Effect of Aliphatic Aldehydes on Flavor Formation in Glutathione–Ribose Maillard Reactions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Chemicals
2.2. Experimental Methods
2.2.1. Model Reactions
2.2.2. UV Absorbance and Fluorescence Analysis
2.2.3. E-Nose and E-Tongue Analysis
2.2.4. HS-SPME-GC-MS Analysis
2.2.5. UPLC-MS Analysis
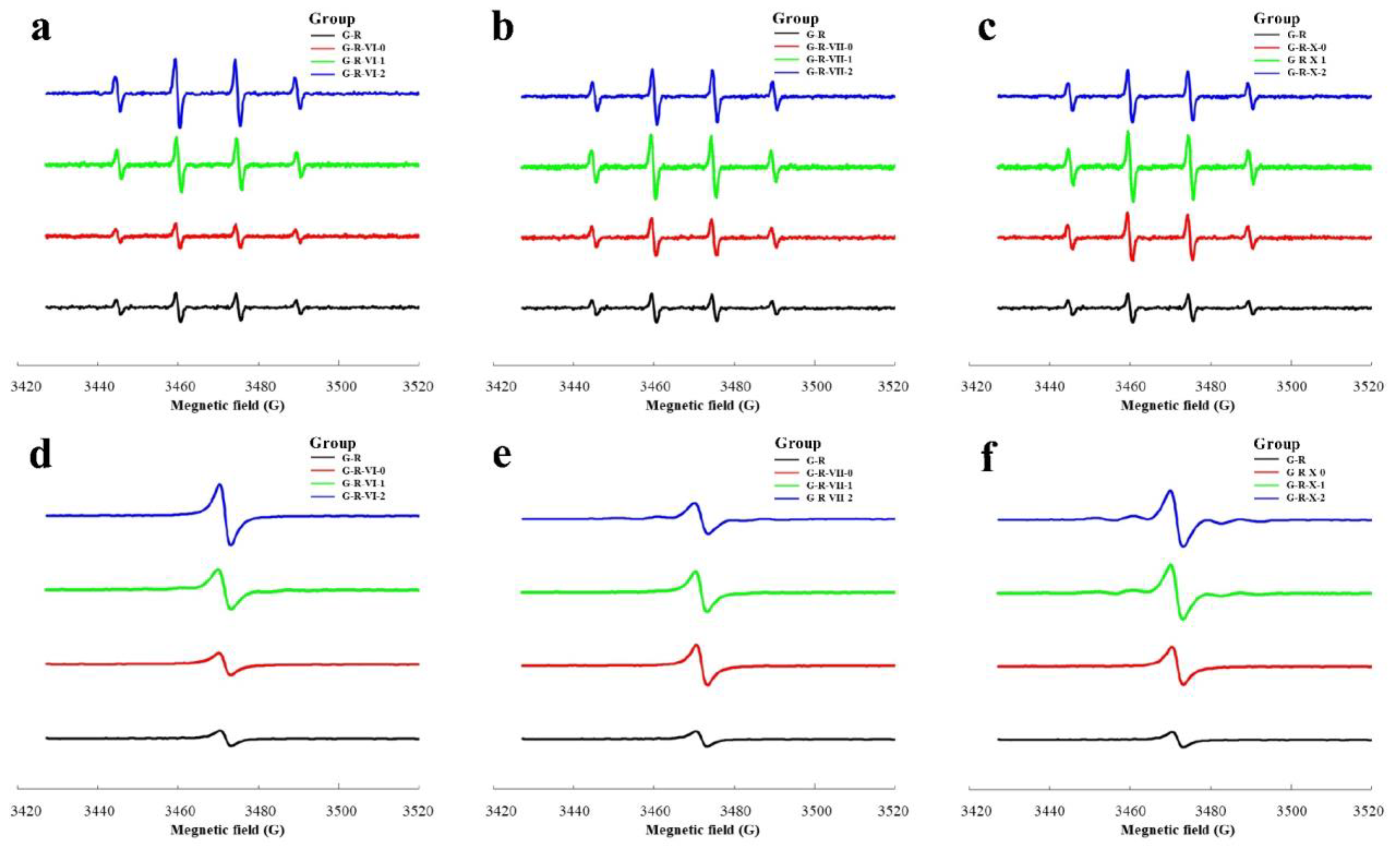
2.2.6. ESR Analysis
2.2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
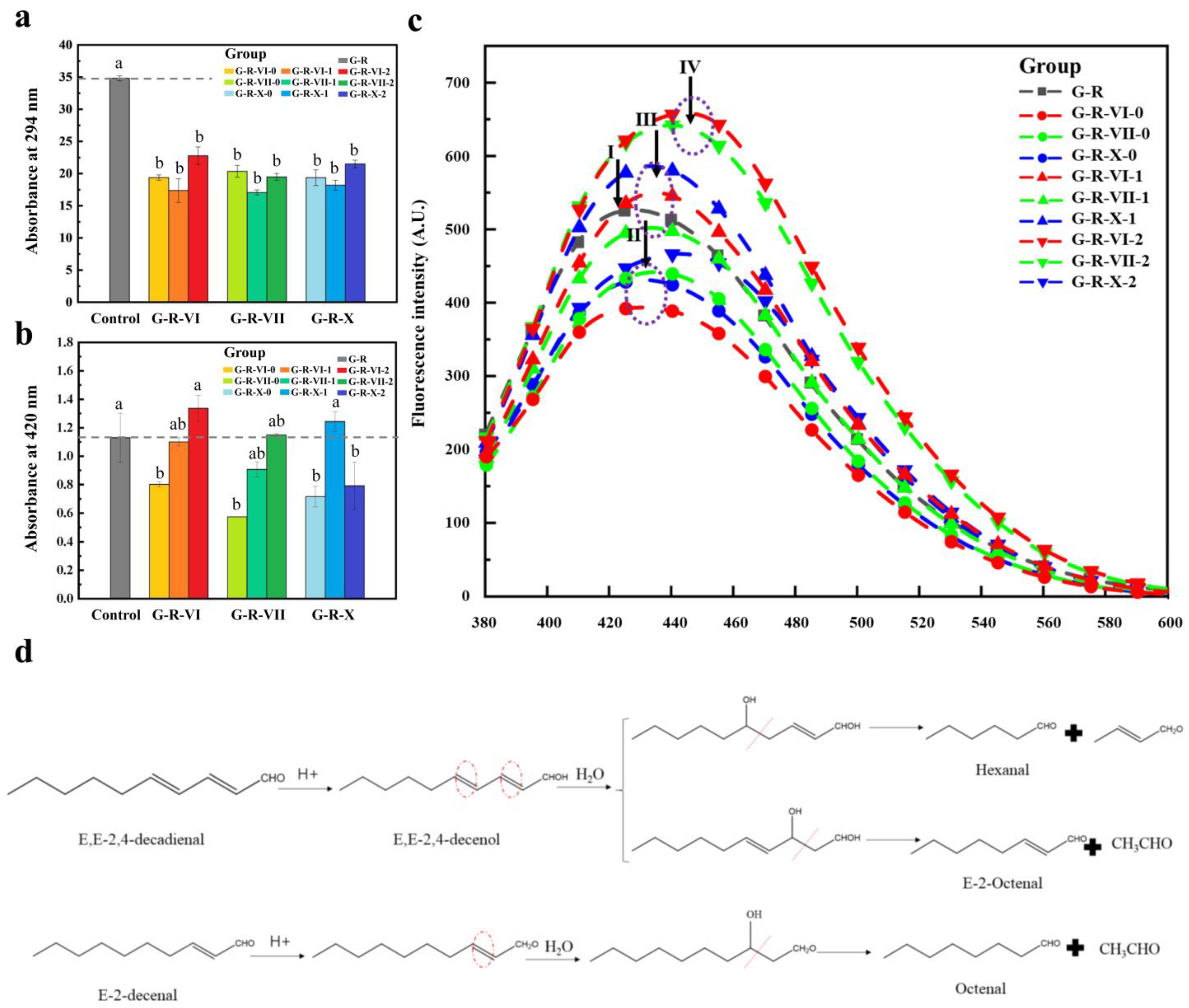
3.1. UV Absorbance and Fluorescence Analysis
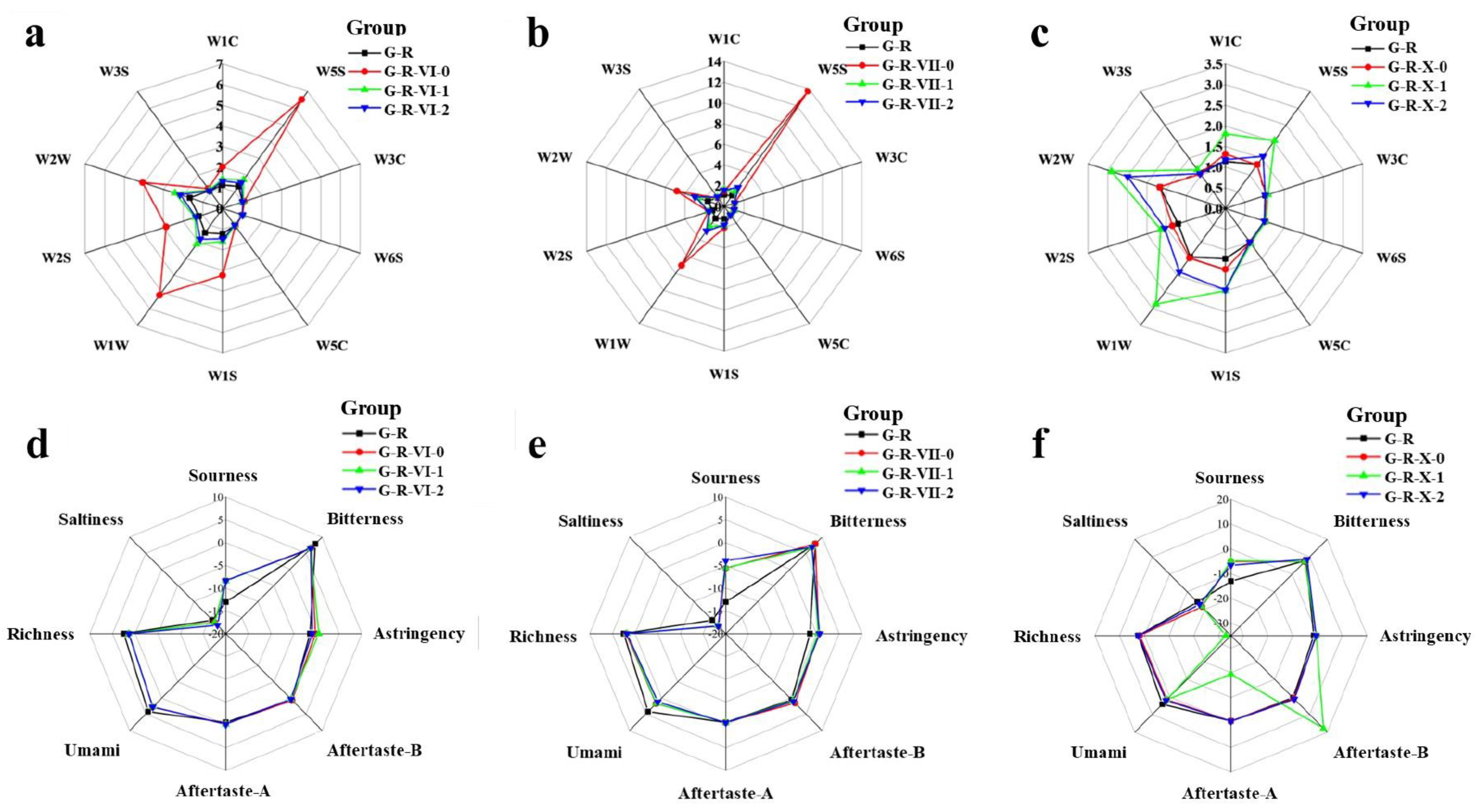
3.2. E-Nose and E-Tongue Analysis
3.3. Differential Analysis of the MRPs Produced by MR Systems with Different Aliphatic Aldehydes Based on GC-MS and HPLC-MS
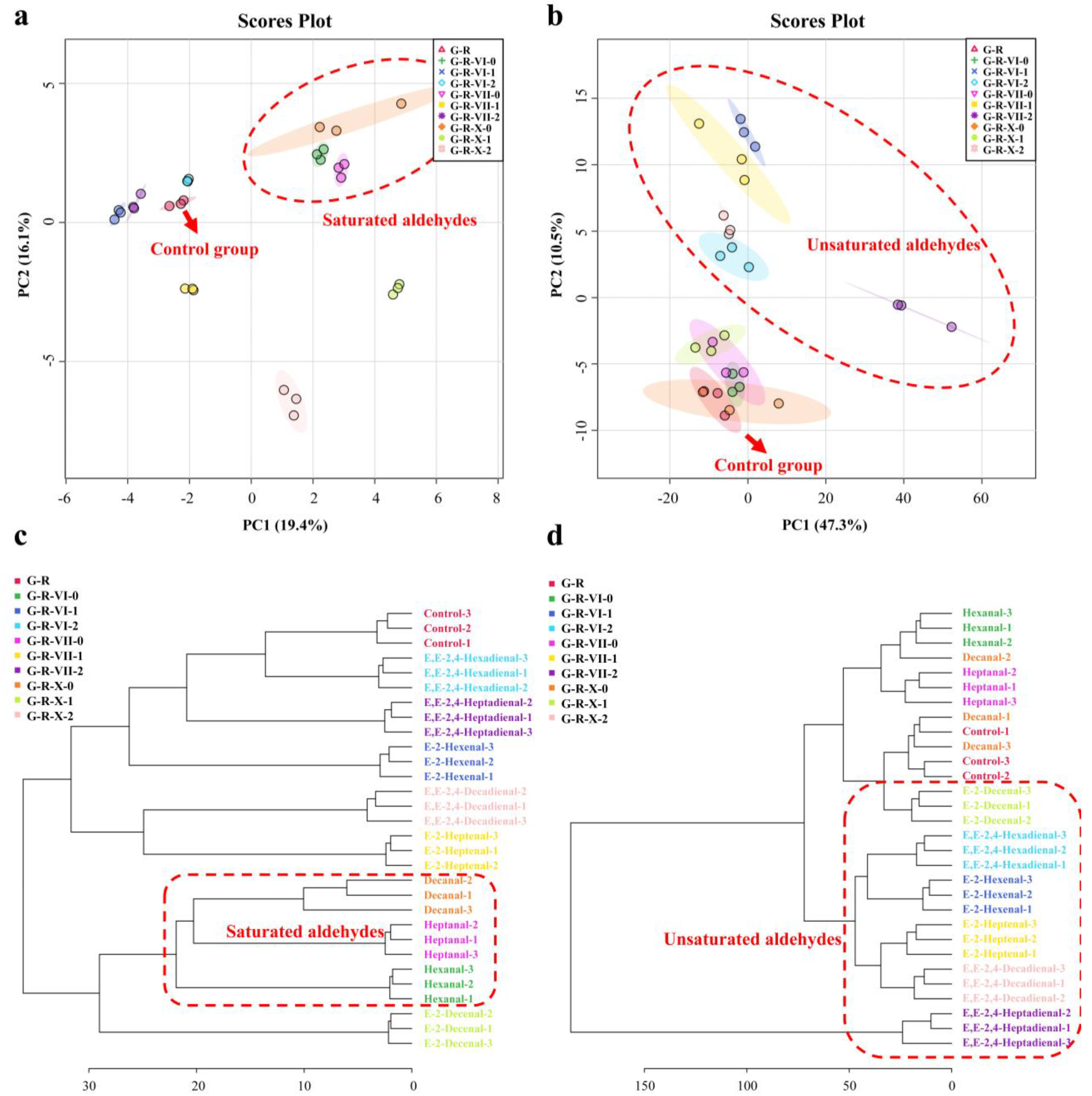
3.3.1. Principal Component Analysis and Hierarchical Cluster Analysis
3.3.2. VOC Analysis Based on GC-MS
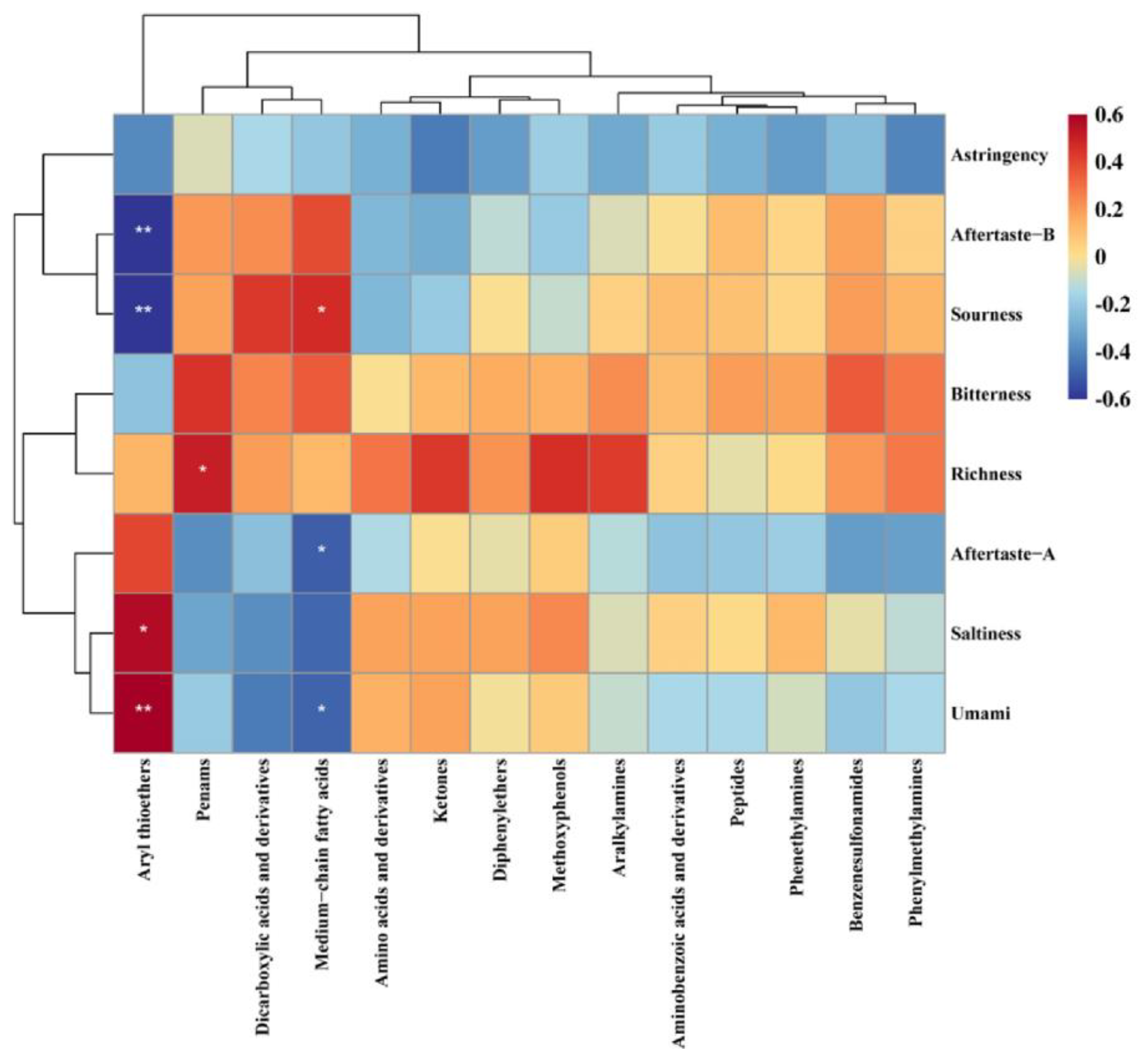
3.3.3. Nonvolatile Compound Analysis based on UPLC-MS
3.4. Antioxidant Activity Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hemmler, D.; Roullier-Gall, C.; Marshall, J.W.; Rychlik, M.; Taylor, A.J.; Schmitt-Kopplin, P. Insights into the chemistry of non-enzymatic browning reactions in different ribose-amino acid model systems. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 16879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamanna, N.; Mahmood, N. Food processing and Maillard reaction products: Effect on human health and nutrition. Int. J. Food Sci. 2015, 2015, 526762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nooshkam, M.; Varidi, M.; Bashash, M. The Maillard reaction products as food-born antioxidant and antibrowning agents in model and real food systems. Food Chem. 2019, 275, 644–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jahn, M.P.; Cavagni, G.M.; Kaiser, D.; Kucharski, L.C. Osmotic effect of choline and glycine betaine on the gills and hepatopancreas of the chasmagnathus granulata crab submitted to hyperosmotic stress. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2006, 334, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, C.F.; Smith, D.M. Use of volatiles as indicators of lipid oxidation in muscle foods. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2006, 5, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hidalgo, F.J.; Zamora, R. Interplay between the Maillard reaction and lipid peroxidation in biochemical systems. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2005, 1043, 319–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, S.I.F.S.; Jongen, W.M.F.; van Boekel, M.A.J.S. A review of Maillard reaction in food and implications to kinetic modelling. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2000, 11, 364–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farmer, L.J.; Mottram, D.S. Interaction of lipid in the maillard reaction between cysteine and ribose: The effect of a triglyceride and three phospholipids on the volatile products. J. Sci. Food Agric. 1990, 53, 505–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmore, J.S.; Campo, M.M.; Enser, M.; Mottram, D.S. Effect of lipid composition on meat-like model systems containing cysteine, ribose, and polyunsaturated fatty acids. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2002, 50, 1126–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.M.; Kwon, G.Y.; Kim, K.O.; Kim, Y.S. Metabolomic approach for determination of key volatile compounds related to beef flavor in glutathione-Maillard reaction products. Anal. Chim. Acta 2011, 703, 204–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Xie, J.C.; Zhang, L.; Du, R.Q.; Cao, C.C.; Wang, M.; Acree, T.; Sun, B.G. Aromatic effect of fat and oxidized fat on a meat-like model reaction system of cysteine and glucose. Flavour. Fragr. J. 2015, 30, 320–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.S.; Lee, Y.S. Effect of reaction pH on enolization and racemization reactions of glucose and fructose on heating with amino acid enantiomers and formation of melanoidins as result of the Maillard reaction. Food Chem. 2008, 108, 582–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werkhoff, P.; Bruening, J.; Emberger, R.; Guentert, M.; Koepsel, M.; Kuhn, W.; Surburg, H. Isolation and characterization of volatile sulfur-containing meat flavor components in model systems. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1990, 38, 777–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, L.; Zhou, Z.; Zhao, Z.Y.; Huang, X.H.; Liu, R.; Dong, X.P.; Zhu, B.W. Rapid identification of different cinnamon using coated direct inlet probe coupled with atmospheric-pressure chemical ionization mass spectrometry. Food Anal. Methods 2021, 14, 1402–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.H.; Zheng, X.; Chen, Z.H.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Du, M.; Dong, X.P.; Qin, L.; Zhu, B.W. Fresh and grilled eel volatile fingerprinting by E-nose, GC-O, GC–MS and GC × GC-QTOF combined with purge and trap and solvent-assisted flavor evaporation. Food Res. Int. 2019, 115, 32–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chong, J.; Soufan, O.; Li, C.; Caraus, I.; Li, S.Z.; Bourque, G.; Wishart, D.S.; Xia, J.G. MetaboAnalyst 4.0: Towards more transparent and integrative metabolomics analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, W486–W494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajandouz, E.H.; Tchiakpe, L.S.; Ore, F.D.; Benajiba, A.; Puigserver, A. Effects of pH on caramelization and Maillard reaction kinetics in fructose-lysine model systems antioxidant activity of coffee model systems. J. Food Sci. 2001, 66, 926–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamora, R.; Lavado-Tena, C.M.; Hidalgo, F.J. Oligomerization of reactive carbonyls in the presence of ammonia-producing compounds: A route for the production of pyridines in foods. Food Chem. 2020, 304, 125284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Wang, T.Z.; Xie, J.C.; Xiao, Q.F.; Cheng, J.; Chen, F.; Wang, S.; Sun, B.G. Formation mechanism of aroma compounds in a glutathione-glucose reaction with fat or oxidized fat. Food Chem. 2019, 270, 436–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, A.; Wu, W.; Soladoye, O.P.; Aluko, R.E.; Bak, K.H.; Fu, Y.; Zhang, Y.H. Maillard reaction of food-derived peptides as a potential route to generate meat flavor compounds: A review. Food Res. Int. 2022, 151, 110823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitfield, F.B.; Mottram, D.S. Volatiles from interactions of Maillard reactions and lipids. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 1992, 31, 1–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, C.K.; Ni, Z.J.; Thakur, K.; Liao, A.M.; Huang, J.H.; Wei, Z.J. Aromatic effects of immobilized enzymatic oxidation of chicken fat on flaxseed (Linum usitatissimum L.) derived Maillard reaction products. Food Chem. 2020, 306, 125560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adams, A.; Kitrytė, V.; Venskutonis, R.; De Kimpe, N. Model studies on the pattern of volatiles generated in mixtures of amino acids, lipid-oxidation-derived aldehydes, and glucose. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 1449–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maniruzzaman, M.; Douroumis, D. An in-vitro–in-vivo taste assessment of bitter drug: Comparative electronic tongues study. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2014, 67, 43–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnett, S.M.; Diako, C.; Ross, C.F. Identification of a salt blend: Application of the electronic tongue, consumer evaluation, and mixture design methodology. J. Food Sci. 2019, 84, 327–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marjanska, E.; Szpakowska, M. Combination of instrumental and qualitative descriptive analysis for evaluation of selected tonic waters quality features. J. Texture Stud. 2020, 51, 870–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, C.F. Considerations of the use of the electronic tongue in sensory science. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2021, 40, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellisle, F. Glutamate and the umami taste: Sensory, metabolic, nutritional and behavioural considerations. A review of the literature published in the last 10 years. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 1999, 23, 423–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domínguez, R.; Pateiro, M.; Gagaoua, M.; Barba, F.J.; Zhang, W.G.; Lorenzo, J.M. A comprehensive review on lipid oxidation in meat and meat products. Antioxidants 2019, 8, 429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.M.; Jo, Y.J.; Kim, Y.S. Investigation of the aroma-active compounds formed in the Maillard reaction between glutathione and reducing sugars. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 3116–3124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blasi, F.; Chiesi, C.; Spogli, R.; Cossignani, L.; Nocchetti, M. Oxidative stability of long-chain fatty acids with different unsaturation degrees into layered double hydroxides. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 7035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, R.A.; Hamilton-Kemp, T.R.; Hildebrand, D.F.; McCracken, C.T., Jr.; Collins, R.W.; Fleming, P.D. Structure-antifungal activity relationships among volatile C6 and C9 aliphatic aldehydes, ketones, and alcohols. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1994, 42, 1563–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.; Kerr, B.J.; Curry, S.M.; Chen, C. Identification of C9-C11 unsaturated aldehydes as prediction markers of growth and feed intake for non-ruminant animals fed oxidized soybean oil. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2020, 11, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miranda, L.T.; Rakovski, C.; Were, L.M. Effect of Maillard reaction products on oxidation products in ground chicken breast. Meat Sci. 2012, 90, 352–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Limacher, A.; Kerler, J.; Davidek, T.; Schmalzried, F.; Blank, I. Formation of furan and methylfuran by Maillard-type reactions in model systems and food. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 3639–3647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Wang, T.; Xie, J.; Xiao, Q.; Du, W.; Wang, Y.; Cheng, J.; Wang, S. Meat flavor generation from different composition patterns of initial Maillard stage intermediates formed in heated cysteine-xylose-glycine reaction systems. Food Chem. 2019, 274, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valle, M.d. Bioinspired sensor systems. Sensors 2011, 11, 10180–10186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, Y.; Habara, M.; Ikezazki, H.; Chen, R.G.; Naito, Y.; Toko, K. Advanced taste sensors based on artificial lipids with global selectivity to basic taste qualities and high correlation to sensory scores. Sensors 2010, 10, 3411–3443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desbois, A.P.; Smith, V.J. Antibacterial free fatty acids: Activities, mechanisms of action and biotechnological potential. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2010, 85, 1629–1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.A.; Rhee, M.S. Marked synergistic bactericidal effects and mode of action of medium-chain fatty acids in combination with organic acids against Escherichia coli O157:H7. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 79, 6552–6560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, J.Y.; Shue, Y.S.; Chang, H.-M. Antioxidative activity of roasted and defatted peanut kernels. Food Res. Int. 2001, 34, 639–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charurin, P.; Ames, J.M.; del Castillo, M.D. Antioxidant activity of coffee model systems. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2002, 50, 3751–3756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartoszek, M.; Polak, J. A comparison of antioxidative capacities of fruit juices, drinks and nectars, as determined by EPR and UV–vis spectroscopies. Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2016, 153, 546–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Locatelli, M.; Gindro, R.; Travaglia, F.; Coïsson, J.D.; Rinaldi, M.; Arlorio, M. Study of the DPPH-scavenging activity: Development of a free software for the correct interpretation of data. Food Chem. 2009, 114, 889–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zang, S.; Tian, S.Z.; Jiang, J.; Han, D.D.; Yu, X.Y.; Wang, K.; Li, D.; Lu, D.Y.; Yu, A.M.; Zhang, Z.W. Determination of antioxidant capacity of diverse fruits by electron spin resonance (ESR) and UV–vis spectrometries. Food Chem. 2017, 221, 1221–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Yuan, X.P.; Jin, Z.Y.; Tian, Y.; Song, H.L. Free radical and reactive oxygen species scavenging activities of peanut skins extract. Food Chem. 2007, 104, 242–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burns, J.M.; Cooper, W.J.; Ferry, J.L.; King, D.W.; DiMento, B.P.; McNeill, K.; Miller, C.J.; Miller, W.L.; Peake, B.M.; Rusak, S.A.; et al. Methods for reactive oxygen species (ROS) detection in aqueous environments. Aquat. Sci. 2012, 74, 683–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konosu, S. Taste of fish and shellfish with special reference to taste-producing substances. Nippon. Shokuhin Kogyo Gakkaishi 1973, 20, 432–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Abbreviation | Class | Components | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Amino Compounds | Reducing Sugars | Aliphatic Aldehydes | ||
| G-R | Control group | GSH | ribose | - |
| G-R-VI-0 | G-R-VI groups | GSH | ribose | Hexanal |
| G-R-VI-1 | GSH | ribose | E-2-hexenal | |
| G-R-VI-2 | GSH | ribose | E,E-2,4-hexadienal | |
| G-R-VII-0 | G-R-VII groups | GSH | ribose | Heptanal |
| G-R-VII-1 | GSH | ribose | E-2-heptenal | |
| G-R-VII-2 | GSH | ribose | E,E-2,4-heptadienal | |
| G-R-X-0 | G-R-X groups | GSH | ribose | Decanal |
| G-R-X-1 | GSH | ribose | E-2-decenal | |
| G-R-X-2 | GSH | ribose | E,E-2,4-decadienal | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, H.; Ma, L.; Chen, J.; Zhao, F.; Huang, X.; Dong, X.; Zhu, B.; Qin, L. Effect of Aliphatic Aldehydes on Flavor Formation in Glutathione–Ribose Maillard Reactions. Foods 2023, 12, 217. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12010217
Liu H, Ma L, Chen J, Zhao F, Huang X, Dong X, Zhu B, Qin L. Effect of Aliphatic Aldehydes on Flavor Formation in Glutathione–Ribose Maillard Reactions. Foods. 2023; 12(1):217. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12010217
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Hao, Lixin Ma, Jianan Chen, Feng Zhao, Xuhui Huang, Xiuping Dong, Beiwei Zhu, and Lei Qin. 2023. "Effect of Aliphatic Aldehydes on Flavor Formation in Glutathione–Ribose Maillard Reactions" Foods 12, no. 1: 217. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12010217
APA StyleLiu, H., Ma, L., Chen, J., Zhao, F., Huang, X., Dong, X., Zhu, B., & Qin, L. (2023). Effect of Aliphatic Aldehydes on Flavor Formation in Glutathione–Ribose Maillard Reactions. Foods, 12(1), 217. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12010217














