Proteomic Profiling of Major Peanut Allergens and Their Post-Translational Modifications Affected by Roasting
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Peanut Thermal Treatment and Extract Preparation
2.2. 1D and 2D Electrophoresis
2.3. Sample Preparation for Nano Liquid Chromatography Coupled to Tandem Mass Spectrometry (nLC-MS/MS)
2.4. nLC-MS/MS
2.5. Identification and PTM Profiling of Major Peanut Allergens
2.6. Western Blot Analysis with Antibodies Specific to Modified AAs
2.7. IgE Binding in ELISA
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
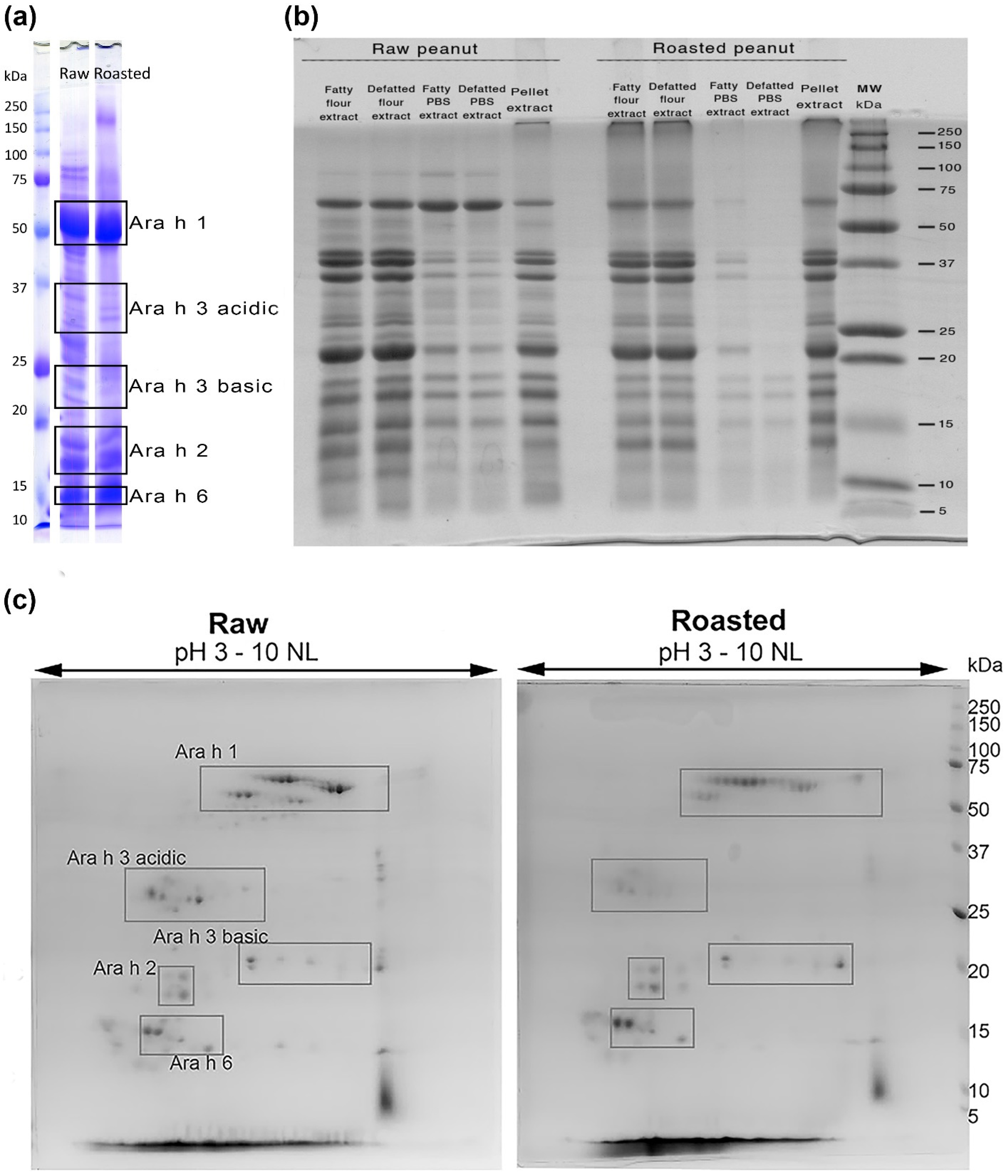
3.1. Protein Electrophoretic and Mass Spectrometry Qualitative Comparison of Allergen Profiles in Raw and Roasted Peanut Samples
3.2. PTM Patterns of Raw and Roasted Allergen Peanut Samples
3.3. 1D Western Blot with Anti-PTM Antibodies in Relation to Mass Spectrometry Relative to PTM-Profiling
3.4. Effects of Thermal Processing on IgE Binding to Raw and Roasted PEs
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ramazi, S.; Zahiri, J. Post-translational modifications in proteins: Resources, tools and prediction methods. Database J. 2021, 2021, baab012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khoury, G.; Baliban, R.; Floudas, C. Proteome-wide post-translational modification statistics: Frequency analysis and curation of the swiss-prot database. Sci. Rep. 2011, 1, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kong, A.; Leprevost, F.; Avtonomov, D.; Mellacheruvu, D.; Nesvizhskii, A. MSFragger: Ultrafast and comprehensive peptide identification in mass spectrometry-based proteomics. Nat. Methods 2017, 14, 513–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Smiljanić, K.; Prodić, I.; Apostolović, D.; Cvetković, A.; Veljović, D.; Mutić, J.; van Hage, M.; Burazer, L.; Veličković, T.C. In-depth quantitative profiling of post-translational modifications of Timothy grass pollen allergome in relation to environmental oxidative stress. Environ. Int. 2019, 126, 644–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smiljanić, K.; Mihailović, J.; Prodić, I.; Đukić, T.; Vasović, T.; Jovanović, V.; Veličković, T.C. Trypsin as a Proteomic Probe for Assessment of Food Protein Digestibility in Relation to Chemical and Post-Translational Modifications. In A Closer Look at Proteolysis, 1st ed.; Radosavljevic, J., Ed.; Nova Science Publishers, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2020; pp. 157–184. [Google Scholar]
- Kolarich, D.; Altmann, F. N-Glycan analysis by matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry of electrophoretically separated nonmammalian proteins: Application to peanut allergen Ara h 1 and olive pollen allergen Ole e 1. Anal. Biochem. 2000, 285, 64–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palladino, C.; Breiteneder, H. Peanut allergens. Mol. Immunol. 2018, 100, 58–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Shefcheck, K.; Callahan, J.; Fenselau, C. Primary sequence and site-selective hydroxylation of prolines in isoforms of a major peanut allergen protein Ara h 2. Protein Sci. 2010, 19, 174–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bernard, H.; Guillon, B.; Drumare, M.-F.; Paty, E.; Dreskin, S.C.; Wal, J.-M.; Adel-Patient, K.; Hazebrouck, S. Allergenicity of peanut component Ara h 2: Contribution of conformational versus linear hydroxyproline-containing epitopes. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2015, 135, 1267–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maleki, S.J.; Chung, S.-Y.; Champagne, E.T.; Raufman, J.-P. The effects of roasting on the allergenic properties of peanut proteins. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2000, 106, 763–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mueller, G.A.; Maleki, S.J.; Johnson, K.; Hurlburt, B.K.; Cheng, H.; Ruan, S.; Nesbit, J.B.; Pomés, A.; Edwards, L.L.; Schorzman, A.; et al. Identification of Maillard reaction products on peanut allergens that influence binding to the receptor for advanced glycation end products. Allergy 2013, 68, 1546–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, S.-Y.; Champagne, E.T. Association of End-Product Adducts with Increased IgE Binding of Roasted Peanuts. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2001, 49, 3911–3916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kollipara, L.; Zahedi, R.P. Protein carbamylation: In vivo modification or in vitro artefact? Proteomics 2013, 13, 941–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smiljanić, K.; Apostolović, D.; Trifunović, S.; Ognjenović, J.; Perusko, M.; Mihajlović, L.; Burazer, L.; van Hage, M.; Veličković, T.C. Subpollen particles are rich carriers of major short ragweed allergens and NADH dehydrogenases: Quantitative proteomic and allergomic study. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2017, 47, 815–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shevchenko, A.; Tomas, H.; Havlis, J.; Olsen, J.V.; Mann, M. In-gel digestion for mass spectrometric characterization of proteins and proteomes. Nat. Protoc. 2006, 1, 2856–2860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prodić, I.; Smiljanić, K.; Simović, A.; Radosavljević, J.; Veličković, T.C. Thermal Processing of Peanut Grains Impairs Their Mimicked Gastrointestinal Digestion While Downstream Defatting Treatments Affect Digestomic Profiles. Foods 2019, 8, 463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Perez-Riverol, Y.; Csordas, A.; Bai, J.; Bernal-Llinares, M.; Hewapathirana, S.; Kundu, D.J.; Inuganti, A.; Griss, J.; Mayer, G.; Eisenacher, M.; et al. The PRIDE database and related tools and resources in 2019: Improving support for quantification data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D442–D450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radosavljević, J.; Dobrijević, D.; Jadranin, M.; Blanusa, M.; Vukmirica, J.; Veličković, T.C. Insights into proteolytic processing of the major peanut allergen Ara h 2 by endogenous peanut proteases. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2010, 90, 1702–1708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitt, D.; Nesbit, J.; Hurlburt, B.; Cheng, H.; Maleki, S. Processing Can Alter the Properties of Peanut Extract Preparations. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 1138–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, T.-J.; Maks, N. Impact of Thermal Processing on ELISA Detection of Peanut Allergens. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 5649–5658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prodić, I.; Stanić-Vučinić, D.; Apostolović, D.; Mihailović, J.; Radibratović, M.; Radosavljević, J.; Burazer, L.; Milčić, M.; Smiljanić, K.; van Hage, M.; et al. Influence of peanut matrix on stability of allergens in gastric-simulated digesta: 2S albumins are main contributors to the IgE reactivity of short digestion-resistant peptides. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2018, 48, 731–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Raina, S.N.; Sharma, M.; Chaudhary, M.; Sharma, S.; Rajpal, V.R. Functional Uses of Peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.) Seed Storage Proteins. In Grain and Seed Proteins Functionality; Jimenez-Lopez, J.C., Ed.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kottapalli, K.R.; Payton, P.; Rakwal, R.; Agrawal, G.K.; Shibato, J.; Burow, M.; Puppala, N. Proteomics analysis of mature seed of four peanut cultivars using two-dimensional gel electrophoresis reveals distinct differential expression of storage, anti-nutritional, and allergenic proteins. Plant Sci. 2008, 175, 321–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, E.P.; Sayers, R.L.; Gethings, L.A.; Balasundaram, A.; Marsh, J.T.; Langridge, J.I.; Mills, E.N.C. Quantitative Proteomic Profiling of Peanut Allergens in Food Ingredients Used for Oral Food Challenges. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 5689–5695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mishra, A.; Jain, A.; Arora, N. Mapping B-cell epitopes of major and minor peanut allergens and identifying residues contributing to IgE binding. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2016, 96, 539–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hellwig, M. The Chemistry of Protein Oxidation in Food. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 16742–16763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nepomuceno, A.I.; Gibson, R.J.; Randall, S.M.; Muddiman, D.C. Accurate Identification of Deamidated Peptides in Global Proteomics Using a Quadrupole Orbitrap Mass Spectrometer. J. Proteome Res. 2014, 13, 777–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ehrenshaft, M.; Deterding, L.J.; Mason, R.P. Tripping up Trp: Modification of protein tryptophan residues by reactive oxygen species, modes of detection, and biological consequences. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2014, 89, 220–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Greifenhagen, U.; Frolov, A.; Blüher, M.; Hoffmann, R. Site-specific analysis of advanced glycation end products in plasma proteins of type 2 diabetes mellitus patients. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2016, 408, 5557–5566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramsøe, A.; Crispin, M.; Mackie, M.; McGrath, K.; Fischer, R.; Demarchi, B.; Collins, M.J.; Hendy, J.; Speller, C. Assessing the degradation of ancient milk proteins through site-specific deamidation patterns. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 7795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walworth, N.C. Cell-cycle checkpoint kinases: Checking in on the cell cycle. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2000, 12, 697–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmström, K.M.; Finkel, T. Cellular mechanisms and physiological consequences of redox-dependent signalling. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2014, 15, 411–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Todd, C.D.; Tipton, P.A.; Blevins, D.G.; Piedras, P.; Pineda, M.; Polacco, J.C. Update on ureide degradation in legumes. J. Exp. Bot. 2006, 57, 5–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delanghe, S.; Delanghe, J.R.; Speeckaert, R.; van Biesen, W.; Speeckaert, M.M. Mechanisms and consequences of carbamoylation. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2017, 13, 580–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Werner, A.K.; Romeis, T.; Witte, C.-P. Ureide Catabolism in Arabidopsis thaliana and Escherichia Coli. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2010, 6, 19–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, X.; Zhang, L.; Natarajan, S.K.; Becker, D.F. Proline mechanisms of stress survival. Antioxid. Redox Signal 2013, 19, 998–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Berlett, B.S.; Stadtman, E.R. Protein oxidation in aging, disease, and oxidative stress. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 20313–20316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Minekus, M.; Alminger, M.; Alvito, P.; Balance, S.; Bohn, T.; Bourlieu, C.; Carrière, F.; Boutrou, R.; Corredig, M.; Dupont, D.; et al. Standardised static in vitro digestion method suitable for food—An international consensus. Food Funct. 2014, 5, 1113–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Di Stasio, L.; Tranquet, O.; Picariello, G.; Ferranti, P.; Morisset, M.; Denery-Papini, S.; Mamone, G. Comparative analysis of eliciting capacity of raw and roasted peanuts: The role of gastrointestinal digestion. Food Res. Int. 2020, 127, 108758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Modification | Δ Mass (Da) | Ara h 1 | Ara h 3 | Ara h 2 | Ara h 6 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Raw | Roasted | Raw | Roasted | Raw | Roasted | Raw | Roasted | ||
| Acetylation (K) | 42.0106 | K222 a | / | / | / | / | / | / | / |
| Amidation (K) | −0.9840 | K222 a | / | / | / | / | / | / | / |
| Carbamoylation | 43.0058 | H223 a | / | / | / | / | / | / | / |
| K542 a | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | ||
| K457 * | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | ||
| Carboxylation (D) | 43.9898 | / | / | / | / | / | / | D81 | / |
| Deamidation (NQ) | 0.984 | N216 a | / | / | N57 d | / | / | / | / |
| / | N270 a | / | / | / | / | / | / | ||
| Q303 a | / | / | Q61 d | / | / | / | / | ||
| N313 a | / | / | N496 d | / | / | / | / | ||
| N324 a | / | / | N503 d | / | / | / | / | ||
| / | N334 a | N381 e | / | / | / | / | / | ||
| / | N388 a | N383 f | / | / | / | / | / | ||
| / | N415 a | / | / | / | / | / | / | ||
| / | Q417 a | / | / | / | / | / | / | ||
| / | Q552 a | / | / | / | / | / | / | ||
| / | Q150 c | / | / | / | / | / | / | ||
| Dehydration (QT) | −18.0106 | Q234 a | / | / | / | / | / | / | / |
| T223 * | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | ||
| Q240 * | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | ||
| Dihydroxy (W) | 31.9898 | / | / | / | W388 d | / | / | / | / |
| / | / | / | W395 g | / | / | / | / | ||
| Dimethylation (R) | 28.0313 | R214 a | / | / | / | / | / | / | / |
| Formylation (KR) | 27.9949 | / | K248 a | / | / | / | / | / | / |
| / | R259 a | / | / | / | / | / | / | ||
| Hydroxylation (P) | 15.9949 | P221 a | / | / | / | / | / | / | / |
| / | P559 a | / | / | / | / | / | / | ||
| / | P161 * | / | / | / | / | / | / | ||
| / | P564 * | / | / | / | / | / | / | ||
| Methylation (R) | 14.0157 | / | R342 a | R196 h | / | / | / | / | / |
| / | R345 * | R195 d | / | / | / | / | / | ||
| Oxidation (MHW) | 15.9949 | / | W152 a | / | W388 d | / | / | / | M56 |
| / | H206 a | / | W396 h | / | / | / | / | ||
| H223 a | / | / | / | / | M125 j | / | / | ||
| / | H256 a | M167 h | / | / | / | M113 | / | ||
| / | W476 a | / | / | / | / | / | / | ||
| / | W158 * | / | / | / | / | / | / | ||
| / | H369 * | / | / | / | / | / | / | ||
| / | W481 * | / | / | / | / | / | / | ||
| / | M431 b | / | / | / | / | / | / | ||
| / | M432 b | / | / | / | / | / | / | ||
| / | M444 b | / | / | / | / | / | / | ||
| / | M290 b | / | / | / | / | / | / | ||
| / | M284 a | / | / | / | / | / | / | ||
| Oxidation or Hydroxylation (N) | 15.9949 | / | N251 a | / | / | / | / | / | / |
| Pyro-glu from E | −18.0106 | / | E432 a | / | / | / | / | / | E120 |
| / | E437 * | / | / | / | / | / | / | ||
| Pyro-glu from Q | −17.0265 | / | Q552 a | / | Q25 d | / | / | / | / |
| / | Q557 * | / | / | / | / | / | / | ||
| Replacement of 2 protons by iron (E) | 59.9193 | E563 a | / | / | E380 d | / | / | / | / |
| E568 * | / | / | E387 g | / | / | / | / | ||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Đukić, T.; Smiljanić, K.; Mihailović, J.; Prodić, I.; Apostolović, D.; Liu, S.-H.; Epstein, M.M.; van Hage, M.; Stanić-Vučinić, D.; Ćirković Veličković, T. Proteomic Profiling of Major Peanut Allergens and Their Post-Translational Modifications Affected by Roasting. Foods 2022, 11, 3993. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11243993
Đukić T, Smiljanić K, Mihailović J, Prodić I, Apostolović D, Liu S-H, Epstein MM, van Hage M, Stanić-Vučinić D, Ćirković Veličković T. Proteomic Profiling of Major Peanut Allergens and Their Post-Translational Modifications Affected by Roasting. Foods. 2022; 11(24):3993. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11243993
Chicago/Turabian StyleĐukić, Teodora, Katarina Smiljanić, Jelena Mihailović, Ivana Prodić, Danijela Apostolović, Shu-Hua Liu, Michelle M. Epstein, Marianne van Hage, Dragana Stanić-Vučinić, and Tanja Ćirković Veličković. 2022. "Proteomic Profiling of Major Peanut Allergens and Their Post-Translational Modifications Affected by Roasting" Foods 11, no. 24: 3993. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11243993
APA StyleĐukić, T., Smiljanić, K., Mihailović, J., Prodić, I., Apostolović, D., Liu, S.-H., Epstein, M. M., van Hage, M., Stanić-Vučinić, D., & Ćirković Veličković, T. (2022). Proteomic Profiling of Major Peanut Allergens and Their Post-Translational Modifications Affected by Roasting. Foods, 11(24), 3993. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11243993







