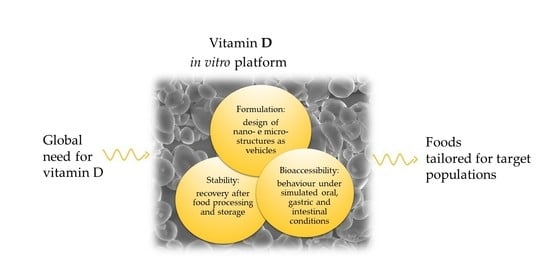
Vitamin D Incorporation in Foods: Formulation Strategies, Stability, and Bioaccessibility as Affected by the Food Matrix
Abstract
:1. Introduction
| Fortified Food | Subjects and Duration | Dose (µg/d) | Outcome | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Water-dispersible vitamin D3 in low-fiber wheat bread | 25–45 years, healthy women n = 41, 1 month | 10.8 | Both vitamin-D3-fortified breads increased serum 25(OH)D as effectively as vitamin D3 supplement. | [16] |
| Water-dispersible vitamin D3 in high-fiber sourdough rye bread | 12.3 | |||
| Vitamin D2 from UV-irradiated yeast in bread | 20–37 years, healthy women n = 33, 2 months | 25 | Vitamin D2 from UV-irradiated yeast in bread did not raise serum 25(OH)D. | [17] |
| Vitamin D2 from UV-irradiated mushrooms in soup | <45 years, healthy n = 26, 1 month | 700 | Vitamin-D2-fortified soup increased serum 25(OH)D as effectively as vitamin D2 supplement. | [18] |
| Water-dispersible vitamin D3 in Ca++-enriched orange juice (Ca++ dose: 350 mg/d) | 18–84 years, healthy n = 105, 3 months | 25 | Vitamin D2 and vitamin D3 were equally bioavailable in Ca++-enriched orange juice and capsules. | [4] |
| Water-dispersible vitamin D2 in Ca++-enriched orange juice (Ca++ dose: 350 mg/d) | ||||
| Vitamin D3 non-specified in Ca++-enriched reduced-fat milk (Ca++ dose: 1000 mg/d) | 50–87 years, healthy men n = 149, 2 years | 20 | Vitamin-D3- and Ca++-fortified milk increased serum 25(OH)D and reduced bone loss. | [19] |
| Vitamin D3 non-specified in Ca++-enriched orange juice (Ca++ dose: 500 mg/d) | 9–12 years, healthy n = 410, 3 months | 2.5 | Vitamin-D3-fortified milk and orange juice increased serum 25(OH). Serum OC and PHT were not affected. | [20] |
| Vitamin D3 non-specified in Ca++-enriched milk (Ca++ dose: 500 mg/d) | ||||
| Water-dispersible vitamin D3 in cheese | ≥60 years, healthy n = 110, 2 months | 15 | Vitamin-D3-fortified cheese had no effect on serum 25(OH)D, OC and PHT. | [21] |
| Water-dispersible vitamin D3 in Cheddar cheese | 18–60 years, healthy n = 30, 2 months | 100 * | Both vitamin-D3-fortified cheeses increased serum 25(OH)D and decreased serum PHT as vitamin D3 supplement | [22] |
| Vitamin D3 non-specified in regular yogurt (Ca++ dose: 150 mg/d) | 30–60 years, diabetic n = 90, 3 months | 25 | Both vitamin-D3-fortified regular yogurt and Ca++-enriched yogurt increased serum 25(OH)D and improved glycemic status. | [23] |
| Vitamin D3 non-specified in Ca++ enriched yogurt (Ca++ dose: 250 mg/d) | ||||
| Vitamin D3 non-specified in Ca++ enriched yogurt (Ca++ dose: 800 mg/d) | ≥65 years, healthy women n = 20, 3 months | 10 | Vitamin-D3-fortified yogurt increased serum 25(OH)D, and maintained cognitive performance. | [24] |
| Water-dispersible vitamin D3 in yogurt | 37–47 years, pre-diabetic n = 60, 3 months | 25 | Vitamin-D3-fortified yogurt increased serum 25(OH)D as effectively as vitamin D3 supplement, and improved serum lipid profile. | [25] |
| Vitamin D3 in casein micelles in low-fat yogurt | 18–61 years, healthy n = 87, single intake | 1250 | Both vitamin D3 carriers in yogurt increased serum 25(OH)D. | [26] |
| Vitamin D3 in emulsion in low-fat yogurt |
2. Vitamin D Fortified Foods: Formulation Strategies
| Structures and Vitamin D Loading | Components | PSD and Average Size | ζ-Potential | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| O/W emulsions S, small; M, medium; L, large 50 mg vitamin D2/100 g oil | Vitamin D2, corn oil, Tween® 80, phosphate buffer | Monomodal S: 0.11 μm, M: 0.53 μm, L: 14.5 μm (volume moment-weighted mean diameter) | S: −12.4 mV, M: −14.1 mV, L: −13.8 mV | [36] |
| O/W nanoemulsion 4 g vitamin D3 /100 g oil | Vitamin D3, corn oil, quillaja saponin, phosphate buffer | Monomodal 0.14 µm (mean particle diameter) | −36.4 mV | [47] |
| W1/O/W2 double emulsion 7 mg vitamin D3/100 g oil | Vitamin D3, vitamin A, vitamin B12, vitamin C, chokeberry extract, folic acid, rapeseed oil, polyglycerol polyricinoleate, milk protein, sodium chloride, water | Monomodal 37.65 µm (volume moment-weighted mean diameter) | [48] | |
| Liposomes 20 g vitamin D3/100 g lipid phase | Vitamin D3, phospholipids, cholesterol in ethanol, distilled water | Monomodal 354.91 nm (equivalent volume diameter at 50% cumulative volume) | −27.62 mV | [50] |
| rCMs: reassembled casein micelles 1.38–1.46 mg vitamin D3/100 mg casein | Vitamin D3 in ethanol, sodium caseinate in water, dipotassium hydrogen phosphate, potassium citrate, calcium chloride | Monomodal from 16.10 to 19.04 µm (average volume-weighted particle sizes) | from −17.3 to −17.8 mV | [61] |
| rCMs: reassembled casein micelles 1.6 mg vitamin D3/100 mg casein | Vitamin D3 in ethanol, sodium caseinate in water, dipotassium hydrogen phosphate, tripotassium citrate, calcium chloride | Bimodal 89 nm and 277 nm (volume moment-weighted mean diameter) | [26] | |
| rCMs: reassembled casein micelles 1 µg vitamin D2/100 mg casein | Vitamin D2 in ethanol, micellar casein in sweet whey permeate | Monomodal from 145 to 303 nm (mean hydrodynamic diameter) | [62] | |
| β-Conglycinin nanoparticles 10 µg vitamin D3/100 mg β-conglycinin | Vitamin D3 in ethanol, β-conglycinin, phosphate buffer | Bimodal 31 nm and 120 nm (volume weighted average particle diameter) | [63] | |
| Zein nanocapsules vitamin D3 loading not specified | Vitamin D3 in ethanol, zein, Tween® 80 | Monomodal 185.7 ± 2.10 nm (Z-average size) | 24.5 mV | [52] |
3. Vitamin D in Fortified Foods: Yield and Stability
| Fortified Food | Vitamin D Content (μg/100 g) | Main Processing Steps | Vitamin D Yield (%) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Free vitamin D3 in soybean oil | 700 | Storage in PET bottles at 30 °C for 50 d in the dark | 56–76 (S) | [29] |
| Storage in PET bottles at 30 °C for 50 d under natural light | 32–39 (S) | |||
| Free vitamin D3 in sunflower oil | 14.5 | Heating at 110 °C for 30 min | 85 (P) | [31] |
| Heating at 210 °C for 10 min | 79 (P) | |||
| Free vitamin D2 in sunflower oil | 11.2 | Heating at 110 °C for 30 min | 89 (P) | |
| Heating at 210 °C for 10 min | 76 (P) | |||
| Vitamin D3 in liposomes in white chocolate | 30 | Three-step tempering process (33 °C–35 °C, 24 °C–25 °C, and 25 °C–26 °C), storage at 25 °C for 120 d | 100 (S) | [50] |
| Free vitamin D3 in white chocolate | 99 (S) | |||
| Free vitamin D3 in whole wheat flour | nd | Storage at aw 0.33 at 25 °C for 173 d | 50 (S) | [68] |
| Storage at aw 0.93 at 25 °C for 116 d | 50 (S) | |||
| Storage at aw 0.33 at 45 °C for 87 d | 50 (S) | |||
| Storage at aw 0.93 at 45 °C for 63 d | 50 (S) | |||
| Vitamin D2 in dry mushroom powder | 4420 | Storage at aw 0.33 at 25 °C for 175 d | 50 (S) | [71] |
| Storage at aw 0.33 at 30 °C for 136 d | 50 (S) | |||
| Storage at aw 0.33 at 45 °C for 55 d | 50 (S) | |||
| Free vitamin D3 in wheat bread | 10.8 | Baking at 170 °C for 60 min | 85 (P) | [28] |
| Free vitamin D3 in rye bread | 8.7 | 69 (P) | ||
| Vitamin D2 yeast in wheat bread | 9.5 | 85 (P) | ||
| Vitamin D2 yeast in rye bread | 8.5 | 73 (P) | ||
| Free vitamin D3 in wheat bread | 40.2 | Baking at 200 °C for 20 min | 40.2 (P) | [68] |
| Free vitamin D3 in cookies | 64 | Baking at 200–205 °C for 12 min | 65.3 (P) | |
| Free vitamin D3 in milk | 12 | Steam injection (95 °C), spray-drying at 149 °C, fluid-bed finish at 107 °C | 100 (P) | [27] |
| Water-dispersible vitamin D3 in milk | 100 | Pasteurization at 73 °C for 15 s, homogenization at 13.8/3.4 MPa, storage at 4 °C for 21 d | 100 (P, S) | [37] |
| Water-dispersible vitamin D2 in milk | 2 | Pasteurization at 63 °C for 30 min, storage in glass bottles at 4°C for 7 d in the dark | 100 (P, S) | [39] |
| Pasteurization at 63 °C for 30 min, storage in glass bottles at 4 °C for 32 h under light | 100 (P, S) | |||
| Pasteurization at 63 °C for 30 min, storage in PET pouches at 4 °C for 7 d in the dark | ~ 90 (P, S) | |||
| Pasteurization at 63 °C for 30 min, storage in PET pouches at 4 °C for 32 h under light | ~ 90 (P, S) | |||
| Sterilization at 121 °C for 15 min | 100 (P) | |||
| Vitamin D2 in casein complexes in cow and buffalo milk (1:1) | 1.25 | Pasteurization at 63 °C for 30 min, storage in glass bottles at 4 °C for 7 d under light | ~ 95 (P), ~ 70 (S) | [51] |
| Pasteurization at 63 °C for 30 min, storage in LDPE pouches at 4 °C for 7 d under light | ~ 95 (P), ~ 65 (S) | |||
| Sterilization at 121 °C for 15 min | ~ 75 (P) | |||
| Free vitamin D2 in cow and buffalo milk (1:1) | 1.25 | Pasteurization at 63 °C for 30 min, storage in glass bottles at 4 °C for 7 d under light | 90 (P), 45 (S) | |
| Pasteurization at 63 °C for 30 min, storage in LDPE pouches at 4 °C for 7 d under light | 90 (P), 45 (S) | |||
| Sterilization at 121 °C for 15 min | 67 (P) | |||
| Water-dispersible vitamin D3 in Cheddar (milk fat 3.9%) | nd | Starter addition, rennet addition, salting, pressing, vacuum packaging, storage at 4° C for 84 d | 90.4 (P) 100 (S) | [34] |
| Free vitamin D3 in Cheddar (milk fat 3.9%) | 86.7 (P) 93.7% (S) | |||
| Water-dispersible vitamin D3 in Cheddar (milk fat 3.8%) | 2085 | Milk pasteurization 72°C for 16 s, starter addition, rennet addition, salting, pressing, vacuum packaging, storage at 4 °C for 365 d | 91 (P) 100 (S) | [35] |
| Water-dispersible vitamin D3 in low-fat cheese (milk fat 0.8%) | 1690 | 55 (P) 100 (S) | ||
| Vitamin D3 in nanoemulsion in cheese (milk fat 2%) | 1 | Milk acidification with lactic acid, rennet addition, cutting, centrifugation, storage at 4 °C for 90 d | 91 (P) 100 (S) | [43] |
| Free vitamin D3 in cheese (17 MPa, 0.9 P/F ratio) | 488 | Skimmed milk powder added with anhydrous milk fat and water at specific protein/fat (P/F) ratio, homogenization at 17–150 MPa, calcium chloride addition, coagulation at 85 °C, salting, pressing | 52 (P) | [32] |
| Free vitamin D3 in cheese (150 MPa, 2 P/F ratio) | 499 | 49.3 (P) | ||
| Water-dispersible vitamin D3 in yogurt (milk fat 3.9%) | nd | Starter inoculation, fermentation, storage at 4 °C for 21 d | 97.8 (P) 100 (S) | [34] |
| Free vitamin D3 in yogurt (milk fat 3.9%) | 96.6 (P) 100 (S) | |||
| Vitamin D3 in W/O emulsion in yogurt | 12.5 | Addition to fresh yogurt, storage at 4 °C for 20 d | 15.97 (S) | [45] |
| Vitamin D3 in W/O emulsion in yogurt + goji berry extract | 74.90 (S) | |||
| Water-dispersible vitamin D3 in yogurt (milk fat 1.5%) | 2.25 | Starter inoculation, fermentation, storage in opaque containers at 4 °C for 21 d | 100 (S) | [38] |
| Vitamin D3 in oil in yogurt (milk fat 1.5%) | 99 (S) | |||
| Water-dispersible vitamin D3 in yogurt (milk fat 1.5%) | 2.25 | Starter inoculation, fermentation, storage in transparent containers at 4 °C for 21 d | 86 (S) | |
| Vitamin D3 in oil in yogurt (milk fat 1.5%) | 80 (S) | |||
| Vitamin D3 in W1/O/W2 emulsion in yogurt (milk fat 6.15%) | 10 | Starter inoculation, fermentation, storage at 4 °C for 20 d | 50 (S) | [49] |
| Free vitamin D3 in yogurt (milk fat 6.15%) | 94 (S) |
4. Vitamin D in Fortified Foods: Bioaccessibility
| Fortified Food | Vitamin D Content (μg/100 g) | Bioaccessibility (%) | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|
| Yeast vitamin D2 in white wheat bread | 4.67 | 15 | [30] |
| Yeast vitamin D2 in whole wheat bread | 4.87 | 9.9 | |
| Free vitamin D2 (control) in whole wheat bread | 3.9 | 38 | |
| Free vitamin D3 in skimmed milk | 1.12 | 32 | [30] |
| Free vitamin D3 in partially defatted milk (2% fat) | 1.02 | 70 | |
| Free vitamin D3 in whole milk (3.25% fat) | 1.28 | 53 | |
| Free vitamin D3 in infant powder formula (4% fat) | 10.94 | 54 | |
| Natural vitamin D3 in whole milk | 3.97 | 30 | [82] |
| Natural vitamin D3 in yogurt | 3.1 | 38 | |
| Natural vitamin D3 in fresh cheese | 13.8 | 24 | |
| Natural vitamin D3 in aged cheese | 21.7 | 21 | |
| Free vitamin D3 in cheese (17 MPa, protein/fat ratio 0.9), | 488 | 64 | [32] |
| Free vitamin D3 in cheese (17 MPa, protein/fat ratio 2), | 498 | 51 | |
| Free vitamin D3 in cheese (150 MPa, protein/fat ratio 2) | 499 | 27 | |
| Vitamin D3 in W1/O/W2 emulsion in high-protein yogurt | 10 | 100 | [49] |
| Vitamin D3 in W1/O/W2 emulsion in high-protein yogurt | 10 | 100 | |
| Vitamin D3 nanoemulsion in oat milk or almond milk | 400 | 20 | [46] |
| Vitamin D3 W/O nanoemulsion in almond milk + CaCl2 or CaCO3 | nd | <20 | [47] |
| Vitamin D3 in refined olive oil in beef | 16.7 | 5 | [33] |
| Vitamin D3 in refined olive oil in semolina or in chickpeas | 3.0 | 25 | |
| Vitamin D3 in canola oil in brownies | nd | 65.2 | [84] |
| Oily vitamin D3 in canola oil + tert-butylhydroquinone in brownies | nd | 98 | |
| Vitamin D3 in zein nanocapsules in a fruit (Acca sellowiana) jelly | 159 | 81 | [52] |
5. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Milešević, J.; Samaniego, L.; Kiely, M.; Glibetić, M.; Roe, M.; Finglas, P. Specialized food composition dataset for vitamin D content in foods based on European standards: Application to dietary intake assessment. Food Chem. 2018, 240, 544–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grant, W.B.; Anouti, F.A.; Moukayed, M. Targeted 25-hydroxyvitamin D concentration measurements and vitamin D3 supplementation can have important patient and public health benefits. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2020, 74, 366–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holick, M.F.; Chen, T.C. Vitamin D deficiency: A worldwide problem with health consequences. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2008, 87, 1080S–1086S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Biancuzzo, R.M.; Young, A.; Bibuld, D.; Cai, M.H.; Winter, M.R.; Klein, E.K.; Ameri, A.; Reitz, R.; Salameh, W.; Chen, T.C.; et al. Fortification of orange juice with vitamin D2 or vitamin D3 is as effective as an oral supplement in maintaining vitamin D status in adults. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2010, 91, 1621–1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khazai, N.B.; Judd, S.E.; Jeng, L.; Wiolfenden, L.L.; Stecenko, A.; Ziegler, T.R.; Tangpricha, V. Treatment and prevention of vitamin D insufficiency in cystic fibrosis patients: Comparative efficacy of ergocalciferol, cholecalciferol, and UV light. J. Clin. Endocr. Metab. 2009, 94, 2037–2043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Romagnoli, E.; Mascia, M.L.; Cipriani, C.; Fassino, V.; Mazzei, F.; D’Erasmo, E.; Carnevale, V.; Scillitani, A.; Minisola, S. Short and long-term variations in serum calciotropic hormones after a single very large dose of ergocalciferol (vitamin D2) or cholecalciferol (vitamin D3) in the elderly. J. Clin. Endocr. Metab. 2008, 93, 3015–3020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakobsen, J.; Andersen, E.A.W.; Christensen, T.; Andersen, R.; Bügel, S. Vitamin D vitamers affect vitamin D status differently in young healthy males. Nutrients 2018, 10, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Holick, M.F.; Biancuzzo, R.M.; Chen, T.C.; Klein, E.K.; Young, A.; Bibuld, D.; Reitz, R.; Salameh, W.; Ameri, A.; Tannenbaum, A.D. Vitamin D2 is as effective as vitamin D3 in maintaining circulating concentrations of 25-hydroxyvitamin D. J. Clin. Endocr. Metab. 2008, 93, 677–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holick, M.F. The vitamin D deficiency pandemic: Approaches for diagnosis, treatment and prevention. Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 2017, 18, 153–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holick, M.F.; Binkley, N.C.; Bischoff-Ferrari, H.A.; Gordon, C.M.; Hanley, D.A.; Heaney, R.P.; Murad, M.H.; Weaver, C.M. Evaluation, treatment, and prevention of vitamin D deficiency: An Endocrine Society clinical practice guideline. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2011, 96, 1911–1930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ekwaru, J.P.; Zwicker, J.D.; Holick, M.F.; Giovannucci, E.; Veugelers, P.J. The importance of body weight for the dose response relationship of oral vitamin D supplementation and serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D in healthy volunteers. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, 111265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cashman, K.D.; Kiely, M.E.; Andersen, R.; Grønborg, I.M.; Madsen, K.H.; Nissen, J.; Tetens, I.; Tripkovic, L.; Lanham-New, S.A.; Toxqui, L.; et al. Individual participant data (IPD)-level meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials with vitamin D-fortified foods to estimate Dietary Reference Values for vitamin D. Eur. J. Nutr. 2021, 60, 939–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roman Viñas, B.; Ribas Barba, L.; Ngo, J.; Gurinovic, M.; Novakovic, R.; Cavelaars, A.; de Groot, L.C.P.G.M.; van’t Veer, P.; Matthys, C.; Serra Majem, L. Projected prevalence of inadequate nutrient intakes in Europe. Ann. Nutr. Metab. 2011, 59, 84–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, C.E.; Radcliffe, J.D.; Liu, Y. Vitamin D intakes of adults differ by income, gender and race/ethnicity in the USA, 2007 to 2010. Public Health Nutr. 2013, 17, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- O’Mahony, L.; Stepien, M.; Gibney, M.J.; Nugent, A.P.; Brennan, L. The potential role of vitamin D enhanced foods in improving vitamin D status. Nutrients 2011, 3, 1023–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Natri, A.M.; Salo, P.; Vikstedt, T.; Palssa, A.; Huttunen, M.; Karkkainen, M.U.; Salovaara, H.; Piironen, V.; Jakobsen, J.; Lamberg-Allardt, C.J. Bread fortified with cholecalciferol increases the serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D concentration in women as effectively as a cholecalciferol supplement. J. Nutr. 2006, 136, 123–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Itkonen, S.T.; Skaffari, E.; Saaristo, P.; Saarnio, E.M.; Erkkola, M.; Jakobsen, J.; Cashman, K.D.; Lamberg-Allardt, C. Effects of vitamin D2-fortified bread v. supplementation with vitamin D2 or D3 on serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D metabolites: An 8-week randomised-controlled trial in young adult Finnish women. Br. J. Nutr. 2016, 115, 1232–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Urbain, P.; Singler, F.; Ihorst, G.; Biesalski, H.K.; Bertz, H. Bioavailability of vitamin D2 from UV-B-irradiated button mushrooms in healthy adults deficient in serum 25 hydroxyvitamin D: A randomized controlled trial. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2011, 65, 965–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Daly, R.M.; Brown, M.; Bass, S.; Kukuljan, S.; Nowson, C. Calcium- and vitamin D3-fortified milk reduces bone loss at clinically relevant skeletal sites in older men: A 2-year randomized controlled trial. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2006, 21, 397–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neyestani, T.R.; Hajifaraji, M.; Omidvar, N.; Nikooyeh, B.; Eshraghian, M.R.; Shariatzadeh, N.; Kalayi, A.; Khalaji, N.; Zahedirad, M.; Abtahi, M.; et al. Calcium-vitamin D-fortified milk is as effective on circulating bone biomarkers a fortified juice and supplement but has less acceptance: A randomised controlled school-based trial. J. Human Nutr. Diet. 2014, 27, 606–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, J.L.; Mistry, V.V.; Vukovich, M.D.; Hogie-Lorenzen, T.; Hollis, B.W.; Specker, B.L. Bioavailability of vitamin D from fortified process cheese and effects on vitamin D status in the elderly. J. Dairy Sci. 2005, 88, 2295–2301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, D.; Sidhom, G.; Whiting, S.J.; Rousseau, D.; Vieth, R. The bioavailability of vitamin D from fortified cheeses and supplements is equivalent in adults. J. Nutr. 2008, 138, 1365–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikooyeh, B.; Neyestani, T.R.; Farvid, M.; Alavi-Majd, H.; Houshiarrad, A.; Kalayi, A.; Shariatzadeh, N.; Gharavi, A.; Heravifard, S.; Tayebinejad, N.; et al. Daily consumption of vitamin D− or vitamin D+ calcium-fortified yogurt drink improved glycemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes: A randomized clinical trial. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2011, 93, 764–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beauchet, O.; Launay, C.P.; Galery, K.; Vilcocq, C.; Dontot-Payen, F.; Rousseau, B.; Benoit, V.; Allali, G. Effects of vitamin D and Calcium fortified yogurts on gait, cognitive performances, and serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D concentrations in older community-dwelling females: Results from the GAit, MEmory, Dietary and vitamin D (GAME-D2) randomized controlled trial. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mostafaia, R.; Nachvakc, S.M.; Mohammadi, R.; Rocha, R.S.; da Silva, M.C.; Esmerinod, E.A.; Nascimento, K.O.; Cruz, A.G.; Mortazavian, A.M. Effects of vitamin D-fortified yogurt in comparison to oral vitamin D supplement on hyperlipidemia in pre-diabetic patients: A randomized clinical trial. J. Func. Foods 2019, 52, 116–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levinson, Y.; Ish-Shalom, S.; Segal, E.; Livney, Y.D. Bioavailability, rheology and sensory evaluation of fat-free yogurt enriched with VD3 encapsulated in re-assembled casein micelles. Food Funct. 2016, 7, 1477–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Indyk, H.; Littlejohn, V.; Woollard, D. Stability of vitamin D3 during spray-drying of milk. Food Chem. 1996, 57, 283–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakobsen, J.; Knuthsen, P. Stability of vitamin D in foodstuffs during cooking. Food Chem. 2014, 148, 170–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemery, Y.M.; Fontan, L.; Moench-Pfanner, R.; Laillou, A.; Berger, A.; Renaud, J.C.; Avallone, S. Influence of light exposure and oxidative status on the stability of vitamins A and D3 during the storage of fortified soybean oil. Food Chem. 2015, 184, 90–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipkie, T.E.; Ferruzzi, M.G.; Weaver, C.W. Low bioaccessibility of vitamin D2 from yeast fortified bread compared to crystalline D2 bread and D3 from fluid milks. Food Funct. 2016, 7, 4589–4596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ložnjak, P.; Jakobsen, J. Stability of vitamin D3 and vitamin D2 in oil, fish and mushrooms after household cooking. Food Chem. 2018, 254, 144–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Castaneda, N.; Lee, Y. Microstructure of a model fresh cheese and bioaccessibility of vitamin D3 using in vitro digestion. Gels 2019, 5, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Antoine, T.; Icard-Verniere, C.; Scorrano, G.; Salhi, A.; Halimi, C.; George, S.; Carriere, F.; Mouquet-Rivier, C.; Reboul, E. Evaluation of vitamin D bioaccessibility and mineral solubility from test meals containing meat and/or cereals and/or pulses using in vitro digestion. Food Chem. 2021, 347, 128621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazmi, S.A.; Vieth, R.; Rosseau, D. Vitamin D3 fortification and quantification in processed dairy products. Int. Dairy J. 2007, 17, 753–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, D.; Rousseau, E.; Sidhom, G.; Pouliot, M.; Audet, P.; Vieth, R. Vitamin D3 fortification, quantification, and long-term stability in Cheddar and low-fat cheeses. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 7964–7969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvia-Trujillo, L.; Fumiaki, L.B.; Park, J.; McClements, D.J. The influence of lipid droplet size on the oral bioavailability of vitamin D2 encapsulated in emulsions: An in vitro and in vivo study. Food Funct. 2017, 8, 767–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanson, A.L.; Metzger, L.E. Evaluation of increased vitamin D fortification in high-temperature, short-time–processed 2% milk, UHT-processed 2% fat chocolate milk, and low-fat strawberry yogurt. J. Dairy Sci. 2010, 93, 801–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jafari, T.; Askari, G.; Mirlohi, M.; Javanmard, S.H.; Faghihimani, E.; Fallah, A.A. Stability of Vitamin D3 in fortified yoghurt and yoghurt drink (Doogh). Adv. Biomed. Res. 2016, 5, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaushik, R.; Sachdeva, B.; Arora, S. Vitamin D2 stability in milk during processing, packaging and storage. LWT—Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 56, 421–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavelli, V. Circular food supply chains—Impact on value addition and safety. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 114, 323–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClements, D.J.; Decker, E.A.; Park, Y.; Weiss, J. Structural design principles for delivery of bioactive components in nutraceuticals and functional foods. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2009, 49, 577–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stratulat, I.; Britten, M.; Salmieri, S.; Fustier, P.; St-Gelais, D.; Champagne, C.P.; Lacroix, M. Enrichment of cheese with bioactive lipophilic compounds. J. Func. Foods 2014, 6, 48–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stratulat, I.; Britten, M.; Salmieri, S.; Fustier, P.; St-Gelais, D.; Champagne, C.P.; Lacroix, M. Enrichment of cheese with vitamin D3 and vegetable omega-3. J. Func. Foods 2015, 13, 300–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maurya, V.K.; Aggarwal, M. Factors influencing the absorption of vitamin D in GIT: An overview. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 54, 3753–3765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurya, V.K.; Aggarwal, M. Impact of Aqueous/ethanolic goji Berry (Lycium barbarum) fruit extract supplementation on vitamin D stability in yoghurt. Int. J. Curr. Microbiol. App. Sci. 2017, 6, 2016–2029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, H.; Liu, J.; Dai, T.; Mundo, J.L.M.; Tan, Y.; Bai, L.; McClements, D.J. The gastrointestinal fate of inorganic and organic nanoparticles in vitamin D-fortified plant-based milks. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 112, 106310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Zheng, B.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, R.; He, L.; McClements, D.J. Fortification of plant-based milk with calcium may reduce vitamin D bioaccessibility: An in vitro digestion study. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 4223–4233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kersien, M.; Jasutien, I.; Eisinait, V.; Venskutonis, P.R.; Leskauskait, D. Designing multiple bioactives loaded emulsions for the formulations for diets of elderly. Food Funct. 2020, 11, 2195–2207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kersien, M.; Jasutien, I.; Eisinait, V.; Pukalskien, M.; Venskutonis, P.R.; Damulevicien, G.; Knasiene, J.; Lesauskait, V.; Leskauskait, D. Development of a high-protein yoghurt-type product enriched with bioactive compounds for the elderly. LWT—Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 131, 109820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Didar, Z. Inclusion of vitamin D3 (free or liposome) into white chocolate and an investigation of its stability during storage. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2021, 45, 15231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syama, M.A.; Arora, S.; Gupta, C.; Sharma, A.; Sharma, V. Enhancement of vitamin D2 stability in fortified milk during light exposure and commercial heat treatments by complexation with milk proteins. Food Biosci. 2019, 29, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zapelini de Melo, A.P.; Gonçalves da Rosa, C.; Montanheiro Noronha, C.; Heck Machado, M.; Sganzerla, W.G.; da Cunha Bellinati, V.N.; Verruck, S.; Schwinden Prudencio, E.; Manique Barreto, P.L. Nanoencapsulation of vitamin D3 and fortification in an experimental jelly model of Acca sellowiana: Bioaccessibility in a simulated gastrointestinal system. LWT—Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 145, 111287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozturk, B. Nanoemulsions for food fortification with lipophilic vitamins: Production challenges, stability, and bioavailability. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2017, 119, 1500539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muschiolik, G.; Dickinson, E. Double emulsions relevant to food systems: Preparation, stability, and applications. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2017, 16, 532–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Taylor, T.M.; Weiss, J.; Davidson, P.M.; Bruce, B.D. Liposomal nanocapsules in food science and agriculture. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2005, 45, 587–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, T.M.; Morris, R.M. Thermal analysis of phase transition behavior in liposomes. Thermochim. Acta 1995, 248, 289–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banville, C.; Vuillemard, J.C.; Lacroix, C. Comparison of different methods for fortifying Cheddar cheese with vitamin D. Int. Dairy J. 2000, 10, 375–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.H. Assembly of food proteins for nano-encapsulation and delivery of nutraceuticals (a mini-review). Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 117, 106710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diarrassouba, F.; Garrait, G.; Remondetto, G.; Alvarez, P.; Beyssac, E.; Subirade, M. Improved bioavailability of vitamin D3 using a β-lactoglobulin-based coagulum. Food Chem. 2015, 172, 361–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasi, A.; Emam-Djomeh, Z.; Mousavi, M.A.E.; Davoodi, D. Stability of vitamin D3 encapsulated in nanoparticles of whey protein isolate. Food Chem. 2014, 143, 379–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loewen, A.; Chan, B.; Li-Chan, E.C. Optimization of vitamins A and D3 loading in re-assembled casein micelles and effect of loading on stability of vitamin D3 during storage. Food Chem. 2018, 240, 472–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menéndez-Aguirre, O.; Kessler, A.; Stuetz, W.; Grune, T.; Weiss, J.; Hinrichs, J. Increased loading of vitamin D2 in reassembled casein micelles with temperature-modulated high pressure treatment. Food Res. Int. 2014, 64, 74–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levinson, Y.; Israeli-Lev, G.; Livney, Y.D. Soybean β-conglycinin nanoparticles for delivery of hydrophobic nutraceuticals. Food Biophys. 2014, 9, 332–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.; Yang, X.; Yang, L.; Liu, Z.L.; Zhang, F. Autoxidation of isotachysterol. Tetrahedron 2004, 60, 2881–2888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, S.-Y.; Lin, H.-Y.; Hong, W.-P.; Lin, C.-P. Evaluation of preliminary causes for vitamin D series degradation via DSC and HPLC analyses. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2017, 130, 1357–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoodani, F.; Perera, C.O.; Fedrizzi, B.; Abernethy, G.; Chen, H. Degradation studies of cholecalciferol (vitamin D3) using HPLC-DAD, UHPLC-MS/MS and chemical derivatization. Food Chem. 2017, 219, 373–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, K.; Latshaw, J. Effects of commercial processing on the fat-soluble vitamin content of menhaden fish oil. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 1991, 68, 234–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajaj, S.R.; Singhal, R.S. Fortification of wheat flour and oil with vitamins B12 and D3: Effect of processing and storage. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2021, 96, 103703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corey, M.E.; Kerr, W.L.; Mulligan, J.H.; Lavelli, V. Phytochemical stability in dried apple and green tea functional products as related to moisture properties. LWT—Food Sci. Technol. 2011, 44, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavelli, V.; Proserpio, C.; Gallotti, F.; Laureati, M.; Pagliarini, E. Circular reuse of bio-resources: The role of Pleurotus spp. in the development of functional foods. Food Funct. 2018, 9, 1353–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pedrali, D.; Gallotti, F.; Proserpio, C.; Pagliarini, E.; Lavelli, V. Kinetic study of vitamin D2 degradation in mushroom powder to improve its applications in fortified foods. LWT—Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 125, 109248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Sevilla, M.D. Kinetic analysis of free-radical reactions in the low temperature autoxidation of triglycerides. J. Phys. Chem. 1990, 94, 1447–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salemi, S.; Saedisomeolia, A.; Azimi, F.; Zolfigol, S.; Mohajerani, E.; Mohammadi, M.; Yaseri, M. Optimizing the production of vitamin D in white button mushrooms (Agaricus bisporus) using ultraviolet radiation and measurement of its stability. LWT—Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 137, 110401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mattila, P.; Ronkainen, R.; Lehikoinen, K.; Piironen, V. Effect of household cooking on the vitamin D content in fish, eggs, and wild mushrooms. J. Food Composit. Anal. 1999, 12, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renken, J.D.; Warthesen, J.J. Vitamin D stability in milk. J. Food Sci. 1993, 58, 552–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Limbo, S.; Pellegrino, L.; D’Incecco, P.; Gobbi, S.; Rosi, V.; Fracassetti, D. Storage of pasteurized milk in clear PET bottles combined with light exposure on a retail display case: A possible strategy to define the shelf life and support a recyclable packaging. Food Chem. 2020, 329, 127116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forrest, S.A.; Yada, R.Y.; Rousseau, D. Interactions of vitamin D3 with bovine β-lactoglobulin A and β-casein. J. Agricul. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 8003–8009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delavari, B.; Saboury, A.A.; Atri, M.S.; Ghasemi, A.; Bigdeli, B.; Khammari, A.; Goliaei, B. Alpha-lactalbumin: A new carrier for vitamin D3 food enrichment. Food Hydrocoll. 2015, 45, 124–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borel, P.; Caillaud, D.; Cano, N. Vitamin D bioavailability: State of the art. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2015, 55, 1193–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.; McClements, D.J. Improving the bioavailability of oil-soluble vitamins by optimizing food matrix effects: A. review. Food Chem. 2021, 348, 129148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dima, C.; Assadpour, E.; Dima, S.; Jafari, S.M. Bioavailability of nutraceuticals: Role of the food matrix, processing conditions, the gastrointestinal tract, and nanodelivery systems. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2020, 19, 954–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernandez-Olivas, E.; Munoz-Pina, S.; Sanchez-Garcia, J.; Andres, A.; Heredia, A. Understanding the role of food matrix on the digestibility of dairy products under elderly gastrointestinal conditions. Food Res. Int. 2020, 137, 109454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamothe, S.; Corbeil, M.-M.; Turgeon, S.L.; Britten, M. Influence of cheese matrix on lipid digestion in a simulated gastro-intestinal environment. Food Funct. 2012, 3, 724–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goebel, S.; Avallone, S.; Detchewa, P.; Prasajak, P.; Sriwichai, W. Natural and synthetic antioxidants prevent the degradation of vitamin D3 fortification in canola oil during baking and in vitro digestion. Appl. Sci. Eng. Prog. 2021, 14, 247–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowson, C.; O’Connell, S. Protein requirements and recommendations for older people: A review. Nutrients 2015, 7, 6874–6899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dima, C.; Dima, S. Bioaccessibility study of calcium and vitamin D3 co-microencapsulated in water-in-oil-in-water double emulsions. Food Chem. 2020, 303, 125416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lavelli, V.; D’Incecco, P.; Pellegrino, L. Vitamin D Incorporation in Foods: Formulation Strategies, Stability, and Bioaccessibility as Affected by the Food Matrix. Foods 2021, 10, 1989. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10091989
Lavelli V, D’Incecco P, Pellegrino L. Vitamin D Incorporation in Foods: Formulation Strategies, Stability, and Bioaccessibility as Affected by the Food Matrix. Foods. 2021; 10(9):1989. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10091989
Chicago/Turabian StyleLavelli, Vera, Paolo D’Incecco, and Luisa Pellegrino. 2021. "Vitamin D Incorporation in Foods: Formulation Strategies, Stability, and Bioaccessibility as Affected by the Food Matrix" Foods 10, no. 9: 1989. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10091989
APA StyleLavelli, V., D’Incecco, P., & Pellegrino, L. (2021). Vitamin D Incorporation in Foods: Formulation Strategies, Stability, and Bioaccessibility as Affected by the Food Matrix. Foods, 10(9), 1989. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10091989