Designing Nanoliposome-in-Natural Hydrogel Hybrid System for Controllable Release of Essential Oil in Gastrointestinal Tract: A Novel Vehicle
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Fabrication of Nanoliposome and Hydrogel Systems
2.2.1. Fabrication Nanoliposomes Preparation
2.2.2. Hydrogel Preparation
2.3. Analyses
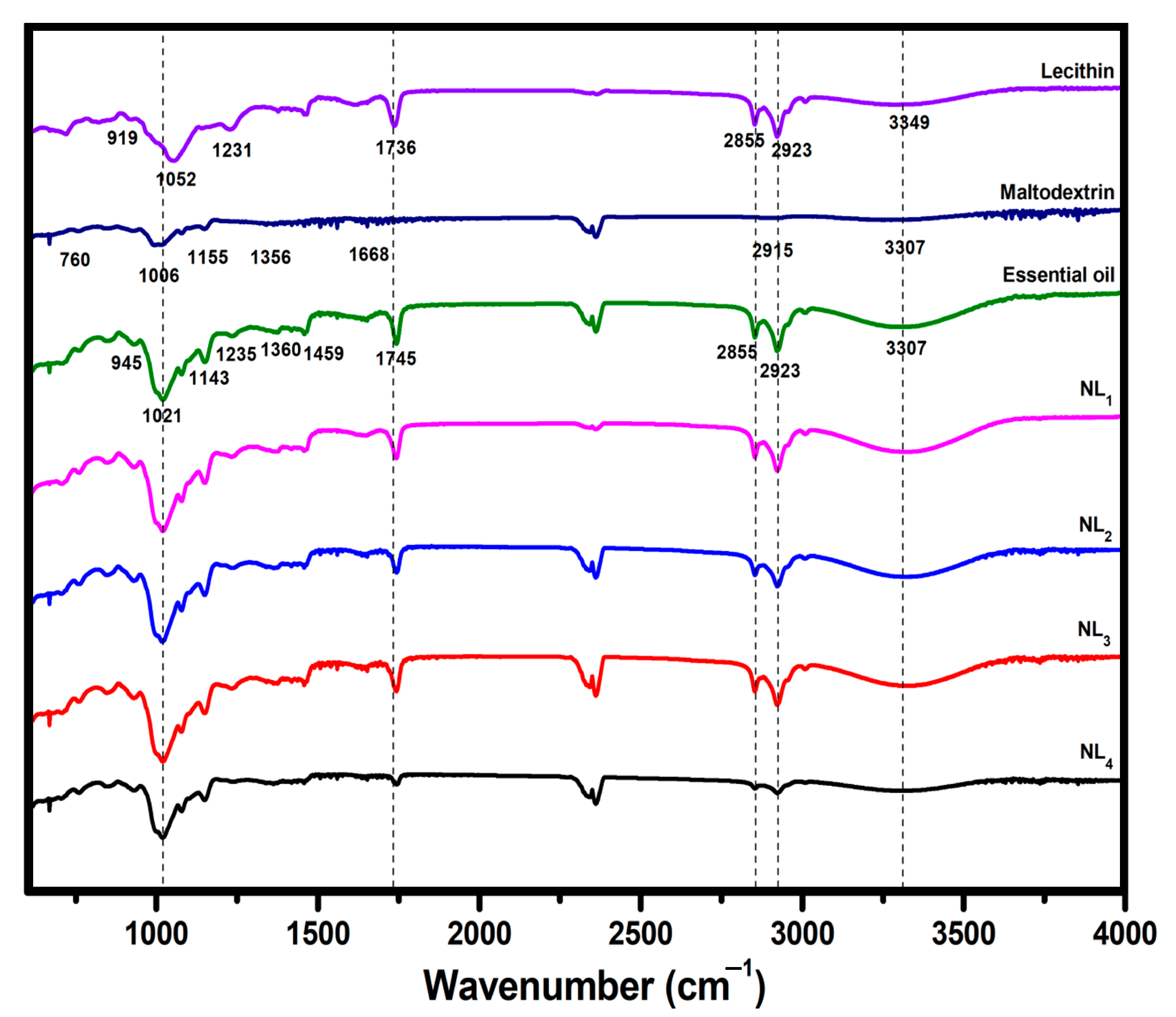
2.3.1. FTIR Spectroscopy
2.3.2. Particle Size and Zeta Potential
2.3.3. Encapsulation Efficiency
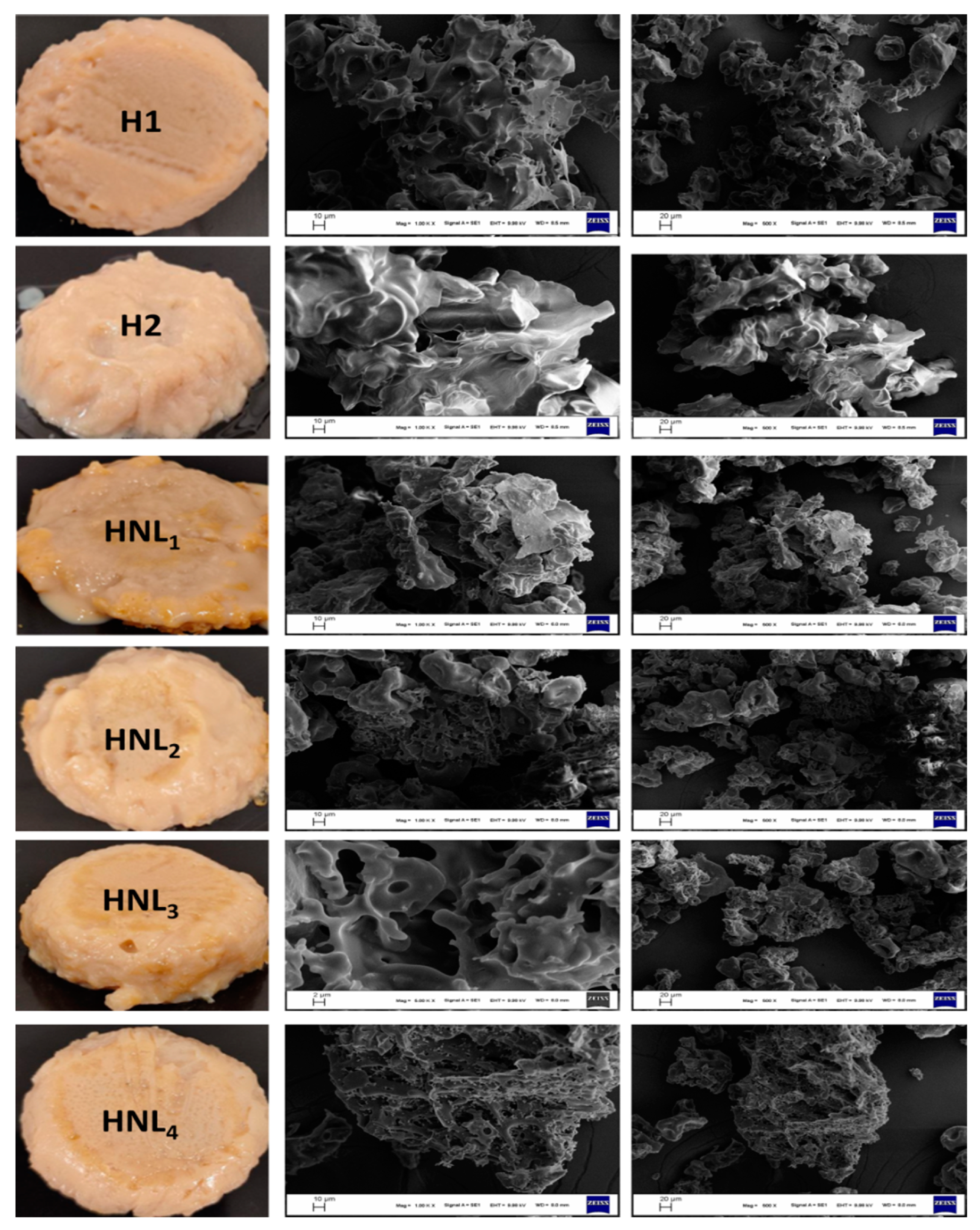
2.3.4. Scanning Electron Microscopy
2.3.5. Water-Holding Capacity
2.3.6. Swelling Ratio
2.3.7. Protein Leachability
2.3.8. Textural Behavior
2.3.9. Rheological Behavior
2.3.10. In Vitro Gastrointestinal Release
2.3.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Authentication of Nanoliposome Systems
3.2. Characteristic Attributes of Thyme Essential Oil-Loaded Nanoliposomes
3.3. Semblance and Scanning Electron Microscopy Images of Hydrogels
3.4. Functional Behaviors of Hydrogels
3.5. Textural Behaviors of Hydrogels
3.6. Rheological Behaviors of Hydrogels
3.7. Release Behavior of Thyme Essential Oil during In Vitro Gastrointestinal Digestion
4. Conclusions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, Z.; Zhang, R.; Chen, L.; Tong, Q.; McClements, D.J. Designing Hydrogel Particles for Controlled or Targeted Release of Lipophilic Bioactive Agents in the Gastrointestinal Tract. Eur. Polym. J. 2015, 72, 698–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amiri, H.; Shabanpour, B.; Pourashouri, P.; Kashiri, M. Encapsulation of Marine Bioactive Compounds Using Liposome Technique: Evaluation of Physicochemical Properties and Oxidative Stability during Storage. Food Struct. 2023, 35, 100308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seyedabadi, M.M.; Rostami, H.; Jafari, S.M.; Fathi, M. Development and Characterization of Chitosan-Coated Nanoliposomes for Encapsulation of Caffeine. Food Biosci. 2021, 40, 100857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Kong, Y.; Ye, A.; Shen, P.; Dong, L.; Xu, X.; Hou, Y.; Wang, Y.; Jin, Y.; Han, J. Preparation, Formation Mechanism and in Vitro Dynamic Digestion Behavior of Quercetin-Loaded Liposomes in Hydrogels. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 104, 105743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebrahimi, A.; Reza Farahpour, M.; Amjadi, S.; Mohammadi, M.; Hamishehkar, H. Nanoliposomal Peptides Derived from Spirulina Platensis Protein Accelerate Full-Thickness Wound Healing. Int. J. Pharm. 2023, 630, 122457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhao, K.; Xie, L.; Li, K.; Zhang, W.; Xi, Z.; Wang, X.; Xia, M.; Xu, L. Construction of Calcium Carbonate-Liposome Dual-Film Coated Mesoporous Silica as a Delayed Drug Release System for Antitumor Therapy. Colloids Surf. B. Biointerfaces 2022, 212, 112357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celia, C.; Cristiano, M.C.; Froiio, F.; Di Francesco, M.; d’Avanzo, N.; Di Marzio, L.; Fresta, M. Nanoliposomes as Multidrug Carrier of Gemcitabine/Paclitaxel for the Effective Treatment of Metastatic Breast Cancer Disease: A Comparison with Gemzar and Taxol. Adv. Ther. 2021, 4, 2000121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Thakur, S.; Virdi, A.S.; Singh, N.; Kour, R.; Kaur, S.; Jain, S.K. Novel Methylcellulose Based Thermosenstive in Situ Nano Liposomes of Docetaxel for Improved Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics with Reduced Toxicity. Mater. Today Commun. 2022, 33, 104167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilal, M.; Qindeel, M.; Raza, A.; Mehmood, S.; Rahdar, A. Stimuli-Responsive Nanoliposomes as Prospective Nanocarriers for Targeted Drug Delivery. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2021, 66, 102916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Li, L.; Peng, Z.; He, Y.; Zhang, C.; Zheng, C. Improved Targeting Delivery of WED-Load Immunoliposomes Modified with SP-A MAb for the Treatment of Pulmonary Fibrosis. Colloids Surf. B. Biointerfaces 2023, 224, 113237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bondu, C.; Yen, F.T. Nanoliposomes, from Food Industry to Nutraceuticals: Interests and Uses. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2022, 81, 103140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mare, R.; Da, H.; Fresta, M.; Cosco, D.; Awasthi, V. Anchoring Property of a Novel Hydrophilic Lipopolymer, HDAS-SHP, Post-Inserted in Preformed Liposomes. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subramani, T.; Ganapathyswamy, H. An Overview of Liposomal Nano-Encapsulation Techniques and Its Applications in Food and Nutraceutical. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 57, 3545–3555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Polo, J.; Monasterio, A.; Cantero-López, P.; Osorio, F.A. Combining Edible Coatings Technology and Nanoencapsulation for Food Application: A Brief Review with an Emphasis on Nanoliposomes. Food Res. Int. 2021, 145, 110402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Chen, W.; Li, C.; Cui, H. Enhancing Stability of Eucalyptus Citriodora Essential Oil by Solid Nanoliposomes Encapsulation. Ind. Crops Prod. 2019, 140, 111615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nada, A.; Hassabo, A.; Mohamed, A.; Mounier, M.; Zeid, N. Liposomal Microencapsulation of Rodent-Repelling Agents onto Jute Burlaps: Assessment of Cytotoxicity and Rat Behavioral Test. J. Appl. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 6, 142–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engel, J.B.; Heckler, C.; Tondo, E.C.; Daroit, D.J.; da Silva Malheiros, P. Antimicrobial Activity of Free and Liposome-Encapsulated Thymol and Carvacrol against Salmonella and Staphylococcus aureus Adhered to Stainless Steel. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2017, 252, 18–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gortzi, O.; Lala, S.; Chinou, I.; Tsaknis, J. Evaluation of the Antimicrobial and Antioxidant Activities of Origanum Dictamnus Extracts before and after Encapsulation in Liposomes. Molecules 2007, 12, 932–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vélez, M.A.; Perotti, M.C.; Hynes, E.R.; Gennaro, A.M. Effect of Lyophilization on Food Grade Liposomes Loaded with Conjugated Linoleic Acid. J. Food Eng. 2019, 240, 199–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pachis, K.; Blazaki, S.; Tzatzarakis, M.; Klepetsanis, P.; Naoumidi, E.; Tsilimbaris, M.; Antimisiaris, S.G. Sustained Release of Intravitreal Flurbiprofen from a Novel Drug-in-Liposome-in-Hydrogel Formulation. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 109, 324–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, E.M. Hydrogel: Preparation, Characterization, and Applications: A Review. J. Adv. Res. 2015, 6, 105–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, S.; Tiwari, S. A Review on Biomacromolecular Hydrogel Classification and Its Applications. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 162, 737–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, X.; Agate, S.; Salem, K.S.; Lucia, L.; Pal, L. Hydrogel-Based Sensor Networks: Compositions, Properties, and Applications—A Review. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2021, 4, 140–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondal, S.; Das, S.; Nandi, A.K. A Review on Recent Advances in Polymer and Peptide Hydrogels. Soft Matter 2020, 16, 1404–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Başyiğit, B.; Altun, G.; Yücetepe, M.; Karaaslan, A.; Karaaslan, M. Locust Bean Gum Provides Excellent Mechanical and Release Attributes to Soy Protein-Based Natural Hydrogels. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 231, 123352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zainal, S.H.; Mohd, N.H.; Suhaili, N.; Anuar, F.H.; Lazim, A.M.; Othaman, R. Preparation of Cellulose-Based Hydrogel: A Review. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2021, 10, 935–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz, A.; Puiggalí, J. Hydrogels for Biomedical Applications: Cellulose, Chitosan, and Protein/Peptide Derivatives. Gels 2017, 3, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, P.; Huang, W.; Guo, X.; Chen, L. Strong and Elastic Pea Protein Hydrogels Formed through pH-Shifting Method. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 117, 106705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhang, R.; Zou, L.; McClements, D.J. Protein Encapsulation in Alginate Hydrogel Beads: Effect of pH on Microgel Stability, Protein Retention and Protein Release. Food Hydrocoll. 2016, 58, 308–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abasalizadeh, F.; Moghaddam, S.V.; Alizadeh, E.; Akbari, E.; Kashani, E.; Fazljou, S.M.B.; Torbati, M.; Akbarzadeh, A. Alginate-Based Hydrogels as Drug Delivery Vehicles in Cancer Treatment and Their Applications in Wound Dressing and 3D Bioprinting. J. Biol. Eng. 2020, 14, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soleimani, S.; Heydari, A.; Fattahi, M. Swelling Prediction of Calcium Alginate/Cellulose Nanocrystal Hydrogels Using Response Surface Methodology and Artificial Neural Network. Ind. Crops Prod. 2023, 192, 116094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirkıran, E.; Başyiğit, B.; Altun, G.; Yücetepe, M.; Sağlam, H.; Karaaslan, M. Facile Construction of Fruit Protein Based Natural Hydrogel via Intra/Inter Molecular Cross-Linking. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 133, 107899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shabkhiz, M.A.; Khalil Pirouzifard, M.; Pirsa, S.; Mahdavinia, G.R. Alginate Hydrogel Beads Containing Thymus daenensis Essential Oils/Glycyrrhizic Acid Loaded in β-Cyclodextrin. Investigation of Structural, Antioxidant/Antimicrobial Properties and Release Assessment. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 344, 117738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekine, Y.; Moritani, Y.; Ikeda-Fukazawa, T.; Sasaki, Y.; Akiyoshi, K. A Hybrid Hydrogel Biomaterial by Nanogel Engineering: Bottom-Up Design with Nanogel and Liposome Building Blocks to Develop a Multidrug Delivery System. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2012, 1, 722–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mosquera, M.; Giménez, B.; da Silva, I.M.; Boelter, J.F.; Montero, P.; Gómez-Guillén, M.C.; Brandelli, A. Nanoencapsulation of an Active Peptidic Fraction from Sea Bream Scales Collagen. Food Chem. 2014, 156, 144–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keivani Nahr, F.; Ghanbarzadeh, B.; Hamishehkar, H.; Kafil, H.S.; Hoseini, M.; Moghadam, B.E. Investigation of Physicochemical Properties of Essential Oil Loaded Nanoliposome for Enrichment Purposes. LWT 2019, 105, 282–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarabandi, K.; Jafari, S.M.; Mohammadi, M.; Akbarbaglu, Z.; Pezeshki, A.; Khakbaz Heshmati, M. Production of Reconstitutable Nanoliposomes Loaded with Flaxseed Protein Hydrolysates: Stability and Characterization. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 96, 442–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Liu, C.; Zhao, J.; Li, W.; Wang, Y. Physicochemical Properties of a Ginkgo Seed Protein-Pectin Composite Gel. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 118, 106781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Li, R.; Gao, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Liao, L.; Cao, Y.; Li, J.; Zhou, W. Encapsulation of Hydrophobic and Low-Soluble Polyphenols into Nanoliposomes by PH-Driven Method: Naringenin and Naringin as Model Compounds. Foods 2021, 10, 963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsakhawy, S.A.; Baghdadi, H.H.; El-Shenawy, M.A.; Sabra, S.A.; El-Hosseiny, L.S. Encapsulation of Thymus vulgaris Essential Oil in Caseinate/Gelatin Nanocomposite Hydrogel: In Vitro Antibacterial Activity and In Vivo Wound Healing Potential. Int. J. Pharm. 2022, 628, 122280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhao, J.; Liu, C.; Li, W. Influence of γ-Aminobutyric Acid on Gelling Properties of Heat-Induced Whey Protein Gels. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 94, 287–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Ma, T.; Zhang, W.; Su, E.; Cao, F.; Huang, M.; Wang, Y. Heat-Induced Gel Formation by Whey Protein Isolate-Lycium Barbarum Polysaccharides at Varying PHs. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 115, 106607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Ji, N.; Li, F.; Qin, Y.; Wang, Y.; Xiong, L.; Sun, Q. Dual Cross-Linked Starch–Borax Double Network Hydrogels with Tough and Self-Healing Properties. Foods 2022, 11, 1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minekus, M.; Alminger, M.; Alvito, P.; Ballance, S.; Bohn, T.; Bourlieu, C.; Carrière, F.; Boutrou, R.; Corredig, M.; Dupont, D.; et al. A Standardised Static in Vitro Digestion Method Suitable for Food—An International Consensus. Food Funct. 2014, 5, 1113–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nazari, M.; Ghanbarzadeh, B.; Samadi Kafil, H.; Zeinali, M.; Hamishehkar, H. Garlic Essential Oil Nanophytosomes as a Natural Food Preservative: Its Application in Yogurt as Food Model. Colloid. Interface Sci. Commun. 2019, 30, 100176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarabandi, K.; Jafari, S.M.; Mahoonak, A.S.; Mohammadi, A. Application of Gum Arabic and Maltodextrin for Encapsulation of Eggplant Peel Extract as a Natural Antioxidant and Color Source. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 140, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Başyiğit, B.; Sağlam, H.; Kandemir, Ş.; Karaaslan, A.; Karaaslan, M. Microencapsulation of Sour Cherry Oil by Spray Drying: Evaluation of Physical Morphology, Thermal Properties, Storage Stability, and Antimicrobial Activity. Powder Technol. 2020, 364, 654–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanei-Dehkordi, A.; Moemenbellah-Fard, M.D.; Saffari, M.; Zarenezhad, E.; Osanloo, M. Nanoliposomes Containing Limonene and Limonene-Rich Essential Oils as Novel Larvicides against Malaria and Filariasis Mosquito Vectors. BMC Complement. Med. Ther. 2022, 22, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marand, S.A.; Almasi, H.; Amjadi, S.; Alamdari, N.G.; Salmasi, S. Ixiolirion tataricum Mucilage/Chitosan Based Antioxidant Films Activated by Free and Nanoliposomal Fennel Essential Oil. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 230, 123119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, H.; Zhao, C.; Lin, L. The Specific Antibacterial Activity of Liposome-Encapsulated Clove Oil and Its Application in Tofu. Food Control 2015, 56, 128–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, X.; Liu, R.; Chen, M.; Li, Z.; Qin, T.; Qian, Y.; Zhao, S.; Liu, M.; Zeng, Q.; Shen, J. Removal of Copper Ions from Water Using Polysaccharide-Constructed Hydrogels. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 209, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Souza, A.G.; Cesco, C.T.; de Lima, G.F.; Artifon, S.E.S.; Rosa, D.d.S.; Paulino, A.T. Arabic Gum-Based Composite Hydrogels Reinforced with Eucalyptus and Pinus Residues for Controlled Phosphorus Release. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 140, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, Q.; Wang, G.; Gao, D.; Wang, L.; Zhang, A.; Wang, X.; Xu, N.; Jiang, L. Improving the Gel Properties of Transgenic Microbial Transglutaminase Cross-Linked Soybean-Whey Mixed Protein by Ultrasonic Pretreatment. Process Biochem. 2020, 91, 104–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Shen, M.; Luo, Y.; Wu, T.; Wen, H.; Xie, J. Construction and Characterization of Mesona chinensis Polysaccharide-Chitosan Hydrogels, Role of Chitosan Deacetylation Degree. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 257, 117608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Shen, M.; Jiang, L.; Song, Q.; Liu, S.; Xie, J. Influence of Mesona blumes Polysaccharide on the Gel Properties and Microstructure of Acid-Induced Soy Protein Isolate Gels. Food Chem. 2020, 313, 126125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.; Mao, L.; Zheng, H.; Chen, H.; Gao, Y. Characterization of β-Carotene Loaded Emulsion Gels Containing Denatured and Native Whey Protein. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 102, 105600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Netanel Liberman, G.; Ochbaum, G.; Bitton, R.; (Malis) Arad, S. Antimicrobial Hydrogels Composed of Chitosan and Sulfated Polysaccharides of Red Microalgae. Polymer 2021, 215, 123353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, W.; Jia, X.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, H.; Zhu, Q.; Yin, L. Interpenetrating Polymer Network Hydrogels of Soy Protein Isolate and Sugar Beet Pectin as a Potential Carrier for Probiotics. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 113, 106453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Q.; Qi, X.; Zhang, M.; Tong, X.; Jiang, N.; Pan, W.; Xiong, W.; Li, Y.; Xu, J.; Shen, J.; et al. Efficient Decontamination of Heavy Metals from Aqueous Solution Using Pullulan/Polydopamine Hydrogels. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 145, 1049–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, C.; Xu, D.; Cui, B.; Wang, Y. Gelation of κ-Carrageenan/Konjac Glucommanan Compound Gel: Effect of Cyclodextrins. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 87, 158–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, F.-H.; Chiang, P.-Y.; Kitamura, Y.; Kokawa, M.; Islam, M.Z. Producing Liquid-Core Hydrogel Beads by Reverse Spherification: Effect of Secondary Gelation on Physical Properties and Release Characteristics. Food Hydrocoll. 2017, 62, 140–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozkurt, H.; Bayram, M. Colour and Textural Attributes of Sucuk during Ripening. Meat Sci. 2006, 73, 344–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dertli, E.; Yilmaz, M.T.; Tatlisu, N.B.; Toker, O.S.; Cankurt, H.; Sagdic, O. Effects of in Situ Exopolysaccharide Production and Fermentation Conditions on Physicochemical, Microbiological, Textural and Microstructural Properties of Turkish-Type Fermented Sausage (Sucuk). Meat Sci. 2016, 121, 156–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, W.; Yin, L.; Li, J.; Yadav, M.P.; Jia, X. Development of Corn Fiber Gum–Soybean Protein Isolate Double Network Hydrogels Through Synergistic Gelation. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2020, 13, 511–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Monzó, J.; Cárdenas, J.; García-Segovia, P. Effect of Temperature on 3D Printing of Commercial Potato Puree. Food Biophys. 2019, 14, 225–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nesrinne, S.; Djamel, A. Synthesis, Characterization and Rheological Behavior of pH Sensitive Poly(Acrylamide-Co-Acrylic Acid) Hydrogels. Arab. J. Chem. 2017, 10, 539–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saxena, A.; Kaloti, M.; Bohidar, H.B. Rheological Properties of Binary and Ternary Protein–Polysaccharide Co-Hydrogels and Comparative Release Kinetics of Salbutamol Sulphate from Their Matrices. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2011, 48, 263–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastos, L.P.H.; dos Santos, C.H.C.; de Carvalho, M.G.; Garcia-Rojas, E.E. Encapsulation of the Black Pepper (Piper nigrum L.) Essential Oil by Lactoferrin-Sodium Alginate Complex Coacervates: Structural Characterization and Simulated Gastrointestinal Conditions. Food Chem. 2020, 316, 126345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahami, A.; Fathi, M. Development of Cress Seed Mucilage/PVA Nanofibers as a Novel Carrier for Vitamin A Delivery. Food Hydrocoll. 2018, 81, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Code | Molar Ratio of Soybean Lecithin to Maltodextrin | Thyme Essential Oil to Total Lipid (%) |
|---|---|---|
| NL1 | 0.20 M/- * | 14.23 |
| NL2 | 0.80 | 20 |
| NL3 | 0.40 | 25 |
| NL4 | 0.20 | 33.33 |
| Code | Particle Size (nm) | Zeta Potential (mV) | Encapsulation Efficiency (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| NL1 | 573.00 ± 4.04 b | −23.50 ± 0.17 c | 56.25 ± 0.92 d |
| NL2 | 521.90 ± 5.72 c | −28.40 ± 2.11 b | 60.39 ± 1.75 c |
| NL3 | 487.10 ± 7.41 d | −38.30 ± 1.06 a | 67.62 ± 0.64 a |
| NL4 | 664.40 ± 2.95 a | −29.10 ± 1.26 b | 63.92 ± 0.56 b |
| Code | Water-Holding Capacity (%) | Swelling Ratio (%) | Protein Leachability (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| H1 | 92.60 ± 0.72 a | 12.49 ± 0.43 b | 10.90 ± 0.07 e |
| H2 | 68.03 ± 0.07 d | 4.65 ± 0.07 e | 37.23 ± 0.48 a |
| HNL1 | 68.71 ± 0.97 d | 4.84 ± 0.76 e | 36.84 ± 0.10 a |
| HNL2 | 80.27 ± 0.22 c | 7.56 ± 0.16 d | 25.51 ± 0.17 b |
| HNL3 | 88.99 ± 0.61 b | 10.78 ± 0.54 c | 23.69 ± 0.07 c |
| HNL4 | 92.13 ± 0.82 a | 13.96 ± 0.37 a | 11.12 ± 0.03 d |
| Code | Hardness | Adhesiveness | Gumminess |
|---|---|---|---|
| H1 | 522.83 ± 2.34 a | −87.59 ± 1.47 b | 92.31 ± 01.33 a |
| H2 | 60.31 ± 1.43 e | −23.53 ± 1.05 c | 17.71 ± 0.60 e |
| HNL1 | 123.01 ± 4.97 d | −22.26 ± 1.23 c | 38.81 ± 1.29 c |
| HNL2 | 288.19 ± 2.46 c | −97.77 ± 1.12 a | 34.46 ± 0.89 d |
| HNL3 | 380.87 ± 1.64 b | −86.94 ± 2.26 b | 50.01 ± 2.15 b |
| HNL4 | 522.01 ± 3.79 a | −87.45 ± 1.35 b | 91.02 ± 3.16 a |
| Code | SSF (%) | SGF (%) | SIF (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| H2 | 1.86 ± 0.12 | 21.81 ± 0.96 a | 45.92 ± 1.18 a |
| HNL1 | nd | 8.29 ± 0.12 d | 32.97 ± 0.72 b |
| HNL2 | nd | 9.35 ± 0.21 c | 20.64 ± 0.57 d |
| HNL3 | nd | 9.58 ± 0.37 c | 20.35 ± 0.41 d |
| HNL4 | nd | 10.42 ± 0.16 b | 23.87 ± 0.22 c |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Basyigit, B. Designing Nanoliposome-in-Natural Hydrogel Hybrid System for Controllable Release of Essential Oil in Gastrointestinal Tract: A Novel Vehicle. Foods 2023, 12, 2242. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12112242
Basyigit B. Designing Nanoliposome-in-Natural Hydrogel Hybrid System for Controllable Release of Essential Oil in Gastrointestinal Tract: A Novel Vehicle. Foods. 2023; 12(11):2242. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12112242
Chicago/Turabian StyleBasyigit, Bulent. 2023. "Designing Nanoliposome-in-Natural Hydrogel Hybrid System for Controllable Release of Essential Oil in Gastrointestinal Tract: A Novel Vehicle" Foods 12, no. 11: 2242. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12112242
APA StyleBasyigit, B. (2023). Designing Nanoliposome-in-Natural Hydrogel Hybrid System for Controllable Release of Essential Oil in Gastrointestinal Tract: A Novel Vehicle. Foods, 12(11), 2242. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12112242





