, C. C. (2021). Microbiota of Chicken Breast and Thigh Fillets Stored under Different Refrigeration Temperatures Assessed by Next-Generation Sequencing. Foods, 10(4), 765. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10040765







