3D Food Printing Applications Related to Dysphagia: A Narrative Review
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Three-dimensional Food Printing
3D Food Printing for Dysphagia
3. Food Safety
4. Nutritional Aspects of 3D Food Printing for Dysphagia
5. Future Research
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Terrado, M.; Russell, C.; Bowman, J.B. Dysphagia: An overview. Medsurg Nurs. 2001, 10, 233–250. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Bhandari, B.; Guo, C.; Zheng, W.; Cao, S.; Lu, H.; Mo, H.; Li, H. 3D printing of Shiitake mushroom incorporated with gums as dysphagia diet. Foods 2021, 10, 2189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crary, M.; Sura, L.; Madhavan, A.; Carnaby-Mann, G. Dysphagia in the elderly: Management and nutritional considerations. Clin. Interv. Aging 2012, 7, 287–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Burke-Shyne, S.; Gallegos, D.; Williams, T. 3D food printing: Nutrition opportunities and challenges. Br. Food J. 2020, 123, 649–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wetscher, G.J.; Glaser, K.; Gadenstaetter, M.; Profanter, C.; Hinder, R.A. The effect of medical therapy and antireflux surgery on dysphagia in patients with gastroesophageal reflux disease without esophageal stricture. Am. J. Surg. 1999, 177, 189–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baiano, A. 3D printed foods: A comprehensive review on technologies, nutritional value, safety, consumer attitude, regulatory framework, and economic and sustainability issues. Food Rev. Int. 2020, 38, 986–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouzani, A.Z.; Adams, S.; Whyte, D.J.; Oliver, R.; Hemsley, B.; Palmer, S.; Balandin, S. 3D printing of food for people with swallowing difficulties. KnE Eng. 2017, 2, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ando, S.; Sakuma, M.; Morimoto, Y.; Arai, H. The effect of various boiling conditions on reduction of phosphorus and protein in meat. J. Ren. Nutr. 2015, 25, 504–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bethke, P.C.; Jansky, S.H. The effects of boiling and leaching on the content of potassium and other minerals in potatoes. J. Food Sci. 2008, 73, H80–H85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esenwah, C.N.; Ikenebomeh, M.J. Processing effects on the nutritional and anti-nutritional contents of African Locust Bean (Parkia biglobosa Benth.) Seed. Pak. J. Nutr. 2008, 7, 214–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wright, L.; Cotter, D.; Hickson, M.; Frost, G. Comparison of energy and protein intakes of older people consuming a texture modified diet with a normal hospital diet. J. Hum. Nutr. Diet. 2005, 18, 213–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrer, O.; Olsen, C.; Mousley, K.; Teo, E. Does presentation of smooth pureed meals improve patients consumption in an acute care setting: A pilot study. Nutr. Diet. 2016, 73, 405–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Germain, I.; Dufresne, T.; Gray-Donald, K. A novel dysphagia diet improves the nutrient intake of institutionalized elders. J. Am. Diet. Assoc. 2006, 106, 1614–1623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saha, D.; Bhattacharya, S. Hydrocolloids as thickening and gelling agents in food: A critical review. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2010, 47, 587–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dick, A.; Bhandari, B.; Dong, X.; Prakash, S. Feasibility study of hydrocolloid incorporated 3D printed pork as dysphagia food. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 107, 105940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, C.; Toh, W.Y.; Wong, G.; Lin, L. Extrusion-based 3D food printing—Materials and machines. Int. J. Bioprint. 2018, 4, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dick, A.; Bhandari, B.; Prakash, S. Printability and textural assessment of modified-texture cooked beef pastes for dysphagia patients. Future Foods 2021, 3, 100006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pant, A.; Lee, A.Y.; Karyappa, R.; Lee, C.P.; An, J.; Hashimoto, M.; Tan, U.-X.; Wong, G.; Chua, C.K.; Zhang, Y. 3D food printing of fresh vegetables using food hydrocolloids for dysphagic patients. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 114, 106546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemsley, B.; Palmer, S.; Kouzani, A.; Adams, S.; Balandin, S. Review informing the design of 3D food printing for people with swallowing disorders: Constructive, conceptual, and empirical problems. In Proceedings of the Hawaii International Conference on System Sciences, Maui, HI, USA, 8–11 January 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tejada-Ortigoza, V.; Cuan-Urquizo, E. Towards the Development of 3D-Printed Food: A Rheological and Mechanical Approach. Foods 2022, 11, 1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godoi, F.C.; Prakash, S.; Bhandari, B.R. 3d printing technologies applied for food design: Status and prospects. J. Food Eng. 2016, 179, 44–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- International Dysphagia Diet Standardization Initiative. Complete IDDSI Framework: Detailed Definitions. 2019. Available online: https://www.iddsi.org/IDDSI/media/images/Complete_IDDSI_Framework_Final_31July2019.pdf (accessed on 26 August 2021).
- Sungsinchai, S.; Niamnuy, C.; Wattanapan, P.; Charoenchaitrakool, M.; Devahastin, S. Texture modification technologies and their opportunities for the production of dysphagia foods: A review. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2019, 18, 1898–1912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Momosaki, R.; Abo, M.; Kobayashi, K. Swallowing analysis for semisolid food texture in poststroke dysphagic patients. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2013, 22, 267–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakagawa, K.; Matsuo, K.; Shibata, S.; Inamoto, Y.; Ito, Y.; Abe, K.; Ishibashi, N.; Fujii, W.; Saitoh, E. Efficacy of a novel training food based on the process model of feeding for mastication and swallowing—A preliminary study in elderly individuals living at a residential facility. Jpn. J. Compr. Rehabil. Sci. 2014, 5, 72–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diañez, I.; Gallegos, C.; Brito-de la Fuente, E.; Martínez, I.; Valencia, C.; Sánchez, M.C.; Franco, J.M. Implementation of a novel continuous solid/liquid mixing accessory for 3D printing of dysphagia-oriented thickened fluids. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 120, 106900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghazal, A.F.; Zhang, M.; Liu, Z. Spontaneous color change of 3D printed healthy food product over time after printing as a novel application for 4D food printing. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2019, 12, 1627–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, X.; Zhang, M.; Mujumdar, A.S. 4D printing: Recent advances and proposals in the food sector. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 110, 349–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phuhongsung, P.; Zhang, M.; Bhandari, B. 4D printing of products based on soy protein isolate via microwave heating for flavor development. Food Res. Int. 2020, 137, 109605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Severini, C.; Derossi, A.; Ricci, I.; Caporizzi, R.; Fiore, A. Printing a blend of fruit and vegetables. New advances on critical variables and shelf life of 3D edible objects. J. Food Eng. 2018, 220, 89–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, G.; Sun, B.; Yuan, J.; Wang, Q. Effects of different cooking methods on health-promoting compounds of broccoli. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B 2009, 10, 580–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Juul, F.; Vaidean, G.; Parekh, N. Ultra-processed foods and cardiovascular diseases: Potential mechanisms of action. Adv. Nutr. 2021, 12, 1673–1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteiro, C.A.; Cannon, G.; Levy, R.B.; Moubarac, J.-C.; Louzada, M.L.; Rauber, F.; Khandpur, N.; Cediel, G.; Neri, D.; Martinez-Steele, E.; et al. Ultra-processed foods: What they are and how to identify them. Public Health Nutr. 2019, 22, 936–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Bhandari, B.; Zhang, M. Incorporation of probiotics (Bifidobacterium animalis subsp. Lactis) into 3D printed mashed potatoes: Effects of variables on the viability. Food Res. Int. 2020, 128, 108795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turgeon, S.L.; Rioux, L.-E. Food matrix impact on macronutrients nutritional properties. Food Hydrocoll. 2011, 25, 1915–1924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Gamlath, S.; Wakeling, L. Nutritional aspects of food extrusion: A review. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2007, 42, 916–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnaraj, P.; Anukiruthika, T.; Choudhary, P.; Moses, J.A.; Anandharamakrishnan, C. 3D extrusion printing and post-processing of fibre-rich snack from indigenous composite flour. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2019, 12, 1776–1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, A.; Anukiruthika, T.; Moses, J.A.; Anandharamakrishnan, C. Preparation of fiber-enriched chicken meat constructs using 3D printing. J. Culin. Sci. Technol. 2021. advance online publication. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Severini, C.; Azzollini, D.; Albenzio, M.; Derossi, A. On printability, quality and nutritional properties of 3D printed cereal based snacks enriched with edible insects. Food Res. Int. 2018, 106, 666–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varghese, C.; Wolodko, J.; Chen, L.; Doschak, M.; Srivastav, P.P.; Roopesh, M.S. Influence of selected product and process parameters on microstructure, rheological, and textural properties of 3D printed cookies. Foods 2020, 9, 907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, X.; Zhang, M.; Bhandri, B. 3D printing of Cordyceps flower powder. J. Food Process Eng. 2019, 42, e13179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhang, M.; Phuhongsung, P. 3D printing of protein-based composite fruit and vegetable gel system. LWT 2021, 141, 110978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derossi, A.; Caporizzi, R.; Azzollini, D.; Severini, C. Application of 3D printing for customized food. A case on the development of a fruit-based snack for children. J. Food Eng. 2018, 220, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azam, S.M.R.; Zhang, M.; Mujumdar, A.S.; Yang, C. Study on 3D printing of orange concentrate and material characteristics. J. Food Process Eng. 2018, 41, e12689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
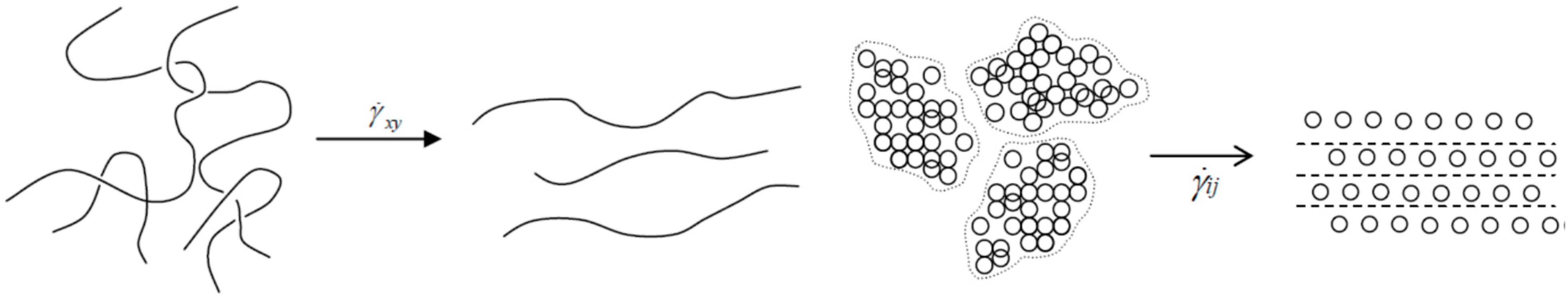
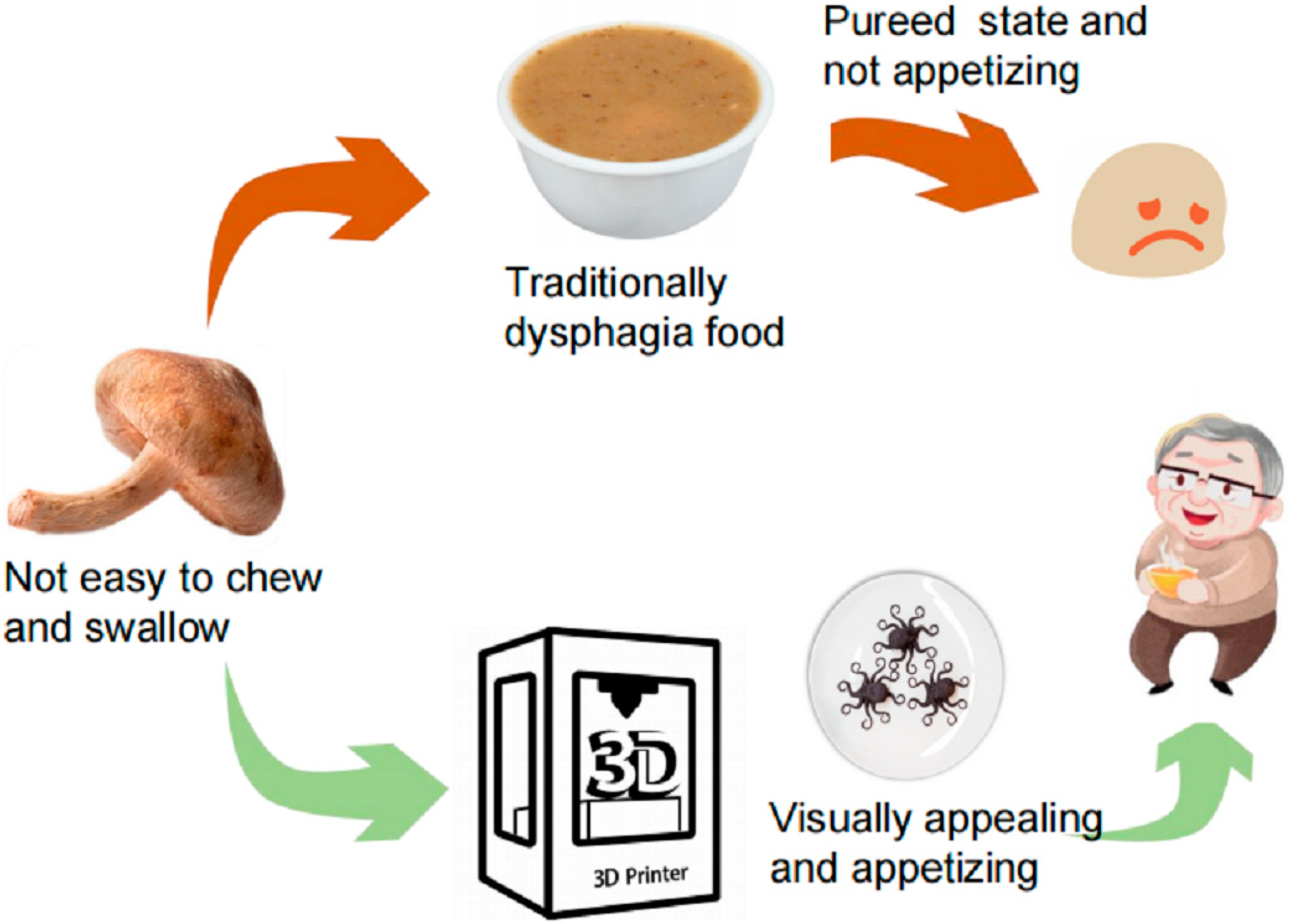
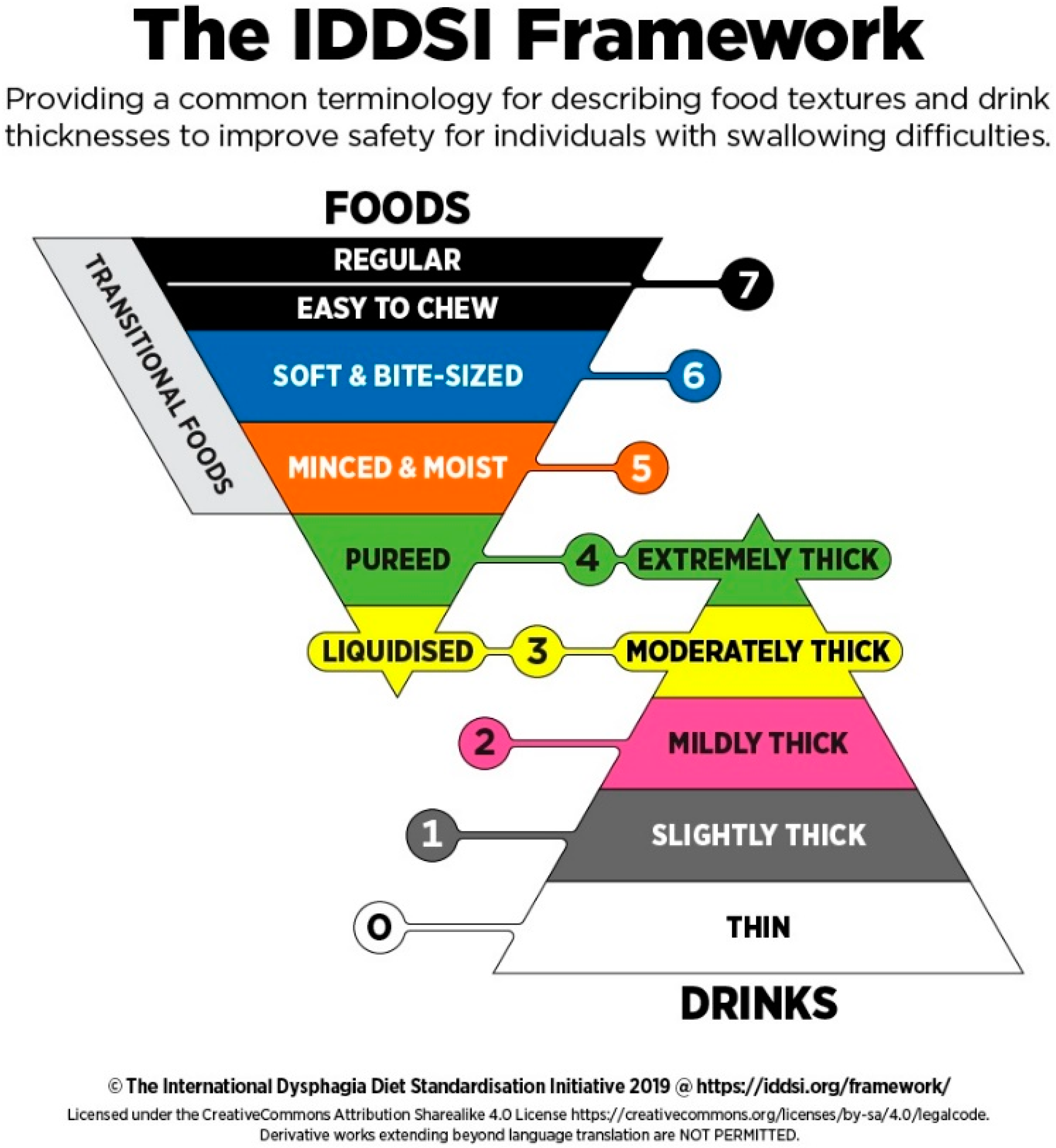
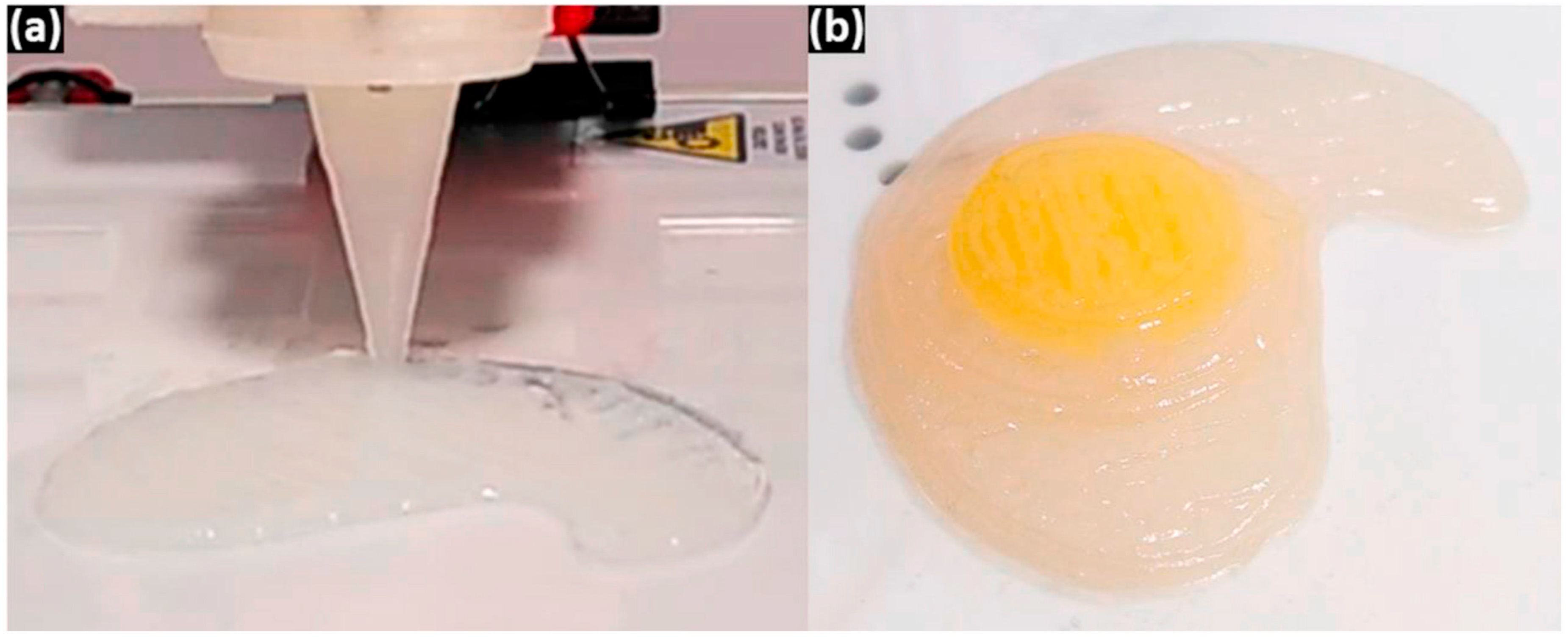
| Normal Diet Group (SD) | Dysphagia Diet Group (SD) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Energy requirements (kJ) | 6472 (882) | 6426 (1029) | 0.79 |
| Protein requirements (g) | 66 (14.2) | 62 (13.1) | 0.29 |
| Energy consumed (kJ) | 6115 (2575) | 3877 (1420) | <0.0001 |
| Protein consumed (g) | 60 (27) | 40 (18.6) | 0.003 |
| Energy deficit (kJ) | 357 (2366) | 2549 (1066) | <0.0001 |
| Protein deficit (g) | 6 (24.8) | 22 (16.9) | 0.013 |
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Foods of many classes can be successfully printed, including protein, vegetable, starch, fruit, and liquids [7,15,17,18,26] | Not all necessary texture levels were achieved for every food class, especially meat [15,17] |
| Hydrocolloids can be added for ink optimization and texture alteration, which is most critical in dysphagia diets [15,17,18] | Hydrocolloids may impart a non- natural flavor to foods but are necessary to achieve desired textures and printability [6,16,18] |
| Three-dimensional printing presents more creative freedom compared to previous methods, such as molding [7] | |
| Three-dimensionally printed foods can be easily fortified because they are broken down and mixed before printing [4] | |
| Four-dimensional food printing can further enhance sensory aspects [27,29] and holds great creative and research potential |
| Concern | Alleviation Method |
|---|---|
| Loss of nutrients due to leaching [7,18] | Steaming, adding cooking water to the puree |
| Negative influence on gut microbiome [32,34] | Adding prebiotics and probiotics |
| Rapid digestion of ultra-processed food [35] | Adding hydrocolloids to increase stomach viscosity |
| Thermal damage to the nutrients during printing [15,17] | Using low heat or room temperature |
| Lacking enough nutrients [4] | Fortification, using milk instead of water, adding fiber and protein |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lorenz, T.; Iskandar, M.M.; Baeghbali, V.; Ngadi, M.O.; Kubow, S. 3D Food Printing Applications Related to Dysphagia: A Narrative Review. Foods 2022, 11, 1789. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11121789
Lorenz T, Iskandar MM, Baeghbali V, Ngadi MO, Kubow S. 3D Food Printing Applications Related to Dysphagia: A Narrative Review. Foods. 2022; 11(12):1789. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11121789
Chicago/Turabian StyleLorenz, Tim, Michèle M. Iskandar, Vahid Baeghbali, Michael O. Ngadi, and Stan Kubow. 2022. "3D Food Printing Applications Related to Dysphagia: A Narrative Review" Foods 11, no. 12: 1789. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11121789
APA StyleLorenz, T., Iskandar, M. M., Baeghbali, V., Ngadi, M. O., & Kubow, S. (2022). 3D Food Printing Applications Related to Dysphagia: A Narrative Review. Foods, 11(12), 1789. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11121789









