Changes in Textural Quality and Water Retention of Spiced Beef under Ultrasound-Assisted Sous-Vide Cooking and Its Possible Mechanisms
Abstract
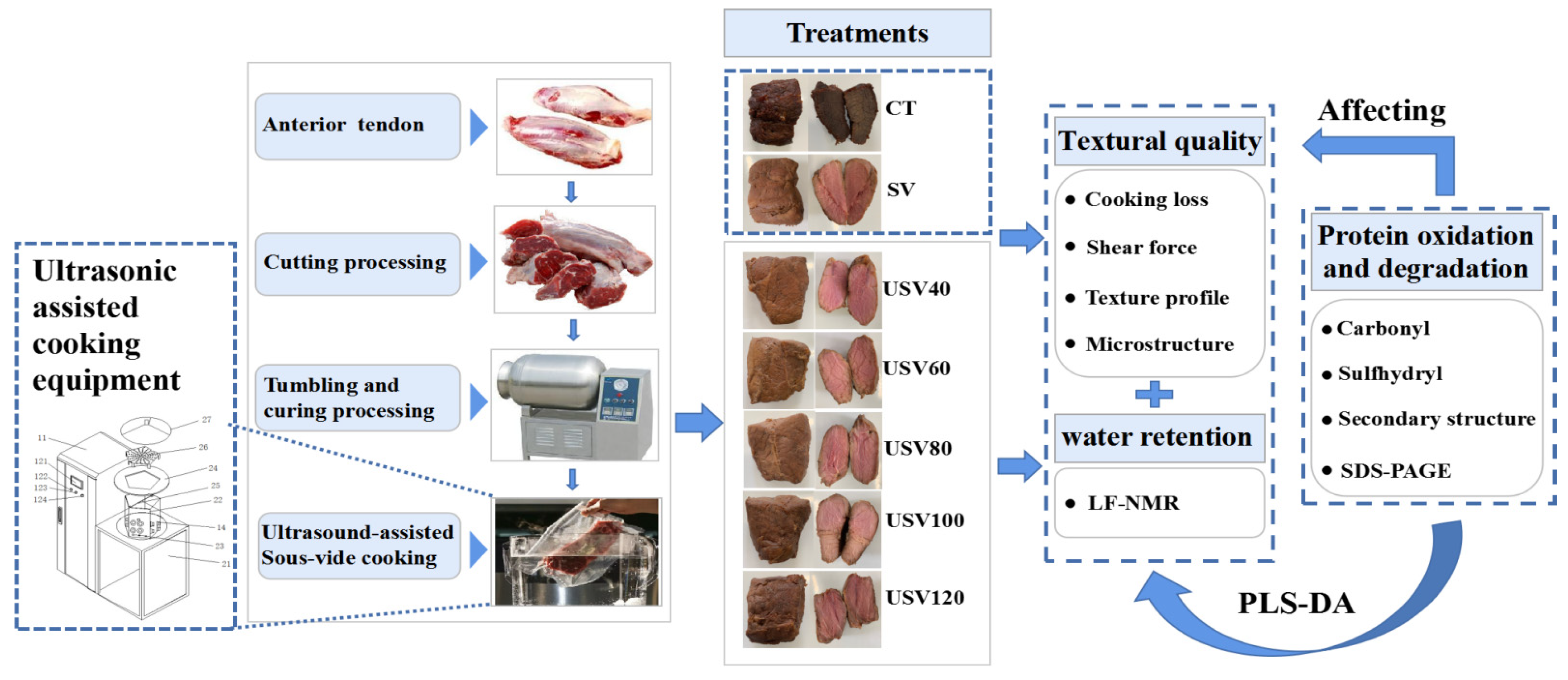
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Chemicals
2.2. Preparation of Meat and Curing Solution
2.3. Preparation of Spiced Beef
2.4. Meat Quality Testing
2.4.1. Measurement of Cooking Loss
2.4.2. Measurement of Warner–Bratzler Shear Force (WBSF)
2.4.3. Analysis of Texture Profile
2.4.4. Analysis of Microstructure by Light Microscopy
2.4.5. Low-Field Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (LF-NMR) Analysis
2.5. Protein Properties Testing
2.5.1. Extraction of Total Protein
2.5.2. Carbonyl Content Determination
2.5.3. Sulfhydryl Content Determination
2.5.4. Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR) Spectroscopy Analysis
2.5.5. Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate-Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) Analysis
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Changes in Cooking Loss and Warner–Bratzler Shear Force
3.2. Changes in Texture Properties
3.3. Changes in Light Microscopy
3.4. Changes in Water Migration and Distribution
3.5. Changes in Protein Oxidation
3.6. Changes in Secondary Structure
3.7. Proteolytic Changes
3.8. Partial Least Squares Discriminant Analysis (PLS-DA)
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zeng, W.; Wen, W.; Deng, Y.; Tian, Y.; Sun, H.; Sun, Q. Chinese ethnic meat products: Continuity and development. Meat Sci. 2016, 120, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zou, Y.; Zhang, W. Effects of ultrasound-assisted cooking on quality characteristics of spiced beef during cold storage. LWT 2021, 136, 110359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dominguez-Hernandez, E.; Salaseviciene, A.; Ertbjerg, P. Low-temperature long-time cooking of meat: Eating quality and underlying mechanisms. Meat Sci. 2018, 143, 104–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jiang, S.; Xue, D.; Zhang, Z.; Shan, K.; Ke, W.; Zhang, M.; Zhao, D.; Nian, Y.; Xu, X.; Zhou, G.; et al. Effect of Sous-vide cooking on the quality and digestion characteristics of braised pork. Food Chem. 2022, 375, 131683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tornberg, E.V.A. Effects of heat on meat proteins-Implications on structure and quality of meat products. Meat Sci. 2005, 70, 493–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayub, H.; Ahmad, A. Physiochemical changes in sous-vide and conventionally cooked meat. Int. J. Gastron. Food Sci. 2019, 17, 100145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, J.; Cao, A.; Cai, L. Effects of vacuum or sous-vide cooking methods on the quality of largemouth bass (Micropterus salmoides). Int. J. Gastron. Food Sci. 2019, 18, 100181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y.; Wu, D.; Liang, D.; Ye, H.; Cai, Z.; Ma, M.; Geng, F. Effects of high-intensity ultrasonic (HIU) treatment on the functional properties and assemblage structure of egg yolk. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2020, 60, 104767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, D.-C.; Gao, X.-Q.; Ge, Q.-F.; Zhou, G.-H.; Zhang, W.-G. Effects of ultrasound on the beef structure and water distribution during curing through protein degradation and modification. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2017, 38, 317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pohlman, F.; Dikeman, M.; Kropf, D. Effects of high intensity ultrasound treatment, storage time and cooking method on shear, sensory, instrumental color and cooking properties of packaged and unpackaged beef pectoralis muscle. Meat Sci. 1997, 46, 89–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.; Zhang, W.; Kang, D.; Zhou, G. Improvement of tenderness and water holding capacity of spiced beef by the application of ultrasound during cooking. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 53, 828–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, X.; Kong, B.; Liu, J.; Diao, X.; Liu, Q. Influence of different thawing methods on physicochemical changes and protein oxidation of porcine longissimus muscle. LWT 2012, 46, 280–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Y.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, H.; Li, X.; Fang, F.; Liang, C.; Wang, Z. Effect of Postmortem Phases on Lamb Meat Quality: A Physicochemical, Microstructural and Water Mobility Approach. Food Sci. Anim. Resour. 2021, 41, 802–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, R.; Ge, Q.; Wu, M.; Xu, B.; Xi, J.; Yu, H. Effects of branched-chain amino acids and Lactobacillus plantarum CGMCC18217 on volatiles formation and textural properties of dry-cured fermented sausage. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 56, 374–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Lin, R.; Cheng, S.; Tan, M. Water dynamics changes and protein denaturation in surf clam evaluated by two-dimensional LF-NMR T1-T2 relaxation technique during heating process. Food Chem. 2020, 320, 126622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Xiao, S.; Lee, E.J.; Ahn, D.U. Consumption of oxidized oil increases oxidative stress in broilers and affects the quality of breast meat. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 969–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kang, D.-C.; Zou, Y.-H.; Cheng, Y.-P.; Xing, L.-J.; Zhou, G.-H.; Zhang, W.-G. Effects of power ultrasound on oxidation and structure of beef proteins during curing processing. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2016, 33, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gangidi, R.R.; Proctor, A.; Pohlman, F.W.; Meullenet, J.-F. Rapid determination of spinal cord content in ground beef by attenuated total reflectance fourier transform infrared spectroscopy. J. Food Sci. 2010, 68, 124–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, X.; Hou, C.; Zhang, D.; Li, X.; Ren, C.; Ijaz, M.; Hussain, Z.; Liu, D. Effect of pre- and post-rigor on texture, flavor, heterocyclic aromatic amines and sensory evaluation of roasted lamb. Meat Sci. 2020, 169, 108220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Liu, R.; Yang, L.; Yang, W.; Li, K.; Qin, M.; Ge, Q.; Yu, H.; Wu, M.; Zhou, X. Improvement strategies for quality defects and oxidation of pale, soft and exudative (PSE)-like chicken meat: Effects of domestic cooking and core temperature. RSC Adv. 2022, 12, 7485–7496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabre, R.; Dalzotto, G.; Perlo, F.; Bonato, P.; Teira, G.; Tisocco, O. Cooking method effect on Warner-Bratzler shear force of different beef muscles. Meat Sci. 2018, 138, 10–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehrabani, A.; Javan, A.J.; Hesarinejad, M.A.; Mahdavi, A.; Parsaeimehr, M. The combined effect of ultrasound treatment and leek (Allium ampeloprasum) extract on the quality properties of beef. Food Biosci. 2022, 47, 101622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, V.; Guizani, N.; Al-Alawi, A.; Claereboudt, M.; Rahman, M.S. Instrumental texture profile analysis (TPA) of date fruits as a function of its physicochemical properties. Ind. Crops Prod. 2013, 50, 866–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Yang, L.; Yang, T.; Qin, M.; Li, K.; Bao, W.; Wu, M.; Yu, H.; Wu, S.; Ge, Q. Effect of nitric oxide treatment on pork meat quality, microstructure, and total bacterial count during postmortem aging. Meat Sci. 2022, 190, 108806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Zhang, M.; Yang, C.-H. Application of ultrasound technology in processing of ready-to-eat fresh food: A review. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2020, 63, 104953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, P.; Sun, L.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y.; Zou, Y.; Yan, Z.; Zhang, M.; Wang, D.; Xu, W. Effects of combined ultrasound and low-temperature short-time heating pretreatment on proteases inactivation and textural quality of meat of yellow-feathered chickens. Food Chem. 2021, 3, 129645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, D.-C.; Wang, A.-R.; Zhou, G.-H.; Zhang, W.-G.; Xu, S.-M.; Guo, G.-P. Power ultrasonic on mass transport of beef: Effects of ultrasound intensity and NaCl concentration. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2016, 35, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz-Garibaldi, B.Y.; Alarcon-Rojo, A.D.; Huerta-Jimenez, M.; Garcia-Galicia, I.A.; Carrillo-Lopez, L.M. Efficacy of Ultrasonic-Assisted Curing Is Dependent on Muscle Size and Ultrasonication System. Processes 2020, 8, 1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, M.; Wang, P.; Xu, X.; Zhou, G. Low-field NMR study of heat-induced gelation of pork myofibrillar proteins and its relationship with microstructural characteristics. Food Res. Int. 2014, 62, 1175–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, D.; Ma, S.; Wang, L.; Zhao, H.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, H.; Chen, W. 1H NMR studies of starch–water interactions during microwave heating. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 97, 406–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Huang, F.; Li, X.; Han, D.; Zhao, L.; Liang, H.; Rui, M.; Wang, J.; Zhang, C. Water status evolution of pork blocks at different cooking procedures: A two-dimensional LF-NMR T1-T2 relaxation study. Food Res. Int. 2021, 148, 110614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, S.; Hu, F.; Mehmood, W.; Li, X.; Zhang, C.; Blecker, C. The rise of thawing drip: Freezing rate effects on ice crystallization and myowater dynamics changes. Food Chem. 2022, 373, 131461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertram, H.C.; Whittaker, A.K.; Andersen, H.J.; Karlsson, A.H. Visualization of drip channels in meat using NMR microimaging. Meat Sci. 2004, 68, 667–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderssen, K.E.; McCarney, E.R. Mechanisms of transverse relaxation of water in muscle tissue. Food Control 2022, 132, 108373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Li, F.; Diao, X.; Kong, B.; Xia, X. Moisture migration, microstructure damage and protein structure changes in porcine longissimus muscle as influenced by multiple freeze-thaw cycles. Meat Sci. 2017, 133, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Straadt, I.K.; Rasmussen, M.; Andersen, H.J.; Bertram, H.C. Aging-induced changes in microstructure and water distribution in fresh and cooked pork in relation to water-holding capacity and cooking loss—A combined confocal laser scanning microscopy (CLSM) and low-field nuclear magnetic resonance relaxation study. Meat Sci. 2007, 75, 687–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDonnell, C.K.; Allen, P.; Duggan, E.; Arimi, J.M.; Casey, E.; Duane, G.; Lyng, J.G. The effect of salt and fibre direction on water dynamics, distribution and mobility in pork muscle: A low field NMR study. Meat Sci. 2013, 95, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearce, K.L.; Rosenvold, K.; Andersen, H.J.; Hopkins, D.L. Water distribution and mobility in meat during the conversion of muscle to meat and ageing and the impacts on fresh meat quality attributes—A review. Meat Sci. 2011, 89, 111–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.-B.; Han, M.-Y.; Yang, H.-J.; Xu, X.-L.; Zhou, G.-H. The effect of pressure-assisted heating on the water holding capacity of chicken batters. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2018, 45, 280–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dean, R.T.; Fu, S.; Stocker, R.; Davies, M.J. Biochemistry and pathology of radical-mediated protein oxidation. Biochem. J. 1997, 324, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Berhe, D.T.; Engelsen, S.B.; Hviid, M.S.; Lametsch, R. Raman spectroscopic study of effect of the cooking temperature and time on meat proteins. Food Res. Int. 2014, 66, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Y.; Zhou, L.; Pereira, J.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, W. Insights into Digestibility and Peptide Profiling of Beef Muscle Proteins with Different Cooking Methods. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 14243–14251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Utrera, M.; Estévez, M. Oxidation of Myofibrillar Proteins and Impaired Functionality: Underlying Mechanisms of the Carbonylation Pathway. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 8002–8011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gülseren, I.; Güzey, D.; Bruce, B.D.; Weiss, J. Structural and functional changes in ultrasonicated bovine serum albumin solutions. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2007, 14, 173–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Li, X.; Wang, J.-Z.; Zhang, C.-H.; Sun, H.-M.; Wang, C.-Q.; Xie, X.-L. Effects of Oxidation on Water Distribution and Physicochemical Properties of Porcine Myofibrillar Protein Gel. Food Biophys. 2014, 9, 169–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.-Y.; Yang, Y.-L.; Tang, X.-Z.; Ni, W.-X.; Zhou, L. Effects of pulsed ultrasound on rheological and structural properties of chicken myofibrillar protein. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2017, 38, 225–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Kong, B.; Li, F.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, H.; Xia, X. Changes in the thermal stability and structure of protein from porcine longissimus dorsi induced by different thawing methods. Food Chem. 2020, 316, 126375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Li, Z.; Wang, Y.; Xue, Y.; Xue, C. Effects of konjac glucomannan on heat-induced changes of physicochemical and structural properties of surimi gels. Food Res. Int. 2016, 83, 152–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Wang, J.; Li, Y.; Wang, Z.; Liang, J.; Wang, R.; Chen, Y.; Ma, W.; Qi, B.; Zhang, M. Effects of ultrasound on the structure and physical properties of black bean protein isolates. Food Res. Int. 2014, 62, 595–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mune, M.; Alain, M.; Sogi, D.; Singh, M.; Samuel, R. Response surface methodology for investigating structure–function relationship of grain legume proteins. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2018, 42, e13524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.; Zhang, J.; Zheng, J.; Li, X.; Shao, J.-H. The study of protein conformation and hydration characteristics of meat batters at various phase transition temperatures combined with Low-field nuclear magnetic resonance and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy. Food Chem. 2018, 280, 263–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Z.; Bertram, H.C.; Böcker, U.; Ofstad, R.; Kohler, A. Myowater Dynamics and Protein Secondary Structural Changes as Affected by Heating Rate in Three Pork Qualities: A Combined FT-IR Microspectroscopic and 1H NMR Relaxometry Study. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2007, 55, 3990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokur, B.; Korkmaz, K. The effects of an iron-catalyzed oxidation system on lipids and proteins of dark muscle fish. Food Chem. 2007, 104, 754–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, L.; Nian, L.; Cao, A.; Zhang, Y.; Li, X. Effect of Carboxymethyl Chitosan Magnetic Nanoparticles Plus Herring Antifreeze Protein on Conformation and Oxidation of Myofibrillar Protein from Red Sea Bream (Pagrosomus major) after Freeze-Thaw Treatment. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2020, 13, 355–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Sample ID | Hardness (N) | Springiness (mm) | Chewiness (mJ) |
|---|---|---|---|
| CT | 55.66 ± 4.48 c | 3.98 ± 0.64 c | 64.36 ± 9.50 c |
| SV | 96.34 ± 5.58 a | 4.59 ± 0.34 b | 210.80 ± 11.85 ab |
| USV40 | 85.91 ± 4.36 bc | 4.55 ± 0.25 b | 191.37 ± 13.65 b |
| USV60 | 92.62 ± 5.60 b | 4.60 ± 0.37 b | 203.04 ± 18.70 b |
| USV80 | 92.19 ± 1.19 b | 4.98 ± 0.22 ab | 222.98 ± 13.27 a |
| USV100 | 93.57 ± 2.70 b | 4.90 ± 0.16 ab | 218.65 ± 16.80 a |
| USV120 | 98.25 ± 4.05 a | 5.33 ± 0.55 a | 246.27 ± 16.25 a |
| Sample ID | T1 (ms) | T2 (ms) | P1 (%) | P2 (%) | P3 (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CT | 666.03 ± 18.59 a | 315.06 ± 10.58 a | 2.04 ± 0.04 d | 89.80 ± 2.14 b | 8.16 ± 0.55 a |
| SV | 609.70 ± 20.14 ab | 300.54 ± 10.21 ab | 9.80 ± 0.53 c | 86.27 ± 2.21 bc | 3.93 ± 0.68 b |
| USV40 | 347.05 ± 12.50 d | 281.19 ± 9.56 b | 11.90 ± 0.75 b | 85.71 ± 3.02 c | 2.39 ± 0.84 c |
| USV60 | 397.94 ± 10.53 c | 280.87 ± 8.74 b | 2.24 ± 0.25 d | 96.47 ± 4.05 a | 1.29 ± 0.15 cd |
| USV80 | 386.15 ± 11.27 c | 242.79 ± 7.55 c | 3.54 ± 0.37 d | 95.70 ± 3.57 a | 0.76 ± 0.10 d |
| USV100 | 488.85 ± 10.83 b | 261.27 ± 6.39 bc | 10.26 ± 0.90 b | 87.18 ± 2.56 bc | 2.56 ± 0.24 c |
| USV120 | 424.34 ± 15.56 bc | 308.88 ± 7.87 ab | 19.44 ± 0.27 a | 77.78 ± 2.30 d | 2.78 ± 0.50 c |
| Sample ID | Secondary Structure Content (%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| α-Helix | β-Sheet | β-Turn | Random Coil | |
| CT | 23.35 ± 0.07 c | 36.01 ± 0.02 a | 15.81 ± 0.04 a | 24.83 ± 0.05 a |
| SV | 24.09 ± 0.08 b | 34.25 ± 0.10 b | 16.20 ± 0.03 a | 25.46 ± 0.03 a |
| USV40 | 33.42 ± 0.04 a | 35.14 ± 0.15 b | 10.94 ± 0.08 b | 20.50 ± 0.08 b |
| USV60 | 33.78 ± 0.14 a | 34.94 ± 0.03 b | 10.91 ± 0.13 b | 20.37 ± 0.13 b |
| USV80 | 32.75 ± 0.05 ab | 36.26 ± 0.09 a | 10.68 ± 0.07 b | 20.31 ± 0.07 b |
| USV100 | 25.86 ± 0.15 b | 31.67 ± 0.11 c | 16.87 ± 0.04 a | 25.59 ± 0.04 a |
| USV120 | 23.89 ± 0.13 c | 35.21 ± 0.21 b | 15.85 ± 0.07 a | 25.05 ± 0.07 a |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, H.; Gao, Z.; Guo, X.; Gao, S.; Wu, D.; Liu, Z.; Wu, P.; Xu, Z.; Zou, X.; Meng, X. Changes in Textural Quality and Water Retention of Spiced Beef under Ultrasound-Assisted Sous-Vide Cooking and Its Possible Mechanisms. Foods 2022, 11, 2251. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11152251
Wang H, Gao Z, Guo X, Gao S, Wu D, Liu Z, Wu P, Xu Z, Zou X, Meng X. Changes in Textural Quality and Water Retention of Spiced Beef under Ultrasound-Assisted Sous-Vide Cooking and Its Possible Mechanisms. Foods. 2022; 11(15):2251. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11152251
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Hengpeng, Ziwu Gao, Xiuyun Guo, Sumin Gao, Danxuan Wu, Zongzhen Liu, Peng Wu, Zhicheng Xu, Xiaobo Zou, and Xiangren Meng. 2022. "Changes in Textural Quality and Water Retention of Spiced Beef under Ultrasound-Assisted Sous-Vide Cooking and Its Possible Mechanisms" Foods 11, no. 15: 2251. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11152251
APA StyleWang, H., Gao, Z., Guo, X., Gao, S., Wu, D., Liu, Z., Wu, P., Xu, Z., Zou, X., & Meng, X. (2022). Changes in Textural Quality and Water Retention of Spiced Beef under Ultrasound-Assisted Sous-Vide Cooking and Its Possible Mechanisms. Foods, 11(15), 2251. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11152251






