Abstract
Oil is extracted from walnut leaves behind large quantities of defatted press cake that is still rich in valuable nutrients. Aspergillus oryzae and Rhizopus oligosporus, two molds traditionally used in Asia, have the necessary enzymes to use the nutrients in the walnut press cake. Walnuts and the press cake contain ellagitannins, known as precursors for ellagic acid and urolithins. In this study, experiments to optimize the solid-state fermentation of walnut press cake were performed in order to liberate ellagic acid from ellagitannins. Extracts of fermented products were then analyzed with an HPLC-DAD to measure the liberation of ellagic acid from ellagitannins. Good growth of R. oligosporus and A. oryzae mycelia on the walnut press cake was observed. A single mold culture was subjected to a hydration of 0.8 mL/g, an addition of 37.5 mmol/kg acetic acid (AA) and 1% NaCl, and an incubation temperature of 25 °C; these were observed to be good conditions for solid-state fermentation for walnut press cake. The highest ellagic acid concentration was obtained at 48 h. At 72 h, degradation dominated the liberation of ellagic acid.
1. Introduction
For thousands of years, fermentation has been used to preserve food, to improve taste, and to enhance digestion. Yet, fermentation provides food qualities that are far beyond the aforementioned properties. Recently, fermentation has received much attention as a means to increase the value of food by-products from the agri-food industry. Fermentative processes can create new economic value from agricultural and food industrial waste. Annually, one-third of the total food production is lost, which equals about 1.3 billion tons, of which 20% is from oilseeds [1]. About half of the total waste comes from cultivation and post-harvest losses, while the other half comes from processing, distribution, and final consumption [2]. For 2016, the European Commission estimated that the lost value from the waste of BP coming from the agri-food industry was 143,000 million euros [3].
The by-products from the agri-food industry can be classified as edible and non-edible. A non-edible by-product contains toxins, and thus cannot be used for human nutrition. Contrarily, edible by-products can be used for animal and human consumption due to their remaining nutritional value and the absence of toxins [2]. Furthermore, edible by-products can be processed further to serve as a source of proteins and antioxidants; they may also be used as substrates for producing enzymes, antibiotics, amino acids, vitamins, flavors, pigments, or surfactants [1].
In the last decade, there has been much interest from the food and cosmetic industry in the oil that comes from walnuts (Junglas regia L.), which is rich in bioactive compounds, such as polyunsaturated fatty acids or fat-soluble vitamins; moreover, the oil is easily extracted via cold pressing [4]. In 2019/2020, the oil production coming from seeds reached 580 million metric tons worldwide [1]. Concomitantly, large amounts of by-products in the form of press cake (pomace) were produced [1]. For instance, the oil extraction from walnuts uses twice the kernels in mass as the volume of oil produced, leaving behind vast quantities of walnut press cake (WPC) [5].
The protein content in nuts varies considerably. Together with peanuts, almonds, pistachios, and cashews, walnuts have the highest protein content, at around 20% or higher [6]. Therefore, WPC is an extremely rich source of protein. However, the resulting composition of WPC depends on the cultivar, provenance, agricultural practices, and the oil recovery process applied. Nevertheless, on average, WPC still contains oil (20–36%), depending on pressure conditions, substantial amounts of protein (30–42%) that become enriched during oil pressing, dietary fiber, phenolic compounds (ellagitannins), and minerals [5,7,8,9]. This interesting composition of WPC explains the high interest in using WPC as a nutritive and functional component in food products, or as a substrate for fermentation [1,5].
Fermentation has historically been used as a way of processing food for human consumption. Initially used for preservation, fermentation enhances the quality and functionality of food [10]. However, in modern times, techniques have improved capabilities to increase the productivity and efficiency of fermentation processes. Currently, there are two principal means of processing used: (I) submerged fermentation and (II) solid-state fermentation (SSF) [9]. SSF, also used in the present study, consists of using a solid substrate in the absence of liquid water where microorganisms can grow; in this way, the nutrients are maximally concentrated in the solid substrate [11,12]. Thus, the advantages of using SSF are high yields at low costs, high activity of microorganisms, low water consumption, little waste production, and higher resistance to contamination [13]. Nonetheless, this process has some shortcomings, making the use of SSF for industrial purposes challenging; some issues include scalability issues, heat accumulation, and difficulties with the regulation of growth parameters [11,14].
The most commonly used microorganisms in SSF are filamentous fungi. The parameter that most affects the growth of microorganisms in SSF is the fermentation temperature. However, growth is also affected by the moisture content, the chemical composition and particle size of the substrate, the height of the substrate layer, oxygen accessibility, the initial concentration of spores, the distribution of microorganisms in the substrate, and the age of the microorganisms [13,15].
For this study, fungi of the genera Aspergillus and Rhizopus were used. It is known that these two genera of fungi can use a broad range of substrates to produce enzymes which are active at lower pH and high temperatures, resulting in the liberation of phenolic compounds of biological interest, such as ellagic acid (EA) [13]. Rhizopus oligosporus exhibits strong lipolytic and proteolytic activities, while Aspergillus oryzae is unique in that it can ferment both carbohydrate-rich and protein-rich foods.
Phenolic compounds such as EA have gained considerable attention, as they are the most abundant antioxidants in the human diet [16]. EA, a hetero-tetracyclic compound that is produced from the dimerization of gallic acid, is a polyphenol that is found in countless fruits, vegetables, and nuts [17]. It is found in the cell vacuole and cell wall in free form, or bound to sugar molecules [18]. EA can be industrially liberated from ellagitannins via acidic or alkaline hydrolysis. However, the liberation of EA comes with many drawbacks, such as high production costs, generation of secondary products, and low yield [19]. Therefore, the liberation of EA using a fermentative process represents a valuable alternative that is in line with green biotechnology and the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals [11,13,16,20].
EA, besides being an antioxidant, provides several health benefits; anti-mutagenic, antitumor, anti-inflammatory, and antimicrobial activities have been reported [1,4,17]. These beneficial effects are mainly attributed to EA metabolites called urolithins, which are formed by colonic microbiota [21,22].
Thus, the aim of the present study was to apply SSF on WPC, using the fungi A. oryzae and R. oligosporus, with a particular interest in the transformation of ellagitannins into EA. From this study, a fermented food-quality WPC that was characterized for its EA content was expected.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Walnut Press Cake (WPC)
Four and a half kg of WPC was provided by Huilerie Pré Girard, Pompaples (Switzerland), as a dry powder. The WPC was homogenized and separated into portions of 500 g and stored under vacuum at 4 °C until used for fermentation experiments.
Characterization of WPC before fermentation showed a dry matter content of 95.45% (Halogen Balance, Mettler-Toledo GmbH, Columbus, OH, USA). Based on DM, the WPC showed a protein content of 29.7% (Kjeldahl), a fat content of 37.6% (Soxhlet), a mineral content (ash) of 4.1%, and carbohydrate and dietary fiber content of 28.6% (calculated). The most frequent particle size was 60 μm, with 50% of the particles being smaller than 340 μm, and 90 % of particles being smaller than 1050 μm (Camsizer® XT, Retsch Technologie, Haan, Germany).
2.2. Hydration Solution
A hydration solution (HS) was prepared that contained 2.5 g/L of NaNO3 (Fluka, Aesch, Switzerland); 1 g/L of KH2PO4 (Sigma-Aldrich, Buchs, Switzerland); 0.5 g/L of KCL (Sigma-Aldrich, Buchs, Switzerland); and 0.5 g/L of MgSO4 (Fluka, Aesch, Switzerland).
2.3. Acidification Solution
An aqueous acetic acid (AA, Nutrex, Lyss, Switzerland) solution with a concentration of 45 g/L (pH of 2.5) was used to acidify the WPC before fermentation.
2.4. Microorganisms
A tempeh starter culture containing freeze dried Rhizopus oligosporus spores in rice flour was obtained from MakrobiotikVersand (Nordhackstedt, Germany). R. oligosporus has previously been shown to have lipase, endoglucanase, endoxylanase, and aminopeptidase activities in soybean tempeh [23]. An active culture of Aspergillus oryzae DSM 1863 was obtained from DSMZ (Braunschweig, Germany). Aspergillus oryzae DSM 1863 has shown great potential for the secretion of hydrolytic enzymes and organic acids, and has an increased tolerance to liquid pyrolysis. [24]. The microorganisms were selected as a result of their commercial availability, robustness, and use in the food industry to produce tempeh.
A. oryzae DSM 1863 was proliferated from conidia on potato dextrose agar (Biolife, Milan, Italy) for 7 d at 30 °C [25,26]. Before WPC inoculation, a suspension of spores of A. oryzae DSM 1863 (3.6 × 107 cfu/mL) was prepared using an isotonic medium of maximum recovery diluent made of 5.0 g/L of peptic digest of animal tissue, and 42.5 g/L of NaCl (Biolife, Milan, Italy). The concentration of spores was measured using a Neubauer counting chamber [26].
2.5. Preparation of WPC
The HS was used for the initial hydration of WPC by adding 80 mL of standard solution for each 100 g of dry WPC at room temperature, and mixing (Stomacher®, Worthing, United Kingdom) for 10 min in a sterile plastic bag. From the acidification solution, 5 mL were added per 100 g of dry WPC. NaCl was added to the hydrated and acidified WPC at a concentration of 1 g/100 g of WPC.
2.6. WPC Inoculation
The prepared WPC (hydrated, acidified, and salted) was inoculated with tempeh starter that contained R. oligosporus, following the manufacturer’s instructions. For 100 g of WPC, 0.76 g of tempeh starter was dissolved in 7.6 mL of distilled water. The dissolved tempeh starter (0.1 g/mL) was then added to the mixing bag containing the conditioned WPC (100 g) and mixed for 10 min at room temperature to yield a spore concentration of 3.6 × 105 spores/g of WPC.
Another incubation was made with A. oryzae using a 3.6 × 107 cfu/mL spore suspension, as described above. To 100 g of the conditioned WPC, 10 mL of a solution containing 3.6 × 106 spores/mL were added and mixed for 10 min at room temperature to yield a spore concentration of 3.6 × 105 spores/g of WPC.
As a third experimental run, both microorganisms, A. oryzae and R. oligosporus, were used in a co-culture. Amounts of 3.6 × 105 spores/g of WPC each of R. oligosporus and A. oryzae were added for these experiments.
2.7. Fermentation
Disks with a diameter of 5 cm, a weight of 30 g, and a thickness of 1 cm, were made from hydrated acidified and inoculated WPC. The disks were placed in a glass mold and were separated spatially from each other so that they did not touch. The glass mold was covered with a perforated plastic film and placed in an incubator at 25 °C.
2.8. Sampling
Samples of the fermenting WPC were taken directly after inoculation (0 h), after 24 h, 48 h, and 72 h. For the sampling, approximately 3 g of the fermenting WPC disks were taken with a spatula at randomized locations and added to a 15-milliliter falcon tube. Tubes were stored at −20 °C until further analysis.
2.9. Sample Preparation
Before extraction, about 2 g of frozen WPC samples were pre-dried for 24 h at 50 °C in an oven [7]. The water content and the dry matter content of the previously dried samples of fermented WPC were determined with a Halogen Balance HE73 Moisture analyzer (Mettler-Toledo GmbH, Greifensee, Switzerland).
2.10. EA Extraction
An volume of 5 mL of an acetone:water (80:20, v:v) solution were added to 200 mg of previously dehydrated samples of fermented WPC, and extracted in an ultrasonic bath for 15 min at room temperature. After that, samples were centrifugated at 3000 rpm for 10 min at room temperature [27]. A volume of 500 μL of supernatant was collected. The remaining pellet was extracted a second time using the same procedure. Again, 500 μL of supernatant was collected and combined with the first 500 μL. The combined extracts were filtered with NM Chromaphil®Xtra 0.45 μm and used for HPLC-DAD analysis [17,28].
2.11. HPLC-DAD Analysis
For quantification of EA, an HPLC-DAD method was applied (HPLC Agilent technologies, 1220 Infinity LC, Santa Clara, USA) with a C18 column Core-shell (Phenomexe, 50 × 2.1 mm, Kinetex 2.6 μm, EVO C18 100Å, Los Angeles, CA, USA). Eluant A consisted of ultrapure water that was acidified with 1% formic acid. Eluant B was acetonitrile with 1% formic acid. The column temperature was maintained at 35 °C. The injected sample volume was 5 μL. The gradient applied was 0–5 min, 5% B; 5–12 min, 5–60% B; 12–20 min, 60–95% B; 20–20.1 min, 95–5% B. The flow rate was maintained at 1 mL/min, and absorption was monitored at 260 nm [29].
2.12. Calibration Curve
A commercial sample of EA (E2250-5G) obtained from Sigma-Aldrich (Buchs, Switzerland) was used as a standard for external calibration. A stock solution was prepared using 25 mg of EA dissolved in 25 mL of dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO, Sigma-Aldrich, Buchs, Switzerland) to obtain a concentration of 1000 mg/mL. The EA stock solution was diluted in a mixture of eluants A and B (1 + 1), in order to obtain concentrations of 100, 75, 50, 25, and 10 mg/mL.
2.13. Statistics
A simple ANOVA was used with a significance level of 0.05 to seek significant differences between EA concentrations obtained from the treatments, and at specific sample collection times.
3. Results and Discussion
Solid-state fermentation for the liberation of ellagic acid in WPC using R. oligosporus and A. oryzae, either alone or in coculture, was performed. For experiments with R. oligosporus, a commercial tempeh starter culture was used. The production of tempeh is usually carried out using R. oligosporus on soybeans. R. oligosporus can degrade the cell wall of plants. In addition, it has proteolytic and lipolytic enzymes and can produce antibiotic substances against pathogenic Gram-negative bacteria. A second mold, A. oryzae, was also applied. It is used mainly to produce koji, sake, shochu, miso, and soy sauce. A. oryzae has multiple enzymatic activities with hydrolytic enzymes, such as proteases, to degrade proteins [30]. The SSF was performed using conditions that were identified as most appropriate to liberate EA.
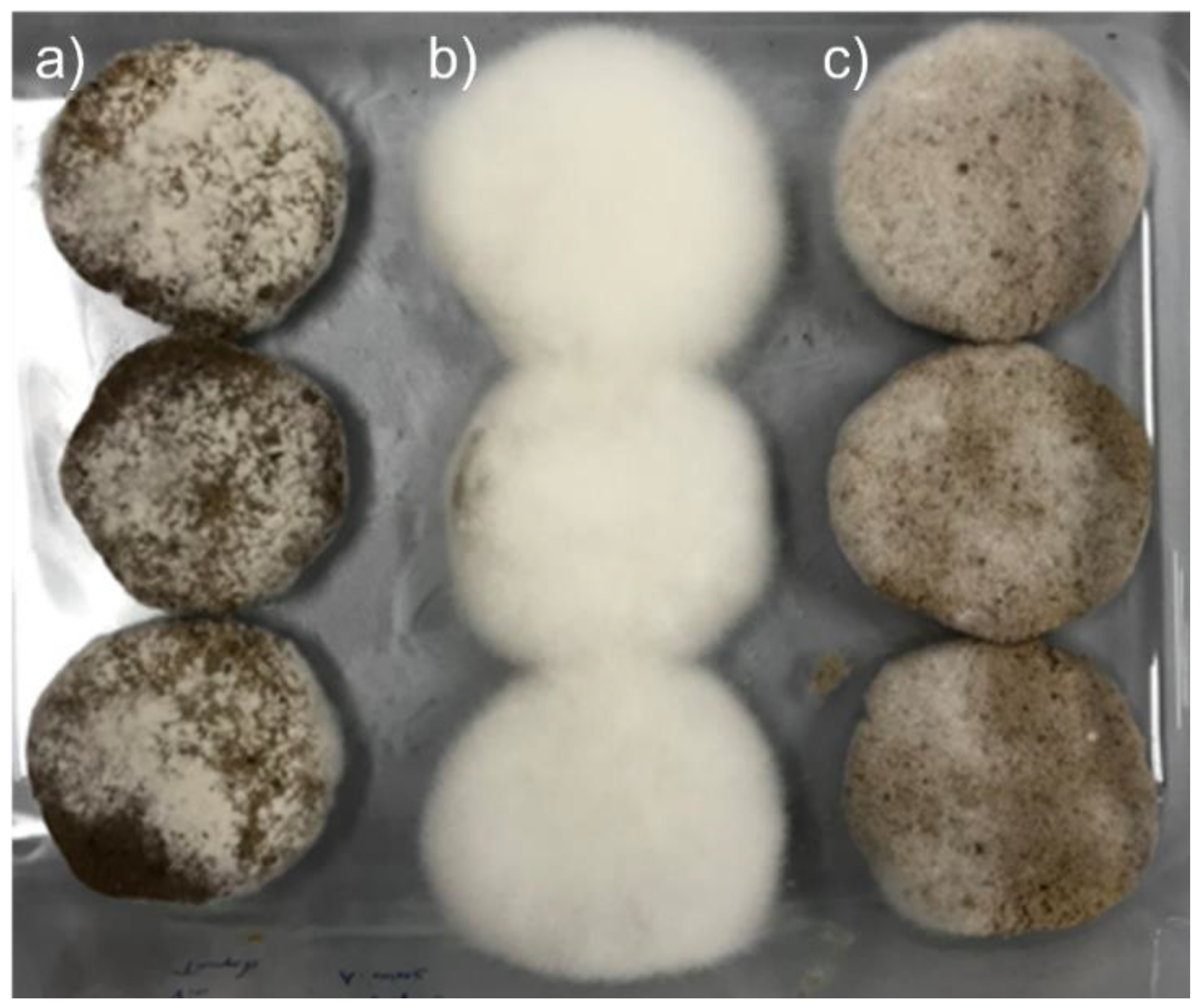
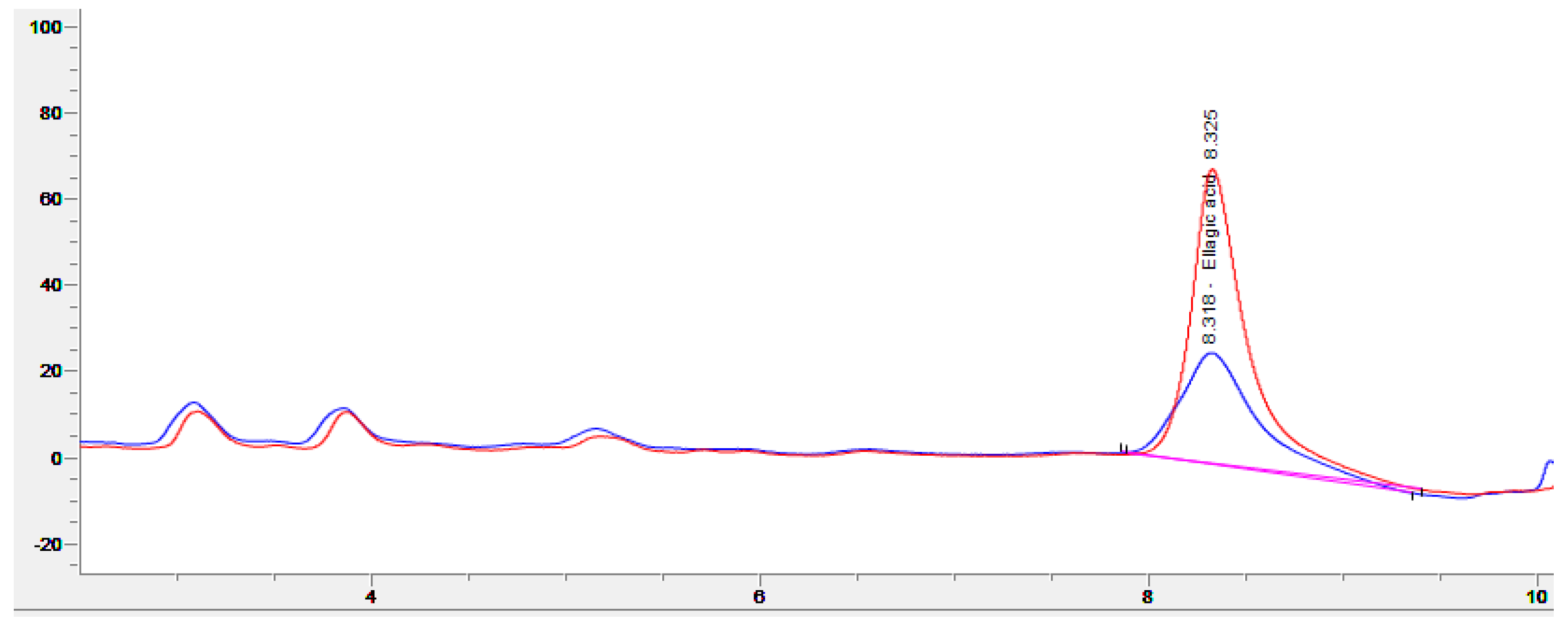
For all fermentations, good growth of R. oligosporus and A. oryzae mycelia, alone or in coculture, was observed on the surface of the WPC tempeh disks after 48 h (Figure 1). The concentration of free EA in WPC is usually low, since EA is mainly bound in ellagitannins. In walnuts, EA is usually found at concentrations of about 600 μg/g [31], which is close to the values we obtained at time 0 h. Figure 2 shows a chromatogram of an water:acetone extract of walnut press cake at 260 nm. In order to identify the EA peak (Rt = 8.3 min), the samples were spiked with an EA reference solution.
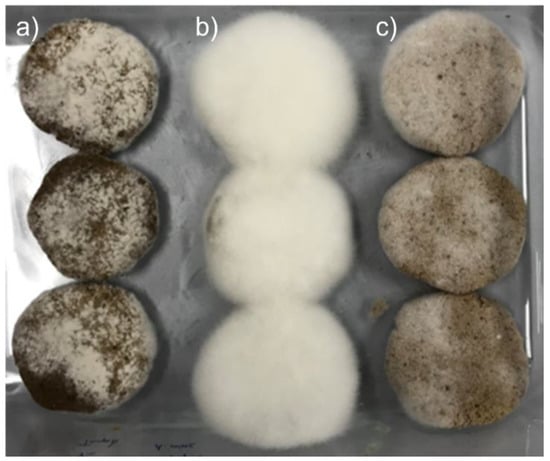

Figure 1.
Growth of mold mycelia on WPC after 48 h: (a) A. oryzae, (b) R. oligosporus, and (c) coculture of A. oryzae and R. oligosporus.
Figure 2.
Chromatogram (260 nm) of an extract from walnut press cake (blue), and the same sample spiked with ellagic acid (red).
In all experiments, a steady increase in the concentration of EA was observed initially. However, a decrease in EA concentration was observed after longer fermentation times, presumably due to a degradation of EA by the fermenting fungi or by the endemic WPC microbiota (Table 1). Using sterilization with an autoclave was not a viable option because overheating the WPC causes a Maillard reaction accompanied by the appearance of off-flavors, compaction of the paste, and negligible liberation of EA.

Table 1.
EA liberation from SSF of WPC using A. oryzae, R. oligosporus, and in coculture, n = 3 (±SD).
The presence of water during fermentation is a fundamental prerequisite; it influences growth, protein stability, production of metabolites, and has a role in substrate transport and as a reactant [32]. Generally, around 60 to 70% moisture content is optimal during SSF for fungi [15]. Hydration is a physical process that is related to permeability and colloidal properties [32]. Low hydration can cause growth disruption and an inability to interact with the substrate. On the other hand, high hydration can cause particle agglomeration, thus limiting oxygen availability [15].
Fungal metabolism and growth are related to the substrate’s water activity. Water activity is dependent on the water available; thus, a slight change in hydration may cause a significant effect on the metabolism of fungi [15]. Decreased water activity slows growth, while high water activity improves growth. However, accelerating effects on the metabolism may also cause stress, leading to degradative reactions [32]. It can be argued that too high an increase in the metabolism may be counterproductive, as EA could be degraded; hence optimal hydration is necessary for SSF, in order to prevent under- or overgrowth.
Temperature is an important parameter to control in SSF. In Indonesia, traditional tempeh fermentation is carried out at ambient temperature (~30 °C) [33]. Molds can survive a broad range of temperatures, from 20 to 55 °C. An optimum temperature will provide the best growth velocity and metabolite output, as mold enzymatic metabolism becomes most efficient [15]. The fastest mold development and the highest EA concentration in fermentations with R. oligosporus was observed at an incubation temperature of 25 °C after 48 h. This result could be related to the metabolic heat and increased incubation temperature, resulting in optimal conditions for growth and metabolic output for R. oligosporus during SSF of the WPC. In addition, heat can cause EA liberation reactions simultaneously as metabolic reactions, increasing EA concentration [15,33].
Degradation was observed after 72 h for most fermentations. It is known that the degradation of polyphenolic compounds such as EA can occur at high temperatures [28]. In our case, an increase in the incubation temperature on the fermenting WPC by the generated metabolic heat may have caused degradation of EA, either by metabolic stress and degradative enzymatic reactions from R. oligosporus and A. oryzae, or as a result of simple heat degradation.
Acidity and pH value are critical factors for the mycelial growth of R. oligosporus and A. oryzae, and the inhibition of contaminating bacteria [34]. The fungi can thrive in a broad range of pH, giving them the advantage of low bacterial competition [15]. In traditional tempeh fermentation using R. oligosporus, the initial pH is between 4.5–5.5, and increases to 6.5–7.0 as fermentation continues in mature tempeh [32]. However, in tempeh production, a low initial pH is obtained when lactic and acetic bacteria grow during the soaking of the soybeans [34]. Therefore, it was decided to add food-grade AA to the WPC before inoculation.
A study that was conducted with rapeseeds found a window for optimal R. oligosporus growth and inhibition of bacteria that was achieved with 40–60 mmol AA per kg of substrate. The fastest growth and complete surface coverage after 24 h were achieved with a concentration of AA of 37.7 mmol/kg of substrate [34]. In our case, the AA solution added at a ratio of ml per 100 g of WPC led to 37.5 mmol of AA per kg of WPC.
The use of an organic acid had a notable effect on the speed and intensity of R. oligosporus mycelial growth. Acidity, and thus pH, directly impact the growth of the mold, increasing the accessibility and liberation of EA by increasing mold metabolism. However, the 37.5 mmol/kg AA solution appeared to have a slight edge on the liberation of EA and in taste. Thus, AA was selected as the optimal organic acid for WPC fermentation.
The salt concentration is known to suppress the growth of spoilage microorganisms and pathogens, while favoring the growth of halotolerant microorganisms that play an essential role in forming flavor molecules [35]. Salt was administered with a focus on taste and surface mycelia formation. The best-perceived taste was with 1% of salt and 37.5 mmol/kg of AA. However, the addition of salt caused a delay in the growth of R. oligosporus and A. oryzae mycelia, affecting the EA concentration at 48 h. It is known that high salt concentrations can inhibit the enzymatic activity of the mold, causing metabolic stress, consequently affecting mycelial growth, and either indirectly slowing the liberation of EA or promoting degradation [35].
The effects on EA liberation due to fermentation in WPC with A. oryzae and R. oligosporus, alone or in coculture, were studied in triplicate. There were no significant differences found in the EA concentrations when fermenting WPC with A. oryzae or R. oligosporus alone. However, the coculture showed significantly lower EA liberation at 48 h (p = 0.01) and 72 h compared to fermentation with A. oryzae or R. oligosporus alone.
The increase in EA concentration observed was comparable for all three fermentations after 24 h. After 24 h, differences began to appear in the liberation of EA. A. oryzae and R. oligosporus can liberate EA with similar efficacy until 48 h, when the concentration of EA seemed to either stabilize or began to degrade at 72 h. When the molds were in coculture, the EA concentrations were equal at 24 h to the single cultures, but changed thereafter. The coculture showed slow mycelial growth, indicating that there was competition between the molds for the substrate. A plateau in the accessibility to EA was reached with lower EA concentrations.
4. Conclusions
A fermentative process is a viable option to take advantage of food by-products from the agricultural industry. The SSF of WPC is an exemplary process for creating products with added nutritional value. For industrial upscaling, parameters such as water content, acidity, and temperature must be optimized. The liberated EA has been shown to be of nutritional value, and may serve as a precursor for beneficial urolithins. It has been shown that the digestion and microbial transformation of EA-containing food releases urolithins [21]. Unfortunately, not all humans are able to produce the most health-promising form, urolithin A. Therefore, another possible approach would be to apply microbial transformation of the fermented WPC to produce urolithin A directly in the food, rendering the product valuable for non-producers of urolithin A.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, W.A. and W.M.B.; methodology, V.D.D.E., W.A. and W.M.B.; validation, W.A. and W.M.B., formal analysis, V.D.D.E. and L.D.-d.-B.; investigation, V.D.D.E., L.D.-d.-B., M.B. and N.N.; writing—original draft preparation, V.D.D.E., W.A. and W.M.B.; writing—review and editing, W.A. and W.M.B.; visualization, V.D.D.E., W.A. and W.M.B.; supervision, W.A. and W.M.B.; project administration, W.A. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
This article is based on the results of a master’s thesis by V.D.D., conducted within the joint Master of Science Life Sciences—Food, Nutrition and Health Program at Bern University of Applied Sciences School of Agricultural, Forest and Food Sciences BFH-HAFL, and the University of Applied Sciences and Arts, Western Switzerland, Valais-Wallis (HES-SO Valais-Wallis). L.D. conducted the pre-experiments to establish the analytical method and to select the optimal fermentation conditions.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Nevara, G.A.; Ibrahim, S.G.; Muhammad, S.K.S.; Zawawi, N.; Mustapha, N.A.; Karim, R. Oilseed meals into foods: An approach for the valorization of oilseed by-products. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 2022, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petraru, A.; Amariei, S. Oil press-cakes and meals valorization through circular economy approaches: A review. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 7432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stenmarck, A.; Jensen, C.; Quested, T.; Moates, G. Estimates of European Food Waste Levels. 2016. Available online: https://www.eu-fusions.org/phocadownload/Publications/Estimates%20of%20European%20food%20waste%20levels.pdf (accessed on 5 August 2022).
- Anwar, F.; Qadir, R.; Abbas, A. Chapter 44—Cold pressed walnut (Juglans regia L.) oil. In Cold Pressed Oils; Ramadan, M.F., Ed.; Academic Press Inc.: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2020; pp. 491–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakkalbasi, E.; Meral, R.; Dogan, I.S. Bioactive Compounds, Physical and Sensory Properties of Cake Made with Walnut Press-Cake. J. Food Qual. 2015, 38, 422–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, J.; Alvarez-Ortí, M.; Sena-Moreno, E.; Rabadán, A.; Pardo, J.E.; Beatriz, P.P.; Oliveira, M. Effect of roasting conditions on the composition and antioxidant properties of defatted walnut flour. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2018, 98, 1813–1820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Day, L.; Cakebread, J.A.; Loveday, S.M. Food proteins from animals and plants: Differences in the nutritional and functional properties. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 119, 428–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pop, A.; Păucean, A.; Socaci, S.A.; Alexa, E.; Man, S.M.; Mureșan, V.; Chiş, M.S.; Salanță, L.; Popescu, I.; Berbecea, A.; et al. Quality Characteristics and Volatile Profile of Macarons Modified with Walnut Oilcake By-Product. Molecules 2020, 25, 2214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakkalbaşı, E. Oxidative stability of enriched walnut oil with phenolic extracts from walnut press-cake under accelerated oxidation conditions and the effect of ultrasound treatment. Food Meas. 2019, 13, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Mendoza, M.d.P.; Espinosa-Pardo, F.A.; Savoire, R.; Etchegoyen, C.; Harscoat-Schiavo, C.; Subra-Paternault, P. Recovery and antioxidant activity of phenolic compounds extracted from walnut press-cake using various methods and conditions. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2021, 167, 113546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamang, J.P.; Cotter, P.D.; Endo, A.; Han, N.S.; Kort, R.; Liu, S.Q.; Mayo, B.; Westerik, N.; Hutkins, R. Fermented foods in a global age: East meets West. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2020, 19, 184–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martí-Quijal, F.J.; Khubber, S.; Remize, F.; Tomasevic, I.; Roselló-Soto, E.; Barba, F.J. Obtaining antioxidants and natural preservatives from food by-products through fermentation: A review. Ferment 2021, 7, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lizardi-Jiménez, M.A.; Hernández-Martínez, R. Solid state fermentation (SSF): Diversity of applications to valorize waste and biomass. 3 Biotech 2017, 7, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Šelo, G.; Planinić, M.; Tišma, M.; Tomas, S.; Koceva Komlenić, D.; Bucić-Kojić, A. A comprehensive review on valorization of agro-food industrial residues by solid-state fermentation. Foods 2021, 10, 927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doriya, K.; Jose, N.; Gowda, M.; Kumar, D.S. Solid-State Fermentation vs. Submerged Fermentation for the Production of L-Asparaginase. In Advances in Food and Nutrition Research; Kim, S.-K., Toldrá, F., Eds.; Academic Press Inc.: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2016; Volume 78, pp. 115–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, N.; Srivastava, M.; Ramteke, P.W.; Mishra, P.K. Chapter 23—Solid-state fermentation strategy for microbial metabolites production: An overview. In New and Future Developments in Microbial Biotechnology and Bioengineering: Microbial Secondary Metabolites Biochemistry and Applications; Gupta, V.K., Pandey, A., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 345–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buenrostro-Figueroa, J.; Ascacio-Valdés, A.; Sepúlveda, L.; Prado-Barragán, A.; Aguilar-González, M.A.; Aguilar, C.N. Ellagic acid production by solid-state fermentation influenced by the inert solid supports. Emir. J. Food Agric. 2018, 30, 750–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulsunoglu-Konuskan, Z.; Karbancioglu-Guler, F.; Kilic-Akyilmaz, M. Development of a bioprocess for production of ellagic acid from chestnut (Castanea sativa Mill.) waste by fermentation with Aspergillus spp. Food Biosci. 2021, 42, 101058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landete, J.M. Ellagitannins, ellagic acid and their derived metabolites: A review about source, metabolism, functions and health. Food Res. Int. 2011, 44, 1150–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devanthi, P.V.P.; Gkatzionis, K. Soy sauce fermentation: Microorganisms, aroma formation, and process modification. Food Res. Int. 2019, 120, 364–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evtyugin, D.D.; Magina, S.; Evtuguin, D.V. Recent Advances in the Production and Applications of Ellagic Acid and Its Derivatives. A Review. Molecules 2020, 25, 2745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasser, H.A.; Mahmoud, M.; Tolba, M.M.; Radwan, R.A.; Gabr, N.M.; ElShamy, A.A.; Yehya, M.S.; Ziemke, A.; Hashem, M.Y. Pros and cons of using green biotechnology to solve food insecurity and achieve sustainable development goals. Euro-Mediterr. J. Environ. Integr. 2019, 6, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varzakas, T. Rhizopus oligosporus mycelial penetration and enzyme diffusion in soya bean tempe. Process Biochem. 1998, 33, 741–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubisch, C.; Kövilein, A.; Aliyu, H.; Ochsenreither, K. RNA-Seq Based Transcriptome Analysis of Aspergillus oryzae DSM 1863 Grown on Glucose, Acetate and an Aqueous Condensate from the Fast Pyrolysis of Wheat Straw. J. Fungi 2022, 8, 765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomás-Barberán, F.A.; González-Sarrías, A.; García-Villalba, R.; Núñez-Sánchez, M.A.; Selma, M.V.; García-Conesa, M.T.; Espín, J.C. Urolithins, the rescue of “old” metabolites to understand a “new” concept: Metabotypes as a nexus among phenolic metabolism, microbiota dysbiosis, and host health status. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2017, 61, 1500901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnan, P.S.; Bajaj, V.; Damle, S.P. Some Observations on the Growth of Aspergillus niger from Spore Inoculum. Appl. Microbiol. 1954, 2, 303–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melnichuk, N.; Braia, M.J.; Anselmi, P.A.; Meini, M.R.; Romanini, D. Valorization of two agroindustrial wastes to produce alpha-amylase enzyme from Aspergillus oryzae by solid-state fermentation. Waste Manag. 2020, 106, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Theocharis, G.; Andlauer, W. Innovative microwave-assisted hydrolysis of ellagitannins and quantification as ellagic acid equivalents. Food Chem. 2013, 138, 2430–2434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ajila, C.M.; Brar, S.K.; Verma, M.; Tyagi, R.D.; Valéro, J.R. Solid-state fermentation of apple pomace using Phanerocheate chrysosporium—Liberation and extraction of phenolic antioxidants. Food Chem. 2011, 126, 1071–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moccia, F.; Flores-Gallegos, A.C.; Chávez-González, M.L.; Sepúlveda, L.; Marzorati, S.; Verotta, L.; Panzella, L.; Ascacio-Valdes, J.A.; Aguilar, C.N.; Napolitano, A. Ellagic Acid Recovery by Solid State Fermentation of Pomegranate Wastes by Aspergillus niger and Saccharomyces cerevisiae: A Comparison. Molecules 2019, 24, 3689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Permana, I.D.G.M.; Duniaji, A.S.; Wisaniyasa, N.W.; Gunam, I.B.W. The effect of inoculation of Aspergillus oryzae and Rhizopus oligosporus in molds fermentation on the characteristics of pigeon pea sauce (Cajanus cajan (L.) Millsp.). Eurasian J. Biosci. 2020, 14, 3527–3535. [Google Scholar]
- Sarrette, M.; Nout, M.J.R.; Gervais, P.; Rombouts, F.M. Effect of Water Activity on Production and Activity of Rhizopus Oligosporus Polysaccharidases. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 1992, 37, 420–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sparringa, R.; Kendall, M.; Westby, A.; Owens, J. Effects of Temperature, PH, Water Activity and CO2 Concentration on Growth of Rhizopus oligosporus NRRL 2710. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2002, 92, 329–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sójka, M.; Janowski, M.; Grzelak-Błaszczyk, K. Stability and transformations of raspberry (Rubus idaeus L.) ellagitannins in aqueous solutions. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2019, 245, 1113–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lücke, F.K.; Fritz, V.; Tannhäuser, K.; Arya, A. Controlled fermentation of rapeseed presscake by Rhizopus, and its effect on some components with relevance to human nutrition. Food Res. Int. 2019, 120, 726–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).