Lactobacillus fermentum Stimulates Intestinal Secretion of Immunoglobulin A in an Individual-Specific Manner
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bacterial Treatment
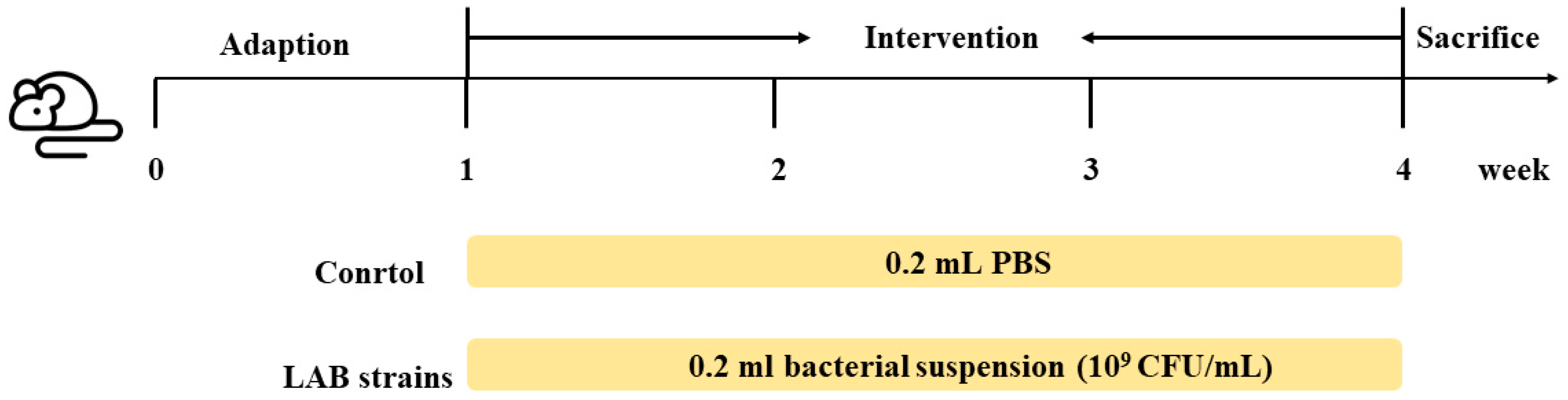
2.2. Animal Experiments
2.3. Tissue Processing
2.4. Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction
2.5. Determination of Short Chain Fatty Acids
2.6. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay
2.7. Immunofluorescence of IgA in Plasma Cells in Mouse Intestinal Segments
2.8. Isolation and Identification of IgA-Coated Bacteria
2.9. 16 S rDNA High-Throughput Sequencing
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. L. fermentum Affects Intestinal Secretion of IgA
3.2. L. fermentum Affects the Host Gut Microbiota and IgA-Coated Bacteria
3.3. L. fermentum May Stimulate Intestinal Production of IgA in Different Ways
3.4. L. fermentum May Produce IgA in a Non-Inflammatory Manner
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Feifei, X.; Newby, J.M.; Schiller, J.L.; Schroeder, H.A.; Wessler, T.; Chen, A.; Forest, M.G.; Lai, S.K. Modeling Barrier Properties of Intestinal Mucus Reinforced with IgG and Secretory IgA against Motile Bacteria. ACS Infect. Dis. 2019, 5, 1570–1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinhoff, U. Who controls the crowd? New findings and old questions about the intestinal microflora. Immunol. Lett. 2005, 99, 12–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maldonado Galdeano, C.; Cazorla, S.I. Beneficial Effects of Probiotic Consumption on the Immune System. Ann. Nutr. Metab. 2019, 74, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fagarasan, S.; Kawamoto, S.; Kanagawa, O.; Suzuki, K. Adaptive Immune Regulation in the Gut: T Cell–Dependent and T Cell–Independent IgA Synthesis. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2010, 28, 243–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.Y.; Seignez, C.; Ahl, D.; Giraud, A.; Guo, F.; Sedin, J.; Walden, T.; Roos, S.; Holm, L.; Bertilsson, S.; et al. Bacteria-immune cell interactions at the intestinal Peyer’s Patches. Free. Radic. Biol. Med. 2019, 139, S3. [Google Scholar]
- Yoda, K.; Miyazawa, K.; Hosoda, M.; Hiramatsu, M.; Yan, F.; He, F. Lactobacillus GG-fermented milk prevents DSS-induced colitis and regulates intestinal epithelial homeostasis through activation of epidermal growth factor receptor. Eur. J. Nutr. 2014, 53, 105–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shroff, K.E.; Meslin, K.; Cebra, J.J. Commensal enteric bacteria engender a self-limiting humoral mucosal immune response while permanently colonizing the gut. Infect. Immun. 1995, 63, 3904–3913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Macpherson, A.J.; Hunziker, L.; McCoy, K.; Lamarre, A. IgA responses in the intestinal mucosa against pathogenic and non-pathogenic microorganisms. Microbes Infect. 2001, 3, 1021–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.; Basu, S.; Bal, V.; Rath, S.; George, A. Gut IgA abundance in adult life is a major determinant of resistance to dextran sodium sulfate-colitis and can compensate for the effects of inadequate maternal IgA received by neonates. Immunology 2019, 158, 19–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawashima, T.; Hayashi, K.; Kosaka, A.; Kawashima, M.; Igarashi, T.; Tsutsui, H.; Tsuji, N.M.; Nishimura, I.; Hayashi, T.; Obata, A. Lactobacillus plantarum strain YU from fermented foods activates Th1 and protective immune responses. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2011, 11, 2017–2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawashima, T.; Ikari, N.; Kouchi, T.; Kowatari, Y.; Kubota, Y.; Shimojo, N.; Tsuji, N.M. The molecular mechanism for activating IgA production by Pediococcus acidilactici K15 and the clinical impact in a randomized trial. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 5065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azagra-Boronat, I.; Tres, A. Lactobacillus fermentum CECT5716 supplementation in rats during pregnancy and lactation affects mammary milk composition. J. Dairy Sci. 2020, 103, 2982–2992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Castillo, V.; Komatsu, R. Evaluation of the Immunomodulatory Activities of the Probiotic Strain Lactobacillus fermentum UCO-979C. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Takeuchi, T.; Miyauchi, E. Acetate differentially regulates IgA reactivity to commensal bacteria. Nature 2021, 595, 560–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashraf, R.; Shah, N.P. Immune system stimulation by probiotic microorganisms. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2014, 54, 938–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geuking, M.B.; McCoy, K.D. The function of secretory IgA in the context of the intestinal continuum of adaptive immune responses in host-microbial mutualism. Semin. Immunol. 2012, 24, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caixin, N.; Xing, J. Evaluation of antioxidant activity of Lactobacillus in vivo using Caenorhabditis elegans and comparison with its antioxidant parameters in vitro. Food Ferment. Ind. 2019, 3, 21–27. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, Y.; Jeon, B.Y.; Shim, T.S.; Jin, H.; Cho, S.N.; Lee, H. Development of a highly sensitive one-tube nested real-time PCR for detecting Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2014, 80, 299–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Wang, L. A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of Bifidobacterium bifidum CCFM16 for manipulation of the gut microbiota and relief from chronic constipation. Food Funct. 2022, 13, 1628–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mattioli, C.A.; Tomasi, T.B. The life span of IgA plasma cells from the mouse intestine. J. Exp. Med. 1973, 138, 452–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sun, J.; Qi, C. IgA-Targeted Lactobacillus jensenii Modulated Gut Barrier and Microbiota in High-Fat Diet-Fed Mice. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Qi, C.; Ding, M. Sex-dependent modulation of immune development in mice by secretory IgA-coated Lactobacillus reuteri isolated from breast milk. J. Dairy Sci. 2021, 104, 3863–3875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, P.; Chen, Y. Pediococcus acidilactici CCFM6432 mitigates chronic stress-induced anxiety and gut microbial abnormalities. Food Funct. 2021, 12, 11241–11249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huus, K.E.; Bauer, K.C. Commensal Bacteria Modulate Immunoglobulin A Binding in Response to Host Nutrition. Cell Host Microbe 2020, 27, 909–921.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macpherson, A.J.; Yilmaz, B. IgA Function in Relation to the Intestinal Microbiota. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2018, 36, 359–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Mogno, I. Fecal IgA Levels Are Determined by Strain-Level Differences in Bacteroides ovatus and Are Modifiable by Gut Microbiota Manipulation. Cell Host Microbe 2020, 27, 467–475.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Daniel, H.; Markus, A.; Diard, M.; Loverdo, C.; Slack, E. Growing, evolving and sticking in a flowing environment: Understanding IgA interactions with bacteria in the gut. Immunology 2020, 159, 52–62. [Google Scholar]
- Bunker, J.J.; Flynn, T.M. Innate and Adaptive Humoral Responses Coat Distinct Commensal Bacteria with Immunoglobulin A. Immunity 2015, 43, 541–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Donaldson, G.P.; Ladinsky, M.S. Gut microbiota utilize immunoglobulin A for mucosal colonization. Science 2018, 360, 795–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fadlallah, J.; El Kafsi, H.; Sterlin, D.; Juste, C.; Parizot, C.; Dorgham, K.; Autaa, G.; Gouas, D.; Almeida, M.; Lepage, P.; et al. Microbial ecology perturbation in human IgA deficiency. Sci. Transl. Med. 2018, 10, eaan1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guzman-Bautista, E.R.; Suzuki, K. Bacteria-immune cells dialog and the homeostasis of the systems. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2020, 66, 82–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Z.-Q.; Tu, P. Gu-Ben-Fang-Xiao attenuates allergic airway inflammation by inhibiting BAFF-mediated B cell activation. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 132, 110801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, F.; Cao, H.W. Colon-specific delivery of a probiotic-derived soluble protein ameliorates intestinal inflammation in mice through an EGFR-dependent mechanism. J. Clin. Investig. 2011, 121, 2242–2253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ramanan, D.; Sefik, E. An Immunologic Mode of Multigenerational Transmission Governs a Gut Treg Setpoint. Cell 2020, 181, 1276–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, N.; Guo, P.; Zhang, J.; He, T.; Kim, S.W.; Zhang, G.; Ma, X. Nutrients Mediate Intestinal Bacteria-Mucosal Immune Crosstalk. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bunker, J.J.; Bendelac, A. IgA Responses to Microbiota. Immunity 2018, 49, 211–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schwab, C.; Ganzle, M. Lactic acid bacteria fermentation of human milk oligosaccharide components, human milk oligosaccharides and galactooligosaccharides. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2011, 315, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dalile, B.; Van Oudenhove, L.; Vervliet, B. The role of short-chain fatty acids in microbiota-gut-brain communication. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 16, 461–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujihashi, K.; McGhee, J.R. Cytoking specific elispot assay single cell analysis of IL-2, IL-4 and IL-6 production cells. J. Immunol. Methods 1993, 160, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isailovic, N.; Daigo, K. Interleukin-17 and innate immunity in infections and chronic inflammation. J. Autoimmun. 2015, 60, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Doare, K.; Bellis, K.; Faal, A.; Birt, J. SIgA, TGF-beta1, IL-10, and TNF alpha in Colostrum Are Associated with Infant Group B Streptococcus Colonization. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pannaraj, P.S.; Li, F. Association between Breast Milk Bacterial Communities and Establishment and Development of the Infant Gut Microbiome. JAMA Pediatr. 2017, 171, 647–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, A.K.; Hollander, G.A. Evolution of the immune system in humans from infancy to old age. Proc. Biol. Sci. 2015, 282, 20143085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goulet, O. Potential role of the intestinal microbiota in programming health and disease. Nutr. Rev. 2015, 73 (Suppl. S1), 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Strain | Species | Origin | Age |
|---|---|---|---|
| 12-1 | Lactobacillus fermenti | Human feces, male | 0 |
| X6L1 | Lactobacillus fermenti | Human feces, female | 0 |
| S24-1 | Lactobacillus fermenti | Human feces, female | 100 |
| 20M5 | Lactobacillus fermenti | Human feces, male | 83 |
| 24M1 | Lactobacillus fermenti | Human feces, female | 75 |
| Gene | Primer (5′-3′) |
|---|---|
| pIgR | F-AGGCAATGACAACATGGGG |
| R-ATGTCAGCTTCCTCCTTGG | |
| MyD88 | F-CACCTGTGTCTGGTCCATTG |
| R-CTGTTGGACACCTGGAGACA | |
| BAFFR | F-GAAACTGCGTGTCCTGTGAG |
| R-CTGAGGCTGCAGAGCTGTC | |
| EGFR | F-GCCATCTGGGCCAAAGATACC |
| R-GTCTTCGCATGAATAGGCCAAT | |
| ACIDA | F-CGTGGTGAAGAGGAGAGATAGTG |
| R-CAGTCTGAGATGTAGCGTAGGAA | |
| GAPDH | F-TGTGTCCGTCGTGGATCTGA |
| R-CCTGCTTCACCACCTTCTTGAT |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mei, L.; Chen, Y.; Wang, J.; Lu, J.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, H.; Wang, G.; Chen, W. Lactobacillus fermentum Stimulates Intestinal Secretion of Immunoglobulin A in an Individual-Specific Manner. Foods 2022, 11, 1229. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11091229
Mei L, Chen Y, Wang J, Lu J, Zhao J, Zhang H, Wang G, Chen W. Lactobacillus fermentum Stimulates Intestinal Secretion of Immunoglobulin A in an Individual-Specific Manner. Foods. 2022; 11(9):1229. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11091229
Chicago/Turabian StyleMei, Liya, Ying Chen, Jialiang Wang, Jian Lu, Jianxin Zhao, Hao Zhang, Gang Wang, and Wei Chen. 2022. "Lactobacillus fermentum Stimulates Intestinal Secretion of Immunoglobulin A in an Individual-Specific Manner" Foods 11, no. 9: 1229. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11091229
APA StyleMei, L., Chen, Y., Wang, J., Lu, J., Zhao, J., Zhang, H., Wang, G., & Chen, W. (2022). Lactobacillus fermentum Stimulates Intestinal Secretion of Immunoglobulin A in an Individual-Specific Manner. Foods, 11(9), 1229. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11091229






