Pickering Emulsion Stabilized by Tea Seed Cake Protein Nanoparticles as Lutein Carrier
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of TSCP
2.3. Preparation and Characteristics of TSCPN
2.4. Preparation and Characteristics of TSCPN-Stabilized Pickering Emulsion
2.5. Storage Stability
2.6. In Vitro Digestion Model
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Result and Discussion
3.1. Effect of TSCP Concentrations on the Properties of TSCPN
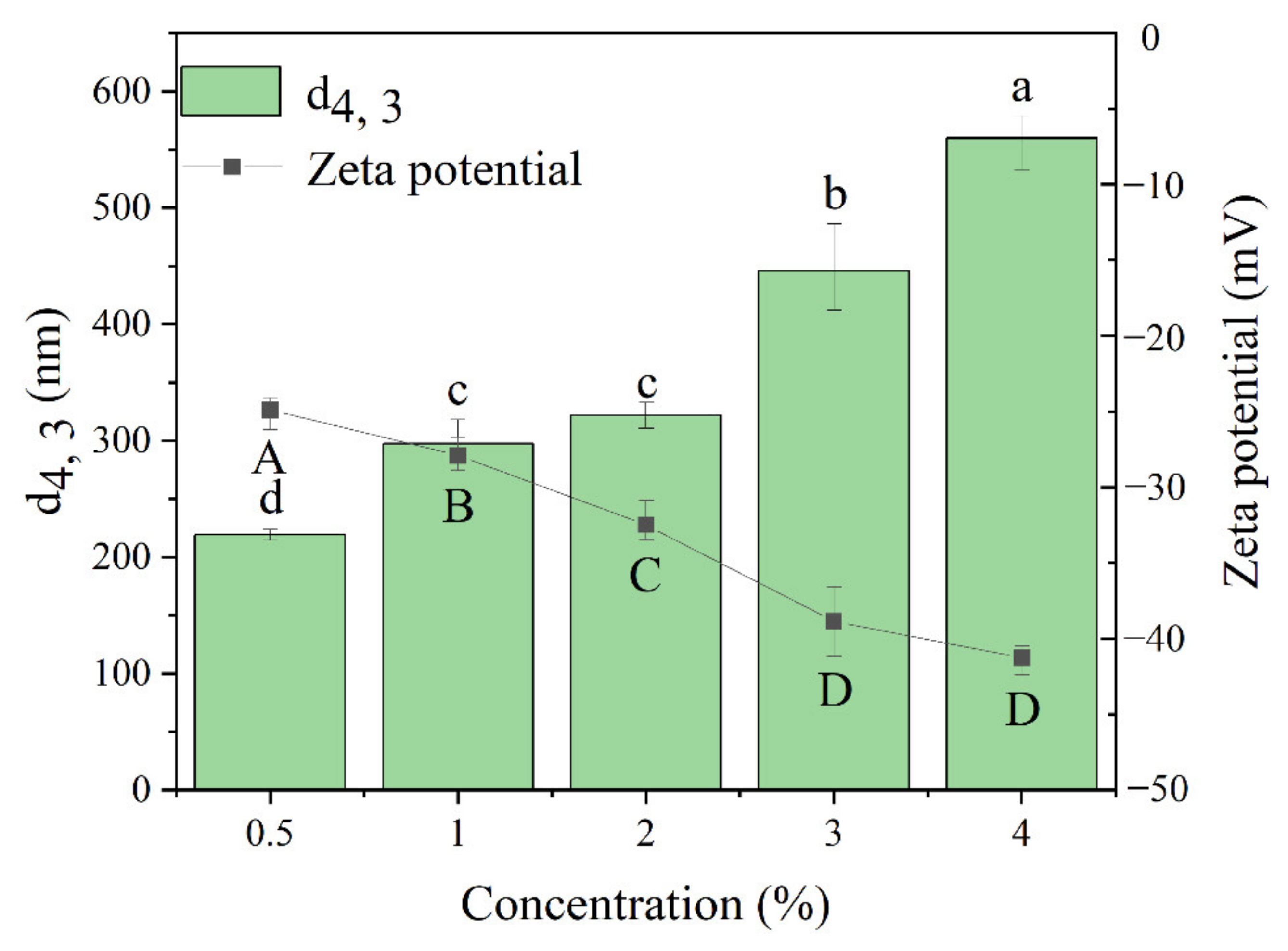
3.1.1. Effect of TSCP Concentrations on the Particle Size and Zeta Potential of TSCPN
3.1.2. The Microstructure of TSCP and TSCPN
3.2. Characteristics of TSCPN-Stabilized PICKERING Emulsion
3.2.1. Type of TSCPN-Stabilized Pickering Emulsion
3.2.2. Effect of TSCPN Concentrations on the Particle Size and Micromorphology of Pickering Emulsions
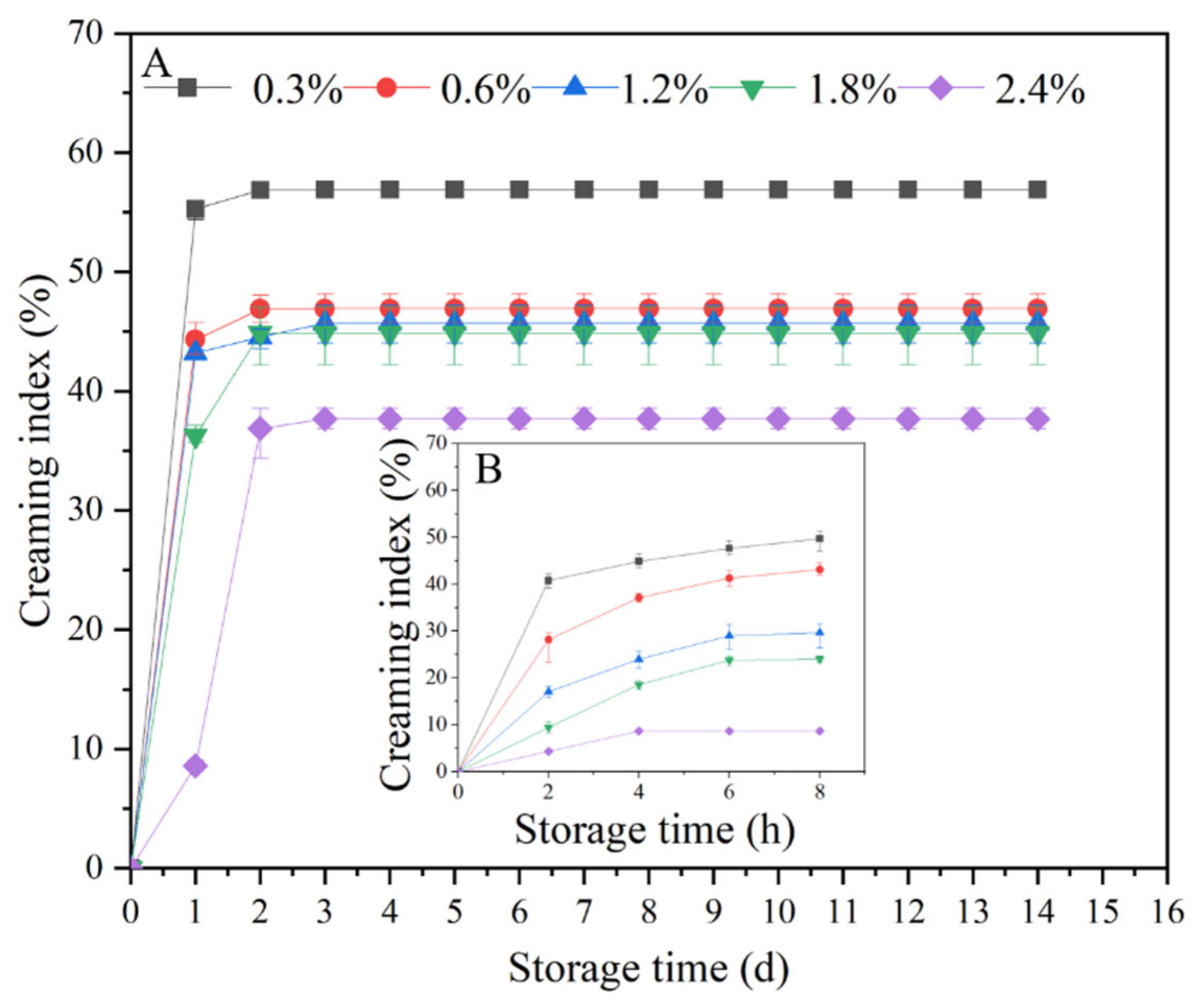
3.2.3. Effect of TSCPN Concentrations on the Storage Stability of Pickering Emulsions
3.2.4. Effect of Ionic Strength on the Particle Size and Zeta Potential of Pickering Emulsions
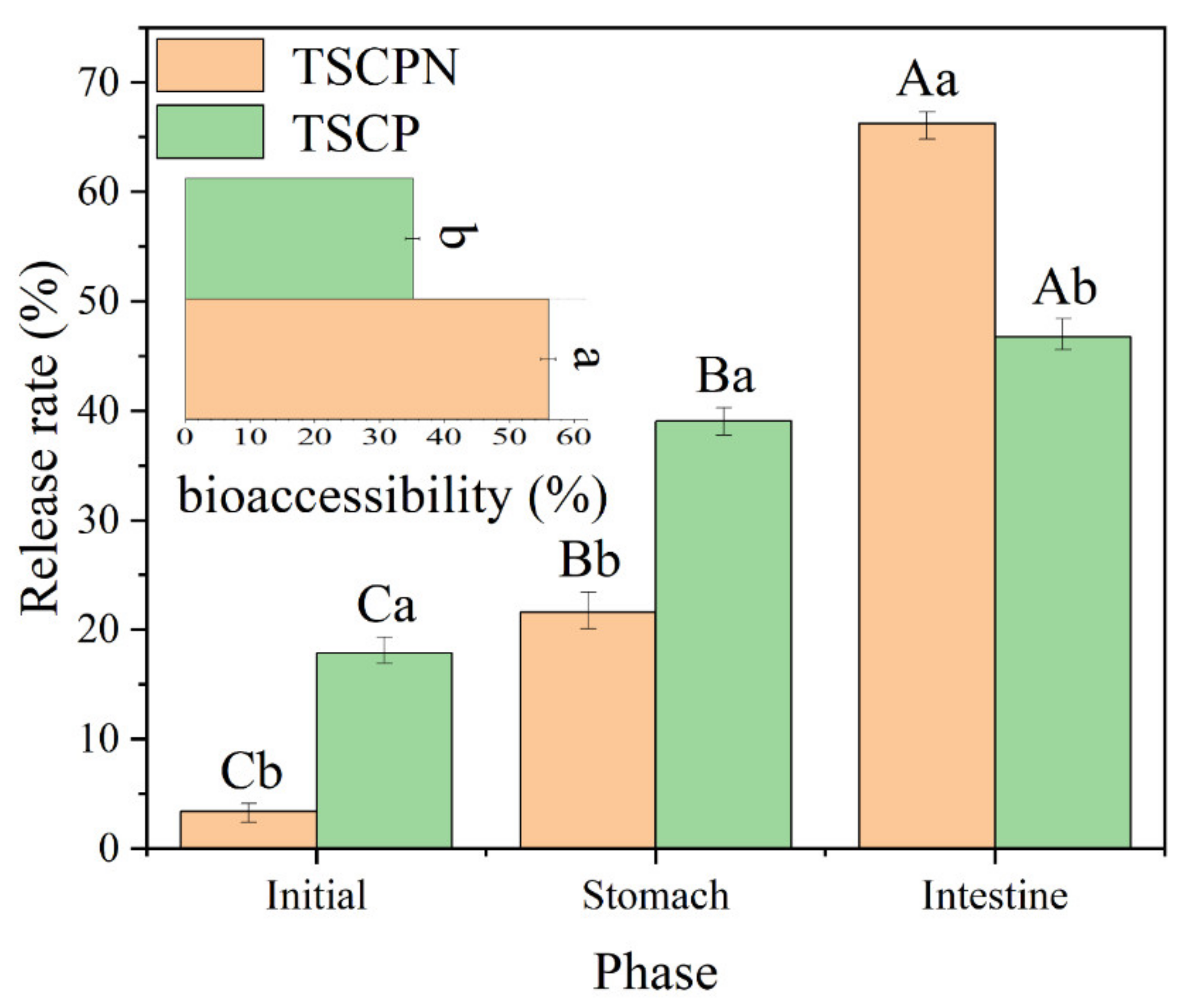
3.3. Encapsulation and Delivery of Lutein: An In Vitro Digestion Model
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Madaan, T.; Choudhary, A.N.; Gyenwalee, S.; Thomas, S.; Mishra, H.; Tariq, M.; Vohora, D.; Talegaonkar, S. Lutein, a versatile phyto-nutraceutical: An insight on pharmacology, therapeutic indications, challenges and recent advances in drug delivery. PharmaNutrition 2017, 5, 64–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sajilata, M.; Singhal, R.; Kamat, M. The carotenoid pigment zeaxanthin—A review. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2008, 7, 29–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kijlstra, A.; Tian, Y.; Kelly, E.R.; Berendschot, T.T. Lutein: More than just a filter for blue light. Prog. Retin Eye Res. 2012, 31, 303–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shegokar, R.; Mitri, K. Carotenoid lutein: A promising candidate for pharmaceutical and nutraceutical applications. J. Diet. Suppl. 2012, 9, 183–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.; Su, Z.; Meng, X.; Zhang, X.; Kennedy, J.F.; Liu, B. Fabrication and characterization of Pickering emulsion stabilized by soy protein isolate-chitosan nanoparticles. Carbohyd. Polym. 2020, 247, 116712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marefati, A.; Rayner, M. Starch granule stabilized Pickering emulsions: An 8-year stability study. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2020, 100, 2807–2811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarkar, A.; Dickinson, E. Sustainable food-grade Pickering emulsions stabilized by plant-based particles. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2020, 49, 69–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marto, J.; Ascenso, A.; Simoes, S.; Almeida, A.J.; Ribeiro, H.M. Pickering emulsions: Challenges and opportunities in topical delivery. Expert Opin. Drug Del. 2016, 13, 1093–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, S.; Li, Y.; Lv, J.; Ma, H.; Liang, G.; Liu, B. Fabrication of food-grade Pickering high internal phase emulsions (HIPEs) stabilized by a dihydromyricetin and lysozyme mixture. Food Chem. 2022, 373, 131576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Zhang, B.; Li, C.; Fu, X.; Huang, Q. Pickering emulsion gel stabilized by octenylsuccinate quinoa starch granule as lutein carrier: Role of the gel network. Food Chem. 2020, 305, 125476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Geng, S.; Jiang, Z.; Liu, B. Fabrication and characterization of food-grade Pickering high internal emulsions stabilized with beta-cyclodextrin. LWT 2020, 134, 110134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Li, Y.; Geng, S.; Mo, H.; Liu, B. Fabrication of food-grade Pickering high internal phase emulsions stabilized by the mixture of beta-cyclodextrin and sugar beet pectin. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 182, 252–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, J.; Guo, Q.; Chen, Y.; Dong, W.; Mao, L.; Gao, Y.; Yuan, F. Characterization and formation mechanism of lutein pickering emulsion gels stabilized by beta-lactoglobulin-gum arabic composite colloidal nanoparticles. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 98, 105276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, J.; Guo, Q.; Chen, Y.; Mao, L.; Gao, Y.; Yuan, F. Utilization of beta-lactoglobulin-(-)-Epigallocatechin-3-gallate(EGCG) composite colloidal nanoparticles as stabilizers for lutein pickering emulsion. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 98, 105293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wani, T.A.; Shah, A.G.; Wani, S.M.; Wani, I.A.; Masoodi, F.A.; Nissar, N.; Shagoo, M.A. Suitability of Different Food Grade Materials for the Encapsulation of Some Functional Foods Well Reported for Their Advantages and Susceptibility. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2016, 56, 2431–2454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebert, S.; Grossmann, L.; Hinrichs, J.; Weiss, J. Emulsifying properties of water-soluble proteins extracted from the microalgae Chlorella sorokiniana and Phaeodactylum tricornutum. Food Funct. 2019, 10, 754–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Ma, C.; Cui, F.; McClements, D.J.; Liu, X.; Liu, F. Protein-stabilized Pickering emulsions: Formation, stability, properties, and applications in foods. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 103, 293–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, A.M.M.; Almeida, F.S.; Sato, A.C.K. Functional characterization of commercial plant proteins and their application on stabilization of emulsions. J. Food Eng. 2021, 292, 110277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y. Study on the Preparation of Tea Seed Cake Protein and Its Functional and Digesion and Absorption Properties; Yangzhou University: Yanghzhou, China, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Jiao, Q.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, B.; Li, D.; Feng, Z.; Liu, C. Preparation and evaluation of a novel high internal phase Pickering emulsion based on whey protein isolate nanofibrils derived by hydrothermal method. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 123, 107180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, A.; Khan, N.M.; Ali, F.; Khan, Z.U.; Ahmad, S.; Jan, A.K.; Rehman, N.; Muhammad, N. Effect of protein and oil volume concentrations on emulsifying properties of acorn protein isolate. Food Chem. 2020, 324, 126894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Z.; Chen, Y.; Kong, X.; Zhang, C.; Hua, Y. Emulsifying properties and oil/water (O/W) interface adsorption behavior of heated soy proteins: Effects of heating concentration, homogenizer rotating speed, and salt addition level. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 1634–1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Z.; Wen, Y.; Yi, J.; Cao, Y.; Liu, F.; McClements, D.J. Comparison of natural and synthetic surfactants at forming and stabilizing nanoemulsions: Tea saponin, Quillaja saponin, and Tween 80. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2019, 536, 80–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.-F.; Yang, S.-L.; Han, Y.-Y.; Zhao, L.; Lu, G.-L.; Xia, T.; Gao, L.-P. Qualitative and quantitative analysis of triterpene saponins from tea seed pomace (Camellia oleifera abel) and their activities against bacteria and fungi. Molecules 2014, 19, 7568–7580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, Z.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Lin, X.; Li, B. Novel food-grade Pickering emulsions stabilized by tea water-insoluble protein nanoparticles from tea residues. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 96, 322–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, L.; Zhang, X.; Wang, X.; Jin, Q.; McClements, D.J. Influence of dairy emulsifier type and lipid droplet size on gastrointestinal fate of model emulsions: In vitro digestion study. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 9761–9769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boostani, S.; Hosseini, S.M.H.; Golmakani, M.-T.; Marefati, A.; Hadi, N.B.A.; Rayner, M. The influence of emulsion parameters on physical stability and rheological properties of Pickering emulsions stabilized by hordein nanoparticles. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 101, 105520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Lee, Y. Surface modification of zein colloidal particles with sodium caseinate to stabilize oil-in-water pickering emulsion. Food Hydrocoll. 2016, 56, 292–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Decker, E.A.; McClements, D.J. Influence of lipid type on gastrointestinal fate of oil-in-water emulsions: In vitro digestion study. Food Res. Int. 2015, 75, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-García, E.; Carvajal-Lérida, I.; Pérez-Gálvez, A. In vitro bioaccessibility assessment as a prediction tool of nutritional efficiency. Nutr. Res. 2009, 29, 751–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutherfurd, S.M. Methodology for determining degree of hydrolysis of proteins in hydrolysates: A review. J. AOAC Int. 2010, 93, 1515–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, H.-N.; Tang, C.-H. pH-dependent emulsifying properties of pea [Pisum sativum (L.)] proteins. Food Hydrocoll. 2013, 33, 309–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Ma, G.H. Recent studies of Pickering emulsions: Particles make the difference. Small 2016, 12, 4633–4648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, F.; Tang, C.-H. Emulsifying properties of soy protein nanoparticles: Influence of the protein concentration and/or emulsification process. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 2644–2654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Tang, C.-H. Soy protein nanoparticle aggregates as pickering stabilizers for oil-in-water emulsions. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 8888–8898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albert, C.; Beladjine, M.; Tsapis, N.; Fattal, E.; Agnely, F.; Huang, N. Pickering emulsions: Preparation processes, key parameters governing their properties and potential for pharmaceutical applications. J. Control. Release 2019, 309, 302–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, M.; Olivier, G.K.; Frechette, J. Electrostatic interactions to modulate the reflective assembly of nanoparticles at the oil–water interface. Soft Matter 2012, 8, 11923–11932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz, D.G.; Pochat-Bohatier, C.; Cambedouzou, J.; Bechelany, M.; Miele, P. Current trends in Pickering emulsions: Particle morphology and applications. Engineering 2020, 6, 468–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Xu, J.; Chen, J.; Wang, Z.; Wang, X.; Zhong, J. Protein nanoparticles for Pickering emulsions: A comprehensive review on their shapes, preparation methods, and modification methods. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 113, 26–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levine, S.; Bowen, B.D.; Partridge, S.J. Stabilization of emulsions by fine particles I. Partitioning of particles between continuous phase and oil/water interface. Colloids Surf. 1989, 38, 325–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frelichowska, J.; Bolzinger, M.-A.; Chevalier, Y. Effects of solid particle content on properties of o/w Pickering emulsions. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2010, 351, 348–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhang, N.; Chen, C.; He, R.; Ju, X. Rapeseed protein nanogels as novel pickering stabilizers for oil-in-water emulsions. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 3607–3614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, A.; Feng, X.; Wang, Q.; Adhikari, B. Pickering and high internal phase Pickering emulsions stabilized by protein-based particles: A review of synthesis, application and prospective. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 109, 106117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chappat, M. Some applications of emulsions. Colloids Surf. A 1994, 91, 57–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Bouchikhi, S.; Ibrahimi, A.; Bensouda, Y. Creaming behavior prediction of argan oil in water emulsion stabilized by lacto-fermentation: Creaming index. BMC Biotech. 2021, 21, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, M.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, H.; Tao, N.; Wang, X.; Zhong, J. Gelatin molecular structures affect behaviors of fish oil-loaded traditional and Pickering emulsions. Food Chem. 2020, 309, 125642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araiza-Calahorra, A.; Sarkar, A. Pickering emulsion stabilized by protein nanogel particles for delivery of curcumin: Effects of pH and ionic strength on curcumin retention. Food Struct. 2019, 21, 100113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; McClements, D.J.; Zhou, W.; Peng, S.; Zhou, L.; Zou, L.; Liu, W. Influence of ionic strength and thermal pretreatment on the freeze-thaw stability of Pickering emulsion gels. Food Chem. 2020, 303, 125401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Yuan, Y.; Zhu, J.; Wang, T.; Wang, D.; Xu, Y. Zein/soluble soybean polysaccharide composite nanoparticles for encapsulation and oral delivery of lutein. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 103, 105715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamatha, B.S.; Baskaran, V. Effect of micellar lipids, dietary fiber and β-carotene on lutein bioavailability in aged rats with lutein deficiency. Nutrition 2011, 27, 960–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, N.; Wang, J.; Jiang, C.; Nie, X.; Hu, Z.; Ye, Q.; Meng, X.; Xiong, H. Development of composite nanoparticles from gum Arabic and carboxymethylcellulose-modified Stauntonia brachyanthera seed albumin for lutein delivery. Food Chem. 2022, 372, 131269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.; Jiao, Y.; Li, D.-J.; Liu, X.-L.; Han, H. Glycosylated zein as a novel nanodelivery vehicle for lutein. Food Chem. 2022, 376, 131927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liang, L.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Wen, C.; Liu, X.; Zhang, J.; Li, Y.; Liu, R.; Ren, J.; et al. Pickering Emulsion Stabilized by Tea Seed Cake Protein Nanoparticles as Lutein Carrier. Foods 2022, 11, 1712. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11121712
Liang L, Zhu J, Zhang Z, Liu Y, Wen C, Liu X, Zhang J, Li Y, Liu R, Ren J, et al. Pickering Emulsion Stabilized by Tea Seed Cake Protein Nanoparticles as Lutein Carrier. Foods. 2022; 11(12):1712. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11121712
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiang, Li, Junlong Zhu, Zhiyi Zhang, Yu Liu, Chaoting Wen, Xiaofang Liu, Jixian Zhang, Youdong Li, Ruijie Liu, Jiaoyan Ren, and et al. 2022. "Pickering Emulsion Stabilized by Tea Seed Cake Protein Nanoparticles as Lutein Carrier" Foods 11, no. 12: 1712. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11121712
APA StyleLiang, L., Zhu, J., Zhang, Z., Liu, Y., Wen, C., Liu, X., Zhang, J., Li, Y., Liu, R., Ren, J., Deng, Q., Liu, G., & Xu, X. (2022). Pickering Emulsion Stabilized by Tea Seed Cake Protein Nanoparticles as Lutein Carrier. Foods, 11(12), 1712. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11121712





