Rice Bran Fermented with Kimchi-Derived Lactic Acid Bacteria Prevents Metabolic Complications in Mice on a High-Fat and -Cholesterol Diet
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Fermented Rice Bran
2.3. Animals and Experimental Design
2.4. Blood and Tissue Sample Processing
2.5. Serum, Hepatic, and Adipose Tissue Lipid Profiles
2.6. Serum Biochemical Parameters
2.7. Histological Examination of the Liver
2.8. Cell Size Measurement of Epididymal Fat Tissue
2.9. RNA Extraction and Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) Analysis
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
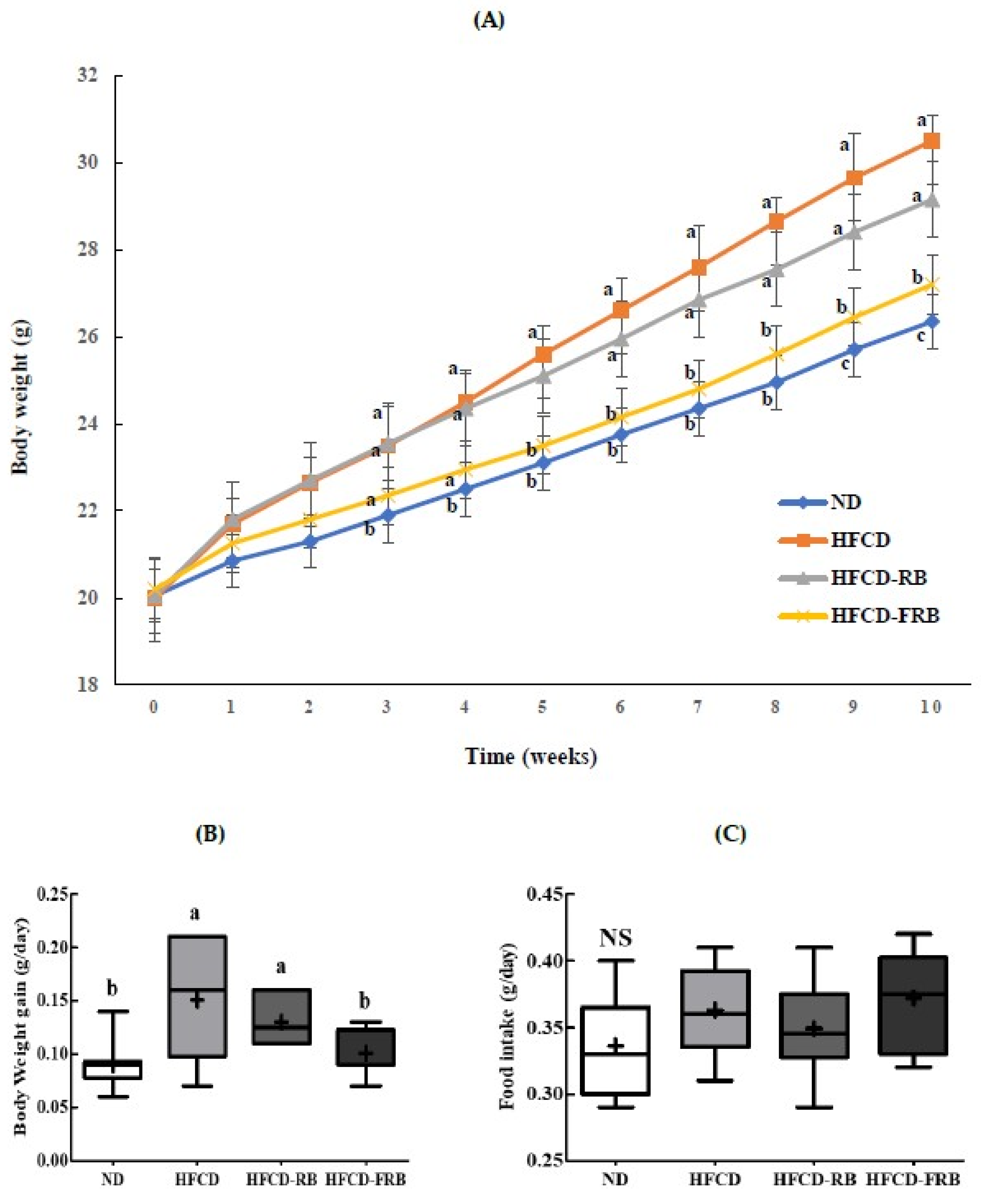
3.1. Rice Bran or Fermented Rice Bran Ameliorated HFCD-Induced Weight Gain
3.2. ALT, AST, ALP, and LDH Activities in Serum
3.3. Lipid Profiles in Serum
3.4. Leptin, Adiponectin, Glucose, and Insulin Contents in Serum
3.5. Hepatic Lipid Levels and Histopathological Changes
3.6. Expression of mRNA of Enzyme-Related to Fat Metabolism in Liver
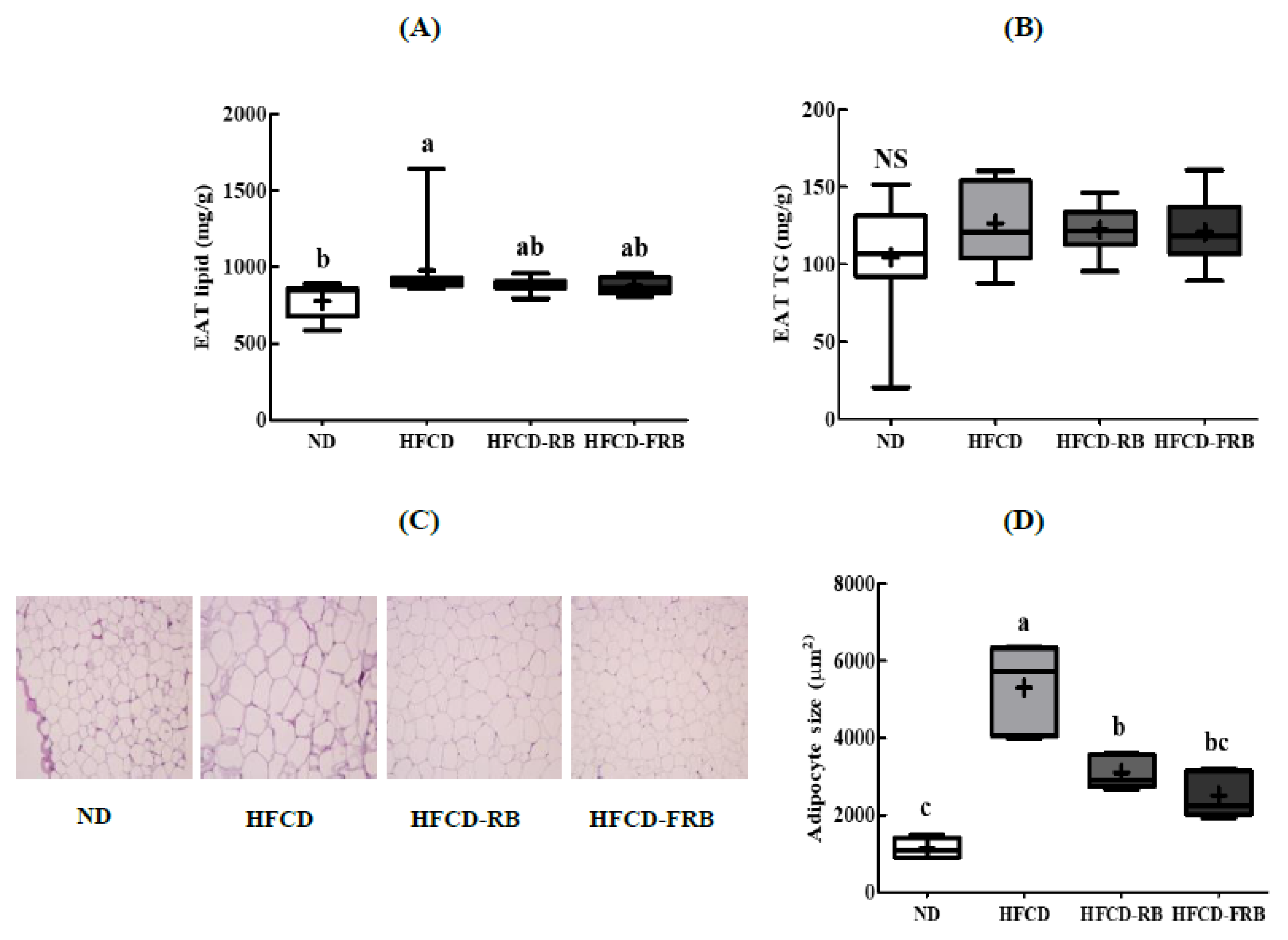
3.7. Epididymal Adipose Tissue Lipid Levels and Histopathological Changes
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gu, Y.R.; Kim, J.H.; Cho, J.-H.; Seo, W.-D.; Hong, J.-H.; Youn, K.-S. Physicochemical characteristics and antioxidant activities of rice bran extracts according to extraction solvent and cultivar. Korean J. Food Preserv. 2018, 25, 668–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, S.B.; Jeon, J.A.; Jeong, B.G. Anti-oxidative activities and tyrosinase inhibition ability of rice bran ethanol extract. J. Kor. Soc. Cosm. 2010, 16, 602–606. [Google Scholar]
- Spaggiari, M.; Dall’Asta, C.; Galaverna, G.; Bilbao, M.D.D.C. Rice Bran By-Product: From Valorization Strategies to Nutritional Perspectives. Foods 2021, 10, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhat, F.M.; Riar, C.S. Extraction, identification and assessment of antioxidative compounds of bran extracts of traditional rice cultivars: An analytical approach. Food Chem. 2017, 237, 264–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, E.H.; Ha, T.Y.; Hwang, I.K. Anti-hyperglycemic and antioxidative activities of phenolic acid concentrates of rice bran and hydroxycinnamic acids in cell assays. Korean J. Food Nutr. 2010, 23, 233–239. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, R.; Ma, Q.; Tong, X.; Liu, L.; Dong, L.; Huang, F.; Deng, Y.; Jia, X.; Chi, J.; Zhang, M. Rice bran phenolic extract supplementation ameliorates impaired lipid metabolism in high-fat-diet fed mice through AMPK activation in liver. J. Funct. Foods 2020, 73, 104131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Zhang, R.; Wu, Y.; Wu, C.; Jia, X.; Dong, L.; Liu, L.; Chen, Y.; Bai, Y.; Zhang, M. Rice Bran Phenolic Extract Protects against Alcoholic Liver Injury in Mice by Alleviating Intestinal Microbiota Dysbiosis, Barrier Dysfunction, and Liver Inflammation Mediated by the Endotoxin–TLR4–NF-κB Pathway. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 68, 1237–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fabian, C.; Ju, Y.-H. A Review on Rice Bran Protein: Its Properties and Extraction Methods. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2011, 51, 816–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, J.H.; Lee, S.S. Effect of rice bran dietary fiber level on serum lipid concentration, bowel function, and mineral absorption in rats. Korean J. Food Nutr. 2011, 24, 622–629. [Google Scholar]
- Rodrigues Silva, C.; Dutra de Oliveira, J.E.; de Souza, R.A.; Silva, H.C. Effect of rice bran fiber diet on serum glucose levels of diabetic patients in Brazil. Arch. Latinoam. Nutr. 2005, 55, 23–27. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Qureshi, A.A.; Sami, S.A.; Khan, F.A. Effects of stabilized rice bran, its soluble and fiber fractions on blood glucose levels and serum lipid parameters in humans with diabetes mellitus types Ⅰ and Ⅱ. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2002, 13, 175–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolsi, R.J.; Rogers, E.J.; Ausman, L.M.; Orthefer, F.T. Rice bran oil and its health benefits. In Rice Science and Technology; Marshal, W.E., Wadsworth, J.I., Eds.; Marcel Dekker: New York, NY, USA, 1993; pp. 421–437. [Google Scholar]
- Park, J.S.; Kim, M.H. Anti-inflammatory effects of rice bran ethanol extract in murine macrophage RAW 264.7 cells. J. Pharm. Soc. Korea 2011, 55, 456–461. [Google Scholar]
- Cicero, A.F.; Gaddi, A. Rice bran oil and gamma-oryzanol in the treatment of hyperlipoproteinaemias and other conditions. Phytother. Res. 2001, 15, 277–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Son, M.J.; Rico, C.W.; Nam, S.H.; Kang, M.Y. Influence of Oryzanol and Ferulic Acid on the Lipid Metabolism and Antioxidative Status in High Fat-Fed Mice. J. Clin. Biochem. Nutr. 2010, 46, 150–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Woo, K.M.; Lee, Y.S.; Kim, Y.H. Antioxidant effects of tocotrienol in rice bran. Korean J. Crop Sci. 2005, 50, 4–7. [Google Scholar]
- Park, T.S.; Lee, S.Y.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, K.T.; Kim, Y.J.; Jeong, I.; Do, W.N.; Lee, H.J. Extracts of adlay, barley and rice bran have antioxidant activity and modulate fatty acid metabolism in adipocytes. Korean J. Food Nutr. 2009, 22, 456–462. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.-Y.; Shin, M.; Heo, Y.-R. Effects of Stabilized Rice Bran on Obesity and Antioxidative Enzyme Activity in High Fat Diet-induced Obese C57BL/6 Mice. J. Korean Soc. Food Sci. Nutr. 2014, 43, 1148–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Teng, J.; Lyu, Y.; Hu, X.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, M. Enhanced Antioxidant Activity for Apple Juice Fermented with Lactobacillus plantarum ATCC14917. Molecules 2018, 24, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Borges, G.; Lean, M.E.J.; Roberts, S.A.; Crozier, A. Bioavailability of dietary (poly)phenols: A study with ileostomists to discriminate between absorption in small and large intestine. Food Funct. 2013, 4, 754–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nisa, K.; Rosyida, V.T.; Nurhayati, S.; Indrianingsih, A.W.; Darsih, C.; Apriyana, W. Total phenolic contents and antioxidant activity of rice bran fermented with lactic acid bacteria. IOP Conf. Series: Earth Environ. Sci. 2019, 251, 012020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashid, N.Y.A.; Razak, D.L.A.; Jamaluddin, A.; Sharifuddin, S.A.; Long, K. Bioactive compounds and antioxidant activity of rice bran fermented with lactic acid bacteria. Malays. J. Microbiol. 2015, 11, 156–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, H.; Curiel, J.A.; Landete, J.M.; de las Rivas, B.; López de Felipe, F.; Gomez-Cordoves, C.; Mancheno, J.M.; Munoz, R. Food phenolics and lactic acid bacteria. Int. J. Food Microbio. 2009, 132, 79–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Valero-Cases, E.; Nuncio-Jáuregui, N.; Frutos, M.J. Influence of Fermentation with Different Lactic Acid Bacteria and in Vitro Digestion on the Biotransformation of Phenolic Compounds in Fermented Pomegranate Juices. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 6488–6496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leroy, F.; De Vuyst, L. Lactic acid bacteria as functional starter cultures for the food fermentation industry. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2004, 15, 67–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhee, S.J.; Lee, J.-E.; Lee, C.-H. Importance of lactic acid bacteria in Asian fermented foods. Microb. Cell Factories 2011, 10, S5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, J.S.; Lee, K.C.; Ahn, J.S.; Mheen, T.I.; Pyun, Y.R.; Park, Y.H. Weissella koreensis sp. Nov., isolated from kimchi. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Micr. 2002, 52, 1257–1261. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, J.J.; Park, H.J.; Kim, S.G.; Oh, S.H. Isolation, identification, and characterization of Weissella strains with high ornithine producing capacity from kimchi. Kor. J. Microbiol. 2009, 45, 339–345. [Google Scholar]
- Mun, S.Y.; Moon, S.H.; Choon, C.H. Characterization of High-Ornithine-Producing Weissella koreensis DB1 Isolated from Kimchi and Its Application in Rice Bran Fermentation as a Starter Culture. Foods 2020, 9, 1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, S.H.; Mun, S.Y.; Chang, H. Characterization of Fermented Rice-Bran Using the Lactic Acid Bacteria Weissella koreensis DB1 Derived from Kimchi. Korean J. Community Living Sci. 2019, 30, 543–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evain-Brion, D.; Donnadieu, M.M.; Roger, M.; Job, J. Simultaneous study of somatotrophic and corticotrophic pituitary secretions during ornithine infusion test. Clinical. Endocrinol. 1982, 17, 119–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeevanandam, M.; Holaday, N.J.; Petersen, S.R. Ornithine-α-Ketoglutarate (OKG) Supplementation Is More Effective than Its Component Salts in Traumatized Rats. J. Nutr. 1996, 126, 2141–2150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chae, G.Y.; Kwon, R.H.; Jang, M.W.; Kim, M.J.; Ha, B.J. Whitening and antioxidative effect of rice bran fermented by Bacillus subtilis. J. Soc. Cosmet. Sci. Korea 2001, 37, 153–159. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, K.M.; Yu, K.W.; Kang, D.H.; Koh, J.H.; Hong, B.S.; Suh, H.J. Anti-stress and Anti-fatigue Effects of Fermented Rice Bran. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2001, 65, 2294–2296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shibayama, J.; Goto, M.; Kuda, T.; Fukunaga, M.; Takahashi, H.; Kimura, B. Effect of rice bran fermented with Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Lactobacillus plantarum on gut microbiome of mice fed high-sucrose diet. Benef. Microbes 2019, 10, 811–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nealon, N.; Parker, K.; Lahaie, P.; Ibrahim, H.; Maurya, A.; Raina, K.; Ryan, E. Bifidobacterium longum-fermented rice bran and rice bran supplementation affects the gut microbiome and metabolome. Benef. Microbes 2019, 10, 823–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.H.; Rhee, K.H.; Cho, C.H. The chemoprotective effect of fermented rice bran on doxorubicin induced toxicity in the rat. Natural Product. Sci. 2014, 20, 29–32. [Google Scholar]
- Alauddin, M.; Shirakawa, H.; Koseki, T.; Kijima, N.; Ardiansyah; Budijanto, S.; Islam, J.; Goto, T.; Komai, M. Fermented rice bran supplementation mitigates metabolic syndrome in stroke-prone spontaneously hypertensive rats. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2016, 16, 442–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rusbana, T.B.; Agista, A.Z.; Shirakawa, H.; Saputra, W.D.; Ohsaki, Y.; Watanabe, K.; Ardiansyah, A.; Budijanto, S.; Koseki, T.; Aso, H.; et al. Supplementation with Fermented Rice Bran Attenuates Muscle Atrophy in a Diabetic Rat Model. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saba, E.; Lee, C.H.; Jeong, D.H.; Lee, K.; Kim, T.-H.; Roh, S.-S.; Kim, S.-H.; Rhee, M.H. Fermented rice bran prevents atopic dermatitis in DNCB-treated NC/Nga mice. J. Biomed. Res. 2016, 30, 334–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Islam, J.; Koseki, T.; Watanabe, K.; Ardiansyah; Budijanto, S.; Oikawa, A.; Alauddin, M.; Goto, T.; Aso, H.; Komai, M.; et al. Dietary supplementation of fermented rice bran effectively alleviates dextran sodium sulfate-induced colitis in mice. Nutrients 2017, 9, 747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Ali, Z.; Khan, S.I.; Khan, I.A. Cytotoxic monacolins from red yeast rice, a Chinese medicine and food. Food Chem. 2016, 202, 262–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.; Karl, M.; Santini, A. Red Yeast Rice. Foods 2017, 6, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stancu, C.; Sima, A. Statins: Mechanism of action and effects. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2001, 5, 378–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mannino, G.; Iovino, P.; Lauria, A.; Genova, T.; Asteggiano, A.; Notarbartolo, M.; Porcu, A.; Serio, G.; Chinigò, G.; Occhipinti, A.; et al. Bioactive Triterpenes of Protium heptaphyllum Gum Resin Extract Display Cholesterol-Lowering Potential. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folch, J.; Lees, M.; Sloane-Stanley, G.H. A simple method for the isolation and purification of total lipides from animal tissues. J. Biol. Chem. 1957, 226, 497–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biggs, H.G.; Erikson, J.M.; Moorehead, W.R. A Manual Colorimetric Assay of Triglycerides in Serum. Clin. Chem. 1975, 21, 437–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zlatkis, A.; Zak, B. Study of a new cholesterol reagent. Anal. Biochem. 1969, 29, 143–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.H.; Moon, T.W. Composition, water-holding capacity and effect on starch retrogradation of rice bran dietary fiber. Korean J. Food Sci. Technol. 1994, 26, 288–294. [Google Scholar]
- Webber, D.M.; Hettiarachchy, N.S.; Li, R.; Horax, R.; Theivendran, S. Phenolic Profile and Antioxidant Activity of Extracts Prepared from Fermented Heat-Stabilized Defatted Rice Bran. J. Food Sci. 2014, 79, H2383–H2391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ju, Z.; Howard, L.R. Subcritical Water and Sulfured Water Extraction of Anthocyanins and Other Phenolics from Dried Red Grape Skin. J. Food Sci. 2006, 70, S270–S276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubert, J.; Berger, M.; Nepveu, F.; Paul, F.; Daydé, J. Effects of fermentation on the phytochemical composition and antioxidant properties of soy germ. Food Chem. 2008, 109, 709–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, B.; Qi, F.; Wu, J.; Yin, G.; Hua, J.; Zhang, Q.; Qin, L. Red Yeast Rice: A Systematic Review of the Traditional Uses, Chemistry, Pharmacology, and Quality Control of an Important Chinese Folk Medicine. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kondo, T.; Kishi, M.; Fushimi, T.; Kaga, T. Acetic Acid Upregulates the Expression of Genes for Fatty Acid Oxidation Enzymes in Liver To Suppress Body Fat Accumulation. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 5982–5986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.M.; Rico, C.W.; Lee, S.C.; Kang, M.Y. Modulatory Effect of Rice Bran and Phytic Acid on Glucose Metabolism in High Fat-Fed C57BL/6N Mice. J. Clin. Biochem. Nutr. 2010, 47, 12–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Munkong, N.; Hansakul, P.; Yoysungnoen, B.; Wongnoppavich, A.; Sireeratawong, S.; Kaendee, N.; Lerdvuthisopon, N. Vasoprotective effects of rice bran water extract on rats fed with high-fat diet. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Biomed. 2016, 6, 778–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Anderson, J.W.; Jones, A.E.; Riddell-Mason, S. Ten Different Dietary Fibers Have Significantly Different Effects on Serum and Liver Lipids of Cholesterol-Fed Rats. J. Nutr. 1994, 124, 78–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ham, H.; Sung, J.; Lee, J. Effect of Rice Bran Unsaponifiables on High-Fat Diet-Induced Obesity in Mice. J. Food Biochem. 2015, 39, 673–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, Y.; Luo, F.; Wang, L.; Yang, T.; Shi, L.; Li, X.; Shen, J.; Xu, W.; Guo, T.; Lin, Q. Anti-hyperlipidemic effect of rice bran polysaccharide and its potential mechanism in high-fat diet mice. Food Funct. 2017, 8, 4028–4041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borkan, G.A.; Hults, B.D.E.; Gerzof, S.G.; Robbins, A.H.; Silbert, C.K. Age Changes in Body Composition Revealed by Computed Tomography. J. Gerontol. 1983, 38, 673–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carr, D.B.; Utzschneider, K.M.; Hull, R.L.; Kodama, K.; Retzlaff, B.M.; Brunzell, J.D.; Shofer, J.B.; Fish, B.E.; Knopp, R.H.; Kahn, S.E. Intra-abdominal fat is a major determinant of the National Cholesterol Education Program Adult Treatment Panel Ⅲ criteria for the metabolic syndrome. Diabetes 2004, 53, 2087–2094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Finelli, C.; Sommella, L.; Gioia, S.; La Sala, N.; Tarantino, G. Should visceral fat be reduced to increase longevity? Ageing Res. Rev. 2013, 12, 996–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parvez, S.; Malik, K.; Kang, S.A.; Kim, H.-Y. Probiotics and their fermented food products are beneficial for health. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2006, 100, 1171–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, Y.; Soh, J.; Yu, J.; Sohn, H.; Cha, Y.; Oh, S. Intracellular lipid accumulation inhibitory effect of Weissella koreensis OK1-6 isolated from Kimchi on differentiating adipocyte. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2012, 113, 652–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, P.-L.; Du, S.-D.; Mao, Y.-L. Advances in preoperative assessment of liver function. Hepatobiliary Pancreat. Dis. Int. 2014, 13, 361–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomkin, G.H. Atherosclerosis, diabetes and lipoproteins. Expert Rev. Cardiovasc. Ther. 2010, 8, 1015–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golan, M.; Fainaru, M.; Weizman, A. Role of behaviour modification in the treatment of childhood obesity with the parents as the exclusive agents of change. Int. J. Obes. 1998, 22, 1217–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grundy, S.; Denke, M. Dietary influences on serum lipids and lipoproteins. J. Lipid Res. 1990, 31, 1149–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellani, W.J. Metabolic and nutritional aspects of the atherogenic atypical lipoproteins: Lipoprotein(a), remnant lipoproteins, and oxidized low-density lipoprotein. Nutr. Res. 2004, 24, 681–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Justo, M.L.; Rodriguez–Rodriguez, R.; Claro, C.M.; De Sotomayor, M.Á.; Parrado, J.; Herrera, M.D. Water-soluble rice bran enzymatic extract attenuates dyslipidemia, hypertension and insulin resistance in obese Zucker rats. Eur. J. Nutr. 2012, 52, 789–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.-X.; Li, Y.; Sun, A.-M.; Wang, F.-J.; Yu, G.-P. Hypolipidemic and Antioxidative Effects of Aqueous Enzymatic Extract from Rice Bran in Rats Fed a High-Fat and -Cholesterol Diet. Nutr. 2014, 6, 3696–3710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yugarani, T.; Tan, B.K.H.; Teh, M.; Das, N.P. Effects of polyphenolic natural products on the lipid profiles of rats fed high fat diets. Lipids 1992, 27, 181–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reed, J. Cranberry Flavonoids, Atherosclerosis and Cardiovascular Health. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2002, 42, 301–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ardiansyah; Ohsaki, Y.; Shirakawa, H.; Shirakawa, H.; Koseki, T.; Komai, M. Novel effects of a single administration of ferulic acid on the regpressure and the hepatic lipid metabolic profile in stroke-prone spontaneously hypertensive rats. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 2825–2830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jayasooriya, A.P.; Sakono, M.; Yukizaki, C.; Kawano, M.; Yamamoto, K.; Fukuda, N. Effects of Momordica charantia powder on serum glucose levels and various lipid parameters in rats fed with cholesterol-free and cholesterol-enriched diets. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2000, 72, 331–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wursch, P. Influence of Tannin-Rich Carob Pod Fiber on the Cholesterol Metabolism in the Rat. J. Nutr. 1979, 109, 685–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rhee, S.J.; Park, H.K. Changes of lipid concentration and histochemical observation in liver of rats fed high fat diet. Kor. J. Nutr. 1984, 17, 113–125. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Noh, S.K.; Koo, S.I. Green tea catechins inhibit pancreatic phospholipase A2 and intestinal absorption of lipids in ovariectomized rats. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2006, 17, 492–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Payne, V.A.; Au, W.-S.; Lowe, C.E.; Rahman, S.M.; Friedman, J.E.; O’Rahilly, S.; Rochford, J.J. C/EBP transcription factors regulate SREBP1c gene expression during adipogenesis. Biochem. J. 2009, 425, 215–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Clarke, S.D. Regulation of fatty acid synthase gene expression: An approach for reducing fat accumulation. J. Anim. Sci. 1993, 71, 1957–1965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gervois, P.; Torra, I.P.; Fruchart, J.-C.; Staels, B. Regulation of Lipid and Lipoprotein Metabolism by PPAR Activators. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2000, 38, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.A.; Tirupathi Pichiah, P.B.; Yu, J.J.; Oh, S.H.; Daily, J.W., 3rd; Cha, Y.S. Anti-obesity effect of kimchi fermented with Weissella koreensis OK1-6 as starter in high-fat diet-induced obese C57BL/6J mice. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2012, 113, 1507–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamashita, H.; Fujisawa, K.; Ito, E.; Idei, S.; Kawaguchi, N.; Kimoto, M.; Hiemori, M.; Tsuji, H. Improvement of Obesity and Glucose Tolerance by Acetate in Type 2 Diabetic Otsuka Long-Evans Tokushima Fatty (OLETF) Rats. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2007, 71, 1236–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trayhurn, P.; Wood, I.S. Adipokines: Inflammation and the pleiotropic role of white adipose tissue. Br. J. Nutr. 2004, 92, 347–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tilg, H.; Moschen, A.R. Adipocytokines: Mediators linking adipose tissue, inflammation and immunity. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2006, 6, 772–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.H.; Chun, H.K.; Chang, S.O.; Lee, Y.S. Effect of γ-oryzanol on blood glucose in diabetic KK mice. Korean Soc. Food Sci. Nutr. 2004, 33, 827–831. [Google Scholar]
- Ivorra, M.D.; D’Ocon, M.P.; Paya, M.; Villar, A. Antihyperglycemic and insulin-releasing effects of beta-sitosterol 3-beta-D-glucoside and its aglycone, beta-sitosterol. Arch. Int. de Pharmacodyn. et de Ther. 1988, 296, 224–231. [Google Scholar]
- Jung, T.-D.; Shin, G.-H.; Kim, J.-M.; Choi, S.-I.; Lee, J.-H.; Lee, S.J.; Park, S.J.; Woo, K.S.; Oh, S.K.; Lee, O.-H. Comparative Analysis of γ-Oryzanol, β-Glucan, Total Phenolic Content and Antioxidant Activity in Fermented Rice Bran of Different Varieties. Nutrients 2017, 9, 571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zajac, A.; Poprzęcki, S.; Żebrowska, A.; Chalimoniuk, M.; Langfort, J. Arginine and Ornithine Supplementation Increases Growth Hormone and Insulin-Like Growth Factor-1 Serum Levels After Heavy-Resistance Exercise in Strength-Trained Athletes. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2010, 24, 1082–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kudo, M.; Yoshitomi, H.; Momoo, M.; Suguro, S.; Yamagishi, Y.; Gao, M. Evaluation of the Effects and Mechanism of L-Citrulline on Anti-obesity by Appetite Suppression in Obese/Diabetic KK-Ay Mice and High-Fat Diet Fed SD Rats. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2017, 40, 524–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






| (g/kg) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Groups | ND (1) | HFCD (2) | HFCD + RB (3) | HFCD + FRB (4) | |
| Ingredients | |||||
| Casein | 200.000 | 200.000 | 193.000 | 188.600 | |
| L-cystine | 3.000 | 3.000 | 3.000 | 3.000 | |
| Corn starch | 397.486 | 254.966 | 228.266 | 232.966 | |
| Maltodextrose | 132.000 | 132.000 | 132.000 | 132.000 | |
| Sucrose | 100.000 | 100.000 | 100.000 | 100.000 | |
| Cellulose | 50.000 | 50.000 | 43.800 | 42.800 | |
| Lard | 130.000 | 130.000 | 130.000 | ||
| Soybean oil | 70.000 | 70.000 | 59.900 | 60.600 | |
| Cholesterol | 12.500 | 12.500 | 12.500 | ||
| Mineral mix (5) | 35.000 | 35.000 | 35.000 | 35.000 | |
| Vitamin mix (6) | 10.000 | 10.000 | 10.000 | 10.000 | |
| Choline chloride | 2.500 | 2.500 | 2.500 | 2.500 | |
| tert-Butylhydroquinone | 0.014 | 0.034 | 0.034 | 0.034 | |
| Rice bran | 50.000 | ||||
| Fermented rice bran | 50.000 | ||||
| Total | 1000.0 | 1000.0 | 1000.0 | 1000.0 | |
| Total energy (kcal) | 3960.0 | 4636.4 | 4657.7 | 4667.1 | |
| Fat (kcal %) | 15.9 | 41.2 | 41.1 | 41.0 | |
| Transcript | Forward Primer | Reverse Primer |
|---|---|---|
| C/EBPα | GTGTGCACGTCTATGCTAAACCA | GCCGTTAGTGAAG AGTCTCAGGTTT |
| SREBP-1c | GATCAAAGAGGAGCCAGTGC | TAGATGGTGGCTGCTGAGTG |
| ACC | CAACGCCTTCACACCACCTT | AGCCCATTACTTCATCAAAGATCCT |
| FAS | GGAACTGAACGGCATTACTCG | CATGCCGTTATCAACTTGTCC |
| β-actin | GTGGGGCGCCCCAGGCACCAGGGC | CTCCTTAATGTCACGCACGATTTC |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Park, S.; Chang, H.-C.; Lee, J.-J. Rice Bran Fermented with Kimchi-Derived Lactic Acid Bacteria Prevents Metabolic Complications in Mice on a High-Fat and -Cholesterol Diet. Foods 2021, 10, 1501. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10071501
Park S, Chang H-C, Lee J-J. Rice Bran Fermented with Kimchi-Derived Lactic Acid Bacteria Prevents Metabolic Complications in Mice on a High-Fat and -Cholesterol Diet. Foods. 2021; 10(7):1501. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10071501
Chicago/Turabian StylePark, Sihoon, Hae-Choon Chang, and Jae-Joon Lee. 2021. "Rice Bran Fermented with Kimchi-Derived Lactic Acid Bacteria Prevents Metabolic Complications in Mice on a High-Fat and -Cholesterol Diet" Foods 10, no. 7: 1501. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10071501
APA StylePark, S., Chang, H.-C., & Lee, J.-J. (2021). Rice Bran Fermented with Kimchi-Derived Lactic Acid Bacteria Prevents Metabolic Complications in Mice on a High-Fat and -Cholesterol Diet. Foods, 10(7), 1501. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10071501








