Improvement of Gel Quality of Squid (Dosidicus gigas) Meat by Using Sodium Gluconate, Sodium Citrate, and Sodium Tartrate
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Reagents
2.2. Solubility of Squid Muscle Protein
2.3. Preparation of Squid Surimi Paste and Gel
2.4. Determination of Rheological Properties
2.5. Texture Analysis
2.6. Water-Holding Capacity (WHC)
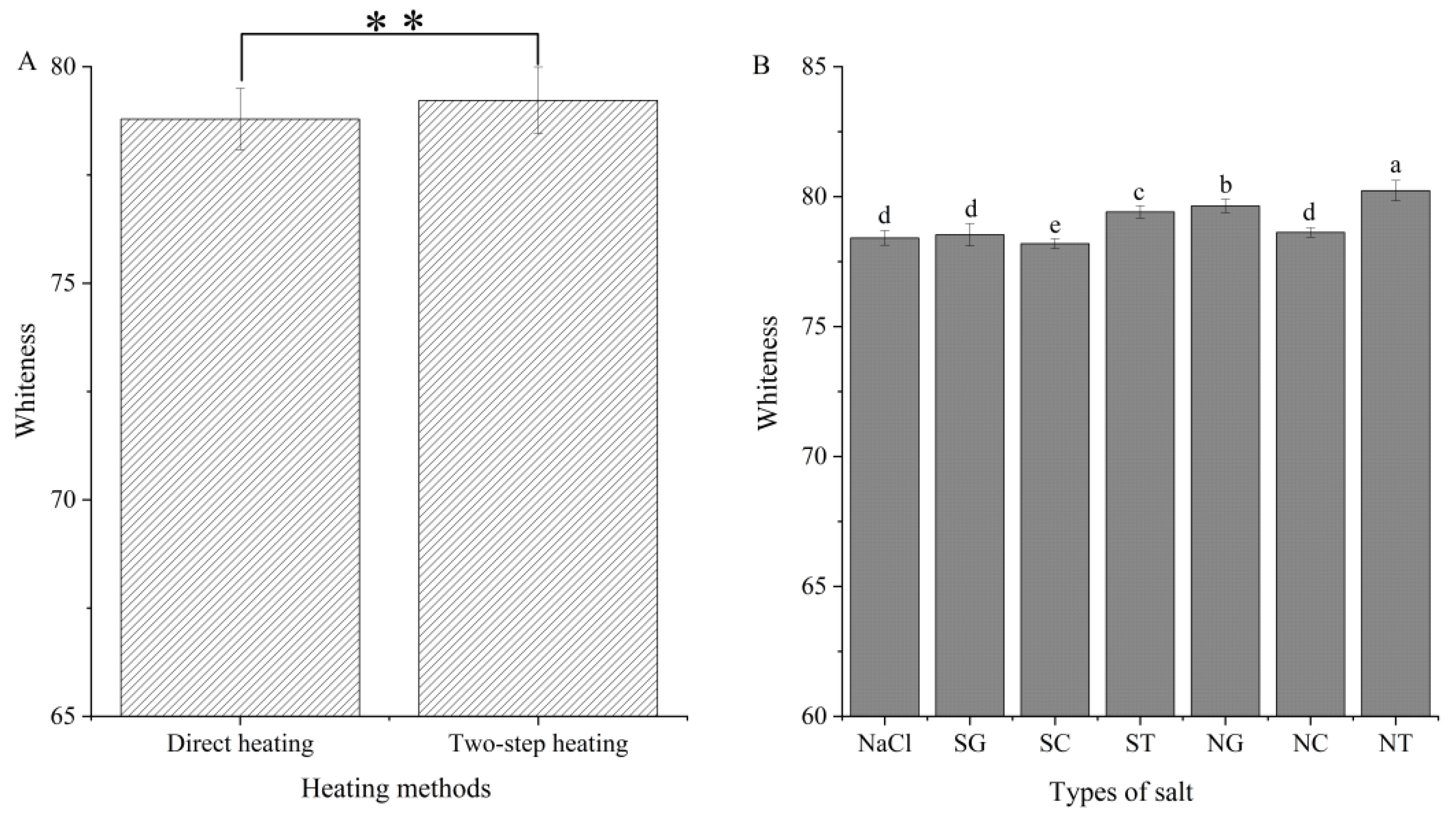
2.7. Determination of Whiteness
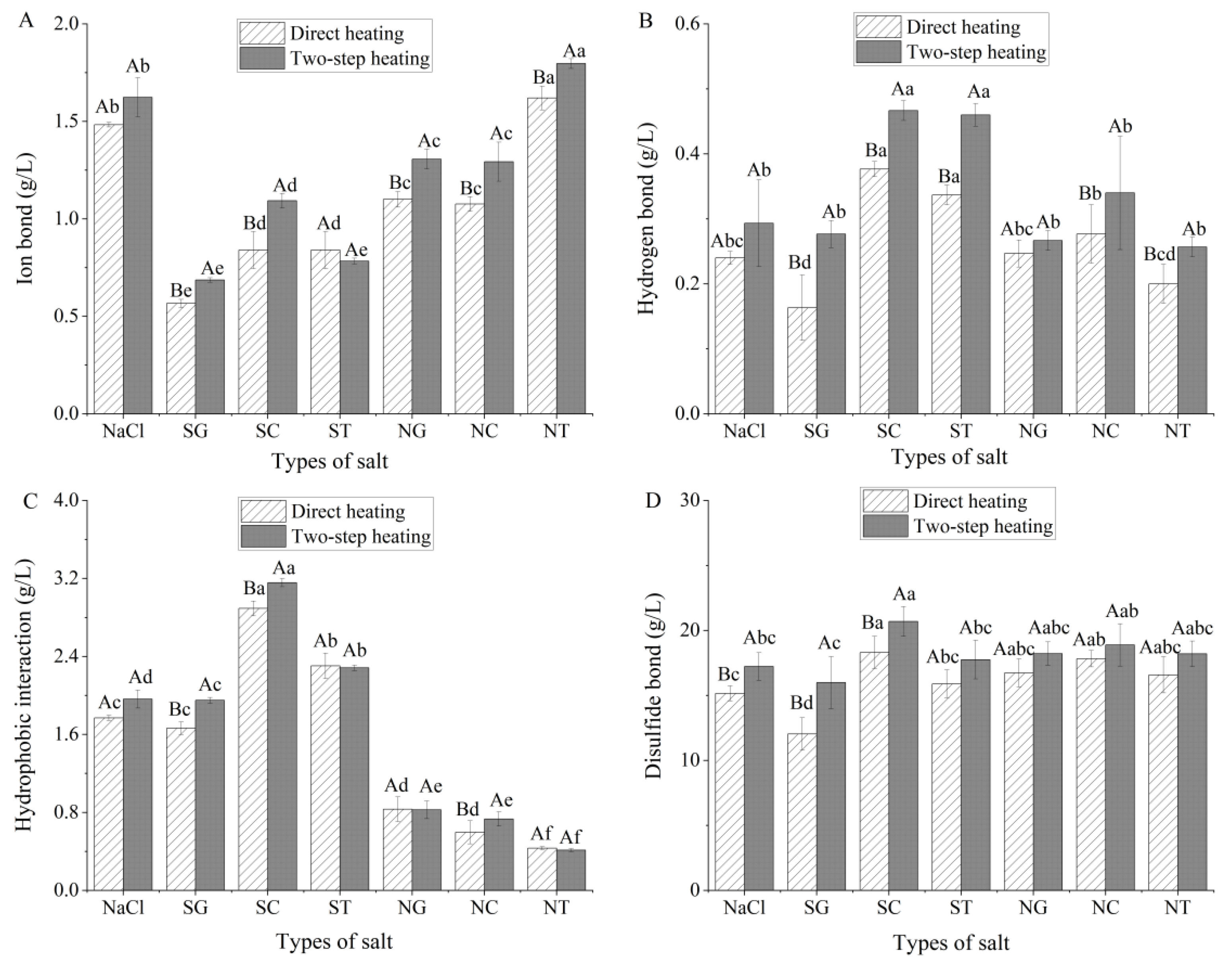
2.8. Determination of Chemical Forces
Hydrogen bond = CS3 − CS2
Hydrophobic interaction = CS4 − CS3
Disulfide bond = CS5
2.9. Data Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
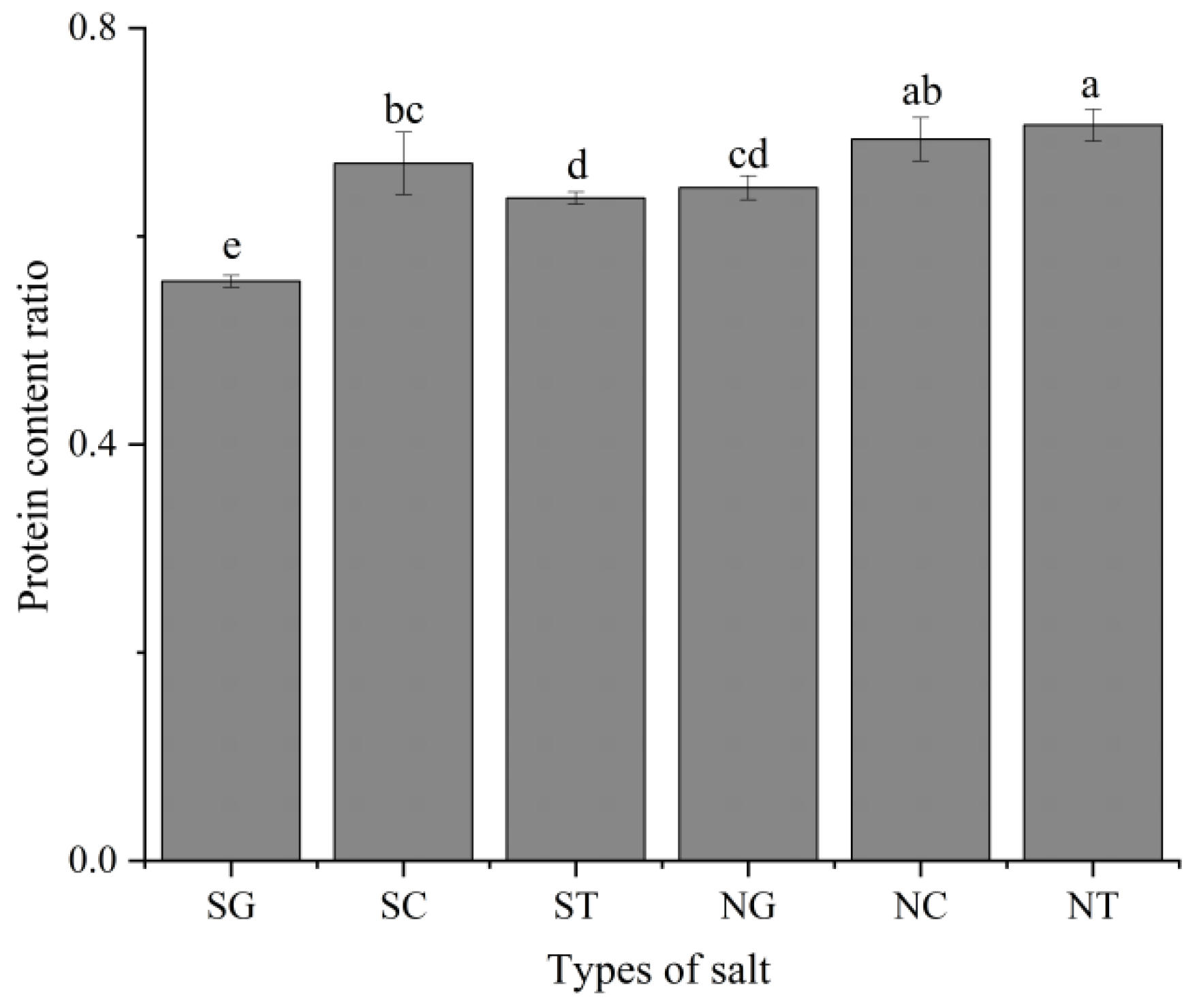
3.1. Solubility of Squid Protein
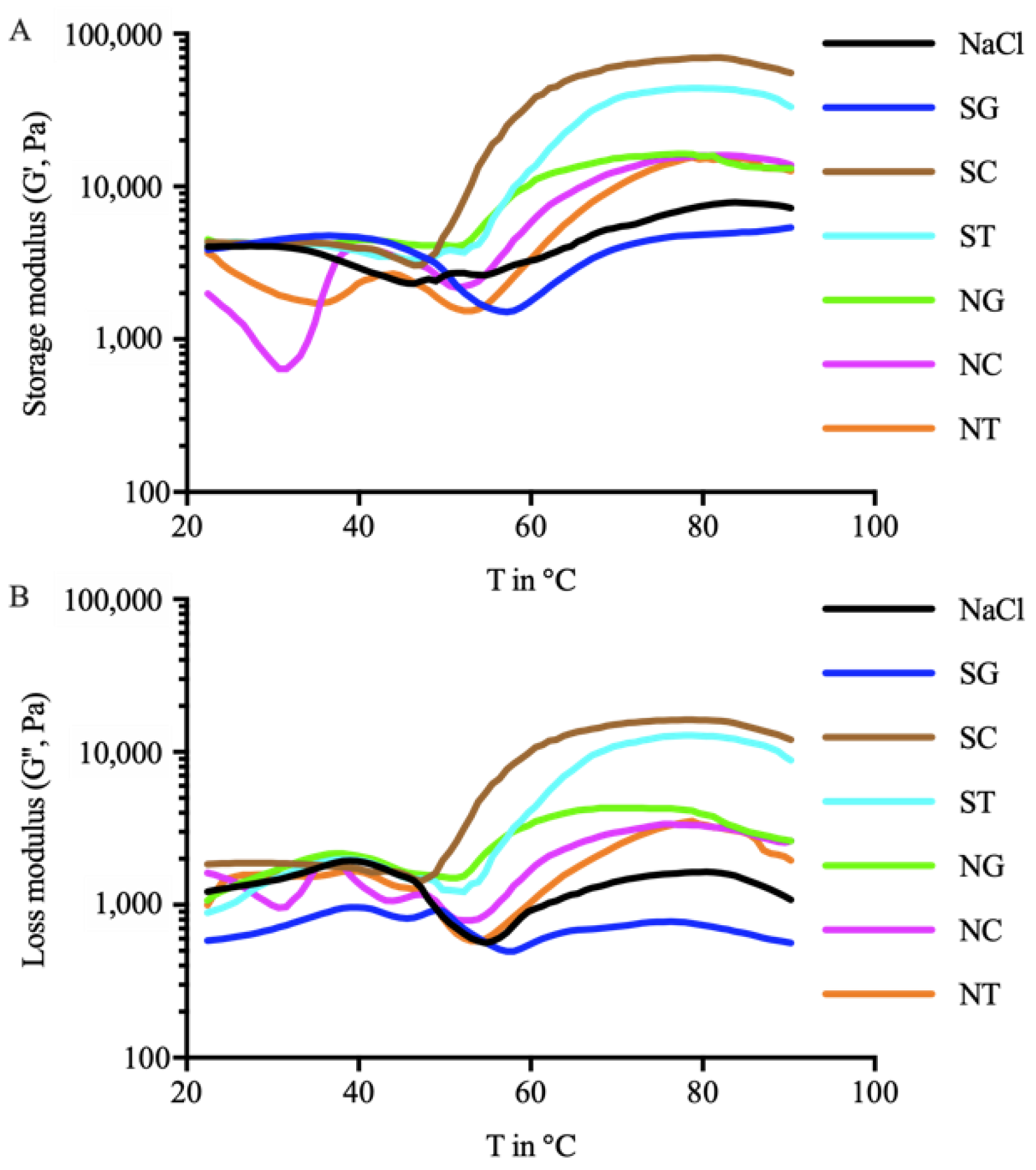
3.2. Rheological Properties of Surimi Ointment
3.3. Texture Analysis
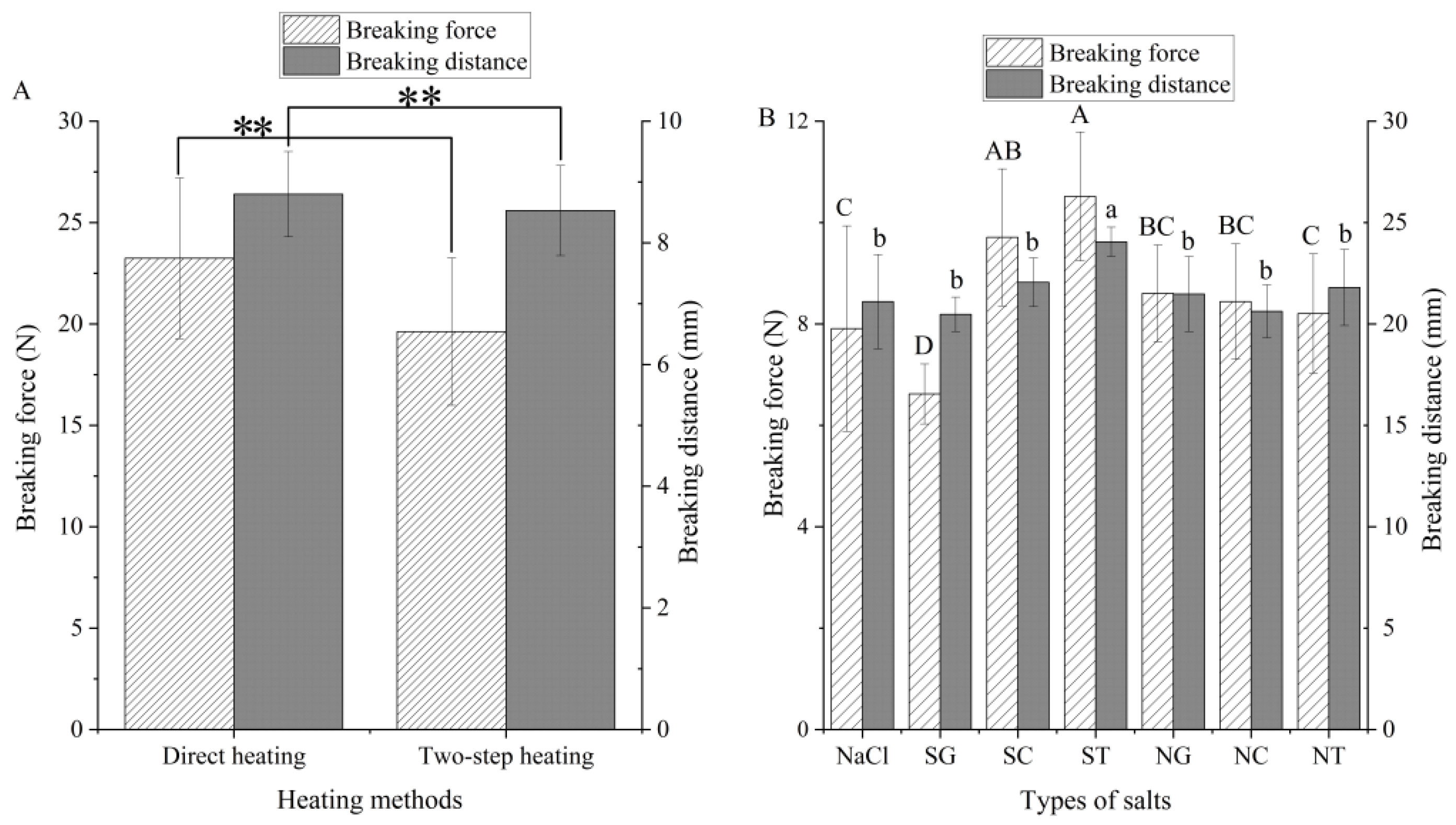
3.3.1. Breaking Strength of Gels
3.3.2. Texture Profile Analysis
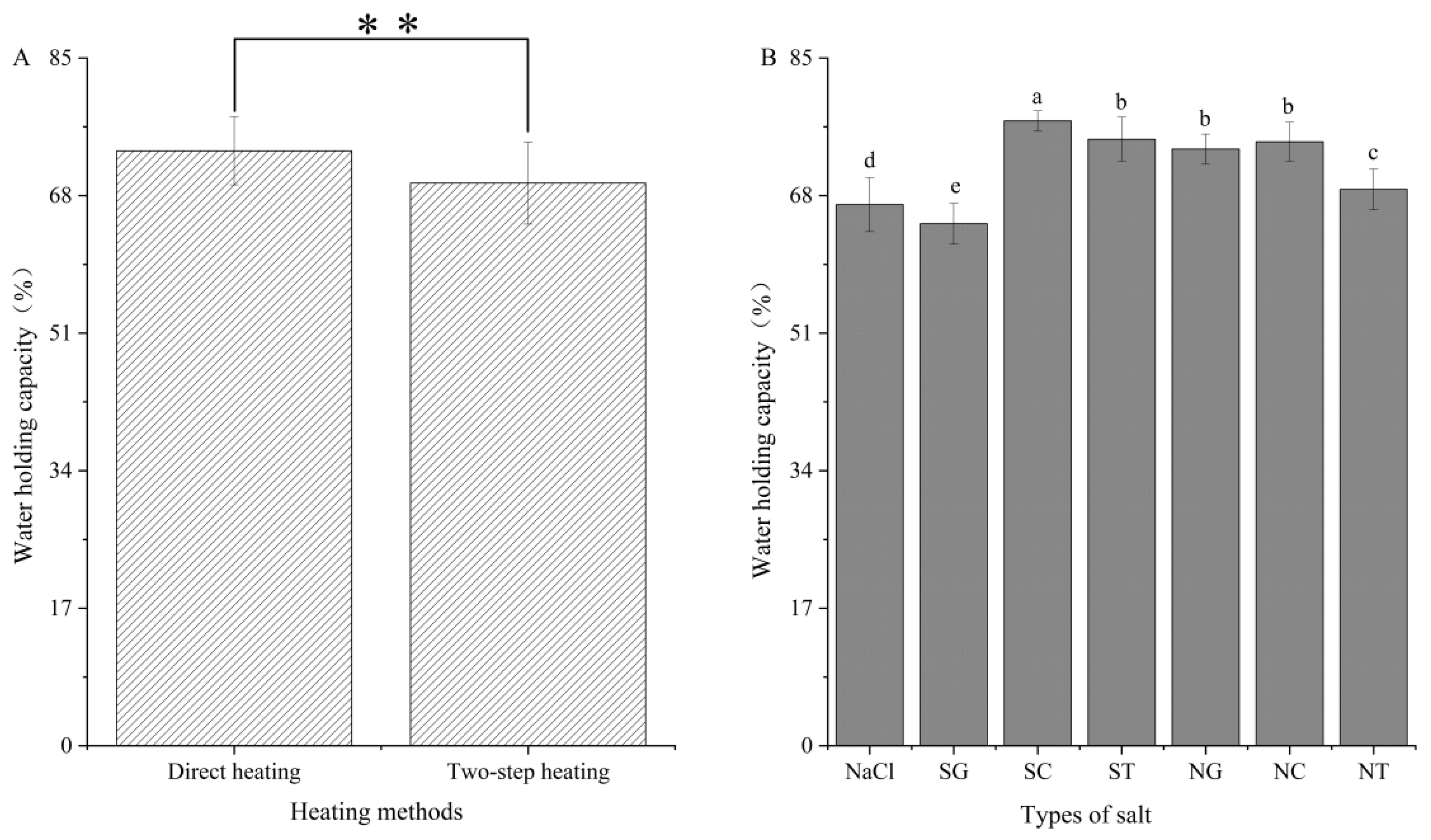
3.4. Water-Holding Capacity (WHC)
3.5. Whiteness Analysis
3.6. Analysis of Chemical Forces
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ge, G.; Han, Y.R.; Zheng, J.B.; Zhao, M.M.; Sun, W.Z. Physicochemical characteristics and gel-forming properties of myofibrillar protein in an oxidative system affected by partial substitution of NaCl with KCl, MgCl2 or CaCl2. Food Chem. 2020, 309, 125614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.X.; Deng, T.Y.; Wang, C.; Mi, H.B.; Yi, S.M.; Li, X.P.; Li, J.R. Effect of hydrocolloids on gel properties and protein secondary structure of silver carp surimi. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 100, 2252–2260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agostini, V.; Souza, M.C.D.; Franz, N.; Friedman, K.; Mair, G.; Plummer, J.; Taconet, M.; Anrooy, R.V.; Viparthi, K. World review. In The State of World Fisheries and Aquaculture 2020. Sustainability in Action; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2020; pp. 1–73. [Google Scholar]
- Doubleday, Z.A.; Prowse, T.A.A.; Arkhipkin, A.; Pierce, G.J.; Semmens, J.; Steer, M.; Leporati, S.C.; Lourenço, S.; Quetglas, A.; Sauer, W.; et al. Global proliferation of cephalopods. Curr. Biol. 2016, 26, 387–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nyaisaba, B.M.; Hatab, S.; Liu, X.; Chen, Y.; Chen, X.; Miao, W.; Chen, M.; Deng, S. Physicochemical changes of myofibrillar proteins of squid (Argentinus ilex) induced by hydroxyl radical generating system. Food Chem. 2019, 297, 124941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortés-Ruiz, J.A.; Pacheco-Aguilar, R.; Ramirez-Suarez, J.C.; Lugo-Sánchez, M.E.; García-Orozco, K.D.; Sotelo-Mundo, R.R.; Peña-Ramos, A. Conformational changes in proteins recovered from jumbo squid (Dosidicus gigas) muscle through pH shift washing treatments. Food Chem. 2016, 196, 769–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.; Cho, S.Y.; Yoshioka, T.; Kimura, M.; Seki, N. Influence of endogenous proteases and transglutaminase on thermal gelation of salted squid muscle paste. J. Food Sci. 2010, 68, 2473–2478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okamoto, Y.; Otsuka-Fuchino, H.; Horiuchi, S.; Tamiya, T.; Matsumoto, J.J.; Tsuchiya, T. Purification and characterization of two metalloproteinases from squid mantle muscle, myosinase I and myosinase II. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1993, 1161, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, J.T.; Takahashi, K.; Kaido, T.; Kasukawa, M.; Okazaki, E.; Osako, K. The effect of organic salts on the browning of dried squid products processed by air-drying. Food Chem. 2018, 269, 212–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB-5009.3; Direct Drying Method. National Food Safety Standard of Chinese: Beijing, China, 2016.
- GB 5009.6; Soxhlet Extraction Method. National Food Safety Standard of Chinese: Beijing, China, 2016.
- GB 5009.4; Total Ash Determination Method. National Food Safety Standard of Chinese: Beijing, China, 2016.
- Gornall, A.G.; Bardawill, C.J.; David, M.M. Determination of Serum Proteins by Means of the Biuret Reaction. J. Biol. Chem. 1949, 177, 751–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.P.; Hideto, F.; Deng, S.G.; Jia, R.; Osako, K.; Okazaki, E. Effect of pH and heating conditions on the properties of Alaska pollock (Theragra chalcogramma) surimi gel fortified with fish oil. J. Texture Stud. 2018, 49, 595–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, S.W.; Yang, H.; Yu, X.B.; Qian, C.; Wang, M.Y.; Zou, Y.F.; Xu, X.L.; Zhou, G.H. Applications of high pressure to pre-rigor rabbit muscles affect the water characteristics of myosin gels. Food Chem. 2018, 240, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaijan, M.; Panpipat, W.; Benjakul, S. Physicochemical properties and gel-forming ability of surimi from three species of mackerel caught in Southern Thailand. Food Chem. 2010, 121, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Guillén, M.C.; Borderías, A.J.; Montero, P. Chemical interactions of nonmuscle proteins in the network of sardine (Sardina pilchardus) muscle gels. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 1997, 30, 602–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, F.J.; Lai, K.M.; Hsu, K.C. A comparative study on physical properties and chemical interactions of gels from tilapia meat pastes induced by heat and pressure. J. Texture Stud. 2010, 41, 153–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahergorabi, R.; Jaczynski, J. Isoelectric Solubilization/precipitation as a means to recover protein and lipids from seafood by-products. In Seafood Processing by-Products; Kim, S.M., Ed.; Springer Science+Business Media: New York, NY, USA, 2014; pp. 101–123. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Tume, R.K.; Xu, X.L.; Zhou, G.H. Solubilization of myofibrillar proteins in water or low ionic strength media: Classical techniques, basic principles and novel functionalities. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2017, 57, 3260–3280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Zhao, S.M.; Liu, Y.M.; Yang, H.; Xiong, S.B.; Xie, B.J.; Qin, L.H. Effect of pH on the gel properties and secondary structure of fish myosin. Food Chem. 2010, 121, 196–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engelmann, M.D.; Bobier, R.T.; Hiatt, T.; Cheng, I.F.; Engelmann, M.D.; Bobier, R.T.; Hiatt, T.; Cheng, I.F. Variability of the Fenton reaction characteristics of the EDTA, DTPA, and citrate complexes of iron. Biometals 2003, 16, 519–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, L.; Tian, L.; Zhang, X.S.; Huang, X.; Long, H.Y.; Chang, F.Y.; Li, T.P.; Li, S.H. Effects of γ-polyglutamic acid on the physicochemical properties and microstructure of grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idellus) surimi during frozen storage. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 134, 109960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, H.; Xu, P.; Zhou, C.L.; Wang, Y.J. Effects of L-Arginine on water holding capacity and texture of heat-induced gel of salt-soluble proteins from breast muscle. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 63, 912–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Zhao, S.M.; Xiong, S.B.; Xie, B.J.; Liu, H.M. Studies on fish and pork paste gelation by dynamic rheology and circular dichroism. J. Food Sci. 2007, 72, E399–E403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chanarat, S.; Benjakul, S. Effect of formaldehyde on protein cross-linking and gel forming ability of surimi from lizardfish induced by microbial transglutaminase. Food Hydrocoll. 2013, 30, 704–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, R.; Jiang, Q.; Kanda, M.; Tokiwa, J.; Nakazawa, N.; Osako, K.; Okazaki, E. Effects of heating processes on changes in ice crystal formation, water holding capacity, and physical properties of surimi gels during frozen storage. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 90, 254–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filomena-Ambrosio, A.; Quintanilla-Carvajal, M.A.X.; Ana-Puig; Hernando, I.; Hernandez-Carrion, M.A.; Sotelo-Dıaz, I. Changes of the water-holding capacity and microstructure of panga and tilapia surimi gels using different stabilizers and processing methods. Food Sci. Technol. Int. 2015, 22, 68–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruusunen, M.; Vainionpää, J.; Puolanne, E.; Lyly, M.; Lähteenmäki, L.; Niemistö, M.; Ahvenainen, R. Effect of sodium citrate, carboxymethyl cellulose and carrageenan levels on quality characteristics of low-salt and low-fat bologna type sausages. Meat Sci. 2003, 64, 371–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz-Vela, J.; Pérez-Chabela, M.D.L.; Totosaus, A. Efecto del pH y de la adición de fosfatos de sodio sobre las propiedades de gelificación y emulsión de surimi de trucha arco-iris (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Ciênc. Tecnol. Alim. 2008, 28, 691–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kuwahara, K.; Konno, K. Suppression of thermal denaturation of myosin and salt-induced denaturation of actin by sodium citrate in carp (Cyprinus carpio). Food Chem. 2010, 122, 997–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Holmer, S.F.; Kutzler, L.W.; Mckeith, F.K.; Killefer, J. Sodium citrate as a replacement for sodium chloride in a brine solution when evaluated in cows of different backfat thickness. Meat Sci. 2009, 81, 349–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boon, D.D. Discoloration in processed crabmeat. A review. J. Food Sci. 1975, 40, 756–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endo, Y.; Yamadera, Y.; Tsukui, T. Antioxidant effects of pH-regulating agents on the thermal deterioration of vegetable oils. J. Oleo Sci. 2014, 63, 805–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, B.; Kong, B.H.; Li, F.F.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, H.W.; Xia, X.F. Changes in the thermal stability and structure of protein from porcine longissimus dorsi induced by different thawing methods. Food Chem. 2020, 316, 126375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Li, Z.; Wang, Y.; Xue, Y.; Xue, C. Effects of konjac glucomannan on heat-induced changes of physicochemical and structural properties of surimi gels. Food Res. Int. 2016, 83, 152–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.M.; Gao, L.L.; Ren, Y.X.; Zhao, Q. Chemical interactions and protein conformation changes during silver carp (Hypophthalmichthys Molitrix) surimi gel formation. Int. J. Food Prop. 2014, 17, 1702–1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
| Treatment | Hardness (N) | Adhesiveness (mJ) | Cohesiveness (Ratio) | Springiness (mm) | Chewiness (mJ) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Heating methods | Direct heating | 9.99 ± 1.41 A | 0.19 ± 0.09 A | 0.64 ± 0.02 A | 5.57 ± 0.31 A | 35.20 ± 5.9 A |
| Two-step heating | 8.76 ± 1.25 B | 0.21 ± 0.09 A | 0.61 ± 0.03 B | 5.40 ± 0.26 A | 28.86 ± 5.48 B | |
| Types of salt | NaCl | 9.84 ± 1.52 b | 0.26 ± 0.10 ab | 0.62 ± 0.03 b | 5.61 ± 0.38 ab | 34.25 ± 7.33 a |
| SG | 7.74 ± 0.89 c | 0.17 ± 0.06 c | 0.61 ± 0.05 b | 5.26 ± 0.24 b | 25.11 ± 5.00 c | |
| SC | 11.24 ± 0.78 a | 0.32 ± 0.06 a | 0.63 ± 0.03 ab | 5.64 ± 0.21 a | 39.72 ± 3.79 b | |
| ST | 9.46 ± 0.71 b | 0.21 ± 0.05 bc | 0.61 ± 0.01 b | 5.56 ± 0.17 ab | 32.27 ± 3.80 b | |
| NG | 9.31 ± 1.36 b | 0.14 ± 0.08 c | 0.63 ± 0.02 ab | 5.48 ± 0.21 ab | 31.97 ± 6.46 b | |
| NC | 9.86 ± 1.07 b | 0.16 ± 0.03 c | 0.65 ± 0.02 a | 5.57 ± 0.43 ab | 34.10 ± 3.08 b | |
| NT | 8.19 ± 0.77 c | 0.14 ± 0.05 c | 0.62 ± 0.01 b | 5.32 ± 0.23 ab | 26.80 ± 3.53 c |
| Treatment | Hardness (N) | Chewiness (mJ) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Direct Heating | Two-Step Heating | Direct Heating | Two-Step Heating | |
| NaCl | 11.20 ± 0.43 Aab | 8.48 ± 0.31 Bc | 40.25 ± 3.56 Aab | 28.25 ± 3.71 Bc |
| SG | 8.52 ± 0.14 Acd | 6.96 ± 0.36 Bd | 29.31 ± 1.45 Ade | 20.90 ± 2.71 Bd |
| SC | 11.89 ± 0.38 Aa | 10.59 ± 0.32 Ba | 42.83 ± 2.00 Aa | 36.62 ± 1.75 Ba |
| ST | 9.96 ± 0.38 Abc | 8.97 ± 0.62 Abc | 35.24 ± 1.78 Abc | 29.30 ± 2.54 Bbc |
| NG | 10.37 ± 0.41 Ab | 8.26 ± 1.04 Bc | 37.44 ± 2.54 Abc | 26.48 ± 2.79 Bc |
| NC | 9.77 ± 1.69 Abc | 9.94 ± 0.11 Aab | 34.39 ± 3.88 Acd | 33.81 ± 2.90 Aab |
| NT | 8.26 ± 0.96 Ad | 8.12 ± 0.75 Ac | 26.96 ± 3.98 Ae | 26.66 ± 3.91 Ac |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chu, Y.; Deng, S.; Lv, G.; Li, M.; Bao, H.; Gao, Y.; Jia, R. Improvement of Gel Quality of Squid (Dosidicus gigas) Meat by Using Sodium Gluconate, Sodium Citrate, and Sodium Tartrate. Foods 2022, 11, 173. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11020173
Chu Y, Deng S, Lv G, Li M, Bao H, Gao Y, Jia R. Improvement of Gel Quality of Squid (Dosidicus gigas) Meat by Using Sodium Gluconate, Sodium Citrate, and Sodium Tartrate. Foods. 2022; 11(2):173. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11020173
Chicago/Turabian StyleChu, Yanjiao, Shanggui Deng, Guancheng Lv, Mingao Li, Hongli Bao, Yuanpei Gao, and Ru Jia. 2022. "Improvement of Gel Quality of Squid (Dosidicus gigas) Meat by Using Sodium Gluconate, Sodium Citrate, and Sodium Tartrate" Foods 11, no. 2: 173. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11020173
APA StyleChu, Y., Deng, S., Lv, G., Li, M., Bao, H., Gao, Y., & Jia, R. (2022). Improvement of Gel Quality of Squid (Dosidicus gigas) Meat by Using Sodium Gluconate, Sodium Citrate, and Sodium Tartrate. Foods, 11(2), 173. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11020173





