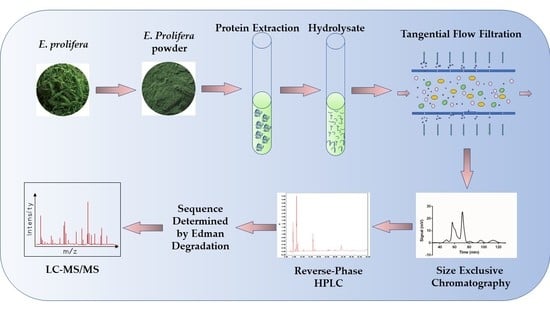
Preparation and Characterization of an Anticancer Peptide from Oriental Tonic Food Enteromorpha prolifera
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents
2.2. Preparation of Algae Powder
2.3. Protein Extraction
2.4. Protein Hydrolysis
2.5. Large Scale Preparation of Anticancer Peptide
2.6. Cell Culture and Cell Growth Inhibition Assay
2.7. Flow Cytometry
2.8. De Novo Sequencing of Peptide by Edman Degradation Assay and Mass Spectrometry Verification
2.9. Characterization of HTDT-6-2-3-2
2.10. Molecular Docking
3. Results
3.1. Hydrolysate of E. prolifera from Papain Digestion Exhibits Remarkable Inhibitory Activity on Cancer Cell Proliferation
3.2. Optimization of Hydrolytic Parameters Using Papain
3.3. Fractionation and Purification of Anticancer Peptide
3.4. Cytotoxicity of Peptide HTDT-6-2-3-2 on Cancer Cell Lines
3.5. Characterization of HTDT-6-2-3-2
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Fuchs, H.E.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics 2022. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2022, 72, 7–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Majeed, U.; Manochakian, R.; Zhao, Y.; Lou, Y. Targeted therapy in advanced non-small cell lung cancer: Current advances and future trends. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2021, 14, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Giglio, A.; di Federico, A.; Nuvola, G.; Deiana, C.; Gelsomino, F. The Landscape of Immunotherapy in Advanced NSCLC: Driving Beyond PD-1/PD-L1 Inhibitors (CTLA-4, LAG3, IDO, OX40, TIGIT, Vaccines). Curr. Oncol. Rep. 2021, 23, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daud, A.I.; Loo, K.; Pauli, M.L.; Sanchez-Rodriguez, R.; Sandoval, P.M.; Taravati, K.; Tsai, K.; Nosrati, A.; Nardo, L.; Alvarado, M.D.; et al. Tumor immune profiling predicts response to anti-PD-1 therapy in human melanoma. J. Clin. Investig. 2016, 126, 3447–3452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.; Siddiqui, B.A.; Anandhan, S.; Yadav, S.S.; Subudhi, S.K.; Gao, J.; Goswami, S.; Allison, J.P. The Next Decade of Immune Checkpoint Therapy. Cancer Discov. 2021, 11, 838–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okai, Y.; Higashi-Okai, K.; Nakamura, S.; Yano, Y.; Otani, S. Suppressive effects of the extracts of Japanese edible seaweeds on mutagen-induced umu C gene expression in Salmonella typhimurium (TA 1535/pSK 1002) and tumor promotor-dependent ornithine decarboxylase induction in BALB/c 3T3 fibroblast cells. Cancer Lett. 1994, 87, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okai, Y.; Higashi-Okai, K. Pheophytin a Is a Potent Suppressor against Genotoxin-Induced umuC Gene Expression in Salmonella typhimurium (TA 1535/pSK 1002). J. Sci. Food Agric. 1997, 74, 531–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higashi-Okai, K.; Otani, S.; Okai, Y. Potent suppressive effect of a Japanese edible seaweed, Enteromorpha prolifera (Sujiao-nori) on initiation and promotion phases of chemically induced mouse skin tumorigenesis. Cancer Lett. 1999, 140, 21–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, W.; He, X.; Long, L.; Fang, Q.; Wei, B.; Sun, J.; Zhang, W.; Wang, H.; Zhang, F.; Linhardt, R.J. Structural characterization and anti-lung cancer activity of a sulfated glucurono-xylo-rhamnan from Enteromorpha prolifera. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 237, 116143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.J.; Wang, Y.H.; Yin, J.; Leng, H.; Shen, S.D. Polysaccharides from Ulva prolifera O.F. Muller inhibit cell proliferation via activating MAPK signaling in A549 and H1650 cells. Food Funct. 2021, 12, 6915–6924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsomaia, N. Peptide therapeutics: Targeting the undruggable space. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 94, 459–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurrikoff, K.; Aphkhazava, D.; Langel, U. The future of peptides in cancer treatment. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2019, 47, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muttenthaler, M.; King, G.F.; Adams, D.J.; Alewood, P.F. Trends in peptide drug discovery. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2021, 20, 309–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, M.; Liu, D.; Yang, Y. Anti-cancer peptides: Classification, mechanism of action, reconstruction and modification. Open Biol. 2020, 10, 200004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheih, I.C.; Fang, T.J.; Wu, T.K.; Lin, P.H. Anticancer and antioxidant activities of the peptide fraction from algae protein waste. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 1202–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, X. Separation, antitumor activities, and encapsulation of polypeptide from Chlorella pyrenoidosa. Biotechnol. Prog. 2013, 29, 681–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhang, X. Inhibitory effects of small molecular peptides from Spirulina (Arthrospira) platensis on cancer cell growth. Food Funct. 2016, 7, 781–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Liu, X.; Li, Y.; You, H.; Yu, Z.; Wang, L.; Liu, X.; Ding, L. Identification and Characterization of Dipeptidyl Peptidase-IV Inhibitory Peptides from Oat Proteins. Foods 2022, 11, 1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, X.; Dai, Z.; Jin, R. Purification and Identification of a Novel Angiotensin Converting Enzyme Inhibitory Peptide from the Enzymatic Hydrolysate of Lepidotrigla microptera. Foods 2022, 11, 1889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbarian, M.; Khani, A.; Eghbalpour, S.; Uversky, V.N. Bioactive Peptides: Synthesis, Sources, Applications, and Proposed Mechanisms of Action. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjellqvist, B.; Hughes, G.J.; Pasquali, C.; Paquet, N.; Ravier, F.; Sanchez, J.C.; Frutiger, S.; Hochstrasser, D. The focusing positions of polypeptides in immobilized pH gradients can be predicted from their amino acid sequences. Electrophoresis 1993, 14, 1023–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bjellqvist, B.; Basse, B.; Olsen, E.; Celis, J.E. Reference points for comparisons of two-dimensional maps of proteins from different human cell types defined in a pH scale where isoelectric points correlate with polypeptide compositions. Electrophoresis 1994, 15, 529–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamiable, A.; Thevenet, P.; Rey, J.; Vavrusa, M.; Derreumaux, P.; Tuffery, P. PEP-FOLD3: Faster de novo structure prediction for linear peptides in solution and in complex. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, W449–W454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Daina, A.; Michielin, O.; Zoete, V. SwissTargetPrediction: Updated data and new features for efficient prediction of protein targets of small molecules. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, W357–W364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, S.C.; Goto, N.K.; Williams, K.A.; Deber, C.M. Alpha-helical, but not beta-sheet, propensity of proline is determined by peptide environment. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 6676–6681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Deveraux, Q.L.; Takahashi, R.; Salvesen, G.S.; Reed, J.C. X-linked IAP is a direct inhibitor of cell-death proteases. Nature 1997, 388, 300–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiozaki, E.N.; Chai, J.; Rigotti, D.J.; Riedl, S.J.; Li, P.; Srinivasula, S.M.; Alnemri, E.S.; Fairman, R.; Shi, Y. Mechanism of XIAP-mediated inhibition of caspase-9. Mol. Cell 2003, 11, 519–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Bai, L.; Mao, X.; Zhang, X. Novel peptides with anti-proliferation activity from the Porphyra haitanesis hydrolysate. Process Biochem. 2017, 60, 98–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acharya, K.R.; Sturrock, E.D.; Riordan, J.F.; Ehlers, M.R. Ace revisited: A new target for structure-based drug design. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2003, 2, 891–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singla, R.K.; Kumar, R.; Khan, S.; Mohit; Kumari, K.; Garg, A. Natural Products: Potential Source of DPP-IV Inhibitors. Curr. Protein Pept. Sci. 2019, 20, 1218–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangiorgio, S.; Vidovic, N.; Boschin, G.; Aiello, G.; Arcidiaco, P.; Arnoldi, A.; Morelli, C.F.; Rabuffetti, M.; Recca, T.; Scarabattoli, L.; et al. Preparation, Characterization and In Vitro Stability of a Novel ACE-Inhibitory Peptide from Soybean Protein. Foods 2022, 11, 2667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, C.; Liu, D.; Hao, H.; Wu, X. Identification of the DPP-IV Inhibitory Peptides from Donkey Blood and Regulatory Effect on the Gut Microbiota of Type 2 Diabetic Mice. Foods 2022, 11, 2148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Level | Factor | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| A, E/S (U/g) | B, pH | C, Temperature (°C) | |
| 1 | 2000 | 4.5 | 45 |
| 2 | 3000 | 5 | 50 |
| 3 | 4500 | 5.5 | 55 |
| Trial Number | Factor | Replication | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | B | C | Blank | X% | Y% | |
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 40.36 | 41.15 |
| 2 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 39.17 | 37.14 |
| 3 | 1 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 35.31 | 32.34 |
| 4 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 56.53 | 57.96 |
| 5 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 42.43 | 42.48 |
| 6 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 34.17 | 35.66 |
| 7 | 3 | 1 | 3 | 2 | 57.22 | 56.53 |
| 8 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 3 | 60.98 | 59.45 |
| 9 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 48.96 | 50.25 |
| K1 | 37.58 | 51.63 | 45.30 | 44.27 | ||
| K2 | 44.87 | 46.94 | 48.34 | 43.32 | ||
| K3 | 55.57 | 39.45 | 44.39 | 50.43 | ||
| R range | 17.99 | 12.18 | 3.95 | 7.11 | ||
| Factor order | A > B > C | |||||
| Priority level | A3B1C2 | |||||
| Target | Common Name | Uniprot ID | chEMBL ID | Target Class | Probability |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Inhibitor of apoptosis protein 3 | XIAP | P98170 | CHEMBL4198 | Other cytosolic protein | 0.76 |
| Angiotensin- converting enzyme | ACE | P12821 | CHEMBL1808 | Protease | 0.65 |
| Dipeptidyl peptidase IV | DPP4 | P27487 | CHEMBL284 | Protease | 0.50 |
| HLA class I histocompatibility antigen A-3 | HLA-A | P04439 | CHEMBL2632 | Surface antigen | 0.29 |
| Beta-secretase 1 | BACE1 | P56817 | CHEMBL4822 | Protease | 0.14 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lin, X.; Dong, L.; Yan, Q.; Dong, Y.; Wang, L.; Wang, F. Preparation and Characterization of an Anticancer Peptide from Oriental Tonic Food Enteromorpha prolifera. Foods 2022, 11, 3507. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11213507
Lin X, Dong L, Yan Q, Dong Y, Wang L, Wang F. Preparation and Characterization of an Anticancer Peptide from Oriental Tonic Food Enteromorpha prolifera. Foods. 2022; 11(21):3507. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11213507
Chicago/Turabian StyleLin, Xiaosi, Le Dong, Qingdan Yan, Yibo Dong, Li Wang, and Fang Wang. 2022. "Preparation and Characterization of an Anticancer Peptide from Oriental Tonic Food Enteromorpha prolifera" Foods 11, no. 21: 3507. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11213507
APA StyleLin, X., Dong, L., Yan, Q., Dong, Y., Wang, L., & Wang, F. (2022). Preparation and Characterization of an Anticancer Peptide from Oriental Tonic Food Enteromorpha prolifera. Foods, 11(21), 3507. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11213507