Overcoming Anxiety Disorder by Probiotic Lactiplantibacillus plantarum LZU-J-TSL6 through Regulating Intestinal Homeostasis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
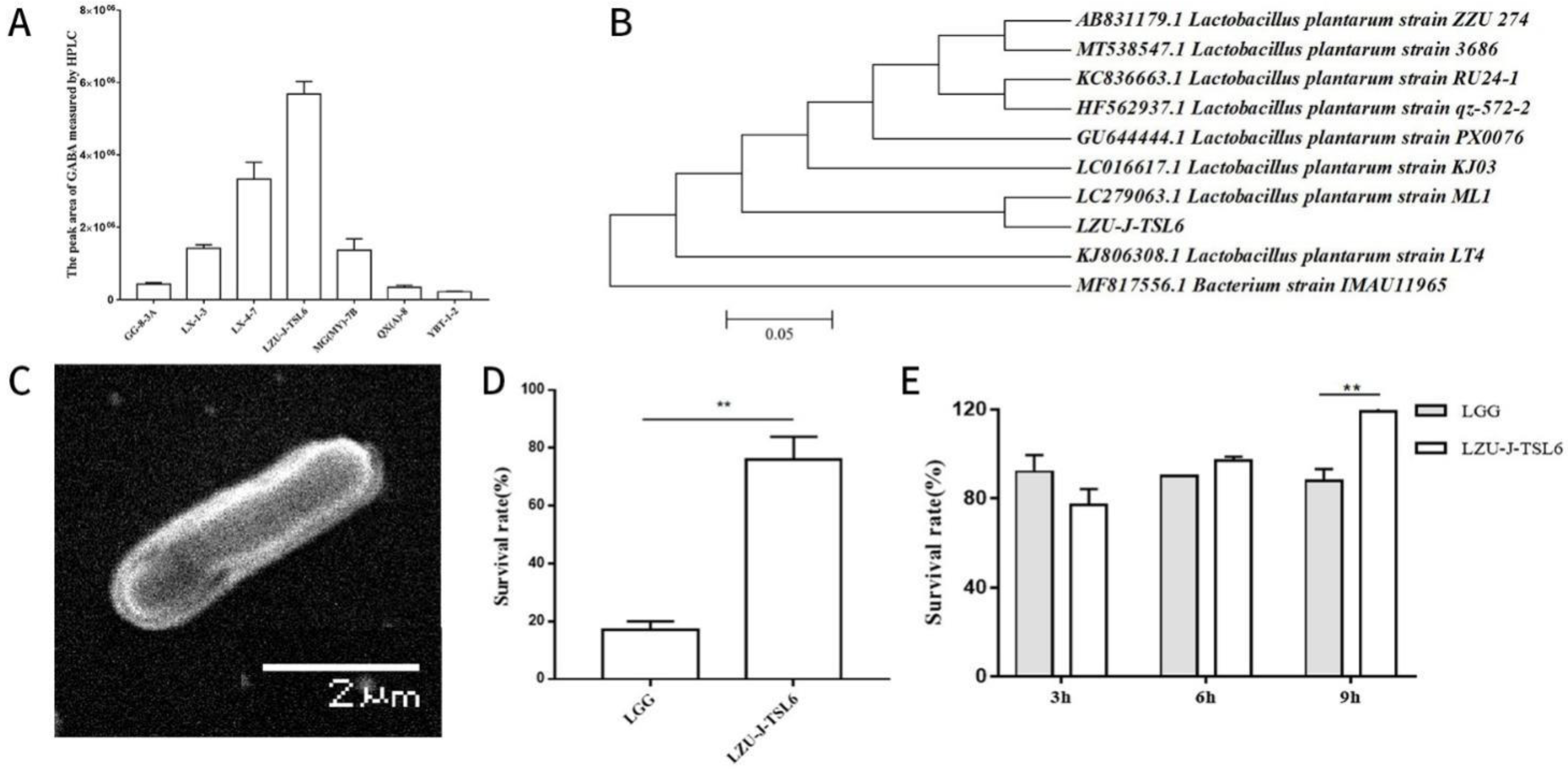
2.1. Screening Strains with Relatively High GABA Yield
2.2. 16S rRNA GENE Sequencing and Phylogenetic Analysis of Strain LZU-J-TSL6
2.3. Scanning Electron Microscope
2.4. In Vitro Determination of Acid and Choline Tolerance of Strains
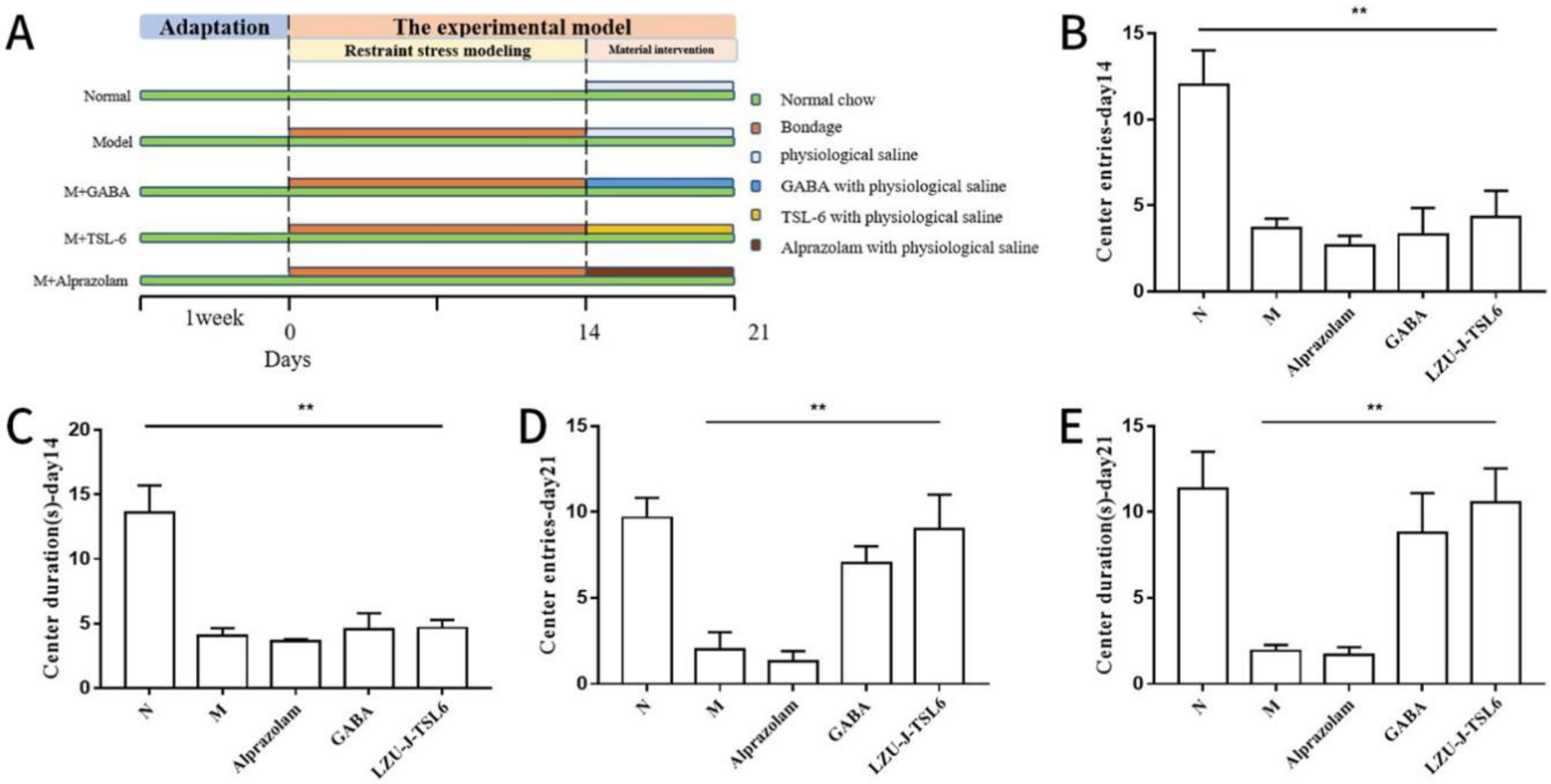
2.5. Animals and Treatments
2.6. Behavioural Testing
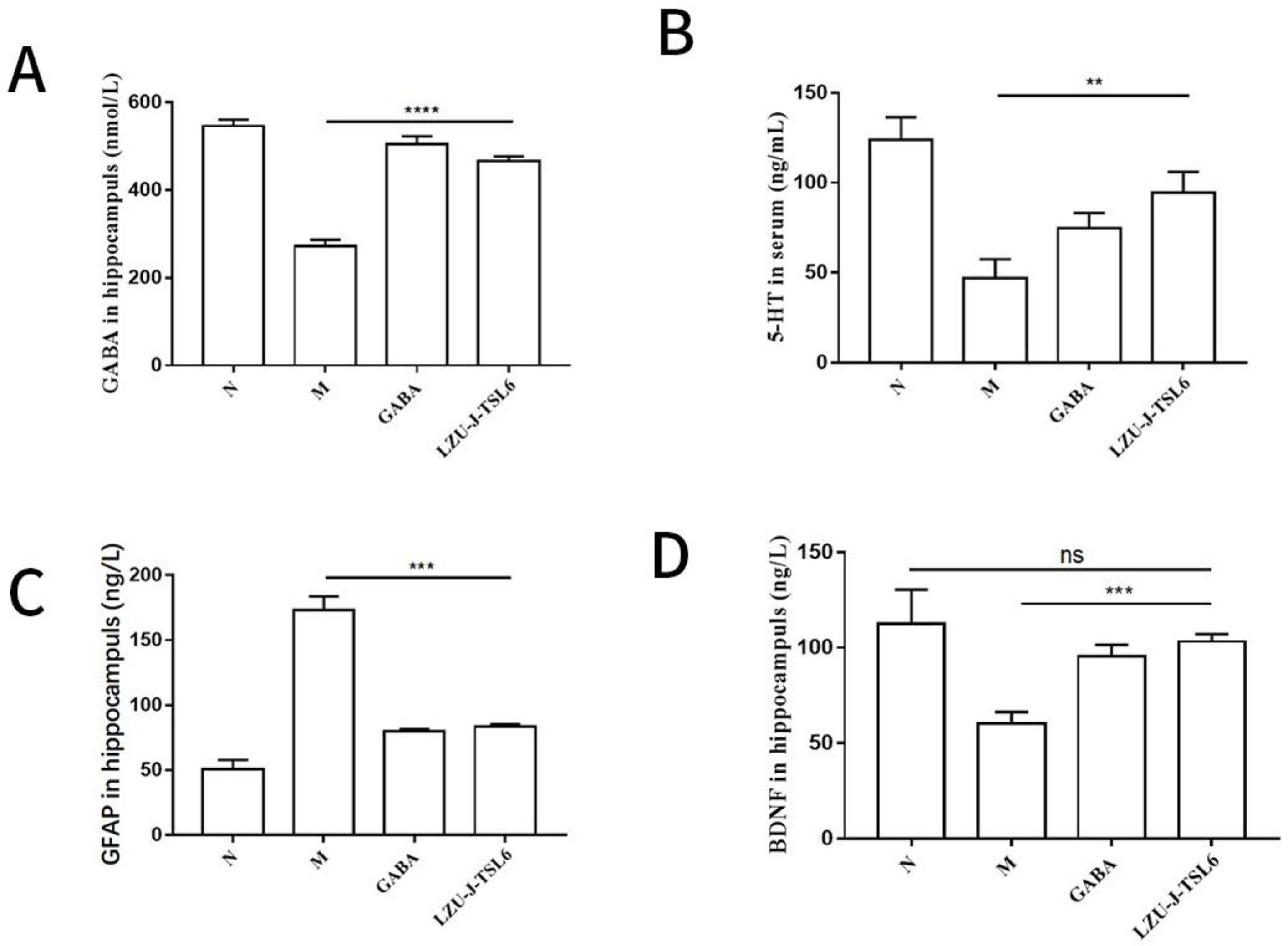
2.7. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay of Hippocampus and Serum in Mice
2.7.1. Blood Collection and Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay
2.7.2. Collection of Mice Hippocampus and Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay
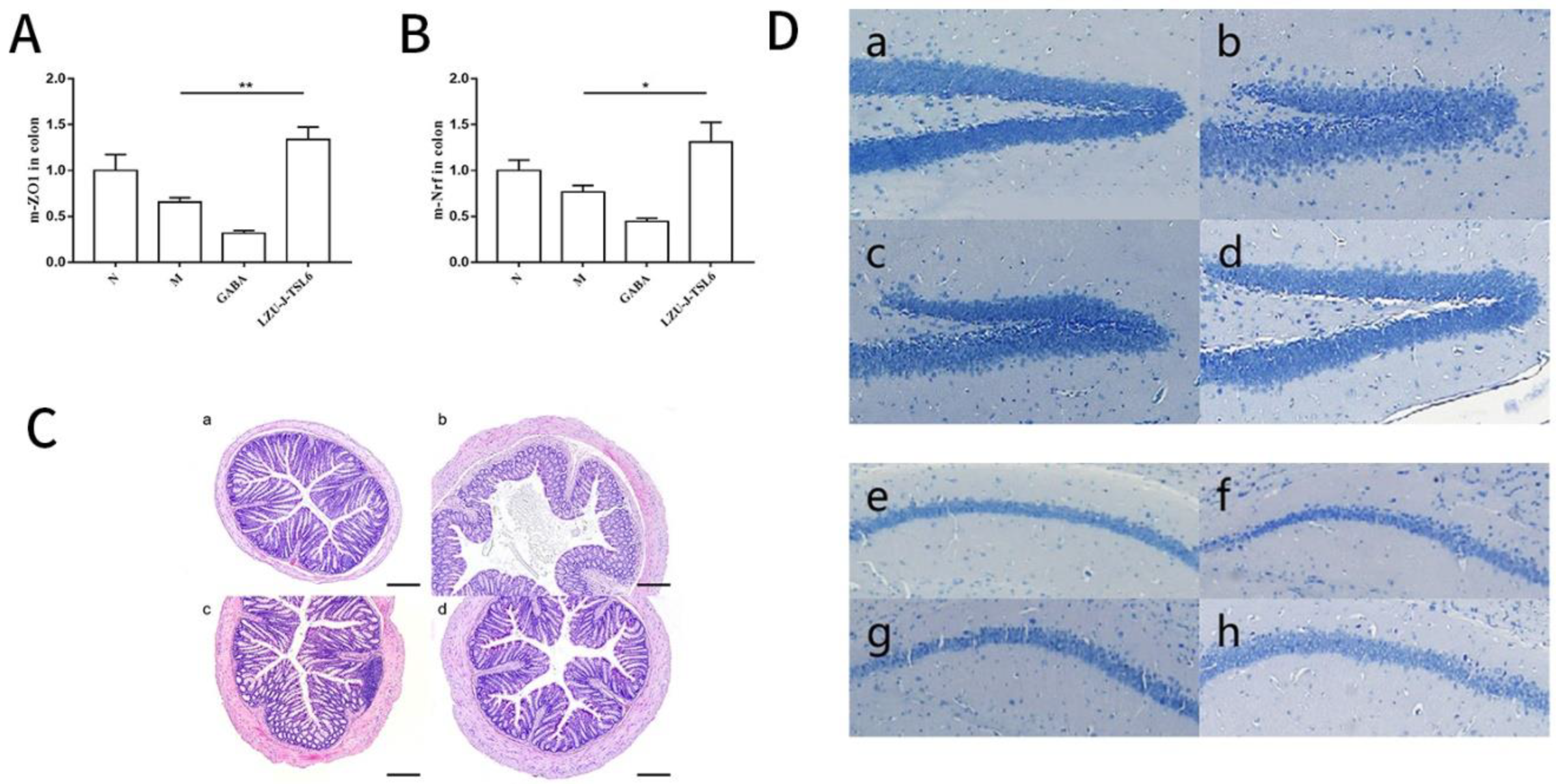
2.8. Slice Staining of Mice Colon Tissue and Hippocampus Tissue
2.8.1. Hematoxylin-Eosin (HE) Staining of Mice Colon Tissue
2.8.2. Nissl Corpuscle Staining in Hippocampus of Mice
2.9. Determination of Nrf-2 and ZO-1 mRNA Expression in Colonic Tissues
2.9.1. RNA Extraction and Detection of Concentration and Purity
2.9.2. Reverse Transcription of RNA
2.9.3. PCR Detection and Data Analysis and Calculation
2.10. Sequencing of Intestinal Flora and Metabolomic Detection and Analysis
2.10.1. Extraction and PCR Amplification of Genomic DNA from Intestinal Microbiota
2.10.2. Mixing and Purification of PCR Products
2.10.3. Library Construction
2.10.4. Computer Sequencing and Data Processing
2.10.5. Extraction of Metabolites
2.11. Bioinformatics and Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Screening of GABA-Producing Strains and Evaluation of Their Characteristics
3.2. Effect of LZU-J-TSL6 on the Behavior of Anxiety Mice
3.3. Effect of LZU-J-TSL6 on the Levels of Related Factors in Hippocampus and Serum of Anxiety Mice
3.4. Repairing Activity of LZU-J-TSL6 in Intestinal Environment and Hippocampus
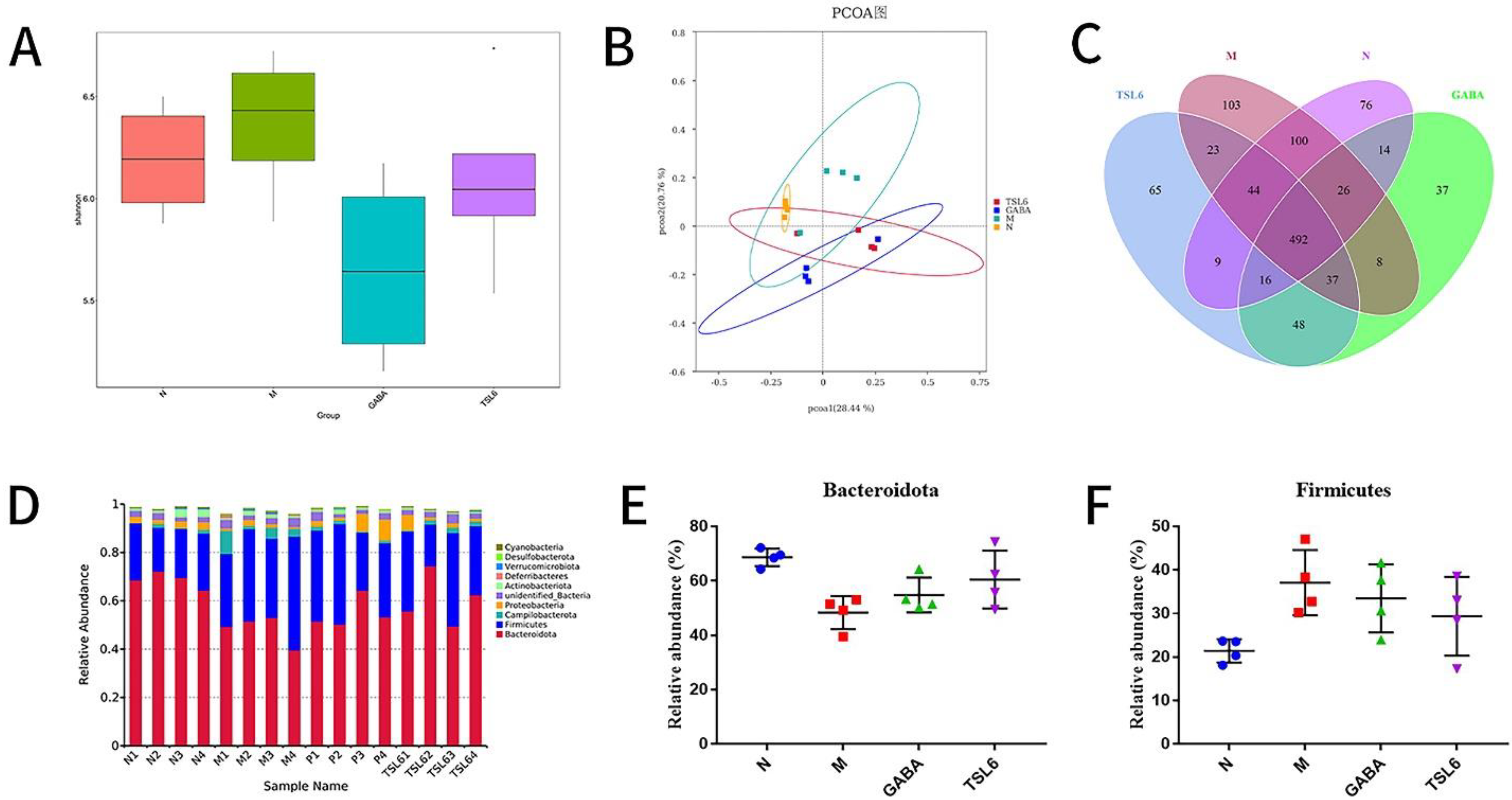
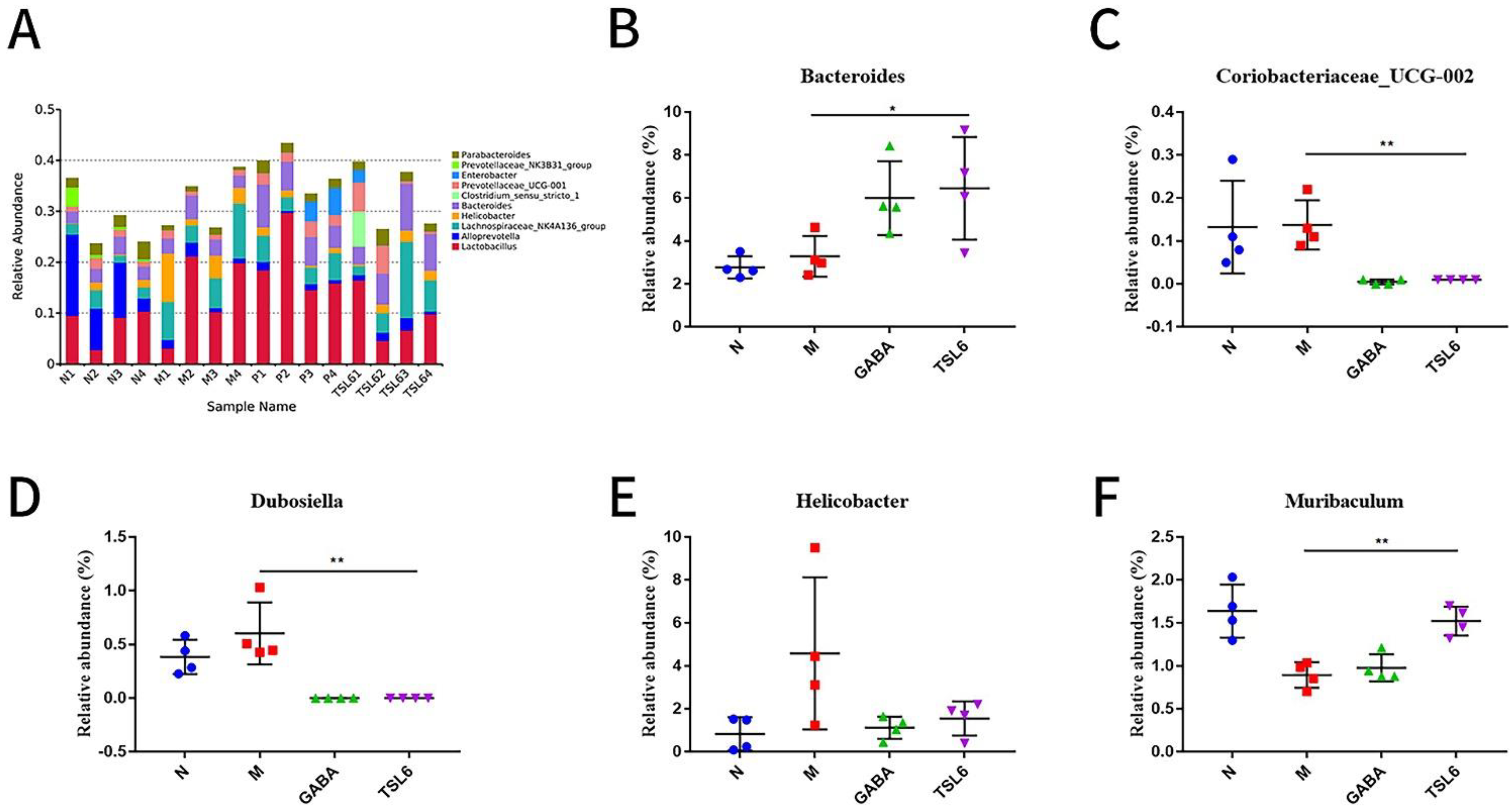
3.5. Effects of LZU-J-TSL6 Treatment on Intestinal Flora Function and Microbial Diversity in Restraint Stress Model Mice
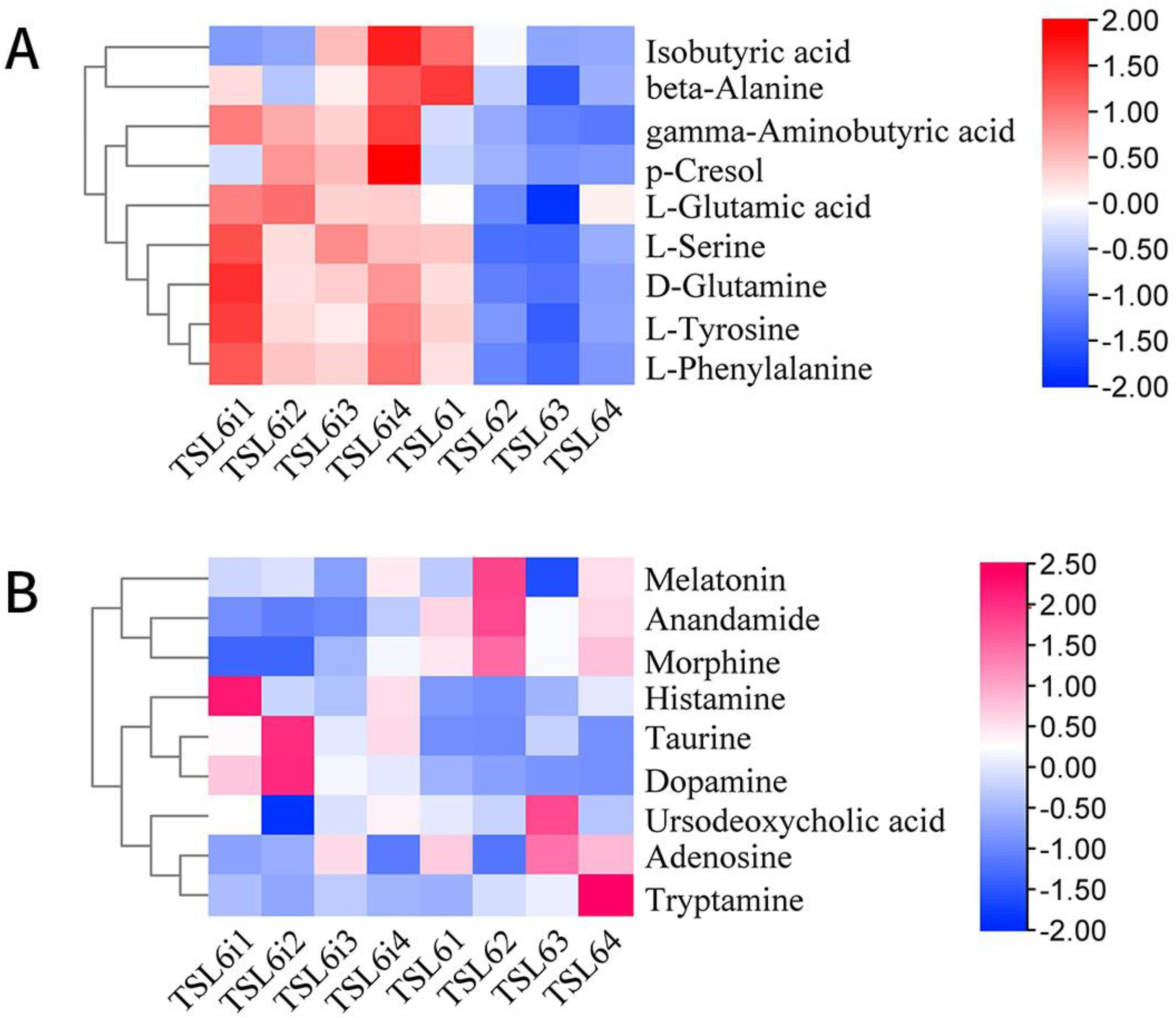
3.6. Prediction of Metabolic Pathway and Changes of Related Differential Metabolites in Mice before and after Intervention with LZU-J-TSL6
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Remes, O.; Brayne, C.; van der Linde, R.; Lafortune, L. A systematic review of reviews on the prevalence of anxiety disorders in adult populations. Brain Behav. 2016, 6, e497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, J.J. Anxiety disorders in Asians and Asian Americans. Asian J. Psychiatry 2014, 7, 74–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, H.; Liu, Z.; Yu, X.; Yan, J.; Yu, Y.; Kou, C.; Xu, X.; Lu, J.; et al. Prevalence of mental disorders in China: A cross-sectional epidemiological study. Lancet Psychiatry 2019, 6, 211–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Härter, M.C.; Conway, K.P.; Merikangas, K.R. Associations between anxiety disorders and physical illness. Eur. Arch. Psychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 2003, 253, 313–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saha, S.; Stedman, T.J.; Scott, J.G.; McGrath, J.J. The co-occurrence of common mental and physical disorders within Australian families: A national population-based study. Aust. N. Z. J. Psychiatry 2013, 47, 754–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Craske, M.G.; Stein, M.B.; Eley, T.C.; Milad, M.R.; Holmes, A.; Rapee, R.M.; Wittchen, H.U. Anxiety disorders. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2017, 3, e17024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chao, T. Change characteristic of neurotransmitters in brain of 45 patient with anxiety disorder. J. Community Med. 2018, 16, 35–36. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, Z.; Rixia, Z.; Haijing, L. Study on the effects of acupuncture combined with music therapy on the balance excitatory and inhibitory of hippocampal Glu/GABA in anxiety model rats. Mod. J. Integr. Tradit. Chin. West. Med. 2016, 25, 917–919. [Google Scholar]
- Weixin, H. The Clinical Effiency of Acupuncture Using “Siguan” Points for Treatment of Anxiety. Available online: https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/detail.aspx?dbcode=CDFD&dbname=CDFDLAST2017&filename=1017194317.nh&uniplatform=NZKPT&v=R2C2bix26ZGR3V4uEAWzmfFXfb_nrvGQiyXGqwLzek7vRQetv-W8w6zaYhoNtozp (accessed on 14 October 2022).
- Nikolaus, S.; Antke, C.; Beu, M.; Müller, H.W. Cortical GABA, striatal dopamine and midbrain serotonin as the key players in compulsive and anxiety disorders--results from in vivo imaging studies. Rev. Neurosci. 2010, 21, 119–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bystritsky, A.; Khalsa, S.S.; Cameron, M.E.; Schiffman, J. Current diagnosis and treatment of anxiety disorders. PT (Lawrenceville N.J.) 2013, 38, 30–57. [Google Scholar]
- Alonso, J.; Liu, Z.; Evans-Lacko, S.; Sadikova, E.; Sampson, N.; Chatterji, S.; Abdulmalik, J.; Aguilar-Gaxiola, S.; Al-Hamzawi, A.; Andrade, L.H. Treatment gap for anxiety disorders is global: Results of the World Mental Health Surveys in 21 countries. Depress. Anxiety 2018, 35, 195–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Messaoudi, M.; Lalonde, R.; Violle, N.; Javelot, H.; Desor, D.; Nejdi, A.; Bisson, J.F.; Rougeot, C.; Pichelin, M.; Cazaubiel, M. Assessment of psychotropic-like properties of a probiotic formulation (Lactobacillus helveticus R0052 and Bifidobacterium longum R0175) in rats and human subjects. Br. J. Nutr. 2011, 105, 755–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takada, M.; Nishida, K.; Kataoka-Kato, A.; Gondo, Y.; Ishikawa, H.; Suda, K.; Kawai, M.; Hoshi, R.; Watanabe, O.; Igarashi, T.; et al. Probiotic Lactobacillus casei strain Shirota relieves stress-associated symptoms by modulating the gut–brain interaction in human and animal models. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2016, 28, 1027–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Lv, J.; Pan, L.; Zhang, Y. Roles and applications of probiotic Lactobacillus strains. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2018, 102, 8135–8143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, W.; Wu, C. Psychotropic effects of Lactobacillus plantarum PS128 in early life-stressed and naïve adult mice. Brain Res. 2016, 1631, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Chuang, H.; Huang, Y.; Wu, C.; Chou, G.; Wang, S.; Tsai, Y. Alteration of behavior and monoamine levels attributable to Lactobacillus plantarum PS128 in germ-free mice. Behav. Brain Res. 2016, 298, 202–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bercik, P.; Park, A.J.; Sinclair, D.; Khoshdel, A.; Lu, J.; Huang, X.; Deng, Y.; Blennerhassett, P.A.; Fahnestock, M.; Moine, D.; et al. The anxiolytic effect of Bifidobacterium longum NCC3001 involves vagal pathways for gut-brain communication. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2011, 23, 1132–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bravo, J.A.; Forsythe, P.; Chew, M.V.; Escaravage, E.; Savignac, H.M.; Dinan, T.G.; Bienenstock, J.; Cryan, J.F. Ingestion of Lactobacillus strain regulates emotional behavior and central GABA receptor expression in a mouse via the vagus nerve. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 16050–16055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Sullivan, E.; Barrett, E.; Grenham, S.; Fitzgerald, P.; Stanton, C.; Ross, Q.P.; Quigley, D.M.M.; Cryan, J.F.; Dinan, T.G. BDNF expression in the hippocampus of maternally separated rats: Does Bifidobacterium breve 6330 alter BDNF levels? Benef. Microbes 2011, 2, 199–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strandwitz, P.; Kim, K.H.; Terekhova, D.; Liu, J.K.; Sharma, A.; Levering, J.; Donald, D.M.; Dietrich, D.; Ramadhar, T.T.; Lekbua, A.; et al. GABA-modulating bacteria of the human gut microbiota. Nat. Microbiol. 2019, 4, 396–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, M.; Weitao, G.; Jinju, W.; Yanping, W. Lactic Acid Bacteria Metabolism and Formation of Food Flavor Substances. China Condiment 2019, 44, 159–163. [Google Scholar]
- Puebla-Barragan, S.; Reid, G. Thirty-year evolution of probiotic therapy. Microb. Cell 2019, 6, 184–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Westfall, S.; Lomis, N.; Kahouli, I.; Dia, S.Y.; Singh, S.P.; Prakash, S. Microbiome, probiotics and neurodegenerative diseases: Deciphering the gut brain axis. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2017, 74, 3769–3787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, Z.; Yuli, W.; Xiaoqian, C.; Ping, Z. Isolation and Initiative Identification of Microorganism from Traditional Fermentative Food-Jiangshui. Food Sci. 2007, 28, 219–222. [Google Scholar]
- Soto, M.; Herzog, C.; Pacheco, J.A.; Fujisaka, S.; Bullock, K.; Clish, C.B.; Kahn, C.R. Gut microbiota modulate neurobehavior through changes in brain insulin sensitivity and metabolism. Mol. Psychiatry 2018, 23, 2287–2301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Zhang, H.F.; Ma, C.L.; Wei, H.; Li, B.M.; Luo, J. Alleviation of Anxiety/Depressive-Like Behaviors and Improvement of Cognitive Functions by Lactobacillus plantarum WLPL04 in Chronically Stressed Mice. Can. J. Infect. Dis. Med. Microbiol. 2021, 2021, 6613903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qianlong, X.; Cuiji, H.; Zhenmei, Y.; Zhaoming, L. Determination of γ-aminobutyric Acid in Lactic Acid Bacteria Fermented Liquid by HPLC. China Condiment 2013, 38, 50–59. [Google Scholar]
- Wooden, J.; Kyes, S.; Sibley, C.H. PCR and strain identification in Plasmodium falciparum. Parasitol. Today 1993, 9, 303–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, D.; Zhu, S.; Chen, Y.; Huang, Y.; Yang, J.; Chen, J. Paracoccus indicus sp. nov., isolated from surface seawater in the Indian Ocean. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 2019, 112, 927–933. [Google Scholar]
- Tamura, K.; Stecher, G.; Peterson, D.; Filipski, A.; Kumar, S. MEGA6: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis Version 6.0. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 2725–2729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.S.; Wang, X.X.; Pan, Y.J.; Wang, Y.J. Isolation and identification of Lactobacillus kefiri from Kefir granules in Tibet. J. Shanghai Ocean. Univ. 2018, 27, 141–148. [Google Scholar]
- He, S.-s.; Bao, Z.-n.; Lin, W.-f.; Xia, F.-g. Screening of Cholesterol-reducing Probiotics and Its Acid and Bile Salt Tolerance. Mod. Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 35, 198–206. [Google Scholar]
- Minghao, Z.; Ning, J.; Wenxia, Z. Establishment and comparison of anxiety models by uncertain empty water bottle stimulation and restraint stress in mice. Chin. J. Pharm. Toxicol. 2019, 33, 102–108. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, S.; Fulton, S. Diet-induced obesity promotes depressive-like behaviour that is associated with neural adaptations in brain reward circuitry. Int. J. Obes. 2013, 37, 382–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caporaso, J.G.; Lauber, C.L.; Walters, W.A.; Berg-Lyons, D.; Huntley, J.; Fierer, N.; Owens, S.M.; Betley, J.; Fraser, L.; Bauer, M.; et al. Ultra-high-throughput microbial community analysis on the Illumina HiSeq and MiSeq platforms. ISME J. 2012, 6, 1621–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Rui, J.; Mao, Y.; Anthony, Y.; Roderick, M. Dynamics of the bacterial community structure in the rhizosphere of a maize cultivar. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2014, 68, 392–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haas, B.J.; Gevers, D.; Earl, A.M.; Feldgarden, M.; Ward, D.V.; Giannoukos, G.; Ciulla, D.; Tabbaa, D.; Highlander, S.K.; Sodergren, E.; et al. Chimeric 16S rRNA sequence formation and detection in Sanger and 454-pyrosequenced PCR amplicons. Genome Res. 2011, 21, 494–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Garrity, G.M.; Tiedje, J.M.; Cole, J.R. Naïve Bayesian Classifier for Rapid Assignment of rRNA Sequences into the New Bacterial Taxonomy. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 5261–5267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edgar, R.C. UPARSE: Highly accurate OTU sequences from microbial amplicon reads. Nat. Methods 2013, 10, 996–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quast, C.; Pruesse, E.; Yilmaz, P.; Gerken, J.; Schweer, T.; Yarza, P.; Peplies, J.; Glöckner, F.O. The SILVA ribosomal RNA gene database project: Improved data processing and web-based tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 41, D590–D596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Shuo, L.; Weijie, Z.; Huawei, Z.; Qian, T.; Hua, W.; He, Y. Impact of traditional Chinese medicine treatment on chronic unpredictable mild stress-induced depression-like behaviors intestinal microbiota and gut microbiome function. Food Funct. 2019, 10, 5886–5897. [Google Scholar]
- Vogt, N.M.; Kerby, R.L.; Dill-McFarland, K.A.; Harding, S.J.; Merluzzi, A.P.; Johnson, S.C.; Carlsson, C.M.; Asthana, S.; Zetterberg, H.; Blennow, K.; et al. Gut microbiome alterations in Alzheimer’s disease. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 13537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strati, F.; Cavalieri, D.; Albanese, D.; Felice, C.D.; Donati, C.; Hayek, J.; Jousson, O.; Leoncini, S.; Renzi, D.; Calabrò, A.; et al. New evidences on the altered gut microbiota in autism spectrum disorders. Microbiome 2017, 5, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carlson, L.A.; Xia, K.; Azcarate-Peril, M.A.; Goldman, B.D.; Ahn, M.; Styner, M.A.; Thompson, A.L.; Geng, X.; Gilmore, J.H.; Knickmeyer, R.C. Infant Gut Microbiome Associated with Cognitive Development. Biol. Psychiatry 2017, 83, 148–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Yu, C.Y.; Li, R.L.; Liu, K.M.; Jin, G.E.; Ge, R.L.; Tang, F.; Cui, S. High-altitude Tibetan fermented milk ameliorated cognitive dysfunction by modified gut microbiota in Alzheimer’s disease transgenic mice. Food Funct. 2020, 11, 5308–5319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yongqiang, S.; Xiangyang, Z.; Xiaoping, W.; Yue, W.; Hui, W.; Xinguo, W.; Yang, J.; Yongqiang, S. Clinical Observation of Bifidobacterium Triple Viable Capsules in the Adjunctive Treatment of Hp Positive Chronic Atrophic Gastritis Complicated with Anxiety-depression. China Pharm. 2017, 28, 2380–2383. [Google Scholar]
- Xiaona, Z.; Lili, C.; Li, W. Relationship between anxiety—Depression and H. Pylori infection among peptic ulcer patients. Med. Pest Control 2012, 28, 698–699. [Google Scholar]
- Budzyński, J. Brain-gut axis in the pathogenesis of Helicobacter pylori infection. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 5212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olbjørn, C.; Småstuen, M.C.; Thiis-Evensen, E.; Nakstad, B.; Vatn, M.H.; Jahnsen, J.; Ricanek, P.; Vatn, S.; Moen, A.E.F.; Tannæs, T.M.; et al. Fecal microbiota profiles in treatment-naïve pediatric inflammatory bowel disease–associations with disease phenotype, treatment, and outcome. Clin. Exp. Gastroenterol. 2019, 12, 37–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagy-Szakal, D.; Hollister, E.B.; Luna, R.A.; Szigeti, R.; Tatevian, N.; Smith, C.W.; Versalovic, J.; Kellermayer, R. Cellulose Supplementation Early in Life Ameliorates Colitis in Adult Mice. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e56685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Tingting, D.; Yan, L.; Yanxia, L.; Yuming, X. Mechanism of gut barrier injury and bacterial translocation in anxiety-depression induced degenerative neurosis. Chin. J. Microecol. 2020, 32, 352–357. [Google Scholar]
- Julio-Pieper, M.; Bravo, J.A.; Aliaga, E.; Gotteland, M. Review article: Intestinal barrier dysfunction and central nervous system disorders—A controversial association. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2014, 40, 1187–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeon, S.; You, Y.S.; Kwon, H.; Yang, E.H.; Ryu, J.; Kang, B.H.; Kang, J. Fermented milk of Lactobacillus helveticus IDCC3801 reduces beta-amyloid and attenuates memory deficit. J. Funct. Foods 2010, 2, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burokas, A.; Arboleya, S.; Moloney, R.D.; Peterson, V.L.; Murphy, K.; Clarke, G.; Stanton, C.; Dinan, T.G.; Cryan, J.F. Targeting the Microbiota-Gut-Brain Axis: Prebiotics Have Anxiolytic and Antidepressant-like Effects and Reverse the Impact of Chronic Stress in Mice. Biol. Psychiatry 2017, 82, 472–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsiao, E.Y.; McBride, S.W.; Hsien, S.; Sharon, G.; Hyde, E.R.; Mc-Cue, T.; Codelli, J.A.; Chow, J.; Reisman, S.E.; Petrosino, J.F.; et al. Microbiota Modulate Behavioral and Physiological Abnormalities Associated with Neurodevelopmental Disorders. Cell 2013, 155, 1451–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharkey, K.A. Emerging roles for enteric glia in gastrointestinal disorders. J. Clin. Investig. 2015, 125, 918–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Wu, G.; Zhou, Z.; Dai, Z.; Sun, Y.; Ji, Y.; Li, W.; Wang, W.; Liu, C.; Han, F.; et al. Glutamine and intestinal barrier function. Amino Acids 2015, 47, 2143–2154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, Z. Effect of glutamine on change in early postoperative intestinal permeability and its relation to systemic inflammatory response. World J. Gastroenterol. 2004, 10, 1992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slykerma, R.F.; Hood, F.; Wickens, K.; Thompson, J.M.D.; Barthow, C.; Murphy, R.; Kang, J.; Rowden, J.; Stone, P.; Crane, J.; et al. Effect of Lactobacillus rhamnosus HN001 in Pregnancy on Postpartum Symptoms of Depression and Anxiety: A Randomised Double-blind Placebo-controlled Trial. EBioMedicine 2017, 24, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, S.; Wang, T.; Hu, X.; Luo, J.; Li, W.; Wu, X.; Duan, Y.; Jin, F. Administration of Lactobacillus helveticus NS8 improves behavioral, cognitive, and biochemical aberrations caused by chronic restraint stress. Neuroscience 2015, 310, 561–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, H.M.; Jang, S.E.; Han, M.J.; Luo, J.; Li, W.; Wu, X.; Duan, Y.; Jin, F. Anxiolytic-like effect of Bifidobacterium adolescentis IM38 in mice with or without immobilisation stress. Benef. Microbes 2018, 9, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Number | Sample Origin | Number of Samples | Production Method | Strain Named |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Guoluo (Maqin), Qinghai, China | 1 | Herders homemade | GL |
| 2 | Guoluo (Maqin), Qinghai, China | 1 | commercial product | GL(AS) |
| 3 | Guoluo (Maqin), Qinghai, China | 1 | commercial product | GL(GQ) |
| 4 | Yushu (Jiegu), Qinghai, China | 1 | Herders homemade | YJG |
| 5 | Yushu (Nangqian), Qinghai, China | 1 | Herders homemade | YNQ |
| 6 | Yushu (Chengduo), Qinghai, China | 1 | Herders homemade | YCD |
| 7 | Yushu (Batang), Qinghai, China | 1 | Herders homemade | YBT |
| 8 | Tongren (Ningxiu), Qinghai, China | 1 | Herders homemade | NX |
| 9 | Tongren (Guanxiu), Qinghai, China | 1 | Herders homemade | GX |
| 10 | Tongren (Duowa), Qinghai, China | 1 | Herders homemade | DW |
| 11 | Tongren (Guashenzi), Qinghai, China | 1 | Herders homemade | GZ |
| 12 | Tongren (Suonaihe), Qinghai, China | 1 | Herders homemade | SN |
| 13 | Tongren (Duofudun), Qinghai, China | 1 | Herders homemade | DFD |
| 14 | Linxia, Gansu, China | 4 | Farmer homemade | LX |
| 15 | Yuzhong, Gansu, China | 1 | Farmer homemade | YZ |
| 16 | Qin’an, Gansu Province, China | 10 | Farmer homemade | QA |
| 17 | Gangu, Gansu, China | 10 | Farmer homemade | GG |
| 18 | Buy different brands and sources of Jiangshui in Lanzhou vegetable market | 13 | commercial product | QX(A), QX(AY), WD(Y), WD(L), JF(J), MG(M), QY(QT), S(L), TS(Q), TS(W), TS, JS(A), MG(MY) |
| Name | Pre-Primer Sequence | Pre-Primer Sequence |
|---|---|---|
| Bacterium 16S rRNA (V3 + V4) | 5′-ACTCCTACGGGAGGCAGCA-3′ | 5′-GGACTACHVGGGTWTCTAAT-3′ |
| Fungus ITS1 region | 5′-CTTGGTCATTTAGAGGAAGTAA-3′ | 5′-GCTGCGTTCATCGATGC-3′ |
| Name | Source | Properties | Function | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lactobacillus plantarum LZU-J-TSL6 | Jiangshui | High yield of GABA | Regulating intestinal flora diversity. Produce glutamine. Repair intestinal mucosal barrier. Increase GABA content in the hippocampus. Repair the levels of BDNF and GFAP in hippocampus of mice. Reduce the damage of Nissl corpuscles in hippocampus. Alleviate anxiety symptoms in mice. | This study |
| Lactobacillus rhamnosus HN001 | / | / | Reduce the incidence of postpartum depression or anxiety | [60] |
| Lactobacillus helveticus NS8 | Natural fermented dairy | / | Improve cognitive dysfunction. Reduce the levels of plasma corticosterone and adrenocorticotropic hormone. Adjust the level of inflammatory factors. Restore the levels of 5-HT and norepinephrine in hippocampus. Increase the expression of BDNFmRNA in hippocampus. | [61] |
| Bifidobacterium adolescentis IM38 | Human faecal microbiota | / | Significantly increase the time for mice to enter the bilateral open arms. Decreased levels of blood corticosterone and IL-6 in mice with or without fixed stress. Reduce the level of TNF-α in blood of stressed mice. IM38 can alleviate anxiety by regulating benzodiazepine sites on GABA receptor and regulate the expression of stress-related cytokines. | [62] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, G.; Khan, I.; Li, Y.; Yang, Y.; Lu, X.; Wang, Y.; Li, J.; Zhang, C. Overcoming Anxiety Disorder by Probiotic Lactiplantibacillus plantarum LZU-J-TSL6 through Regulating Intestinal Homeostasis. Foods 2022, 11, 3596. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11223596
Liu G, Khan I, Li Y, Yang Y, Lu X, Wang Y, Li J, Zhang C. Overcoming Anxiety Disorder by Probiotic Lactiplantibacillus plantarum LZU-J-TSL6 through Regulating Intestinal Homeostasis. Foods. 2022; 11(22):3596. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11223596
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Guanlan, Israr Khan, Yuxi Li, Yun Yang, Xuerui Lu, Yafei Wang, Junxiang Li, and Chunjiang Zhang. 2022. "Overcoming Anxiety Disorder by Probiotic Lactiplantibacillus plantarum LZU-J-TSL6 through Regulating Intestinal Homeostasis" Foods 11, no. 22: 3596. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11223596
APA StyleLiu, G., Khan, I., Li, Y., Yang, Y., Lu, X., Wang, Y., Li, J., & Zhang, C. (2022). Overcoming Anxiety Disorder by Probiotic Lactiplantibacillus plantarum LZU-J-TSL6 through Regulating Intestinal Homeostasis. Foods, 11(22), 3596. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11223596







