Preparing a Personalized Meal by Using Soy, Cricket, and Egg Albumin Protein Based on 3D Printing
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Sample Preparation
2.3. Rheological Measurements
2.3.1. Frequency Sweep Test
2.3.2. Rotational Rheological Measurements, Viscosity, and Yield Stress
2.4. Texture Properties Characterization
2.4.1. TPA
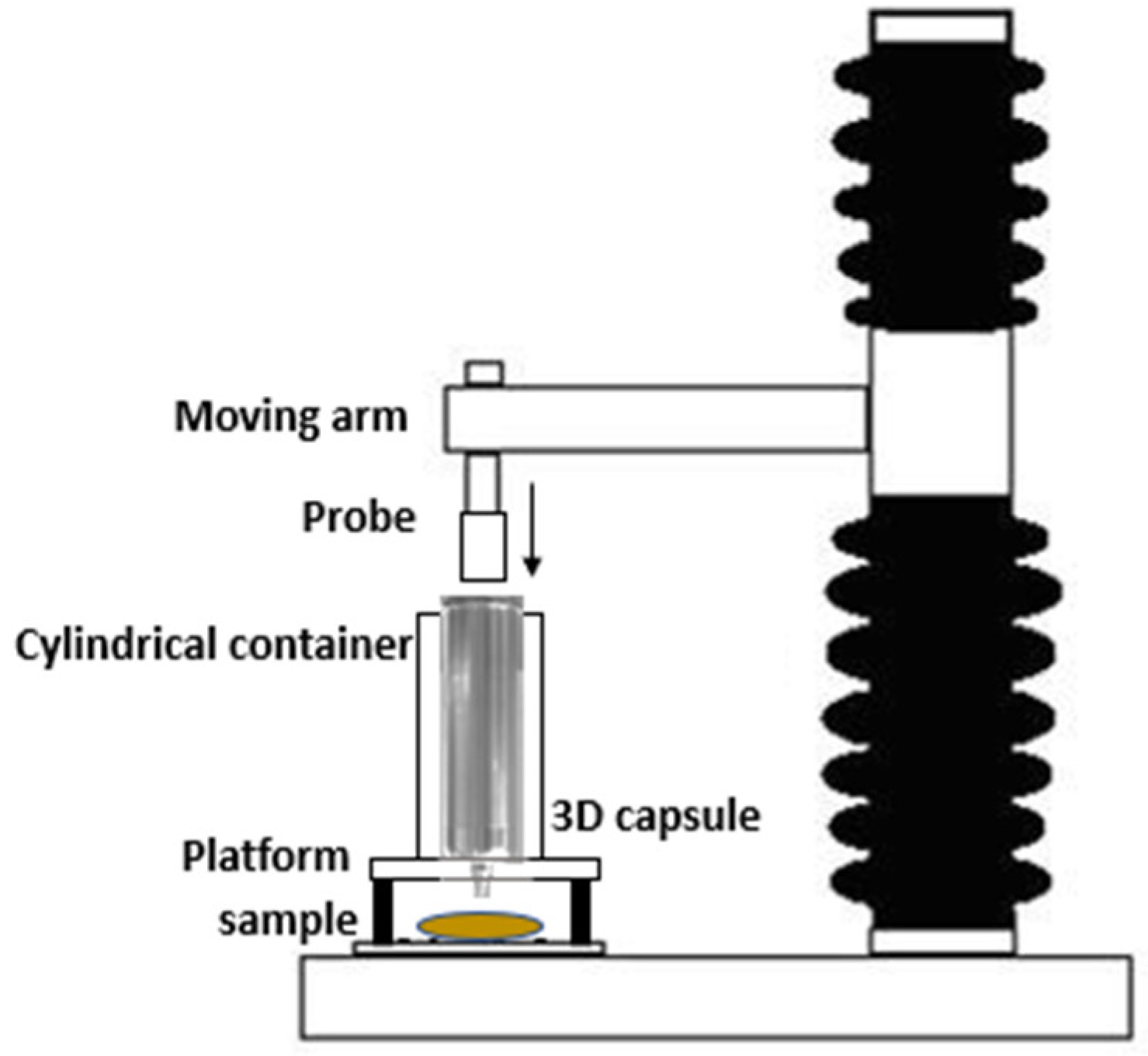
2.4.2. Backward-Extrusion Test
2.4.3. Force of Extrusion
2.5. Conditions of 3D Food Printing
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Rheological Properties
3.1.1. Viscosity and Yield Stress
3.1.2. Viscoelastic Behavior
3.2. Texture
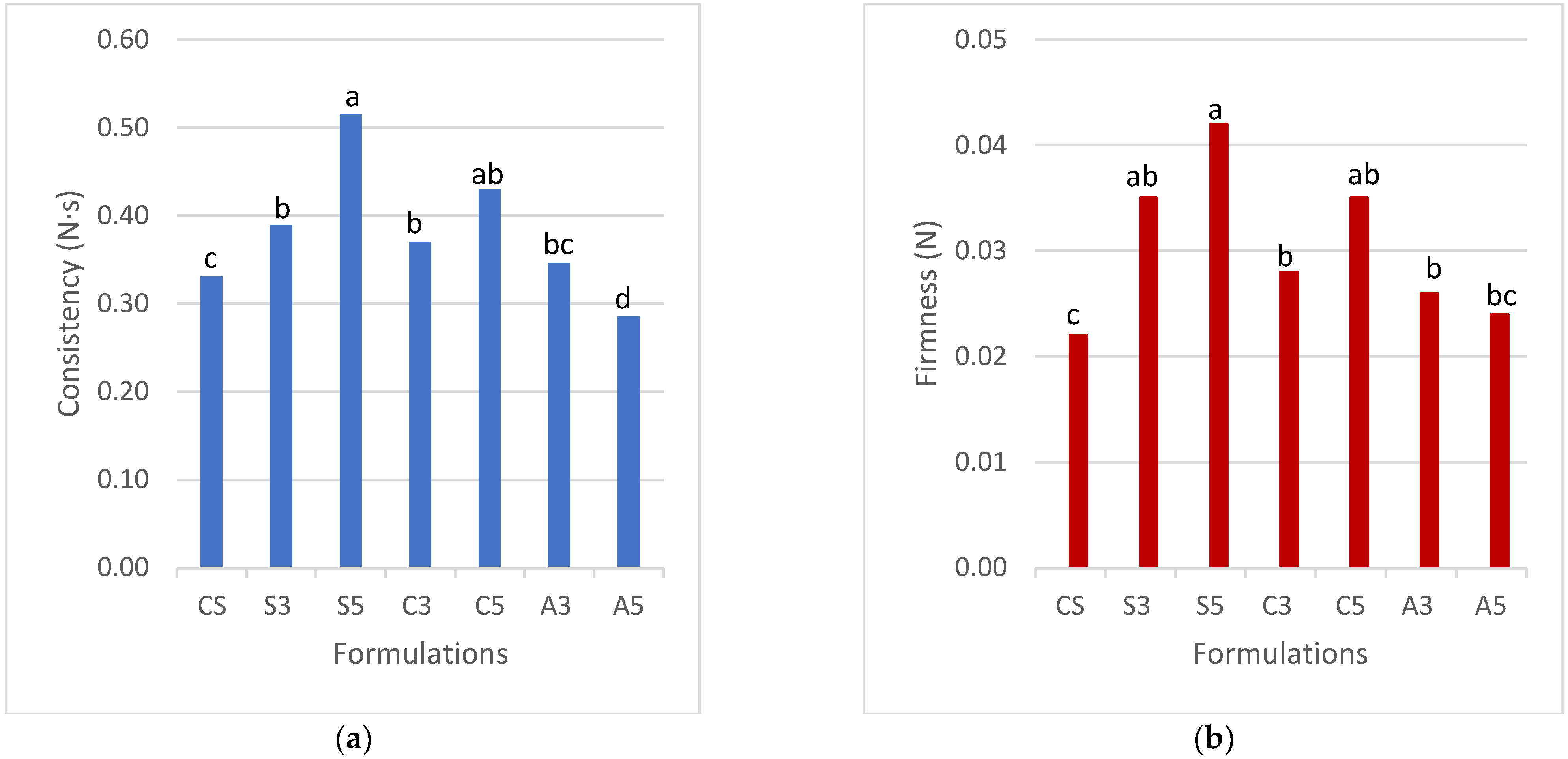
3.2.1. TPA
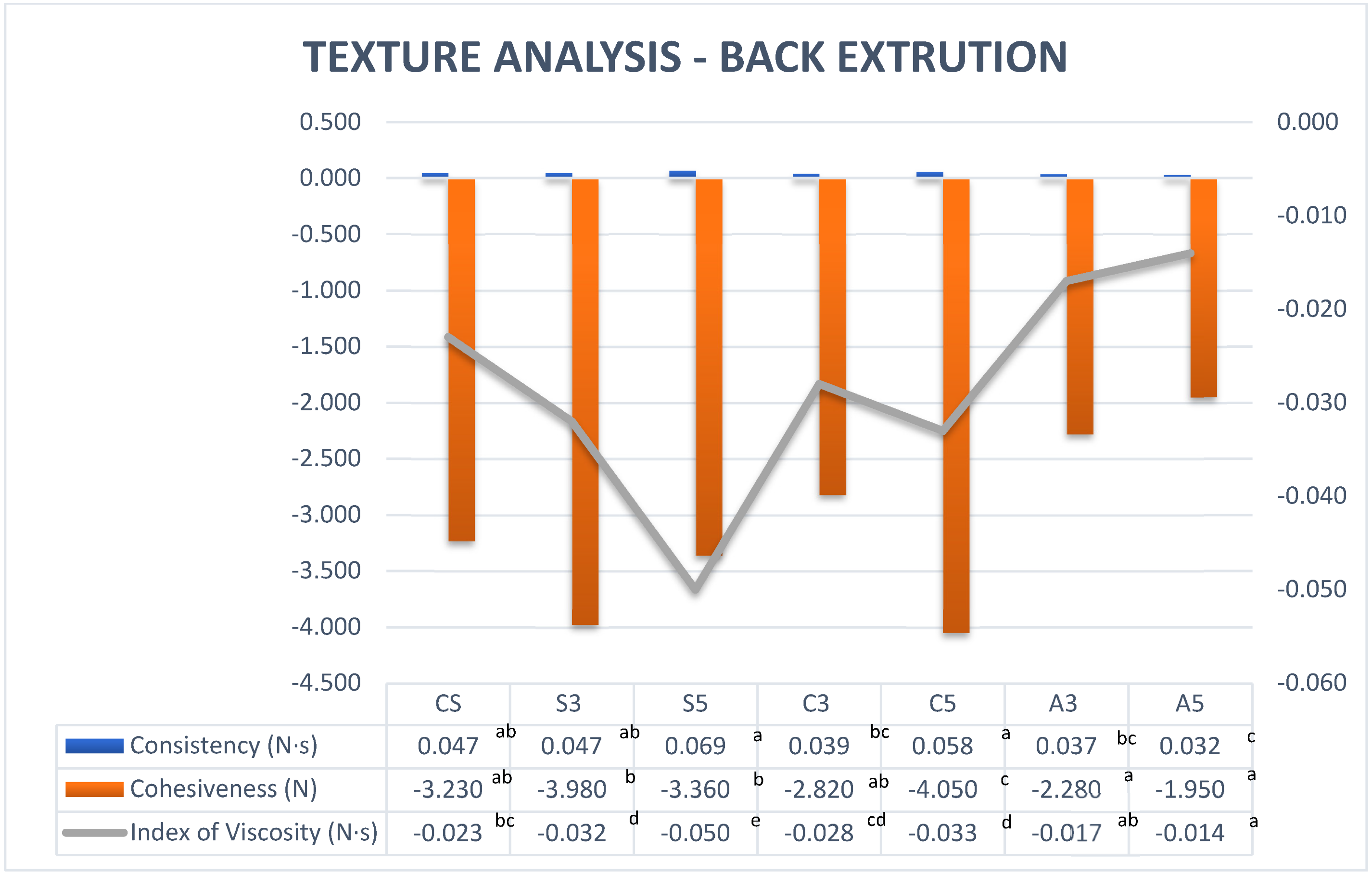
3.2.2. Back Extrusion
3.2.3. Force of Extrusion
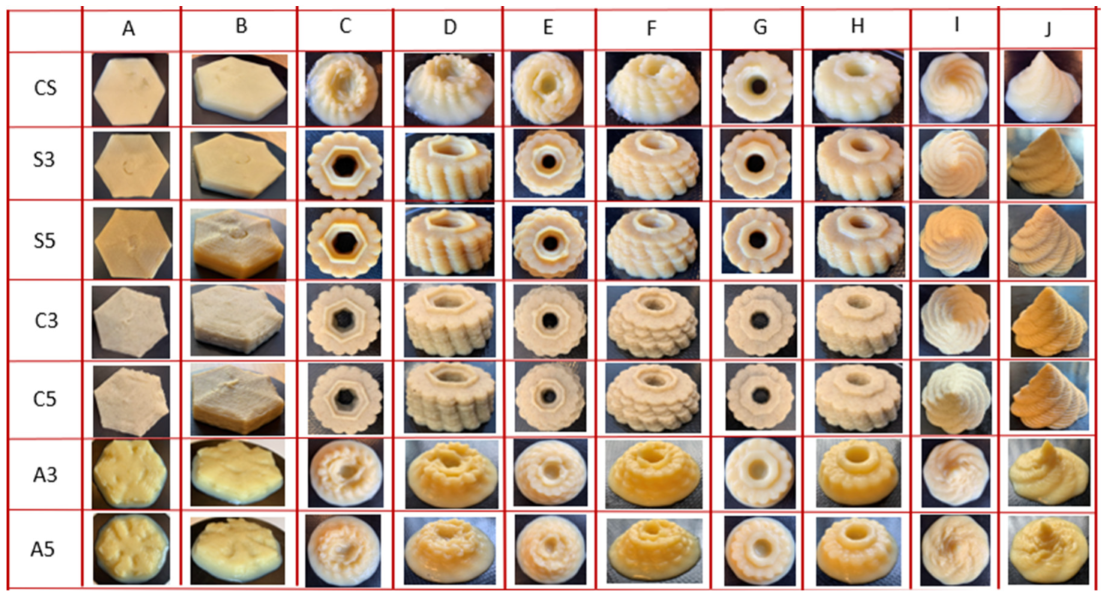
3.3. 3D Printing Test and Correlations
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lille, M.; Nurmela, A.; Nordlund, E.; Metsä-Kortelainen, S.; Sozer, N. Applicability of protein and fiber-rich food materials in extrusion-based 3D printing. J. Food Eng. 2018, 220, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Zhou, W.; Huang, D.; Fuh, J.Y.H.; Hong, G.S. An Overview of 3D Printing Technologies for Food Fabrication. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2015, 8, 1605–1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baishakhi, D.; Koushik, B.; Gt, K. Innovative Technologies in Tailoring Designer Food and Personalized Nutrition. Nov. Tech. Nutr. Food Sci. 2019, 2, 319–323. [Google Scholar]
- Trumbo, P.; Schlicker, S.; Yates, A.A.; Poos, M. Dietary Reference Intakes for Energy, Carbohydrate, Fiber, Fat, Fatty Acids, Cholesterol, Protein and Amino Acids. J. Am. Diet Assoc. 2002, 102, 1621–1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soenen, S.; Bonomi, A.G.; Lemmens, S.G.T.; Scholte, J.; Thijssen, M.A.M.A.; Van Berkum, F.; Westerterp-Plantenga, M.S. Relatively high-protein or ‘low-carb’ energy-restricted diets for body weight loss and body weight maintenance? Physiol. Behav. 2012, 107, 374–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lejeune, M.P.G.M.; Kovacs, E.M.R.; Westerterp-Plantenga, M.S. Additional protein intake limits weight regain after weight loss in humans. Br. J. Nutr. 2005, 93, 281–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Weigle, D.S.; Breen, P.A.; Matthys, C.C.; Callahan, H.S.; Meeuws, K.E.; Burden, V.R.; Purnell, J.Q. A high-protein diet induces sustained reductions in appetite, ad libitum caloric intake, and body weight despite compensatory changes in diurnal plasma leptin and ghrelin concentrations. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2005, 82, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.Z.; Zhang, H.; Gao, L.; Wang, L.; Qian, H.F. Influence of pH and ionic strength on heat-induced formation and rheological properties of cottonseed protein gels. Food Bioprod. Process. 2015, 96, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frigolet, M.E.; Torres, N.; Tovar, A.R. Soya protein attenuates abnormalities of the renina-angiotensin system in adipose tissue from obese rats. Br. J. Nutr. 2012, 107, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Torres, N.; Torre-Villalvazo, I.; Tovar, A.R. Regulation of lipid metabolism by soy protein and its implication in diseases mediated by lipid disorders. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2006, 17, 365–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panasevich, M.R.; Schuster, C.M.; Phillips, K.E.; Meers, G.M.; Chintapalli, S.V.; Wankhade, U.D.; Shankar, K.; Butteiger, D.N.; Krul, E.S.; Thyfault, J.P.; et al. Soy compared with milk protein in a Western diet changes fecal microbiota and decreases hepatic steatosis in obese OLETF rats. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2017, 46, 125–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirazimi, F.; Saldo, J.; Sepulcre, F.; Gràcia, A.; Pujolà, M. Enriched puree potato with soy protein for dysphagia patients by using 3D printing. Food Front. 2022, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duda, A.; Jezowski, P.; Radzikowska, D.; Kowalczewski, P.L. Partial wheat flour replacement with gluten-free flours in bread-quality, texture and antioxidant activity. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. Food Sci. 2019, 9, 505–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belluco, S.; Losasso, C.; Maggioletti, M.; Alonzi, C.C.; Paoletti, M.G.; Ricci, A. Edible insects in a food safety and nutritional perspective: A critical review. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2013, 12, 296–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rumpold, B.A.; Schlüter, O.K. Nutritional composition and safety aspects of edible insects. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2013, 57, 802–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hall, F.G.; Jones, O.G.; O’Haire, M.E.; Liceaga, A.M. Functional properties of tropical banded cricket (Gryllodes sigillatus) protein hydrolysates. Food Chem. 2017, 224, 414–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abeyrathne, E.D.N.S.; Lee, H.Y.; Ahn, D.U. Egg white proteins and their potential use in food processing or as nutraceutical and pharmaceutical agents—A review. Poult. Sci. 2013, 92, 3292–3299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mine, Y. Recent advances in the understanding of egg white protein functionality. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 1995, 6, 225–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mine, Y.; Noutomi, T.; Haga, N. Emulsifying and Structural Properties of Ovalbumin. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1991, 39, 443–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zicari, G.; Carraro, E.; Bonetta, S. The Regulation (EC) N. 1924/2006 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 20 December 2006 on nutrition and health claims made on foods. Prog. Nutr. 2007, 404, 9–25. [Google Scholar]
- Dankar, I.; Pujolà, M.; El Omar, F.; Sepulcre, F.; Haddarah, A. Impact of Mechanical and Microstructural Properties of Potato Puree-Food Additive Complexes on Extrusion-Based 3D Printing. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2018, 11, 2021–2031. [Google Scholar]
- Tabilo-Munizaga, G.; Barbosa-Cánovas, G.V. Rheology for the food industry. J. Food Eng. 2005, 67, 147–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sungsinchai, S.; Niamnuy, C.; Wattanapan, P.; Charoenchaitrakool, M.; Devahastin, S. Texture Modification Technologies and Their Opportunities for the Production of Dysphagia Foods: A Review. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2019, 18, 1898–1912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cappelli, A.; Oliva, N.; Bonaccorsi, G.; Lorini, C.; Cini, E. Assessment of the rheological properties and bread characteristics obtained by innovative protein sources (Cicer arietinum, Acheta domesticus, Tenebrio molitor): Novel food or potential improvers for wheat flour? LWT 2020, 118, 108867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Vora, A.; Han, W.J.; Wojtecki, R.; Maune, H.B.A.; Le, A.E.; Thompson, L.M.; McClelland, G.; Ribet, F.C.; Engler, A.; et al. Dual-Responsive Hydrogels for Direct-Write 3D Printing. Macromolecules 2015, 48, 6482–6488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montoya, J.; Medina, J.; Molina, A.; Gutiérrez, J.; Rodríguez, B.; Marín, R. Impact of viscoelastic and structural properties from starch-mango and starch-arabinoxylans hydrocolloids in 3D food printing. Addit. Manuf. 2021, 39, 101891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J. Food oral processing—A review. Food Hydrocoll. 2009, 23, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, M.; Kristo, E.; Corredig, M.; Duizer, L. Food Hydrocolloids Effect of hydrocolloid type on texture of pureed carrots: Rheological and sensory measures. Food Hydrocoll. 2017, 63, 478–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Hadde, E.K.; Chen, J. Development of a ball back extrusion technique for texture analysis of fluid food. J. Texture Stud. 2021, 52, 461–469. [Google Scholar]
- Nasaruddin, F.; Chin, N.L.; Yusof, Y.A. Effect of processing on instrumental textural properties of traditional dodol using back extrusion. Int. J. Food Prop. 2012, 15, 495–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.; Kennedy, J.F.; Li, B.; Xu, X.; Xie, B.J. Characters of rice starch gel modified by gellan, carrageenan, and glucomannan: A texture profile analysis study. Carbohydr. Polym. 2007, 69, 411–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Zhang, M.; Bhandari, B.; Yang, C. Impact of rheological properties of mashed potatoes on 3D printing. J. Food Eng. 2018, 220, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Z.; Bhandari, B.; Prakash, S.; Mantihal, S.; Zhang, M. Linking rheology and printability of a multicomponent gel system of carrageenan-xanthan-starch in extrusion based additive manufacturing. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 87, 413–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, R.; Wang, K.; Tian, H.; Liu, X.; Liu, G.; Hu, Z.; Zhao, L. Analysis on the printability and rheological characteristics of bigel inks: Potential in 3D food printing. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 129, 107675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, W.; Ren, C.; Tian, M.; Yang, X.; Li, J.; Li, B. Complex coacervation of ovalbumin-carboxymethylcellulose assessed by isothermal titration calorimeter and rheology: Effect of ionic strength and charge density of polysaccharide. Food Hydrocoll. 2017, 73, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickinson, E. Hydrocolloids at interfaces and the influence on the properties of dispersed systems. Food Hydrocoll. 2003, 17, 25–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razi, S.M.; Motamedzadegan, A.; Shahidi, S.A.; Rashidinejad, A. Physical and Rheological Properties of Egg Albumin Foams Are Affected by Ionic Strength and Basil Seed Gum Supplementation. Int. J. Chem. Eng. 2019, 2019, 2502908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Kruif, C.G.; Tuinier, R. Polysaccharide protein interactions. Food Hydrocoll. 2001, 15, 555–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polyakov, V.I.; Grinberg, V.Y.; Tolstoguzov, V.B. Thermodynamic incompatibility of proteins. Food Hydrocoll. 1997, 11, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grinberg, V.Y.; Tolstoguzov, V.B. Thermodynamic incompatibility of proteins and polysaccharides in solutions. Food Hydrocoll. 1997, 11, 145–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Energy | 1475 KJ/348 Kcal |
|---|---|
| Fat | 0.8 g |
| Carbohydrates | 75 g |
| Fiber | 6.8 g |
| Proteins | 7.4 g |
| Salt | 0.06 g |
| Moisture | 16.7 g |
| Protein | Soy Protein (S) | Cricket Protein (C) | Egg Albumin (A) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Protein % in recipe | 3 | 5 | 3 | 5 | 3 | 5 |
| Protein/100 g product | 2.9 | 4.6 | 2.7 | 4.4 | 2.9 | 4.6 |
| Energy Kcal/100 g product | 59.3 | 67.6 | 61.3 | 71.5 | 58.9 | 66.8 |
| Samples | Yield Point (Pa) | ηᵨ (Pa·s) | τ₀ (Pa) |
|---|---|---|---|
| CS | 620 bc | 105 bc | 302 b |
| S3 | 636 bc | 254 b | 469 ab |
| S5 | 981 a | 451 a | 535 a |
| C3 | 742 bc | 302 ab | 486 ab |
| C5 | 917 b | 397 ab | 503 a |
| A3 | 530 c | 87 c | 290 c |
| A5 | 558 c | 92 c | 270 c |
| Samples | G′ (Pa) | G″ (Pa) | TANGENT δ (−) |
|---|---|---|---|
| CS | 686 b | 106 bc | 0.16 ab |
| S3 | 717 b | 121 b | 0.16 ab |
| S5 | 995 a | 163 a | 0.13 b |
| C3 | 816 ab | 130 ab | 0.15 b |
| C5 | 827 ab | 131 ab | 0.15 b |
| A3 | 661 bc | 96 c | 0.19 a |
| A5 | 404 c | 88 c | 0.19 a |
| Samples | Hardness (N) | Adhesiveness (N·s) | Cohesiveness (−) | Springiness (−) | Gumminess (N) | Chewiness (−) | Resilience (−) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CS | 2.68 a | −4.16 b | 0.005 a | 0.009 a | 2.21 a | 2.08 a | 0.0007 a |
| S3 | 3.36 a | −5.55 a | 0.006 a | 0.009 a | 2.30 a | 2.11 a | 0.0007 a |
| S5 | 3.34 a | −5.70 a | 0.006 a | 0.009 a | 2.39 a | 2.21 a | 0.0006 a |
| C3 | 3.61 a | −5.75 a | 0.006 a | 0.009 a | 2.52 a | 2.35 a | 0.0006 a |
| C5 | 3.58 a | −6.19 a | 0.006 a | 0.009 a | 2.55 a | 2.36 a | 0.0006 a |
| A3 | 2.72 a | −3.80 c | 0.005 a | 0.008 a | 2.12 a | 2.01 a | 0.0007 a |
| A5 | 2.79 a | −3.73 c | 0.005 a | 0.009 a | 2.32 a | 2.04 a | 0.0007 a |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mirazimi, F.; Saldo, J.; Sepulcre, F.; Gràcia, A.; Pujolà, M. Preparing a Personalized Meal by Using Soy, Cricket, and Egg Albumin Protein Based on 3D Printing. Foods 2022, 11, 2244. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11152244
Mirazimi F, Saldo J, Sepulcre F, Gràcia A, Pujolà M. Preparing a Personalized Meal by Using Soy, Cricket, and Egg Albumin Protein Based on 3D Printing. Foods. 2022; 11(15):2244. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11152244
Chicago/Turabian StyleMirazimi, Farnaz, Jordi Saldo, Francesc Sepulcre, Alvar Gràcia, and Montserrat Pujolà. 2022. "Preparing a Personalized Meal by Using Soy, Cricket, and Egg Albumin Protein Based on 3D Printing" Foods 11, no. 15: 2244. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11152244
APA StyleMirazimi, F., Saldo, J., Sepulcre, F., Gràcia, A., & Pujolà, M. (2022). Preparing a Personalized Meal by Using Soy, Cricket, and Egg Albumin Protein Based on 3D Printing. Foods, 11(15), 2244. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11152244








