Heat Treatment, Cultivar and Formulation Modify the Sensory Properties and Consumer Acceptability of Gels Containing Faba Bean (Vicia faba L. minor) Protein Concentrates
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Faba Bean Protein Concentrates
2.2. Gel Formulation
2.3. Gel Consistency
2.4. Sensory Analyses
2.4.1. Experimental Conditions
2.4.2. Sensory Profiling
| Descriptor Groups | Descriptors | Scale Anchors | Definitions | Standards |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Texture | Sticky | Not much/very | Sticky feeling perceived between the palate and tongue when manipulating the gel in the mouth. | - |
| Thick | Fluid/thick | Thick feeling perceived in the mouth related to the gel viscosity. | - | |
| Granular | Smooth/granular | Grainy feeling perceived in the mouth related to grains or granules in the gel. | - | |
| Foamy | Not much/very | Foamy feeling perceived in the mouth related to bubbles in the gel. | - | |
| Tastes * | Salty | Absent/very intense | Basic taste caused by dilute aqueous solutions of various substances such as sodium chloride. | 2 g/L of sodium chloride solution (Cooper Standard, Northville, MI, USA). |
| Bitter | Basic taste caused by dilute aqueous solutions of various substances such as caffeine. | 0.5 g/L of caffeine solution (Cooper Standard, Northville, MI, USA). | ||
| Umami | Basic taste caused by dilute aqueous solutions of various substances such as umami. | 0.6 g/L of monosodium glutamate solution (99% pure; Ajinomoto, Tokyo, Japan). | ||
| Aromas ** | Green note | Absent/very intense | Aromas of peas, French beans, asparagus, green legumes and grass. | Filtered infusion of mashed frozen pea (Carrefour Classic’, Massy, France) in water at 4 °C for 24 h. |
| Mushroom | Specific aroma of mushroom. | Filtered infusion of mushroom cooked for 5 min in boiling water. | ||
| Broth | Specific aroma of broth. | Filtered homemade broth with onion, celery, carrot, turnip, leek and clove in water cooked for 1 h. | ||
| Haricot bean | Aromas of haricot bean, dry beans and chickpea. | Juice of haricot bean can (Carrefour®, France). | ||
| Cereal | Specific aroma of cereal. | 3 g of type 55 wheat flour (Carrefour®, France). | ||
| Metallic *** | Specific aroma of metallic. | 0.05 g/L of ferrous sulphate (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Quentin Fallavier, France). | ||
| Potato | Specific aroma of potato. | Filtered infusion of potato cooked for 5 min in boiling water. | ||
| Grilled | Specific aroma of grilled. | Filtered infusion of grilled bread (200 °C—10 min) in water. | ||
| Rancid | Specific aroma of rancid. | Piece of a wafer sheet (Modecor Italiana, Cuvio, Italy) exposed to light and dioxygen at ambient temperature. | ||
| Yeast | Aroma of yeast and cheese. | 3 g of yeast (Gerblé®, France). |
2.4.3. Consumer Liking
2.5. Statistical Data Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Sensory Profiling
3.1.1. Performance of the Panel
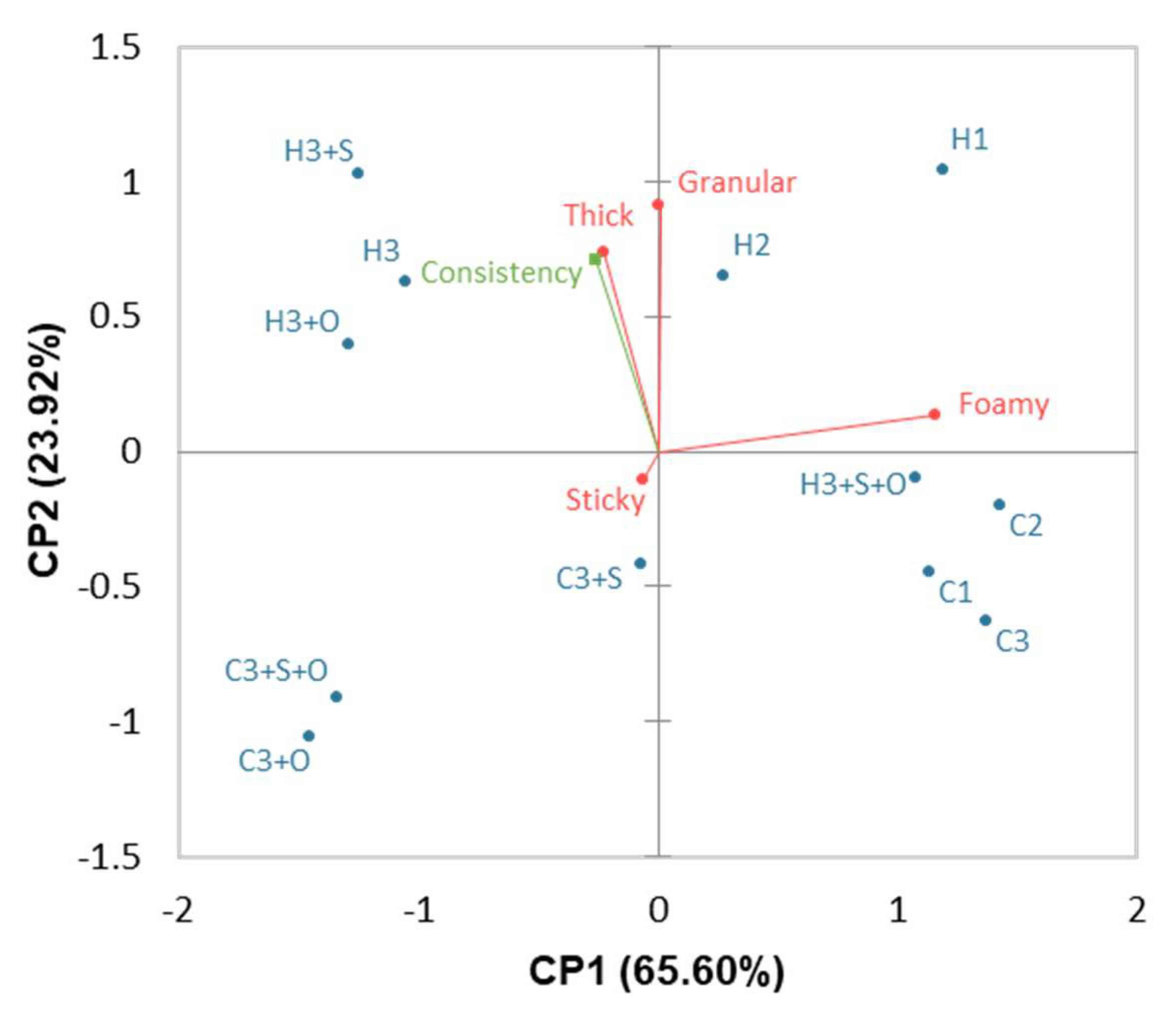
3.1.2. Effects of the Heat Treatment and Formulation on the Gel Texture
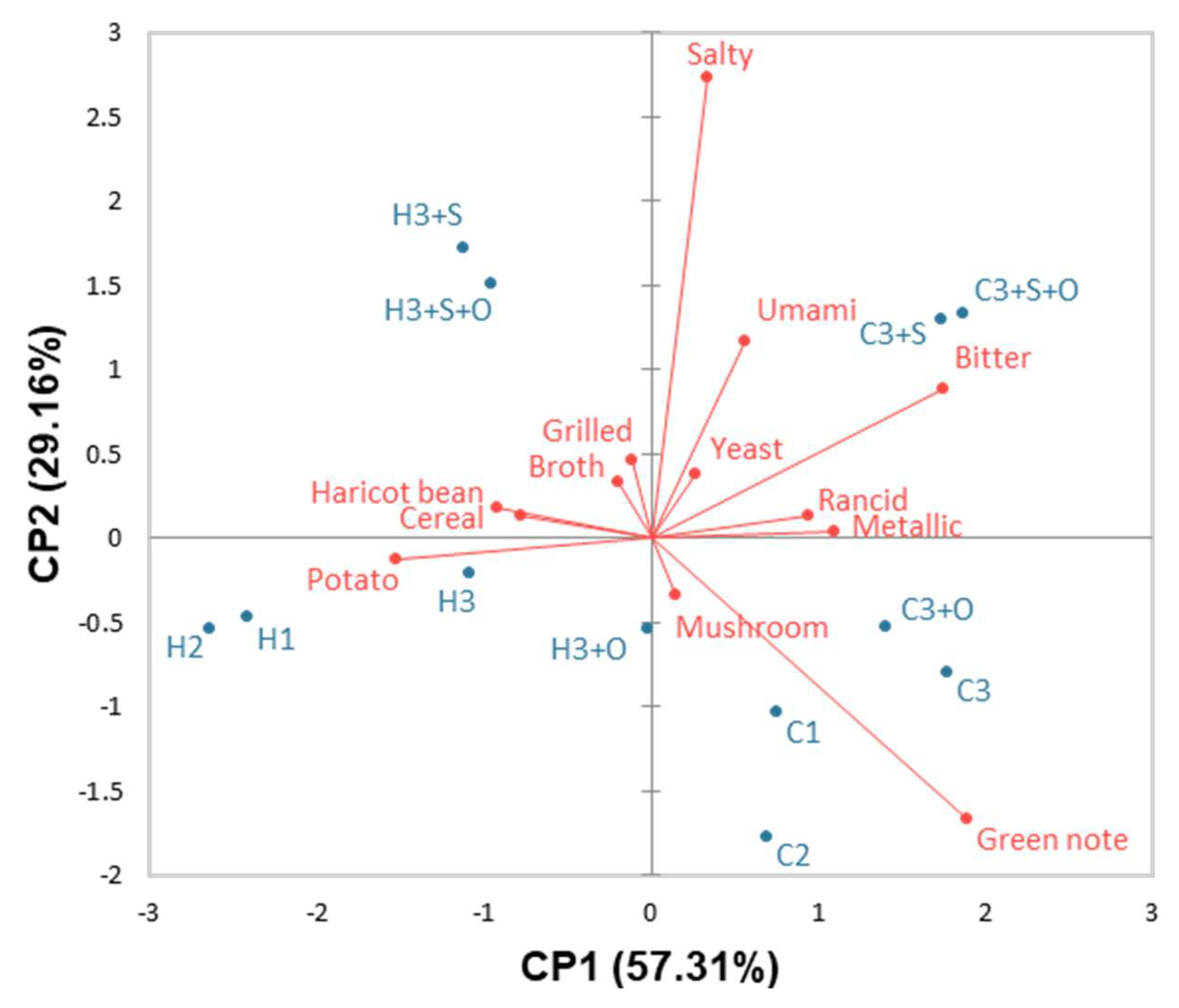
3.1.3. Effects of the Cultivar and Heat Treatment on the Gel Flavour
3.1.4. Effect of the Formulation on the Gel Flavour
3.2. Consumer Liking
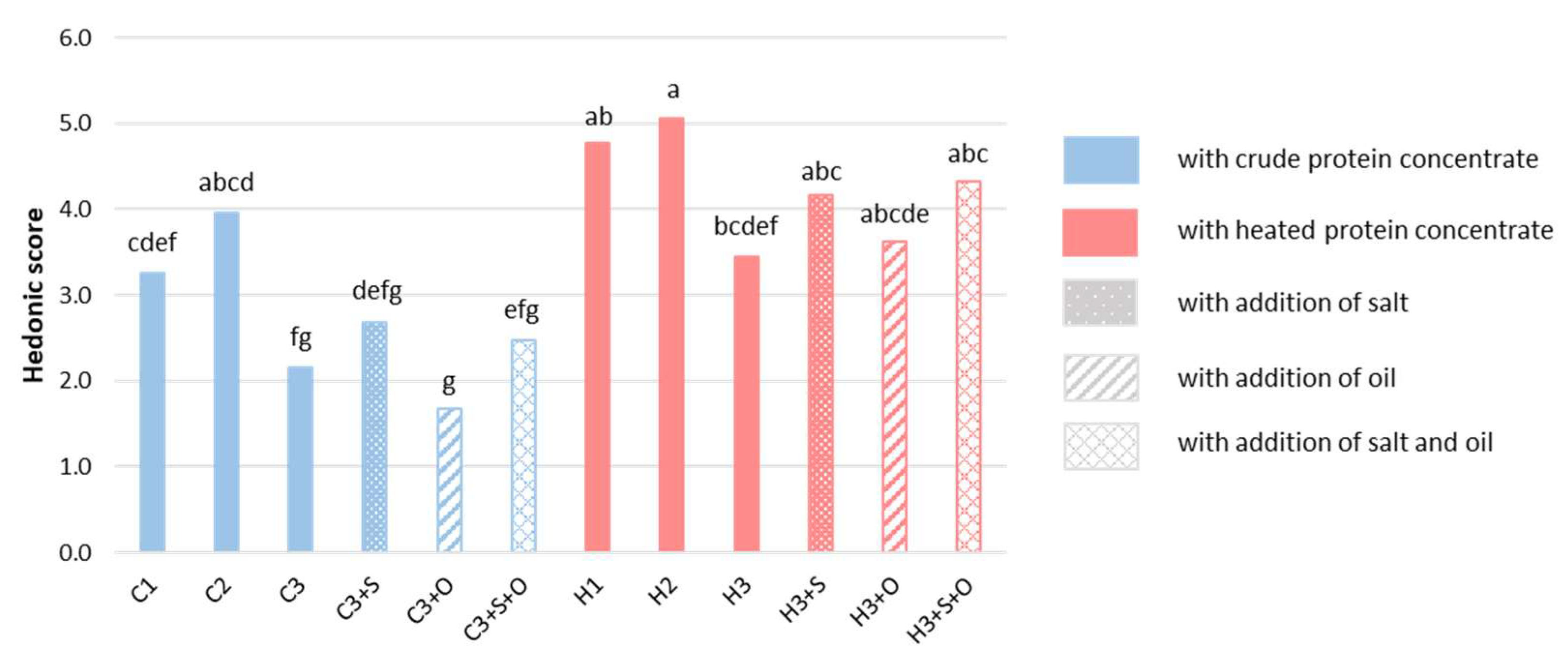
3.2.1. Effects of the Cultivar, Heat Treatment and Formulation on Gel Appreciation
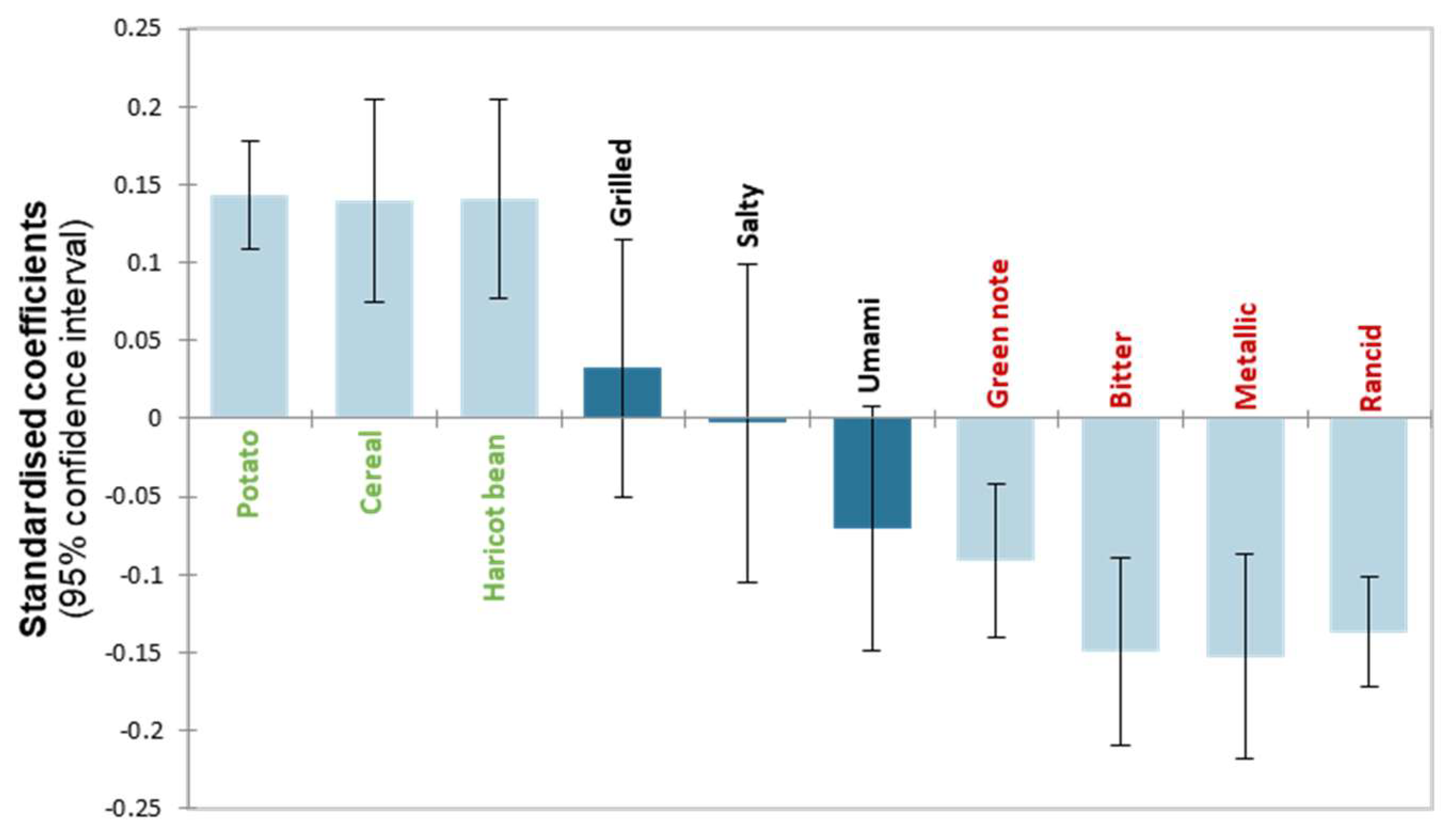
3.2.2. Taste and Aroma Properties Guiding Gel Acceptability
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- FAOSTAT. Production/Yield Quantities of Broad Beans, Horse Beans, Dry in World, 1994–2020. Available online: https://www.fao.org/faostat/en/#data/QCL/visualize (accessed on 13 June 2022).
- Duc, G. Faba Bean (Vicia faba L.). Field Crops Res. 1997, 53, 99–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chéreau, D.; Videcoq, P.; Ruffieux, C.; Pichon, L.; Motte, J.-C.; Belaid, S.; Ventureira, J.; Lopez, M. Combination of Existing and Alternative Technologies to Promote Oilseeds and Pulses Proteins in Food Applications. OCL 2016, 23, D406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Multari, S.; Stewart, D.; Russell, W.R. Potential of Fava Bean as Future Protein Supply to Partially Replace Meat Intake in the Human Diet. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2015, 14, 511–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guinet, M.; Nicolardot, B.; Voisin, A.-S. Provision of Contrasted Nitrogen-Related Ecosystem Services among Grain Legumes. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2020, 40, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crews, T.E.; Peoples, M.B. Legume versus Fertilizer Sources of Nitrogen: Ecological Tradeoffs and Human Needs. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2004, 102, 279–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guéguen, J.; Walrand, S.; Bourgeois, O. Les protéines végétales: Contexte et potentiels en alimentation humaine. Cah. Nutr. Diet. 2016, 51, 177–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharan, S.; Zanghelini, G.; Zotzel, J.; Bonerz, D.; Aschoff, J.; Saint-Eve, A.; Maillard, M.-N. Fava Bean (Vicia faba L.) for Food Applications: From Seed to Ingredient Processing and Its Effect on Functional Properties, Antinutritional Factors, Flavor, and Color. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2021, 20, 401–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boye, J.; Zare, F.; Pletch, A. Pulse Proteins: Processing, Characterization, Functional Properties and Applications in Food and Feed. Food Res. Int. 2010, 43, 414–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voisin, A.-S.; Guéguen, J.; Huyghe, C.; Jeuffroy, M.-H.; Magrini, M.-B.; Meynard, J.M.; Mougel, C.; Pellerin, S.; Pelzer, E. Les légumineuses dans l’Europe du XXIè siècle: Quelle place dans les systèmes agricoles et alimentaires actuels et futurs? Quels nouveaux défis pour la recherche? Innov. Agron. 2013, 30, 283–312. [Google Scholar]
- Havasi, A. La Filière de la Féverole en France 2021. Available online: http://www.terresunivia.fr/ (accessed on 13 June 2022).
- Melendrez-Ruiz, J.; Arvisenet, G.; Laugel, V.; Chambaron, S.; Monnery-Patris, S. Do French Consumers Have the Same Social Representations of Pulses as Food Industry Professionals? Foods 2020, 9, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roland, W.S.U.; Pouvreau, L.; Curran, J.; van de Velde, F.; de Kok, P.M.T. Flavor Aspects of Pulse Ingredients. Cereal Chem. 2017, 94, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Karolkowski, A.; Guichard, E.; Briand, L.; Salles, C. Volatile Compounds in Pulses: A Review. Foods 2021, 10, 3140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azarnia, S.; Boye, J.I.; Warkentin, T.; Malcolmson, L. Changes in Volatile Flavour Compounds in Field Pea Cultivars as Affected by Storage Conditions. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2011, 46, 2408–2419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khrisanapant; Kebede; Leong; Oey A Comprehensive Characterisation of Volatile and Fatty Acid Profiles of Legume Seeds. Foods 2019, 8, 651. [CrossRef]
- Fauconnier, M.L.; Vanzeveren, E.; Marlier, M.; Lognay, G.; Wathelet, J.P.; Severin, M. Assessment of Lipoxygenase Activity in Seed Extracts from 35 Plant Species. Grasas Aceites 1995, 46, 6–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heng, L.; Vincken, J.-P.; van Koningsveld, G.; Legger, A.; Gruppen, H.; van Boekel, T.; Roozen, J.; Voragen, F. Bitterness of Saponins and Their Content in Dry Peas. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2006, 86, 1225–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amarowicz, R.; Yoshiki, Y.; Pegg, R.B.; Okubo, K. Presence of Two Saponins in Faba Bean (Vicia faba L.) Seeds. Nahrung 1997, 41, 352–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldin, E.; Reitmeier, H.A.; Murphy, P. Bitterness of Soy Extracts Containing Isoflavones and Saponins. J. Food Sci. 2006, 71, S211–S215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roland, W.S.U.; Vincken, J.-P.; Gouka, R.J.; van Buren, L.; Gruppen, H.; Smit, G. Soy Isoflavones and Other Isoflavonoids Activate the Human Bitter Taste Receptors HTAS2R14 and HTAS2R39. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 11764–11771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de los A. Gremasqui, I.; Giménez, M.A.; Lobo, M.O.; Sammán, N.C. Evaluation of Functional and Nutritional Properties of Hydrolyzed Broad Bean and Quinoa Flours. Biol. Life Sci. Forum 2022, 8, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briand, L.; Salles, C. Taste Perception and Integration; Elsevier Ltd.: Duxford, UK, 2016; pp. 101–119. ISBN 978-0-08-100295-7. [Google Scholar]
- Soares, S.; Brandão, E.; Guerreiro, C.; Soares, S.; Mateus, N.; de Freitas, V. Tannins in Food: Insights into the Molecular Perception of Astringency and Bitter Taste. Molecules 2020, 25, 2590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ployon, S.; Morzel, M.; Belloir, C.; Bonnotte, A.; Bourillot, E.; Briand, L.; Lesniewska, E.; Lherminier, J.; Aybeke, E.; Canon, F. Mechanisms of Astringency: Structural Alteration of the Oral Mucosal Pellicle by Dietary Tannins and Protective Effect of BPRPs. Food Chem. 2018, 253, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canon, F.; Belloir, C.; Bourillot, E.; Brignot, H.; Briand, L.; Feron, G.; Lesniewska, E.; Nivet, C.; Septier, C.; Schwartz, M.; et al. Perspectives on Astringency Sensation: An Alternative Hypothesis on the Molecular Origin of Astringency. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 3822–3826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amarowicz, R.; Troszyńska, A.; Baryłko-Pikielna, N.; Shahidi, F. Polyphenolics Extracts from Legume Seeds: Correlations between Total Antioxidant Activity, Total Phenolics Content, Tannins Content and Astringency. J. Food Lipids 2004, 11, 278–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ömür-Özbek, P.; Dietrich, A.M.; Duncan, S.E.; Lee, Y. Role of Lipid Oxidation, Chelating Agents, and Antioxidants in Metallic Flavor Development in the Oral Cavity. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 2274–2280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khazaei, H.; Vandenberg, A. Seed Mineral Composition and Protein Content of Faba Beans (Vicia faba L.) with Contrasting Tannin Contents. Agronomy 2020, 10, 511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delompré, T.; Guichard, E.; Briand, L.; Salles, C. Taste Perception of Nutrients Found in Nutritional Supplements: A Review. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos-Díaz, J.; Suvanto, S.; Forsten, E.; Seppa, L. Investigación Preliminar de La Influencia Del Tratamiento Térmico y Tiempo de Almacenamiento Sobre El Aroma de Habas (Vicia faba). Cátedra Villarreal 2016, 1, 11–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karolkowski, A.; Gourrat, K.; Bouzidi, E.; Albouy, J.-F.; Levavasseur, L.; Briand, L.; Guichard, E.; Salles, C. Origins of Volatile Compounds and Identification of Odour-Active Compounds in Air-Classified Fractions of Faba Bean (Vicia faba L. Minor). Food Res. Int. 2022; submitted. [Google Scholar]
- Schultz, M.; Hoppe, K.; Schmandke, H. Off-Flavour Reduction in Vicia faba Bean Protein Isolate. Food Chem. 1988, 30, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vekeman, F.; Reheul, D.; Van Bockstaele, F. Potential of Faba Beans (Vicia faba L.) for Human Consumption. Master’s Thesis, Universiteit Gent, Gent, Belgium, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Hinchcliffe, J.I. Flavour Characteristics of Fababeans. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Manitoba, Winnipeg, MB, Canada, 1975. [Google Scholar]
- Samaei, S.P.; Ghorbani, M.; Tagliazucchi, D.; Martini, S.; Gotti, R.; Themelis, T.; Tesini, F.; Gianotti, A.; Gallina Toschi, T.; Babini, E. Functional, Nutritional, Antioxidant, Sensory Properties and Comparative Peptidomic Profile of Faba Bean (Vicia faba, L.) Seed Protein Hydrolysates and Fortified Apple Juice. Food Chem. 2020, 330, 127120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montemurro, M.; Coda, R.; Rizzello, C.G. Recent Advances in the Use of Sourdough Biotechnology in Pasta Making. Foods 2019, 8, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cunha, L.M.; Fonseca, S.C.; Lima, R.C.; Loureiro, J.; Pinto, A.S.; Vaz Patto, M.C.; Brites, C. Consumer-Driven Improvement of Maize Bread Formulations with Legume Fortification. Foods 2019, 8, 235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saldanha do Carmo, C.; Knutsen, S.H.; Malizia, G.; Dessev, T.; Geny, A.; Zobel, H.; Myhrer, K.S.; Varela, P.; Sahlstrøm, S. Meat Analogues from a Faba Bean Concentrate Can Be Generated by High Moisture Extrusion. Future Foods 2021, 3, 100014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sworn, G.; Stouby, L. Chapter 28—Gellan Gum. In Handbook of Hydrocolloids, 3rd. ed.; Phillips, G.O., Williams, P.A., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing Series in Food Science, Technology and Nutrition; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2021; pp. 855–885. ISBN 978-0-12-820104-6. [Google Scholar]
- Nussinovitch, A. Gellan Gum. In Hydrocolloid Applications: Gum Technology in the Food and Other Industries; Nussinovitch, A., Ed.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1997; pp. 63–82. ISBN 978-1-4615-6385-3. [Google Scholar]
- Cosson, A.; Souchon, I.; Richard, J.; Descamps, N.; Saint-Eve, A. Using Multiple Sensory Profiling Methods to Gain Insight into Temporal Perceptions of Pea Protein-Based Formulated Foods. Foods 2020, 9, 969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makri, E.A.; Papalamprou, E.M.; Doxastakis, G.I. Textural Properties of Legume Protein Isolate and Polysaccharide Gels. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2006, 86, 1855–1862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monnet, A.-F.; Michon, C.; Jeuffroy, M.-H.; Blumenthal, D. Taking into Account Upstream Variability of Flours with Processing Variables in Legume-Enriched Soft Cakes: Conception of a Multiobjective Model for the Monitoring of Physical Properties. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2019, 12, 625–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueller, C.A.; Pintscher, K.; Renner, B. Clinical Test of Gustatory Function Including Umami Taste. Ann. Otol. Rhinol. Laryngol. 2011, 120, 358–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cecchini, M.P.; Knaapila, A.; Hoffmann, E.; Boschi, F.; Hummel, T.; Iannilli, E. A Cross-Cultural Survey of Umami Familiarity in European Countries. Food Qual Prefer. 2019, 74, 172–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macfie, H.J.; Bratchell, N.; Greenhoff, K.; Vallis, L.V. Designs to Balance the Effect of Order of Presentation and First-Order Carry-Over Effects in Hall Tests. J. Sens. Stud. 1989, 4, 129–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, C.; Maire, A.; Chabanet, C.; Issanchou, S. Equi-Intensity across the SpectrumTM Taste Scales. Food Qual Prefer. 2015, 44, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chigwedere, C.M.; Wanasundara, J.P.D.; Shand, P.J. Sensory Descriptors for Pulses and Pulse-Derived Ingredients: Toward a Standardized Lexicon and Sensory Wheel. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2022, 21, 999–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peltier, C. Statistical Analysis of Sensory Profiling Data Revisited by a Database Approach. Ph.D. Thesis, Université de Bourgogne, Dijon, France, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Yasumatsu, K.; Sawada, K.; Moritaka, S.; Misaki, M.; Toda, J.; Wada, T.; Ishii, K. Whipping and Emulsifying Properties of Soybean Products. Agric. Biol. Chem. 1972, 36, 719–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbey, B.W.; Ibeh, G.O. Functional Properties of Raw and Heat Processed Cowpea (Vigna unguiculata, Walp) Flour. J. Food Sci. 1988, 53, 1775–1777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akintayo, E.T.; Oshodi, A.A.; Esuoso, K.O. Effects of NaCl, Ionic Strength and PH on the Foaming and Gelation of Pigeon Pea (Cajanus cajan) Protein Concentrates. Food Chem. 1999, 66, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inyang, U.E.; Nwadimkpa, C.U. Functional Properties of Dehulled Sesame (Sesamum indicum L.) Seed Flour. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 1992, 69, 819–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.R.; Hettiarachchy, N.S. Effect of Xanthan Gum on Enhancing the Foaming Properties of Soy Protein Isolate. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 1998, 75, 729–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, L.; Miao, S.; Yuan, F.; Gao, Y. Study on the Textural and Volatile Characteristics of Emulsion Filled Protein Gels as Influenced by Different Fat Substitutes. Food Res. Int. 2018, 103, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudre, T.G.; Benjakul, S.; Kishimura, H. Comparative Study on Chemical Compositions and Properties of Protein Isolates from Mung bean, Black bean and Bambara groundnut. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2013, 93, 2429–2436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potes, N.; Kerry, J.P.; Roos, Y.H. Protein Modifications in High Protein-Oil and Protein-Oil-Sugar Systems at Low Water Activity. Food Biophys. 2014, 9, 49–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, N. Pulses: An Overview. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 54, 853–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Boekel, M.A.J.S. Formation of Flavour Compounds in the Maillard Reaction. Biotechnol. Adv. 2006, 24, 230–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bühler, J.M.; Dekkers, B.L.; Bruins, M.E.; van der Goot, A.J. Modifying Faba Bean Protein Concentrate Using Dry Heat to Increase Water Holding Capacity. Foods 2020, 9, 1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Z.; Pulkkinen, M.; Wang, Y.; Lampi, A.-M.; Stoddard, F.L.; Salovaara, H.; Piironen, V.; Sontag-Strohm, T. Faba Bean Flavour and Technological Property Improvement by Thermal Pre-Treatments. LWT 2016, 68, 295–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gürbüz, G.; Liu, C.; Jiang, Z.; Pulkkinen, M.; Piironen, V.; Sontag-Strohm, T.; Heinonen, M. Protein-Lipid Co-Oxidation in Emulsions Stabilized by Microwave-Treated and Conventional Thermal-Treated Faba Bean Proteins. Food Sci. Nutr. 2018, 6, 1032–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murat, C.; Bard, M.-H.; Dhalleine, C.; Cayot, N. Characterisation of Odour Active Compounds along Extraction Process from Pea Flour to Pea Protein Extract. Food Res. Int. 2013, 53, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardador-Martínez, A.; Maya-Ocaña, K.; Ortiz-Moreno, A.; Herrera-Cabrera, B.E.; Dávila-Ortiz, G.; Múzquiz, M.; Martín-Pedrosa, M.; Burbano, C.; Cuadrado, C.; Jiménez-Martínez, C. Effect of Roasting and Boiling on the Content of Vicine, Convicine and L-3,4-Dihydroxyphenylalanine in Vicia faba L. J. Food Qual. 2012, 35, 419–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heng, L.; Vincken, J.-P.; Hoppe, K.; van Koningsveld, G.A.; Decroos, K.; Gruppen, H.; van Boekel, M.A.J.S.; Voragen, A.G.J. Stability of Pea DDMP Saponin and the Mechanism of Its Decomposition. Food Chem. 2006, 99, 326–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siah, S.; Konczak, I.; Wood, J.A.; Agboola, S.; Blanchard, C.L. Effects of Roasting on Phenolic Composition and In Vitro Antioxidant Capacity of Australian Grown Faba Beans (Vicia faba L.). Plant Foods Hum. Nutr. 2014, 69, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, S.; Takahashi, C. Interactions of Monosodium Glutamate and Sodium Chloride on Saltiness and Palatability of a Clear Soup. J. Food Sci. 1984, 49, 82–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, P.K.W.; Hoehn, E.; Bushuk, W. Binding of Vanillin by Fababean Proteins. J. Food Sci. 1989, 54, 105–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guichard, E. Interactions between Flavor Compounds and Food Ingredients and Their Influence on Flavor Perception. Food Rev. Int. 2002, 18, 49–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salles, C. 16-Odour–Taste Interactions in Flavour Perception. In Flavour in Food; Voilley, A., Etiévant, P., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing Series in Food Science, Technology and Nutrition; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2006; pp. 345–368. ISBN 978-1-85573-960-4. [Google Scholar]
- Benjamin, O.; Silcock, P.; Leus, M.; Everett, D.W. Multilayer Emulsions as Delivery Systems for Controlled Release of Volatile Compounds Using PH and Salt Triggers. Food Hydrocoll. 2012, 27, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas-Danguin, T.; Sinding, C.; Tournier, C.; Saint-Eve, A. 5—Multimodal Interactions. In Flavor; Etiévant, P., Guichard, E., Salles, C., Voilley, A., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing Series in Food Science, Technology and Nutrition; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2016; pp. 121–141. ISBN 978-0-08-100295-7. [Google Scholar]
- Gardze, C.; Bowers, J.A.; Caul, J.F. Effect of Salt and Textured Soy Level on Sensory Characteristics of Beef Patties. J. Food Sci. 1979, 44, 460–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tenenhaus, M.; Pagès, J.; Ambroisine, L.; Guinot, C. PLS Methodology to Study Relationships between Hedonic Judgements and Product Characteristics. Food Qual Prefer. 2005, 16, 315–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Gel Samples | Type of Concentrate | Protein Concentrate (g) | Xanthan Gum (g) | MSG 1 (g) | Water (g) | NaCl (%) | Oil (%) | Consistency 2 (N.mm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1 | P1 | 20 | 1.0 | 0.6 | 79 | - | - | 1.80 h ± 0.08 |
| H1 | HP1 | - | - | 2.62 de ± 0.04 | ||||
| C2 | P2 | - | - | 1.89 gh ± 0.21 | ||||
| H2 | HP2 | - | - | 3.17 bc ± 0.17 | ||||
| C3 | P3 | - | - | 2.12 fgh ± 0.01 | ||||
| C3+S | 0.25 | - | 2.86 cd ± 0.01 | |||||
| C3+O | - | 3.0 | 2.13 fg ± 0.06 | |||||
| C3+S+O | 0.25 | 3.0 | 2.40 ef ± 0.06 | |||||
| H3 | HP3 | - | - | 3.30 b ± 0.02 | ||||
| H3+S | 0.25 | - | 3.70 a ± 0.19 | |||||
| H3+O | - | 3.0 | 3.27 b ± 0.14 | |||||
| H3+S+O | 0.25 | 3.0 | 3.44 ab ± 0.06 |
| Panel | French Population 1,2 | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Sex | Women (%) | 49 | 52 |
| Men (%) | 51 | 48 | |
| Age (year) | 20–39 (%) | 33 | 31 |
| 40–59 (%) | 34 | 35 | |
| 60 and over (%) | 33 | 34 | |
| Level of education | <Baccalaureate * (%) | 18 | 29 |
| ≥Baccalaureate (%) | 82 | 40 | |
| Pulse consumption frequency | 1 to 3 times a month (%) | 10 | - |
| ≥once a week (%) | 90 | 48 |
| Descriptor | Product | Panellist*Product | RMSE * | Gmean ** | Gel Mean | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F | p-Value | F | p-Value | C1 | H1 | C2 | H2 | C3 | C3+S | C3+O | C3+S+O | H3 | H3+S | H3+O | H3+S+O | |||
| Foamy | 14.65 | <0.001 | 1.44 | <0.01 | 1.68 | 2.90 | +1.09 | +1.15 | +1.44 | +1.27 | −1.62 | −1.44 | −1.00 | −1.02 | +1.03 | −1.20 | ||
| Green note | 12.74 | <0.001 | 0.90 | 0.79 | 2.06 | 3.39 | +0.89 | −1.23 | +2.14 | −1.03 | +0.85 | +0.63 | −0.71 | −1.13 | −1.19 | |||
| Granular | 11.64 | <0.001 | 1.39 | <0.01 | 0.96 | 0.84 | −0.49 | +1.29 | +0.38 | −0.40 | −0.43 | −0.59 | −0.59 | +0.52 | +0.61 | |||
| Bitter | 10.75 | <0.001 | 1.91 | <0.001 | 1.27 | 2.66 | −1.33 | −0.52 | −1.67 | +0.94 | +0.90 | +1.05 | +0.97 | |||||
| Salty | 10.29 | <0.001 | 2.25 | <0.001 | 1.27 | 2.68 | −0.71 | −0.61 | −0.61 | −0.83 | +1.30 | −0.60 | +1.29 | −0.59 | +1.35 | −0.64 | +1.13 | |
| Potato | 6.73 | <0.001 | 2.19 | <0.001 | 1.17 | 1.88 | +1.14 | +1.07 | −0.81 | −0.54 | −0.53 | −1.00 | ||||||
| Metallic | 6.31 | <0.001 | 1.34 | <0.05 | 1.15 | 1.43 | −0.66 | −0.90 | +0.62 | +0.52 | +0.70 | |||||||
| Thick | 6.12 | <0.001 | 0.91 | 0.77 | 1.58 | 3.95 | +0.48 | −0.72 | −0.69 | +0.50 | +1.17 | +0.62 | ||||||
| Cereal | 4.79 | <0.001 | 0.45 | 1.00 | 1.66 | 1.62 | +0.34 | +0.37 | −0.45 | −0.48 | −0.47 | +0.39 | +0.37 | +0.48 | ||||
| Umami | 4.21 | <0.001 | 1.74 | <0.001 | 1.14 | 1.72 | −0.66 | −0.55 | +0.89 | +0.79 | ||||||||
| Rancid | 4.04 | <0.001 | 2.17 | <0.001 | 0.98 | 0.90 | −0.53 | −0.52 | +0.63 | +0.78 | −0.47 | |||||||
| Haricot bean | 3.98 | <0.001 | 1.71 | <0.001 | 1.18 | 2.31 | +0.90 | −0.62 | +0.71 | |||||||||
| Grilled | 2.06 | <0.05 | 0.65 | 1.00 | 1.02 | 1.08 | −0.33 | +0.25 | +0.32 | |||||||||
| Sticky | 1.96 | <0.05 | 1.30 | <0.05 | 1.47 | 3.68 | +0.54 | +0.59 | −0.57 | |||||||||
| Yeast | 1.20 | 0.29 | 1.87 | <0.001 | 1.15 | 1.65 | −0.49 | +0.61 | ||||||||||
| Broth | 0.95 | 0.49 | 1.00 | 0.50 | 1.44 | 1.73 | +0.49 | |||||||||||
| Mushroom | 0.81 | 0.62 | 1.49 | <0.001 | 1.15 | 1.29 | ||||||||||||
| Descriptors | Panellist | Cultivar | Heat Treatment | Cultivar*Heat Treatment | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F | p-Value | F | p-Value | F | p-Value | F | p-Value | |
| Green note | 10.61 | <0.0001 | 2.57 | 0.081 | 74.29 | <0.0001 | 3.17 | 0.046 |
| Bitter | 16.69 | <0.0001 | 18.88 | <0.0001 | 31.55 | <0.0001 | 0.03 | 0.966 |
| Salty | 24.80 | <0.0001 | 0.34 | 0.709 | 0.15 | 0.697 | 0.43 | 0.653 |
| Potato | 15.12 | <0.0001 | 2.90 | 0.059 | 30.91 | <0.0001 | 0.13 | 0.880 |
| Metallic | 17.04 | <0.0001 | 4.93 | 0.009 | 26.77 | <0.0001 | 0.15 | 0.858 |
| Cereal | 49.08 | <0.0001 | 0.19 | 0.830 | 16.95 | <0.0001 | 0.29 | 0.751 |
| Umami | 19.97 | <0.0001 | 2.73 | 0.070 | 1.46 | 0.230 | 1.72 | 0.185 |
| Rancid | 6.74 | <0.0001 | 1.14 | 0.324 | 13.08 | <0.001 | 0.82 | 0.443 |
| Haricot bean | 32;35 | <0.0001 | 7.72 | 0.001 | 15.27 | <0.001 | 0.00 | 1.000 |
| Grilled | 59.25 | <0.0001 | 2.05 | 0.135 | 2.61 | 0.110 | 0.60 | 0.553 |
| Yeast | 22.22 | <0.0001 | 0.81 | 0.449 | 0.02 | 0.896 | 1.43 | 0.265 |
| Broth | 50.07 | <0.0001 | 0.18 | 0.837 | 4.15 | 0.044 | 0.56 | 0.572 |
| Mushroom | 11.71 | <0.0001 | 0.48 | 0.621 | 0.71 | 0.402 | 0.58 | 0.562 |
| Hedonic | 5.18 | <0.0001 | 26.36 | <0.0001 | 43.04 | <0.0001 | 0.38 | 0.685 |
| Descriptors | Cultivar | Heat Treatment | Cultivar*Heat Treatment | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | No | Yes | 1*No | 2*No | 3*No | 1*Yes | 2*Yes | 3*Yes | |
| Green note | 4.69 a | 2.40 b | 4.28 a | 5.53 a | 4.24 a | 2.16 b | 2.36 b | 2.68 b | |||
| Bitter | 1.94 b | 1.56 b | 3.05 a | 2.76 a | 1.61 b | ||||||
| Potato | 1.46 b | 2.77 a | |||||||||
| Metallic | 1.23 ab | 0.90 b | 1.56 a | 1.67 a | 0.79 b | ||||||
| Cereal | 1.43 b | 1.99 a | |||||||||
| Rancid | 1.13 a | 0.39 b | |||||||||
| Haricot bean | 2.22 b | 2.86 a | 2.05 b | 2.02 b | 2.73 a | ||||||
| Broth | 1.56 b | 1.85 a | |||||||||
| Hedonic | 4.01 a | 4.51 a | 2.79 b | 3.12 b | 4.42 a | ||||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Karolkowski, A.; Martin, C.; Bouzidi, E.; Albouy, J.-F.; Levavasseur, L.; Briand, L.; Salles, C. Heat Treatment, Cultivar and Formulation Modify the Sensory Properties and Consumer Acceptability of Gels Containing Faba Bean (Vicia faba L. minor) Protein Concentrates. Foods 2022, 11, 3018. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11193018
Karolkowski A, Martin C, Bouzidi E, Albouy J-F, Levavasseur L, Briand L, Salles C. Heat Treatment, Cultivar and Formulation Modify the Sensory Properties and Consumer Acceptability of Gels Containing Faba Bean (Vicia faba L. minor) Protein Concentrates. Foods. 2022; 11(19):3018. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11193018
Chicago/Turabian StyleKarolkowski, Adeline, Christophe Martin, Emilie Bouzidi, Jean-François Albouy, Loïc Levavasseur, Loïc Briand, and Christian Salles. 2022. "Heat Treatment, Cultivar and Formulation Modify the Sensory Properties and Consumer Acceptability of Gels Containing Faba Bean (Vicia faba L. minor) Protein Concentrates" Foods 11, no. 19: 3018. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11193018
APA StyleKarolkowski, A., Martin, C., Bouzidi, E., Albouy, J.-F., Levavasseur, L., Briand, L., & Salles, C. (2022). Heat Treatment, Cultivar and Formulation Modify the Sensory Properties and Consumer Acceptability of Gels Containing Faba Bean (Vicia faba L. minor) Protein Concentrates. Foods, 11(19), 3018. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11193018






