In Vitro and In Situ Characterization of Psychrotrophic Spoilage Bacteria Recovered from Chilled Chicken
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bacterial Species
2.2. Evaluation of Extracellular Protease Activity
2.3. Spoilage Potential Evaluation
2.3.1. Strain Culture and Inoculation
2.3.2. Microbial Analysis
2.3.3. pH and Total Volatile Basic Nitrogen (TVB-N) Analysis
2.3.4. Polypeptide Content Assessment
2.3.5. Electronic Nose Measurement
2.4. Correlation Analysis
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Proteolytic Activity Screening
3.2. Growth of Bacterial Strains in Meat
3.3. pH Changes
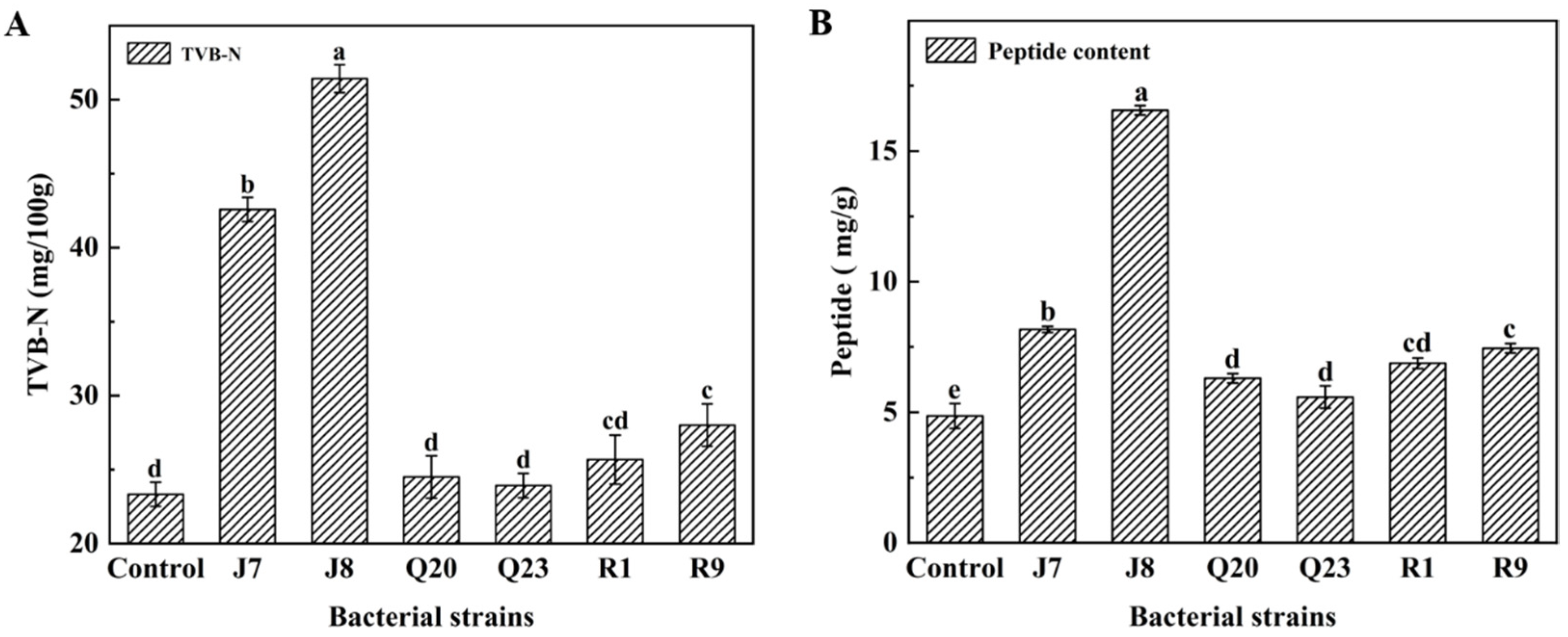
3.4. TVB-N Results
3.5. Proteolysis Extent Assay
3.6. E−nose Response Analysis
3.7. Correlation Analysis of Spoilage Indexes and E-Nose Responses
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, T.; Ding, H.; Chen, L.; Zhang, S.S.; Wu, P.F.; Xie, K.Z.; Pan, Z.M.; Zhang, G.X.; Dai, G.J.; Wu, H.Q.; et al. Characterization of chilled chicken spoilage using an integrated microbiome and metabolomics analysis. Food Res. Int. 2021, 144, 110328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.B.; Sun, J.Y.; Li, J.L.; Sun, Z.L.; Liu, F.; Du, L.H.; Wang, D.W. Preparation and characterization of gelatin/zein nanofiber films loaded with perillaldehyde, thymol, or varepsilon-polylysine and evaluation of their effects on the preservation of chilled chicken breast. Food Chem. 2022, 373, 131439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, T.; Zhang, S.S.; Chen, L.; Ding, H.; Wu, P.F.; Zhang, G.X.; Xie, K.Z.; Dai, G.J.; Wang, J.Y. UHPLC-MS/MS-based nontargeted metabolomics analysis reveals biomarkers related to the freshness of chilled chicken. Foods 2020, 9, 1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malvano, F.; Montone, A.M.I.; Capuano, F.; Colletti, C.; Roveri, N.; Albanese, D.; Capparellid, R. Effects of active alginate edible coating enriched with hydroxyapatite-quercetin complexes during the cold storage of fresh chicken fillets. Food Packag. Shelf Life 2022, 32, 100847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syahida, S.N.; Ismail-Fitry, M.R.; Ainun, A.M.A.; Hanani, Z.A.N. Effects of gelatin/palm wax/lemongrass essential oil (GPL)-coated Kraft paper on the quality and shelf life of ground beef stored at 4 °C. Food Packag. Shelf Life 2021, 28, 100640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.H.; Fegan, N.; Kocharunchitt, C.; Bowman, J.P.; Duffy, L.L. Changes of the bacterial community diversity on chicken carcasses through an Australian poultry processing line. Food Microbiol. 2020, 86, 103350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, H.Y.; Yang, H.Y.; Adel-Samie, M.A.; Siva, S.; Lin, L. Controlled-realease casein/cinnamon essential oil nanospheres for the inactivation of Campylobacter jejuni in duck. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2021, 341, 109074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dourou, D.; Spyrelli, E.D.; Doulgeraki, A.I.; Argyri, A.A.; Grounta, A.; Nychas, G.J.E.; Chorianopoulos, N.G.; Tassou, C.C. Microbiota of chicken breast and thigh fillets stored under different refrigeration temperatures assessed by next-generation sequencing. Foods 2021, 10, 765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.Z.; Chen, W.Q.; Siva, S.; Cui, H.Y.; Lin, L. Electrospun phosphlipid nanofibers encapsulated with cinnamaldehyde/HP-β-CD inclusion complex as a novel food packaging material. Food Packag. Shelf Life 2021, 28, 100647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, X.X.; Duan, S.; Wang, Q.; Ji, R.; Cao, Y.; Miao, J.Y. Effects of the natural antimicrobial substance from Lactobacillus paracasei FX-6 on shelf life and microbial composition in chicken breast during refrigerated storage. Food Control 2020, 109, 106906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crowley, K.M.; Prendergast, D.M.; Sheridan, J.J.; McDowell, D.A. Survival of Pseudomonas fluorescens on beef carcass surfaces in a commercial abattoir. Meat Sci. 2010, 85, 550–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, R.; Zhong, Z.T.; Gao, X.M.; Jia, L. Graphene oxide quantum dots assisted construction of fluorescent aptasensor for rapid detection of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in Food Samples. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 10898–10905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Kutsanedzie, F.Y.H.; Sun, H.; Wang, M.X.; Chen, Q.S.; Guo, Z.M. Rapid Pseudomonas species identification from chicken by integrating colorimetric sensors with near-infrared spectroscopy. Food Anal. Methods 2018, 11, 1199–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales, P.A.; Aguirre, J.S.; Troncoso, M.R.; Figueroa, G.O. Phenotypic and genotypic characterization of Pseudomonas spp. present in spoiled poultry fillets sold in retail settings. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 73, 609–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heir, E.; Moen, B.; Asli, W.A.; Sunde, M.; Langsrud, S. Antibiotic resistance and phylogeny of Pseudomonas spp. isolated over three decades from chicken meat in the norwegian food chain. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.H.; Zhang, X.X.; Wang, G.Y.; Jia, K.; Xu, X.L.; Zhou, G.H. Bacterial community and spoilage profiles shift in response to packaging in yellow-feather broiler, a highly popular meat in Asia. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 2588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Elbehiry, A.; Marzouk, E.; Aldubaib, M.; Moussa, I.; Abalkhail, A.; Ibrahem, M.; Hamada, M.; Sindi, W.; Alzaben, F.; Almuzaini, A.M.; et al. Pseudomonas species prevalence, protein analysis, and antibiotic resistance: An evolving public health challenge. AMB Express. 2022, 12, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Wei, Y.R.; Jin, X.L.; Liu, Z.B.; Ni, L. Spoilage of tilapia by Pseudomonas putida with different adhesion abilities. Curr. Res. Food Sci. 2022, 5, 710–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadopoulou, O.S.; Iliopoulos, V.; Mallouchos, A.; Panagou, E.Z.; Chorianopoulos, N.; Tassou, C.C.; Nychas, G.J.E. Spoilage potential of Pseudomonas (P. fragi, P. putida) and LAB (Leuconostoc mesenteroides, Lactobacillus sakei) strains and their volatilome profile during storage of sterile pork meat using GC/MS and data analysis. Foods 2020, 9, 633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.Y.; Wang, H.H.; Han, Y.W.; Xing, T.; Ye, K.P.; Xu, X.L.; Zhou, G.H. Evaluation of the spoilage potential of bacteria isolated from chilled chicken in vitro and in situ. Food Microbiol. 2017, 63, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seike, S.; Kobayashi, H.; Ueda, M.; Takahashi, E.; Okamoto, K.; Yamanaka, H. Outer membrane vesicles released from Aeromonas strains are involved in the biofilm formation. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 613650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, L.T.; Tian, Y.; Chen, S.S.; Xu, X.L.; Wang, H.H. Characterization of the spoilage heterogeneity of Aeromonas isolated from chilled chicken meat: In vitro and in situ. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 162, 113470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nychas, G.J.E.; Skandamis, P.N.; Tassou, C.C.; Koutsoumanis, K.P. Meat spoilage during distribution. Meat Sci. 2008, 78, 77–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narvhus, J.A.; Bækkelund, O.N.; Tidemann, E.M.; Qstlie, H.M.; Abrahamsen, R.K. Isolates of Pseudomonas spp. from cold-stored raw milk show variation in proteolytic and lipolytic properties. Int. Dairy J. 2021, 123, 105049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odeyemi, O.A.; Burke, C.M.; Bolch, C.J.S.; Stanley, R. Evaluation of spoilage potential and volatile metabolites production by Shewanella baltica isolated from modified atmosphere packaged live mussels. Food Res. Int. 2018, 103, 415–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.Y.; Qing, L.; Tang, W.Q.; Ma, F.; Wang, H.H.; Xu, X.X.; Qiu, W.F. AprD is important for extracellular proteolytic activity, physicochemical properties and spoilage potential in meat-borne Pseudomonas fragi. Food Control 2021, 124, 107868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwanhlem, W.; Jaffrès, E.; Dousset, X.; Pillot, G.; Choiset, Y.; Haertle, T.; H-Kittikun, A.; Chobert, J. Application of a nisin Z-producing Lactococcus lactis subsp. lactis KT2W2L isolated from brackish water for biopreservation in cooked, peeled and ionized tropical shrimps during storage at 8 °C under modified atmosphere packaging. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2015, 240, 1259–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsushita, M.; Irino, T.; Komoda, T.; Sakagishi, T. Determination of proteins by a reverse biuret method combined with the copper-bathocuproine chelate reaction. Clin. Chim. Acta 1993, 216, 101–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, X.Y.; Lv, Y.C.; Wen, R.X.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Q.; Kong, B.H. Characterization of selected Harbin red sausages on the basis of their flavour profiles using HS-SPME-GC/MS combined with electronic nose and electronic tongue. Meat Sci. 2021, 172, 108345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolbeck, S.; Abele, M.; Hilgarth, M.; Vogel, R. Comparative proteomics reveals the anaerobic lifestyle of meat-spoiling Pseudomonas Species. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 664061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanborough, T.; Fegan, N.; Powell, S.M.; Singh, T.; Tamplin, M.; Chandry, P.S. Genomic and metabolic characterization of spoilage-associated Pseudomonas species. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2018, 268, 61–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickramasinghe, N.N.; Ravensdale, J.R.; Coorey, R.; Dykes, G.A.; Chandry, P.S. In situ characterisation of biofilms formed by psychrotrophic meat spoilage pseudomonads. Biofouling 2019, 35, 840–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, J.; Wang, H.W.; Cai, L.L.; Wang, H.H.; Xu, X.X.; Zhou, G.H. Aeromonas salmonicida isolates: Attachment ability and sensitivity to four disinfectants. Food Control 2018, 88, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marmion, M.; Macori, G.; Ferone, M.; Whyte, P.; Scannell, A.G.M. Survive and thrive: Control mechanisms that facilitate bacterial adaptation to survive manufacturing-related stress. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2022, 368, 109612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, X.; Feng, L.; Zhu, J.Y.; Li, Y.; Tu, K.; Dong, Q.L.; Pan, L.Q. Application of gas sensors for modelling the dynamic growth of Pseudomonas in pork stored at different temperatures. Meat Sci. 2021, 171, 108282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, X.X.; Chen, S.Y.; Duan, S.; Lan, C.; Yang, Z.N.; Cao, Y.; Miao, J. Antibiotic activities of the natural antimicrobial substance produced by Lactobacillus paracasei FX-6 against Pseudomonas putida. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 123, 109096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickramasinghe, N.N.; Ravensdale, J.; Coorey, R.; Chandry, S.P.; Dykes, G.A. The predominance of Psychrotrophic Pseudomonas on aerobically stored chilled red meat. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2019, 18, 1622–1635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mehdizadeh, T.; Langroodi, A.M. Chitosan coatings incorporated with propolis extract and Zataria multiflora Boiss oil for active packaging of chicken breast meat. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 141, 401–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbut, S.; Zhang, L.; Marcone, M. Effects of pale, normal, and dark chicken breast meat on microstructure, extractable proteins, and cooking of marinated fillets. Poul. Sci. 2005, 84, 797–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.; Lee, H.J.; Jung, D.Y.; Kim, H.J.; Jang, A.; Jo, C. Effect of an animal-friendly raising environment on the quality, storage stability, and metabolomic profiles of chicken thigh meat. Food Res. Int. 2022, 155, 111046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katiyo, W.; Kock, H.L.D.; Coorey, R.; Buys, E.M. Sensory implications of chicken meat spoilage in relation to microbial and physicochemical characteristics during refrigerated storage. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 128, 109468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braun, P.; Sutherland, J.P. Predictive modelling of growth and enzyme production and activity by a cocktail of Pseudomonas spp., Shewanella putrefaciens and Acinetobacter sp. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2003, 86, 271–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Argyri, A.A.; Mallouchos, A.; Panagou, E.Z.; Nychas, G.J.E. The dynamics of the HS/SPME-GC/MS as a tool to assess the spoilage of minced beef stored under different packaging and temperature conditions. Int. J. Food Microbial. 2015, 193, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.N.; Wang, R.; Wang, D.B.; Sun, Z.L.; Liu, F.; Zhang, D.Q.; Wang, D.Y. Development of a food packaging antibacterial hydrogel based on gelatin, chitosan, and 3-phenyllactic acid for the shelf-life extension of chilled chicken. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 127, 107546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, S.L.; Li, Y.; Zhuang, S.; Sun, X.H.; Zhang, L.T.; Shi, J.; Hong, H.; Luo, Y.K. Biochemical changes induced by dominant bacteria in chill-stored silver carp (Hypophthalmichthys molitrix) and GC-IMS identification of volatile organic compounds. Food Microbiol. 2019, 84, 103248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.C.; Huang, Z.; Jia, S.L.; Zhang, J.B.; Li, K.F.; Luo, Y.K. The roles of bacteria in the biochemical changes of chill-stored bighead carp (Aristichthys nobilis): Proteins degradation, biogenic amines accumulation, volatiles production, and nucleotides catabolism. Food Chem. 2018, 255, 174–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, J.Y.; Feng, L.F.; Lu, H.X.; Zhu, J.L. Metabolomics reveals spoilage characteristics and interaction of Pseudomonas lundensis and Brochothrix thermosphacta in refrigerated beef. Food Res. Int. 2022, 156, 111139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, J.; Fan, Y.; Zhu, L.L.; Wang, Y.C.; Hou, H. Characteristic flavor of Antarctic krill (Euphausia superba) and white shrimp (Penaeus vannamei) induced by thermal treatment. Food Chem. 2022, 378, 132074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pleva, D.; Lanyi, K.; Darnay, L.; Laczay, P. Predictive correlation between apparent sensory properties and the formation of heterocyclic amines in chicken breast as a function of grilling temperature and time. Foods 2020, 9, 412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Klein, D.; Maurer, S.; Herbert, U.; Kreyenschmidt, J.; Kual, P. Detection of volatile organic compounds arising from chicken breast filets under modified atmosphere packaging using TD-GC/MS. Food Anal. Methods 2018, 11, 88–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
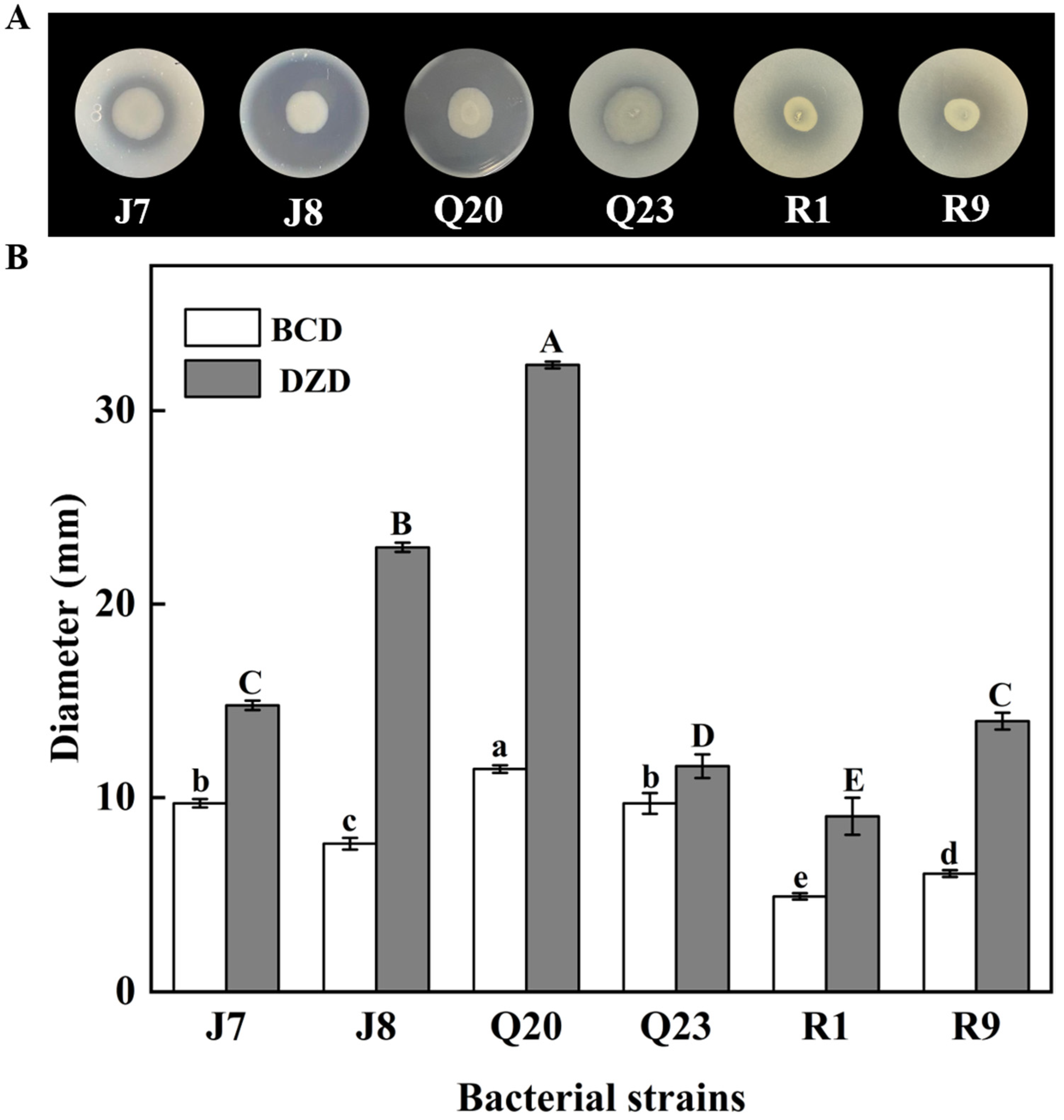



| Genera | Species | Number of Isolates | Isolates | Proteolytic Activity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pseudomonas spp. | P. gessardii | 1 | J1 | ++++ |
| P. putida | 1 | J4 | No proteolytic activity | |
| P. libanensis | 1 | J5 | +++ | |
| P. fluorescens | 1 | J6 | +++ | |
| P. lundensis | 2 | J7 | ++ | |
| J8 | +++++ | |||
| P. psychrophile | 1 | J9 | +++ | |
| P. azotoformans | 2 | J10 and J11 | ++++ | |
| P. poae | 2 | J13 and J14 | +++ | |
| Aeromonas spp. | A. media | 5 | Q15 | +++ |
| Q18, Q23, and Q26 | + | |||
| Q22 | ++ | |||
| A. salmonicida | 2 | Q16 and Q19 | +++ | |
| A. rivipollensis | 2 | Q17 | + | |
| Q25 | ++ | |||
| A. hydrophila | 2 | Q20 and Q21 | ++++ | |
| A. caviae | 1 | Q24 | + | |
| A. popoffii | 1 | Q27 | ++++ | |
| Psychrobacter spp. | P. pulmonis | 1 | F28 | No proteolytic activity |
| Cronobacter spp. | 1 | B29 | + | |
| Escherichia spp. | 1 | D30 | +++++ | |
| Brochothrix spp. | B. thermosphacta | 9 | R1 and R3 | ++ |
| R2, R6, R7, R8, R9, R10, and R11 | +++ |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, X.; Wang, Z.; Sun, Z.; Wang, D.; Liu, F.; Lin, L. In Vitro and In Situ Characterization of Psychrotrophic Spoilage Bacteria Recovered from Chilled Chicken. Foods 2023, 12, 95. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12010095
Wang X, Wang Z, Sun Z, Wang D, Liu F, Lin L. In Vitro and In Situ Characterization of Psychrotrophic Spoilage Bacteria Recovered from Chilled Chicken. Foods. 2023; 12(1):95. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12010095
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Xinxia, Zaitian Wang, Zhilan Sun, Daoying Wang, Fang Liu, and Lin Lin. 2023. "In Vitro and In Situ Characterization of Psychrotrophic Spoilage Bacteria Recovered from Chilled Chicken" Foods 12, no. 1: 95. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12010095
APA StyleWang, X., Wang, Z., Sun, Z., Wang, D., Liu, F., & Lin, L. (2023). In Vitro and In Situ Characterization of Psychrotrophic Spoilage Bacteria Recovered from Chilled Chicken. Foods, 12(1), 95. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12010095







