The Stance4Health Project: Evaluating a Smart Personalised Nutrition Service for Gut Microbiota Modulation in Normal- and Overweight Adults and Children with Obesity, Gluten-Related Disorders or Allergy/Intolerance to Cow’s Milk
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Eligibility Criteria
- (1)
- Apparently healthy adult subjects (both sexes), aged 20–65 years, with a body mass index (BMI) between 20–28 kg/m2, stable weight, ability to use a smartphone, and Internet connection availability. Exclusion criteria are the diagnosis of chronic gastrointestinal (GI) disorders, coeliac disease, or chronic diseases such as diabetes or other metabolic diseases; present pregnancy or lactation (<6 weeks before study start), or intention to become pregnant in the next 12 weeks; recent inflammation and/or long-term use of an-ti-inflammatory drugs; medically prescribed diet or specific dietary regimens for any reasons (i.e., high-protein diet, vegetarianism, veganism, etc.); antibiotic treatment (<3 months before study start); intake of antioxidant, pre- or probiotic supplements (<1 month before study start); intense physical activity (>10 h/week); alcohol consumption >21 drinks/week for men and >14 drinks/week for women.
- (2)
- Normal weight children (of both sexes), aged 6–11 years, with a BMI >5th and <85th percentile for age, gender, and height. Exclusion criteria are the diagnosis of chronic GI disorders and any other chronic disease, elimination diet, intake of probiotics (<2 weeks before study start).
- (3)
- Children (of both sexes) with obesity, aged 6–11 years, with a BMI ≥95th percentile for age, gender, and height. Exclusion criteria are the diagnosis of chronic GI disorders and endocrinopathies, intake of probiotics (<2 weeks before study start).
- (4)
- Children (of both sexes) with gluten-related disorders, aged 6–11 years, diagnosed with coeliac disease or wheat allergy (sIgE), on elimination diet. The exclusion criteria are the absence of symptoms.
- (5)
- Children (of both sexes) with allergy/intolerance to cow’s milk, aged 6–11 years, with an IgE-mediated milk allergy on an elimination diet from infancy, lactose intolerance (symptoms plus breath hydrogen positive test), overgrown IgE-mediated milk allergy but current aversion for milk, or nondefinable phenotype (children who avoid milk but do not belong to any of the previous phenotypes). Exclusion criteria are the diagnosis of other GI comorbidities.
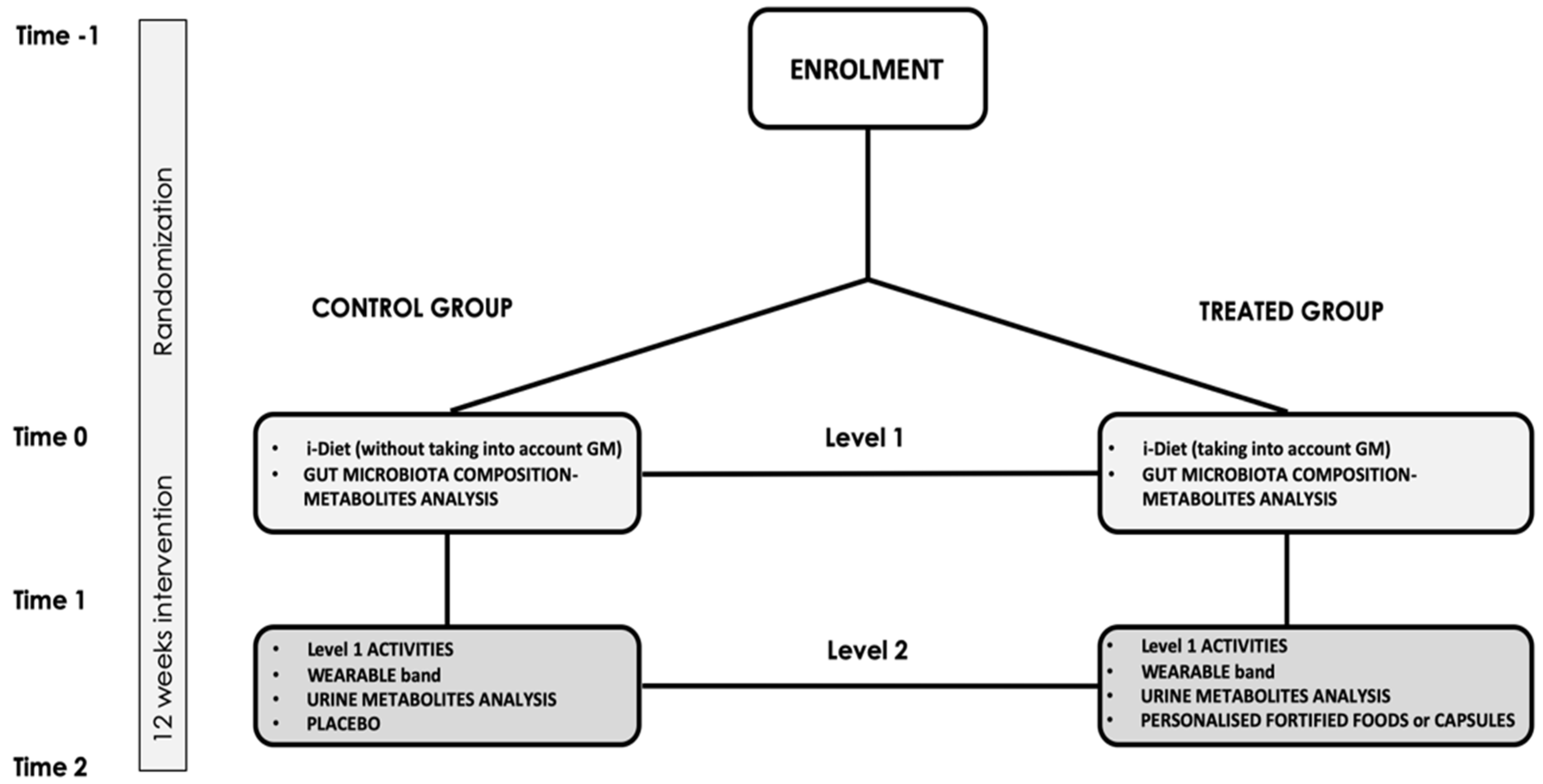
2.3. Intervention Study and Mobile App i-Diet Stance4Health
2.4. Participants Timeline
2.5. Outcome Measures
2.6. Sample Size and Power Calculation
2.7. Recruitment and Randomization
2.8. Blinding
2.9. Data Collection
2.10. Compliance
2.11. Anthropometric Measurements and Body Composition
2.12. Blood Pressure and Heart Rate
2.13. Stool Samples
2.14. Urine Samples
2.15. Blood Samples
2.16. Storage of Biological Specimens
2.17. Data Management
2.18. Statistical Analysis
2.19. Monitoring
3. Results
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wells, J.C.; Sawaya, A.L.; Wibaek, R.; Mwangome, M.; Poullas, M.S.; Yajnik, C.S.; Demaio, A. The double burden of malnutrition: Aetiological pathways and consequences for health. Lancet 2020, 395, 75–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauria, F.; Russo, M.D.; Formisano, A.; De Henauw, S.; Hebestreit, A.; Hunsberger, M.; Krogh, V.; Intemann, T.; Lissner, L.; Molnar, D.; et al. Ultra-processed foods consumption and diet quality of European children, adolescents and adults: Results from the I. Family study. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2021, 31, 3031–3043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, R.K.; Chang, H.-W.; Yan, D.; Lee, K.M.; Ucmak, D.; Wong, K.; Abrouk, M.; Farahnik, B.; Nakamura, M.; Zhu, T.H.; et al. Influence of diet on the gut microbiome and implications for human health. J. Transl. Med. 2017, 15, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rabassa, M.; Zamora-Ros, R.; Urpi-Sarda, M.; Bandinelli, S.; Ferrucci, L.; Andres-Lacueva, C.; Cherubini, A. Association of habitual dietary resveratrol exposure with the development of frailty in older age: The Invecchiare in Chianti study. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2015, 102, 1534–1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hills, R.D., Jr.; Pontefract, B.A.; Mishcon, H.R.; Black, C.A.; Sutton, S.C.; Theberge, C.R. Gut Microbiome: Profound Implications for Diet and Disease. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pecora, F.; Persico, F.; Gismondi, P.; Fornaroli, F.; Iuliano, S.; De’Angelis, G.L.; Esposito, S. Gut Microbiota in Celiac Disease: Is There Any Role for Probiotics? Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Ho, H.-E.; Bunyavanich, S. The gut microbiome in food allergy. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2019, 122, 276–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Heiss, C.N.; Olofsson, L.E. Gut Microbiota-Dependent Modulation of Energy Metabolism. J. Innate Immun. 2018, 10, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres-Fuentes, C.; Schellekens, H.; Dinan, T.G.; Cryan, J.F. The microbiota–gut–brain axis in obesity. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 2, 747–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrea, L.; Annunziata, G.; Bordoni, L.; Muscogiuri, G.; Colao, A.; Savastano, S. Nutrigenetics—Personalized nutrition in obesity and cardiovascular diseases. Int. J. Obes. Suppl. 2020, 10, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Obesity and Overweight. Fact Sheet No. 311. May 2012. (accessed on 18 March 2022).
- Gujral, N. Celiac disease: Prevalence, diagnosis, pathogenesis and treatment. World J. Gastroenterol. 2012, 18, 6036–6059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nwaru, B.; Hickstein, L.; Panesar, S.S.; Muraro, A.; Werfel, T.; Cardona, V.; Dubois, A.E.J.; Halken, S.; Hoffmann-Sommergruber, K.; Poulsen, L.K.; et al. The epidemiology of food allergy in Europe: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Allergy 2014, 69, 62–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Du Toit, G.; Foong, R.-X.; Lack, G. The role of dietary interventions in the prevention of IgE-mediated food allergy in children. Pediatr. Allergy Immunol. 2017, 28, 222–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Montero, C.; Fraile-Martínez, O.; Gómez-Lahoz, A.; Pekarek, L.; Castellanos, A.; Noguerales-Fraguas, F.; Coca, S.; Guijarro, L.; García-Honduvilla, N.; Asúnsolo, A.; et al. Nutritional Components in Western Diet versus Mediterranean Diet at the Gut Microbiota–Immune System Interplay. Implications for Health and Disease. Nutrients 2021, 13, 699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molino, S.; Lerma-Aguilera, A.; Jiménez-Hernández, N.; Gosalbes, M.J.; Rufián-Henares, J.Á.; Francino, M.P. Enrichment of Food with Tannin Extracts Promotes Healthy Changes in the Human Gut Microbiota. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 625782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinojosa-Nogueira, D.; Pérez-Burillo, S.; Navajas-Porras, B.; Ortiz-Viso, B.; de la Cueva, S.P.; Lauria, F.; Fatouros, A.; Priftis, K.N.; González-Vigil, V.; Rufián-Henares, J.Á. Development of an Unified Food Composition Database for the European Project “Stance4Health”. Nutrients 2021, 13, 4206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Maldonado, A.; Pastoriza, S.; Rufián-Henares, J.Á. Assessing the antioxidant and metabolic effect of an alpha-lipoic acid and acetyl-L-carnitine nutraceutical. Curr. Res. Food Sci. 2021, 4, 336–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henares, J. MetaCliniq: A metabolomics tool for the development of a personalised nutrition service within the Stance4Health project. Proj. Repos. J. 2021, 10, 42–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De’, R.; Pandey, N.; Pal, A. Impact of digital surge during Covid-19 pandemic: A viewpoint on research and practice. Int. J. Inf. Manag. 2020, 55, 102171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pala, V.; Reisch, L.A.; Lissner, L. on behalf of the IDEFICS and I.Family consortia. Dietary behaviour in children, adolescents and families: The Eating Habits Questionnaire (EHQ). In Instruments for Health Surveys in Children and Adolescents; Bammann, K., Lissner, L., Pigeot, I., Ahrens, W., Eds.; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 103–133. [Google Scholar]
- Davis, S.C.; Yadav, J.; Barrow, S.D.; Robertson, B.K. Gut microbiome diversity influenced more by the Westernized dietary regime than the body mass index as assessed using effect size statistic. MicrobiologyOpen 2017, 6, e00476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maskarinec, G.; Hullar, M.A.J.; Monroe, K.R.; Shepherd, J.; Hunt, J.; Randolph, T.W.; Wilkens, L.R.; Boushey, C.J.; Le Marchand, L.; Lim, U.; et al. Fecal Microbial Diversity and Structure Are Associated with Diet Quality in the Multiethnic Cohort Adiposity Phenotype Study. J. Nutr. 2019, 149, 1575–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, T.S.; Rampelli, S.; Jeffery, I.B.; Santoro, A.; Neto, M.; Capri, M.; Giampieri, E.; Jennings, A.; Candela, M.; Turroni, S.; et al. Mediterranean diet intervention alters the gut microbiome in older people reducing frailty and improving health status: The NU-AGE 1-year dietary intervention across five European countries. Gut 2020, 69, 1218–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Johnson, A.; Vangay, P.; Al-Ghalith, G.A.; Hillmann, B.M.; Ward, T.L.; Shields-Cutler, R.R.; Kim, A.D.; Shmagel, A.K.; Syed, A.N.; Walter, J.; et al. Daily Sampling Reveals Personalized Diet-Microbiome Associations in Humans. Cell Host Microbe 2019, 25, 789–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Study Period | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Enrollment | Allocation | Middle of the Study | End of the Study | |
| PROTOCOL ACTIVITY | Day −60 to 1 | Day 0 | Week 6 | Week 12 |
| TIMEPOINT | −T1 | T0 | T1 | T2 |
| ENROLLMENT: | ||||
| Eligibility screen | X | |||
| Informed consent | X | |||
| Demographic details | X | |||
| Lifestyle questionnaire | X | X | ||
| FFQ_IDEFICS/i.Family | X | X | ||
| FFQ_S4H | X | X | ||
| Bowel habits questionnaire | X | X | ||
| Allocation | X | |||
| INTERVENTIONS: | ||||
| Study populations—Level 1 |  | |||
| Study populations—Level 2 |  | |||
| ASSESMENTS: | ||||
| Nutritional app i.Diet |  | |||
| Anthropometric measurements | X | X | ||
| Stool samples | X | X | X | |
| Urine samples | X | |||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dello Russo, M.; Russo, P.; Rufián-Henares, J.Á.; Hinojosa-Nogueira, D.; Pérez-Burillo, S.; de la Cueva, S.P.; Rohn, S.; Fatouros, A.; Douros, K.; González-Vigil, V.; et al. The Stance4Health Project: Evaluating a Smart Personalised Nutrition Service for Gut Microbiota Modulation in Normal- and Overweight Adults and Children with Obesity, Gluten-Related Disorders or Allergy/Intolerance to Cow’s Milk. Foods 2022, 11, 1480. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11101480
Dello Russo M, Russo P, Rufián-Henares JÁ, Hinojosa-Nogueira D, Pérez-Burillo S, de la Cueva SP, Rohn S, Fatouros A, Douros K, González-Vigil V, et al. The Stance4Health Project: Evaluating a Smart Personalised Nutrition Service for Gut Microbiota Modulation in Normal- and Overweight Adults and Children with Obesity, Gluten-Related Disorders or Allergy/Intolerance to Cow’s Milk. Foods. 2022; 11(10):1480. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11101480
Chicago/Turabian StyleDello Russo, Marika, Paola Russo, José Ángel Rufián-Henares, Daniel Hinojosa-Nogueira, Sergio Pérez-Burillo, Silvia Pastoriza de la Cueva, Sascha Rohn, Alexandra Fatouros, Konstantinos Douros, Verónica González-Vigil, and et al. 2022. "The Stance4Health Project: Evaluating a Smart Personalised Nutrition Service for Gut Microbiota Modulation in Normal- and Overweight Adults and Children with Obesity, Gluten-Related Disorders or Allergy/Intolerance to Cow’s Milk" Foods 11, no. 10: 1480. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11101480
APA StyleDello Russo, M., Russo, P., Rufián-Henares, J. Á., Hinojosa-Nogueira, D., Pérez-Burillo, S., de la Cueva, S. P., Rohn, S., Fatouros, A., Douros, K., González-Vigil, V., Epstein, D., Francino, M. P., Siani, A., & Lauria, F. (2022). The Stance4Health Project: Evaluating a Smart Personalised Nutrition Service for Gut Microbiota Modulation in Normal- and Overweight Adults and Children with Obesity, Gluten-Related Disorders or Allergy/Intolerance to Cow’s Milk. Foods, 11(10), 1480. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11101480











