Pickering Emulsion Stabilized by β-Cyclodextrin and Cinnamaldehyde/β-Cyclodextrin Composite
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation and Characterization of CA/β-CD Composite
2.3. Preparation of the Pickering Emulsion
2.3.1. Preparation of the Pickering Emulsion
2.3.2. Storage Stability, Particle Size, and Zeta Potential of Pickering Emulsion
2.3.3. Measurements of Texture Properties
2.3.4. Measurements of Rheological Properties
2.3.5. Fluorescence Microscope Observation
2.3.6. Measurement of Oxidation Resistance
2.3.7. In Vitro Simulated Digestion of Emulsion
2.3.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Analyses of Storage Stability and Particle Size and Zeta Potential
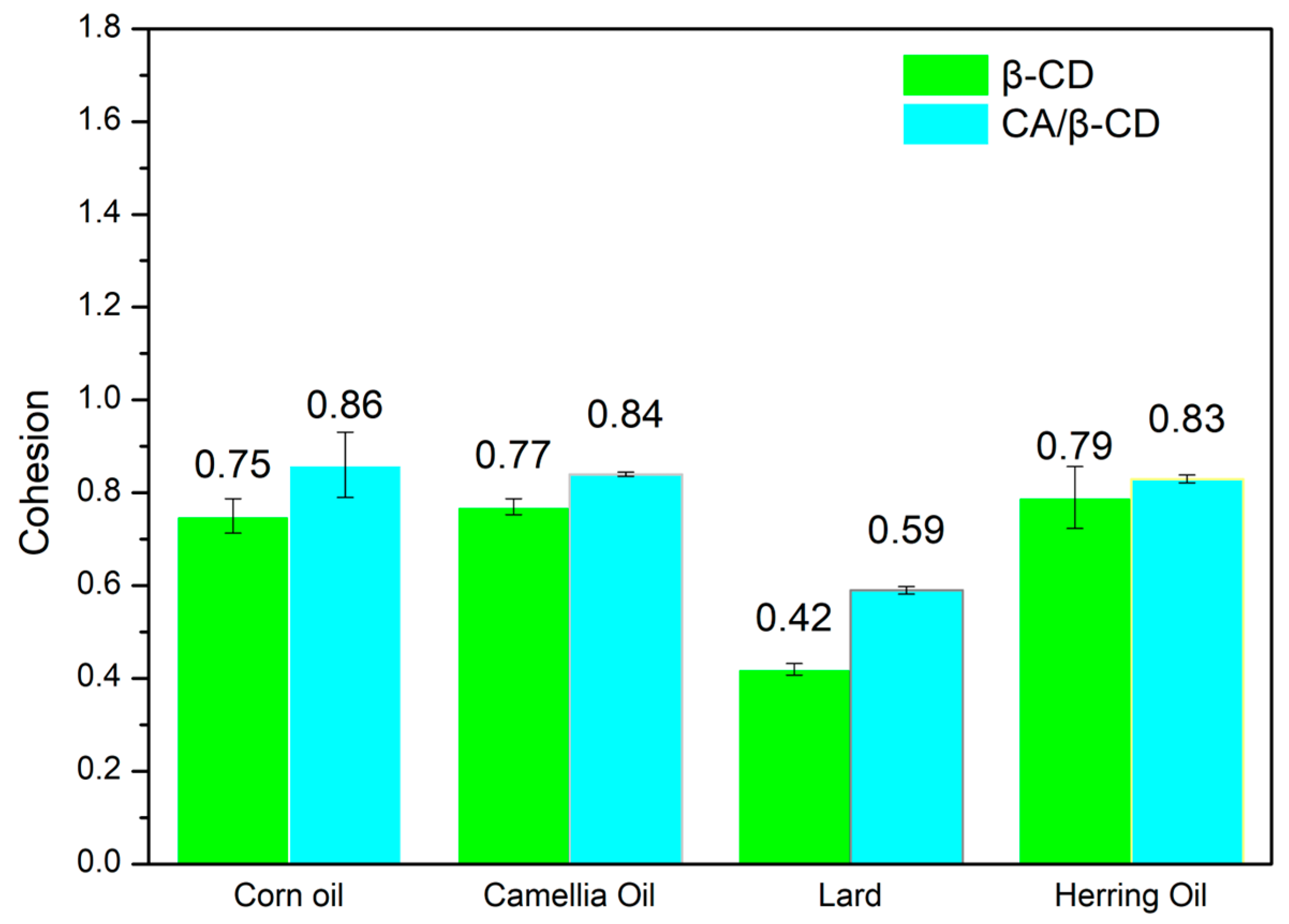
3.2. Analyses of Texture Properties
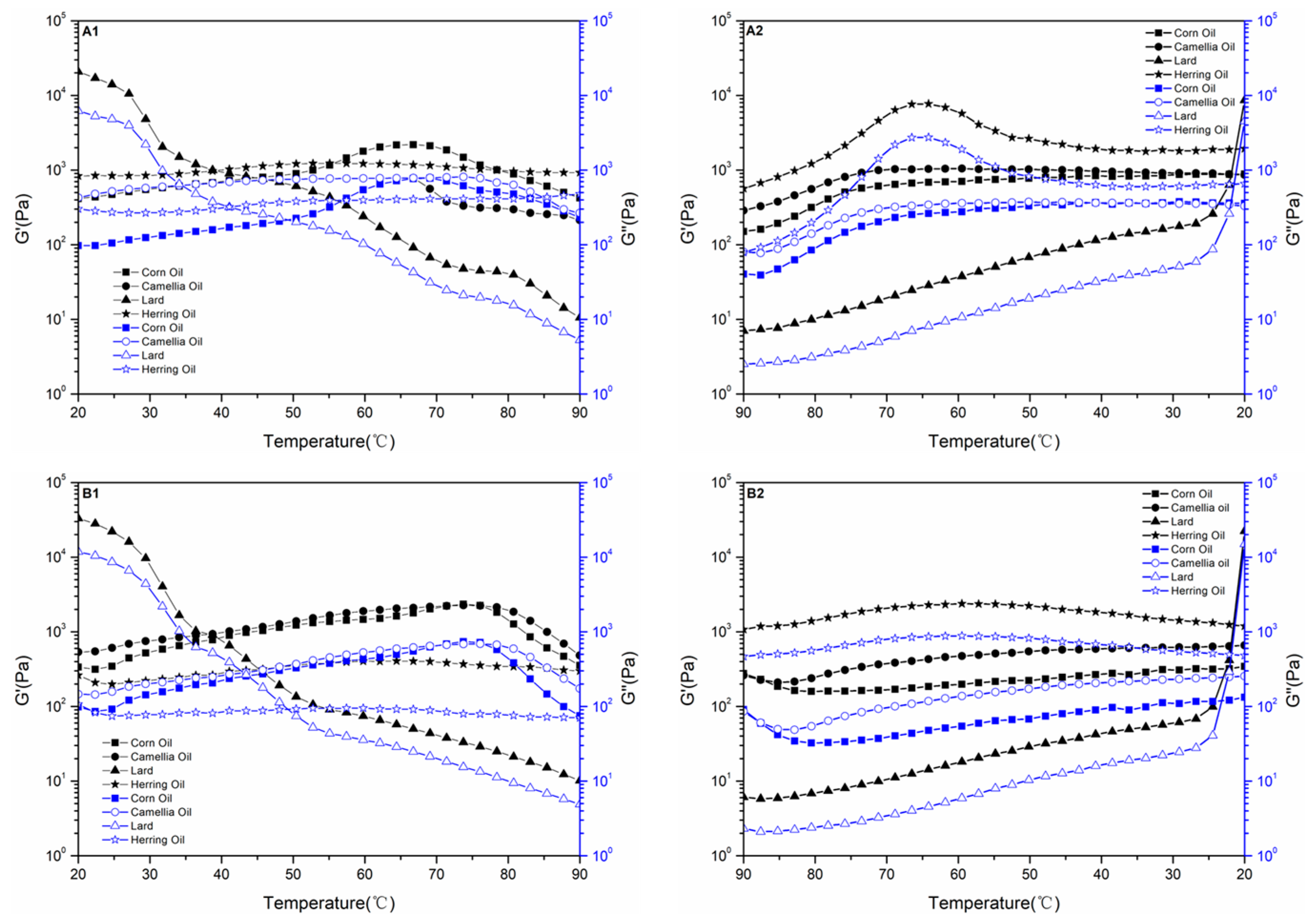
3.3. Analyses of Rheological Properties
3.4. Analyses of Microstructure
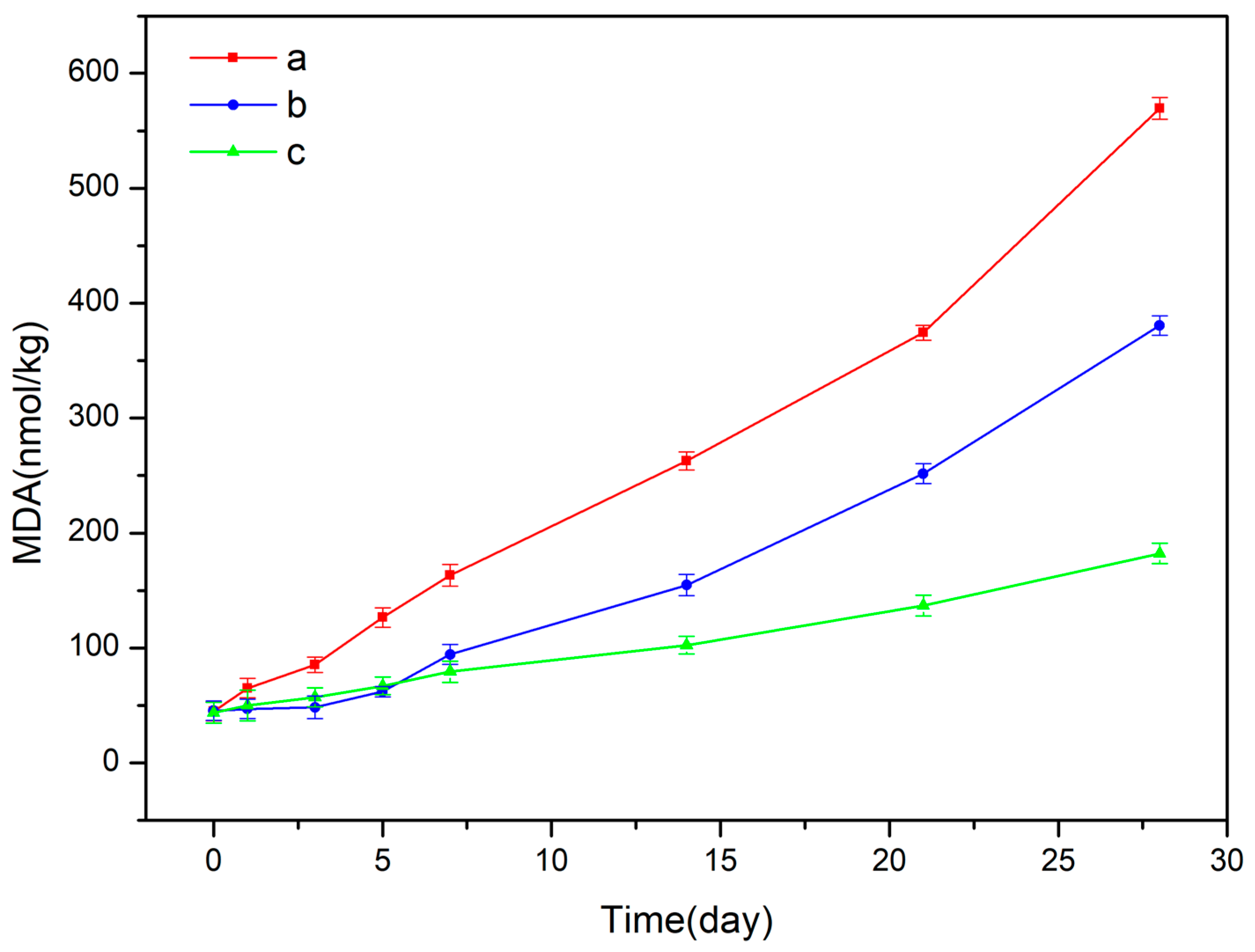
3.5. Analyses of Antioxidant Capacity
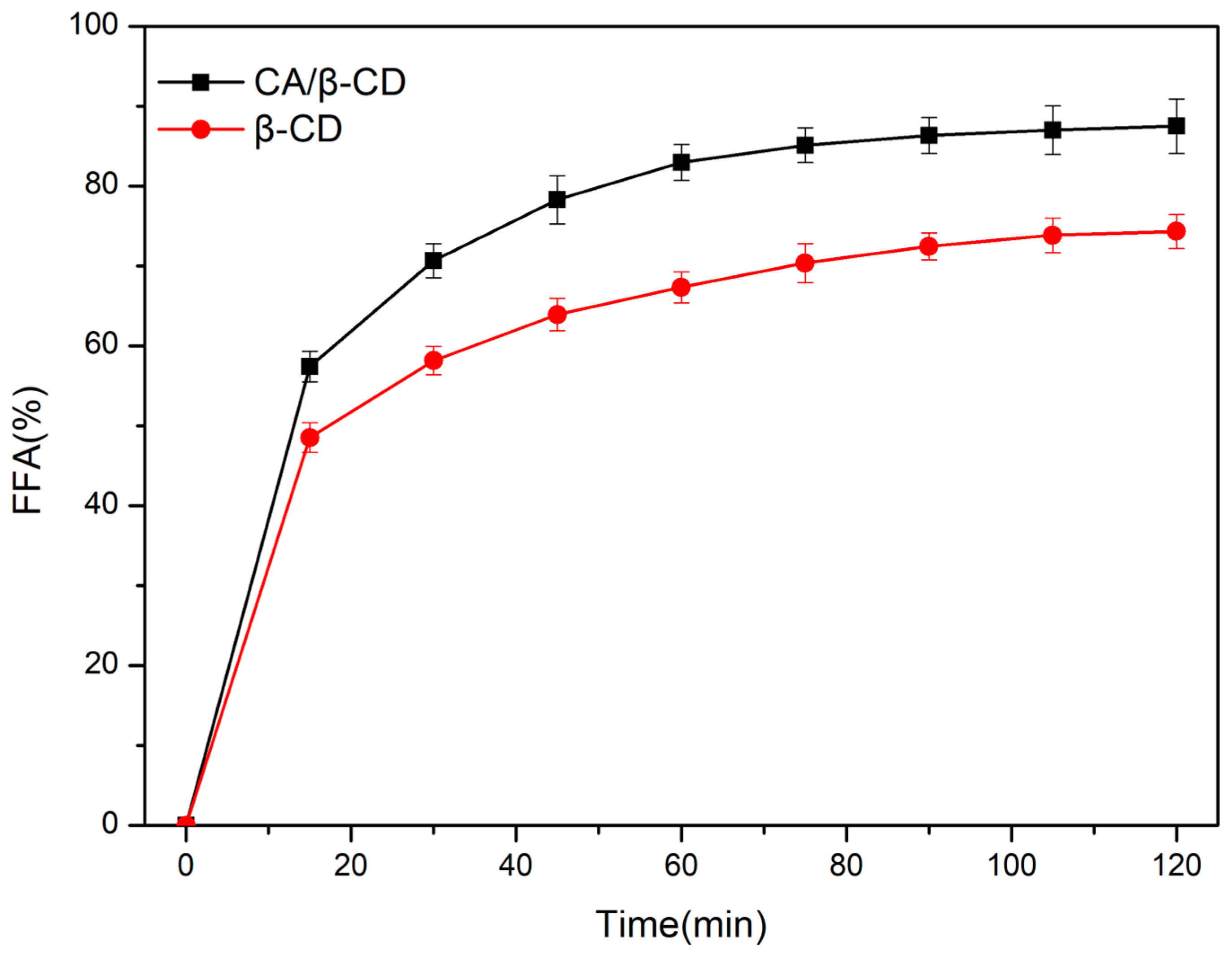
3.6. Analyses of In Vitro Digestion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jug, M.; Yoon, B.K.; Jackman, J.A. Cyclodextrin-based Pickering emulsions: Functional properties and drug delivery applications. J. Incl. Phenom. Macrocycl. Chem. 2021, 101, 31–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, Y.; Yuan, C.; Cui, B.; Lu, L.; Zhao, M.; Liu, P.; Wu, Z.; Li, J. Pickering emulsions stabilized by β-cyclodextrin and cinnamaldehyde essential oil/β-cyclodextrin composite: A comparison study. Food Chem. 2022, 377, 131995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Ao, F.; Ge, X.; Shen, W. Food-Grade Pickering Emulsions: Preparation, Stabilization and Applications. Molecules 2020, 25, 3202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, X.; Dai, H.; Ma, L.; Fu, Y.; Yu, Y.; Zhou, H.; Guo, T.; Zhu, H.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Y. Properties of Pickering emulsion stabilized by food-grade gelatin nanoparticles: Influence of the nanoparticles concentration. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2020, 196, 111294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Ni, Y.; Yu, Q.; Li, J.; Fan, L.; Eskin, N.A.M. Deep learning in food science: An insight in evaluating Pickering emulsion properties by droplets classification and quantification via object detection algorithm. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022, 304, 102663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, L.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Feng, Z.; Gu, P.; Huang, Y.; Liu, J.; Wu, Y.; Wang, D. Lentinan PLGA-stabilized pickering emulsion for the enhanced vaccination. Int. J. Pharm. 2022, 611, 121348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Bu, X.; Zhou, S.; Wang, X.; Bilal, M.; Hassan, F.U.; Hassanzadeh, A.; Xie, G.; Chelgani, S.C. Pickering emulsion prepared by nano-silica particles–A comparative study for exploring the effect of various mechanical methods. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2022, 83, 105928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Carvalho-Guimarães, F.B.; Correa, K.L.; de Souza, T.P.; Rodríguez Amado, J.R.; Ribeiro-Costa, R.M.; Silva-Júnior, J.O.C. A Review of Pickering Emulsions: Perspectives and Applications. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, P.; Liu, C.; Zhong, F.; Xu, M.; Zhao, Y.; Xu, X.; Zhao, Y.; Xue, W.; Xu, Y.; Fan, D. Dummy-template Pickering emulsion imprinted microspheres online pretreatment and analysis for the estrogens in cosmetics. J. Chromatogr. A 2023, 1691, 463815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.S.; Niu, Z.C.; Wang, F.Q.; Feng, K.; Zong, M.H.; Wu, H. A novel Pickering emulsion system as the carrier of tocopheryl acetate for its application in cosmetics. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2020, 109, 110503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rigg, A.; Champagne, P.; Cunningham, M.F. Polysaccharide-Based Nanoparticles as Pickering Emulsifiers in Emulsion Formulations and Heterogenous Polymerization Systems. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2022, 43, e2100493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, L.; Yu, C.; Wei, Q.; Liu, D.; Qiu, J. Pickering Emulsion Catalysis: Interfacial Chemistry, Catalyst Design, Challenges, and Perspectives. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2022, 61, e202115885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, W.; Sun, H.; Mu, T.; Garcia-Vaquero, M. Chitosan-based Pickering emulsion: A comprehensive review on their stabilizers, bioavailability, applications and regulations. Carbohydr. Polym. 2023, 304, 120491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Light, K.; Karboune, S. Emulsion, hydrogel and emulgel systems and novel applications in cannabinoid delivery: A review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 62, 8199–8229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niro, C.M.; Medeiros, J.A.; Freitas, J.A.; Azeredo, H.M. Advantages and challenges of Pickering emulsions applied to bio-based films: A mini-review. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2021, 101, 3535–3540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillot, S.; Bergaya, F.; de Azevedo, C.; Warmont, F.; Tranchant, J.F. Internally structured pickering emulsions stabilized by clay mineral particles. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2009, 333, 563–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Sui, H.; Liang, H.; Li, J.; Li, B. Effects of M/G Ratios of Sodium Alginate on Physicochemical Stability and Calcium Release Behavior of Pickering Emulsion Stabilized by Calcium Carbonate. Front. Nutr. 2021, 8, 818290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffith, C.; Daigle, H. On the shear stability of water-in-water Pickering emulsions stabilized with silica nanoparticles. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2018, 532, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffith, C.; Daigle, H. Destabilizing Pickering emulsions using fumed silica particles with different wettabilities. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2019, 547, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Li, Q.; Wang, B.; Feng, X.; Xu, H.; Mao, Z.; You, C.; Sui, X. Synthetic semicrystalline cellulose oligomers as efficient Pickering emulsion stabilizers. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 254, 117445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, X.; He, S.; Liu, D.; Zhang, Y. Multistimuli-Responsive Pickering Emulsion Stabilized by Se-Containing Surfactant-Modified Chitosan. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 3986–3994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, X.; Zhou, C.; Qayum, A.; Tang, J.; Liang, Q. Pickering emulsion: A multi-scale stabilization mechanism based on modified lotus root starch/xanthan gum nanoparticles. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 233, 123459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, B.; Liu, C.; Grossmann, L.; Weiss, J. Pickering emulsion stabilized by hydrolyzed starch: Effect of the molecular weight. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022, 612, 525–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, X.; Gong, H.; Zhu, W.; Wang, J.; Zhai, Y.; Lin, S. Pickering emulsion stabilized by composite-modified waxy corn starch particles. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 205, 66–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Chen, F.; Gao, C.; Zhang, Y.; Tang, X. Environmental stability and curcumin release properties of Pickering emulsion stabilized by chitosan/gum arabic nanoparticles. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 157, 202–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meirelles, A.A.D.; Costa, A.L.R.; Cunha, R.L. Cellulose nanocrystals from ultrasound process stabilizing O/W Pickering emulsion. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 158, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Huang, G.; Ma, Y.; Liu, Y.; Huang, X.; Zheng, Q.; Yue, P.; Yang, M. Cellulose nanocrystals based clove oil Pickering emulsion for enhanced antibacterial activity. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 170, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, X.; Ngai, T. pH-Sensitive W/O Pickering High Internal Phase Emulsions and W/O/W High Internal Water-Phase Double Emulsions with Tailored Microstructures Costabilized by Lecithin and Silica Inorganic Particles. Langmuir ACS J. Surf. Colloids 2021, 37, 2843–2854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zafeiri, I.; Smith, P.; Norton, I.T.; Spyropoulos, F. Fabrication, characterisation and stability of oil-in-water emulsions stabilised by solid lipid particles: The role of particle characteristics and emulsion microstructure upon Pickering functionality. Food Funct. 2017, 8, 2583–2591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Song, T.; Xiong, Z.; Shi, T.; Yuan, L.; Gao, R. Effect of glutamic acid on the preparation and characterization of Pickering emulsions stabilized by zein. Food Chem. 2022, 366, 130598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.; Zhang, S.; Jiang, X.; Hou, P.; Xin, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, D. Impact of weakly charged insoluble karaya gum on zein nanoparticle and mechanism for stabilizing Pickering emulsions. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 222 Pt A, 121–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Chu, Y.; Feng, X.; Gao, C.; Wu, D.; Cheng, W.; Meng, L.; Zhang, Y.; Tang, X. Effects of zein stabilized clove essential oil Pickering emulsion on the structure and properties of chitosan-based edible films. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 156, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, B.R.; Xu, W.; Mráz, J. Formulation and characterization of zein/chitosan complex particles stabilized Pickering emulsion with the encapsulation and delivery of vitamin D(3). J. Sci. Food Agric. 2021, 101, 5419–5428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashaolu, T.J.; Zhao, G. Fabricating a Pickering Stabilizer from Okara Dietary Fibre Particulates by Conjugating with Soy Protein Isolate via Maillard Reaction. Foods 2020, 9, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, F.; Tang, C.H. Soy protein nanoparticle aggregates as pickering stabilizers for oil-in-water emulsions. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 8888–8898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Li, L.; Zhang, H.; Sun, L.; Jia, B.; Yang, H.; Zuo, F. Interaction mechanism between soybean protein isolate and citrus pectin. J. Food Sci. 2022, 87, 2538–2548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Gao, Y.; Wei, Z.; Xue, C. Ovalbumin fibril-stabilized oleogel-based Pickering emulsions improve astaxanthin bioaccessibility. Food Res. Int. 2022, 161, 111790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.T.; Tang, C.H.; Liu, T.X.; Liu, R. Ovalbumin as an Outstanding Pickering Nanostabilizer for High Internal Phase Emulsions. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 8795–8804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, Y.; Zou, Y.; Luo, Z.; Qi, L.; Lu, X. pH-Responsive Emulsions with β-Cyclodextrin/Vitamin E Assembled Shells for Controlled Delivery of Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 11931–11941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahjoubin-Tehran, M.; Kovanen, P.T.; Xu, S.; Jamialahmadi, T.; Sahebkar, A. Cyclodextrins: Potential therapeutics against atherosclerosis. Pharmacol. Ther. 2020, 214, 107620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, L.J.; Hulu, S.L.; Hee, P.C.; Sang, K.C. Enhancing the anti-bacterial activity of nanofibrous polyurethane membranes by incorporating glycyrrhizic acid-conjugated β-Cyclodextrin. Mater. Lett. 2023, 338, 134030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yuan, C.; Liu, Y.; Xu, D.; Cui, B. The influence of a hydroxypropyl-beta-cyclodextrin composite on the gelation of kappa-carrageenan. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 90, 276–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šimko, P.; Kolarič, L. Decrease in Aflatoxin M(1) Concentration in Milk during Cholesterol Removal by Application of β-Cyclodextrin. Toxins 2022, 14, 379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Hu, L.; Peng, L.; Du, J.; Lan, M.; Cheng, Y.; Ma, L.; Zhang, Y. Dual encapsulation of β-carotene by β-cyclodextrin and chitosan for 3D printing application. Food Chem. 2022, 378, 132088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bangalore, D.V.; McGlynn, W.; Scott, D.D. Effect of beta-cyclodextrin in improving the correlation between lycopene concentration and ORAC values. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 1878–1883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghorbanzade, T.; Akhavan-Mahdavi, S.; Kharazmi, M.S.; Ibrahim, S.A.; Jafari, S.M. Loading of fish oil into β-cyclodextrin nanocomplexes for the production of a functional yogurt. Food Chem. X 2022, 15, 100406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopedota, A.; Cutrignelli, A.; Laquintana, V.; Franco, M.; Donelli, D.; Ragni, L.; Tongiani, S.; Denora, N. β-cyclodextrin in personal care formulations: Role on the complexation of malodours causing molecules. Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2015, 37, 438–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandura, L.; Białoszewska, M.; Leiviskä, T.; Franus, M. The Role of Zeolite Structure in Its β-cyclodextrin Modification and Tetracycline Adsorption from Aqueous Solution: Characteristics and Sorption Mechanism. Materials 2022, 15, 6317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beserra-Filho, J.I.A.; de Macêdo, A.M.; Leão, A.; Bispo, J.M.M.; Santos, J.R.; de Oliveira-Melo, A.J.; Menezes, P.D.P.; Duarte, M.C.; de Souza, A.A.A.; Silva, R.H.; et al. Eplingiella fruticosa leaf essential oil complexed with β-cyclodextrin produces a superior neuroprotective and behavioral profile in a mice model of Parkinson’s disease. Food Chem. Toxicol. Int. J. Publ. Br. Ind. Biol. Res. Assoc. 2019, 124, 17–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, Y.; Luo, Z.; Lu, X.; Peng, X. Modulation of Cyclodextrin Particle Amphiphilic Properties to Stabilize Pickering Emulsion. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 228–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimada, K.; Ohe, Y.; Ohguni, T.; Kawano, K.; Ishii, J.; Nakamura, T. Emulsifying properties of α-, β-and γ-cyclodextrins. Nippon. Shokuhin Kogyo Gakkaishi 1991, 38, 16–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durante, M.; Milano, F.; Caroli, M.; Giotta, L.; Piro, G.; Mita, G.; Frigione, M.; Lenucci, M.S. Tomato Oil Encapsulation by α-, β-, and γ-Cyclodextrins: A Comparative Study on the Formation of Supramolecular Structures, Antioxidant Activity, and Carotenoid Stability. Foods 2020, 9, 1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goñi-Ciaurriz, L.; Senosiain-Nicolay, M.; Vélaz, I. Aging Studies on Food Packaging Films Containing β-Cyclodextrin-Grafted TiO(2) Nanoparticles. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubin Pedrazzo, A.; Trotta, F.; Hoti, G.; Cesano, F.; Zanetti, M. Sustainable mechanochemical synthesis of β-cyclodextrin polymers by twin screw extrusion. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2022, 29, 251–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berdimurodov, E.; Eliboyev, I.; Berdimuradov, K.; Kholikov, A.; Akbarov, K.; Dagdag, O.; Rbaa, M.; El Ibrahimi, B.; Verma, D.K.; Haldhar, R.; et al. Green β-cyclodextrin-based corrosion inhibitors: Recent developments, innovations and future opportunities. Carbohydr. Polym. 2022, 292, 119719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kibici, D.; Kahveci, D. Effect of Emulsifier Type, Maltodextrin, and β-Cyclodextrin on Physical and Oxidative Stability of Oil-In-Water Emulsions. J. Food Sci. 2019, 84, 1273–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fasihi, H.; Noshirvani, N.; Hashemi, M.; Fazilati, M.; Salavati, H.; Coma, V. Antioxidant and antimicrobial properties of carbohydrate-based films enriched with cinnamon essential oil by Pickering emulsion method. Food Packag. Shelf Life 2019, 19, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasconcelos, N.G.; Croda, J.; Simionatto, S. Antibacterial mechanisms of cinnamon and its constituents: A review. Microb. Pathog. 2018, 120, 198–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Sun, C.; Lu, W.; Gul, K.; Mata, A.; Fang, Y. Emulsion structure design for improving the oxidative stability of polyunsaturated fatty acids. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2020, 19, 2955–2971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, C.Y.; Chen, D.; Luo, J.L.; Shi, Y.H.; Zhang, Y.P. Protective role of down-regulated microRNA-31 on intestinal barrier dysfunction through inhibition of NF-κB/HIF-1α pathway by binding to HMOX1 in rats with sepsis. Mol. Med. 2018, 24, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mella, C.; Quilaqueo, M.; Zúñiga, R.N.; Troncoso, E. Impact of the Simulated Gastric Digestion Methodology on the In Vitro Intestinal Proteolysis and Lipolysis of Emulsion Gels. Foods 2021, 10, 321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaur, N.; Chugh, V.; Gupta, A.K. Essential fatty acids as functional components of foods—A review. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 51, 2289–2303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cen, S.; Li, Z.; Guo, Z.; Shi, J.; Huang, X.; Zou, X.; Holmes, M. Fabrication of Pickering emulsions stabilized by citrus pectin modified with β-cyclodextrin and its application in 3D printing. Carbohydr. Polym. 2023, 312, 120833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.; Qiu, C.; Jin, Z.; Qin, Y.; Zhan, C.; Xu, X.; Wang, J. Pickering emulsions with enhanced storage stabilities by using hybrid β-cyclodextrin/short linear glucan nanoparticles as stabilizers. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 229, 115418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, T.; Deng, A.; Yang, D.; Li, H.; Qi, C.; Gao, Y. Triple-Responsive Pickering Emulsion Stabilized by Core Cross-linked Supramolecular Polymer Particles. Langmuir ACS J. Surf. Colloids 2019, 35, 11872–11880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kou, X.; Zhang, X.; Ke, Q.; Meng, Q. Pickering emulsions stabilized by β-CD microcrystals: Construction and interfacial assembly mechanism. Front. Nutr. 2023, 10, 1161232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Lampi, A.-M.; Ertbjerg, P. Unsaturated fat fraction from lard increases the oxidative stability of minced pork. Meat Sci. 2018, 143, 87–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huynh, M.D.; Kitts, D.D.; Hu, C.; Trites, A.W. Comparison of fatty acid profiles of spawning and non-spawning Pacific herring, Clupea harengus pallasi. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part B Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2007, 146, 504–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrera-Arellano, D.; Badan-Ribeiro, A.P.; Serna-Saldivar, S.O. Chapter 21–Corn Oil: Composition, Processing, and Utilization. In Corn, 3rd ed.; Serna-Saldivar, S.O., Ed.; AACC International Press: Oxford, UK, 2019; pp. 593–613. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, J.; Ye, H.; Rui, Y.; Chen, G.; Zhang, N. Fatty acid composition of Camellia oleifera oil. J. Verbrauch. Lebensm. 2011, 6, 9–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, I.K.; Kim, S.I.; Lee, S.B. Effects of HLB value on oil-in-water emulsions: Droplet size, rheological behavior, zeta-potential, and creaming index. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2018, 67, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pematilleke, N.; Kaur, M.; Adhikari, B.; Torley, P.J. Relationship between instrumental and sensory texture profile of beef semitendinosus muscles with different textures. J. Texture Stud. 2022, 53, 232–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.D.; Hong, J.S.; Pyo, S.M.; Ko, E.; Shin, H.Y.; Kim, J.Y. Starch nanoparticles produced via acidic dry heat treatment as a stabilizer for a Pickering emulsion: Influence of the physical properties of particles. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 239, 116241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Guan, X.; Wang, C.; Ngai, T.; Lin, W. pH-Responsive Pickering high internal phase emulsions stabilized by Waterborne polyurethane. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022, 610, 994–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Lee, W.J.; Tan, C.P.; Lai, O.M.; Wang, Y.; Qiu, C. W/O high internal phase emulsion featuring by interfacial crystallization of diacylglycerol and different internal compositions. Food Chem. 2022, 372, 131305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Song, Z.; Wang, Q.; Xu, X.; Liu, Y.; Xiong, Y.L. Ultrasound-mediated interfacial protein adsorption and fat crystallization in cholesterol-reduced lard emulsion. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2019, 58, 104641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadiya, K.; Sharma, M.; Ghosh, S. Effect of the chitosan second layer on the gelation and controlled digestion of Citrem-chitosan bilayer emulsions. Food Funct. 2022, 13, 2515–2533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatry, M.C.; Galanopoulo, P.; Waldmann, L.; Lapeyre, V.; Garrigue, P.; Schmitt, V.; Ravaine, V. Pickering emulsions stabilized by thermoresponsive oligo(ethylene glycol)-based microgels: Effect of temperature-sensitivity on emulsion stability. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 589, 96–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, T.; Kumar, G.S.; Chon, B.H.; Sangwai, J.S. Thermal stability of oil-in-water Pickering emulsion in the presence of nanoparticle, surfactant, and polymer. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2015, 22, 324–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chevalier, Y.; Bolzinger, M.-A. Emulsions stabilized with solid nanoparticles: Pickering emulsions. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2013, 439, 23–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vryzas, Z.; Kelessidis, V.C.; Nalbantian, L.; Zaspalis, V.; Gerogiorgis, D.I.; Wubulikasimu, Y. Effect of temperature on the rheological properties of neat aqueous Wyoming sodium bentonite dispersions. Appl. Clay Sci. 2017, 136, 26–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, J.; Ma, Y.; Luo, Q.; Liang, Z.; Lu, P.; Song, F.; Zhang, Z.; Zhou, T.; Zhang, J. Improving the solubility of vorinostat using cyclodextrin inclusion complexes: The physicochemical characteristics, corneal permeability and ocular pharmacokinetics of the drug after topical application. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2022, 168, 106078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ranka, M.; Katepalli, H.; Blankschtein, D.; Hatton, T.A. Schizophrenic Diblock-Copolymer-Functionalized Nanoparticles as Temperature-Responsive Pickering Emulsifiers. Langmuir ACS J. Surf. Colloids 2017, 33, 13326–13331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.; McClements, D.J.; Zhou, W.; Peng, S.; Zhou, L.; Zou, L.; Liu, W. Influence of ionic strength and thermal pretreatment on the freeze-thaw stability of Pickering emulsion gels. Food Chem. 2020, 303, 125401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ke, D.; Chen, W.; Chen, W.; Yun, Y.H.; Zhong, Q.; Su, X.; Chen, H. Preparation and Characterization of Octenyl Succinate β-Cyclodextrin and Vitamin E Inclusion Complex and Its Application in Emulsion. Molecules 2020, 25, 654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, J.; Wang, Y.J.; Huang, X.Y.; Li, X.Z.; Ma, C.G.; McClements, D.J. NMR Analysis of Lipid Oxidation in Flaxseed Oil-in-Water Emulsions. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 8417–8429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Sample | Effective Diameter (μm) | ζ-Potential (mV) |
|---|---|---|
| β-CD (Corn Oil) | 10.52 ± 0.75 b | −32.31 ± 2.47 b |
| β-CD (Camellia Oil) | 11.92 ± 0.63 b | −30.56 ± 0.89 b |
| β-CD (Lard) | 25.57 ± 5.87 a | −23.20 ± 1.32 a |
| β-CD (Herring Oil) | 10.86 ± 1.15 b | −31.33 ± 1.66 b |
| CA/β-CD (Corn Oil) | 11.02 ± 0.45 b | −32.36 ± 1.57 b |
| CA/β-CD (Camellia Oil) | 11.67 ± 0.40 b | −33.40 ± 1.04 b |
| CA/β-CD (Lard) | 27.39 ± 6.67 a | −21.37 ± 1.71 a |
| CA/β-CD (Herring Oil) | 10.67 ± 0.87 b | −29.67 ± 1.37 b |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, C.; Tian, Y.; Ma, Z.; Zhou, L. Pickering Emulsion Stabilized by β-Cyclodextrin and Cinnamaldehyde/β-Cyclodextrin Composite. Foods 2023, 12, 2366. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12122366
Liu C, Tian Y, Ma Z, Zhou L. Pickering Emulsion Stabilized by β-Cyclodextrin and Cinnamaldehyde/β-Cyclodextrin Composite. Foods. 2023; 12(12):2366. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12122366
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Caihua, Yachao Tian, Zihan Ma, and Linyi Zhou. 2023. "Pickering Emulsion Stabilized by β-Cyclodextrin and Cinnamaldehyde/β-Cyclodextrin Composite" Foods 12, no. 12: 2366. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12122366
APA StyleLiu, C., Tian, Y., Ma, Z., & Zhou, L. (2023). Pickering Emulsion Stabilized by β-Cyclodextrin and Cinnamaldehyde/β-Cyclodextrin Composite. Foods, 12(12), 2366. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12122366





