Study on the Changes in Volatile Flavor Compounds in Whole Highland Barley Flour during Accelerated Storage after Different Processing Methods
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Materials
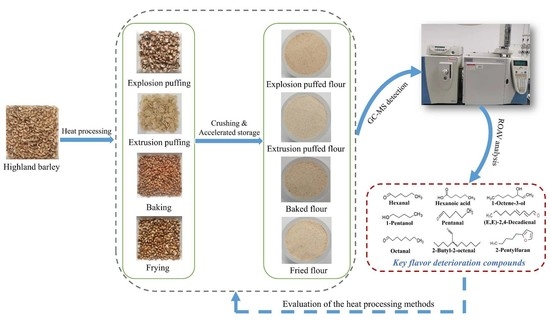
2.2. Preparation of Highland Barley Flour by Different Processing Methods
2.3. Accelerated Storage Tests
2.4. The Gas Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry Detection of Volatile Flavor Compounds of Highland Barley Flour
2.5. Analysis of Key Volatile Flavor Compounds
2.6. Data Processing
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Volatiles in Different Highland Barley Flour
3.2. Differential Volatile Compounds in Different Highland Barley Flour
3.3. Analysis of Key Volatile Compounds
| No. | Compounds | OT (μg/kg−1) | Odorant Description | ROAV | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Y0 | Q0 | J0 | H0 | C0 | Y14 | Q14 | J14 | H14 | C14 | Y84 | Q84 | J84 | H84 | C84 | ||||
| 1 | 2-Methylfuran | 9 | Chocolate, vanilla | 3.05 | 0.95 | 0.97 | ||||||||||||
| 2 | 2-Methylbutanal | 20 | Musty, cocoa, pungent, sweet | 0.55 | ||||||||||||||
| 3 | Pentanal | 20 | Fermented, bready, woodsy, fruity | 0.63 | 1.55 | 0.74 | 1.92 | 1.45 | ||||||||||
| 4 | Hexanal | 4.5 | Grass-like, green, fatty | 100.00 | 4.53 | 100.00 | 6.74 | 8.18 | 5.41 | 100.00 | 8.13 | 100.00 | 27.96 | 68.44 | 4.53 | 15.88 | ||
| 5 | Pyridine | 7.9 | Sour, fishy | 1.54 | ||||||||||||||
| 6 | 2-Pentylfuran | 6 | Green bean, butter, vegetable | 5.66 | 29.06 | 12.83 | 7.70 | 3.66 | 5.17 | 4.22 | 2.43 | 12.10 | 5.67 | 40.12 | 7.12 | 27.03 | ||
| 7 | 1-Pentanol | 5 | Grassy, fruity | 6.53 | 9.76 | 9.61 | 33.49 | 17.03 | ||||||||||
| 8 | 2-Methylpyrazine | 60 | Nutty, cocoa, roasted | 4.34 | 3.49 | 3.75 | 1.79 | 3.93 | 3.49 | 1.24 | 4.61 | 3.98 | ||||||
| 9 | 4-Methylthiazole | 20 | Nutty, green, vegetable | 0.89 | ||||||||||||||
| 10 | Acetoin | 55 | Sweet, milky, buttery | 0.43 | ||||||||||||||
| 11 | Octanal | 0.7 | Fatty, soapy, green | 32.87 | 69.94 | 22.50 | ||||||||||||
| 12 | 2,6-Dimethylpyrazine | 1.5 | Chocolate, nutty, roasted | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | ||||||
| 13 | 2,3- Dimethyl pyrazine | 400 | Nutty, peanut, butter | 0.13 | 0.11 | |||||||||||||
| 14 | 2-Ethyl-6-methylpyrazine | 40 | Earthy, roasted | 1.25 | 3.37 | 2.00 | 0.71 | 2.80 | 1.42 | 0.80 | 3.06 | 1.94 | ||||||
| 15 | 2-Ethyl-5-methylpyrazine | 100 | Coffee bean, nutty, roasted | 0.21 | 0.88 | 1.09 | 0.11 | 0.66 | 0.59 | 0.70 | 0.57 | |||||||
| 16 | Nonanal | 260 | Citrus-like, rose, grassy | 0.43 | 0.12 | 0.81 | 0.10 | 0.14 | 0.31 | |||||||||
| 17 | 2,3,5-Trime-thylpyrazine | 400 | Nutty, baked potato, roasted peanut | 0.17 | 0.36 | 0.48 | 0.23 | 0.22 | 0.14 | 0.25 | 0.39 | |||||||
| 18 | 3-Ethyl-2, 5-dimethylpyrazine | 8.6 | Roasted, nutty, earthy | 5.99 | 31.44 | 29.87 | 4.28 | 14.46 | 20.59 | 5.33 | 15.41 | 36.30 | ||||||
| 19 | 1-Octene-3-ol | 1 | Mushroom | 10.94 | 33.33 | 100.00 | 71.60 | |||||||||||
| 20 | 2-Ethyl-3, 5-dimethylpyrazine | 40 | Roasted, chocolate, cacoa-like | 1.47 | 1.23 | 0.97 | 0.87 | 0.69 | ||||||||||
| 21 | 2-Ethyl-1-hexanol | 0.8 | Floral, citrus, sweet | 85.96 | 100.00 | 12.05 | 19.03 | 8.28 | ||||||||||
| 22 | Benzaldehyde | 300 | Almond, burnt sugar, cherry | 0.15 | 0.13 | 0.13 | 0.20 | |||||||||||
| 23 | Propionic acid | 57 | Pungent, acidic, cheesy | 0.69 | 0.27 | 2.23 | 0.70 | 0.27 | 0.39 | 0.14 | 0.64 | |||||||
| 24 | Benzoic acid methyl ester | 73 | Floral, fruity | 1.37 | 0.39 | 1.91 | 0.17 | 1.92 | 0.21 | 0.37 | 0.26 | 0.33 | 0.30 | 0.46 | 0.61 | |||
| 25 | Benzeneacetaldehyde | 9 | Flora, honey-like | 1.29 | 0.32 | |||||||||||||
| 26 | 2-Butyl-2-octenal | 20 | Lemony, fruity | 2.69 | ||||||||||||||
| 27 | 3-Methylbutyric acid | 12 | Sweaty | 2.18 | ||||||||||||||
| 28 | (E,E)-2,4-Decadienal | 1.81 | Fatty, green | 1.27 | ||||||||||||||
| 29 | Hexanoic acid | 2.52 | Sweaty, sour, fatty | 29.00 | 14.15 | 16.18 | 6.54 | 3.03 | 50.71 | 3.08 | 4.88 | 6.21 | 9.80 | 38.87 | 20.34 | 91.37 | 16.06 | 95.22 |
| 30 | 2-Methoxyphenol | 0.84 | Gammon-like, smoky | 24.99 | 9.84 | 5.93 | 4.07 | 12.10 | 3.92 | 5.12 | 8.40 | |||||||
| 31 | Benzyl alcohol | 100 | Sweet, flowery | 0.58 | 0.57 | |||||||||||||
| 32 | Phenol | 0.65 | Rubber, phenolic | 9.46 | 3.18 | 2.91 | 8.51 | |||||||||||
| 33 | Furaneol | 27.4 | Caramel-like, sweet, maltol-like | 0.96 | 0.14 | 0.10 | ||||||||||||
| 34 | 2-Methoxy-4-vinylphenol | 21 | Smoky, clove-like | 2.03 | 1.00 | 0.76 | 0.31 | 0.59 | 0.24 | 0.07 | 0.18 | 0.15 | ||||||
3.4. Changes in Key Volatile Compounds during Storage
3.5. Analysis of the Formation Mechanism of Key Volatile Compounds
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dang, B.; Zhang, W.-G.; Zhang, J.; Yang, X.-J.; Xu, H.-D. Evaluation of nutritional components, phenolic composition, and antioxidant capacity of highland barley with different grain colors on the Qinghai Tibet Plateau. Foods 2022, 11, 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, X.; Guo, Y.; Xu, Q.; Mascher, M.; Guo, G.; Li, S.; Tashi, N. Origin and evolution of qingke barley in Tibet. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 5433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obadi, M.; Sun, J.; Xu, B. Highland barley: Chemical composition, bioactive compounds, health effects, and applications. Food Res. Int. 2021, 140, 110065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikram, S.; Zhang, H.; Ming, H.; Wang, J. Recovery of major phenolic acids and antioxidant activity of highland barley brewer’s spent grains extracts. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2019, 44, 14308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuersuntuoheti, T.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, M.; Pan, F.; Liang, S.; Sohail, A.; Wang, X. Different preparation methods affect the phenolic profiles and antioxidant properties of Qingke barley foods. Cereal Chem. 2021, 98, 729–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, S.; Wang, A.; Lao, F.; Shen, Q.; Liao, X.; Zhang, P.; Wu, J. Effects of frying, roasting and boiling on aroma profiles of adzuki beans (Vigna angularis) and potential of adzuki bean and millet flours to improve flavor and sensory characteristics of biscuits. Food Chem. 2021, 339, 127878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diez-Simon, C.; Mumm, R.; Hall, R.D. Mass spectrometry-based metabolomics of volatiles as a new tool for understanding aroma and flavour chemistry in processed food products. Metabolomics 2019, 15, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Li, Y.; Chen, F.; Yong, F. Lipid oxidation of brown rice stored at different temperatures. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 52, 188–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takemitsu, H.; Amako, M.; Sako, Y.; Kita, K.; Ozeki, T.; Inui, H.; Kitamura, S. Reducing the undesirable odor of barley by cooking with superheated steam. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 56, 4732–4741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatsu, S.; Matsuo, Y.; Nakahara, K.; Hofmann, T.; Steinhaus, M. Key odorants in Japanese roasted barley tea (Mugi-Cha)-Differences between roasted barley tea prepared from naked barley and roasted barley tea prepared from hulled barley. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 2728–2737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Li, W.; Hu, Y.; Zhou, X.; Ji, M.; Yu, D.; Luan, G. Comparison of pregelatinization methods on physicochemical, functional and structural properties of tartary buckwheat flour and noodle quality. J. Cereal Sci. 2018, 80, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wang, L.; Qiu, J.; Li, Z. Effects of superheated steam processing on common buckwheat grains: Lipase inactivation and its association with lipidomics profile during storage. J. Cereal Sci. 2020, 95, 103057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wang, L.; Wang, A.; Qiu, J.; Li, Z. Superheated steam processing improved the qualities of noodles by retarding the deterioration of buckwheat grains during storage. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 138, 110746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Chen, Y.; Ren, J.; Guo, S. Aroma stability of millet powder during storage and effects of cooking methods and antioxidant treatment. Cereal Chem. 2014, 91, 262–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, S.; Zhu, D.; Deng, Y.; Zhao, Y. Effects of hot air-assisted radio frequency heating on quality and shelf-life of roasted peanuts. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2015, 9, 308–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaneko, S.; Kodama, T.; Kohyama, N.; Watanabe, H.; Hayase, F. Aroma components characterizing the odor of cooked barley. J. Jpn. Soc. Food Sci. 2013, 60, 439–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adebowale, O.J.; Taylor, J.R.N.; de Kock, H.L. Stabilization of wholegrain sorghum flour and consequent potential improvement of food product sensory quality by microwave treatment of the kernels. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 132, 109827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Zhang, C.; Feng, T.; Zhuang, H. Analysis of volatile flavor compounds of corn under different treatments by GC-MS and GC-IMS. Front. Chem. 2022, 10, 725208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Q.; Wang, Z.; Xiong, F.; Zhang, G. Enzyme inactivation induced by thermal stabilization in highland barley and impact on lipid oxidation and aroma profiles. Front. Nutr. 2023, 10, 1097775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.; Wu, G.; Zhang, H.; Jin, Q.; Wang, X. Deep-fried flavor: Characteristics, formation mechanisms, and influencing factors. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 60, 1496–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franklin, L.M.; King, E.S.; Chapman, D.; Byrnes, N.; Huang, G.; Mitchell, A.E. Flavor and acceptance of roasted California almonds during accelerated storage. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 1222–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warner, K.J.H.; Dimick, P.S.; Ziegler, G.R.; Mumma, R.O. ‘Flavor-fade’ and off flavors in ground roasted peanuts as related to selected pyrazines and aldehydes. J. Food Sci. Technol. 1996, 61, 469–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lampi, A.-M.; Damerau, A.; Li, J.; Moisio, T.; Partanen, R.; Forssell, P.; Piironen, V. Changes in lipids and volatile compounds of oat flours and extrudates during processing and storage. J. Cereal Sci. 2015, 62, 102–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, S.; Xu, X.; Luo, D.; Lao, F.; Pang, X.; Shen, Q.; Wu, J. Characterization of key aroma compounds in raw and roasted peas (Pisum sativum L.) by application of instrumental and sensory techniques. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 2718–2727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.-H.; Yang, Y.-Y.; Zhang, J.-Y.; Zhang, Q.-D.; Xu, F.; Li, Z.-J. Characterization of volatiles and aroma in Chinese steamed bread during elaboration. J. Cereal Sci. 2021, 101, 103310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franklin, L.M.; Chapman, D.M.; King, E.S.; Mau, M.; Huang, G.; Mitchell, A.E. Chemical and sensory characterization of oxidative changes in roasted almonds undergoing accelerated shelf life. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 2549–2563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkins, C.K.; Scholl, S. Volatile metabolites of some barley storage molds. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 1989, 8, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, S.; Wang, A.; Wang, Y.; Xu, X.; Luo, D.; Shen, Q.; Wu, J. Effect of cooking on aroma profiles of Chinese foxtail millet (Setaria italica) and correlation with sensory quality. Food Chem. 2019, 289, 680–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGorrin, R.J. Key aroma compounds in oats and oat cereals. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 13778–13789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, Q.; Zhang, B.; Shen, C.; Xu, Y.; Tang, K. Identification, quantitation and sensorial contribution of lactones in brandies between China and France. Food Chem. 2021, 357, 129761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, B.; Zhang, W.-G.; Zhang, J.; Yang, X.-J.; Xu, H.-D. Effect of thermal treatment on the internal structure, physicochemical properties and storage stability of whole grain highland barley flour. Foods 2022, 11, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maoz, I.; Lewinsohn, E.; Gonda, I. Amino acids metabolism as a source for aroma volatiles biosynthesis. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2022, 67, 102221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, Y.; Li, Q.; Yan, J.; Baldwin, E.; Plotto, A.; Rosskopf, E.; Li, J. Effects of harvest maturity, refrigeration and blanching treatments on the volatile profiles of ripe “Tasti-Lee” tomatoes. Foods 2021, 10, 1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Yang, S.; Zhang, R.; Liu, S.; Zhang, C.; Li, Y.; Li, J. Characterization of honey peach (Prunus persica (L.) Batsch) aroma variation and unraveling the potential aroma metabolism mechanism through proteomics analysis under abiotic stress. Food Chem. 2022, 386, 132720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzi, G.P. The strecker degradation of amino acids: Newer avenues for flavor formation. Food Rev. Int. 2008, 24, 416–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, T.; Honda, Y.; Mukasa, Y.; Kim, S.J. Effects of lipase, lipoxygenase, peroxidase, and rutin on quality deteriorations in buckwheat flour. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 8400–8405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contreras, C.; Tjellström, H.; Beaudry, R.M. Relationships between free and esterified fatty acids and LOX-derived volatiles during ripening in apple. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2016, 112, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ao, X.; Mu, Y.; Xie, S.; Meng, D.; Zheng, Y.; Meng, X.; Lv, Z. Impact of UHT processing on volatile components and chemical composition of sea buckthorn (Hippophae rhamnoides) pulp: A prediction of the biochemical pathway underlying aroma compound formation. Food Chem. 2022, 390, 133142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suh, J.H.; Madden, R.T.; Sung, J.; Chambers, A.H.; Crane, J.; Wang, Y. Pathway-based metabolomics analysis reveals biosynthesis of key flavor compounds in mango. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 10389–10399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Yang, J.; Dong, H.; Liu, Q.; Li, X.; Zeng, X.; Bai, W. Key aroma compounds of Chinese dry-cured Spanish mackerel (Scomberomorus niphonius) and their potential metabolic mechanisms. Food Chem. 2021, 342, 128381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Hua, Y.; Li, X.; Kong, X.; Chen, Y. Key volatile off-flavor compounds in peas (Pisum sativum L.) and their relations with the endogenous precursors and enzymes using soybean (Glycine max) as a reference. Food Chem. 2020, 333, 127469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teshima, T.; Funai, R.; Nakazawa, T.; Ito, J.; Utsumi, T.; Kakumyan, P.; Matsui, K. Coprinopsis cinerea dioxygenase is an oxygenase forming 10(S)-hydroperoxide of linoleic acid, essential for mushroom alcohol, 1-octen-3-ol, synthesis. J. Biol. Chem. 2022, 298, 102507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, W.; Yang, X.; Zhang, J.; Lan, Y.; Dang, B. Study on the Changes in Volatile Flavor Compounds in Whole Highland Barley Flour during Accelerated Storage after Different Processing Methods. Foods 2023, 12, 2137. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12112137
Zhang W, Yang X, Zhang J, Lan Y, Dang B. Study on the Changes in Volatile Flavor Compounds in Whole Highland Barley Flour during Accelerated Storage after Different Processing Methods. Foods. 2023; 12(11):2137. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12112137
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Wengang, Xijuan Yang, Jie Zhang, Yongli Lan, and Bin Dang. 2023. "Study on the Changes in Volatile Flavor Compounds in Whole Highland Barley Flour during Accelerated Storage after Different Processing Methods" Foods 12, no. 11: 2137. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12112137
APA StyleZhang, W., Yang, X., Zhang, J., Lan, Y., & Dang, B. (2023). Study on the Changes in Volatile Flavor Compounds in Whole Highland Barley Flour during Accelerated Storage after Different Processing Methods. Foods, 12(11), 2137. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12112137