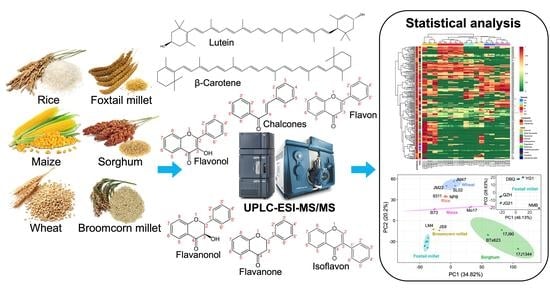
Differential Flavonoids and Carotenoids Profiles in Grains of Six Poaceae Crops
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Materials
2.2. Chemicals
2.3. Sample Preparation and Extraction for Flavonoid metabolites
2.4. UPLC Conditions for Flavonoid Metabolomics Analysis
2.5. ESI-Q TRAP-MS/MS System for Flavonoid Metabolomics Analysis
2.6. Qualitative and Quantitative Analysis of Flavonoids Content
2.7. Sample Preparation and Extraction for Carotenoid metabolites
2.8. UPLC Conditions for Carotenoid metabolites
2.9. APCI-MS/MS Conditions for Carotenoid metabolites
2.10. Quality Control Analysis of Samples
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Metabolic Profiling in Different Species
3.2. PCA Based on the Differences of Flavonoids and Carotenoids
3.3. Differential Metabolite Analysis
3.4. Enrichment Analysis, Functional Annotation, and Differential Metabolite Screening
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jin, M.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, M.; Deng, M.; Du, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, S.; Tohge, T.; Fernie, A.R.; Willmitzer, L.; et al. Integrated genomics-based mapping reveals the genetics underlying maize flavonoid biosynthesis. BMC Plant Biol. 2017, 17, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Scarano, A.; Chieppa, M.; Santino, A. Looking at Flavonoid Biodiversity in Horticultural Crops: A Colored Mine with Nutritional Benefits. Plants 2018, 7, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, A.; Li, R.; Ren, L.; Gao, X.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, Z.; Ma, D.; Luo, Y. A comparative metabolomics study of flavonoids in sweet potato with different flesh colors (Ipomoea batatas (L.) Lam). Food Chem. 2018, 260, 124–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez-Mejia, M.E.; Voss, O.H.; Murnan, E.J.; Doseff, A.I. Apigenin-induced apoptosis of leukemia cells is mediated by a bimodal and differentially regulated residue-specific phosphorylation of heat-shock protein-27. Cell Death Dis. 2010, 1, e64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shukla, S.; Gupta, S. Apigenin: A promising molecule for cancer prevention. Pharm. Res. 2010, 27, 962–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargo, M.A.; Voss, O.H.; Poustka, F.; Cardounel, A.J.; Grotewold, E.; Doseff, A.I. Apigenin-induced-apoptosis is mediated by the activation of PKCdelta and caspases in leukemia cells. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2006, 72, 681–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte, S.; Arango, D.; Parihar, A.; Hamel, P.; Yasmeen, R.; Doseff, A.I. Apigenin protects endothelial cells from lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced inflammation by decreasing caspase-3 activation and modulating mitochondrial function. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 17664–17679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Patra, A.K.; Saxena, J. A new perspective on the use of plant secondary metabolites to inhibit methanogenesis in the rumen. Phytochemistry 2010, 71, 1198–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olagaray, K.E.; Bradford, B.J. Plant flavonoids to improve productivity of ruminants—A review. Anim. Feed. Sci. Technol. 2019, 251, 21–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanty, B.; Lakshmanan, M.; Lim, S.H.; Kim, J.K.; Ha, S.H.; Lee, D.Y. Light-specific transcriptional regulation of the accumulation of carotenoids and phenolic compounds in rice leaves. Plant Signal. Behav. 2016, 11, e1184808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- van Poppel, G.; Goldbohm, R.A. Epidemiologic evidence for beta-carotene and cancer prevention. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1995, 62 (Suppl. 6), 1393s–1402s. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenwald, P.; McDonald, S.S. The beta-carotene story. Nutr. Cancer Prev. 2001, 492, 219–231. [Google Scholar]
- Lem, D.W.; Gierhart, D.L.; Davey, P.G. A Systematic Review of Carotenoids in the Management of Diabetic Retinopathy. Nutrients 2021, 13, 2441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trono, D. Carotenoids in Cereal Food Crops: Composition and Retention throughout Grain Storage and Food Processing. Plants 2019, 8, 551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Peng, M.; Shahzad, R.; Gul, A.; Subthain, H.; Shen, S.; Lei, L.; Zheng, Z.; Zhou, J.; Lu, D.; Wang, S.; et al. Differentially evolved glucosyltransferases determine natural variation of rice flavone accumulation and UV-tolerance. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 1975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Guo, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, M.; Li, K.; Liu, X.; Fang, C.; Luo, J. Metabolomic Analysis Reveals Nutritional Diversity among Three Staple Crops and Three Fruits. Foods 2022, 11, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamberts, L.; Delcour, J.A. Carotenoids in raw and parboiled brown and milled rice. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 11914–11919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dykes, L.; Rooney, L.W.; Waniska, R.D.; Rooney, W.L. Phenolic compounds and antioxidant activity of sorghum grains of varying genotypes. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 6813–6818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barton, L.; Newsome, S.D.; Chen, F.H.; Wang, H.; Guilderson, T.P.; Bettinger, R.L. Agricultural origins and the isotopic identity of domestication in northern China. Proc Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 5523–5528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lu, H.; Zhang, J.; Liu, K.B.; Wu, N.; Li, Y.; Zhou, K.; Ye, M.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, H.; Yang, X.; et al. Earliest domestication of common millet (Panicum miliaceum) in East Asia extended to 10,000 years ago. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 7367–7372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nithiyanantham, S.; Kalaiselvi, P.; Mahomoodally, M.F.; Zengin, G.; Abirami, A.; Srinivasan, G. Nutritional and functional roles of millets—A review. J. Food Biochem. 2019, 43, e12859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Gao, J.; Qie, Q.; Yang, Y.; Hou, S.; Wang, X.; Li, X.; Han, Y. Comparative Analysis of Flavonoid Metabolites in Foxtail Millet (Setaria italica) with Different Eating Quality. Life 2021, 11, 578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Wen, L.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Pang, X.; Deng, Z.; Liu, T.; Guo, Y. Study on metabolic variation in whole grains of four proso millet varieties reveals metabolites important for antioxidant properties and quality traits. Food Chem. 2021, 357, 129791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.; Chen, W.; Wang, W.; Zhang, H.; Liu, X.; Luo, J. Comprehensive profiling and natural variation of flavonoids in rice. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2014, 56, 876–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Gong, L.; Guo, Z.; Wang, W.; Zhang, H.; Liu, X.; Yu, S.; Xiong, L.; Luo, J. A novel integrated method for large-scale detection, identification, and quantification of widely targeted metabolites: Application in the study of rice metabolomics. Mol. Plant 2013, 6, 1769–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fraga, C.G.; Clowers, B.H.; Moore, R.J.; Zink, E.M. Signature-discovery approach for sample matching of a nerve-agent precursor using liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry, XCMS, and chemometrics. Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 4165–4173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartley, G.E.; Scolnik, P.A. Plant carotenoids: Pigments for photoprotection, visual attraction, and human health. Plant Cell 1995, 7, 1027–1038. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Inbaraj, B.S.; Lu, H.; Hung, C.F.; Wu, W.B.; Lin, C.L.; Chen, B.H. Determination of carotenoids and their esters in fruits of Lycium barbarum Linnaeus by HPLC-DAD-APCI-MS. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2008, 47, 812–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krinsky, N.I.; Mayne, S.T.; Sies, H. Carotenoids in Health and Disease; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Geyer, R.; Peacock, A.D.; White, D.C.; Lytle, C.; Van Berkel, G.J. Atmospheric pressure chemical ionization and atmospheric pressure photoionization for simultaneous mass spectrometric analysis of microbial respiratory ubiquinones and menaquinones. J. Mass Spectrom. 2004, 39, 922–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crespy, V.; Williamson, G. A review of the health effects of green tea catechins in in vivo animal models. J. Nutr. 2004, 134 (Suppl. 12), 3431S–3440S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, J.; Li, K.; Shi, Y.; Li, Y.; Dong, L.; Liu, L.; Li, M.; Ren, H.; Liu, X.; Fang, C.; et al. Cross-Species Comparison of Metabolomics to Decipher the Metabolic Diversity in Ten Fruits. Metabolites 2021, 11, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.; Chen, F.; Wang, X.; Kim, H.-J.; He, G.-Q.; Haley-Zitlin, V.; Huang, G. Antioxidant constituents in feverfew (Tanacetum parthenium) extract and their chromatographic quantification. Food Chem. 2006, 96, 220–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Middleton, E., Jr.; Kandaswami, C.; Theoharides, T.C. The effects of plant flavonoids on mammalian cells: Implications for inflammation, heart disease, and cancer. Pharmacol. Rev. 2000, 52, 673–751. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Li, X.; Ma, B.; Gao, Q.; Du, H.; Han, Y.; Li, Y.; Cao, Y.; Qi, M.; Zhu, Y.; et al. The Tartary Buckwheat Genome Provides Insights into Rutin Biosynthesis and Abiotic Stress Tolerance. Mol. Plant 2017, 10, 1224–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Calfío, C.; Donoso, F.; Huidobro-Toro, J.P. Anthocyanins Activate Membrane Estrogen Receptors with Nanomolar Potencies to Elicit a Nongenomic Vascular Response Via NO Production. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2021, 10, e020498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bando, S.I.; Hatano, O.; Takemori, H.; Kubota, N.; Ohnishi, K. Potentiality of syringetin for preferential radiosensitization to cancer cells. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 2017, 93, 286–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, Y.L.; Liang, H.L.; Hung, C.H.; Kuo, P.L. Syringetin, a flavonoid derivative in grape and wine, induces human osteoblast differentiation through bone morphogenetic protein-2/extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 pathway. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2009, 53, 1452–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.Z.; Li, X.W.; Jin, Y.R.; Yu, X.F.; Qu, S.C.; Sui, D.Y. Hypolipidemic effects of kaempferide-7-O-(4″-O-acetylrhamnosyl)-3-O-rutinoside in hyperlipidemic rats induced by a high-fat diet. Mol. Med. Rep. 2012, 5, 837–841. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wu, W.-Y.; Li, Y.-D.; Cui, Y.-K.; Wu, C.; Hong, Y.-X.; Li, G.; Wu, Y.; Jie, L.-J.; Wang, Y.; Li, G.-R. The Natural Flavone Acacetin Confers Cardiomyocyte Protection Against Hypoxia/Reoxygenation Injury via AMPK-Mediated Activation of Nrf2 Signaling Pathway. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.R.; Park, C.G.; Jung, J.Y. Acacetin (5,7-dihydroxy-4′-methoxyflavone) exhibits in vitro and in vivo anticancer activity through the suppression of NF-κB/Akt signaling in prostate cancer cells. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2014, 33, 317–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]





| Species | Cultivars | Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| Wheat | JM47 | Jinmai47, commercial variety |
| JM22 | Jimai22, medium gluten | |
| SL02 | strong gluten | |
| Maize | B73 | female line, reference genome available |
| Mo17 | male line, reference genome available | |
| Rice | NPB | japonica cultivar, reference genome available |
| 93-11 | indica cultivar | |
| Sorghum | BTx623 | reference genome available |
| 17J90 | edible | |
| 17J1344 | brewing | |
| Foxtail millet | JG21 | Jingu21, cultivar of high-quality conventional, reference genome available |
| QZH | Qinzhouhuang, cultivar of typical representative | |
| YG1 | Yugu1, cultivar, reference genome available | |
| NMB | Niumaobai, landrace | |
| DBQ | Daobaqi, landrace | |
| Broomcorn millet | LM4 | Longmi4, reference genome available |
| JS9 | Jinsu9, waxy grains cultivar |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tang, J.; Li, X.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Sun, R.; Li, Y.; Gao, J.; Han, Y. Differential Flavonoids and Carotenoids Profiles in Grains of Six Poaceae Crops. Foods 2022, 11, 2068. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11142068
Tang J, Li X, Zhang Y, Yang Y, Sun R, Li Y, Gao J, Han Y. Differential Flavonoids and Carotenoids Profiles in Grains of Six Poaceae Crops. Foods. 2022; 11(14):2068. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11142068
Chicago/Turabian StyleTang, Jiaoyan, Xukai Li, Yakun Zhang, Yulu Yang, Rong Sun, Yajun Li, Jianhua Gao, and Yuanhuai Han. 2022. "Differential Flavonoids and Carotenoids Profiles in Grains of Six Poaceae Crops" Foods 11, no. 14: 2068. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11142068
APA StyleTang, J., Li, X., Zhang, Y., Yang, Y., Sun, R., Li, Y., Gao, J., & Han, Y. (2022). Differential Flavonoids and Carotenoids Profiles in Grains of Six Poaceae Crops. Foods, 11(14), 2068. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11142068