Crosslinking Mechanism on a Novel Bacillus cereus Transglutaminase-Mediated Conjugation of Food Proteins
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Strains, Plasmids, Materials, and Growth Media
2.2. Strains Construction
2.3. Production and Purification of TGs
2.4. TGs Activity Assays
2.5. Characterization of TGs
2.6. Molecular Dynamics Simulations
2.7. Protein Substrates Crosslinked by BCETG
2.8. Analysis of Protein Substrate’s Crosslinked Amino Acid Sites by BCETG
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Molecular Cloning and Genes Sequence of bamtg, bcetg, bsatg, and bartg Genes
3.2. Heterologous Production and Purification of TGs
3.3. Biochemical Characterization of BAMTG, BCETG, BSATG, and BARTG
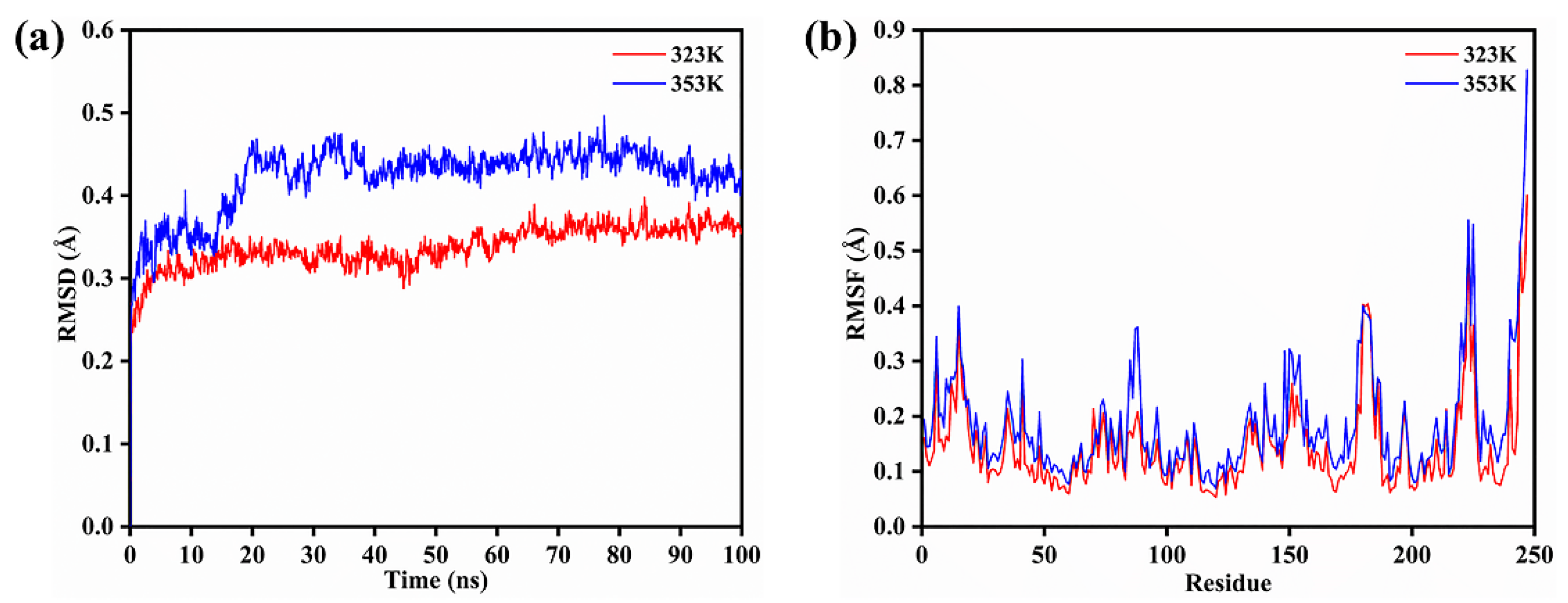
3.4. Molecular Dynamics Simulation
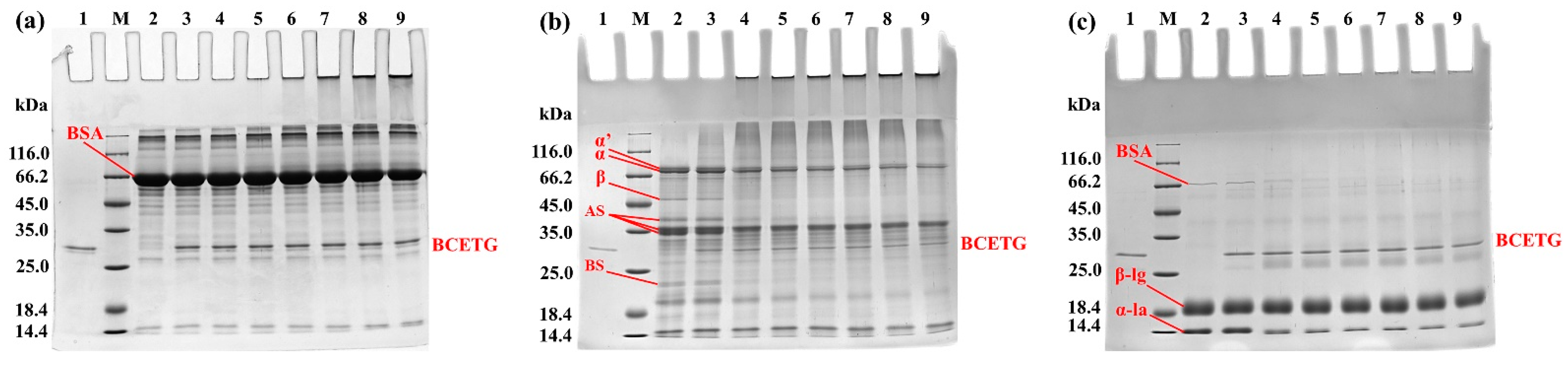
3.5. Electrophoresis Analysis of Protein Substrates Crosslinked by BCETG
3.6. Crosslinked Amino Acid Preference in Protein Substrates by BCETG Treatment
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Miwa, N. Innovation in the food industry using microbial transglutaminase: Keys to success and future prospects. Anal. Biochem. 2020, 597, 113638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feeney, R.E.; Yamasaki, R.B.; Geoghegan, K.F. Chemical Modification of Proteins: An Overview. Modif. Proteins 1982, 98, 3–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Heck, T.; Faccio, G.; Richter, M.; Thöny-Meyer, L. Enzyme-catalyzed protein crosslinking. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2013, 97, 461–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Deweid, L.; Avrutina, O.; Kolmar, H. Microbial transglutaminase for biotechnological and biomedical engineering. Biol. Chem. 2019, 400, 257–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Xu, Z.; Shan, M.; Ge, X.; Zhang, Y.; Shao, S.; Huang, L.; Wang, W.; Lu, F. Effects of Bacillus subtilis transglutaminase treatment on the functional properties of whey protein. LWT 2019, 116, 108559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostafa, H.S. Microbial transglutaminase: An overview of recent applications in food and packaging. Biocatal. Biotransform. 2020, 38, 161–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Huang, L.; Zheng, D.; Fu, Y.; Shan, M.; Li, Y.; Xu, Z.; Jia, L.; Wang, W.; Lu, F. Characterization of transglutaminase from Bacillus subtilis and its cross-linking function with a bovine serum albumin model. Food Funct. 2018, 9, 5560–5568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Wang, Y.; Yuan, Z.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Song, P.; Lu, F.; Liu, Y. Insight into the cross-linking preferences and characteristics of the transglutaminase from Bacillus subtilis by in vitro RNA display. LWT 2021, 151, 112152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Lin, S.; Zhang, X.; Liu, X.; Wang, J.; Lu, F. A novel approach for improving the yield of Bacillus subtilis transglutaminase in heterologous strains. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 41, 1227–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, G.M.; Huey, R.; Lindstrom, W.; Sanner, M.F.; Belew, R.K.; Goodsell, D.S.; Olson, A.J. AutoDock4 and AutoDockTools4: Automated docking with selective receptor flexibility. J. Comput. Chem. 2009, 30, 2785–2791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abraham, M.J.; Murtola, T.; Schulz, R.; Páll, S.; Smith, J.C.; Hess, B.; Lindahl, E. GROMACS: High performance molecular simulations through multi-level parallelism from laptops to supercomputers. SoftwareX 2015, 1–2, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Y.; Hu, X.; Sang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Lu, F.; Liu, F. An acid-stable β-glucosidase from Aspergillus aculeatus: Gene expression, biochemical characterization and molecular dynamics simulation. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 119, 462–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; Shang, J.; Li, Y.; Zhang, H.; Lu, F.; Liu, F. Biochemical characterization and molecular mechanism of acid denaturation of a novel α-amylase from Aspergillus niger. Biochem. Eng. J. 2018, 137, 222–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humphrey, W.; Dalke, A.; Schulten, K. VMD: Visual molecular dynamics. J. Mol. Graph. 1996, 14, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, Z.; Wang, C.; Kang, H.; Li, J.; Wang, W.; Li, Y.; Lu, F.; Liu, Y. Enhancing the functional characteristics of soy protein isolate via cross-linking catalyzed by Bacillus subtilis transglutaminase. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2021, 101, 4154–4160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandes, C.G.; Plácido, D.; Lousa, D.; Brito, J.A.; Isidro, A.; Soares, C.M.; Pohl, J.; Carrondo, M.A.; Archer, M.; Henriques, A.O. Structural and Functional Characterization of an Ancient Bacterial Transglutaminase Sheds Light on the Minimal Requirements for Protein Cross-Linking. Biochemistry 2015, 54, 5723–5734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agyare, K.K.; Damodaran, S. pH-Stability and Thermal Properties of Microbial Transglutaminase-Treated Whey Protein Isolate. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 1946–1953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Damodaran, S.; Agyare, K.K. Effect of microbial transglutaminase treatment on thermal stability and pH-solubility of heat-shocked whey protein isolate. Food Hydrocoll. 2013, 30, 12–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.D.; Arntfield, S.D. Gelation properties of salt-extracted pea protein isolate catalyzed by microbial transglutaminase cross-linking. Food Hydrocoll. 2011, 25, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truong, V.-D.; Clare, D.A.; Catignani, G.L.; Swaisgood, H.E. Cross-Linking and Rheological Changes of Whey Proteins Treated with Microbial Transglutaminase. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2004, 52, 1170–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
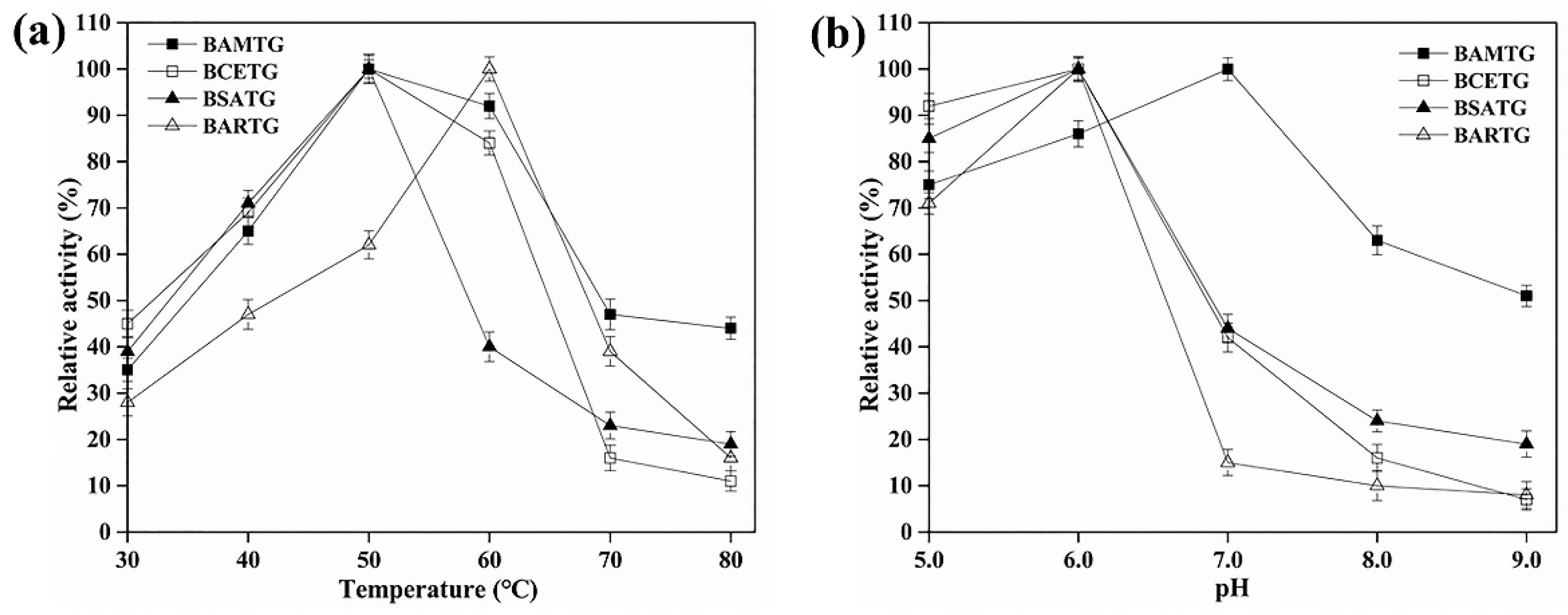
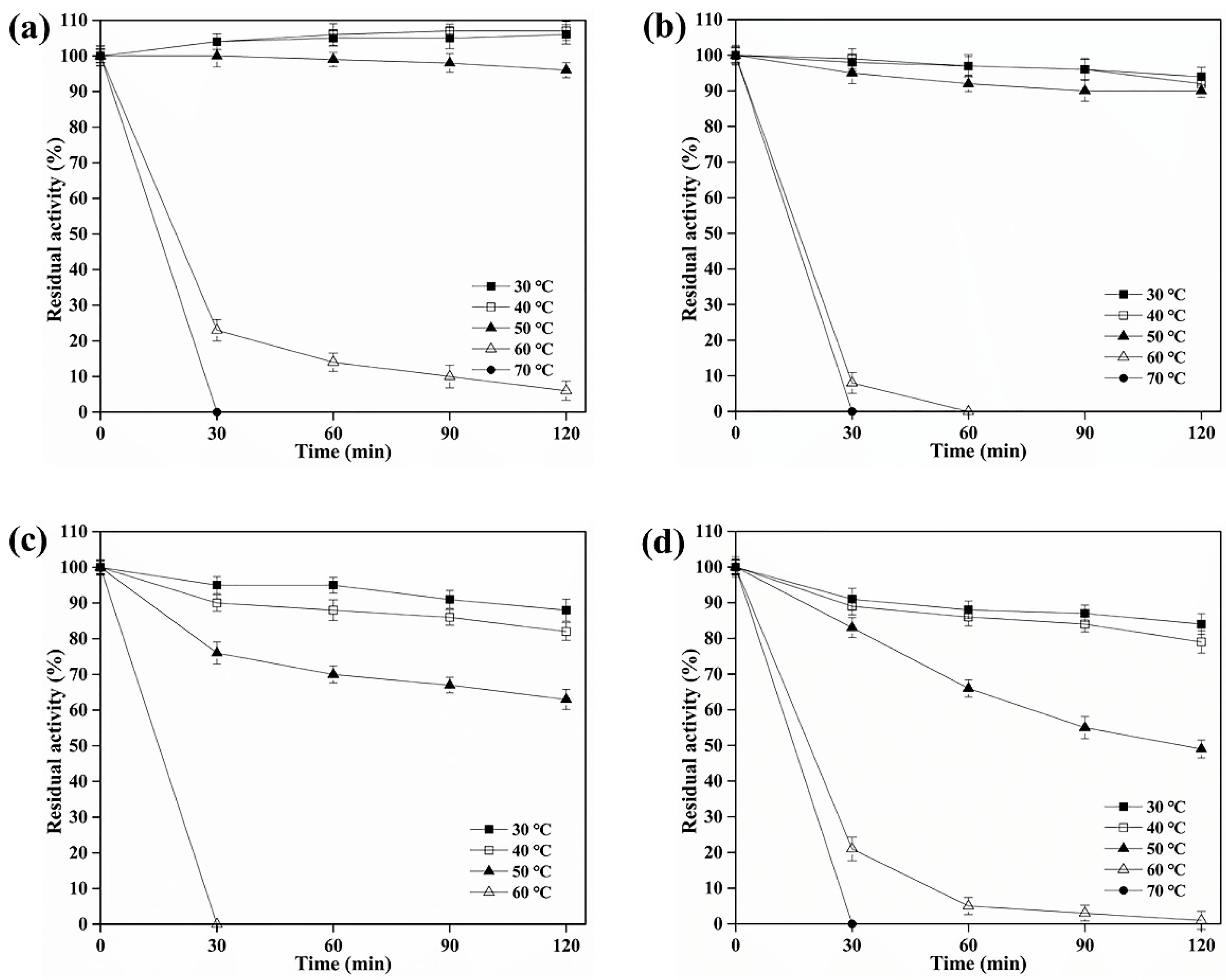



| Enzymes | Optimum Temperature | Optimum pH | Thermostability Range | pH Stability Range |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BAMTG | 50 °C | 7.0 | ≤50 °C | 5.0–9.0 |
| BCETG | 50 °C | 6.0 | ≤50 °C | 5.0–9.0 |
| BSATG | 50 °C | 6.0 | ≤50 °C | 5.0–9.0 |
| BARTG | 60 °C | 6.0 | ≤50 °C | 5.0–9.0 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Yuan, Z.; Zou, X.; Ji, Y.; Hou, J.; Zhang, J.; Lu, F.; Liu, Y. Crosslinking Mechanism on a Novel Bacillus cereus Transglutaminase-Mediated Conjugation of Food Proteins. Foods 2022, 11, 3722. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11223722
Wang H, Zhang Y, Yuan Z, Zou X, Ji Y, Hou J, Zhang J, Lu F, Liu Y. Crosslinking Mechanism on a Novel Bacillus cereus Transglutaminase-Mediated Conjugation of Food Proteins. Foods. 2022; 11(22):3722. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11223722
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Hongbin, Yuanfu Zhang, Zhaoting Yuan, Xiaotong Zou, Yuan Ji, Jiayi Hou, Jinfang Zhang, Fuping Lu, and Yihan Liu. 2022. "Crosslinking Mechanism on a Novel Bacillus cereus Transglutaminase-Mediated Conjugation of Food Proteins" Foods 11, no. 22: 3722. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11223722
APA StyleWang, H., Zhang, Y., Yuan, Z., Zou, X., Ji, Y., Hou, J., Zhang, J., Lu, F., & Liu, Y. (2022). Crosslinking Mechanism on a Novel Bacillus cereus Transglutaminase-Mediated Conjugation of Food Proteins. Foods, 11(22), 3722. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11223722







