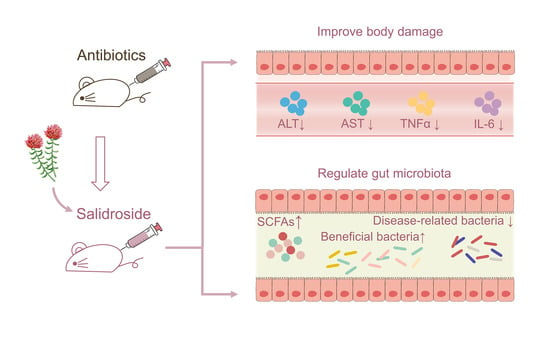
Salidroside Improves Antibiotic-Induced Gut Microbiota Disturbance and Low Levels of Short-Chain Fatty Acids in Mice
Abstract
Share and Cite
Sun, T.; Yang, J.; Lu, L. Salidroside Improves Antibiotic-Induced Gut Microbiota Disturbance and Low Levels of Short-Chain Fatty Acids in Mice. Foods 2022, 11, 3073. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11193073
Sun T, Yang J, Lu L. Salidroside Improves Antibiotic-Induced Gut Microbiota Disturbance and Low Levels of Short-Chain Fatty Acids in Mice. Foods. 2022; 11(19):3073. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11193073
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Tong, Jingyi Yang, and Lili Lu. 2022. "Salidroside Improves Antibiotic-Induced Gut Microbiota Disturbance and Low Levels of Short-Chain Fatty Acids in Mice" Foods 11, no. 19: 3073. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11193073
APA StyleSun, T., Yang, J., & Lu, L. (2022). Salidroside Improves Antibiotic-Induced Gut Microbiota Disturbance and Low Levels of Short-Chain Fatty Acids in Mice. Foods, 11(19), 3073. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11193073