High-Frequency Focused Ultrasound on Quality Traits of Bovine Triceps brachii Muscle
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
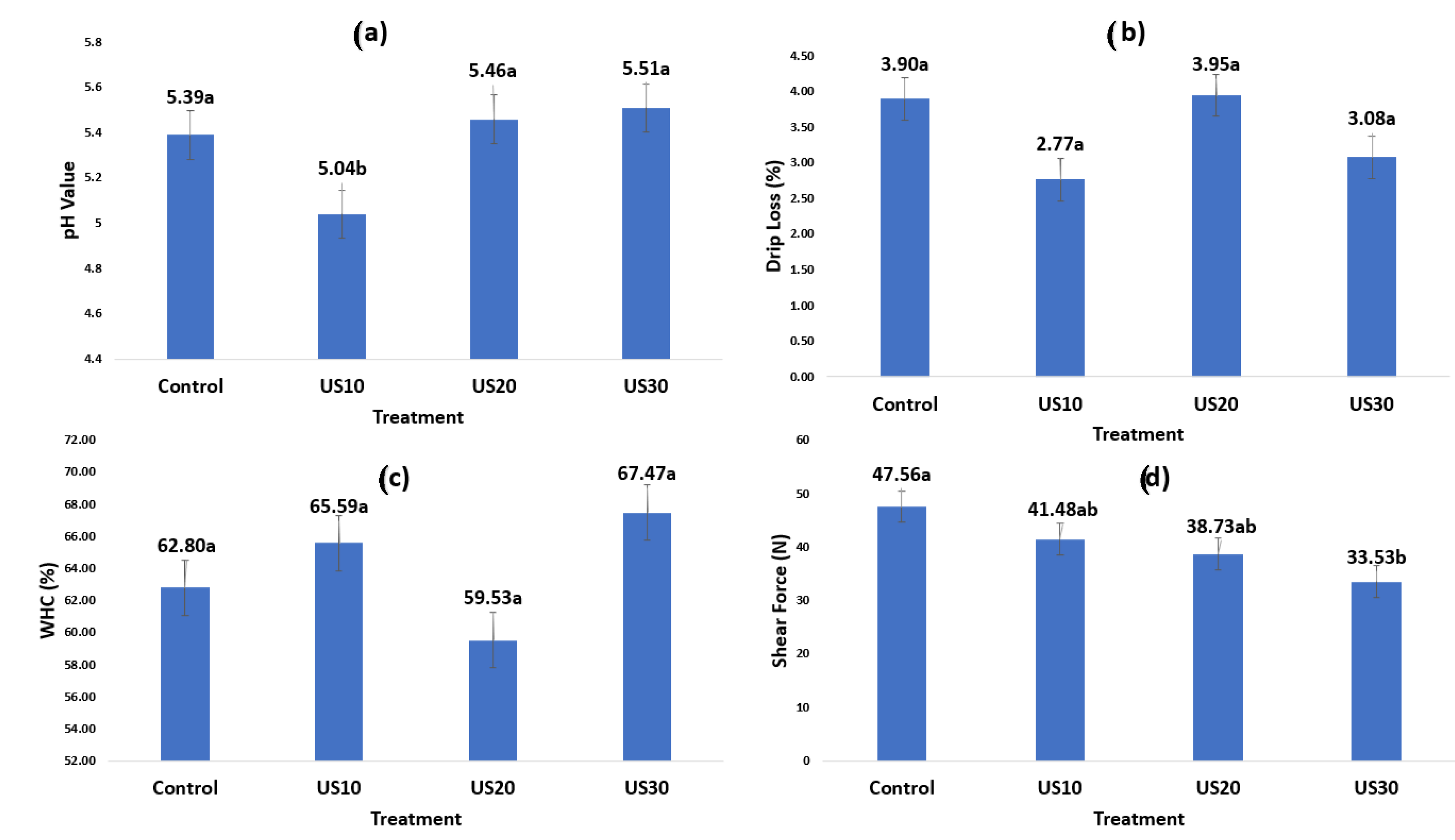
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ashokkumar, M.; Mason, T.J. Sonochemistry. In Kirk-Othmer Encyclopedia of Chemical Technology; John Wiley and Sons Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Ashokkumar, M. The characterization of acoustic cavitation bubbles an overview. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2011, 18, 864–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayasooriya, S.D.; Torley, P.J.; D’Arcy, B.R.; Bhandari, B.R. Effect of high power ultrasound and ageing on the physical properties of bovine Semitendinosus and Longissimus muscles. Meat Sci. 2007, 75, 628–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojha, K.S.; Keenan, D.F.; Bright, A.; Kerry, J.P.; Tiwari, B.K. Ultrasound assisted diffusion of sodium salt replacer and effect on physicochemical properties of pork meat. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 51, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, G.; Zhang, L.; Zhan, G.W.; Wu, J. Influence of ultrasound and proteolytic enzyme inhibitors on muscle degradation, tenderness, and cooking loss of hens during aging. Czech. J. Food Sci. 2012, 30, 195–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Awad, T.S.; Moharram, H.A.; Shaltout, O.E.; Asker, D.; Youssef, M.M. Applications of ultrasound in analysis, processing and quality control of food: A review. Food Res. Int. 2012, 48, 410–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chemat, F.; Zill-e-Huma; Khan, M.K. Applications of ultrasound in food technology: Processing preservation and extraction. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2011, 18, 813–835. [Google Scholar]
- Leong, T.; Ashokkumar, M.; Kentish, S. The fundamentals of power ultrasound-a review. Acoust. Aust. 2011, 39, 43–52. [Google Scholar]
- Dalecki, D. Mechanical bioeffects of ultrasound. Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2004, 6, 229–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, H.; Pahk, K.J.; Kim, H. A review of low-intensity focused ultrasound for neuromodulation. Biom. Eng. Lett. 2017, 7, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ter Haar, G. Therapeutic applications of ultrasound. Prog. Biophys. Mol. Biol. 2007, 93, 111–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jewell, M.L.; Solish, N.J.; Desilets, C.S. Noninvasive body sculpting technologies with an emphasis on high-intensity focused ultrasound. Aesthet. Plast. Surg. 2011, 35, 901–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honikel, K.O.; Hamm, R. Measurement of water-holding capacity and juiciness. In Quality Attributes and Their Measurement in Meat, Poultry and Fish Products; Pearson, A.M., Dutson, T.R., Eds.; Springer US: Boston, MA, USA, 1994; pp. 125–161. [Google Scholar]
- Grau, R.; Hamm, R. Eine einfache methode zur bestimmung der wasserbildung im muskel. Sci. Nat. 1953, 40, 29–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, T.C.; Ockerman, H.W. Water binding measurement of meat. J. Food Sci. 1981, 46, 697–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AMSA. Research Guidelines for Cookery, Sensory Evaluation, and Instrumental Tenderness Measurements of Meat; AMSA: Champaign, IL, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- SAS, Institute. SAS/STAT User’s Guide; SAS Inst. Inc.: Cary, NC, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Ripoll, G.; Albertí, P.; Joy, M. Influence of alfalfa grazing-based feeding systems on carcass fat colour and meat quality of light lambs. Meat Sci. 2012, 90, 457–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alarcon-Rojo, A.D.; Carrillo-Lopez, L.M.; Reyes-Villagrana, R.; Huerta-Jiménez, M.; Garcia-Galicia, I.A. Ultrasound and meat quality: A review. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2019, 55, 369–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peña-Gonzalez, E.; Alarcon-Rojo, A.D.; Garcia-Galicia, I.; Carrillo-Lopez, L.; Huerta-Jimenez, M. Ultrasound as a potential process to tenderize beef: Sensory and technological parameters. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2019, 53, 134–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stadnik, J.; Dolatowski, Z.J. Influence of sonication on Warner-Bratzler shear force, colour and myoglobin of beef (m. semimembranosus). Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2011, 233, 553–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sala, F.J.; Burgos, J.; Condón, S.; Lopez, P.; Raso, J. Effect of heat and ultrasound on microorganisms and enzymes. In New Methods of Food Preservation; Gould, J.W., Ed.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Portenlänger, G.; Heusinger, H. Chemical reactions induced by ultrasound and γ-rays in aqueous solutions of l-ascorbic acid. Carbohydr. Res. 1992, 232, 291–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Got, F.; Culioli, J.; Berge, P.; Vignon, X.; Astruc, T.; Quideau, J.M.; Lethiecq, M. Effects of high-intensity high-frequency ultrasound on aging rate, ultrastructure and some physico-chemical properties of beef. Meat Sci. 1999, 51, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawrie, R.A.; Ledward, D.A. Lawrie’s Meat Science; Woodhead Publishing: Cornwall, UK, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Belew, J.B.; Brooks, J.C.; McKenna, D.R.; Savell, J.W. Warner-Bratzler shear evaluations of 40 bovine muscles. Meat Sci. 2003, 64, 507–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Gonzalez, L.; Alarcon-Rojo, A.D.; Carrillo-Lopez, L.M.; Garcia-Galicia, I.A.; Huerta-Jimenez, M.; Paniwnyk, L. Does ultrasound equally improve the quality of beef? An insight into longissimus lumborum, infraspinatus and cleidooccipitalis. Meat Sci. 2020, 160, 107963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Galicia, I.A.; Gonzalez-Vacame, V.G.; Huerta-Jimenez, M.; Carrillo-Lopez, L.M.; Tirado-Gallegos, J.M.; Reyes-Villagrana, R.A.; Alarcon-Rojo, A.D. Ultrasound Versus traditional ageing: Physicochemical properties in beef longissimus lumborum. CyTA-J. Food 2020, 18, 675–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashokkumar, M.; Sunartio, D.; Kentish, S.; Mawson, R.; Simons, L.; Vilkhu, K.; Versteeg, C. Modification of food ingredients by ultrasound to improve functionality: A preliminary study on a model system. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2008, 9, 155–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sikes, A.L.; Mawson, R.; Stark, J.; Warner, R. Quality properties of pre-and post-rigor beef muscle after interventions with high frequency ultrasound. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2014, 21, 2138–2143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.-S.; Rhim, H.; Choi, M.J.; Lim, H.K.; Choi, D. High-intensity focused ultrasound therapy: An overview for radiologists. Korean J. Radiol. 2008, 9, 291–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bindal, V.N. Water-based couplants for general purpose use for ultrasonic NDT applications. J. Sci. Ind. Res. 2000, 59, 935–939. [Google Scholar]
- Theobald, P.; Zeqiri, B.; Avison, J. Couplants and their influence on AE sensor sensitivity. J. Acoust. Emiss. 2008, 26, 91–97. [Google Scholar]
- García-Álvarez, J.; Rosell, C.M.; García-Hernández, M.J.; Chávez, J.A.; Turó, A.; Salazar, J. Ultrasonic analysis to discriminate bread dough of different types of flour. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2012, 42, 012042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kennedy, J.E.; Ter Haar, G.R.; Cranston, D. High intensity focused ultrasound: Surgery of the future? Br. J. Radiol. 2003, 76, 590–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| CIE L*a*b* 1 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Treatment 2 | L* | a* | b* | C* | H* | ΔE |
| Control | 36.34 ± 8.98 a | 22.05 ± 1.28 a | 12.64 ± 1.75 a | 25.42 ± 1.10 a | 29.85 ± 14.38 a | 0.01 a |
| US10 | 38.05 ± 8.98 a | 17.41 ± 1.28 b | 10.76 ± 1.75 a | 20.49 ± 1.10 a | 31.64 ± 14.38 a | 6.77 b |
| US20 | 37.38 ± 8.98 a | 16.70 ± 1.28 b | 11.27 ± 1.75 a | 20.20 ± 1.10 a | 33.88 ± 14.38 a | 7.60 c |
| US30 | 37.97 ± 8.98 a | 19.37 ± 1.28 a,b | 11.65 ± 1.75 a | 22.64 ± 1.10 a | 31.15 ± 14.38 a | 5.26 d |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Caraveo-Suarez, R.O.; Garcia-Galicia, I.A.; Santellano-Estrada, E.; Carrillo-Lopez, L.M.; Huerta-Jimenez, M.; Vargas-Bello-Pérez, E.; Alarcon-Rojo, A.D. High-Frequency Focused Ultrasound on Quality Traits of Bovine Triceps brachii Muscle. Foods 2021, 10, 2074. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10092074
Caraveo-Suarez RO, Garcia-Galicia IA, Santellano-Estrada E, Carrillo-Lopez LM, Huerta-Jimenez M, Vargas-Bello-Pérez E, Alarcon-Rojo AD. High-Frequency Focused Ultrasound on Quality Traits of Bovine Triceps brachii Muscle. Foods. 2021; 10(9):2074. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10092074
Chicago/Turabian StyleCaraveo-Suarez, Reyes Omaro, Ivan Adrian Garcia-Galicia, Eduardo Santellano-Estrada, Luis Manuel Carrillo-Lopez, Mariana Huerta-Jimenez, Einar Vargas-Bello-Pérez, and Alma Delia Alarcon-Rojo. 2021. "High-Frequency Focused Ultrasound on Quality Traits of Bovine Triceps brachii Muscle" Foods 10, no. 9: 2074. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10092074
APA StyleCaraveo-Suarez, R. O., Garcia-Galicia, I. A., Santellano-Estrada, E., Carrillo-Lopez, L. M., Huerta-Jimenez, M., Vargas-Bello-Pérez, E., & Alarcon-Rojo, A. D. (2021). High-Frequency Focused Ultrasound on Quality Traits of Bovine Triceps brachii Muscle. Foods, 10(9), 2074. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10092074











