Preparation of an Immunoaffinity Column Based on Bispecific Monoclonal Antibody for Aflatoxin B1 and Ochratoxin A Detection Combined with ic-ELISA
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents and Material
2.2. Apparatus
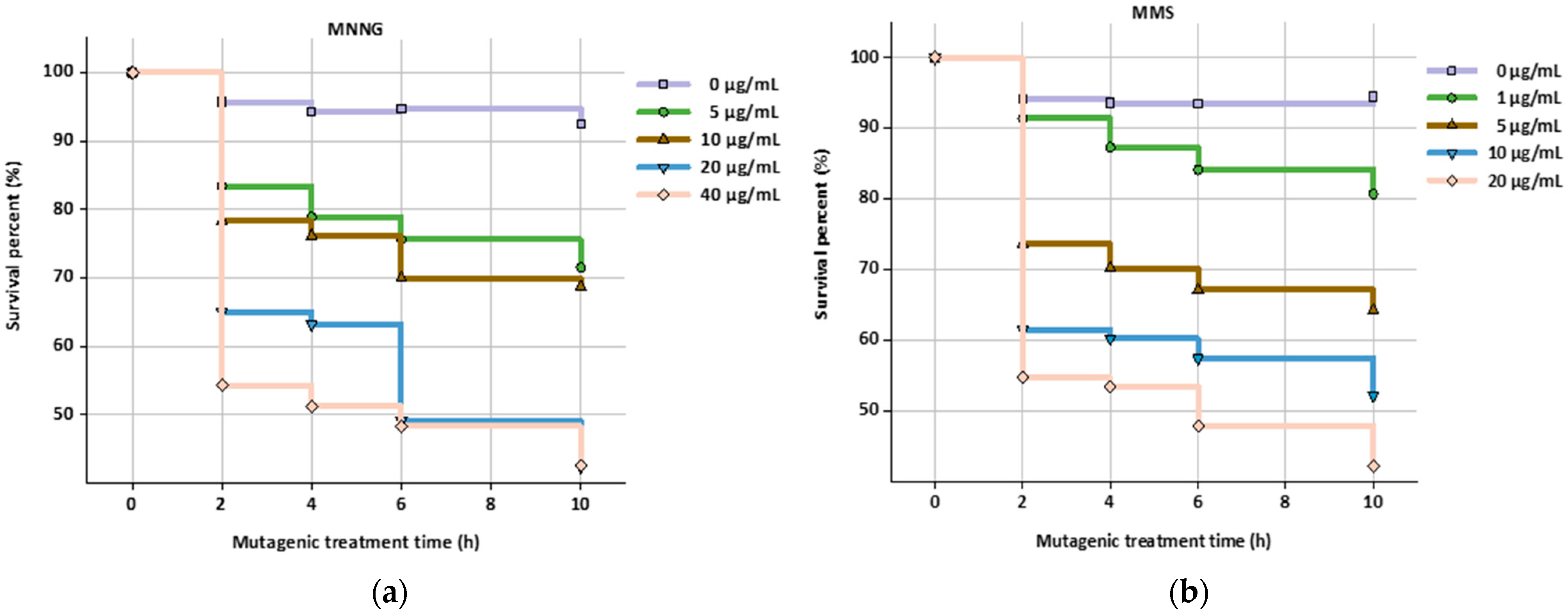
2.3. Mutagenesis of HGPRT and TK Deficient Hybridoma Cell Lines
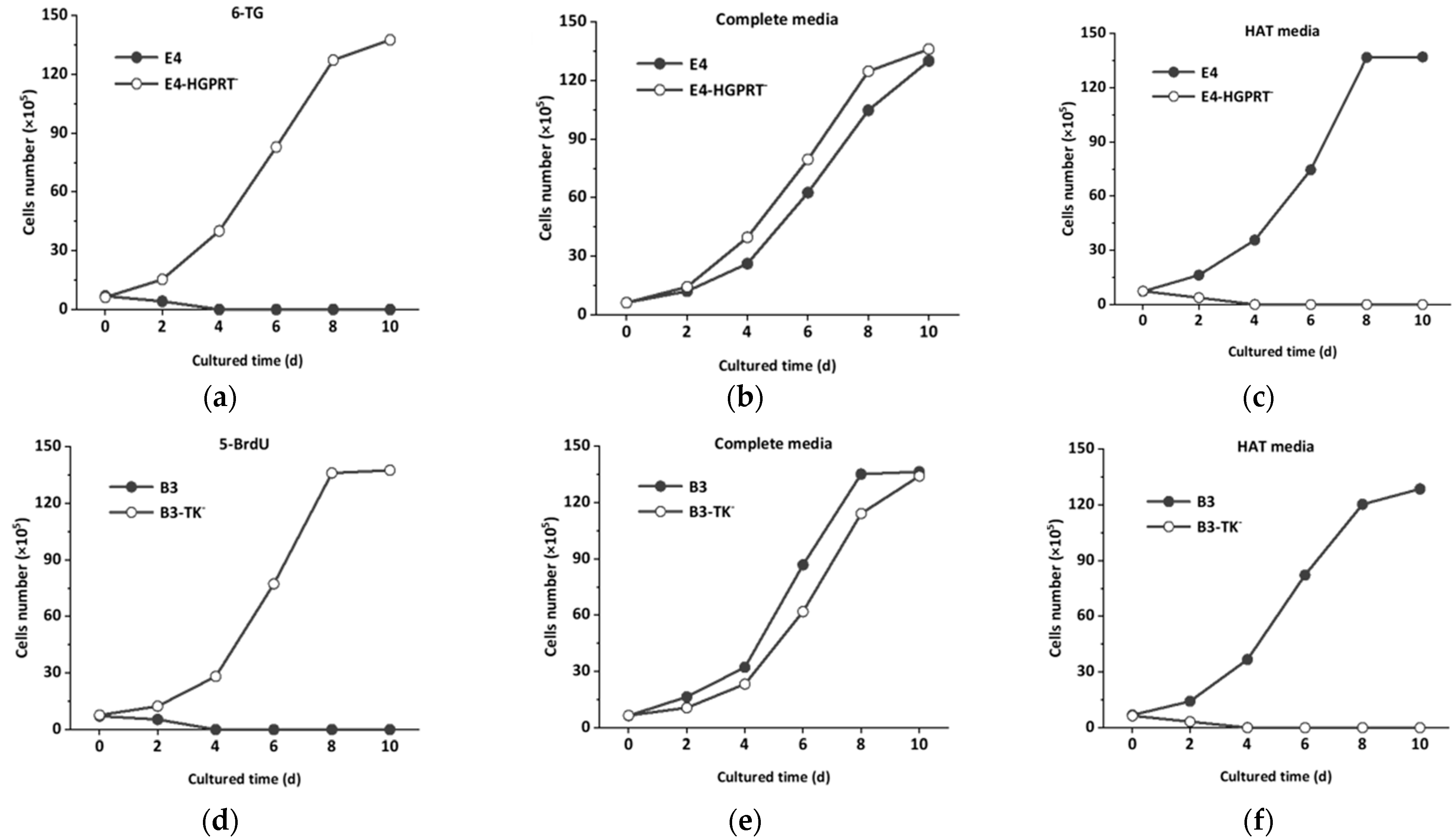
2.4. Screening of HGPRT and TK Deficient Hybridoma Cell Lines
2.5. Generation and Characterization of BsMAb
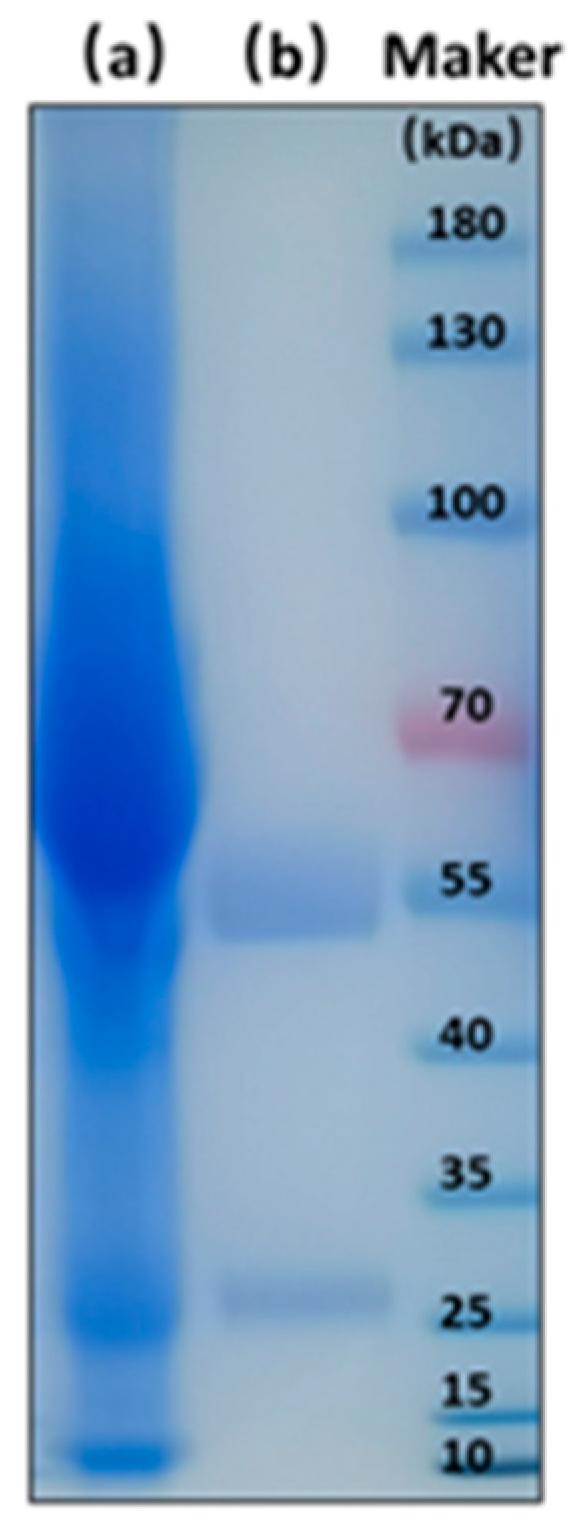
2.5.1. Generation of BsMAb
2.5.2. Antibody Specificity Determination
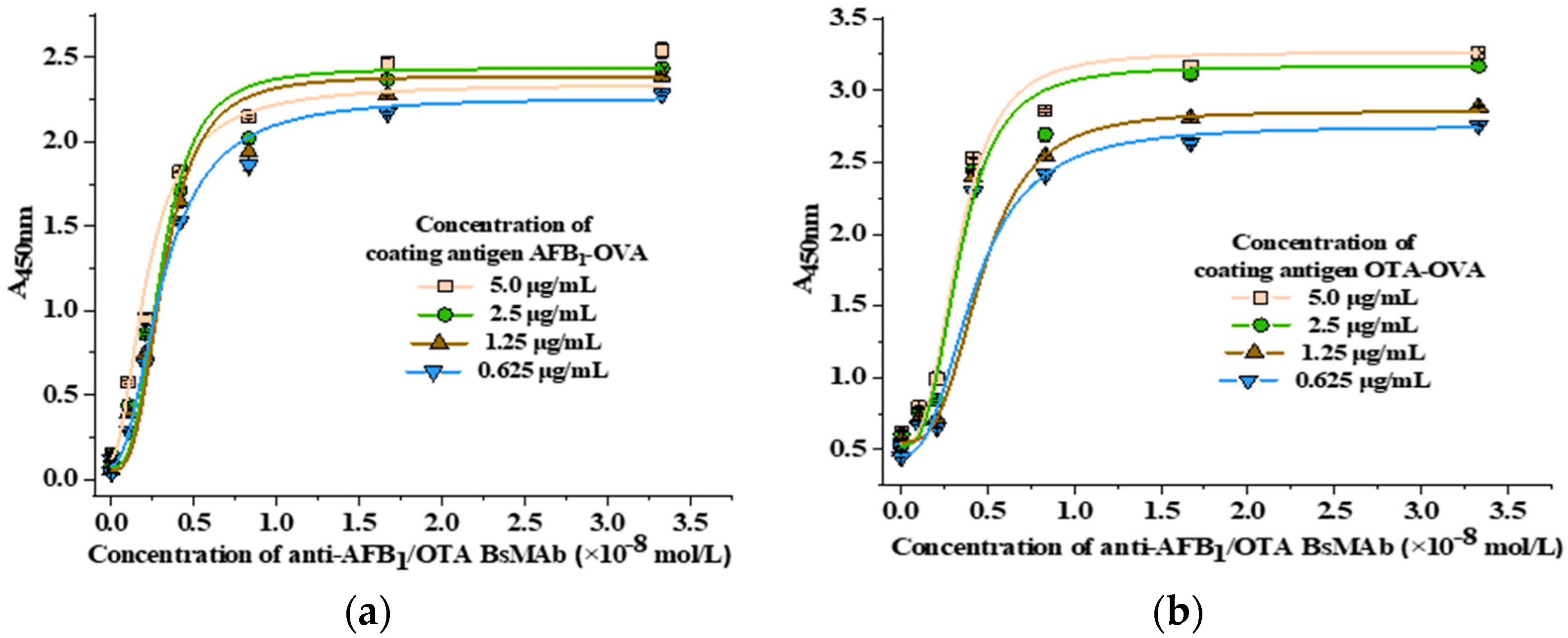
2.5.3. Antibody Affinity Determination
2.6. Preparation of BsMAb Based IAC
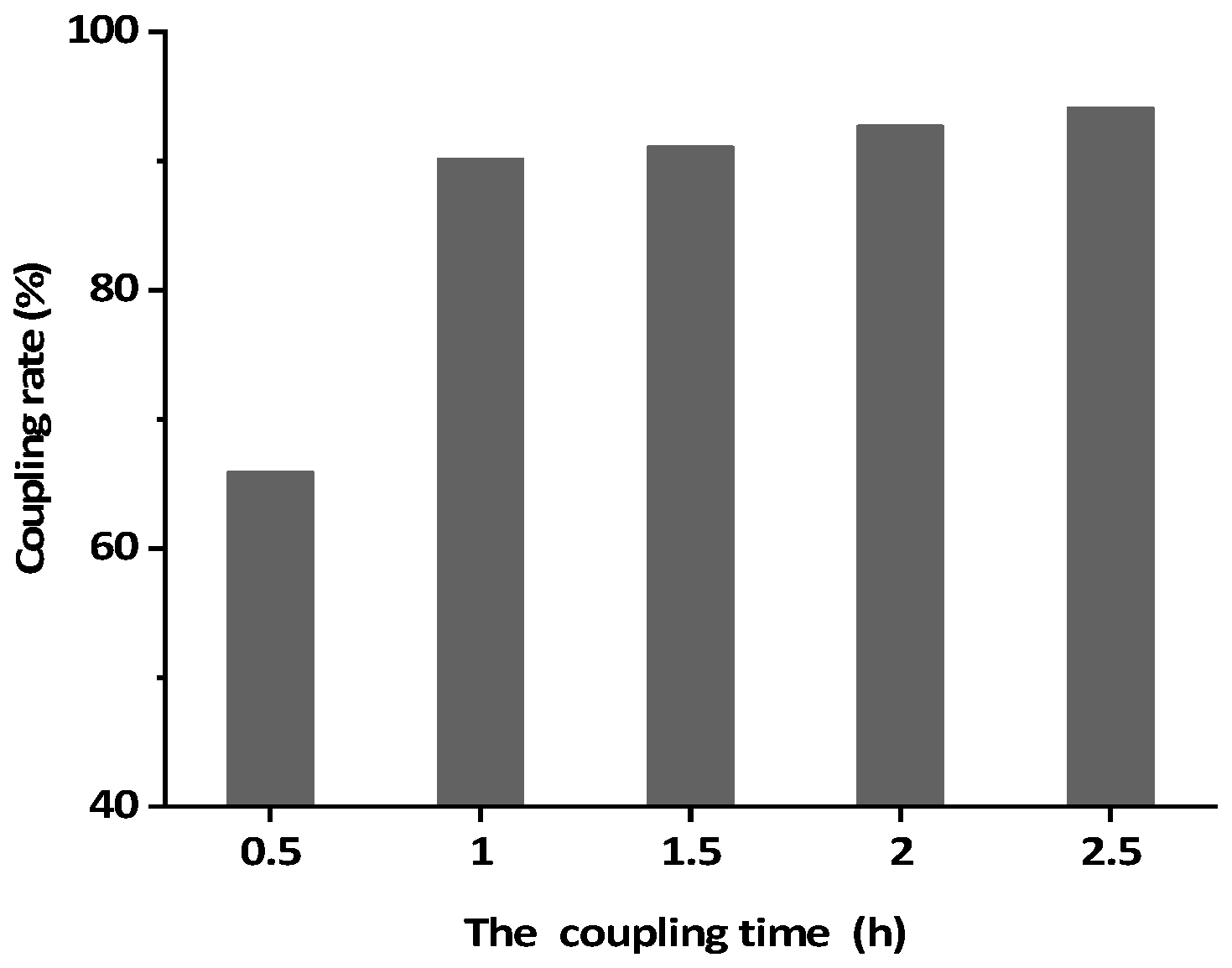
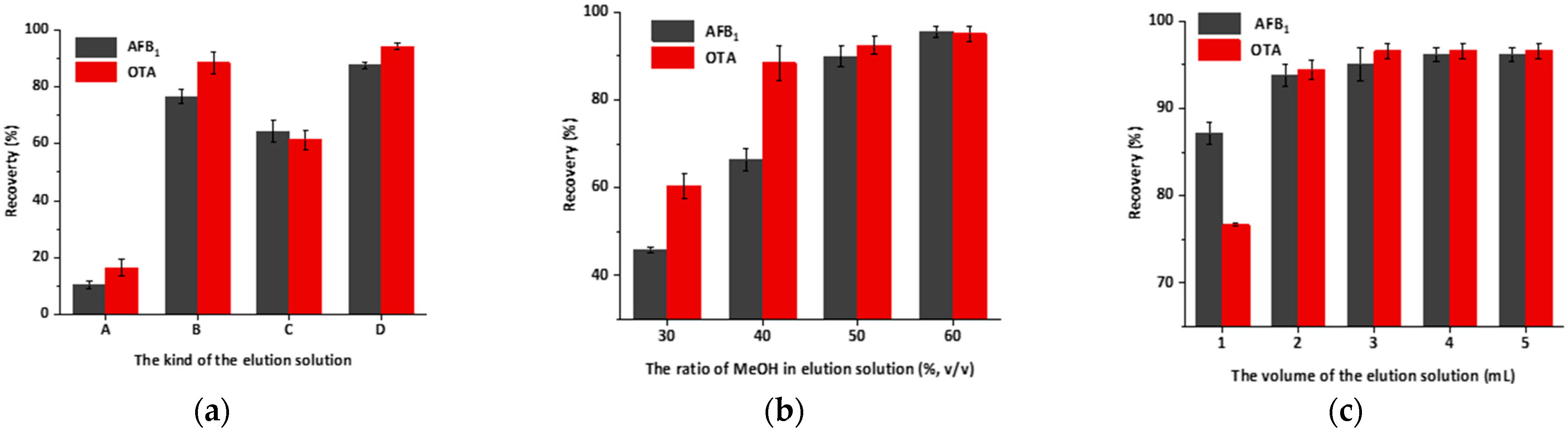
2.7. Optimization of Elution Conditions and Evaluation of the IAC Capacity
2.8. ic-ELISA Combined with IAC
2.9. Analysis of Corn and Wheat Samples
3. Results
3.1. Mutagenesis and Screening of HGPRT and TK Deficient Hybridoma Cell Lines
3.2. Generation and Characterization of BsMAb
3.2.1. Generation of BsMAb
3.2.2. Antibody Specificity Determination
3.2.3. Antibody Affinity Determination
3.3. Preparation of BsMAb Based IAC
3.4. Optimization of Elution Conditions and Evaluating of the IAC Capacity
3.5. Analysis of Corn and Wheat Samples
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Duarte, S.C.; Lino, C.M.; Pena, A. Ochratoxin A in feed of food-producing animals: An undesirable mycotoxin with health and performance effects. Vet. Microbiol. 2011, 154, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egmond, H.; Dekker, W.H. Worldwide regulations for mycotoxins. Nat. Toxins 2010, 3, 332–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuchs, R.; Peraica, M. Ochratoxin A in human kidney diseases. Food Addit. Contam. 2005, 22, 53–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Santacroce, M.P.; Conversano, M.C.; Casalino, E.; Lai, O.; Zizzadoro, C.; Centoducati, G.; Crescenzo, G. Aflatoxins in aquatic species: Metabolism, toxicity and perspectives. Rev. Fish Biol. Fish. 2008, 18, 99–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO International Agency for Research on Cancer. IARC Monographs on the Identification of Carcinogenic Hazards to Humans. 2021. Available online: https://monographs.iarc.who.int/list-of-classifications (accessed on 14 December 2021).
- Kumar, A.; Jindal, N.; Shukla, C.L.; Pal, Y.; Ledoux, D.R.; Rottinghaus, G.E. Effect of ochratoxin A on Escherichia coli-challenged broiler chicks. Avian Dis. 2003, 47, 15–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alassane-Kpembi, I.; Schatzmayr, G.; Taranu, I.; Marin, D.; Puel, O.; Oswald, I.P. Mycotoxins co-contamination: Methodological aspects and biological relevance of combined toxicity studies. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2016, 57, 3489–3507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madrigal-Santillan, E.; Morales-Gonzalez, J.A.; Vargas-Mendoza, N.; Reyes-Ramírez, P.; Cruz-Jaime, S.; Sumaya-Martínez, T.; Pérez-Pastén, R.; Madrigal-Bujaidar, E. Antigenotoxic Studies of Different Substances to Reduce the DNA Damage Induced by Aflatoxin B-1 and Ochratoxin A. Toxins 2010, 2, 738–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- European Commission. Commission Regulation (EC) No. 1881/2006 of 19 December 2006 setting maximum levels for certain contaminants in foodstuffs. Off. J. Eur. Union 2006, L364, 20–23. [Google Scholar]
- GB2761-2017; Chinese National Food Safety Standard, Maximum Residue Limits for Mycotoxins in Food. National Medical Products Administration: Beijing, China, 2017.
- Amino, N.; Hidaka, Y. Various types of immunoassay. Nihon Rinsho Jpn. J. Clin. Med. 1995, 53, 2107–2111. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, N.; Wang, S.; Allan, R.D.; Kennedy, I.R. A Rapid Aflatoxin B1 ELISA: Development and Validation with Reduced Matrix Effects for Peanuts, Corn, Pistachio, and Soybeans. J. Agric. Food. Chem. 2004, 52, 2746–2755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, X.; Zhao, X.; Tang, J.; Jun, Z.; Chu, F.S. Preparation of gold-labeled antibody probe and its use in immunochromatography assay for detection of aflatoxin B1. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2005, 99, 185–194. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, X.; Huang, T.; Li, X.; Huang, Z. Flower-like gold nanoparticles-based immunochromatographic test strip for rapid simultaneous detection of fumonisin B1 and deoxynivalenol in Chinese traditional medicine. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2019, 177, 112895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Machado, J.M.; Soares, R.R.; Chu, V.; Conde, J.P. Multiplexed capillary microfluidic immunoassay with smartphone data acquisition for parallel mycotoxin detection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 99, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Jin, B.; You, M.; Wang, J.; Li, X.; Lin, M.; Xu, F.; Li, F. A portable and universal upconversion nanoparticle-based lateral flow assay platform for point-of-care testing. Talanta 2019, 201, 126–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, J.; Xie, H.; Zhang, S.; Luo, P.; Guo, P.; Chen, X.; Ke, Y.; Zhuang, J.; Zhou, F.; Jiang, W. Multiplex Flow Cytometric Immunoassays for High-Throughput Screening of Multiple Mycotoxin Residues in Milk. Food Anal. Methods 2019, 12, 877–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qileng, A.; Liang, H.; Huang, S.; Liu, W.; Xu, Z.; Liu, Y. Dual-function of ZnS/Ag 2 S nanocages in ratiometric immunosensors for the discriminant analysis of ochratoxins: Photoelectrochemistry and electrochemistry. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2020, 314, 128066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.; Tang, Z.; Jiang, K.; Huang, Q.; Meng, J.; Nie, D.; Zhao, Z. Dual-target electrochemical aptasensor based on co-reduced molybdenum disulfide and Au NPs (rMoS 2 -Au) for multiplex detection of mycotoxins. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 150, 111894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Pan, D.; Li, G.; Hu, H.; Xue, H.; Zhang, M.; Zhu, M.; Gong, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wan, Y. Direct Immunoassay for Facile and Sensitive Detection of Small Molecule Aflatoxin B1 based on Nanobody. Chemistry 2018, 24, 9869–9876. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Zhang, J.; Ding, K.; Chen, X.; Han, T. The development and characterization of an immunoaffinity column used for the simultaneous selective extraction of Fusarium toxins from grain products. Qual. Assur. Saf. Crops Foods 2019, 11, 325–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Li, Z.; Yang, Y.; Wan, D.; Vasylieva, N.; Zhang, Y.; Cai, J.; Wang, H.; Shen, Y.; Xu, Z. Chemiluminescent Enzyme Immunoassay and Bioluminescent Enzyme Immunoassay for Tenuazonic Acid Mycotoxin by Exploitation of Nanobody and Nanobody-Nanoluciferase Fusion. Anal. Chem. 2020, 72, 11935–11942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moldenhauer, G. Bispecific Antibodies from Hybrid Hybridoma. In Bispecific Antibodies; Kontermann, R., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; pp. 29–46. [Google Scholar]
- Sedykh, S.E.; Prinz, V.V.; Buneva, V.N.; Nevinsky, G.A. Bispecific antibodies: Design, therapy, perspectives. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2018, 12, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Byrne, H.; Conroy, P.J.; Whisstock, J.C.; O’Kennedy, R.J. A tale of two specificities: Bispecific antibodies for therapeutic and diagnostic applications. Trends Biotechnol. 2013, 31, 621–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouyang, H.; Wang, L.; Yang, S.; Wang, W.; Wang, L.; Liu, F.; Fu, Z. Chemiluminescence reaction kinetics-resolved multianalyte immunoassay strategy using a bispecific monoclonal antibody as the unique recognition reagent. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 2952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, M.; Fuller, S.A. Production of murine hybrid-hybridomas secreting bispecific monoclonal antibodies for use in urease-based immunoassays. Clin. Chem. 1988, 34, 1693–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Wang, H.; Shen, Y.; Li, Y.; Dong, J.; Xu, Z.; Yang, J.; Sun, Y.; Xiao, Z. Bispecific Monoclonal Antibody-Based Multianalyte ELISA for Furaltadone Metabolite, Malachite Green, and Leucomalachite Green in Aquatic Products. J. Agric. Food. Chem. 2016, 64, 8054–8061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, R.; Guo, Y.; Wang, C.; Wu, J.; Zhu, G. Development of a Bispecific Monoclonal Antibody to Pesticide Carbofuran and Triazophos Using Hybrid Hybridomas. J. Food Sci. 2009, 74, T1–T6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trucksess, M.W.; Weaver, C.M.; Oles, C.J.; Oles, C.J.; Fry, F.S.; Noonan, G.O.; Betz, J.M.; Rader, J.I. Determination of aflatoxins B1, B2, G1, and G2 and ochratoxin A in ginseng and ginger by multitoxin immunoaffinity column cleanup and liquid chromatographic quantitation: Collaborative study. J. AOAC Int. 2008, 91, 511–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Suarez-Bonnet, E.; Carvajal, M.; Mendez-Ramirez, I.; Castillo-Urueta, P.; Cortés-Eslava, J.; Gómez-Arroyo, S.; Melero-Vara, J.M. Aflatoxin (B1, B2, G1, and G2) contamination in rice of Mexico and Spain, from local sources or imported. J. Food Sci. 2013, 78, T1822–T1829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chan, D.; Macdonald, S.J.; Boughtflower, V.; Brereton, P. Simultaneous determination of aflatoxins and ochratoxin A in food using a fully automated immunoaffinity column clean-up and liquid chromatography–fluorescence detection. J. Chromatogr. A 2004, 1059, 13–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Y.; Yang, T.; Xiaosong, M.O.; Mo, X.; Zhang, H.; Huang, W.; Lu, T.; Zhang, D.; Wang, H. Preparation of Immunoaffinity Column for AFB1 with Monoclonal Antibodies Immobilized on Protein A-Sepharose. Food Sci. 2015, 21, 193–198. [Google Scholar]
- Göbel, R.; Lusky, K. Simultaneous determination of aflatoxins ochratoxin A, and zearalenone in grains by new immunoaffinity column/liquid chromatography. J. AOAC Int. 2004, 87, 411–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Krska, R. Performance of modern sample preparation techniques in the analysis of Fusarium mycotoxins in cereals. J. Chromatogr. A 1998, 815, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Zhang, Q.; He, T.; Zhang, Z.; Ding, X. Immunosorbent and Immunoaffinity Column for Aflatoxin M1 Nanobody and Preparation Method Thereof. U.S. Patent 2015/0276729 A1, 6 September 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, J.; Sun, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Wang, C.; Sun, S.; Li, J.; Ding, S.; Xia, X.; Jiang, H. Preparation and application of immunoaffinity column coupled with dcELISA detection for aflatoxins in eight grain foods. Food Control 2017, 73, 445–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ediage, E.N.; Van Poucke, C.; De Saeger, S. A multi-analyte LC–MS/MS method for the analysis of 23 mycotoxins in different sorghum varieties: The forgotten sample matrix. Food Chem. 2015, 177, 397–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ardic, M.; Karakaya, Y.; Atasever, M.; Durmaz, H. Determination of aflatoxin B1 levels in deep-red ground pepper (isot) using immunoaffinity column combined with ELISA. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2008, 46, 1596–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arroyo-Manzanares, N.; Gámiz-Gracia, L.; García-Campaña, A.M. Determination of ochratoxin A in wines by capillary liquid chromatography with laser induced fluorescence detection using dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction. Food Chem. 2012, 135, 368–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goryacheva, I.Y.; Karagusheva, M.A.; Van Peteghem, C.; Sibanda, L.; Saeger, S.D. Immunoaffinity pre-concentration combined with on-column visual detection as a tool for rapid aflatoxin M1 screening in milk. Food Control 2009, 20, 802–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juan, C.; Zinedine, A.; Molto, J.C.; Idrissi, L.; Manes, J. Aflatoxins levels in dried fruits and nuts from Rabat-Salé area, Morocco. Food Control 2008, 19, 849–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goryacheva, I.Y.; Saeger, S.D.; Delmulle, B.; Lobeau, M.; Eremin, S.A.; Barna-VetrÓ, I.; Van Peteghem, C. Simultaneous non-instrumental detection of aflatoxin B1 and ochratoxin A using a clean-up tandem immunoassay column. Anal. Chim. Acta 2007, 590, 118–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Lv, Y.; Zhang, D.; Tang, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Zhang, H.; Wang, H. Preparation and Application of Immunoaffinity Column for Multi-mycotoxins. Chin. J. Anal. Chem. 2016, 44, 1243–1249. [Google Scholar]
- Hsie, A.W.; Brimer, P.A.; Mitchell, T.J.; Gosslee, D.G. The dose-response relationship for ethyl methanesulfonate-induced mutations at the hypoxanthine-guanine phosphoribosyl transferase locus in Chinese hamster ovary cells. Somat. Cell Mol. Genet. 1975, 1, 247–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tergel; Tai, D.; Liu, G.; Daorna; Wang, R.; Guo, H.; Li, Y.; Li, Y. Establishment of Hypoxanthine Guanine Phosphoribosyl Transferase Mutant from Human Liver Cancer Cell Line HepG2. China Anim. Husb. Vet. Med. 2011, 38, 92–95. [Google Scholar]
- Kufer, P.; Lutterbüse, R.; Baeuerle, P.A. A Revival of Bispecific Antibodies. Trends Biotechnol. 2004, 22, 238–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beatty, J.D.; Beatty, B.G.; Vlahos, W.G. Measurement of monoclonal antibody affinity by non-competitive enzyme immunoassay. J. Immunol. Methods 1987, 100, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delmulle, B.; Saeger, S.D.; Adams, A.; Kimpe, N.D.; Van Peteghem, C. Development of a liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry method for the simultaneous determination of 16 mycotoxins on cellulose filters and in fungal cultures. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2006, 20, 771–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Junsai, T.; Poapolathep, S.; Sutjarit, S.; Giorgi, M.; Zhang, Z.; Logrieco, A.F.; Li, P.; Poapolathep, A. Determination of Multiple Mycotoxins and Their Natural Occurrence in Edible Vegetable Oils Using Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry. Foods 2021, 10, 2795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akinyemi, M.O.; Braun, D.; Windisch, P.; Warth, B.; Ezekiel, C.N. Assessment of multiple mycotoxins in raw milk of three different animal species in Nigeria. Food Control 2022, 131, 108258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Liu, Y.; Liang, B.; Zhang, Y.; Zhong, X.; Luo, X.; Huang, J.; Wang, Y.; Cheng, W.; Chen, K. Probabilistic risk assessment of dietary exposure to aflatoxin B1 in Guangzhou, China. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 7973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, K.; Ji, F.; Xu, J.; Qian, M.; Duan, J.; Nie, D.; Tang, Z.; Zhao, Z.; Shi, J.; Han, Z. Natural Occurrence and Characteristic Analysis of 40 Mycotoxins in Agro-Products from Yangtze Delta Region. Sci. Agric. Sin. 2021, 54, 2870–2884. [Google Scholar]


| Target Analyte | AFB1 | OTA |
|---|---|---|
| Coating antigen | AFB1-OVA | OTA-OVA |
| Coating concentration (μg/mL) | 0.31 | 0.26 |
| Coating buffer | 0.05 M carbonate buffer (pH 9.6) | |
| Coating condition | 14 h, 4 °C | |
| MAb | Anti-AFB1 MAb | Anti-OTA MAb |
| Standard analyte | AFB1 | OTA |
| Competition condition | 30 min, 37 °C | |
| HRP-IgG dilution | 1:5000 | |
| HRP-IgG incubation condition | 30 min, 37 °C | |
| Mycotoxin Analyte | Structure | IC50 (ng/mL) | CR (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| AFB1 | 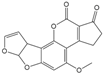 | 0.037 | 100 |
| AFB2 | 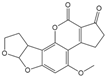 | 0.101 | 37 |
| AFG1 | 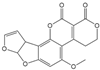 | 0.252 | 15 |
| AFG2 | 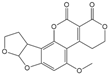 | 3.584 | 1 |
| AFM1 | 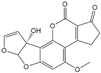 | 0.077 | 48 |
| AFM2 | 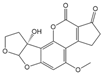 | 0.377 | 10 |
| OTA | 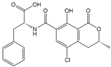 | 2.040 | 100 |
| OTB | 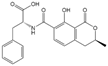 | 5.620 | 36 |
| OTC | 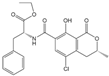 | 201.535 | 1 |
| ZEN | 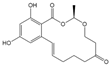 | >1000 | <0.1 |
| DON | 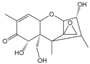 | >1000 | <0.1 |
| FB1 | 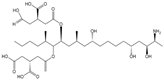 | >1000 | <0.1 |
| T-2 | 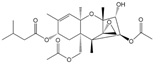 | >1000 | <0.1 |
| Cycle | AFB1 | OTA | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Column Capacity (ng) | Preservation Rate (%) | Column Capacity (ng) | Preservation Rate (%) | |
| 1 | 165.0 | 100.0 | 171.1 | 100.0 |
| 2 | 162.5 | 98.5 | 169.5 | 99.1 |
| 3 | 159.0 | 96.4 | 166.4 | 97.3 |
| 4 | 153.6 | 93.1 | 156.2 | 91.3 |
| 5 | 147.5 | 89.4 | 145.8 | 85.2 |
| 6 | 128.9 | 78.1 | 133.3 | 77.9 |
| 7 | 114.4 | 69.3 | 116.3 | 68.0 |
| Samples | Analyte | Spiked Concentration (μg/kg) | IAC-ELISA | LC-MS | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Measured (μg/kg) | Recovery (%) | CV (%) | Measured (μg/kg) | Recovery (%) | CV (%) | |||
| Corn 0 | AFB1 | 0 | ND a | NC b | NC | ND | NC | NC |
| OTA | 0 | ND | NC | NC | ND | NC | NC | |
| Corn 1 | AFB1 | 100 | 95.6 | 95.6 | 5.0 | 97.3 | 97.3 | 3.3 |
| OTA | 100 | 98.6 | 98.6 | 4.5 | 97.9 | 97.9 | 3.5 | |
| Corn 2 | AFB1 | 50 | 49.2 | 98.4 | 4.7 | 49.8 | 99.6 | 3.3 |
| OTA | 50 | 49.1 | 98.2 | 4.4 | 49.4 | 98.8 | 3.1 | |
| Corn 3 | AFB1 | 20 | 19.2 | 96.0 | 4.3 | 19.2 | 96.0 | 3.5 |
| OTA | 20 | 19.6 | 98.0 | 4.4 | 19.2 | 96.0 | 3.2 | |
| Corn 4 | AFB1 | 10 | 9.9 | 99.0 | 3.4 | 9.8 | 98.0 | 3.8 |
| OTA | 10 | 10.3 | 103.0 | 4.2 | 9.8 | 98.0 | 3.6 | |
| Corn 5 | AFB1 | 4 | 4.1 | 102.5 | 2.6 | 3.8 | 95.0 | 3.2 |
| OTA | 4 | 4.2 | 105.0 | 2.4 | 3.9 | 97.5 | 3.5 | |
| Wheat 0 | AFB1 | 0 | ND | NC | NC | ND | NC | NC |
| OTA | 0 | ND | NC | NC | ND | NC | NC | |
| Wheat 1 | AFB1 | 100 | 99.1 | 99.1 | 4.8 | 98.2 | 98.2 | 3.1 |
| OTA | 100 | 98.9 | 98.9 | 4.6 | 97.5 | 97.5 | 3.1 | |
| Wheat 2 | AFB1 | 50 | 47.7 | 95.4 | 4.5 | 48.7 | 97.4 | 3.8 |
| OTA | 50 | 47.7 | 95.4 | 3.3 | 49.2 | 98.4 | 3.5 | |
| Wheat 3 | AFB1 | 20 | 19.5 | 97.5 | 4.0 | 19.2 | 96.0 | 3.2 |
| OTA | 20 | 19.4 | 97.0 | 3.3 | 19.7 | 98.5 | 3.1 | |
| Wheat 4 | AFB1 | 10 | 9.6 | 96.0 | 3.3 | 9.8 | 98.0 | 3.8 |
| OTA | 10 | 9.9 | 99.0 | 3.2 | 9.9 | 99.0 | 3.5 | |
| Wheat 5 | AFB1 | 4 | 3.9 | 97.5 | 3.1 | 3.9 | 97.5 | 3.2 |
| OTA | 4 | 3.9 | 97.5 | 2.8 | 4.0 | 100.0 | 3.8 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lu, D.; Wang, X.; Su, R.; Cheng, Y.; Wang, H.; Luo, L.; Xiao, Z. Preparation of an Immunoaffinity Column Based on Bispecific Monoclonal Antibody for Aflatoxin B1 and Ochratoxin A Detection Combined with ic-ELISA. Foods 2022, 11, 335. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11030335
Lu D, Wang X, Su R, Cheng Y, Wang H, Luo L, Xiao Z. Preparation of an Immunoaffinity Column Based on Bispecific Monoclonal Antibody for Aflatoxin B1 and Ochratoxin A Detection Combined with ic-ELISA. Foods. 2022; 11(3):335. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11030335
Chicago/Turabian StyleLu, Disha, Xu Wang, Ruijue Su, Yongjian Cheng, Hong Wang, Lin Luo, and Zhili Xiao. 2022. "Preparation of an Immunoaffinity Column Based on Bispecific Monoclonal Antibody for Aflatoxin B1 and Ochratoxin A Detection Combined with ic-ELISA" Foods 11, no. 3: 335. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11030335
APA StyleLu, D., Wang, X., Su, R., Cheng, Y., Wang, H., Luo, L., & Xiao, Z. (2022). Preparation of an Immunoaffinity Column Based on Bispecific Monoclonal Antibody for Aflatoxin B1 and Ochratoxin A Detection Combined with ic-ELISA. Foods, 11(3), 335. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11030335






