First Report of Potentially Pathogenic Klebsiella pneumoniae from Serotype K2 in Mollusk Tegillarca granosa and Genetic Diversity of Klebsiella pneumoniae in 14 Species of Edible Aquatic Animals
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection
2.2. Isolation and Identification of K. pneumoniae
2.3. Identification of Virulence Genes
2.4. Enterobacterial Repetitive Intergenic Consensus-PCR (ERIC-PCR) Assay
2.5. Antibiotic Susceptibility and Heavy Metal–Tolerance Assays
2.6. Serotyping of K. pneumoniae Strains
2.7. Genome Sequencing, Assembling and Annotation
2.8. Multilocus Sequence Typing (MLST) Analysis
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. K. pneumoniae in the 41 Species of Aquatic Animals
3.2. Virulence-Related Genes in the K. pneumoniae Strains by PCR Assay
3.3. Antimicrobial-Resistance Profiles of the K. pneumoniae Strains
3.4. MDR Phenotypes of the K. pneumoniae Strains
3.5. Heavy Metal–Tolerance Profiles of the K. pneumoniae Strains
3.6. Genetic Diversity of the K. pneumoniae Strains
3.7. Heavy Metal Tolerance and MDR of the K. pneumoniae Strains
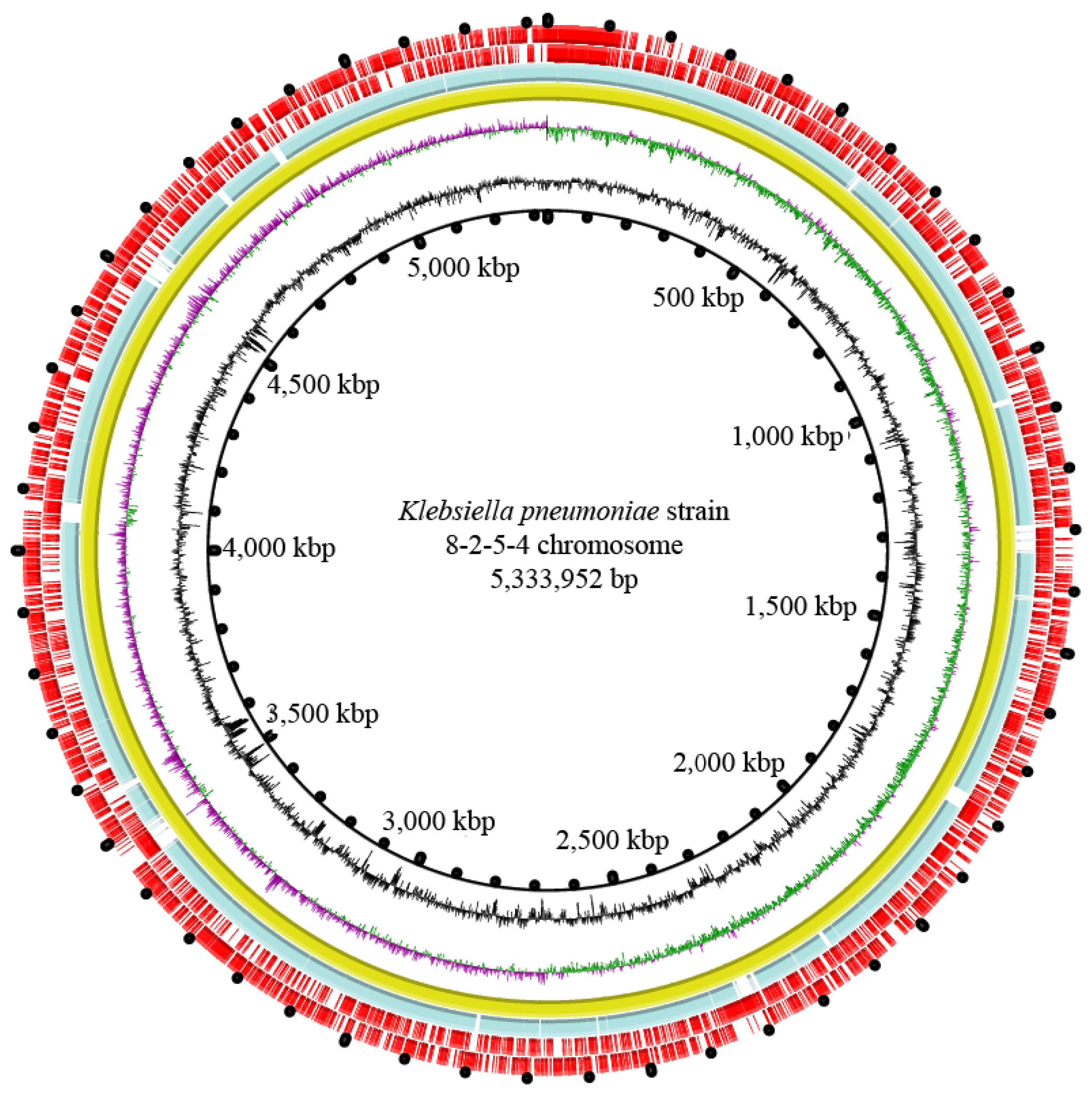
3.8. Genome Features of the K. pneumoniae 8-2-5-4 Isolate from Serotype K2
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Podschun, R.; Ullmann, U. Klebsiella spp. as nosocomial pathogens: Epidemiology, taxonomy, typing methods, and pathogenicity factors. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 1998, 11, 589–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Holt, K.E.; Wertheim, H.; Zadoks, R.N.; Baker, S.; Whitehouse, C.A.; Dance, D.; Jenney, A.; Connor, T.R.; Hsu, L.Y.; Severin, J.; et al. Genomic analysis of diversity, population structure, virulence, and antimicrobial resistance in Klebsiella pneumoniae, an urgent threat to public health. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, E3574–E3581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Girometti, N.; Lewis, R.E.; Giannella, M.; Ambretti, S.; Bartoletti, M.; Tedeschi, S.; Tumietto, F.; Cristini, F.; Trapani, F.; Gaibani, P.; et al. Klebsiella pneumoniae bloodstream infection: Epidemiology and impact of inappropriate empirical therapy. Medicine 2014, 93, 298–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paczosa, M.K.; Mecsas, J. Klebsiella pneumoniae: Going on the offense with a strong defense. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2016, 80, 629–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Friedlaender, C. Ueber die Schizomyceten bei der acuten fibrösen Pneumonie. Archiv. Pathol. Anat. 1882, 87, 319–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Zhao, G.; Chao, X.; Xie, L.; Wang, H. The characteristic of virulence, biofilm and antibiotic resistance of Klebsiella pneumoniae. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 6278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, C.; Chen, Z.; Zhou, D. Molecular pathogenesis of Klebsiella pneumoniae. Future Microbiol. 2014, 9, 1071–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, P.; Jiang, Y.; Zhou, J.; Yu, Y. A global perspective on the convergence of hypervirulence and carbapenem resistance in Klebsiella pneumoniae. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2021, 25, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turton, J.F.; Perry, C.; Elgohari, S.; Hampton, C.V. PCR characterization and typing of Klebsiella pneumoniae using capsular type-specific, variable number tandem repeat and virulence gene targets. J. Med. Microbiol. 2010, 59, 541–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Turton, J.F.; Englender, H.; Gabriel, S.N.; Turton, S.E.; Kaufmann, M.E.; Pitt, T.L. Genetically similar isolates of Klebsiella pneumoniae serotype K1 causing liver abscesses in three continents. J. Med. Microbiol. 2007, 56, 593–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aris, P.; Robatjazi, S.; Nikkhahi, F.; Amin Marashi, S.M. Molecular mechanisms and prevalence of colistin resistance of Klebsiella pneumoniae in the middle east region: A review over the last 5 years. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2020, 22, 625–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wasfi, R.; Elkhatib, W.F.; Ashour, H.M. Molecular typing and virulence analysis of multidrug resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae clinical isolates recovered from Egyptian hospitals. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 38929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ye, M.; Tu, J.; Jiang, J.; Bi, Y.; You, W.; Zhang, Y.; Ren, J.; Zhu, T.; Cao, Z.; Yu, Z.; et al. Clinical and genomic analysis of liver abscess-causing Klebsiella pne umoniae identifies new liver abscess-associated virulence genes. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2016, 6, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fu, L.; Huang, M.; Zhang, X.; Yang, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, G.; Zhou, Y. Frequency of virulence factors in high biofilm formation bla (KPC-2) producing Klebsiella pneumoniae strains from hospitals. Microb. Pathog. 2018, 116, 168–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, W.L.; Ko, W.C.; Cheng, K.C.; Lee, C.C.; Lai, C.C.; Chuang, Y.C. Comparison of prevalence of virulence factors for Klebsiella pneumoniae liver abscesses between isolates with capsular K1/K2 and non-K1/K2 serotypes. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2008, 62, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control (ECDC). Antimicrobial Consumption in the EU/EEA (ESAC-Net)—Annual Epidemiological Report 2021; European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control (ECDC): Stockholm, Sweden, 2022.
- Liao, W.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, W. Virulence evolution, molecular mechanisms of resistance and prevalence of ST11 carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae in China: A review over the last 10 years. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2020, 23, 174–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Deng, W.; Liu, S.; Yu, X.; Mustafa, G.R.; Chen, S.; He, L.; Ao, X.; Yang, Y.; Zhou, K.; et al. Presence of heavy metal resistance genes in Escherichia coli and Salmonella isolates and analysis of resistance gene structure in E. coli E308. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2020, 21, 420–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, J.; Davies, D. Origins and evolution of antibiotic resistance. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2010, 74, 417–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tong, S.; Bambrick, H.; Beggs, P.J.; Chen, L.; Hu, Y.; Ma, W.; Steffen, W.; Tan, J. Current and future threats to human health in the Anthropocene. Environ. Int. 2022, 158, 106892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wuana, R.A.; Okieimen, F.E. Heavy metals in contaminated soils: A review of sources, chemistry, risks and best available strategies for remediation. ISRN Ecol. 2011, 2011, 402647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, L.; Chen, D.; Fu, H.; Xie, Q.; Lu, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, L. Residual levels of antimicrobial agents and heavy metals in 41 species of commonly consumed aquatic products in Shanghai, China, and cumulative exposure risk to children and teenagers. Food Control 2021, 129, 108225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seiler, C.; Berendonk, T.U. Heavy metal driven co-selection of antibiotic resistance in soil and water bodies impacted by agriculture and aquaculture. Front. Microbiol. 2012, 3, 399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Conceição-Neto, O.C.; da Costa, B.S.; Pontes, L.D.S.; Silveira, M.C.; Justo-da-Silva, L.H.; de Oliveira Santos, I.C.; Teixeira, C.B.T.; Tavares, E.O.T.R.; Hermes, F.S.; Galvão, T.C.; et al. Polymyxin resistance in clinical isolates of K. pneumoniae in Brazil: Update on molecular mechanisms, clonal dissemination and relationship with KPC-producing strains. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 898125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Hooste, W.; Vanrentergem, M.; Nulens, E.; Snauwaert, C.; De Geyter, D.; Mertens, R.; Van Praet, J.T. Infections caused by hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae in non-endemic countries: Three case reports and review of the literature. Acta Clin. Belg. 2022, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manges, A.R. Editorial commentary: Genomic epidemiology: Revealing hidden reservoirs for Klebsiella pneumoniae. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2015, 61, 900–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Håkonsholm, F.; Hetland, M.A.K.; Svanevik, C.S.; Sundsfjord, A.; Lunestad, B.T.; Marathe, N.P. Antibiotic sensitivity screening of Klebsiella spp. and Raoultella spp. isolated from marine bivalve molluscs reveal presence of CTX-M-producing K. pneumoniae. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, B.M.; Levy, S.B. Food animals and antimicrobials: Impacts on human health. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2011, 24, 718–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Iyer, R.; Moussa, S.H.; Tommasi, R.; Miller, A.A. Role of the Klebsiella pneumoniae TolC porin in antibiotic efflux. Res. Microbiol. 2019, 170, 112–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rupp, M.E.; Fey, P.D. Extended spectrum beta-lactamase (ESBL)-producing enterobacteriaceae: Considerations for diagnosis, prevention and drug treatment. Drugs 2003, 63, 353–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartantyo, S.H.P.; Chau, M.L.; Koh, T.H.; Yap, M.; Yi, T.; Cao, D.Y.H.; GutiÉrrez, R.A.; Ng, L.C. Foodborne Klebsiella pneumoniae: Virulence potential, antibiotic resistance, and risks to food safety. J. Food Prot. 2020, 83, 1096–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joslyn, L.J. Sterilization by Heat. In Disinfection, Sterilization, and Preservation, 5th ed.; Block, S.S., Ed.; Lippincott Williams & Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2000; pp. 695–728. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, D.; Li, X.; Ni, L.; Xu, D.; Xu, Y.; Ding, Y.; Xie, L.; Chen, L. First experimental evidence for the presence of potentially toxic Vibrio cholerae in snails, and virulence, cross-resistance and genetic diversity of the bacterium in 36 species of aquatic food animals. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, L.; Xu, Y.; Chen, L. First experimental evidence for the presence of potentially virulent Klebsiella oxytoca in 14 species of commonly consumed aquatic animals, and phenotyping and genotyping of K. oxytoca Isolates. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Plowman, J.E.; Tian, B.; Clerens, S.; On, S.L.W. An improved method for MALDI-TOF analysis of wine-associated yeasts. J. Microbiol. Methods 2020, 172, 105904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caneiras, C.; Lito, L.; Melo-Cristino, J.; Duarte, A. Community- and hospital-acquired Klebsiella pneumoniae urinary tract infections in portugal: Virulence and antibiotic resistance. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- El Fertas-Aissani, R.; Messai, Y.; Alouache, S.; Bakour, R. Virulence profiles and antibiotic susceptibility patterns of Klebsiella pneumoniae strains isolated from different clinical specimens. Pathol. Biol. 2013, 61, 209–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamlouk, K.; Boutiba-Ben Boubaker, I.; Gautier, V.; Vimont, S.; Picard, B.; Ben Redjeb, S.; Arlet, G. Emergence and outbreaks of CTX-M beta-lactamase-producing Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae strains in a Tunisian hospital. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2006, 44, 4049–4056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Turton, J.F.; Baklan, H.; Siu, L.K.; Kaufmann, M.E.; Pitt, T.L. Evaluation of a multiplex PCR for detection of serotypes K1, K2 and K5 in Klebsiella sp. and comparison of isolates within these serotypes. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2008, 284, 247–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Candan, E.D.; Aksöz, N. Klebsiella pneumoniae: Characteristics of carbapenem resistance and virulence factors. Acta Biochim. Pol. 2015, 62, 867–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Yang, G.; Ye, Q.; Wu, Q.; Zhang, J.; Huang, Y. Phenotypic and genotypic characterization of Klebsiella pneumoniae isolated from retail foods in China. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Wu, J.; Chen, L. Virulence, antimicrobial and heavy metal tolerance, and genetic diversity of Vibrio cholerae recovered from commonly consumed freshwater fish. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 27338–27352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meacham, K.J.; Zhang, L.; Foxman, B.; Bauer, R.J.; Marrs, C.F. Evaluation of genotyping large numbers of Escherichia coli isolates by enterobacterial repetitive intergenic consensus-PCR. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2003, 41, 5224–5226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sheng, Z.; Li, J.; Chen, T.; Zhu, Y.; Yu, X.; He, X.; Zheng, Y.; Ma, C.; Zheng, M.; Wang, P.; et al. Clinical and microbiological characteristics of Klebsiella pneumoniae bloodstream infection in a Chinese hospital: Hypervirulent and multiclonal. Infect. Drug Resist. 2022, 15, 3981–3990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, R.; Liu, B.; Xie, Y.; Li, Z.; Huang, W.; Yuan, J.; He, G.; Chen, Y.; Pan, Q.; Liu, Y.; et al. Erratum: SOAPdenovo2: An empirically improved memory-efficient short-read de novo assembler. Gigascience 2015, 4, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Delcher, A.L.; Bratke, K.A.; Powers, E.C.; Salzberg, S.L. Identifying bacterial genes and endosymbiont DNA with Glimmer. Bioinformatics 2007, 23, 673–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chan, P.P.; Lowe, T.M. tRNAscan-SE: Searching for tRNA genes in genomic sequences. In Gene Prediction; Humana: New York, NY, USA, 2019; Volume 1962, pp. 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, D.; Peng, X.; Xie, L.; Chen, L. Survival and genome diversity of Vibrio parahaemolyticus isolated from edible aquatic animals. Diversity 2022, 14, 350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcock, B.P.; Raphenya, A.R.; Lau, T.T.Y.; Tsang, K.K.; Bouchard, M.; Edalatmand, A.; Huynh, W.; Nguyen, A.V.; Cheng, A.A.; Liu, S.; et al. CARD 2020: Antibiotic resistome surveillance with the comprehensive antibiotic resistance database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, D517–D525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera, I.G.; Chowdhury, M.A.; Huq, A.; Jacobs, D.; Martins, M.T.; Colwell, R.R. Enterobacterial repetitive intergenic consensus sequences and the PCR to generate fingerprints of genomic DNAs from Vibrio cholerae O1, O139, and non-O1 strains. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1995, 61, 2898–2904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, D.; Xiao, L.; Hong, D.; Zhao, Y.; Hu, X.; Shi, S.; Chen, F. Epidemiology of resistance of carbapenemase-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae to ceftazidime-avibactam in a Chinese hospital. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2022, 132, 237–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magill, S.S.; Edwards, J.R.; Bamberg, W.; Beldavs, Z.G.; Dumyati, G.; Kainer, M.A.; Lynfield, R.; Maloney, M.; McAllister-Hollod, L.; Nadle, J.; et al. Emerging Infections Program Healthcare-Associated Infections and Antimicrobial Use Prevalence Survey Team. Multistate point-prevalence survey of health care-associated infections. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 370, 1198–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barati, A.; Ghaderpour, A.; Chew, L.L.; Bong, C.W.; Thong, K.L.; Chong, V.C.; Chai, L.C. Isolation and characterization of aquatic-borne Klebsiella pneumoniae from tropical estuaries in Malaysia. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2016, 13, 426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Effendi, M.H.; Bintari, I.G.; Aksono, E.B.; Hermawan, I.P. Detection of blaTEM gene of Klebsiella pneumoniae isolated from swab of food-producing animals in East Java. Trop. Anim. Sci. J. 2018, 41, 174–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bobbadi, S. Occurrence and genetic diversity of ESBL producing Klebsiella species isolated from livestock and livestock products. J. Food Saf. 2020, 40, e12738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brüssow, H. Growth promotion and gut microbiota: Insights from antibiotic use. Environ. Microbiol. 2015, 17, 2216–2227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durkin, M.J.; Feng, Q.; Warren, K.; Lockhart, P.B.; Thornhill, M.H.; Munshi, K.D.; Henderson, R.R.; Hsueh, K.; Fraser, V.J. Assessment of inappropriate antibiotic prescribing among a large cohort of general dentists in the United States. J. Am. Dent. Assoc. 2018, 149, 372–381.e371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabbani, M.A.G.; Howlader, M.Z.H.; Kabir, Y. Detection of multidrug resistant (MDR) bacteria in untreated waste water disposals of hospitals in Dhaka City, Bangladesh. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2017, 10, 120–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navon-Venezia, S.; Kondratyeva, K.; Carattoli, A. Klebsiella pneumoniae: A major worldwide source and shuttle for antibiotic resistance. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2017, 41, 252–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Zhang, X.; Wu, Q.; Zheng, X.; Dong, G.; Fang, R.; Zhang, Y.; Cao, J.; Zhou, T. Clinical, microbiological, and molecular epidemiological characteristics of Klebsiella pneumoniae-induced pyogenic liver abscess in southeastern China. Antimicrob. Resist. Infect. Control 2019, 8, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatima, S.; Liaqat, F.; Akbar, A.; Sahfee, M.; Samad, A.; Anwar, M.; Iqbal, S.; Khan, S.A.; Sadia, H.; Makai, G.; et al. Virulent and multidrug-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae from clinical samples in Balochistan. Int. Wound J. 2021, 18, 510–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voigt, A.; Felder, C.; Skutlarek, D.; Färber, H.; Schreiber, C.; Timm, C.; Exner, M. Liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry as a fast and simple method for the determination of several antibiotics in different aqueous matrices. Environ. Chem. 2019, 17, 54–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briffa, J.; Sinagra, E.; Blundell, R. Heavy metal pollution in the environment and their toxicological effects on humans. Heliyon 2020, 6, e04691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, M.; Wang, E.; Xia, P.; Feng, A.; Chi, Y.; Sun, Y. Distribution and pollution assessment of heavy metals in the intertidal zone environments of typical sea areas in China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 138, 397–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sudha Rani, K.; Srinivas, B.; GouruNaidu, K.; Ramesh, K.V. Removal of copper by adsorption on treated laterite. Mater. Today Proc. 2018, 5, 463–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez, C.C.; Bravo Gómez, M.E.; Hernández Zavala, A. Hexavalent chromium: Regulation and health effects. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2021, 65, 126729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waluyo, L.; Prihanta, W.; Bachtiar, Z.; Permana, T.I. Potential bioremediation of lead (Pb) using marine microalgae Nannochloropsis oculata. In Proceedings of the AIP Conference Proceedings, Malang, Indonesia, 26 August 2020; Volume 2231, p. 040088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landrigan, P.J.; Stegeman, J.J.; Fleming, L.E.; Allemand, D.; Anderson, D.M.; Backer, L.C.; Brucker-Davis, F.; Chevalier, N.; Corra, L.; Czerucka, D.; et al. Human health and ocean pollution. Ann. Glob. Health 2020, 86, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickinson, A.W.; Power, A.; Hansen, M.G.; Brandt, K.K.; Piliposian, G.; Appleby, P.; O’Neill, P.A.; Jones, R.T.; Sierocinski, P.; Koskella, B.; et al. Heavy metal pollution and co-selection for antibiotic resistance: A microbial palaeontology approach. Environ. Int. 2019, 132, 105117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Decré, D.; Verdet, C.; Emirian, A.; Le Gourrierec, T.; Petit, J.C.; Offenstadt, G.; Maury, E.; Brisse, S.; Arlet, G. Emerging severe and fatal infections due to Klebsiella pneumoniae in two university hospitals in France. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2011, 49, 3012–3014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fang, C.T.; Lai, S.Y.; Yi, W.C.; Hsueh, P.R.; Liu, K.L. The function of wzy_K1 (magA), the serotype K1 polymerase gene in Klebsiella pneumoniae cps gene cluster. J. Infect. Dis. 2010, 201, 1268–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Catalán-Nájera, J.C.; Garza-Ramos, U.; Barrios-Camacho, H. Hypervirulence and hypermucoviscosity: Two different but complementary Klebsiella spp. phenotypes? Virulence 2017, 8, 1111–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahly, H.; Podschun, R.; Oelschlaeger, T.A.; Greiwe, M.; Parolis, H.; Hasty, D.; Kekow, J.; Ullmann, U.; Ofek, I.; Sela, S. Capsule impedes adhesion to and invasion of epithelial cells by Klebsiella pneumoniae. Infect Immun. 2000, 68, 6744–6749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Majumdar, S.; Yu, J.; Fookes, M.; McAteer, S.P.; Llobet, E.; Finn, S.; Spence, S.; Monahan, A.; Monaghan, A.; Kissenpfennig, A.; et al. Elucidation of the RamA regulon in Klebsiella pneumoniae reveals a role in LPS regulation. PLoS Pathog. 2015, 11, e1004627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Weisburg, W.G.; Barns, S.M.; Pelletier, D.A.; Lane, D.J. 16S ribosomal DNA amplification for phylogenetic study. J. Bacteriol. 1991, 173, 697–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Compain, F.; Babosan, A.; Brisse, S.; Genel, N.; Audo, J.; Ailloud, F.; Kassis-Chikhani, N.; Arlet, G.; Decré, D. Multiplex PCR for detection of seven virulence factors and K1/K2 capsular serotypes of Klebsiella pneumoniae. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2014, 52, 4377–4380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
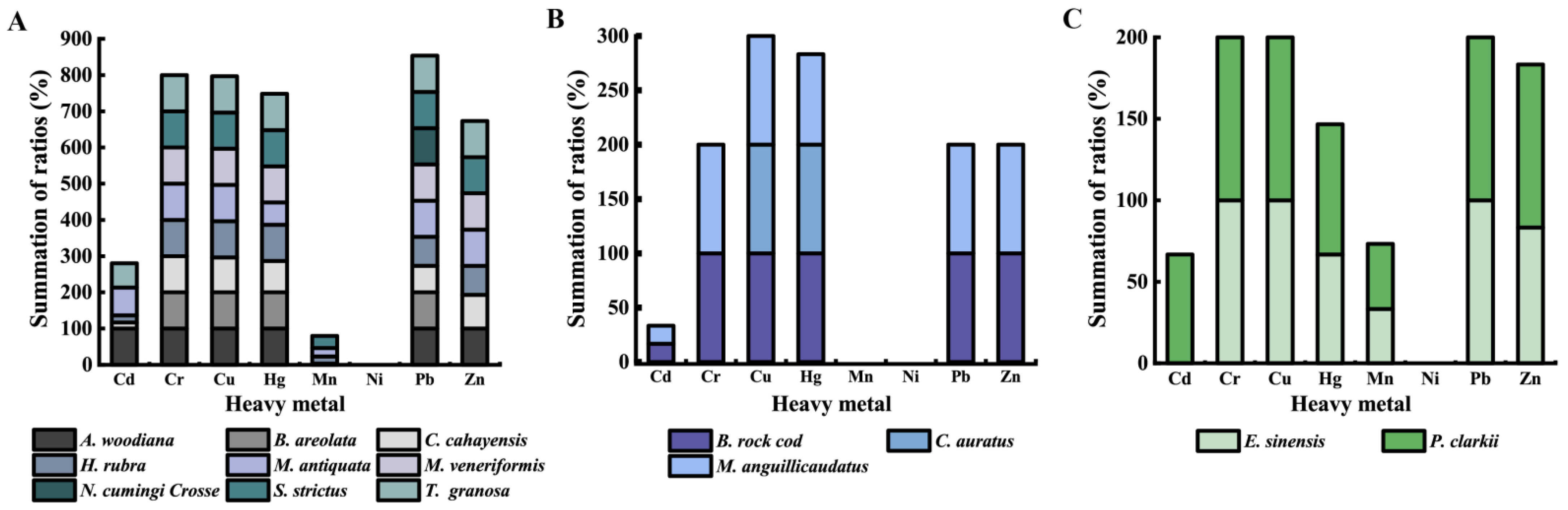
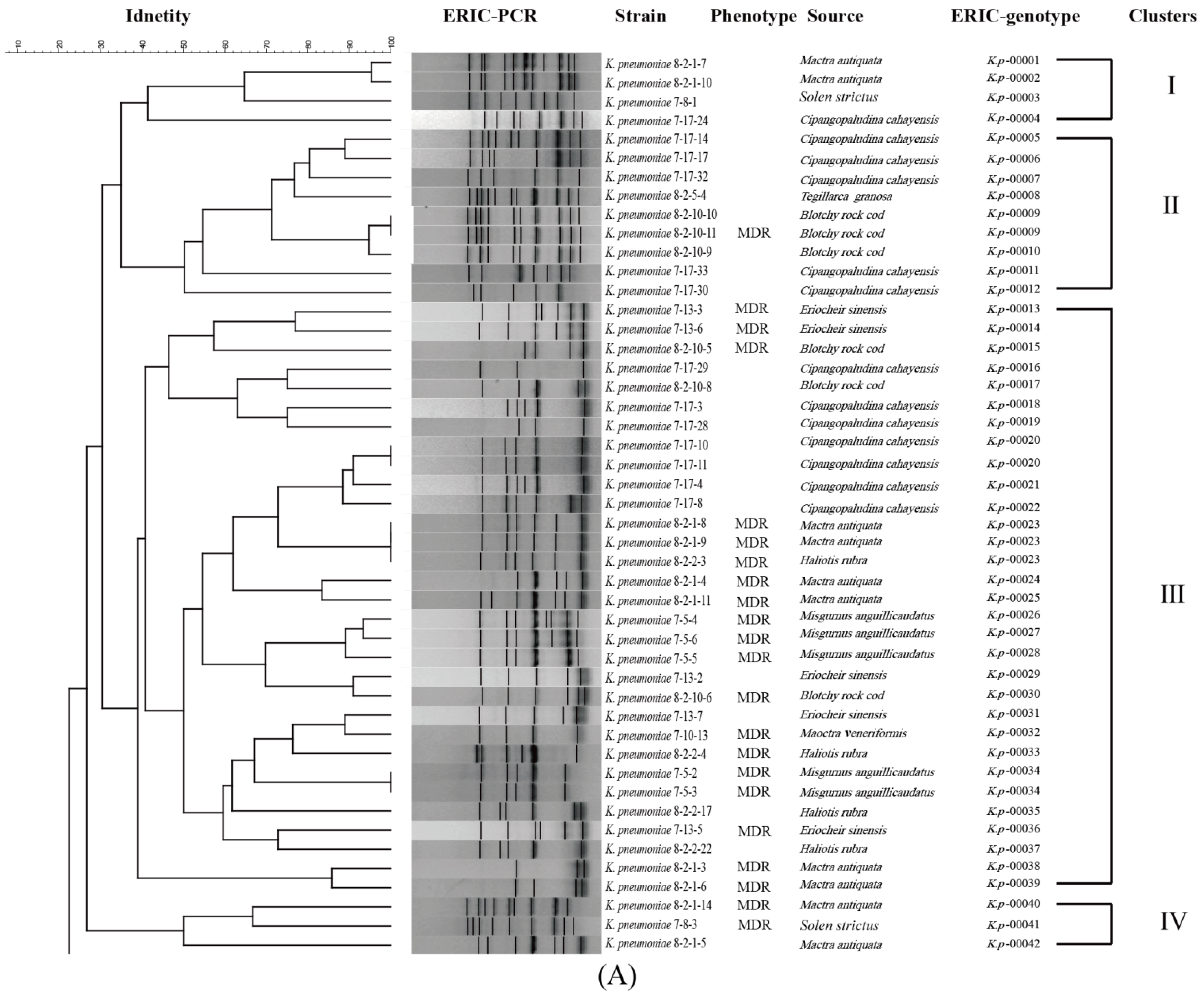
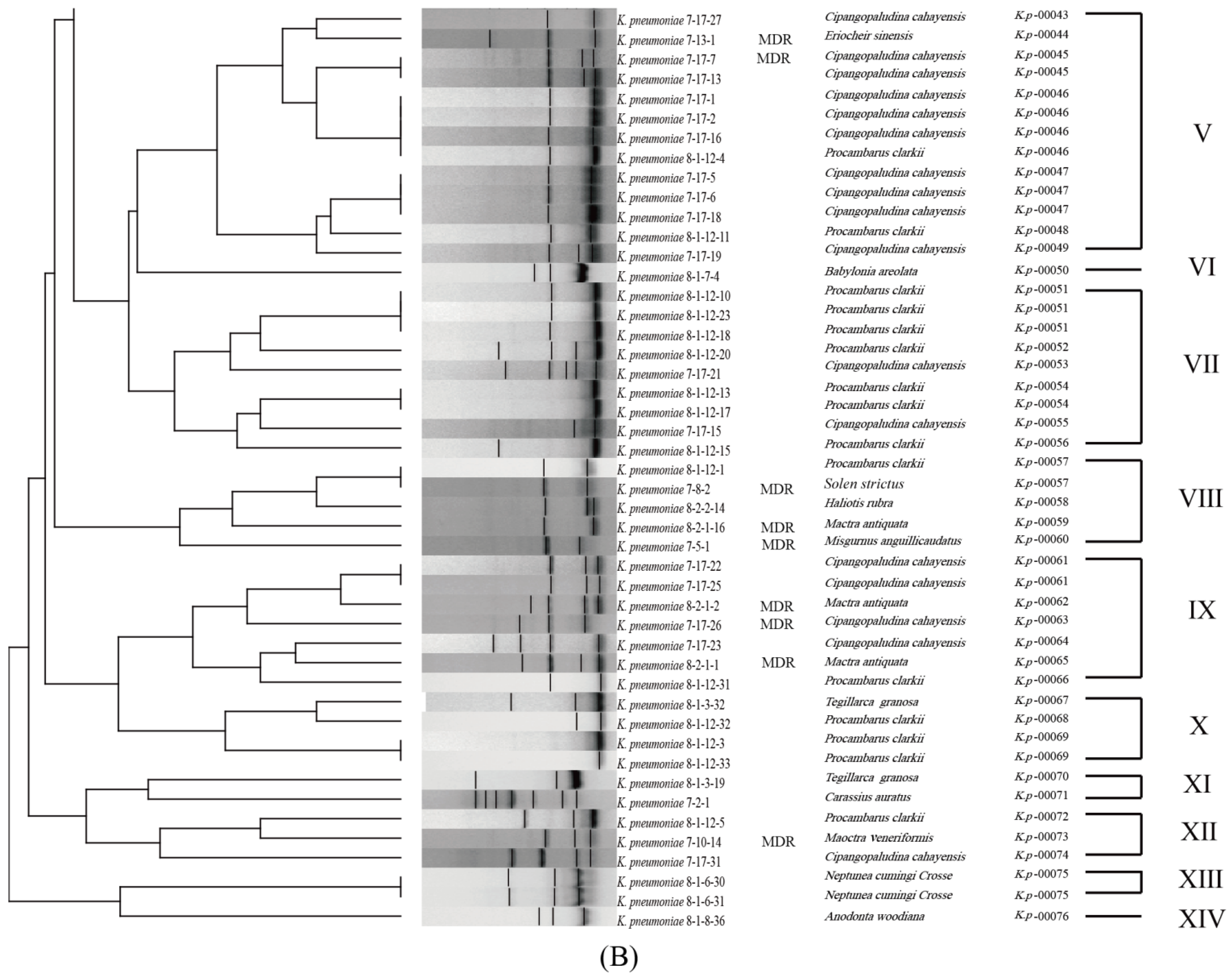
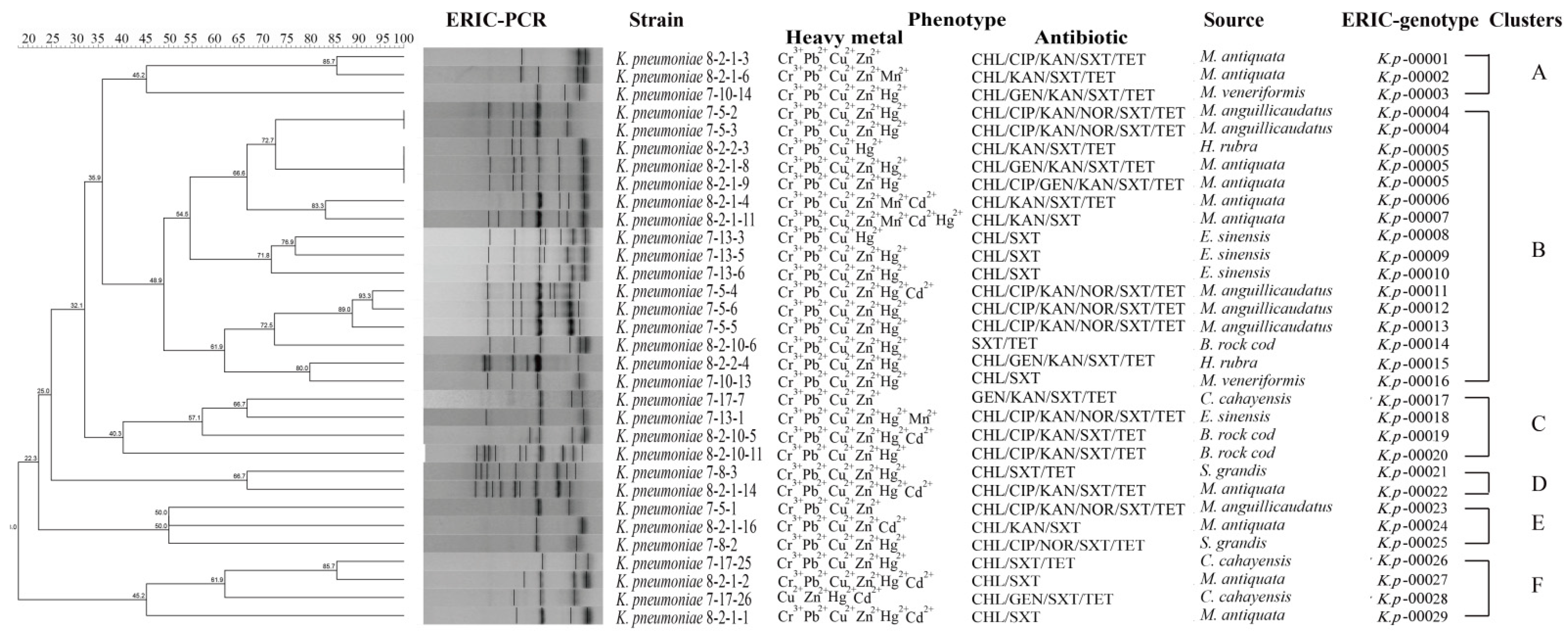
| Aquatic Animal | Species | Percentage of Virulence-Related Gene (%) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| aerobactin | allS | entB | fimH | iroN | mrkD | rmpA | traT | wcaG | ybtA | ||
| Mollusks | A. woodiana | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| B. areolata | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 | |
| C. cahayensis | 0 | 0 | 100 | 96.7 | 0 | 83.3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 16.7 | |
| H. rubra | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| M. antiquata | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| M. veneriformis | 0 | 0 | 100 | 50.0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| N. cumingi Crosse | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| S. strictus | 0 | 0 | 100 | 100 | 0 | 66.7 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| T. granosa | 0 | 0 | 100 | 33.3 | 0 | 33.3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Fish | B. rock cod | 0 | 0 | 83.3 | 0 | 0 | 83.3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| C. auratus | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| M. anguillicaudatus | 0 | 0 | 100 | 100 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Crustaceans | E. sinensis | 0 | 0 | 100 | 100 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| P. clarkii | 0 | 0 | 100 | 6.7 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 53.3 | |
| No. of Genes | Gene | No. of Strains |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | entB+ | 7 |
| mrkD+ | 1 | |
| 2 | entB+/fimH+ | 5 |
| entB+/mrkD+ | 29 | |
| entB+/ybtA+ | 1 | |
| 3 | entB+/fimH+/mrkD+ | 38 |
| entB+/mrkD+/ybtA+ | 9 | |
| entB+/fimH+/ybtA+ | 1 | |
| 4 | entB+/fimH+/mrkD+/ybtA+ | 3 |
| Percentage of the Strains (%) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CHL | CIP | GEN | IPM | KAN | MEM | NOR | SXT | TET | |
| Resistance | 31.9 | 13.8 | 6.4 | 0.00 | 22.3 | 0 | 8.5 | 52.1 | 27.7 |
| Intermediary sensitivity | 1.1 | 18.1 | 9.6 | 1.10 | 13.8 | 0 | 9.6 | 8.5 | 9.6 |
| Sensitivity | 67 | 68.1 | 84 | 98.90 | 63.8 | 100 | 81.9 | 39.4 | 62.8 |
| Aquatic Animal | Species | Percentage of Resistant Strains (%) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CHL | CIP | GEN | IPM | KAN | NOR | MEM | SXT | TET | ||
| Mollusks | A. woodiana | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| B. areolata | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | |
| C. cahayensis | 6.7 | 0 | 6.7 | 0 | 3.3 | 0 | 0 | 46.7 | 10 | |
| H. rubra | 40.0 | 0 | 20 | 0 | 40 | 0 | 0 | 40.0 | 40 | |
| M. antiquata | 76.9 | 23.1 | 15.4 | 0 | 61.5 | 0 | 0 | 84.6 | 46.2 | |
| M. veneriformis | 100 | 0 | 50 | 0 | 50 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 50 | |
| N. cumingi Crosse | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| S. strictus | 66.7 | 33.3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 33.3 | 0 | 100 | 66.7 | |
| T. granosa | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 33.3 | 33.3 | |
| Fish | B. rock cod | 33.3 | 33.3 | 0 | 0 | 33.3 | 0 | 0 | 50 | 50 |
| C. auratus | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| M. anguillicaudatus | 100 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 100 | 0 | 100 | 100 | |
| Crustaceans | E. sinensis | 66.7 | 16.7 | 0 | 0 | 16.7 | 16.7 | 0 | 66.7 | 16.7 |
| P. clarkii | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 13.3 | 6.7 | |
| Genome Feature | K. pneumoniae 8-2-5-4 |
|---|---|
| Genome size (bp) | 5,432,731 |
| DNA G + C (%) | 57.32 |
| DNA scaffold | 64 |
| Predicted gene | 5143 |
| Protein-coding gene | 5042 |
| RNAs gene | 224 |
| Genes assigned to COG | 4777 |
| Genes with unknown function | 1230 |
| Genomic island | 11 |
| Prophage gene cluster | 1 |
| Integron | 0 |
| Insertion sequence | 2 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, Y.; Ni, L.; Guan, H.; Chen, D.; Qin, S.; Chen, L. First Report of Potentially Pathogenic Klebsiella pneumoniae from Serotype K2 in Mollusk Tegillarca granosa and Genetic Diversity of Klebsiella pneumoniae in 14 Species of Edible Aquatic Animals. Foods 2022, 11, 4058. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11244058
Xu Y, Ni L, Guan H, Chen D, Qin S, Chen L. First Report of Potentially Pathogenic Klebsiella pneumoniae from Serotype K2 in Mollusk Tegillarca granosa and Genetic Diversity of Klebsiella pneumoniae in 14 Species of Edible Aquatic Animals. Foods. 2022; 11(24):4058. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11244058
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Yingwei, Ling Ni, Huiqiong Guan, Dailing Chen, Si Qin, and Lanming Chen. 2022. "First Report of Potentially Pathogenic Klebsiella pneumoniae from Serotype K2 in Mollusk Tegillarca granosa and Genetic Diversity of Klebsiella pneumoniae in 14 Species of Edible Aquatic Animals" Foods 11, no. 24: 4058. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11244058
APA StyleXu, Y., Ni, L., Guan, H., Chen, D., Qin, S., & Chen, L. (2022). First Report of Potentially Pathogenic Klebsiella pneumoniae from Serotype K2 in Mollusk Tegillarca granosa and Genetic Diversity of Klebsiella pneumoniae in 14 Species of Edible Aquatic Animals. Foods, 11(24), 4058. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11244058







