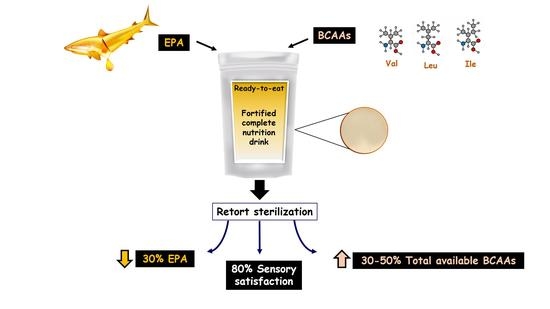
Loss of Eicosapentaenoic Acid (EPA) after Retort Sterilization of the EPA-BCAA Fortified Complete Nutrition Drink
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Formula Preparation
2.2. Sterilization
2.3. Physicochemical Properties
2.4. Analysis of EPA
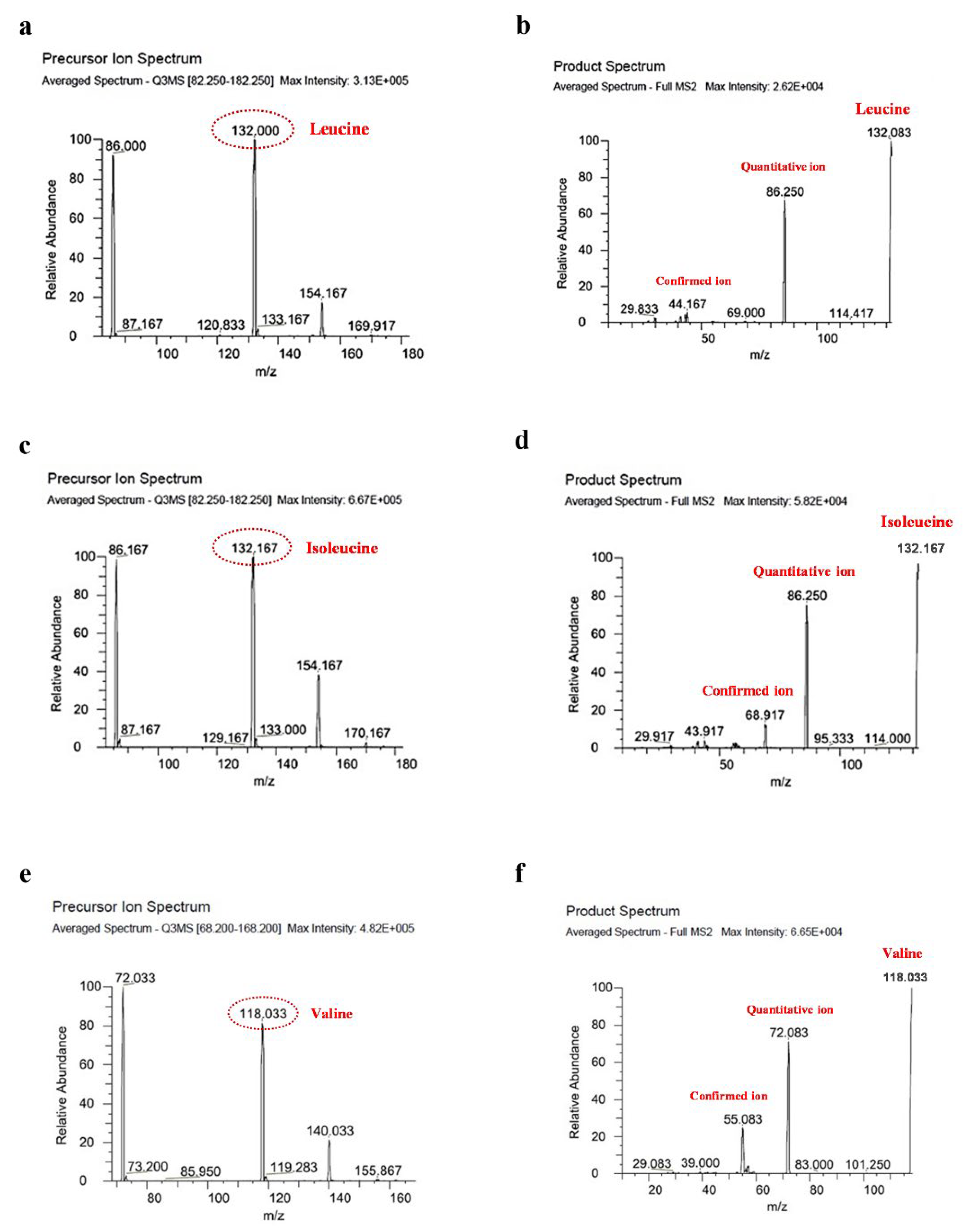
2.5. Analysis of BCAAs
2.6. Sensory Evaluation
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Microbial Load, Proximate Composition, Nutrients, Osmolality, Color, and pH of the Processed Control and Fortified Formulas
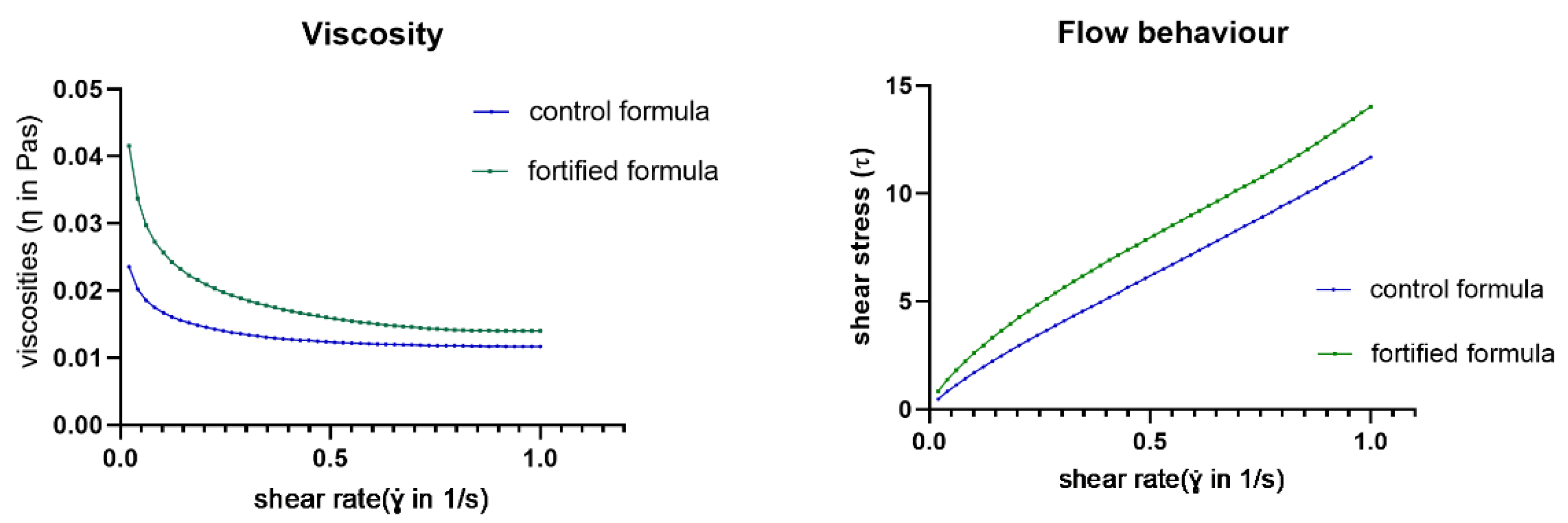
3.2. Rheological Properties and Texture of the Processed Control and Fortified Formulas
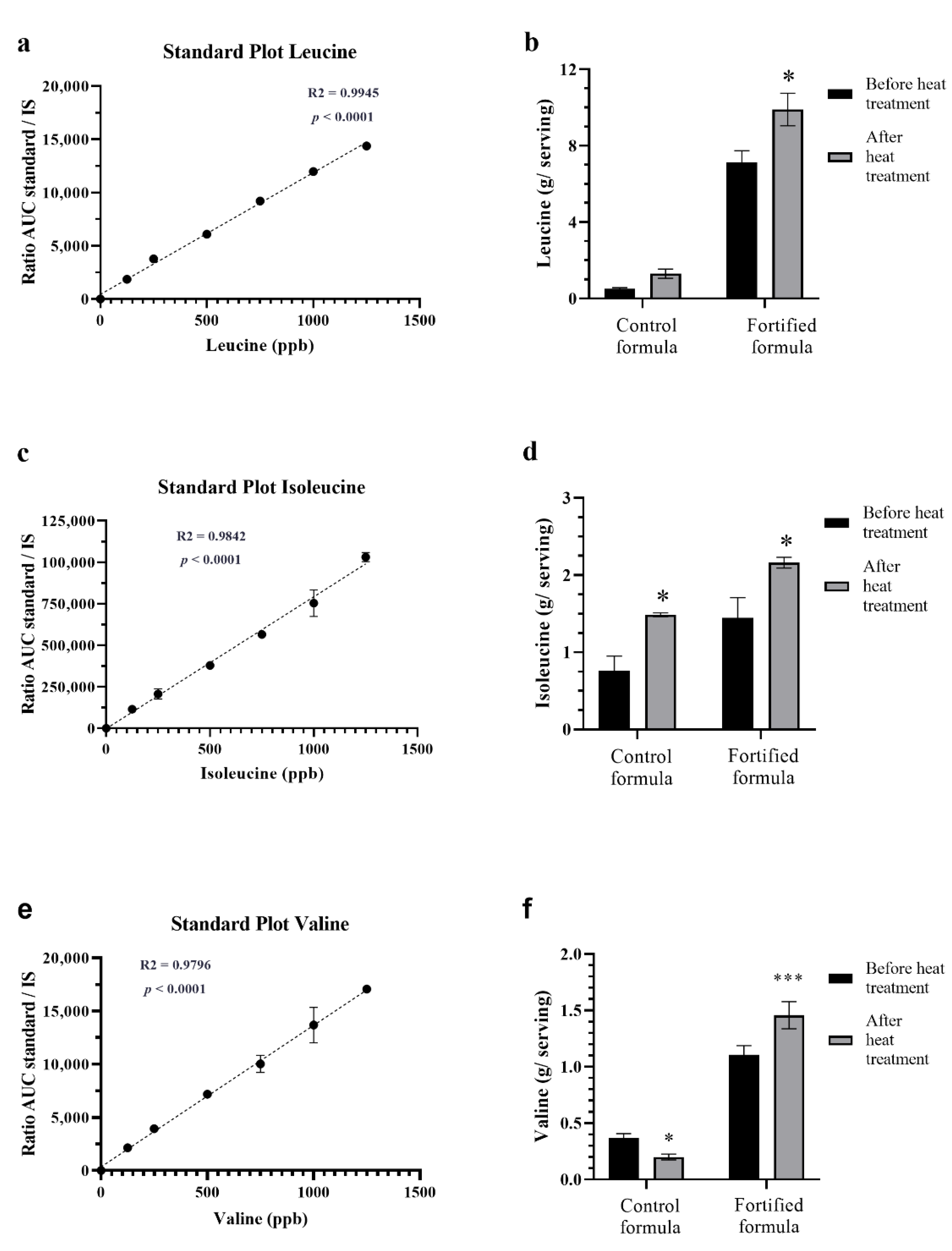
3.3. Effect of Retort Sterilization on BCAA
3.4. Effect of Retort Sterilization on EPA
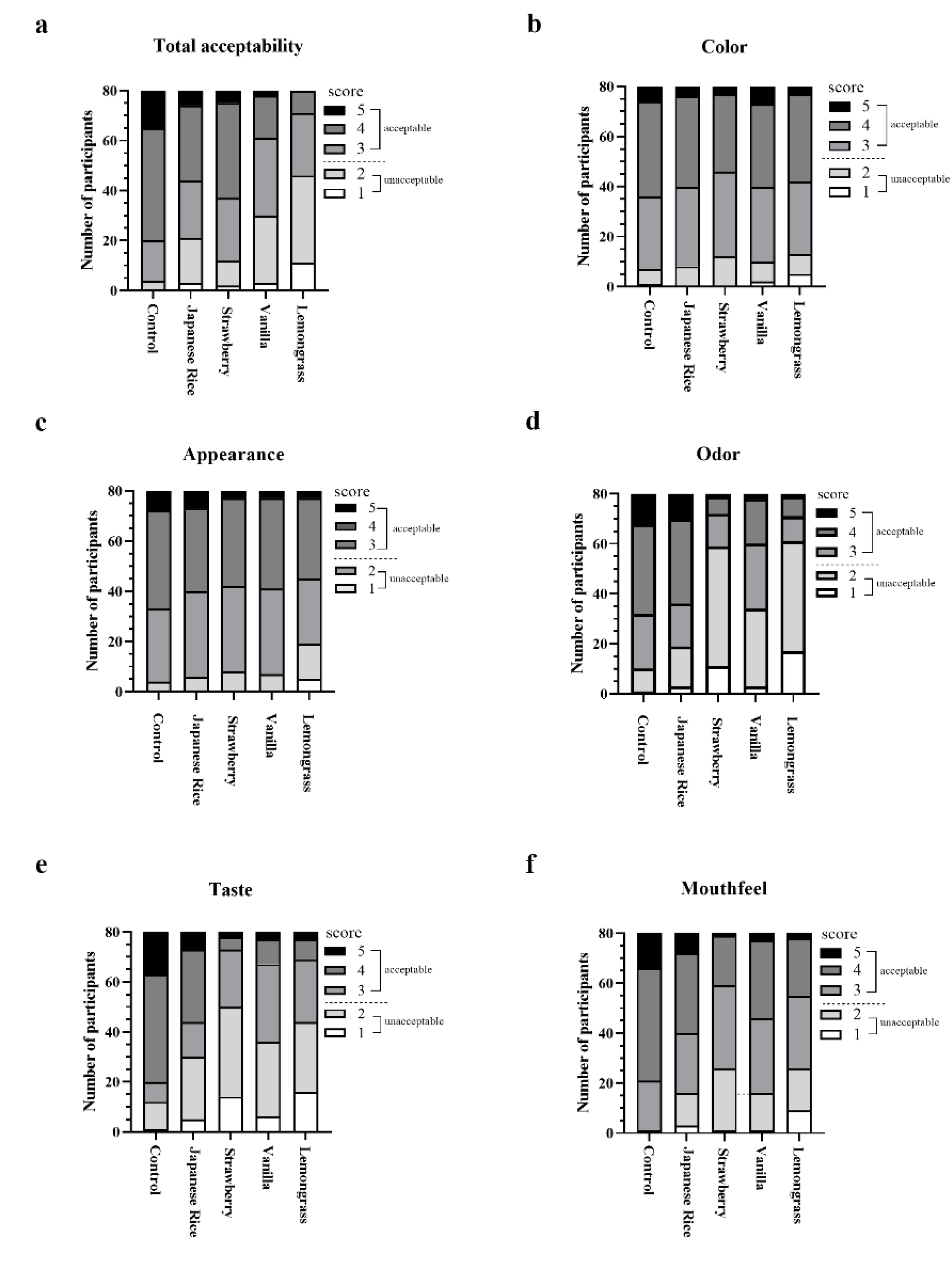
3.5. Sensory Evaluation of Fortified Formula
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Volkert, D.; Beck, A.M.; Cederholm, T.; Cruz-Jentoft, A.; Goisser, S.; Hooper, L.; Kiesswetter, E.; Maggio, M.; Raynaud-Simon, A.; Sieber, C.C.; et al. ESPEN guideline on clinical nutrition and hydration in geriatrics. Clin. Nutr. 2019, 38, 10–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Limketkai, B.N.; Shah, N.D.; Sheikh, G.N.; Allen, K. Classifying enteral nutrition: Tailored for clinical practice. Curr. Gastroenterol. Rep. 2019, 21, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joerger, M.; Schneider, S.M. Enteral Nutrition to Prevent and Treat Undernutrition. In Advanced Nutrition and Dietetics in Nutrition Support; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd: New Jersey, NJ, USA, 2018; pp. 194–206. [Google Scholar]
- Bankhead, R.; Boullata, J.; Brantley, S.; Corkins, M.; Guenter, P.; Krenitsky, J.; Lyman, B.; Metheny, N.A.; Mueller, C.; Robbins, S.; et al. A.S.P.E.N. Enteral nutrition practice recommendations. J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 2009, 33, 122–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Blumenstein, I.; Shastri, Y.M.; Stein, J. Gastroenteric tube feeding: Techniques, problems and solutions. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 8505–8524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karel, M.; Lund, D.B. Physical Principles of Food Preservation: Revised and Expanded, 2nd ed.; Marcel Dekker, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2003; pp. 170–177. [Google Scholar]
- D’Incecco, P.; Limbo, S.; Hogenboom, J.A.; Pellegrino, L. Novel technologies for extending the shelf life of drinking milk: Concepts, research trends, and current applications. LWT 2021, 148, 111746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasane, P.; Sharma, N.; Fatma, S.; Kaur, S.; Jha, A.; Kaur, D.; Singh, J. Ultra-high temperature (UHT) processing: Technological significance and updates. Curr. Nutr. Food Sci. 2020, 16, 1183–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oamen, E.E.; Hansen, A.P.; Swartzel, K.R. Effect of ultra-high temperature steam injection processing and aseptic storage on labile water-soluble vitamins in milk. J. Dairy Sci. 1989, 72, 614–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sevenich, R.; Mathys, A. Continuous versus discontinuous ultra-high-pressure systems for food sterilization with focus on ultra-high-pressure homogenization and high-pressure thermal sterilization: A review. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. 2018, 17, 646–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mesías, M.; Holgado, F.; Sevenich, R.; Briand, J.C.; Márquez Ruiz, G.; Morales, F.J. Fatty acids profile in canned tuna and sardine after retort sterilization and high-pressure thermal sterilization treatment. J. Food Nutr. Res. 2015, 54, 171–178. [Google Scholar]
- Beasley, J.M.; Shikany, J.M.; Thomson, C.A. The role of dietary protein intake in the prevention of sarcopenia of aging. Nutr. Clin. Pract. 2013, 28, 684–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Landi, F.; Camprubi-Robles, M.; Bear, D.E.; Cederholm, T.; Malafarina, V.; Welch, A.A.; Cruz-Jentoft, A.J. Muscle loss: The new malnutrition challenge in clinical practice. Clin. Nutr. 2019, 38, 2113–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Calder, P.C. Omega-3 fatty acids and inflammatory processes. Nutrients 2010, 2, 355–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mann, G.; Mora, S.; Madu, G.; Adegoke, O.A.J. Branched-chain amino acids: Catabolism in skeletal muscle and implications for muscle and whole-body metabolism. Front. Physiol. 2021, 12, 702826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iberahim, N.I.; Tan, B.C. Hexane-isopropanol extraction and quality assessment of omega-3 fish oil from Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar). IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 932, 012038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serafim, V.; Tiugan, D.-A.; Andreescu, N.; Mihailescu, A.; Paul, C.; Velea, I.; Puiu, M.; Niculescu, M.D. Development and validation of a LC–MS/MS-based assay for quantification of free and total omega 3 and 6 fatty acids from human plasma. Molecules 2019, 24, 360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Le, T.T.; Shafaei, A.; Genoni, A.; Christophersen, C.; Devine, A.; Lo, J.; Wall, P.L.; Boyce, M.C. Development and validation of a simple LC-MS/MS method for the simultaneous quantitative determination of trimethylamine-N-oxide and branched chain amino acids in human serum. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2019, 411, 1019–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marino, R.; Iammarino, M.; Santillo, A.; Muscarella, M.; Caroprese, M.; Albenzio, M. Technical note: Rapid method for determination of amino acids in milk. J. Dairy Sci. 2010, 93, 2367–2370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Tang, Q.; Wasim Iqbal, M.; Xia, Z.; Huang, F.; Li, L.; Liang, M.; Lin, B.; Qin, G.; Zou, C. A Comparison of milk protein, fat, lactose, total solids and amino acid profiles of three different buffalo breeds in Guangxi, China. Ital. J. Anim. Sci. 2018, 17, 873–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gacula, M., Jr.; Rutenbeck, S. Sample size in consumer test and descriptive analysis. J. Sens. Stud. 2006, 21, 129–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jukic, P.N.; Gagliardi, C.; Fagnani, D.; Venturini, C.; Orlandoni, P. Home enteral nutrition therapy: Difficulties, satisfactions and support needs of caregivers assisting older patients. Clin. Nutr. 2017, 36, 1062–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, S.; Daly, A.; Ashmore, C.; Gokmen-Ozel, H.; Dileva, R.; Dumbleton, B.; Chahal, S.; MacDonald, A. Nutritional content of modular feeds: How accurate is feed production? Arch. Dis. Child. 2013, 98, 184–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hurt, R.T.; Edakkanambeth Varayil, J.; Epp, L.M.; Pattinson, A.K.; Lammert, L.M.; Lintz, J.E.; Mundi, M.S. Blenderized tube feeding use in adult home enteral nutrition patients. Nutr. Clin. Pract. 2015, 30, 824–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Escuro, A.A.; Hummell, A.C. Enteral formulas in nutrition support practice. Nutr. Clin. Pract. 2016, 31, 709–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arends, J.; Bachmann, P.; Baracos, V.; Barthelemy, N.; Bertz, H.; Bozzetti, F.; Fearon, K.; Hütterer, E.; Isenring, E.; Kaasa, S.; et al. ESPEN guidelines on nutrition in cancer patients. Clin. Nutr. 2017, 36, 11–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kreissl, A.; Zwiauer, V.; Repa, A.; Binder, C.; Haninger, N.; Jilma, B.; Berger, A.; Haiden, N. Effect of fortifiers and additional protein on the osmolarity of human milk: Is it still safe for the premature infant? J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2013, 57, 432–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starowicz, M.; Zieliński, H. How maillard reaction influences sensorial properties (color, flavor, and texture) of food products? Food Rev. Int. 2019, 35, 707–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohi, H.; Sultana, Y.; Khar, R.K. Taste masking technologies in oral pharmaceuticals: Recent developments and approaches. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2004, 30, 429–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Itou, M.; Kawaguchi, T.; Taniguchi, E.; Shiraishi, S.; Ibi, R.; Mutou, M.; Okada, T.; Uchida, Y.; Otsuka, M.; Oriishi, T.; et al. Heating improves poor compliance with branchebranched-chainacid-rich supplementation in patients with liver cirrhosis: A before-after pilot study. Mol. Med. Rep. 2009, 2, 983–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeung, C.-Y.; Lee, H.-C.; Lin, S.-P.; Yang, Y.-C.; Huang, F.-Y.; Chuang, C.-K. Negative effect of heat sterilization on the free amino acid concentrations in infant formula. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2006, 60, 136–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- van Lieshout, G.A.A.; Lambers, T.T.; Bragt, M.C.E.; Hettinga, K.A. How processing may affect milk protein digestion and overall physiological outcomes: A systematic review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 60, 2422–2445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Domiszewski, Z.; Mierzejewska, S. Effect of technological process on true retention rate of eicosapentaenoic and docosahexaenoic acids, lipid oxidation and physical properties of canned smoked sprat (Sprattus sprattus). Int. J. Food Sci. 2021, 2021, e5539376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wesselink, E.; Koekkoek, K.W.A.C.; Looijen, M.; van Blokland, D.A.; Witkamp, R.F.; van Zanten, A.R.H. Associations of hyperosmolar medications administered via nasogastric or nasoduodenal tubes and feeding adequacy, food intolerance and gastrointestinal complications amongst critically ill patients: A retrospective study. Clin. Nutr. ESPEN 2018, 25, 78–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Btaiche, I.F.; Chan, L.-N.; Pleva, M.; Kraft, M.D. critical illness, gastrointestinal complications, and medication therapy during enteral feeding in critically ill adult patients. Nutr. Clin. Pract. 2010, 25, 32–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwok, K.C.; Liang, H.H.; Niranjan, K. Optimizing conditions for thermal processes of soy milk. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2002, 50, 4834–4838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzales, R.O.; Baleta, F.N.; Bolaños, J.M. Acceptability of selected herbs as off-odor remover and flavor enhancer for dried parrot fish Scarus rivulatus. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2017, 2, 31–37. [Google Scholar]
- Champagne, E.T. Rice Aroma and flavor: A literature review. Cereal Chem. 2008, 85, 445–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mak, J.; Cowan, T.M.; Le, A. Quantitative Analysis of Underivatized Amino Acids by Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry. In Amino Acid Analysis: Methods and Protocols; Cooper, C., Packer, N., Williams, K., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2019; pp. 85–109. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, C.; Nickerson, M.T. Encapsulation of omega 3-6-9 fatty acids-rich oils using protein-based emulsions with spray drying. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 55, 2850–2861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Ingredient | Control Formula | Fortified Formula |
|---|---|---|
| Maltodextrin | 22.14 | 22.14 |
| Sucrose | 11.00 | 11.00 |
| Soy protein | 9.37 | 9.37 |
| Rice bran oil | 7.61 | 7.61 |
| Multimineral mixture | 1.25 | 1.25 |
| Fructo-oligosaccharide (FOS) | 1.24 | 1.24 |
| Sodium caseinate | 0.81 | 0.81 |
| MCT oil | 0.66 | 0.66 |
| Multivitamin mixture | 0.19 | 0.19 |
| EPA | - | 1.10 |
| Leucine | - | 1.66 |
| Isoleucine | - | 0.41 |
| Valine | - | 0.41 |
| Parameter | Control Formula | Fortified Formula |
|---|---|---|
| Energy (kcal) Moisture (g) | 98.74 84.08 | 108.65 82.16 |
| Carbohydrate (g) | 13.93 | 14.03 |
| Protein (g) | 3.60 | 4.20 |
| Fat (g) | 3.18 | 3.97 |
| Dietary fiber (g) | 0.32 | 0.76 |
| Ash (g) | 0.61 | 0.54 |
| Parameter | Control Formula | Fortified Formula | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Osmolality (mOsmol/kg H2O) | 428.80 ± 3.30 | 549.80 ± 1.50 | <0.0001 |
| Color L * | 65.27 ± 0.14 | 65.60 ± 0.94 | >0.9999 |
| a * | 6.99 ± 0.09 | 8.01 ± 0.44 | <0.0001 |
| b * | 21.24 ± 0.2 | 27.42 ± 0.33 | <0.0001 |
| pH | 6.7 | 6.59 |
| Parameter | Viscosity (Pa.s) | p-Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control Formula | Fortified Formula | |||
| Shear rate (1/s) | 100 | 0.016 ± 0.001 | 0.024 ± 0.002 | <0.0001 |
| 250 | 0.013 ± 0.001 | 0.019 ± 0.001 | 0.0002 | |
| 500 | 0.012 ± 0.001 | 0.016± 2.567 | 0.006 | |
| 750 | 0.012 ± 3.719 | 0.014 ± 6.930 | 0.042 | |
| 1000 | 0.012 ± 2.758 | 0.014± 4.950 | 0.062 | |
| Parameter | Flow Behavior (Shear Stress: Pa) | p-Value | ||
| Control Formula | Fortified Formula | |||
| Shear rate (1/s) | 100 | 1.60 ± 0.150 | 2.493 ± 0.173 | 0.0251 |
| 250 | 4.038 ± 0.536 | 4.984 ± 0.191 | 0.0177 | |
| 500 | 6.102 ± 0.269 | 7.981± 0.131 | 0.0001 | |
| 750 | 8.724 ± 0.281 | 10.758 ± 0.052 | <0.0001 | |
| 1000 | 11.501 ± 0.276 | 14.002 ± 0.049 | <0.0001 | |
| Formula | Total Acceptability | Color | Appearance | Odor | Taste | Mouthfeel |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 3.89 ± 0.76 | 3.53 ± 0.80 | 3.64 ± 0.73 | 3.61 ± 0.92 | 3.80 ± 0.97 | 3.90 ± 0.69 |
| Japaneserice | 3.23 ± 1.01 **** | 3.45 ± 0.74 | 3.51 ± 0.76 | 3.40 ± 1.06 | 3.10 ± 1.13 *** | 3.36 ± 1.00 *** |
| Strawberry | 2.84 ± 0.93 **** | 3.45 ± 0.90 | 3.43 ± 0.78 | 2.89 ± 1.04 **** | 2.56 ± 1.07 **** | 3.09 ± 0.93 **** |
| Vanilla | 2.85 ± 0.89 **** | 3.44 ± 0.88 | 3.44 ± 0.71 | 2.81 ± 0.92 **** | 2.68 ± 0.92 **** | 3.25 ± 0.85 **** |
| Lemongrass | 2.58 ± 0.88 **** | 3.31 ± 0.77 | 3.41 ± 0.72 | 2.24 ± 0.85 **** | 2.31 ± 0.92 **** | 2.94 ± 0.82 **** |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Khoonin, W.; Shantavasinkul, P.C.; Santivarangkna, C.; Trachootham, D. Loss of Eicosapentaenoic Acid (EPA) after Retort Sterilization of the EPA-BCAA Fortified Complete Nutrition Drink. Foods 2022, 11, 2023. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11142023
Khoonin W, Shantavasinkul PC, Santivarangkna C, Trachootham D. Loss of Eicosapentaenoic Acid (EPA) after Retort Sterilization of the EPA-BCAA Fortified Complete Nutrition Drink. Foods. 2022; 11(14):2023. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11142023
Chicago/Turabian StyleKhoonin, Watcharapol, Prapimporn Chattranukulchai Shantavasinkul, Chalat Santivarangkna, and Dunyaporn Trachootham. 2022. "Loss of Eicosapentaenoic Acid (EPA) after Retort Sterilization of the EPA-BCAA Fortified Complete Nutrition Drink" Foods 11, no. 14: 2023. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11142023
APA StyleKhoonin, W., Shantavasinkul, P. C., Santivarangkna, C., & Trachootham, D. (2022). Loss of Eicosapentaenoic Acid (EPA) after Retort Sterilization of the EPA-BCAA Fortified Complete Nutrition Drink. Foods, 11(14), 2023. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11142023