Effect of High-Intensity Ultrasound Pretreatment on the Properties of the Transglutaminase (TGase)-Induced β-Conglycinin (7S) Gel
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Regents
2.2. Preparation of 7S Protein
2.3. High-Intensity Ultrasound Pretreatment
2.4. Determination of Particle Size
2.5. Determination of Surface Hydrophobicity (Ho)
2.6. Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate-Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) Analysis
2.7. Determination of Intrinsic Fluorescence Spectra
2.8. Circular Dichroism (CD) Analysis
2.9. Transglutaminase-Reduced β-Conglycinin Gel Formation
2.10. Determination of Free Sulfhydryl (FSH) and Total Sulfhydryl (TSH) Contents of Gel
2.11. Determination of the Gel Solubility
2.12. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) Analysis
2.13. Determination of Water-Holding Capacity (WHC)
2.14. Determination of Gel Strength
2.15. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC) Analysis
2.16. Rheological Measurements
2.17. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Effect of HIU Pretreatment Time on Conformational Characteristics of 7S
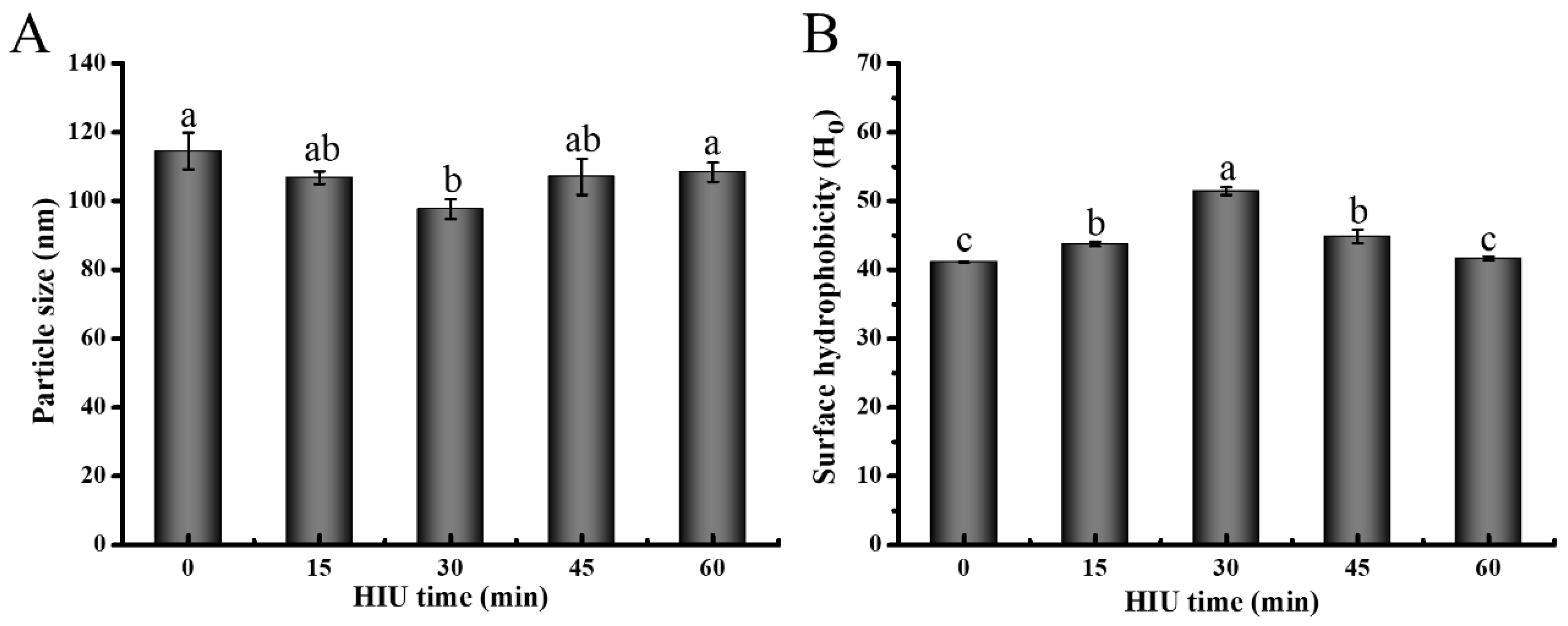
3.1.1. Particle Size
3.1.2. Surface Hydrophobicity (Ho)
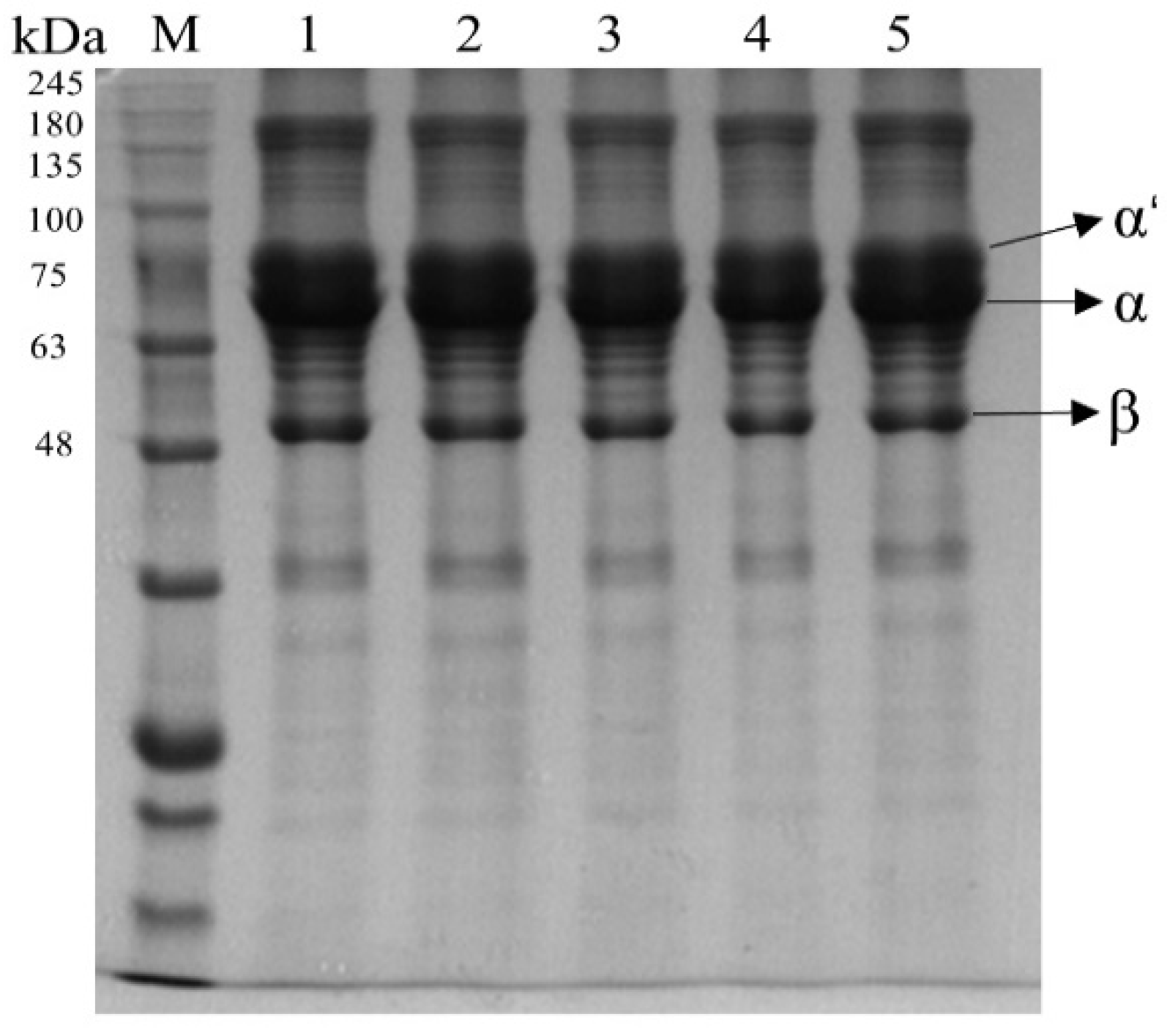
3.1.3. SDS-PAGE
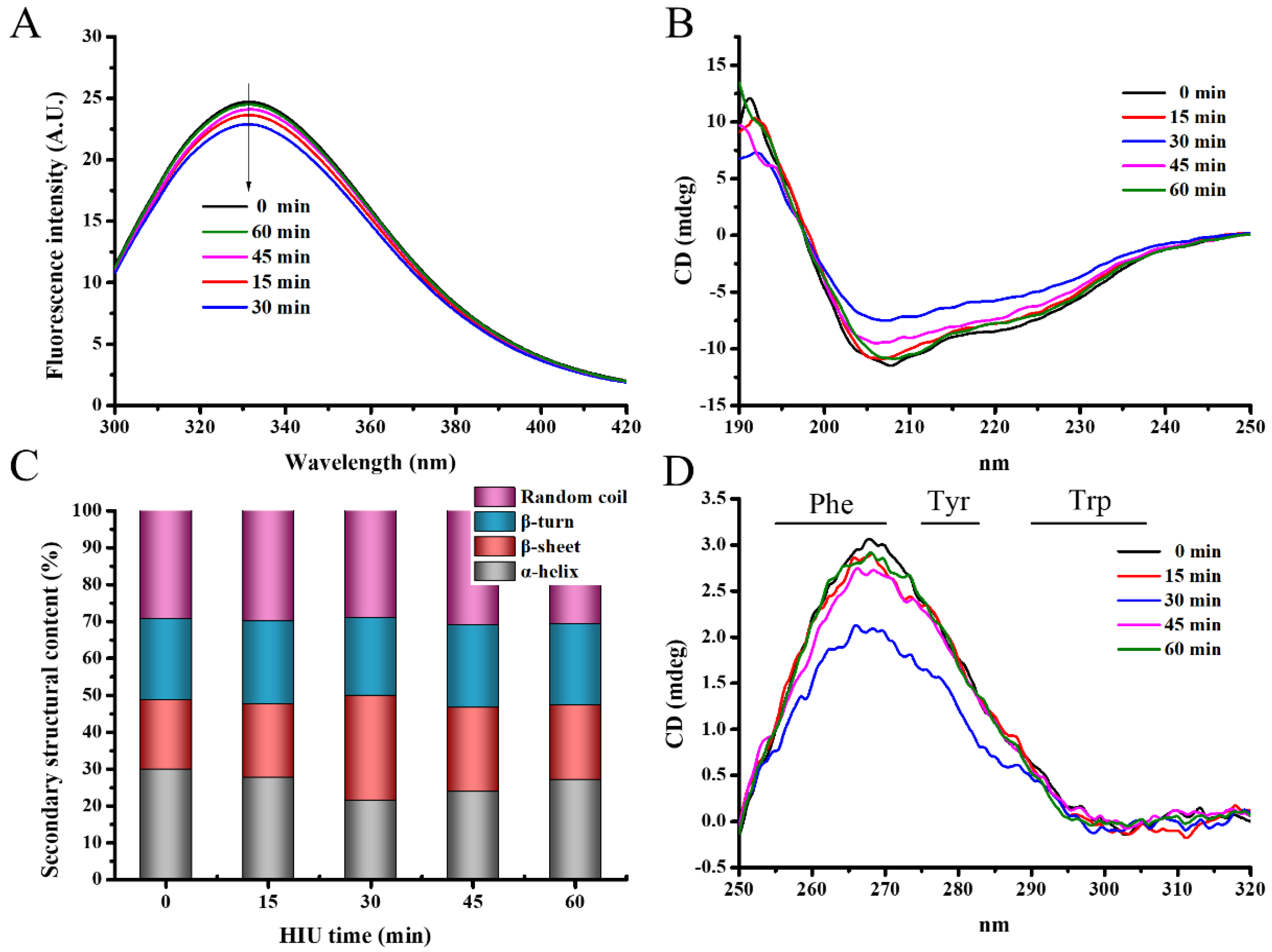
3.1.4. Intrinsic Fluorescence Spectra
3.1.5. Circular Dichroism (CD) Spectra
3.2. Structure Properties of TGase-Induced 7S Gels
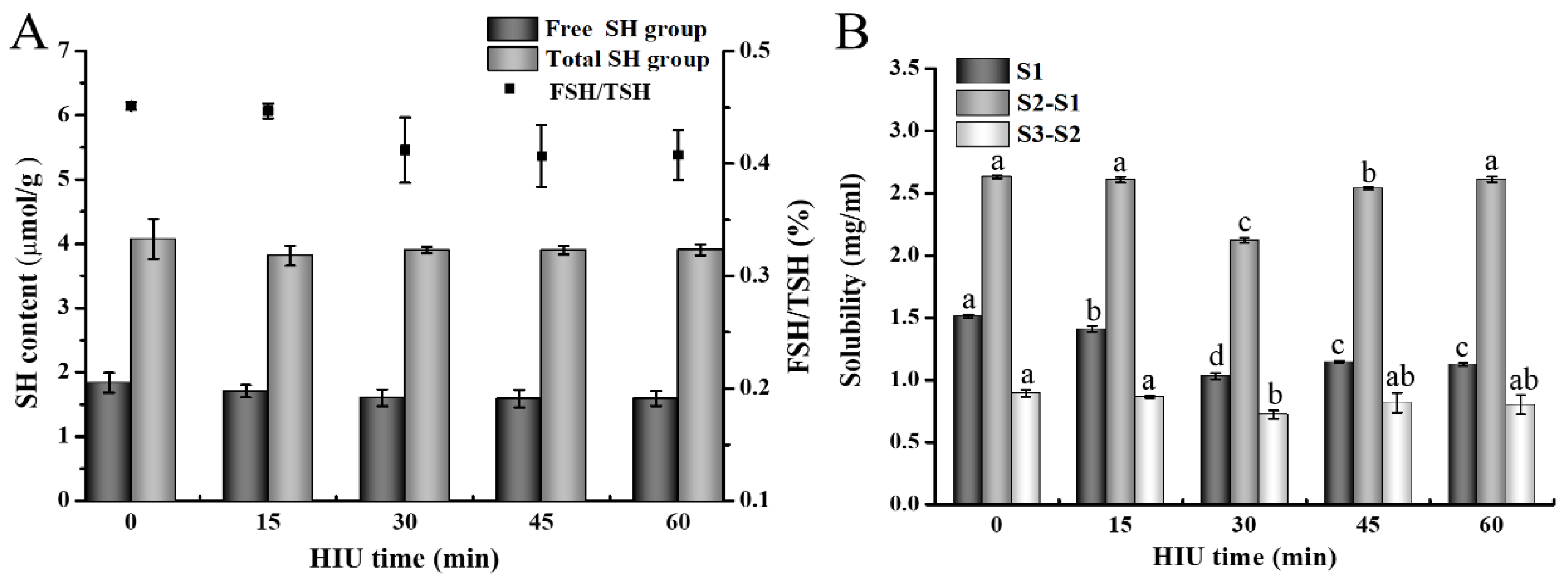
3.2.1. Free Sulfhydryl (FSH) and Total Sulfhydryl (TSH) Contents of Gel
3.2.2. Solubility of Gel
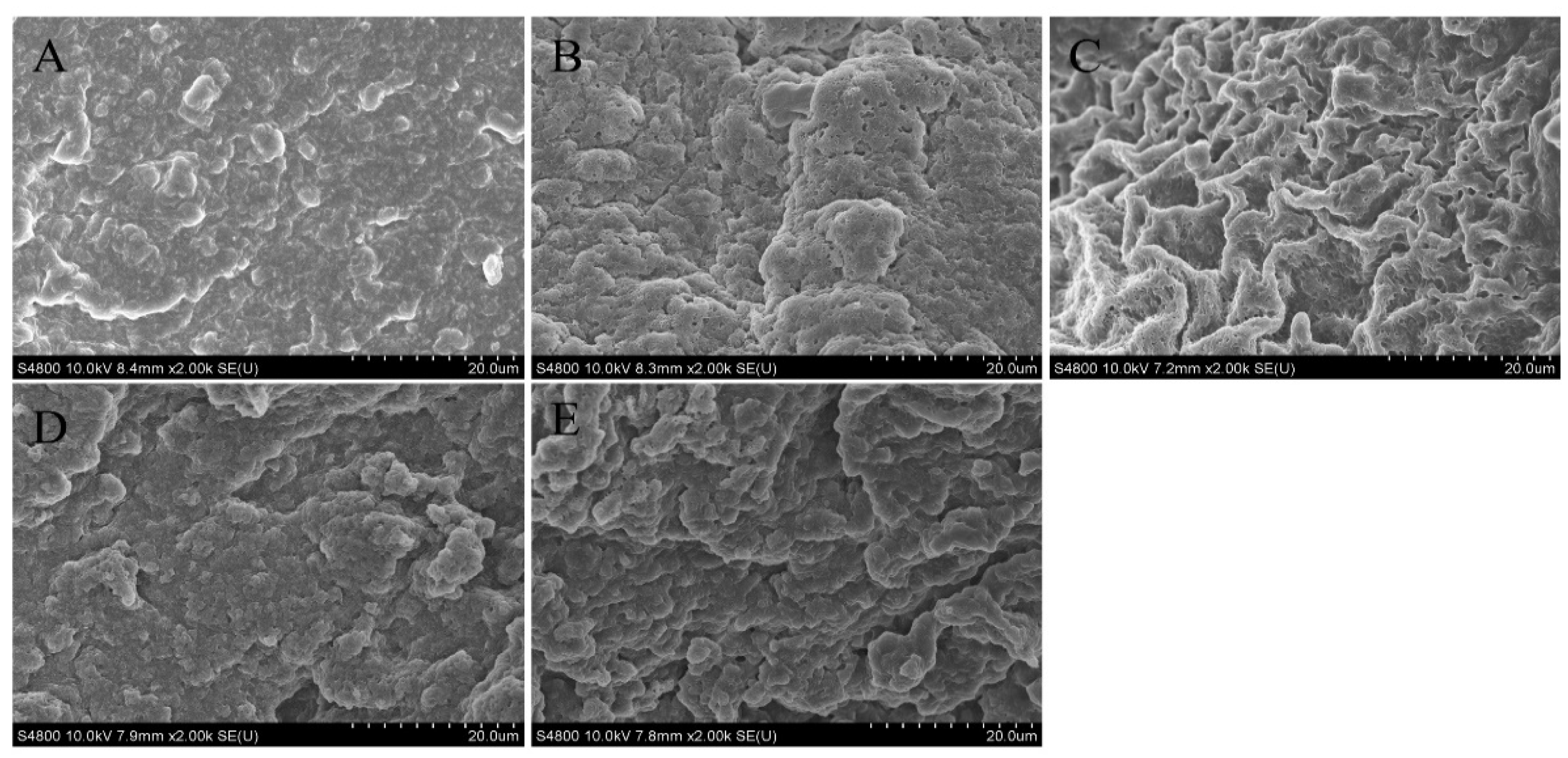
3.2.3. Microstructure
3.3. Functional Properties of TGase-Induced 7S Gels
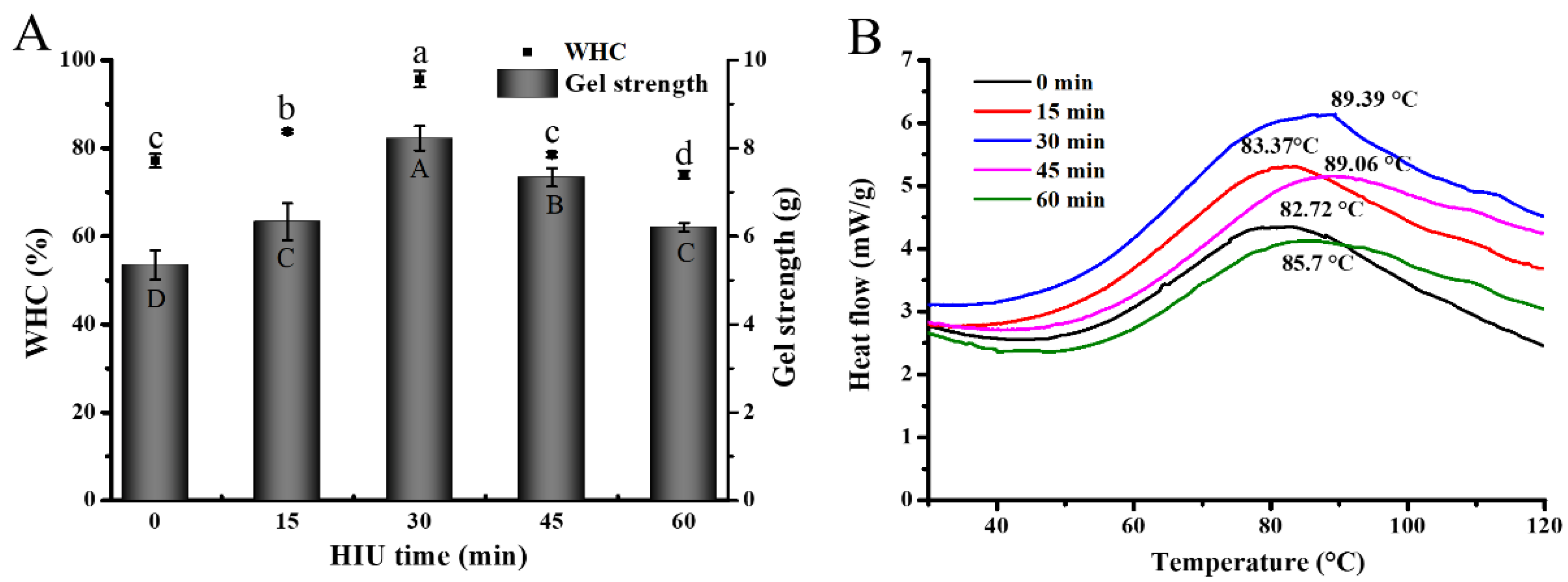
3.3.1. Gel Strength and Water-Holding Capability (WHC) of Gel
3.3.2. Thermal Properties Analysis
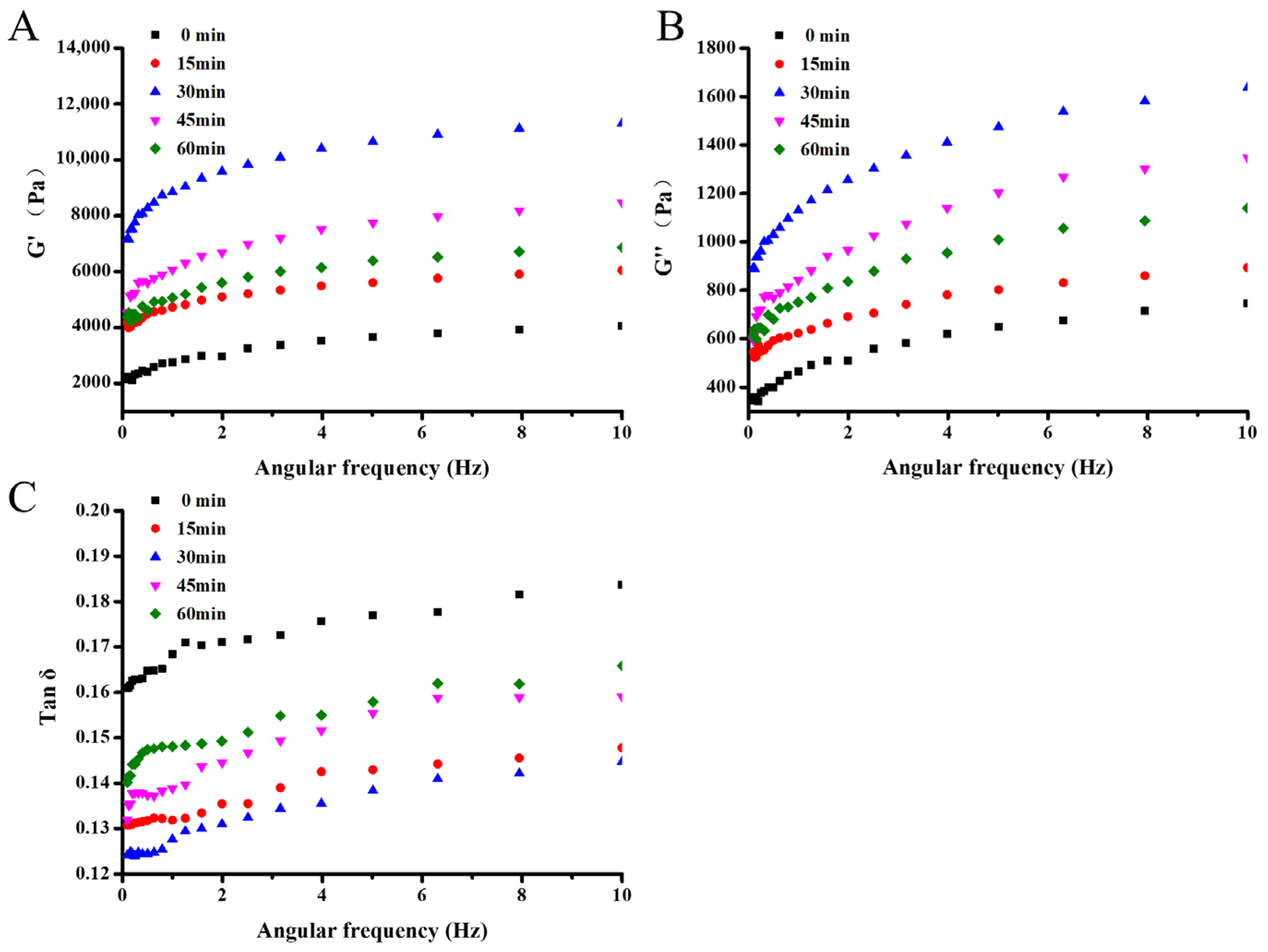
3.3.3. Rheological Behavior
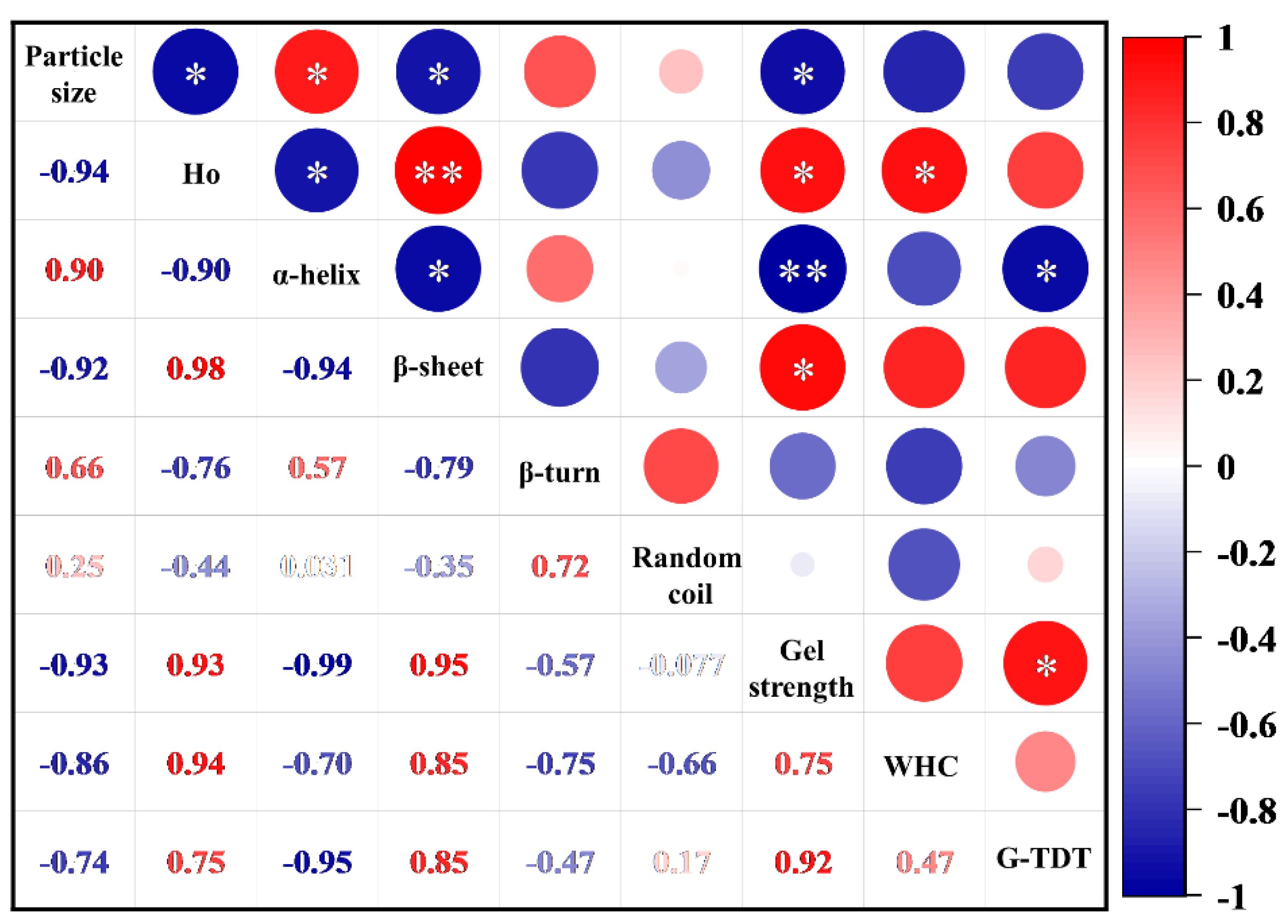
3.4. Correlation between Protein Conformation and Gel Properties
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nogueira-de-Almeida, C.A.; Ferraz, I.S.; Ued, F.d.V.; Almeida, A.C.F.; Ciampo, L.A.D. Impact of soy consumption on human health: Integrative review. Braz. J. Food Technol. 2020, 23, e2019129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, W. Global Non-GMO Soybean Production and Trade Consumption. Heilongjiang Grain 2022, 233, 28–29. [Google Scholar]
- Thanh, V.H.; Shibasaki, K. Heterogeneity of beta-conglycinin. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1976, 439, 326–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Q.; Chen, S.L. Experimental study on the hypolipidemic effect of soy protein. Food Sci. Technol. 2003, 2, 15–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arzeni, C.; Martínez, K.; Zema, P.; Arias, A.; Pérez, O.E.; Pilosof, A.M.R. Comparative study of high intensity ultrasound effects on food proteins functionality. J. Food Eng. 2012, 108, 463–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Li, C.; Eunice, C.Y.; Wan, L.; Tian, M.; Pan, S. The effect of high intensity ultrasonic pre-treatment on the properties of soybean protein isolate gel induced by calcium sulfate. Food Hydrocoll. 2013, 32, 303–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chin, K.B.; Go, M.Y.; Xiong, Y.L. Effect of soy protein substitution for sodium caseinate on the transglutaminate-induced cold and thermal gelation of myofibrillar protein. Food Res. Int. 2009, 42, 941–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedrosa, V.A.; Yan, J.; Simonian, A.L.; Revzin, A. Micropatterned Nanocomposite Hydrogels for Biosensing Applications. Electroanalysis 2011, 23, 1142–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, F.; Liu, W.H.; Chen, Z.G. Analysis of the structure and thermal gel properties of soybean 7S and 11S protein. Food Sci. 2020, 41, 58–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohyama, K.; Murata, M.; Tani, F.; Sano, Y.; Doi, E. Effects of Protein Composition on Gelation of Mixtures Containing Soybean 7S and 11S Globulins. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2014, 59, 240–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akharume, F.U.; Aluko, R.E.; Adedeji, A.A. Modification of plant proteins for improved functionality: A review. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2021, 20, 198–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaspar, A.L.; de Goes-Favoni, S.P. Action of microbial transglutaminase (MTGase) in the modification of food proteins: A review. Food Chem. 2015, 171, 315–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, X.D.; Arntfield, S.D. Gelation properties of myofibrillar/pea protein mixtures induced by transglutaminase crosslinking. Food Hydrocoll. 2012, 27, 394–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.D.; Arntfield, S.D. Gelation properties of salt-extracted pea protein isolate catalyzed by microbial transglutaminase cross-linking. Food Hydrocoll. 2011, 25, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, R.; Ju, X.; He, R.; Wang, Z. Enzyme-catalyzed acylation improves gel properties of rapeseed protein isolate. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2020, 100, 4182–4189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, X.S.; Luo, S.Z.; Cai, J.; Zhong, X.Y.; Jiang, S.T.; Zhao, Y.Y.; Zheng, Z. Transglutaminase-induced gelation properties of soy protein isolate and wheat gluten mixtures with high intensity ultrasonic pretreatment. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2016, 31, 590–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.-H.; Li, L.; Wang, J.-L.; Yang, X.-Q. Formation and rheological properties of ‘cold-set’ tofu induced by microbial transglutaminase. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2007, 40, 579–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hugo, A.A.; Pérez, P.F.; Añón, M.C.; Speroni, F. Incorporation of Lactobacillus delbrueckii subsp lactis (CIDCA 133) in cold-set gels made from high pressure-treated soybean proteins. Food Hydrocoll. 2014, 37, 34–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ercan, S.Ş.; Soysal, Ç. Use of ultrasound in food preservation. Nat. Sci. 2013, 5, 5–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chemat, F.; Zille, H.; Khan, M.K. Applications of ultrasound in food technology: Processing, preservation and extraction. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2011, 18, 813–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashokkumar, M. Applications of ultrasound in food and bioprocessing. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2015, 25, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Claver, I.P.; Zhu, K.-X.; Zhou, H. The Effect of Ultrasound on the Functional Properties of Wheat Gluten. Molecules 2011, 16, 4231–4240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vera, A.; Tapia, C.; Abugoch, L. Effect of high-intensity ultrasound treatment in combination with transglutaminase and nanoparticles on structural, mechanical, and physicochemical properties of quinoa proteins/chitosan edible films. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 144, 536–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Xue, H.; Chen, Z.; Ding, Q.; Wang, X. Comparative studies on the physicochemical properties of peanut protein isolate–polysaccharide conjugates prepared by ultrasonic treatment or classical heating. Food Res. Int. 2014, 57, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Fan, X.; Zhou, Z.; Xu, X.; Fan, G.; Wang, L.; Huang, X.; Pan, S.; Zhu, L. Acid-induced gelation behavior of soybean protein isolate with high intensity ultrasonic pre-treatments. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2013, 20, 187–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Chu, Z.; Miao, Z.; Liu, J.; Liu, J.; Xu, X.; Wu, Y.; Qi, B.; Yan, J. Ultrasound heat treatment effects on structure and acid-induced cold set gel properties of soybean protein isolate. Food Biosci. 2021, 39, 100827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.-H.; Wang, X.-Y.; Yang, X.-Q.; Li, L. Formation of soluble aggregates from insoluble commercial soy protein isolate by means of ultrasonic treatment and their gelling properties. J. Food Eng. 2009, 92, 432–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Hu, T.; Feng, S.; Xu, Q.; Zheng, T.; Zhou, M.; Chu, X.; Huang, X.; Lu, X.; Pan, S.; et al. Effect of high intensity ultrasound on transglutaminase-catalyzed soy protein isolate cold set gel. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2016, 29, 380–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Wang, H.; Cui, Z.; He, X.; Wang, X.; Zeng, X.; Ma, H. Optimization of extraction and isolation for 11S and 7S globulins of soybean seed storage protein. Food Chem. 2007, 102, 1310–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, A.; Nakai, S. Hydrophobicity determined by a fluorescence probe method and its correlation with surface properties of proteins. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1980, 624, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Cui, Q.; Li, R.; Hao, L.; Liu, H.; Wang, X.; Xu, N.; Zhao, X. Structural and emulsifying properties of soybean protein isolate glycated with glucose based on pH treatment. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2022, 102, 4462–4472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Huang, X.; Peng, Q.; Shan, Y.; Xue, F. Physicochemical properties of peanut protein isolate-glucomannan conjugates prepared by ultrasonic treatment. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2014, 21, 1722–1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beveridge, T.; Toma, S.J.; Nakai, S. Determination of Sh- and Ss-Groups in Some Food Proteins Using Ellman’s Reagent. J. Food Sci. 1974, 39, 49–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Guillén, M.C.; Borderıías, A.J.; Montero, P. Chemical Interactions of Nonmuscle Proteins in the Network of Sardine (Sardina pilchardus) Muscle Gels. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 1997, 30, 602–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maltais, A.; Remondetto, G.E.; Subirade, M. Soy protein cold-set hydrogels as controlled delivery devices for nutraceutical compounds. Food Hydrocoll. 2009, 23, 1647–1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valdez-Hurtado, S.; López-Bermúdez, L.S.; Higuera-Barraza, O.A.; Del Toro-Sanchez, C.L.; Ruiz-Cruz, S.; Suárez-Jiménez, M.G.; Marquez-Rios, E. Effect of ultrasonication time on the functional properties of giant squid (Dosidicus gigas) mantle protein concentrate. Food Biosci. 2019, 27, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.; Liu, X.; Ding, X.; Dong, H.; Wang, W. Effects of High-Intensity Ultrasound Pretreatment on Structure, Properties, and Enzymolysis of Soy Protein Isolate. Molecules 2019, 24, 3637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Hua, Y.; Chen, Y.; Kong, X.; Zhang, C. Effect of temperature, ionic strength and 11S ratio on the rheological properties of heat-induced soy protein gels in relation to network proteins content and aggregates size. Food Hydrocoll. 2017, 66, 389–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulseren, I.; Guzey, D.; Bruce, B.D.; Weiss, J. Structural and functional changes in ultrasonicated bovine serum albumin solutions. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2007, 14, 173–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, N.H.A.; Anema, S.G. Effect of ultrasonication on the properties of skim milk used in the formation of acid gels. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2010, 11, 616–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Wu, Q.; Le, G.; Wang, J.; Yin, K.; Shi, Y. Structural and antioxidant modification of wheat peptides modified by the heat and lipid peroxidation product malondialdehyde. J. Food Sci. 2012, 77, H16–H22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, C.; Zhao, M.; Yuan, B.; Zhang, Y.; Ren, J. Effect of pH and pepsin limited hydrolysis on the structure and functional properties of soybean protein hydrolysates. J. Food Sci. 2013, 78, C1871–C1877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandrapala, J.; Zisu, B.; Palmer, M.; Kentish, S.; Ashokkumar, M. Effects of ultrasound on the thermal and structural characteristics of proteins in reconstituted whey protein concentrate. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2011, 18, 951–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, H.; Wu, J.; Li-Chan EC, Y.; Zhu, L.; Zhang, F.; Xu, X.; Fan, G.; Wang, L.; Huang, X.; Pan, S. Effects of ultrasound on structural and physical properties of soy protein isolate (SPI) dispersions. Food Hydrocoll. 2013, 30, 647–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eftink, M.R. Fluorescence techniques for studying protein structure. Methods Biochem. Anal. 1991, 35, 127–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Wang, J.; Li, Y.; Wang, Z.; Liang, J.; Wang, R.; Chen, Y.; Ma, W.; Qi, B.; Zhang, M. Effects of ultrasound on the structure and physical properties of black bean protein isolates. Food Res. Int. 2014, 62, 595–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vivian, J.T.; Callis, P.R. Mechanisms of tryptophan fluorescence shifts in proteins. Biophys. J. 2001, 80, 2093–2109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, S.M.; Jess, T.J.; Price, N.C. How to study proteins by circular dichroism. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2005, 1751, 119–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenfield, N.J. Using circular dichroism spectra to estimate protein secondary structure. Nat. Protoc. 2006, 1, 2876–2890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Zhao, S.M.; Xiong, S.B.; Xie, B.J.; Qin, L.H. Role of secondary structures in the gelation of porcine myosin at different pH values. Meat Sci. 2008, 80, 632–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Wang, M.; Xue, F.; Adhikari, B. Application of ultrasound treatment to improve the technofunctional properties of hemp protein isolate. Future Foods 2022, 6, 100176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Zhang, X.; Jia, J.; Kuang, C.; Yang, H. Effect of ultrasonic pretreatment on whey protein hydrolysis by alcalase: Thermodynamic parameters, physicochemical properties and bioactivities. Process Biochem. 2018, 67, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munialo, C.D.; Martin, A.H.; van der Linden, E.; de Jongh, H.H. Fibril formation from pea protein and subsequent gel formation. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 2418–2427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Y.; Shan, A.; Wang, R.; Zhao, Y.; Chi, Y. Characterization of egg white powder gel structure and its relationship with gel properties influenced by pretreatment with dry heat. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 110, 106149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, N.; Hirose, M. Determination of sulfhydryl groups and disulfide bonds in a protein by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Anal. Biochem. 1990, 188, 359–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Sun, J.; Zhao, L.; He, W.; Liu, T.; Liu, B. Analysis of the gel properties, microstructural characteristics, and intermolecular forces of soybean protein isolate gel induced by transglutaminase. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 10, 772–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu Yang, Z.L.; Bai, J.; Wang, Z.; Qi, B.; Jiag, L. Effects of extreme pH treatment on the structural and functional properties of soy protein isolate, β-plus soy globulin, and soy globulin. J. Chin. Inst. Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 18, 306–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, A.; Deng, H.; Zu, Q.; Lu, J.; Wu, Z.; Li, X.; Tong, P.; Chen, H. Structure characterization and IgE-binding of soybean 7S globulin after enzymatic deglycosylation. Int. J. Food Prop. 2018, 21, 171–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, H.; Jiao, X.; Fan, D.; Huang, J.; Zhao, J.; Yan, B.; Zhou, W.; Zhang, H.; Wang, M. Microwave irradiation promotes aggregation behavior of myosin through conformation changes. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 96, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.Z.; Sha, X.M.; Huang, T.; Zhang, L.; Wang, G.Y.; Tu, Z.C. Microbial transglutaminase (MTGase) modified fish gelatin-gamma-polyglutamic acid (gamma-PGA): Rheological behavior, gelling properties, and structure. Food Chem. 2021, 348, 129093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Zhu, X.; Hu, T.; Cheung IW, Y.; Pan, S.; Li-Chan, E.C.Y. Effect of ultrasound pre-treatment on formation of transglutaminase-catalysed soy protein hydrogel as a riboflavin vehicle for functional foods. J. Funct. Foods 2015, 19, 182–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Li, L.; Wu, C.; Huang, Y.; Teng, F.; Li, Y. Effects of combined enzymatic and ultrasonic treatments on the structure and gel properties of soybean protein isolate. LWT 2022, 158, 113123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; McClements, D.J.; He, M.; Fan, Z.; Li, Y.; Teng, F. Preparation of okara cellulose hydrogels using ionic liquids: Structure, properties, and performance. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 331, 115744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.; Wang, Z.; Kong, Y.; Ma, Z.; Wu, C.; Regenstein, J.M.; Teng, F.; Li, Y. Different commercial soy protein isolates and the characteristics of Chiba tofu. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 110, 106115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Ma, C.; Yan, X.; Zeng, H.; McClements, D.J.; Liu, X.; Liu, F. Structure, rheology and functionality of whey protein emulsion gels: Effects of double cross-linking with transglutaminase and calcium ions. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 102, 105569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.-F.; Lu, C.-P.; Hsieh, J.-F.; Kuo, M.-I. Effect of ultrasonic treatment on the rheological property and microstructure of tofu made from different soybean cultivars. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2016, 37, 98–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madadlou, A.; Emam-Djomeh, Z.; Mousavi, M.E.; Mohamadifar, M.; Ehsani, M. Acid-induced gelation behavior of sonicated casein solutions. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2010, 17, 153–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, L.; Zhang, J.; Wen, P.; Xu, J.; Xu, H.; Cui, G.; Wang, J. Effect of High-Intensity Ultrasound Pretreatment on the Properties of the Transglutaminase (TGase)-Induced β-Conglycinin (7S) Gel. Foods 2023, 12, 2037. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12102037
Zhang L, Zhang J, Wen P, Xu J, Xu H, Cui G, Wang J. Effect of High-Intensity Ultrasound Pretreatment on the Properties of the Transglutaminase (TGase)-Induced β-Conglycinin (7S) Gel. Foods. 2023; 12(10):2037. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12102037
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Lan, Jixin Zhang, Pingping Wen, Jingguo Xu, Huiqing Xu, Guiyou Cui, and Jun Wang. 2023. "Effect of High-Intensity Ultrasound Pretreatment on the Properties of the Transglutaminase (TGase)-Induced β-Conglycinin (7S) Gel" Foods 12, no. 10: 2037. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12102037
APA StyleZhang, L., Zhang, J., Wen, P., Xu, J., Xu, H., Cui, G., & Wang, J. (2023). Effect of High-Intensity Ultrasound Pretreatment on the Properties of the Transglutaminase (TGase)-Induced β-Conglycinin (7S) Gel. Foods, 12(10), 2037. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12102037




