Interrelating Grain Hardness Index of Wheat with Physicochemical and Structural Properties of Starch Extracted Therefrom
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Grain Hardness Index and Proximate Compositions of Wheat Grains
2.3. Starch Extraction
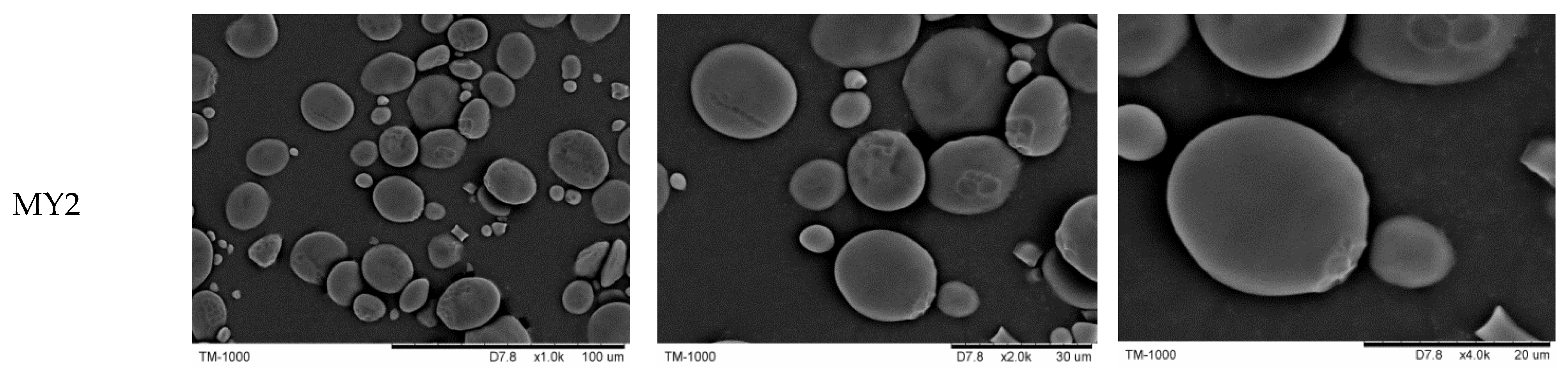
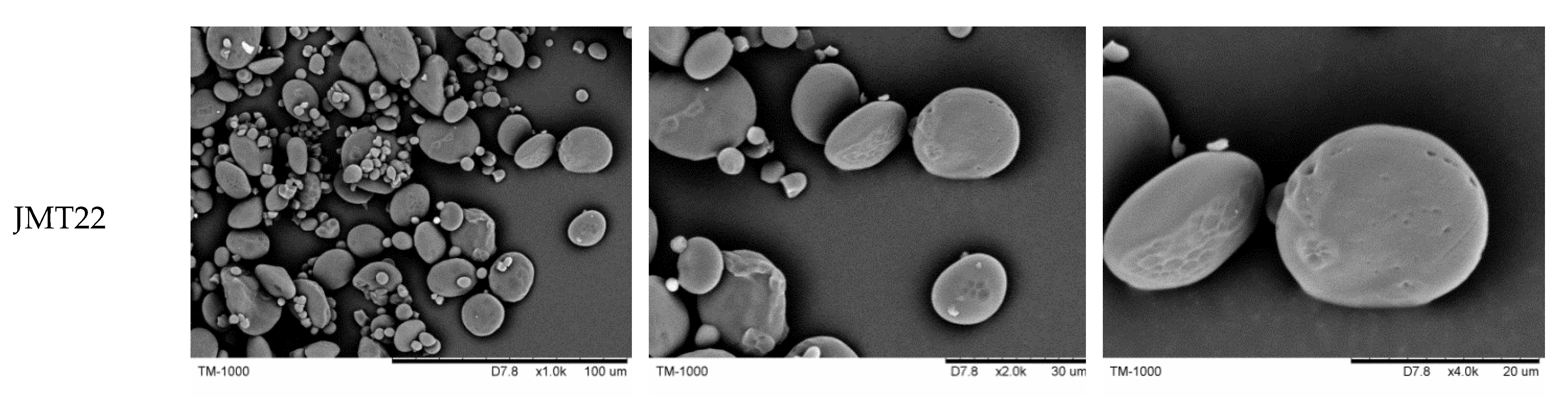
2.4. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
2.5. Apparent Amylose Content Determination
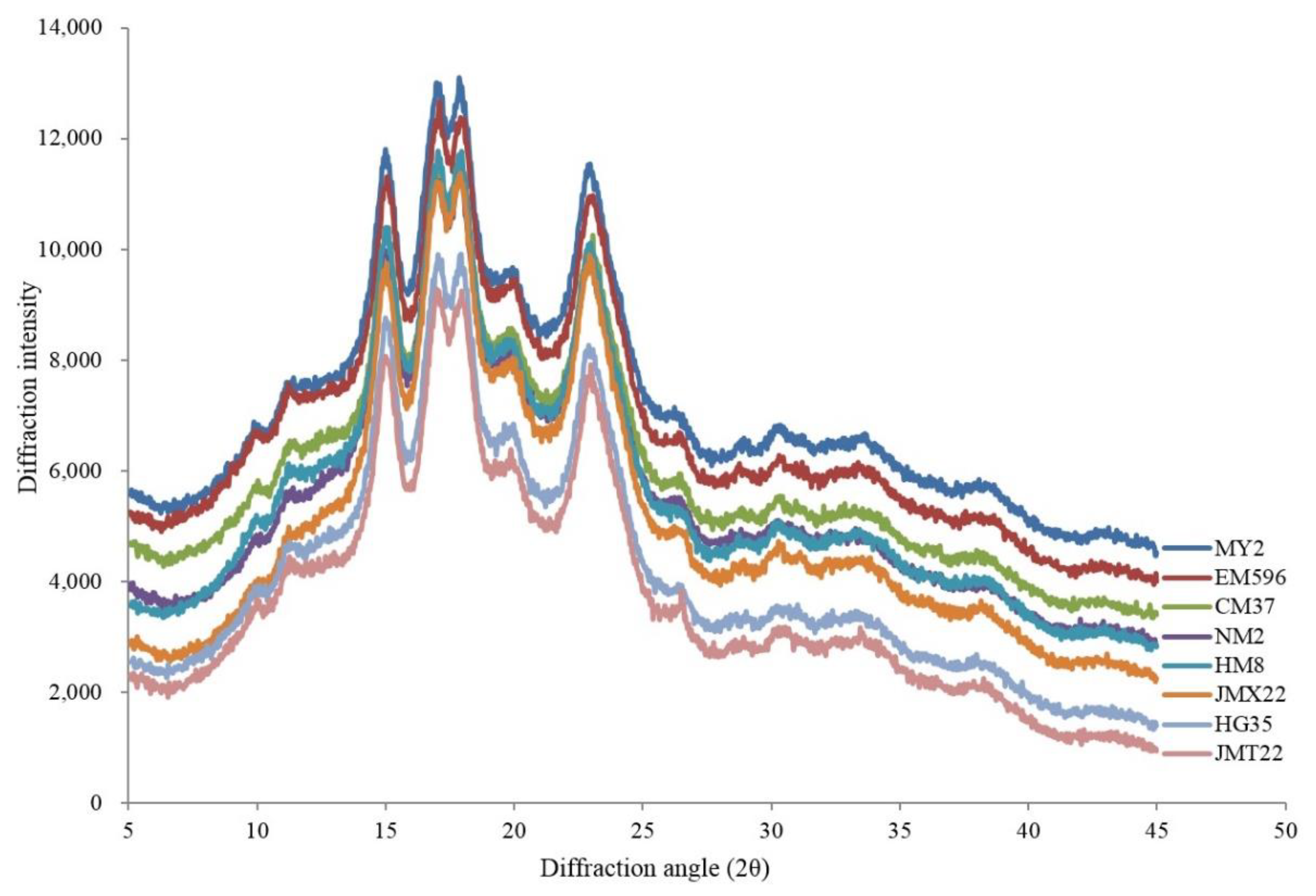
2.6. X-ray Diffraction
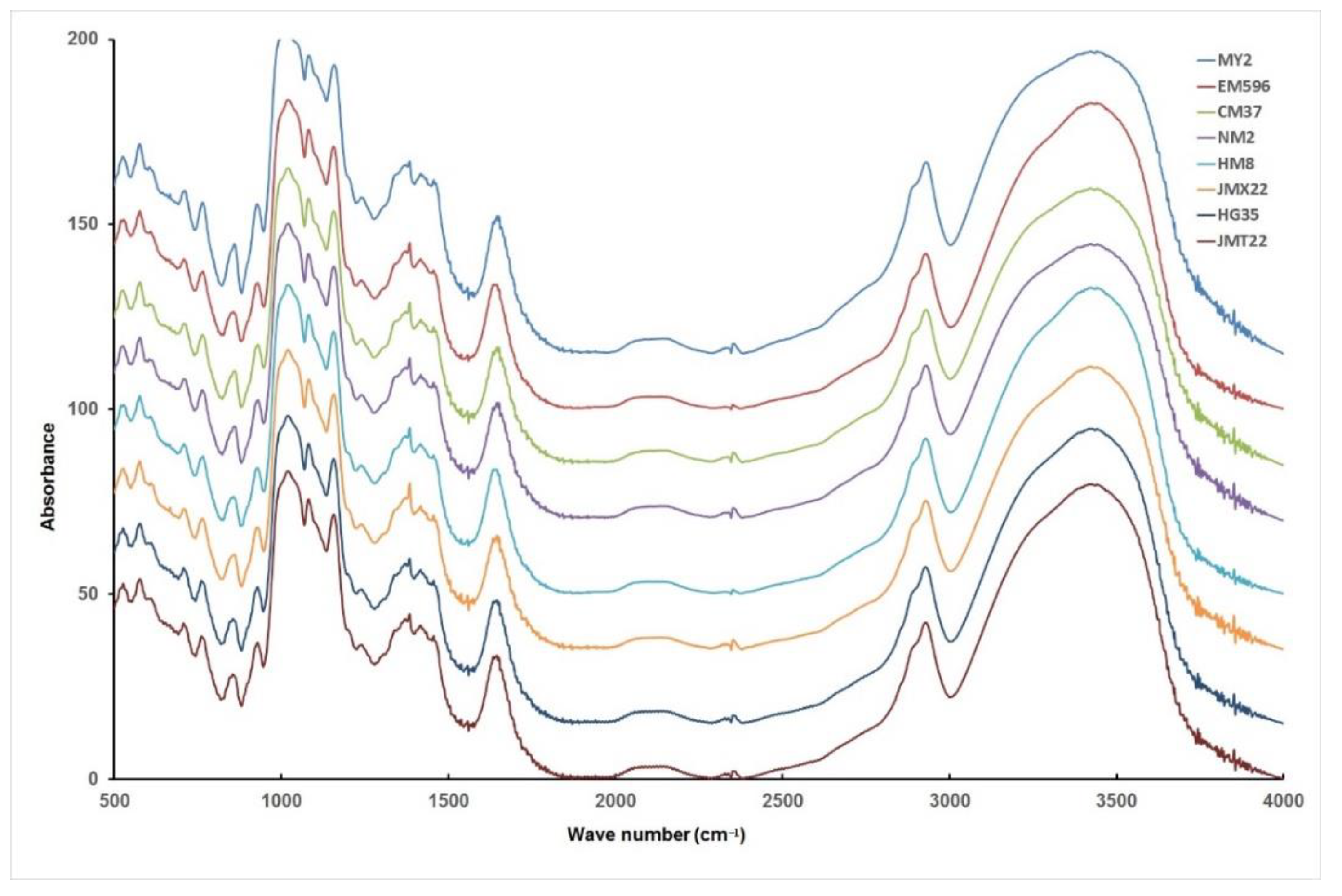
2.7. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR)
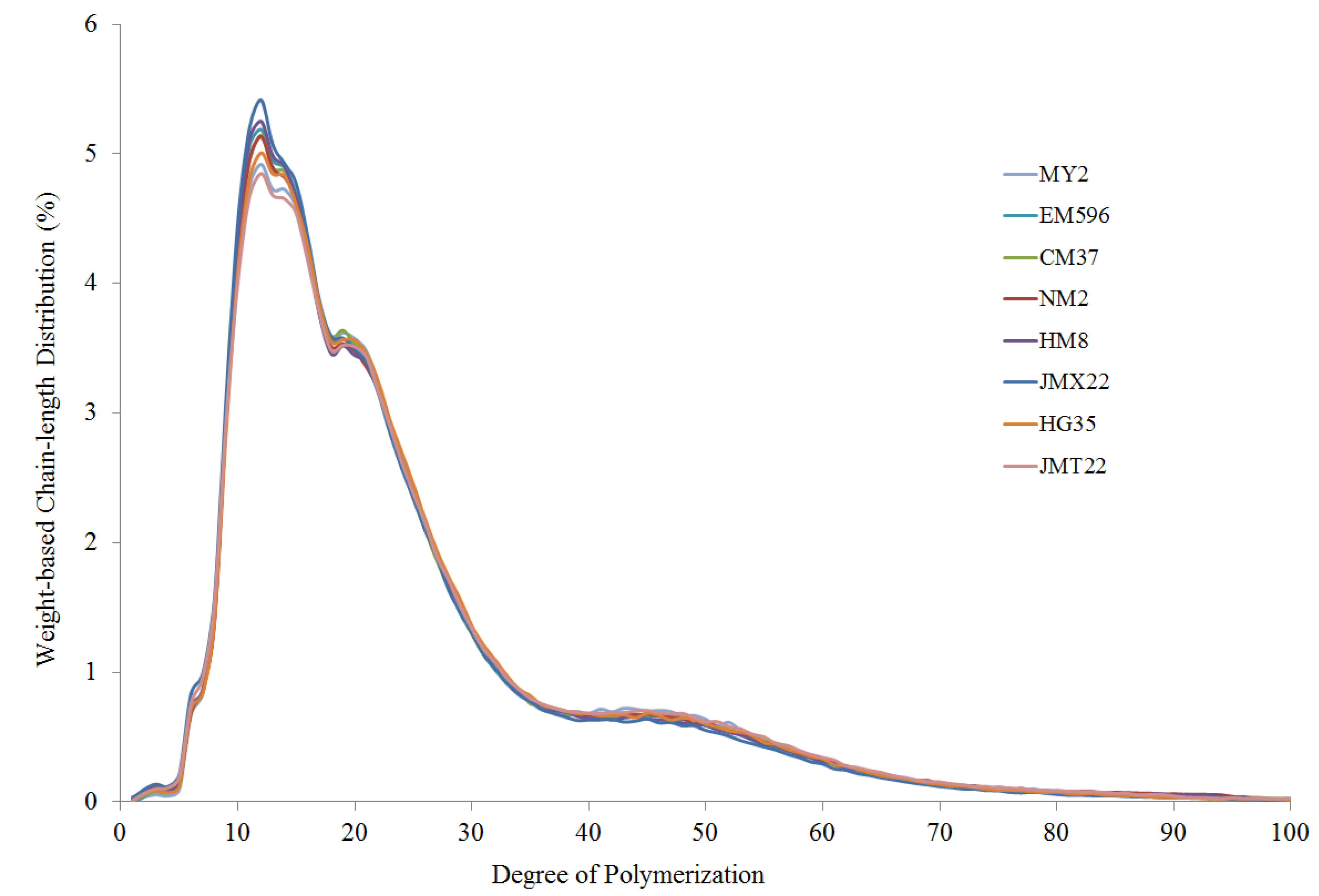
2.8. Amylopectin Chain-Length Distribution
2.9. Thermal Properties
2.10. Pasting Properties
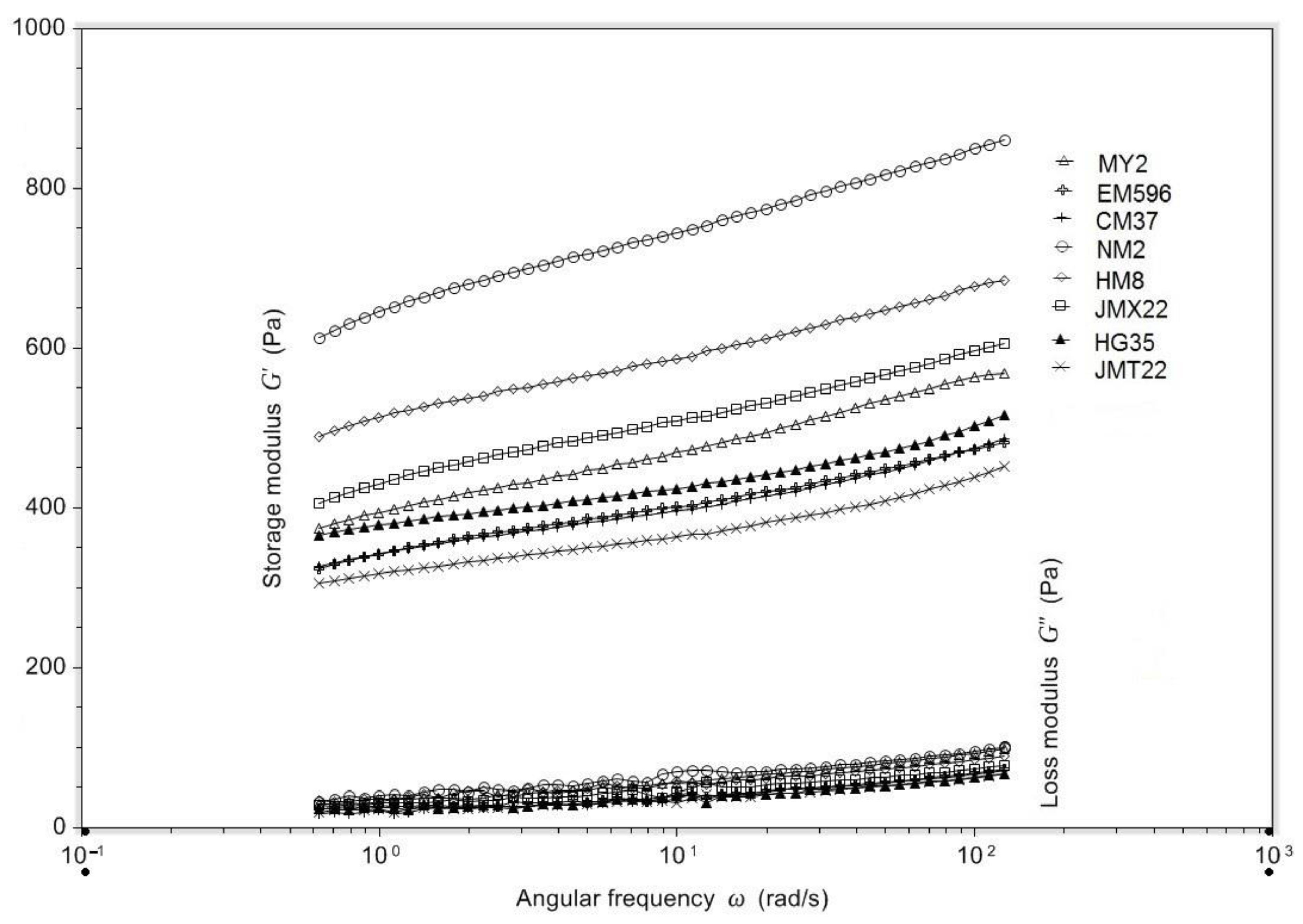
2.11. Dynamic Rheological Properties
2.12. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Proximate Composition of Wheat Grains
3.2. Starch Granular Morphology
3.3. Amylose Content and Structural Characteristics
3.4. Gelatinization Properties
3.5. Pasting Properties
3.6. Dynamic Rheological Properties
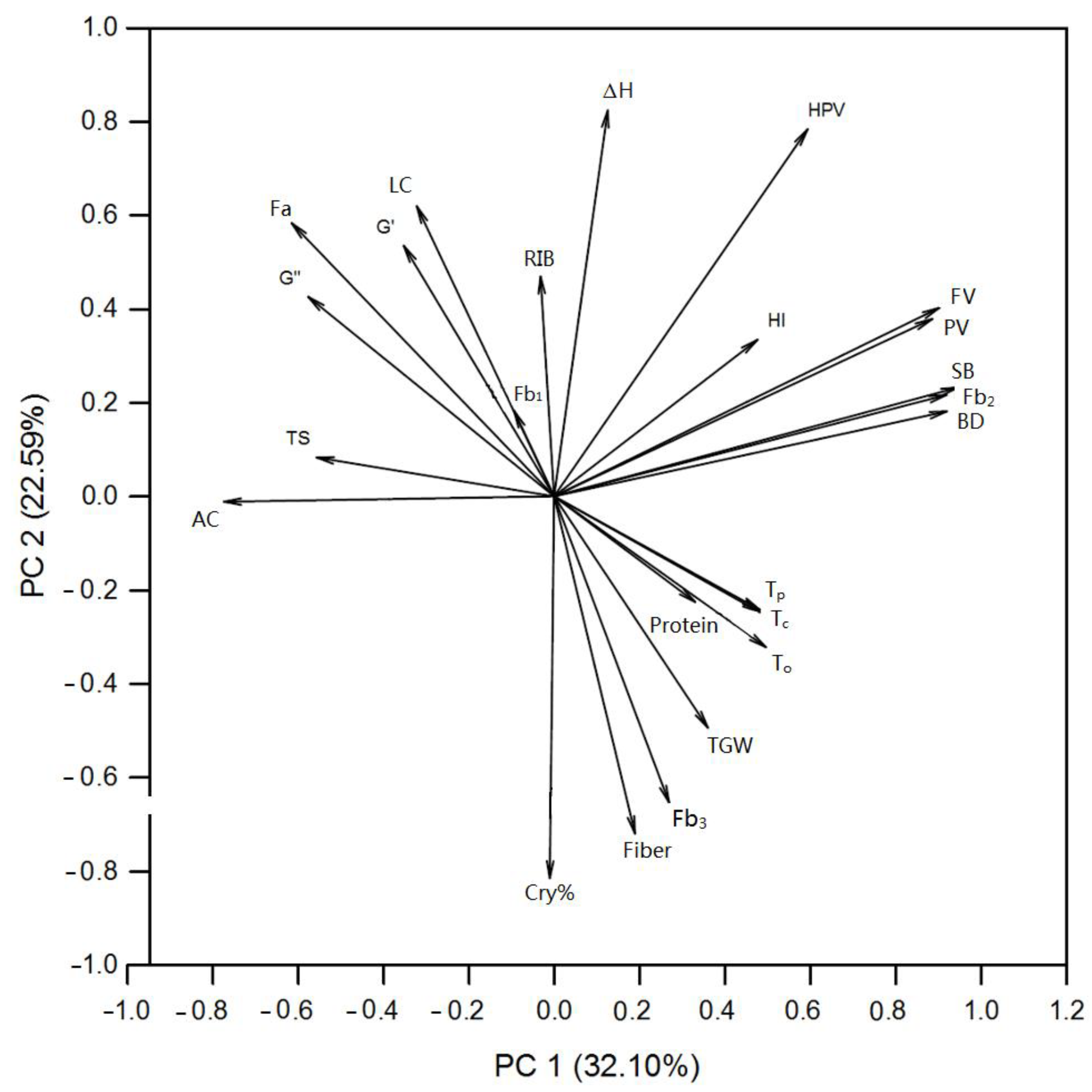
3.7. Pearson and Principal Correlations among the Wheat Quality and Starch Physicochemical Properties
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Soleimani, Z.; Ramshini, H.; Mortazavian, M.; Fazelnajafabadi, M.; Foughi, B. Screening for drought tolerance in Iranian wheat genotypes (Triticum aestivum L.) using physiological traits evaluated under drought stress and normal condition. Aust. J. Crop Sci. 2014, 8, 200–207. [Google Scholar]
- Surma, M.; Adamski, T.; Banaszak, Z.; Kaczmarek, Z.; Kuczyńska, A.; Majcher, M.; Ługowska, B.; Obuchowski, W.; Salmanowicz, B.; Krystkowiak, K. Effect of genotype, environment and their interaction on quality parameters of wheat breeding lines of diverse grain hardness. Plant. Prod. Sci. 2012, 15, 192–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geneix, N.; Dalgalarrondo, M.; Tassy, C.; Nadaud, I.; Barret, P.; Bakan, B.; Elmorjani, K.; Marion, D. Relationships between puroindoline A-prolamin interactions and wheat grain hardness. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0225293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obuchowski, W.; Salmanowicz, B.; Banaszak, Z.; Adamski, T.; Surma, M.; Kaczmarek, Z.; Majcher, M.; Ługowska, B.; Kuczyñska, A.; Krystkowiak, K. Grain hardness of wheat bred in Poland and its relationship to starch damage during milling. Int. Agrophysics 2010, 24, 69–74. [Google Scholar]
- Wada, N.; Kajiyama, S.; Cartagena, J.A.; Lin, L.; Akiyama, Y.; Otani, M.; Suzuki, G.; Mukai, Y.; Aoki, N.; Fukui, K. The effects of puroindoline b on the ultrastructure of endosperm cells and physicochemical properties of transgenic rice plant. J. Cereal Sci. 2010, 51, 182–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayala, M.; Guzmán, C.; Peña, R.J.; Alvarez, J.B. Genetic diversity and molecular characterization of puroindoline genes (Pina-D1 and Pinb-D1) in bread wheat landraces from Andalusia (Southern Spain). J. Cereal Sci. 2016, 71, 61–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, J.; Li, L.; Zhao, B.; Liu, M.; Zheng, X. Comparative studies on physicochemical properties of total, A- and B-type starch from soft and hard wheat varieties. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 154, 714–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasha, I.; Anjum, F.M.; Morris, C.F. Grain hardness: A major determinant of wheat quality. Food Sci. Technol. Int. 2010, 16, 511–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giroux, M.J.; Morris, C.F. Wheat grain hardness results from highly conserved mutations in the friabilin components puroindoline a and b. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 6262–6266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Muqaddasi, Q.H.; Brassac, J.; Ebmeyer, E.; Kollers, S.; Korzun, V.; Argillier, O.; Stiewe, G.; Plieske, J.; Ganal, M.W.; Röder, M.S. Prospects of GWAS and predictive breeding for European winter wheat’s grain protein content, grain starch content, and grain hardness. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 12541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.Y.; Yan, S.H.; Yin, Y.P.; Li, Y.; Liang, T.B.; Gu, F.; Dai, Z.M.; Wang, Z.L. Comparison of Starch Granule Size Distribution Between Hard and Soft Wheat Cultivars in Eastern China. Agric. Sci. China 2008, 7, 907–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katyal, M.; Singh, N.; Chopra, N.; Kaur, A. Hard, medium-hard and extraordinarily soft wheat varieties: Comparison and relationship between various starch properties. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 123, 1143–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.L.; Sun, B.G. Effect of Fermentation Processing on the Flavor of Baijiu. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 5425–5432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agu, R.C.; Swanston, J.S.; Walker, J.W.; Pearson, S.Y.; Bringhurst, T.A.; Brosnan, J.M.; Jack, F.R. Predicting alcohol yield from UK soft winter wheat for grain distilling: Combined influence of hardness and nitrogen measurements. J. Inst. Brew. 2009, 115, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AACC. Approved Methods of American Association of Cereal Chemists, 10th ed.; AACC Press: St. Paul, MN, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Beta, T.; Corke, H.; Rooney, L.W.; Taylor, J.R.N. Starch properties as affected by sorghum grain chemistry. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2000, 81, 245–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Rubio, A.; Flanagan, B.M.; Gilbert, E.P.; Gidley, M.J. A novel approach for calculating starch crystallinity and its correlation with double helix content: A combined XRD and NMR study. Biopolymers 2008, 89, 761–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayakawa, K.; Tanaka, K.; Nakamura, T.; Endo, S.; Hoshino, T. Quality characteristics of waxy hexaploid wheat (Triticumaestivum L.): Properties of starch gelatinization and retrogradation. Cereal Chem. 1997, 74, 576–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, X.; Bertoft, E.; Bao, J.; Corke, H. Molecular structure of amylopectin from amaranth starch and its effect on physicochemical properties. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2008, 43, 377–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, X.; Chen, Y.; Zhu, P.; Sui, Z.; Corke, H.; Bao, J. Relationships among Genetic, Structural, and Functional Properties of Rice Starch. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 6241–6248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, X.; Zhu, P.; Sui, Z.; Bao, J. Physicochemical properties of starches from diverse rice cultivars varying in apparent amylose content and gelatinisation temperature combinations. Food Chem. 2015, 172, 433–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari Felisberto, M.H.; Souza Costa, M.; Villas Boas, F.; Lopes Leivas, C.; Maria Landi Franco, C.; de Souza, S.M.; Pedrosa Silva Clerici, M.T.; Cordeiro, L.M.C. Characterization and technological properties of peach palm (Bactris gasipaes var. gasipaes) fruit starch. Food Res. Int. 2020, 136, 109569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, C.F. Development of soft kernel durum wheat. Front. Agric. Sci. Eng. 2019, 6, 273–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iftikhar, A.; Ali, I. Kernel softness in wheat is determined by starch granule bound Puroindoline proteins. J. Plant Biochem. Biotechnol. 2017, 26, 247–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abecassis, J.; Chaurand, M.; Autran, J.C. Structural basis of wheat hardness and technological consequences. Int. Agrophys. 1997, 11, 273–281. [Google Scholar]
- Katyal, M.; Singh, N.; Virdi, A.S.; Kaur, A.; Chopra, N.; Ahlawat, A.K.; Singh, A.M. Extraordinarily soft, medium-hard and hard Indian wheat varieties: Composition, protein profile, dough and baking properties. Food Res. Int. 2017, 100, 306–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsson, H.; Eliasson, A. Influence of the starch granule surface on the rheological behavior of wheat flour dough. J. Texture Stud. 1997, 28, 487–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, D.; Qin, H.; Ding, H.; Zhang, J.; Wang, C.; Guo, T. Surface lipids play a role in the interaction of puroindolines with wheat starch and kernel hardness. Cereal Chem. 2016, 93, 523–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brites, C.M.; Santos, C.A.L.D.; Bagulho, A.S.; Beirão-Da-Costa, M.L. Effect of wheat puroindoline alleles on functional properties of starch. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2008, 226, 1205–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Singh, N.; Kaur, N.; Katyal, M.; Kaur, A.; Shevkani, K. Characteristics of starch separated from coarse and fine flour fractions obtained from hard, medium-hard, and soft Indian wheat cultivars. Starch-Stärke 2017, 69, 1600012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Kumar, A.; Sharma, N.K.; Kaur, N.; Chunduri, V.; Chawla, M.; Sharma, S.; Singh, K.; Garg, M. Soft and hard textured wheat differ in starch properties as indicated by trimodal distribution, morphology, thermal and crystalline properties. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, 0147622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanashiro, I.; Abe, J.; Hizukuri, S. A periodic distribution of the chain length of amylopectin as revealed by high-performance anionexchange chromatography. Carbohydr. Res. 1996, 283, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warren, F.J.; Gidley, M.J.; Flanagan, B.M. Infrared spectroscopy as a tool to characterise starch ordered structure—A joint FTIR-ATR, NMR, XRD and DSC study. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 139, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kong, X.; Zhou, X.; Sui, Z.; Bao, J. Effects of gamma irradiation on physicochemical properties of native and acetylated wheat starches. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 91, 1141–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jane, J.-L.; Chen, Y.Y.; Lee, L.F.; McPherson, A.E.; Wong, K.S.; Radosavljevic, M.; Kasemsuwan, T. Effects of amylopectin branch chain length and amylose content on the gelatinization and pasting properties of starch. Cereal Chem. 1999, 76, 629–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, X.; Kasapis, S.; Zhu, P.; Sui, Z.; Bao, J.; Corke, H. Physicochemical and structural characteristics of starches from Chinese hull-less barley cultivars. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 51, 509–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Li, Y.; Sun, F.; Li, X.; Wang, P.; Chang, J.; Wang, Y.; Yang, G.; He, G. Co-expression of high-molecular-weight glutenin subunit 1Ax1 and Puroindoline a (Pina) genes in transgenic durum wheat (Triticum turgidum ssp. durum) improves milling and pasting quality. BMC Plant Biol. 2019, 19, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalczewski, P.Ł.; Walkowiak, K.; Masewicz, Ł.; Bartczak, O.; Lewandowicz, J.; Kubiak, P.; Baranowska, H.M. Gluten-Free Bread with Cricket Powder—Mechanical Properties and Molecular Water Dynamics in Dough and Ready Product. Foods 2019, 8, 240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, H.; Li, J.; Guo, L. Rheological and pasting characteristics of wheat starch modified with sequential triple enzymes. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 230, 115667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Li, E.; Fan, X.; Yang, C.; Ma, H.; Gilbert, R.G. The effects of the chain-length distributions of starch molecules on rheological and thermal properties of wheat flour paste. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 101, 105563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, X.; Kasapis, S.; Bao, J. Viscoelastic properties of starches and flours from two novel rice mutants induced by gamma irradiation. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 60, 578–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Setia, R.; Warkentin, T.; Ai, Y. Functionality and starch digestibility of wrinkled and round pea flours of two different particle sizes. Food Chem. 2021, 336, 127711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, C.; Wu, R.; Shao, Y. The effects of ultrasonic treatment on physicochemical properties and in vitro digestibility of semigelatinized high amylose maize starch. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 119, 106831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Cultivars | Hardness Index | Thousand Grain Weight (g) | Total Starch (%, DW) | Lipids (%, DW) | Proteins (%, DW) | Fiber (%, DW) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MY2 | 37.2 ± 0.3 e | 41.9 ± 0.6 a | 80.4 ± 0.9 a,b | 1.9 ± 0.3 a | 13.1 ± 0.2 b | 2.8 ± 0.1 a,b |
| EM596 | 38.1 ± 0.2 e | 37.0 ± 0.3 b | 83.7 ± 0.5 a | 1.7 ± 0.0 a | 13.1 ± 0.1 b | 3.3 ± 0.0 a |
| CM37 | 39.5 ± 0.5 e | 34.3 ± 0.3 c | 81.1 ± 1.1 a,b | 1.3 ± 0.2 b | 14.3 ± 0.2 a | 2.6 ± 0.1 b,c |
| NM2 | 44.2 ± 0.1 d | 34.3 ± 0.2 c | 78.4 ± 0.3 b | 1.8 ± 0.1 a | 14.5 ± 0.1 a | 2.5 ± 0.2 b,c |
| HM8 | 49.2 ± 0.2 c | 34.1 ± 0.4 c | 81.9 ± 1.2 a,b | 1.8 ± 0.1 a | 13.1 ± 0.5 b | 1.9 ± 0.0 c |
| JMX22 | 53.1 ± 0.4 b,c | 32.6 ± 0.2 d | 83.9 ± 0.7 a | 1.9 ± 0.0 a | 13.0 ± 0.2 b | 2.2 ± 0.2 c |
| HG35 | 56.0 ± 0.6 b | 38.0 ± 0.3 a,b | 79.5 ± 0.6 b | 1.6 ± 0.2 a | 13.9 ± 0.2 a,b | 2.8 ± 0.1 a,b |
| JMT22 | 60.6 ± 0.4 a | 39.0 ± 0.4 a,b | 80.9 ± 1.0 a,b | 1.6 ± 0.1 a | 13.4 ± 0.1 b | 2.6 ± 0.3 b,c |
| Cultivars | Amylose (g/100 g DW) | fa DP6–12 (%) | fb1 DP13–24 (%) | fb2 DP25–36 (%) | fb3 DP > 36 (%) | Crystallinity (%) | Ratios of Infrared Band (1047 cm−1/1022 cm−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MY2 | 12.7 ± 0.1 b | 19.7 ± 0.2 b | 45.2 ± 0.3 a,b | 16.3 ± 0.2 b | 18.6 ± 0.1 a,b | 24.6 ± 0.2 a | 0.967 ± 0.005 a,b |
| EM596 | 14.3 ± 0.3 a,b | 20.5 ± 0.1 a | 45.5 ± 0.2 a | 16.2 ± 0.2 b | 17.4 ± 0.1 b | 24.0 ± 0.1 a,b | 0.954 ± 0.002 b,c |
| CM37 | 12.0 ± 0.0 b,c | 20.2 ± 0.4 a,b | 45.4 ± 0.5 a | 16.2 ± 0.4 b | 17.8 ± 0.3 b | 24.1 ± 0.3 a,b | 0.948 ± 0.003 c |
| NM2 | 12.1 ± 0.2 b,c | 20.2 ± 0.2 a,b | 44.9 ± 0.1 a,b | 16.5 ± 0.2 a,b | 17.9 ± 0.3 b | 22.2 ± 0.2 c | 0.954 ± 0.006 b,c |
| HM8 | 11.7 ± 0.1 c | 20.7 ± 0.0 a | 45.0 ± 0.1 a,b | 16.5 ± 0.2 a,b | 17.3 ± 0.2 b | 22.8 ± 0.2 b | 0.972 ± 0.002 a |
| JMX22 | 15.0 ± 0.4 a | 21.6 ± 0.3 a | 45.6 ± 0.4 a | 16.2 ± 0.3 b | 16.1 ± 0.2 c | 22.6 ± 0.1 b,c | 0.953 ± 0.010 b,c |
| HG35 | 10.4 ± 0.1 d | 19.7 ± 0.1 b | 45.4 ± 0.2 a | 17.0 ± 0.1 a | 17.6 ± 0.0 b | 23.1 ± 0.3 b | 0.956 ± 0.004 b |
| JMT22 | 12.6 ± 0.2 b | 19.7 ± 0.0 b | 44.4 ± 0.1 b | 16.6 ± 0.2 a,b | 18.8 ± 0.1 a | 24.4 ± 0.2 a | 0.953 ± 0.008 b,c |
| Cultivars | To (°C) | Tp (°C) | Tc (°C) | ∆H (J/g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MY2 | 57.8 ± 0.2 b | 61.9 ± 0.1 c | 67.4 ± 0.3 b | 12.6 ± 0.1 a |
| EM596 | 59.3 ± 0.1 a | 63.6 ± 0.2 a,b | 69.5 ± 0.2 a | 12.3 ± 0.2 a,b |
| CM37 | 59.2 ± 0.0 a | 63.8 ± 0.1 a,b | 69.0 ± 0.4 a,b | 12.1 ± 0.0 b |
| NM2 | 59.3 ± 0.3 a | 63.3 ± 0.3 b | 68.0 ± 0.1 b | 12.4 ± 0.3 a,b |
| HM8 | 57.9 ± 0.1 b | 62.2 ± 0.2 c | 67.8 ± 0.2 b | 12.7 ± 0.1 a |
| JMX22 | 58.1 ± 0.2 b | 62.6 ± 0.1 b,c | 68.4 ± 0.1 b | 12.7 ± 0.4 a |
| HG35 | 59.7 ± 0.4 a | 64.2 ± 0.1 a | 69.8 ± 0.4 a | 12.7 ± 0.2 a |
| JMT22 | 58.4 ± 0.1 b | 62.4 ± 0.2 c | 68.2 ± 0.5 b | 11.9 ± 0.1 b |
| Cultivars | PV (RVU) | HPV (RVU) | FV (RVU) | BD (RVU) | SB (RVU) | G’ (Pa) | G” (Pa) | tanδ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MY2 | 156 ± 2 b | 88 ± 1 b | 229 ± 4 c | 68 ± 1 b | 141 ± 6 b,c | 432 ± 6 c,d | 70 ± 3 c,d | 0.16 ± 0.01 a |
| EM596 | 129 ± 3 d | 77 ± 3 c | 217 ± 6 d | 52 ± 0 d | 140 ± 1 b,c | 488 ± 8 c,d | 74 ± 1 c | 0.15 ± 0.01 a,b |
| CM37 | 127 ± 1 d | 83 ± 1 c | 219 ± 2 d | 44 ± 3 e | 137 ± 3 c | 489 ± 15 c | 69 ± 1 c,d | 0.14 ± 0.00 b,c |
| NM2 | 138 ± 2 c | 91 ± 2 b | 234 ± 2 b,c | 47 ± 1 e | 142 ± 4 b,c | 891 ± 32 a | 106 ± 7 a | 0.12 ± 0.02 c |
| HM8 | 160 ± 6 b | 99 ± 4 a,b | 249 ± 4 b | 61 ± 2 c | 150 ± 2 b | 649 ± 31 b | 87 ± 4 b | 0.13 ± 0.01 c |
| JMX22 | 148 ± 4 b,c | 95 ± 3 a,b | 241 ± 3 b | 53 ± 2 d | 146 ± 2 b | 612 ± 9 b | 79 ± 2 b,c | 0.13 ± 0.01 c |
| HG35 | 221 ± 5 a | 106 ± 4 a | 324 ± 5 a | 116 ± 3 a | 218 ± 1 a | 430 ± 25 d | 54 ± 3 d | 0.13 ± 0.01 c |
| JMT22 | 151 ± 2 b,c | 85 ± 2 b,c | 240 ± 2 b | 65 ± 2 b,c | 155 ± 3 b | 382 ± 19 d | 62 ± 6 d | 0.16 ± 0.02 a,b |
| HI | TGW | TS | LC | PC | FC | AC | fa | fb1 | fb2 | fb3 | Cry% | RIB | To | Tp | Tc | ∆H | PV | HPV | FV | BD | SB | G’ | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TGW | −0.08 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| TS | −0.06 | −0.29 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| LC | −0.01 | 0.07 | 0.15 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| PC | −0.08 | −0.23 | −0.73 | −0.56 | |||||||||||||||||||
| FC | −0.39 | 0.57 | 0.01 | −0.24 | 0.06 | ||||||||||||||||||
| AC | −0.19 | −0.21 | 0.78 | 0.40 | −0.56 | 0.11 | |||||||||||||||||
| fa | −0.01 | −0.78 | 0.72 | 0.36 | −0.37 | −0.47 | 0.67 | ||||||||||||||||
| fb1 | −0.42 | −0.28 | 0.46 | 0.02 | −0.13 | 0.22 | 0.31 | 0.48 | |||||||||||||||
| fb2 | 0.64 | 0.26 | −0.60 | −0.10 | 0.28 | −0.05 | −0.77 | −0.53 | −0.34 | ||||||||||||||
| fb3 | −0.08 | 0.76 | −0.61 | −0.26 | 0.24 | 0.35 | −0.45 | −0.91 | −0.69 | 0.26 | |||||||||||||
| Cry% | −0.08 | 0.73 | 0.12 | −0.35 | −0.25 | 0.55 | 0.07 | −0.54 | −0.15 | −0.23 | 0.64 | ||||||||||||
| RIB | −0.10 | 0.27 | −0.03 | 0.58 | −0.50 | −0.38 | −0.22 | −0.04 | −0.15 | 0.13 | 0.10 | −0.04 | |||||||||||
| To | −0.05 | −0.12 | −0.33 | −0.57 | 0.69 | 0.54 | −0.34 | −0.29 | 0.23 | 0.35 | 0.01 | −0.16 | −0.63 | ||||||||||
| Tp | −0.06 | −0.23 | −0.18 | −0.62 | 0.63 | 0.46 | −0.30 | −0.14 | 0.42 | 0.28 | −0.17 | −0.17 | −0.64 | 0.96 | |||||||||
| Tc | 0.10 | −0.12 | 0.16 | −0.56 | 0.23 | 0.53 | −0.11 | −0.04 | 0.49 | 0.26 | −0.28 | 0.01 | −0.57 | 0.81 | 0.89 | ||||||||
| ∆H | −0.03 | −0.15 | 0.07 | 0.63 | −0.30 | −0.33 | −0.06 | 0.37 | 0.51 | 0.17 | −0.56 | −0.54 | 0.58 | −0.23 | −0.12 | −0.10 | |||||||
| PV | 0.54 | 0.30 | −0.36 | 0.06 | −0.01 | −0.05 | −0.61 | −0.34 | 0.05 | 0.87 | 0.00 | −0.18 | 0.27 | 0.17 | 0.21 | 0.30 | 0.51 | ||||||
| HPV | 0.54 | −0.16 | −0.31 | 0.25 | 0.05 | −0.54 | −0.52 | 0.07 | 0.07 | 0.70 | −0.31 | −0.60 | 0.38 | −0.03 | 0.04 | 0.01 | 0.72 | 0.83 | |||||
| FV | 0.60 | 0.12 | −0.36 | −0.04 | 0.13 | −0.07 | −0.62 | −0.26 | 0.07 | 0.89 | −0.10 | −0.32 | 0.11 | 0.33 | 0.37 | 0.42 | 0.46 | 0.97 | 0.84 | ||||
| BD | 0.48 | 0.45 | −0.34 | −0.02 | −0.02 | 0.16 | −0.59 | −0.46 | 0.05 | 0.85 | 0.12 | 0.00 | 0.19 | 0.25 | 0.27 | 0.39 | 0.39 | 0.97 | 0.68 | 0.93 | |||
| SB | 0.57 | 0.22 | −0.35 | −0.15 | 0.15 | 0.10 | −0.61 | −0.35 | 0.08 | 0.89 | −0.02 | −0.18 | 0.00 | 0.43 | 0.46 | 0.54 | 0.33 | 0.95 | 0.72 | 0.98 | 0.96 | ||
| G’ | −0.15 | −0.65 | −0.23 | 0.37 | 0.38 | −0.45 | 0.04 | 0.43 | −0.04 | −0.11 | −0.35 | −0.82 | 0.06 | 0.07 | −0.00 | −0.32 | 0.28 | −0.28 | 0.18 | −0.18 | −0.44 | −0.30 | |
| G” | −0.30 | −0.55 | −0.10 | 0.46 | 0.20 | −0.41 | 0.20 | 0.44 | −0.11 | −0.32 | −0.25 | −0.65 | 0.18 | −0.13 | −0.21 | −0.49 | 0.19 | −0.49 | −0.04 | −0.43 | −0.62 | −0.54 | 0.95 |
| PC 1 | PC 2 | PC 3 | PC 4 | PC 5 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HI | 0.172 | 0.144 | −0.057 | 0.021 | −0.576 |
| TGW | 0.130 | −0.212 | −0.322 | 0.105 | 0.226 |
| TS | −0.200 | 0.036 | 0.073 | 0.404 | −0.176 |
| LC | −0.116 | 0.266 | −0.203 | 0.062 | 0.231 |
| Protein | 0.119 | −0.097 | 0.237 | −0.393 | 0.054 |
| Fiber | 0.068 | −0.309 | 0.079 | 0.166 | 0.320 |
| AC | −0.279 | −0.005 | 0.055 | 0.252 | −0.077 |
| Fa | −0.221 | 0.250 | 0.189 | 0.161 | −0.145 |
| Fb1 | −0.034 | 0.079 | 0.268 | 0.320 | 0.341 |
| Fb2 | 0.331 | 0.093 | −0.059 | −0.103 | −0.088 |
| Fb3 | 0.097 | −0.281 | −0.274 | −0.218 | 0.050 |
| Cry% | −0.004 | −0.350 | −0.208 | 0.182 | 0.003 |
| RIB | −0.012 | 0.201 | −0.335 | 0.013 | 0.258 |
| To | 0.179 | −0.138 | 0.353 | −0.090 | 0.127 |
| Tp | 0.174 | −0.104 | 0.395 | −0.004 | 0.102 |
| Tc | 0.174 | −0.106 | 0.339 | 0.217 | −0.011 |
| ΔH | 0.045 | 0.354 | −0.023 | 0.144 | 0.355 |
| PV | 0.319 | 0.163 | −0.075 | 0.109 | 0.041 |
| HPV | 0.214 | 0.336 | −0.028 | −0.018 | −0.017 |
| FV | 0.325 | 0.173 | 0.020 | 0.072 | −0.023 |
| BD | 0.332 | 0.078 | −0.081 | 0.152 | 0.070 |
| SB | 0.341 | 0.100 | 0.036 | 0.103 | −0.027 |
| G’ | −0.127 | 0.230 | 0.153 | −0.350 | 0.137 |
| G” | −0.208 | 0.183 | 0.073 | −0.326 | 0.168 |
| Proportion of Variance Interpretation (%) | 32.100 | 22.590 | 18.310 | 14.280 | 7.310 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ni, D.; Yang, F.; Lin, L.; Sun, C.; Ye, X.; Wang, L.; Kong, X. Interrelating Grain Hardness Index of Wheat with Physicochemical and Structural Properties of Starch Extracted Therefrom. Foods 2022, 11, 1087. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11081087
Ni D, Yang F, Lin L, Sun C, Ye X, Wang L, Kong X. Interrelating Grain Hardness Index of Wheat with Physicochemical and Structural Properties of Starch Extracted Therefrom. Foods. 2022; 11(8):1087. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11081087
Chicago/Turabian StyleNi, Derang, Fan Yang, Lin Lin, Chongde Sun, Xingqian Ye, Li Wang, and Xiangli Kong. 2022. "Interrelating Grain Hardness Index of Wheat with Physicochemical and Structural Properties of Starch Extracted Therefrom" Foods 11, no. 8: 1087. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11081087
APA StyleNi, D., Yang, F., Lin, L., Sun, C., Ye, X., Wang, L., & Kong, X. (2022). Interrelating Grain Hardness Index of Wheat with Physicochemical and Structural Properties of Starch Extracted Therefrom. Foods, 11(8), 1087. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11081087







