Dispersive Liquid-Liquid Microextraction Followed by HS-SPME for the Determination of Flavor Enhancers in Seafood Using GC-MS
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
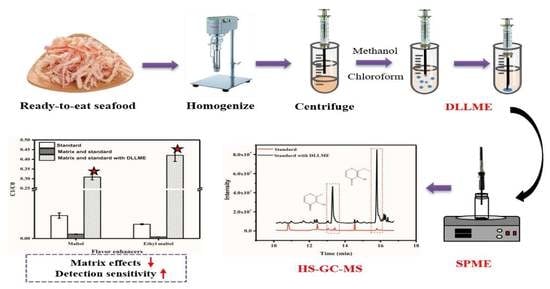
2.2. Preprocessing Method of DLLME/HS-SPME
2.3. GC-MS Determination of Flavor Enhancers
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Optimization of the DLLME/HS-SPME Conditions
3.2. Verification of Pretreatment Effect of DLLME
3.3. Evaluation of the Analytical Method
3.4. Determination of Maltol and Ethyl Maltol in Authentic Seafood
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alonso, M.; Zamora, L.L.; Calatayud, J.M. Determination of the flavor enhancer maltol through a FIA—Direct chemiluminescence procedure. Anal. Chim. Acta 2001, 438, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.J.; Moon, T.W.; Lee, J. Increases of 2-furanmethanol and maltol in Korean red ginseng during explosive puffing process. J. Food Sci. 2010, 75, C147–C151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altunay, N.; Gurkan, R.; Orhan, U. Indirect determination of the flavor enhancer maltol in foods and beverages through flame atomic absorption spectrometry after ultrasound assisted-cloud point extraction. Food Chem. 2017, 235, 308–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Zhao, L.; Sun, Z.; Cheng, N.; Xue, X.; Wu, L.; Cao, W. Determination of three flavor enhancers using HPLC-ECD and its application in detecting adulteration of honey. Anal. Methods 2018, 10, 743–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanchin, G.; Dainese, F.; Trucco, M.; Mainardi, F.; Mampreso, E.; Maggioni, F. Osmophobia in migraine and tension-type headache and its clinical features in patients with migraine. Cephalalgia 2007, 27, 1061–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Wei, M.; Hu, Y.; Yang, Y.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, F. Simultaneous Determination of Maltol, Ethyl Maltol, Vanillin, and Ethyl Vanillin in Foods by Isotope Dilution Headspace Solid-Phase Microextraction Coupled with Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry. Food Anal. Methods 2019, 12, 1725–1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domotor, O.; Aicher, S.; Schmidlehner, M.; Novak, M.S.; Roller, A.; Jakupec, M.A.; Kandioller, W.; Hartinger, C.G.; Keppler, B.K.; Enyedy, E.A. Antitumor pentamethylcyclopentadienyl rhodium complexes of maltol and allomaltol: Synthesis, solution speciation and bioactivity. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2014, 134, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gralla, E.J.; Stebbins, R.B.; Coleman, G.L.; Delahunt, C.S. Toxicity studies with ethyl maltol. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 1969, 15, 604–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Risner, C.H.; Kiser, M.J. High-performance liquid chromatography procedure for the determination of flavor enhancers in consumer chocolate products and artificial flavors. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2008, 88, 1423–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Zhang, B.; Wang, Y.; Hou, X.; He, L. Determination of flavor enhancers in milk powder by one-step sample preparation and two-dimensional liquid chromatography. J. Sep. Sci. 2014, 37, 920–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, L. Development and validation of a LC-MS/MS method for the determination of isoeugenol in finfish. Food Chem. 2017, 228, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goncalves, C.; Alpendurada, M.F. Solid-phase micro-extraction-gas chromatography-(tandem) mass spectrometry as a tool for pesticide residue analysis in water samples at high sensitivity and selectivity with confirmation capabilities. J. Chromatogr. A 2004, 1026, 239–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alder, L.; Greulich, K.; Kempe, G.; Vieth, B. Residue analysis of 500 high priority pesticides: Better by GC-MS or LC-MS/MS? Mass Spectrom. Rev. 2010, 25, 838–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guerra, P.V.; Yaylayan, V.A. Double Schiff base adducts of 2,3-butanedione with glycine: Formation of pyrazine rings with the participation of amino acid carbon atoms. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 11440–11445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, X.; Lv, Y.; Wen, R.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Q.; Kong, B. Characterization of selected Harbin red sausages on the basis of their flavour profiles using HS-SPME-GC/MS combined with electronic nose and electronic tongue. Meat Sci. 2021, 172, 108345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panseri, S.; Soncin, S.; Chiesa, L.M.; Biondi, P.A. A headspace solid-phase microextraction gas-chromatographic mass-spectrometric method (HS-SPME-GC/MS) to quantify hexanal in butter during storage as marker of lipid oxidation. Food Chem. 2011, 127, 886–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamm, S.; Bleton, J.; Connan, J.; Tchapla, A. A chemical investigation by headspace SPME and GC-MS of volatile and semi-volatile terpenes in various olibanum samples. Phytochemistry 2005, 66, 1499–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezquerro, Ó.; Pons, B.; Tena, M.A.T. Multiple headspace solid-phase microextraction for the quantitative determination of volatile organic compounds in multilayer packagings. J. Chromatogr. A 2003, 999, 155–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duran Guerrero, E.; Chinnici, F.; Natali, N.; Marin, R.N.; Riponi, C. Solid-phase extraction method for determination of volatile compounds in traditional balsamic vinegar. J. Sep. Sci. 2008, 31, 3030–3036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Lin, H.; Sui, J.; Cao, L. The effect of fish matrix on the enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay of antibiotics. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2013, 93, 1603–1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhang, J.; Liu, Y. Optimization of solid-phase-extraction cleanup and validation of quantitative determination of eugenol in fish samples by gas chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2015, 407, 6563–6568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Liu, H.; Wang, C.; Wu, L.; Liu, D. Determination of eugenol in fish and shrimp muscle tissue by stable isotope dilution assay and solid-phase extraction coupled gas chromatography-triple quadrupole mass spectrometry. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2016, 408, 6537–6544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouyang, G.; Pawliszyn, J. SPME in environmental analysis. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2006, 386, 1059–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortada, C.; Vidal, L.; Canals, A. Determination of nitroaromatic explosives in water samples by direct ultrasound-assisted dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction followed by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. Talanta 2011, 85, 2546–2552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, T.-T.; Liang, X.; Wu, J.-H.; Qin, L.; Tan, M.-Q.; Zhu, B.-W.; Xu, X.-B. Isotope dilution quantification of 5-hydroxymethyl-2-furaldehyde in beverages using vortex-assisted liquid–liquid microextraction coupled with ESI-HPLC-MS/MS. Anal. Methods 2017, 9, 3839–3844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, M.; Man, Y.; Ma, H.; Luan, F.; Liu, H.; Gao, Y. Determination of Vanillin in Milk Powder by Capillary Electrophoresis Combined with Dispersive Liquid-Liquid Microextraction. Food Anal. Methods 2015, 9, 1706–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pizarro, C.; Sáenz-González, C.; Pérez-Del-Notario, N.; González-Sáiz, J. Development of a dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction method for the simultaneous determination of the main compounds causing cork taint and Brett character in wines using gas chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2011, 1218, 1576–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khalilian, F.; Rezaee, M. Ultrasound-Assisted Extraction Followed by Solid-Phase Extraction Followed by Dispersive Liquid–Liquid Microextraction for the Sensitive Determination of Diazinon and Chlorpyrifos in Rice. Food Anal. Methods 2016, 10, 885–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agus, B.; Hussain, N.; Selamat, J. Quantification of PAH4 in roasted cocoa beans using QuEChERS and dispersive liquid-liquid micro-extraction (DLLME) coupled with HPLC-FLD. Food Chem. 2020, 303, 125398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galuch, M.B.; Magon, T.; Silveira, R.; Nicácio, A.; Pizzo, J.S.; Bonafe, E.G.; Maldaner, L.; Santos, O.O.; Visentainer, J.V. Determination of acrylamide in brewed coffee by dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction (DLLME) and ultra-performance liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry (UPLC-MS/MS). Food Chem. 2019, 282, 120–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viñas, P.; Campillo, N.; López-García, I.; Hernández-Córdoba, M. Dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction in food analysis. A critical review. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2014, 406, 2067–2099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, X.; Feng, T.-T.; Wu, J.-H.; Du, M.; Qin, L.; Wang, Z.-Y.; Xu, X.-B. Vortex-Assisted Liquid-Liquid Micro-extraction Followed by Head Space Solid Phase Micro-extraction for the Determination of Eugenol in Fish Using GC-MS. Food Anal. Methods 2017, 11, 790–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, N.S.; Utture, S.; Banerjee, K.; Ahammed Shabeer, T.P.; Kamble, N.; Mathew, S.; Ashok Kumar, K. Multiresidue analysis of multiclass pesticides and polyaromatic hydrocarbons in fatty fish by gas chromatography tandem mass spectrometry and evaluation of matrix effect. Food Chem. 2016, 196, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Y.J.; Bi, A.Q.; Wang, X.Y.; Qin, L.; Du, M.; Dong, L.; Xu, X.B. Dispersive solid-phase extraction and dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction for the determination of flavor enhancers in ready-to-eat seafood by HPLC-PDA. Food Chem. 2020, 309, 125753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.-B.; Fan, Y.-C.; Qian, Y.-L.; Tang, H.-F.; Ruan, Z.; Liu, D.-H.; Wang, H. Determination of spices in food samples by ionic liquid aqueous solution extraction and ion chromatography. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2014, 25, 465–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Hu, B.; Chen, X.; Miao, Q.; Wang, C.; Zhu, Z.; Han, C. Determination of four flavorings in infant formula by solid-phase extraction and gas chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 10881–10888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Zhang, K.; Li, Y.; Li, K.; Ye, B. Study on the electrochemical properties of maltol at a carbon paste electrode and its analytical application. Anal. Methods 2012, 4, 3206–3211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Compounds | Maltol | Ethyl Maltol |
|---|---|---|
| Matrix effect (%) | −81.12% | −88.72% |
| Enrichment factor | 19 | 66 |
| Calibration range (μg/g) | 0.25–25.00 | 0.05–40.00 |
| Regression equation a | y = 0.2806x − 0.0142 | y = 0.6744x + 0.2082 |
| R2 | 0.9975 | 0.9967 |
| LOD (μg/kg) b | 5.0 | 2.5 |
| LOQ (μg/kg) c | 15.0 | 5.0 |
| Intraday precision RSD (n = 3, %) | 5.7 | 2.8 |
| Interday precision RSD (n = 3, %) | 4.3 | 3.5 |
| Detection Methods | Matrix | Analytes | LOD | LOQ | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DSPE/DLLME-HPLC-PDA | Ready-to-eat seafood | Flavor enhancers (maltol, ethyl maltol, vanillin, methyl vanillin, ethyl vanillin) | 60–150 μg/kg | 200–500 μg/kg | [34] |
| IL-IC | Biscuit, chocolate, and milk powder | Spices (vanillin, ethyl vanillin and ethyl maltol) | 20–45 μg/kg | 70–150 μg/kg | [35] |
| SPE-GC–MS | Infant formula | Flavoring agents (vanillin, methyl vanillin, ethyl vanillin and coumarin) | - | 10 µg/kg | [36] |
| DLLME/HS-SPME/GC-MS | Seafood | Flavor enhancers (maltol, ethyl maltol) | 2.5–5.0 µg/kg | 5–15 µg/kg | This work |
| Flavor Enhancers | Spiking Level (μg/g) | Recovery (RSD%) |
|---|---|---|
| Maltol | 1.00 | 89.0 (4.2) |
| 12.50 | 98.1(4.8) | |
| 20.00 | 118.6 (3.3) | |
| Ethyl maltol | 2.50 | 106.1 (6.8) |
| 12.50 | 96.0 (1.1) | |
| 25.00 | 112.1 (4.4) |
| Sample | Maltol (μg/g) | Ethyl Maltol (μg/g) |
|---|---|---|
| Squid larvae | 0.7 (5.5) | 1.1 (9.0) |
| Dried squid | 1.4 (8.0) | 34.7 (7.5) |
| Seasoned kelp | 2.2 (4.6) | 5.3 (3.8) |
| Crispy yellow croaker | 0.7 (8.8) | 0.9 (7.1) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Luo, X.; Wang, X.; Du, M.; Xu, X. Dispersive Liquid-Liquid Microextraction Followed by HS-SPME for the Determination of Flavor Enhancers in Seafood Using GC-MS. Foods 2022, 11, 1507. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11101507
Luo X, Wang X, Du M, Xu X. Dispersive Liquid-Liquid Microextraction Followed by HS-SPME for the Determination of Flavor Enhancers in Seafood Using GC-MS. Foods. 2022; 11(10):1507. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11101507
Chicago/Turabian StyleLuo, Xiaolin, Xiaoyuan Wang, Ming Du, and Xianbing Xu. 2022. "Dispersive Liquid-Liquid Microextraction Followed by HS-SPME for the Determination of Flavor Enhancers in Seafood Using GC-MS" Foods 11, no. 10: 1507. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11101507
APA StyleLuo, X., Wang, X., Du, M., & Xu, X. (2022). Dispersive Liquid-Liquid Microextraction Followed by HS-SPME for the Determination of Flavor Enhancers in Seafood Using GC-MS. Foods, 11(10), 1507. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11101507