A Systematic and a Scoping Review on the Psychometrics and Clinical Utility of the Volume-Viscosity Swallow Test (V-VST) in the Clinical Screening and Assessment of Oropharyngeal Dysphagia
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Protocol for the SR and ScR
2.2. Systematic Review (SR)
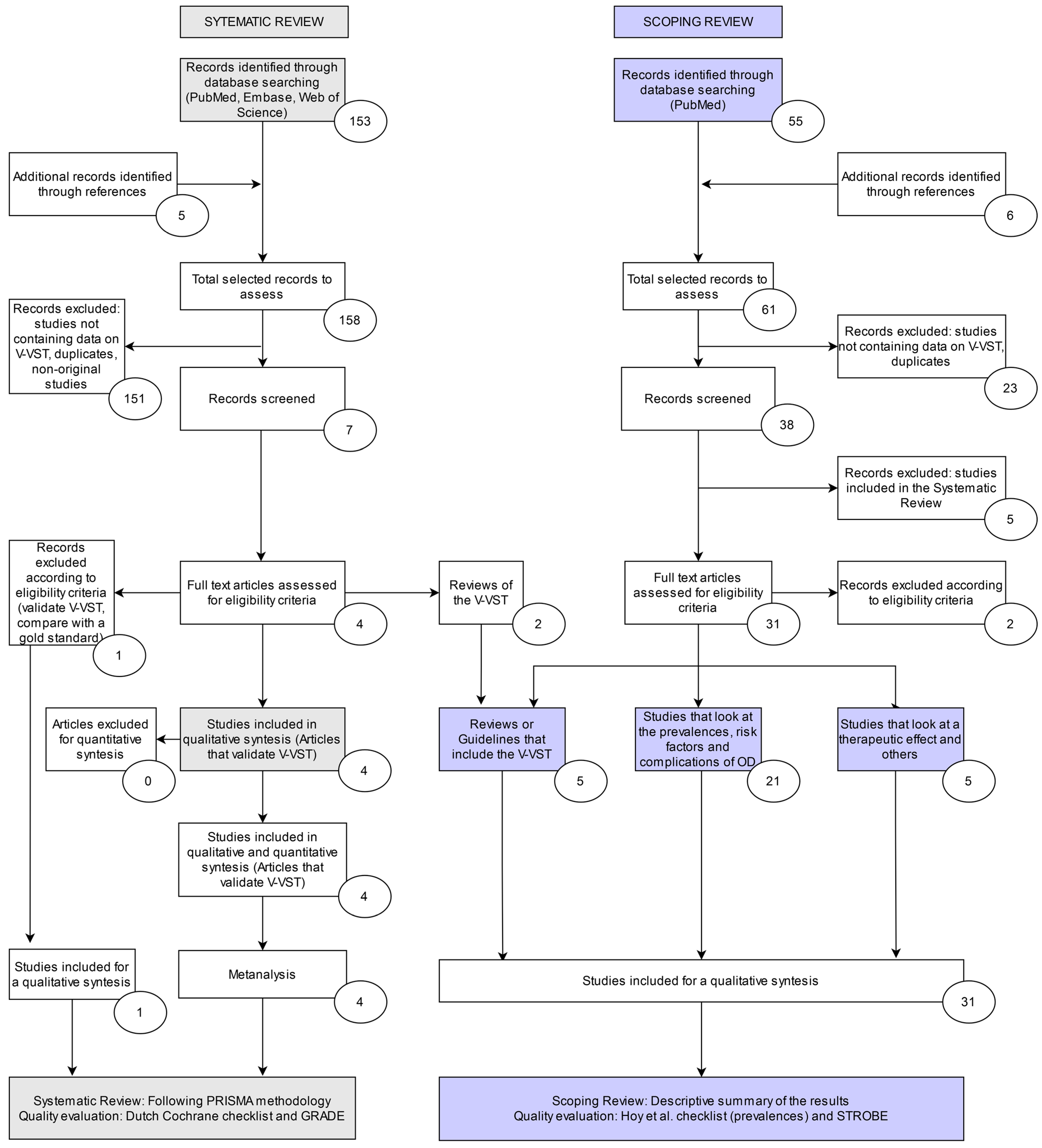
2.2.1. Search Strategy
2.2.2. Selection Process
2.2.3. Data Presentation, Summary Measures, and Data Analysis
2.2.4. Quality Evaluation and Strength of the Evidence
2.3. Scoping Review (ScR)
2.3.1. Search Strategy
2.3.2. Eligibility Criteria
2.3.3. Selection Process
2.3.4. Data Presentation, Summary Measures, and Data Analysis
2.3.5. Quality of Reporting and Strength of the Evidence
3. Results
3.1. Systematic Review (SR)
3.1.1. Studies Included
3.1.2. VST Psychometrics: Se and SP, Likelihood Ratio, and Odds Ratio
3.1.3. Reliability of the V-VST
3.1.4. The V-VST as a Tool for Therapeutic Recommendations on Bolus Modification
3.1.5. Quality of Studies in the SR
3.2. Scoping Review (ScR)
3.2.1. Studies Included
3.2.2. STROBE Report on the Studies in the ScR
3.2.3. Methods to Perform the V-VST in the Studies Included in the SR and the ScR
4. Discussion
4.1. Systematic Review (SR)
4.2. Scoping Review (ScR)
The V-VST
4.3. Study Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems. Available online: http://apps.who.int/classifications/apps/icd/%0Aicd10online/?gr10.htm±r13 (accessed on 2 August 2019).
- Clavé, P.; Shaker, R. Dysphagia: Current reality and scope of the problem. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2015, 12, 259–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rofes, L.; Arreola, V.; Clave, P. The Volume-Viscosity Swallow Test for Clinical Screening of Dysphagia and Aspiration. Issues Complement. Feed. 2012, 72, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carrión, S.; Roca, M.; Costa, A.; Arreola, V.; Ortega, O.; Palomera, E.; Serra-Prat, M.; Cabré, M.; Clavé, P. Nutritional status of older patients with oropharyngeal dysphagia in a chronic versus an acute clinical situation. Clin. Nutr. 2017, 36, 1110–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrión, S.; Cabré, M.; Monteis, R.; Roca, M.; Palomera, E.; Serra-Prat, M.; Rofes, L.; Clavé, P. Oropharyngeal dysphagia is a prevalent risk factor for malnutrition in a cohort of older patients admitted with an acute disease to a general hospital. Clin. Nutr. 2015, 34, 436–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rofes, L.; Arreola, V.; Mukherjee, R.; Clavé, P. Sensitivity and specificity of the Eating Assessment Tool and the Volume-Viscosity Swallow Test for clinical evaluation of oropharyngeal dysphagia. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2014, 26, 1256–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clavé, P.; Arreola, V.; Romea, M.; Medina, L.; Palomera, E.; Serra-Prat, M. Accuracy of the volume-viscosity swallow test for clinical screening of oropharyngeal dysphagia and aspiration. Clin. Nutr. 2008, 27, 806–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paris, G.; Martinaud, O.; Hannequin, D.; Petit, A.; Cuvelier, A.; Guedon, E.; Ropenneck, P.; Verin, E. Clinical screening of oropharyngeal dysphagia in patients with ALS. Ann. Phys. Rehab. Med. 2012, 55, 601–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillén-Solà, A.; Marco, E.; Martínez-Orfila, J.; Mejías, M.F.D.; Passalacqua, M.D.; Duarte, E.; Escalada, F. Usefulness of the volume-viscosity swallow test for screening dysphagia in subacute stroke patients in rehabilitation income. Neurorehabilitation 2013, 33, 631–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biomedical Research Center in Network of Liver and Digestive Diseases [CIBERehd] SC de D [SCD] and H de M [HM]. Basic Procedures to Assess and Treat Oropharyngeal Dysphagia in Patients with Covid-19 Infection. Expert Opinion Practical Guidance from Hospital De Mataró, Catalonia, Spain. 2020. Available online: https://www.rcslt.org/-/media/docs/Covid/RCSLT-PPE-guidance (accessed on 27 March 2020).
- Espinosa-Val, M.C.; Martín-Martínez, A.; Graupera, M.; Arias, O.; Elvira, A.; Cabré, M.; Palomera, E.; Bolívar-Prados, M.; Clavé, P.; Ortega, O. Prevalence, Risk Factors, and Complications of Oropharyngeal Dysphagia in Older Patients with Dementia. Nutrients 2020, 12, 863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cooper, S.; Cant, R.; Kelly, M.; Levett-Jones, T.; McKenna, L.; Seaton, P.; Ng, L.; Borgossian, F. Online Supplemental Material. Table 3. The Scoping Review Checklist. Clin. Nurs. Res. 2019, 4–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riera, S.; Marin, S.; Serra, M.; Clave, P. A Systematic Review to Assess the Psychometrics of the Volume Viscosity Swallow Test (V-VST) on the Clinical Diagnosis of Oropharyngeal Dysphagia. Available online: https://www.crd.york.ac.uk/prospero/display_record.php?RecordID=136252 (accessed on 15 July 2020).
- Campbell, J.; Kulgar, M.; Ding, S.; Carmody, D.; Hakonsen, S.; Jadotte, Y.; Ws, C. Diagnostic Test Accuracy Systematic Reviews. JBI Manual for Evidence Synthesis. 2020. Available online: https://synthesismanual.jbi.global (accessed on 20 February 2020).
- Liberati, A.; Altman, D.G.; Tetzlaff, J.; Mulrow, C.D.; Gøtzsche, P.C.; Ioannidis, J.P.A.; Clarke, M.; Devereaux, P.; Kleijnen, J.; Moher, D. The PRISMA Statement for Reporting Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses of Studies That Evaluate Health Care Interventions: Explanation and Elaboration. PLoS Med. 2009, 6, e1000100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deeks, J.J. Meta-Analysis, Decision Analysis, and Cost-Effectiveness Analysis. Methods for Quantitative Synthesis in Medicine; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- CEBM. The Centre for Evidence-Based Medicine Develops, Promotes and Disseminates Better Evidence for Healthcare. Available online: https://www.cebm.net/2014/02/likelihood-ratios/ (accessed on 17 November 2020).
- Caraguel, C.G.B.; Vanderstichel, R. The two-step Fagan’s nomogram: Ad hoc interpretation of a diagnostic test result without calculation. Evid. Based Med. 2013, 18, 125–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cochrane Collaboration. Cochrane Handbook for Diagnostics Test Accuracy. 2011. Available online: http://srdta.cochrane.org/handbook-dta-reviews (accessed on 17 November 2020).
- Whiting, P.F.; Rutjes, A.W.; Westwood, M.E.; Mallett, S.; Deeks, J.J.; Reitsma, J.B.; Leeflang, M.M.; Sterne, J.A.; Bossuyt, P.M. The QUADAS-2 Group: QUADAS-2: A revised tool for the quality assessment of diagnostic accuracy studies. Ann. Intern. Med. 2011, 155, 529–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guyatt, G.; Oxman, A.D.; Akl, E.A.; Kunz, R.; Vist, G.; Brozek, J.; Norris, S.; Falck-Ytter, Y.; Glasziou, P.; Debeer, H. GRADE guidelines: Introduction—GRADE evidence profiles and summary of findings tables. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2011, 64, 383–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cooper, S.; Cant, R.; Kelly, M.; Levett-Jones, T.; McKenna, L.; Seaton, P.; Bogossian, F. An Evidence-Based Checklist for Improving Scoping Review Quality. Clin. Nurs. Res. 2021, 30, 230–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Equator. STROBE_checklist_v4_combined. 2009. Available online: https://www.equator-network.org/reporting-guidelines/strobe/ (accessed on 10 December 2020).
- Cuschieri, S. The STROBE guidelines. Saudi J. Anaesth. 2019, 13, S31–S34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoy, D.; Brooks, P.; Woolf, A.; Blyth, F.; March, L.; Bain, C.; Baker, P.; Smith, E.; Buchbinder, R. Assessing risk of bias in prevalence studies: Modification of an existing tool and evidence of interrater agreement. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2012, 65, 934–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jørgensen, L.W.; Søndergaard, K.; Melgaard, D.; Warming, S. Interrater reliability of the Volume-Viscosity Swallow Test; screening for dysphagia among hospitalized elderly medical patients. Clin. Nutr. ESPEN 2017, 22, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benfield, J.K.; Everton, L.F.; Bath DSc, F.P.M.; England, T.J. Accuracy and clinical utility of comprehensive dysphagia screening assessments in acute stroke: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Clin. Nurs. 2020, 29, 1527–1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Busto, F.; Andia, V.; De Alegria, L.R.; Francés, I. Abordaje de la disfagia en la demencia avanzada. Rev. Esp. Geriatr. Gerontol. 2009, 44, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silveira Guijarro, L.J.; Domingo García, V.D.; Montero Fernández, N.; Osuna del Pozo, C.M.; Álvarez Nebreda, L.; Serra-Rexach, J.A. Disfagia orofaríngea en ancianos ingresados en una unidad de convalecencia. Nutr. Hosp. 2011, 26, 501–510. [Google Scholar]
- Serra-Prat, M.; Palomera, M.; Gómez, C.; Sar-Shalom, D.; Saiz, A.; Montoya, J.G.; Navajs, M.; Palomera, E.; Clave, P. Oropharyngeal dysphagia as a risk factorfor malnutrition and lower respiratory tractinfection in independently living olderpersons: A population-based prospective study. Age Ageing 2012, 41, 376–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Almirall, J.; Cabré, M.; Clave, P. Complications of Oropharyngeal Dysphagia: Aspiration Pneumonia. Issues Complement. Feed. 2013, 72, 67–76. [Google Scholar]
- Kertscher, B.; Speyer, R.; Palmieri, M.; Plant, C. Bedside Screening to Detect Oropharyngeal Dysphagia in Patients with Neurological Disorders: An Updated Systematic Review. Dysphagia 2013, 29, 204–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miarons, M.; Campins, L.; Palomera, E.; Serra-Prat, M.; Cabré, M.; Rofes, L. Drugs Related to Oropharyngeal Dysphagia in Older People. Dysphagia 2016, 31, 697–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilardell, N.; Rofes, L.; Arreola, V.; Speyer, R.; Clavé, P. A Comparative Study between Modified Starch and Xanthan Gum Thickeners in Post-Stroke Oropharyngeal Dysphagia. Dysphagia 2016, 31, 169–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilardell, N.; Rofes, L.; Arreola, V.; Martin, A.; Muriana, D.; Palomeras, E.; Ortega, O.; Clavé, P. Videofluoroscopic assessment of the pathophysiology of chronic poststroke oropharyngeal dysphagia. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2017, 29, e13111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melgaard, D.; Baandrup, U.; Bøgsted, M.; Bendtsen, M.D.; Hansen, T. The Prevalence of Oropharyngeal Dysphagia in Danish Patients Hospitalised with Community-Acquired Pneumonia. Dysphagia 2017, 32, 383–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilardell, N.; Rofes, L.; Nascimento, W.V.; Muriana, D.; Palomeras, E.; Clavé, P. Cough reflex attenuation and swallowing dysfunction in sub-acute post-stroke patients: Prevalence, risk factors, and clinical outcome. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2017, 29, e12910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamolar Andrés, S.; Santamaria Rabanal, M.L.; Granda Membiela, C.M.; Fernández Gutiérrez, M.J.; Sirgo Rodríguez, P.; Álvarez Marcos, C. Trastornos de la deglución en la enfermedad de Parkinson. Acta Otorrinolaringol. Esp. 2017, 68, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melgaard, D.; Rodrigo-Domingo, M.; Mørch, M.M. The Prevalence of Oropharyngeal Dysphagia in Acute Geriatric Patients. Geriatrics 2018, 3, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fernández-Rosati, J.; Lera, L.; Fuentes-López, E.; Albala, C. Validation of the eat-10 score to detect dysphagia in older people. Rev. Med. Chile 2018, 146, 1008–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ye, T.; Huang, S.; Dong, Y.; Dong, Q. Comparison of two bedside evaluation methods of dysphagia in patients with acute stroke. Stroke Vasc. Neurol. 2018, 3, 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Miarons, M.; Tomsen, N.; Nascimento, W.; López-Faixó, D.; Clavé, P.; Rofes, L. Increased levels of substance P in patients taking beta-blockers are linked with a protective effect on oropharyngeal dysphagia. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2018, 30, e13397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Westmark, S.; Melgaard, D.; Rethmeier, L.O.; Ehlers, L.H. The cost of dysphagia in geriatric patients. Clin. Outcomes Res. 2018, 10, 321–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wegner, D.A.; Steidl, E.M.S.; Pasqualoto, A.S.; Mancopes, R. Oropharyngeal deglutition, nutrition, and quality of life in individuals with chronic pulmonary disease. Codas 2018, 30, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Michel, A.; Vérin, E.; Gbaguidi, X.; Druesne, L.; Roca, F.; Chassagne, P. Oropharyngeal Dysphagia in Community-Dwelling Older Patients with Dementia: Prevalence and Relationship with Geriatric Parameters. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2018, 19, 770–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rofes, L.; Muriana, D.; Palomeras, E.; Vilardell, N.; Alvarez-Berdugo, D.; Casado, V.; Clavé, P. Prevalence, risk factors and complications of oropharyngeal dysphagia in stroke patients: A cohort study. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2018, 30, e13338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamora, M.A.; Palacín, A.C.; Guardia, C.A.I.; Zamora, C.A.; Clemente, R.E.; Santaliestra, G.J. Importance of the detection of dysphagia in geriatric patients. Semergen 2018, 44, 168–173. [Google Scholar]
- Spronk, P.E.; Spronk, L.E.J.; Lut, J.; Gnacke, E.; Mijnes, D.; Van Munster, B.; Kröner, A. Prevalence and characterization of dysphagia in hospitalized patients. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2019, 32, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peñalva-Arigita, A.; Prats, R.; Lecha, M.; Sansano, A.; Vila, L. Prevalence of dysphagia in a regional hospital setting: Acute care hospital and a geriatric sociosanitary care hospital: A cross-sectional study. Clin. Nutr. ESPEN 2019, 33, 86–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández-Pombo, A.; Seijo-Raposo, I.M.; López-Osorio, N.; Cantón-Blanco, A.; González-Rodríguez, M.; Arias-Rivas, S.; Rodríguez-Yáñez, M.; Santamaría-Nieto, A.; Díaz-Ortega, C.; Gómez-Vázquez, E.; et al. Lesion location and other predictive factors of dysphagia and its complications in acute stroke. Clin. Nutr. ESPEN 2019, 33, 178–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arreola, V.; Vilardell, N.; Ortega, O.; Rofes, L.; Muriana, D.; Palomeras, E.; Álvarez-Berdugo, D.; Clavé, P. Natural History of Swallow Function during the Three-Month Period after Stroke. Geriatrics 2019, 4, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Z.; Wu, L.; Fang, Q.; Shen, M.; Zhang, L.; Liu, X. Effects of capsaicin on swallowing function in stroke patients with dysphagia: A randomized controlled trial. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2019, 28, 1744–1751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayer Silva da Cunha, K.; de Campos Moreira, T.; Tamanini de Almeida, S.; Tannhauser Barros, H.M.; Ferigolo, M. Symptoms Suggestive of Dysphagia and the Quality of Life in Cocaine and/or Crack Users. Dysphagia 2020, 35, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.-Y.; Zhang, X.-P.; Mo, M.-M.; Ye, R.-C.; Hu, C.-X.; Jiang, M.-Q.; Lin, M.-Q. Impact of the systematic use of the volume-viscosity swallow test in patients with acute ischaemic stroke: A retrospective study. BMJ Open 2020, 20, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mateos-Nozal, J.; Montero-Errasquín, B.; García, E.S.; Rodríguez, E.R.; Cruz-Jentoft, A.J. High Prevalence of Oropharyngeal Dysphagia in Acutely Hospitalized Patients Aged 80 Years and Older. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2020, 21, 2008–2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melgaard, D.; Sørensen, L.R.; Lund, D.; Leutscher, P.; Ludwig, M. Systematic Dysphagia Screening of Elderly Persons in the Emergency Department—A Feasibility Study. Geriatrics 2020, 5, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bours, G.J.J.W.; Speyer, R.; Lemmens, J.; Limburg, M.; De Wit, R. Bedside screening tests vs. videofluoroscopy or fibreoptic endoscopic evaluation of swallowing to detect dysphagia in patients with neurological disorders: Systematic review. J. Adv. Nurs. 2009, 65, 477–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoy, D.; Brooks, P.; Woolf, A.; Blyth, F.; March, L.; Bain, C. S2 Table. Quality assessment checklist for prevalence studies. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2012, 65, 934–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altman, D.; Bland, J.; Massif, E.B. Diagnostic tests. 1: Sensitivity and specificity. BMJ 1994, 308, 1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McHugh, M.L. Lessons in biostatistics interrater reliability: The kappa statistic. Biochem. Med. 2012, 22, 276–282. Available online: https://hrcak.srce.hr/89395 (accessed on 6 April 2020). [CrossRef]
- Baijens, L.W.; Clavé, P.; Cras, P.; Ekberg, O.; Forster, A.; Kolb, G.F.; Leners, J.C.; Masiero, S.; del Nozal, J.M.; Ortega, O.; et al. European Society for Swallowing Disorders—European Union Geriatric Medicine Society white paper: Oropharyngeal dysphagia as a geriatric syndrome. Clin. Interv. Aging 2016, 11, 1403–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Almirall, J.; Rofes, L.; Serra-Prat, M.; Icart, R.; Palomera, E.; Arreola, V.; Clavé, P. Oropharyngeal dysphagia is a risk factor for community-acquired pneumonia in the elderly. Eur. Respir. J. 2012, 41, 923–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martino, R.; Silver, F.; Teasell, R.; Bayley, M.; Nicholson, G.; Streiner, D.L.; Diamant, N.E. The toronto bedside swallowing screening test (TOR-BSST) development and validation of a dysphagia screening tool for patients with stroke. Stroke 2009, 40, 555–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Serra-Prat, M.; Hinojosa, G.; López, D.; Juan, M.; Fabré, E.; Voss, D.S.; Calvo, M.; Marta, V.; Ribó, L.; Palomera, E.; et al. Prevalence of oropharyngeal dysphagia and impaired safety and efficacy of swallow in independently living older persons. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2011, 59, 186–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolivar-Prados, M.; Rofes, L.; Arreola, V.; Guida, S.; Nascimento, W.V.; Martin, A.; Vilardell, N.; Fernández, O.O.; Ripken, D.; Lansink, M.; et al. Effect of a gum-based thickener on the safety of swallowing in patients with poststroke oropharyngeal dysphagia. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2019, 31, e13695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marin, S.; Serra-Prat, M.; Ortega, O.; Clavé, P. Cost of oropharyngeal dysphagia after stroke: Protocol for a systematic review. BMJ Open 2018, 8, e022775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]

| Dysphagia | Diagnostics | V-VST |
|---|---|---|
| Deglutition (MeSH) | sensitive * (ti/abs) | Volume viscosity Swallowing test |
| Deglutition disorders (MeSH) | sensitivity and specificity (MeSH) | V-VST |
| Deglutition disorders/diagnosis (MeSH) | diagnose (ti/abs) | volume-viscosity swallow test |
| Deglutition disorders/nursing (MeSH) | diagnosed (ti/abs) | |
| Swallow (ti/abs) | diagnoses (ti/abs) | |
| Dysphagia (tw) | diagnosing (ti/abs) | |
| Dysphag */ | diagnosis (ti/abs) | |
| Dysphag * (ti/abs) | diagnostic (ti/abs) | |
| Deglut * (ti/abs) | diagnosis (MeSH:noexp) | |
| diagnostic * (MeSH:noexp) | ||
| diagnosis, differential (MeSH:noexp) | ||
| diagnosis (Subheading:noexp) |
| Title | Accuracy of the V-VST for clinical screening OD | Clinical screening of OD in patients with ALS | Usefulness of the V-VST for screening dysphagia in subacute stroke patients in rehabilitation income | Sensitivity and specificity of the EAT and the V-VST for clinical evaluation of OD | Value Ranges | Mean | |||||||||||||||||||
| Author | P. Clavé et al. | G. Paris et al. | A. Guillén-Solà et al. | L. Rofes et al. | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Year | 2008 (7) | 2012 (8) | 2013 (9) | 2014 (6) | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Patient Phenotype | Elderly, NDD, H&N, HV | ALS | Subacute stroke patients | Ageing, stroke, NDD, HV | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Sample Size | 97: 40/24/21/12 | 20 | 52 | 134 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Reference Standard | VFS | VFS | VFS | VFS | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Psychometrics | Se | Sp | PPV | NPV | Se | Sp | PPV | NPV | Se | Sp | PPV | NPV | Se | Sp | PPV | NPV | Se | Sp | PPV | NPV | Se | Sp | PPV | NPV | n total |
| OD | 93 | 80 | 100 | 83.3 | 94.0 | 88.0 | 98.0 | 70.0 | 98.8–93 | 88–25 | 100–96.4 | 83.3–50 | 93.2 * | 81.4 * | 95.2 | 65.0 | 251 | ||||||||
| Impaired Safety | 88.2 | 64.7 | 90.9 | 57.9 | 84.2 | 64.3 | 86.4 | 60 | 87.0 | 81.0 | 93.0 | 46.0 | 88.2–84.2 | 81–64.3 | 93.0–86.4 | 60–46.0 | 86.1 * | 68.5 * | 90.1 | 56.3 | 283 | ||||
| Penetrations | 83.7 | 64.7 | 87.2 | 57.9 | 34.3 | 70.6 | 70.6 | 34.3 | 83.7–34.3 | 70.6–64.7 | 87.2–70.6 | 57.9–34.3 | 59.0 | 67.7 | 78.9 | 46.1 | 149 | ||||||||
| Aspirations | 100 | 28.8 | 28.8 | 100 | 88.2 | 71.4 | 60.0 | 92.6 | 91.0 | 28.0 | 21.0 | 94.0 | 100–88.2 | 71.4–28.0 | 60–21 | 100–92.6 | 93.1 | 42.3 | 36.6 | 76.1 | 283 | ||||
| Cough | 82.4 | 54.3 | 46.7 | 86.4 | 82.4 | 54.3 | 46.7 | 86.4 | 82.4 | 54.3 | 46.7 | 86.4 | 52 | ||||||||||||
| Voice Change | 80.0 | 50.0 | 34.8 | 88.2 | 80.0 | 50.0 | 34.8 | 88.2 | 80.0 | 50.0 | 34.8 | 88.2 | 52 | ||||||||||||
| O2 Desaturation (>3%) | 41.2 | 97.1 | 88 | 77.3 | 41.2 | 97.1 | 88 | 77.3 | 41.2 | 97.1 | 88 | 77.3 | 52 | ||||||||||||
| Impaired Efficacy | 92.4 | 33.3 | 94.8 | 25.0 | 79.0 | 75.0 | 93.0 | 67.0 | 92.4–79 | 75-33.3 | 94.8–93 | 67-25 | 85.7 | 54.2 | 93.0 | 67.0 | 231 | ||||||||
| Oral Residue | 69.2 | 80.6 | 39.1 | 93.5 | 93.7 | 65 | 81.1 | 86.6 | 93.7–69.2 | 80.6–65 | 81.1–39.1 | 93.5–86.6 | 81.5 | 72.8 | 60.1 | 90.1 | 149 | ||||||||
| Pharyngeal Residue | 86.4 | 34.6 | 75.0 | 52.9 | 40.0 | 70.8 | 55.5 | 55.9 | 86.4–40 | 70.8–34.6 | 75–55.5 | 55.9–52.9 | 63.2 | 52.7 | 65.3 | 54.4 | 149 | ||||||||
| Piecemeal Deglutition | 88.4 | 87.5 | 96.8 | 63.6 | 88.4 | 87.5 | 96.8 | 63.6 | 88.4 | 87.5 | 96.8 | 63.6 | 97 | ||||||||||||
| Sensitivity | Specificity | LHR+ | LHR− | DOR | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OD | 93.2 * | 81.4 * | 5.01 | 0.08 | 51.18 |
| Impaired Safety | 86.1 * | 68.5 * | 2.73 | 0.20 | 11.67 |
| Penetrations | 59.0 | 67.7 | 1.82 | 0.61 | 4.32 |
| Aspirations | 93.1 | 42.3 | 1.63 | 0.16 | 10.17 |
| Cough | 82.4 | 54.3 | 1.80 | 0.32 | 5.56 |
| Voice Change | 80.0 | 50.0 | 1.60 | 0.40 | 4.00 |
| O2 Desaturation (>3%) | 41.2 | 97.1 | 14.21 | 0.61 | 23.46 |
| Impaired Efficacy | 85.7 | 54.2 | 1.87 | 0.26 | 14.07 |
| Oral Residue | 81.5 | 72.8 | 2.99 | 0.25 | 11.89 |
| Pharyngeal Residue | 63.2 | 52.7 | 1.34 | 0.70 | 2.51 |
| Piecemeal Deglutition | 88.4 | 87.5 | 7.07 | 0.13 | 53.34 |
| Author | Year | Country | Title | Quality * |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Clavé et al. [7] | 2008 | Spain | Accuracy of the volume-viscosity swallow test for clinical screening of oropharyngeal dysphagia and aspiration. | Sufficient 1; Sufficient (8/9) 2; High Quality 3 |
| Gómez-Busto et al. [28] | 2009 | Spain | Approach to dysphagia in advanced dementia. | |
| Silveira Guijarro et al. [29] | 2011 | Spain | Oropharyngeal dysphagia in elderly inpatients in a unit of convalescence. | |
| Paris et al. [8] | 2012 | France | Clinical screening of oropharyngeal dysphagia in patients with ALS. | Sufficient 1; High Quality 3 |
| Rofes et al. [3] | Spain | The volume-viscosity swallow test for clinical screening of dysphagia and aspiration. | Sufficient (8/9) 2 | |
| Serra-Prat et al. [30] | Spain | Oropharyngeal dysphagia as a risk factor for malnutrition and lower respiratory tract infection in independently living older persons: a population-based prospective study. | 0 (low risk) 4 | |
| Guillén-Solà et al. [9] | 2013 | Spain | Usefulness of the volume-viscosity swallow test for screening dysphagia in subacute stroke patients in rehabilitation income. | Sufficient 1; High Quality 3 |
| Almirall et al. [31] | Spain | Oropharyngeal dysphagia is a risk factor for community-acquired pneumonia in the elderly. | 2 (low risk) 4 | |
| Kertscher et al. [32] | Netherlands | Bedside screening to detect oropharyngeal dysphagia in patients with neurological disorders: an updated systematic review. | Sufficient 1 | |
| Rofes et al. [6] | 2014 | Spain | Sensitivity and specificity of the eating assessment tool and the volume-viscosity swallow test for clinical evaluation of oropharyngeal dysphagia. | Sufficient 1; High Quality 3 |
| Carrión et al. [5] | 2015 | Spain | Oropharyngeal dysphagia is a prevalent risk factor for malnutrition in a cohort of older patients admitted with an acute disease to a general hospital. | 1 (low risk) 4 |
| Miarons et al. [33] | 2016 | Spain | Drugs related to oropharyngeal dysphagia in older people. | 1 (low risk) 4 |
| Vilardell et al. [34] | Spain | A comparative study between modified starch and xanthan gum thickeners in post-stroke oropharyngeal dysphagia. | ||
| Jørgensen et al. [26] | 2017 | Denmark | Interrater reliability of the volume-viscosity swallow test; screening for dysphagia among hospitalized elderly medical patients. | |
| Vilardell et al. [35] | Spain | Videofluoroscopic assessment of the pathophysiology of chronic poststroke oropharyngeal dysphagia. | ||
| Melgaard et al. [36] | Denmark | The prevalence of oropharyngeal dysphagia in Danish patients hospitalised with community-acquired pneumonia. | 1 (low risk) 4 | |
| Vilardell et al. [37] | Spain | Cough reflex attenuation and swallowing dysfunction in sub-acute post-stroke patients: prevalence, risk factors, and clinical outcome. | 2 (low risk) 4 | |
| Mamolar et al. [38] | Spain | Swallowing disorders in Parkinson’s disease. | 2 (low risk) 4 | |
| Melgaard et al. [39] | 2018 | Denmark | The prevalence of oropharyngeal dysphagia in acute geriatric patients. | 0 (low risk) 4 |
| Fernández-Rosati et al. [40] | Chile | Validation of the EAT-10 score to detect dysphagia in older people. | ||
| Ye et al. [41] | China | Comparison of two bedside evaluation methods of dysphagia in patients with acute stroke. | ||
| Miarons et al. [42] | Spain | Increased levels of substance P in patients taking beta-blockers are linked with a protective effect on oropharyngeal dysphagia. | 0 (low risk) 4 | |
| Westmark et al. [43] | Denmark | The cost of dysphagia in geriatric patients. | ||
| Wegner et al. [44] | Brazil | Oropharyngeal deglutition, nutrition, and quality of life in individuals with chronic pulmonary disease. | 3 (low risk) 4 | |
| Michel et al. [45] | France | Oropharyngeal dysphagia in community-dwelling older patients with dementia: prevalence and relationship with geriatric parameters. | 1 (low risk) 4 | |
| Rofes et al. [46] | Spain | Prevalence, risk factors and complications of oropharyngeal dysphagia in stroke patients: a cohort study. | 0 (low risk) 4 | |
| Zamora Mur et al. [47] | Spain | Importance of the detection of dysphagia in geriatric patients. | 2 (low risk) 4 | |
| Spronk et al. [48] | 2019 | Netherlands | Prevalence and characterization of dysphagia in hospitalized patients. | 1 (low risk) 4 |
| Peñalva-Arigita et al. [49] | Spain | Prevalence of dysphagia in a regional hospital setting: acute care hospital and a geriatric sociosanitary care hospital: a cross-sectional study. | 2 (low risk) 4 | |
| Fernández-Pombo et al. [50] | Spain | Lesion location and other predictive factors of dysphagia and its complications in acute stroke. | 0 (low risk) 4 | |
| Arreola et al. [51] | Spain | Natural history of swallow function during the three-month period after stroke. | 1 (low risk) 4 | |
| Wang et al. [52] | China | Effects of capsaicin on swallowing function in stroke patients with dysphagia: a randomized controlled trial. | ||
| Mayer Silva da Cunha et al. [53] | 2020 | Brasil | Symptoms suggestive of dysphagia and the quality of life in cocaine and/or crack users. | |
| Benfield et al. [27] | UK | Accuracy and clinical utility of comprehensive dysphagia screening assessments in acute stroke: a systematic review and meta-analysis. | ||
| Liu et al. [54] | China | Impact of the systematic use of volume-viscosity swallow test in patients with acute ischaemic stroke: a retrospective study. | ||
| Mateos-Nozal et al. [55] | Spain | High prevalence of oropharyngeal dysphagia in acutely hospitalized patients aged 80 and older. | ||
| Melgaard et al. [56] | Denmark | Systematic dysphagia screening of elderly persons in the emergency department—a feasibility study. | 3 (low risk) 4 |
| Phenotype | Target Population | Prevalence % | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Older | Community | 86.6 | Michel (2018) [45] |
| 40.3 | Almirall (2013) [62] | ||
| 25.0 | Serra-Prat (2012) [30] | ||
| Hospitalized AGU | 30.7 | Spronk (2019) [48] | |
| 28.5 | Peñalva-Arigita (2019) [49] | ||
| 50.0 | Melgaard (2018) [39] | ||
| 50.0 | Miarons (2018) [42] | ||
| 86.0 | Zamora Mur (2018) [47] | ||
| 41.9 | Miarons (2016) [33] | ||
| 47.4 | Carrión (2015) [5] | ||
| 82.4 | Mateos-Nozal (2020) [55] | ||
| 28.42 | Melgaard (2020) [56] | ||
| Hospitalized with CAP | 34.4 | Melgaard (2017) [36] | |
| 91.7 | Almirall (2013) [62] | ||
| Rehabilitation centre with COPD | 52.9 Impaired efficacy 11.8 Impaired efficacy and safety | Wegner (2018) [44] | |
| NDD | Parkinson | 78.9 | Mamolar (2017) [38] |
| Stroke | Acute phase | 56.6 | Fernandez-Pombo (2019) [50] |
| 39.7 | Arreola (2019) [51] | ||
| 45.1 | Rofes (2018) [46] | ||
| Hospitalized AGU Chronic phase Acute phase | 54.7 | Liu et al. (2020) [54] | |
| 41.7 | Arreola (2019) [51] | ||
| 60.4 Impaired safety 95.9 Impaired efficacy | Vilardell (2017) [35] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Riera, S.A.; Marin, S.; Serra-Prat, M.; Tomsen, N.; Arreola, V.; Ortega, O.; Walshe, M.; Clavé, P. A Systematic and a Scoping Review on the Psychometrics and Clinical Utility of the Volume-Viscosity Swallow Test (V-VST) in the Clinical Screening and Assessment of Oropharyngeal Dysphagia. Foods 2021, 10, 1900. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10081900
Riera SA, Marin S, Serra-Prat M, Tomsen N, Arreola V, Ortega O, Walshe M, Clavé P. A Systematic and a Scoping Review on the Psychometrics and Clinical Utility of the Volume-Viscosity Swallow Test (V-VST) in the Clinical Screening and Assessment of Oropharyngeal Dysphagia. Foods. 2021; 10(8):1900. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10081900
Chicago/Turabian StyleRiera, Stephanie A., Sergio Marin, Mateu Serra-Prat, Noemí Tomsen, Viridiana Arreola, Omar Ortega, Margaret Walshe, and Pere Clavé. 2021. "A Systematic and a Scoping Review on the Psychometrics and Clinical Utility of the Volume-Viscosity Swallow Test (V-VST) in the Clinical Screening and Assessment of Oropharyngeal Dysphagia" Foods 10, no. 8: 1900. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10081900
APA StyleRiera, S. A., Marin, S., Serra-Prat, M., Tomsen, N., Arreola, V., Ortega, O., Walshe, M., & Clavé, P. (2021). A Systematic and a Scoping Review on the Psychometrics and Clinical Utility of the Volume-Viscosity Swallow Test (V-VST) in the Clinical Screening and Assessment of Oropharyngeal Dysphagia. Foods, 10(8), 1900. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10081900







