Xylitol and Maltitol Improve the Rheological Property of Kappa-Carrageenan
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Sample Preparation
2.2. Rheological Measurements
2.2.1. Strain Sweep Measurement
2.2.2. Temperature Sweep Measurement
2.2.3. Frequency Sweep Measurement
2.2.4. Small Deformation Oscillatory Shear Rheology
2.3. Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR) Spectroscopy Measurement
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
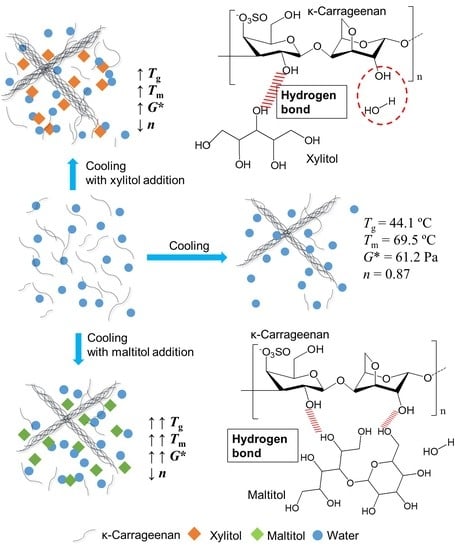
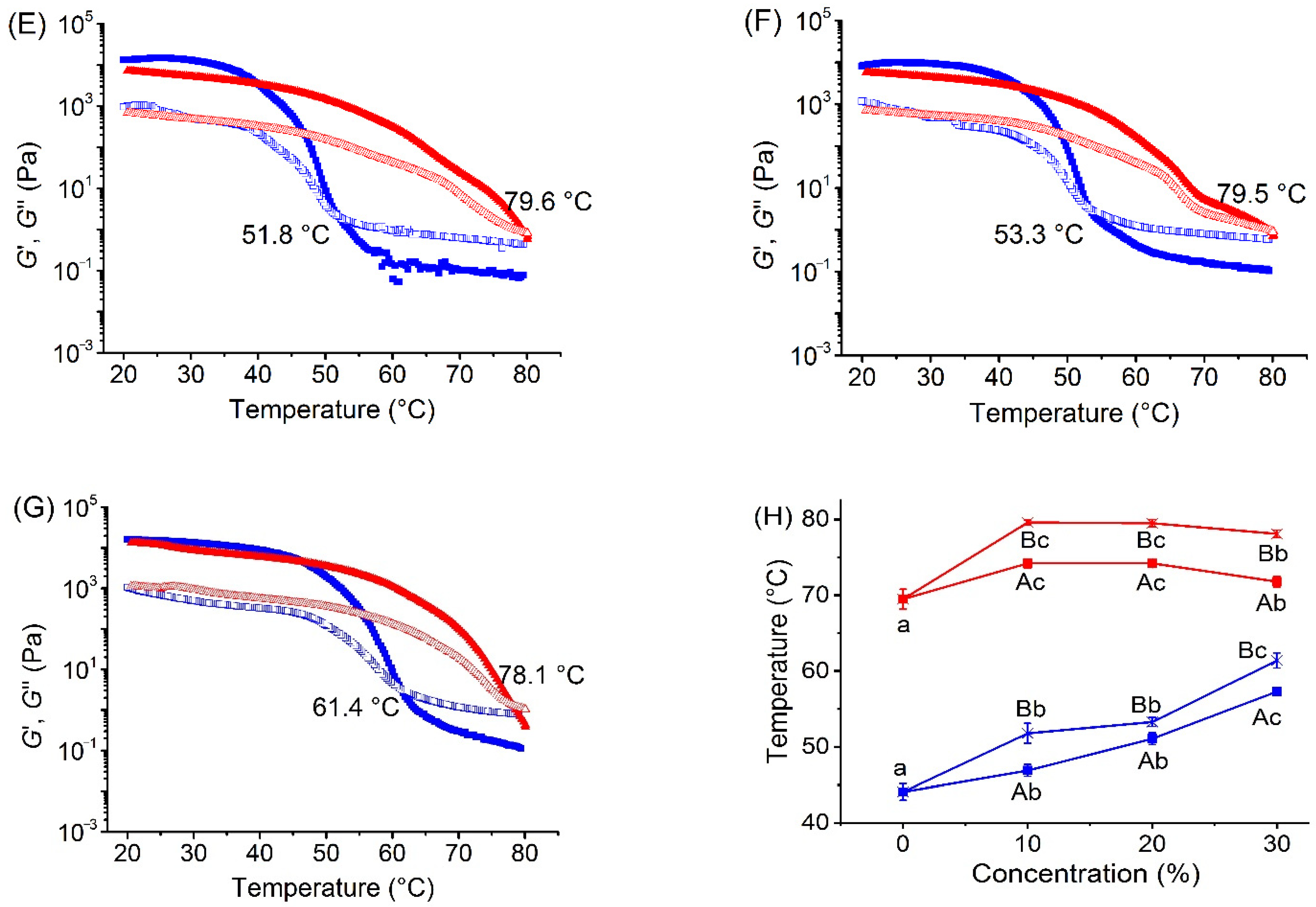
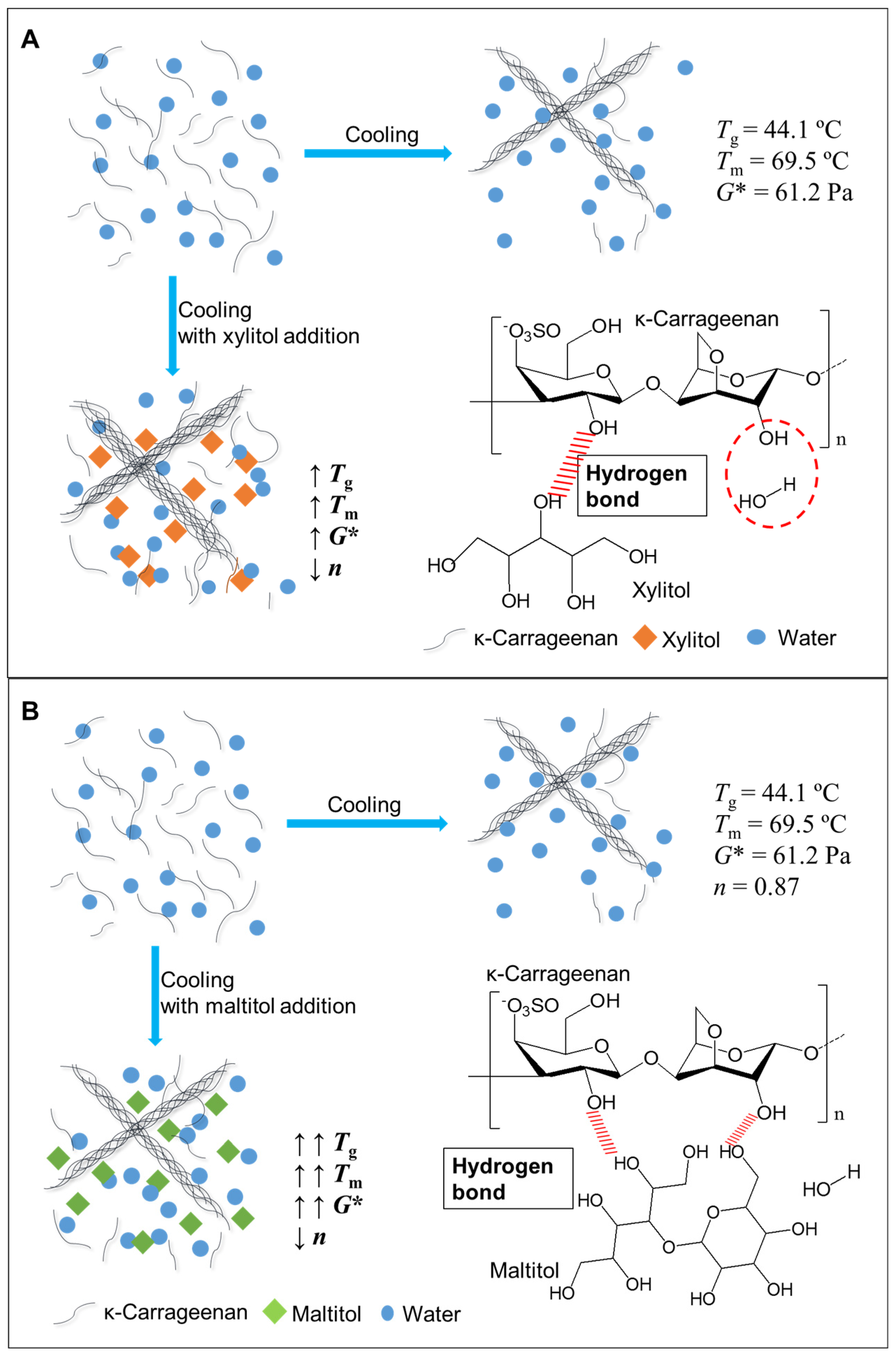
3.1. Effects of Xylitol and Maltitol on Thermoreversible Behaviour of κ-C
3.2. Effects of Xylitol and Maltitol on Critical Viscoelastic Behaviour of κ-C
3.3. Effects of Xylitol and Maltitol on Small and Large Deformation Rheological Characteristics of κ-C
3.4. Effect of Xylitol and Maltitol on the Structures of κ-C
3.5. Schematic Mechanism Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, L.; Ni, R.; Shao, Y.; Mao, S. Carrageenan and its applications in drug delivery. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 103, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickinson, E.; Pawlowsky, K. Influence of κ-carrageenan on the properties of a protein-stabilized emulsion. Food Hydrocoll. 1998, 12, 417–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakado, A.; Toyotama, A.; Yamamoto, M.; Nagano, R.; Okuzono, T.; Yamanaka, J. Thermoreversible crystallization of charged colloids due to adsorption/desorption of ionic surfactants. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2016, 465, 200–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derkach, S.R.; Ilyin, S.O.; Maklakova, A.A.; Kulichikhin, V.G.; Malkin, A.Y. The rheology of gelatin hydrogels modified by κ-carrageenan. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 63, 612–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyrby, M.; Petersen, R.; Larsen, J.; Rudolf, B.; Nørgaard, L.; Engelsen, S. Towards on-line monitoring of the composition of commercial carrageenan powders. Carbohydr. Polym. 2004, 57, 337–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rochas, C.; Rinaudo, M. Mechanism of gel formation in κ-carrageenan. Biopolym. Orig. Res. Biomol. 1984, 23, 735–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paoletti, S.; Delben, F.; Cesaro, A.; Grasdalen, H. Conformational transition of. kappa.-carrageenan in aqueous solution. Macromolecules 1985, 18, 1834–1841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Yang, H.; Yang, H. Effects of sucrose addition on the rheology and microstructure of κ-carrageenan gel. Food Hydrocoll. 2018, 75, 164–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasapis, S.; Mitchell, J.; Abeysekera, R.; MacNaughtan, W. Rubber-to-glass transitions in high sugar/biopolymer mixtures. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2004, 15, 298–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gekko, K.; Mugishima, H.; Koga, S. Effects of sugars and polyols on the sol-gel transition of k-carrageenan: Calorimetric study. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 1987, 9, 146–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, M.E. Xylitol. Top. Companion Anim. Med. 2013, 28, 18–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahiner, N. One step preparation of polymeric maltitol particles, from a sugar molecule, maltitol for biomedical applications. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2018, 89, 205–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keukenmeester, R.; Slot, D.; Rosema, N.; Van Loveren, C.; Van der Weijden, G. Effects of sugar-free chewing gum sweetened with xylitol or maltitol on the development of gingivitis and plaque: A randomized clinical trial. Int. J. Dent. Hyg. 2014, 12, 238–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bicer, A.; Sarı, A. Synthesis and thermal energy storage properties of xylitol pentastearate and xylitol pentapalmitate as novel solid–liquid PCMs. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2012, 102, 125–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penna, A.; Oliveira, M.; Tamime, A. Influence of carrageenan and total solids content on the rheological properties of lactic beverage made with yogurt and whey. J. Texture Stud. 2003, 34, 95–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Gao, S.; Yang, H. Effects of sucrose addition on the rheology and structure of iota-carrageenan. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 99, 105317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.; Theng, A.H.P.; Yang, D.; Yang, H. Influence of κ-carrageenan on the rheological behaviour of a model cake flour system. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 136, 110324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.; Zhao, X.; Mao, Y.; Chen, L.; Yang, H. Metabolite release and rheological properties of sponge cake after in vitro digestion and the influence of a flour replacer rich in dietary fibre. Food Res. Int. 2021, 144, 110355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chambon, F.; Winter, H.H. Linear viscoelasticity at the gel point of a crosslinking PDMS with imbalanced stoichiometry. J. Rheol. 1987, 31, 683–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Lv, N.; Ren, G.; Wu, R.; Wang, B.; Cao, Z.; Xie, H. Explore the interaction mechanism between zein and EGCG using multi-spectroscopy and molecular dynamics simulation methods. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 120, 106906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sow, L.C.; Nicole Chong, J.M.; Liao, Q.X.; Yang, H. Effects of κ-carrageenan on the structure and rheological properties of fish gelatin. J. Food Eng. 2018, 239, 92–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michon, C.; Cuvelier, G.; Launay, B. Concentration dependence of the critical viscoelastic properties of gelatin at the gel point. Rheol. Acta 1993, 32, 94–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.H.; Yang, X.Q.; Ahmad, I.; Li, L.; Wang, X.Y.; Liu, C. Rheological properties of κ-carrageenan and soybean glycinin mixed gels. Food Res. Int. 2008, 41, 219–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yuan, C.; Liu, Y.; Xu, D.; Cui, B. The influence of a hydroxypropyl-beta-cyclodextrin composite on the gelation of kappa-carrageenan. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 90, 276–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stenner, R.; Matubayasi, N.; Shimizu, S. Gelation of carrageenan: Effects of sugars and polyols. Food Hydrocoll. 2016, 54, 284–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loret, C.; Ribelles, P.; Lundin, L. Mechanical properties of κ-carrageenan in high concentration of sugar solutions. Food Hydrocoll. 2009, 23, 823–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oakenfull, D. Solvent structure and gelation of polysaccharides in concentrated solutions of simple sugars. In Gums and Stabilisers for the Food Industry 10; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2000; pp. 277–284. [Google Scholar]
- Del Carmen Núñez-Santiago, M.; Tecante, A. Rheological and calorimetric study of the sol–gel transition of κ-carrageenan. Carbohydr. Polym. 2007, 69, 763–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaucage, G. Small-angle scattering from polymeric mass fractals of arbitrary mass-fractal dimension. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 1996, 29, 134–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van der Sman, R. Sugar and polyol solutions as effective solvent for biopolymers. Food Hydrocoll. 2016, 56, 144–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Ordóñez, E.; Rupérez, P. FTIR-ATR spectroscopy as a tool for polysaccharide identification in edible brown and red seaweeds. Food Hydrocoll. 2011, 25, 1514–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.; Mao, Y.; Li, H.; Yang, H. Kappa-carrageenan enhances the gelation and structural changes of egg yolk via electrostatic interactions with yolk protein. Food Chem. 2021, 360, 129972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira, L.; Sousa, A.; Coelho, H.; Amado, A.M.; Ribeiro-Claro, P.J.A. Use of FTIR, FT-Raman and 13C-NMR spectroscopy for identification of some seaweed phycocolloids. Biomol. Eng. 2003, 20, 223–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mathlouthi, M.; Seuvre, A.-M.; Birch, G.G. Relationship between the structure and the properties of carbohydrates in aqueous solutions: Sweetness of chlorinated sugars. Carbohydr. Res. 1986, 152, 47–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Şen, M.; Erboz, E.N. Determination of critical gelation conditions of κ-carrageenan by viscosimetric and FT-IR analyses. Food Res. Int. 2010, 43, 1361–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salaün, F.; Bedek, G.; Devaux, E.; Dupont, D.; Gengembre, L. Microencapsulation of a cooling agent by interfacial polymerization: Influence of the parameters of encapsulation on poly (urethane–urea) microparticles characteristics. J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 370, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, C.; Gao, J.; Ye, H.; Ren, G.; Ma, X.; Xie, H.; Fang, S.; Lei, Q.; Fang, W. Development of ovalbumin-pectin nanocomplexes for vitamin D3 encapsulation: Enhanced storage stability and sustained release in simulated gastrointestinal digestion. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 106, 105926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Mao, Y.; Xiang, C.; Cao, M.; Ren, G.; Wang, K.; Ma, X.; Wu, D.; Xie, H. Preparation of β-lactoglobulin/gum arabic complex nanoparticles for encapsulation and controlled release of EGCG in simulated gastrointestinal digestion model. Food Chem. 2021, 354, 129516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasko, P.; Blackwell, J.; Koenig, J. Infrared and raman spectroscopy of carbohydrates.: Part II: Normal coordinate analysis of α-D-glucose. Carbohydr. Res. 1972, 23, 407–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishinari, K.; Watase, M. Effects of polyhydric alcohols on thermal and rheological properties of polysaccharide gels. Agric. Biol. Chem. 1987, 51, 3231–3238. [Google Scholar]
- Ako, K. Influence of elasticity on the syneresis properties of κ-carrageenan gels. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 115, 408–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangione, M.; Giacomazza, D.; Bulone, D.; Martorana, V.; San Biagio, P. Thermoreversible gelation of κ-Carrageenan: Relation between conformational transition and aggregation. Biophys. Chem. 2003, 104, 95–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugiyama, M.; Yuasa, C.; Hara, K.; Hiramatsu, N.; Nakamura, A.; Hayakawa, Y.; Maeda, Y. Structural change of κ-carrageenan gel near sol-gel transition point. Phys. B Condens. Matter 1997, 241, 999–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

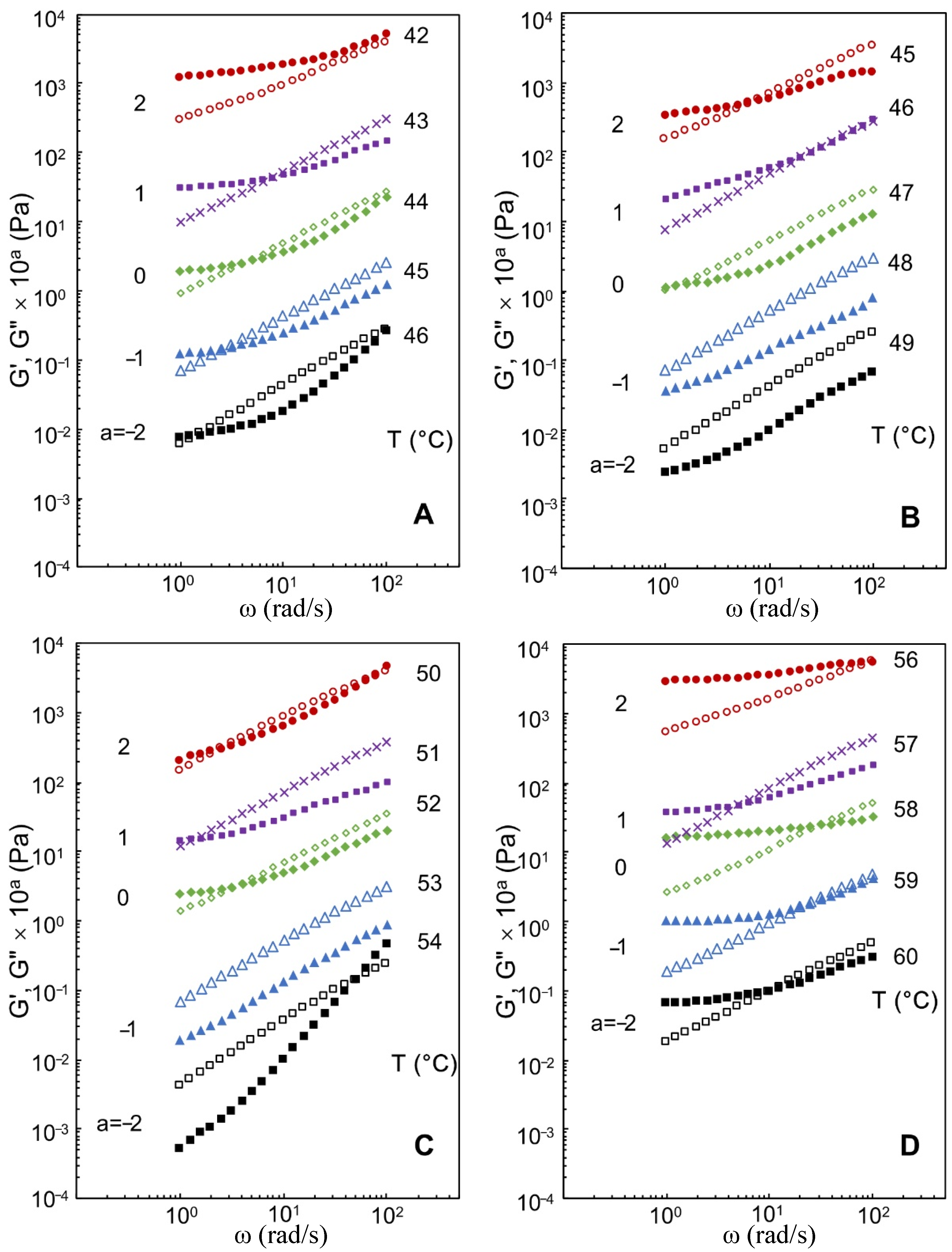


| Samples | Critical Relaxation Exponent n | Fractal Dimension df | Complex Modulus G* (Pa) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 0.87 ± 0.02 f | 2.30 ± 0.01 a | 61.2 ± 10.5 a |
| 10% xylitol | 0.51 ± 0.01 c | 2.40 ± 0.02 b | 192.3 ± 57.1 b |
| 20% xylitol | 0.48 ± 0.01 b | 2.40 ± 0.01 b | 229.7 ± 17.7 b,c |
| 30% xylitol | 0.35 ± 0.01 a | 2.43 ± 0.01 c | 289.4 ± 30.2 c |
| 10% maltitol | 0.82 ± 0.02 e | 2.31 ± 0.01 a | 251.2 ± 6.7 b,c |
| 20% maltitol | 0.79 ± 0.01 d | 2.32 ± 0.01 a | 312.5 ± 17.7 c |
| 30% maltitol | 0.78 ± 0.01 d | 2.32 ± 0.01 a | 411.5 ± 67.0 d |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, M.; Mao, Y.; Mao, Y.; Yang, H. Xylitol and Maltitol Improve the Rheological Property of Kappa-Carrageenan. Foods 2022, 11, 51. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11010051
Huang M, Mao Y, Mao Y, Yang H. Xylitol and Maltitol Improve the Rheological Property of Kappa-Carrageenan. Foods. 2022; 11(1):51. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11010051
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Min, Yihan Mao, Yuzhu Mao, and Hongshun Yang. 2022. "Xylitol and Maltitol Improve the Rheological Property of Kappa-Carrageenan" Foods 11, no. 1: 51. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11010051
APA StyleHuang, M., Mao, Y., Mao, Y., & Yang, H. (2022). Xylitol and Maltitol Improve the Rheological Property of Kappa-Carrageenan. Foods, 11(1), 51. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11010051