Extending Regulatory Biokinetic Lead Models towards Food Safety: Evaluation of Consumer Baby Food Contribution to Infant Blood Lead Levels and Variability
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Dietary Conversion Factor
2.2. Biokinetic Model versus Conversion Factor Estimated BLLs
2.3. Probabilistic Assessment
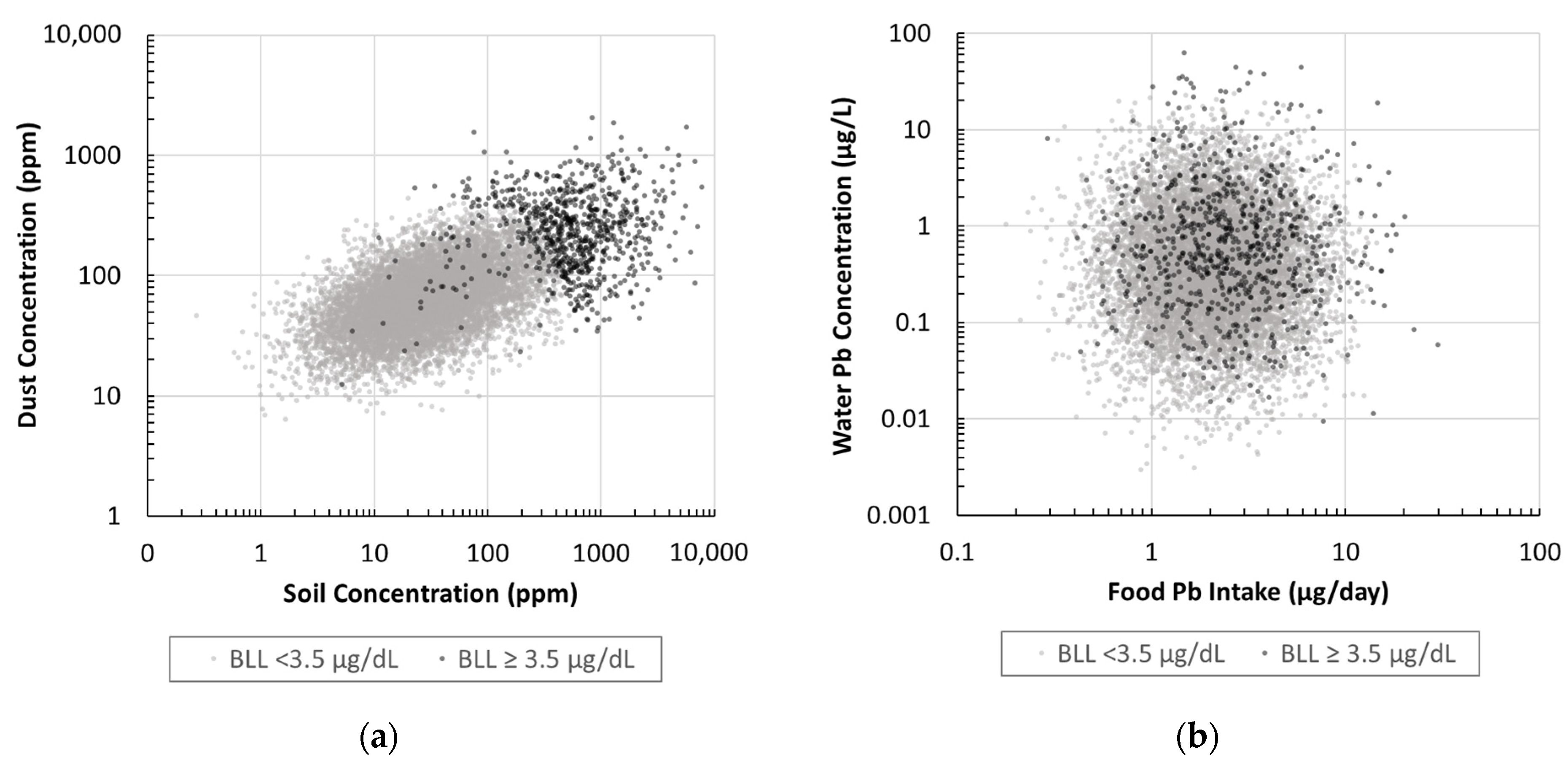
2.3.1. Soil, Dust, Water, and Food Distributions
2.3.2. Soil, Dust, Water, and Food Correlations
2.3.3. IUEBK Monte Carlo Assessment
| Consideration | IEUBK v1.1/v2 | ICRP v4 | ICRP v5 | AALM |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aims | Prediction of the likely BLL distribution for children of ages 6 to 84 months from environmental exposures. | Multicompartmental occupational tissue/organ predictions of occupational Pb biokinetics to age 60. | Multicompartmental general child and adult tissue/organ predictions of Pb biokinetics to age 60. | Predictions of lifetime Pb concentrations in blood, other body tissues, and excreta for ages 0 up to 90. |
| Modules | Intake, uptake, biokinetics | Intake, uptake, biokinetics | Intake, uptake, biokinetics | Intake, uptake, biokinetics |
| Defined Pathways | Water, Food, Soil, Dust, Air | Injection, Inhalation, Oral | Water, Food, Soil, Dust, Air | Water, Food, Soil, Dust, Air |
| BLL prediction | Geometric mean and %-ile | Central tendency | Central tendency | Central tendency |
| Bone lead prediction | No | Yes (mineral weight basis) | Yes (mineral weight basis) | Yes (mineral weight basis) |
| Calibrated w/child data | Yes | No | Yes | Yes |
| Calibration data | Autopsy study of children; two field studies. | Radiolabel studies of humans; animal data. | 2007–2008 National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey; occupational blood and bone lead studies conducted in 1994, 1999, and 2008. | Occupational studies, human child and adult volunteer studies with known dose, and post-mortem soft tissue data. |
| Integration time step | Pseudo-steady state (month) | User-defined (e.g., 0.1 day) | User-defined (e.g., 0.1 day) | User-defined (e.g., 0.1 day) |
| Preceding modeling framework | Infant and juvenile baboon calibrated model [33]. Version 0.99d considered human data in children [34] | ICRP model for bone-seeking radionuclides [17,35]. | Update of ICRP v4. | Update of ICRP v5. |
| Key changes from preceding framework | Version 1.1 reflected minor updates to dietary lead intake, maternal blood lead, and bone weight [36]. Version 2.0 updates dietary lead intake, drinking water consumption, maternal blood concentration, inhalation rates, and soil/dust ingestion rates [37]. | Version 1 added chelation; Version 2 added output for bone Pb wet weight converted to dry weight as µg of Pb per g of bone mineral; Version 3 converted output time from days to years, and Version 4 added output options. | Version 5 added scaling of tissue mass by age, updated bone lead transfer rates, and calibration data considering both children and adults. | AALM added growth parameters; revised gastrointestinal absorption factors, and kinetic parameter refinement. |
| Default Pb media concentration or intakes | Yes; soil and dust defaults characterized as “starting values” modifiable by site specific data. | No | No | Described in Technical support document [38] |
| Gastrointestinal absorption factor (%) | Food and water: 50%; Soil and dust: 30% | Varies from 45% to 15% decreasing with age | Varies from 45% to 15% decreasing with age | Varies from 39% to 12% decreasing with age |
| Relative bioavailability | Included in absorption factor | None by default | None by default | Soil dust RBA = 60% |
| Model reference | U.S. EPA, 2007; U.S. EPA, 2021a | Leggett, 1993; Pounds and Leggett, 1998 | U.S. EPA 2014 | USEPA 2019b |
| Parameter | Unit a | Distribution | Parameter 1 b | Parameter 2 b | Probabilistic Median a [5th–95th %-ile] c | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (a) Unit BLL concentration (incremental BLL per unit increase in oral Pb intake | ||||||
| Dietary Pb intake | µg/day | Point | 1 or 5 | -- | -- | Hypothetical |
| Other Pb intake | µg/day | Point | 0 | -- | -- | Dietary only |
| (b) Distributions of predicted BLLs using the IEUBK model for national scenario | ||||||
| Food Pb intake | ||||||
| …age 0 to 0.5 | µg/day | Lognormal | AM = 0.70 | SD = 0.98 | 0.41 [0.07–2.3] | [22] |
| …age 1 to <2 | µg/day | Lognormal | AM = 2.6 | SD = 1.8 | 2.1 [0.73–6.0] | [22] |
| …age 2 to <3 | µg/day | Lognormal | AM = 3.4 | SD = 2.0 | 3.0 [1.2–7.3] | [22] |
| …age 3 to <4 | µg/day | Lognormal | AM = 3.5 | SD = 2.1 | 3.1 [1.3–7.4] | [22] |
| …age 4 to <5 | µg/day | Lognormal | AM = 3.6 | SD = 2.2 | 3.1 [1.2–7.7] | [22] |
| …age 5 to <6 | µg/day | Lognormal | AM = 3.9 | SD = 2.2 | 3.4 [1.4–8.0] | [22] |
| …age 6 to <7 | µg/day | Lognormal | AM = 3.8 | SD = 2.0 | 3.4 [1.5–7.6] | [22] |
| Correlation age i to j | -- | Spearmans’s r | 0.7 | -- | -- | [39] |
| Soil and Dust | ||||||
| …Homes built < 1950 | fraction | Bernoulli | p = 0.169 | -- | -- | [40] |
| …Dust built < 1950 | ppm | Lognormal | AM = 196 | SD = 212 | -- | [22] d |
| …Dust built ≥ 1950 | ppm | Lognormal | AM = 75 | SD = 52 | -- | [22] d |
| …Dust combined | ppm | Calculated | -- | -- | 67 [23–255] | |
| …Soil built < 1950 | ppm | Lognormal | AM = 505 | SD = 1062 | -- | [22] d |
| …Soil built ≥ 1950 | ppm | Lognormal | AM = 42 | SD = 59 | -- | [22] d |
| …Soil combined | ppm | Calculated | -- | -- | 30 [4.7–455] | [22] |
| Correlation soil–dust | -- | Spearmans’s r | 0.48 | -- | -- | [22] |
| Drinking water | ||||||
| Drinking water | ppb | Lognormal | AM = 1.0 | SD = 2.4 | 0.39 [0.04–3.7] | [25] |
| Correl. soil–water | -- | Spearmans’s r | 0.2 | -- | -- | [22] |
| Correl. dust–water | -- | Spearmans’s r | 0.2 | -- | -- | [22] |
3. Results
3.1. Dietary Conversion Factor
| Dietary Intake (µg/day) | Age | Dietary Intake to BLL Conversion Factor (µg/dL per µg/day) | FDA Conversion Factor a | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IEUBK v1.1 | IEUBK v2 | ICRP v4 | ICRP v5 | AALM | ||||
| Sex -> | M/F | M/F | M/F | M/F | M | F | M/F | |
| 1 | 0.5 to <1 | 0.28 | 0.28 | 0.45 | 0.26 | 0.29 | 0.31 | 0.16 |
| 1 to <2 | 0.23 | 0.22 | 0.33 | 0.19 | 0.24 | 0.25 | 0.16 | |
| 2 to <3 | 0.19 | 0.19 | 0.28 | 0.16 | 0.21 | 0.22 | 0.16 | |
| 3 to 7 | 0.16 | 0.16 | 0.25 | 0.14 | 0.16 | 0.17 | 0.16 | |
| 5 | 0.5 to <1 | 0.27 | 0.27 | 0.39 | 0.24 | 0.27 | 0.28 | 0.16 |
| 1 to <2 | 0.22 | 0.22 | 0.30 | 0.18 | 0.23 | 0.24 | 0.16 | |
| 2 to <3 | 0.19 | 0.19 | 0.26 | 0.15 | 0.21 | 0.22 | 0.16 | |
| 3 to <7 | 0.16 | 0.16 | 0.24 | 0.14 | 0.16 | 0.16 | 0.16 | |
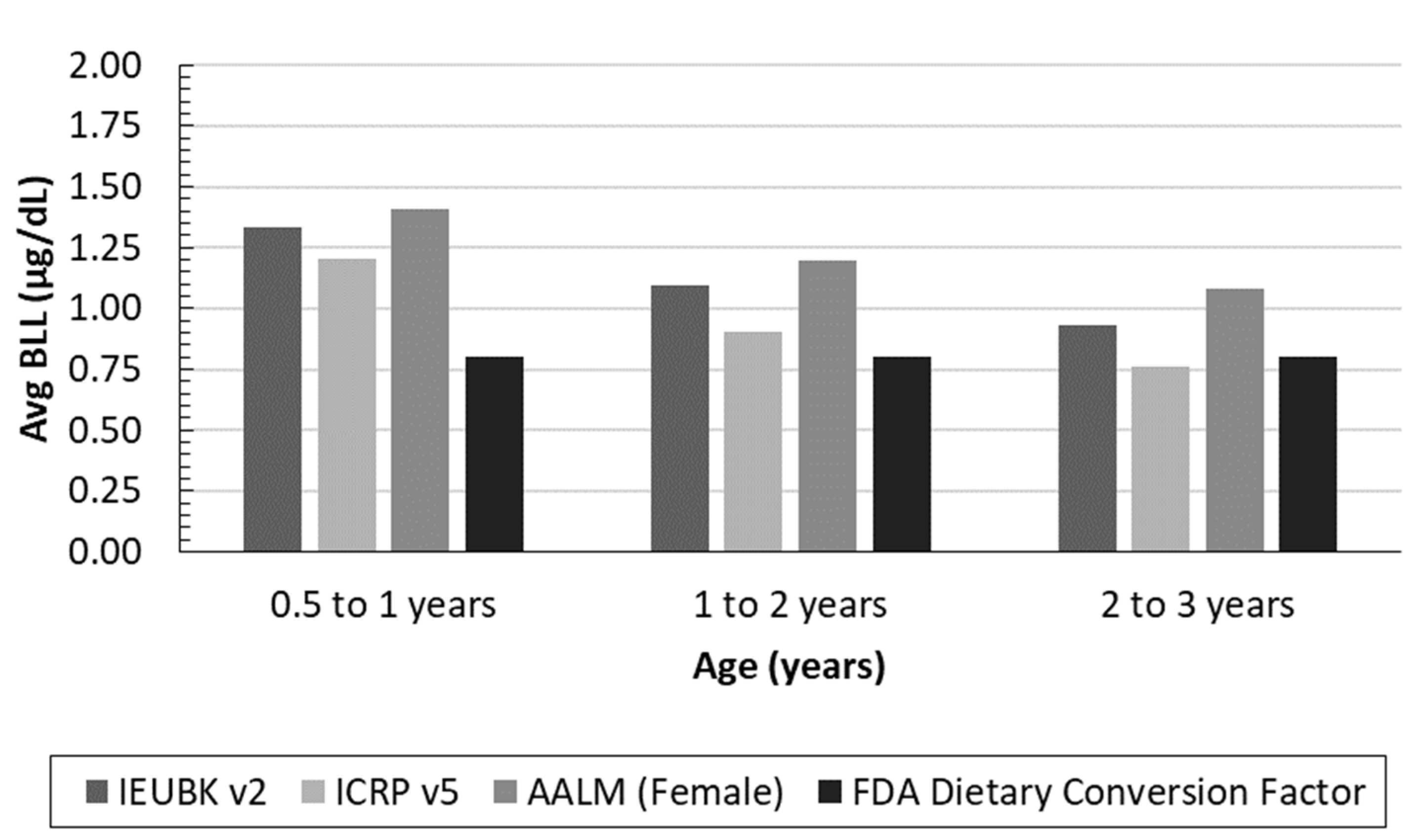
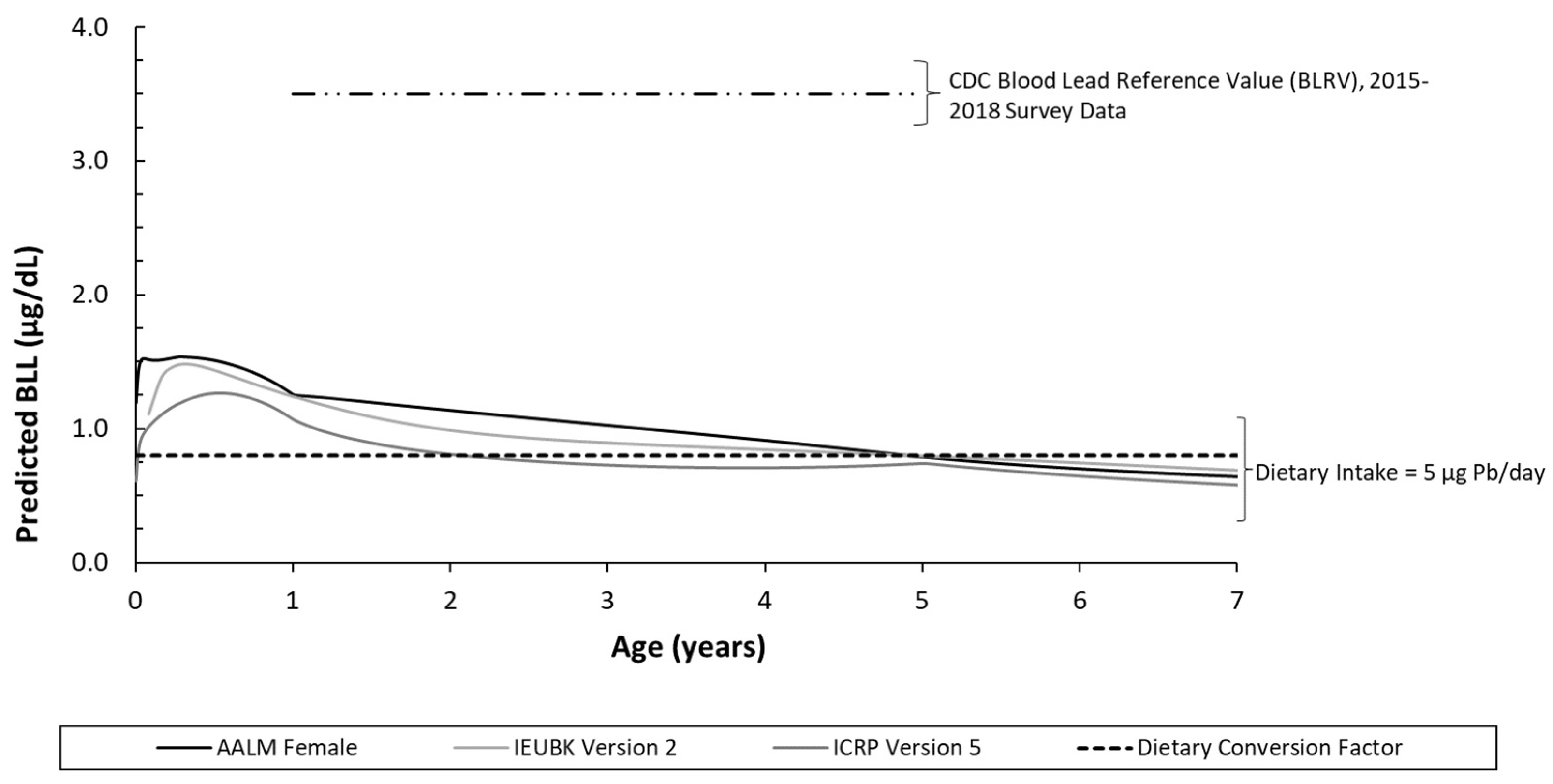
3.2. Predicted BLL Model Comparison
3.3. IEUBK Probabilistic Exposure Pathway Analysis
| NHANES or Model BLL Distribution | Age | Monte Carlo Distributions | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Distribution of IEUBK Predicted BLLs (µg/dL) | |||||||
| Mean (SD) | GM (GSD) | 25th | 50th | 75th | 90th | ||
| IEUBK National Baseline | 1–2 | 1.8 (1.8) | 1.4 (1.8) | 0.95 | 1.3 | 1.9 | 3.1 |
| IEUBK 30% Reduction Pb Diet Intake | 1–2 | 1.6 (1.8) | 1.3 (1.9) | 0.82 | 1.2 | 1.7 | 2.8 |
| IEUBK 50% Reduction in Pb Soil Conc. | 1–2 | 1.6 (1.3) | 1.3 (1.8) | 0.88 | 1.2 | 1.8 | 2.6 |
| NHANES 2011–2016 a | 1–2 | -- | 0.9; CI: 0.9, 1.0 | -- | -- | -- | -- |
| IEUBK National Baseline | 1–5 | 1.6 (1.5) | 1.3 (1.8) | 0.85 | 1.2 | 1.7 | 2.6 |
| IEUBK 30% Reduction Pb Diet Intake | 1–5 | 1.4 (1.5) | 1.1 (1.9) | 0.72 | 1.0 | 1.5 | 2.4 |
| IEUBK 50% Reduction in Pb Soil Conc. | 1–5 | 1.4 (1.1) | 1.2 (1.7) | 0.80 | 1.1 | 1.6 | 2.3 |
| NHANES 2009–2014 b | 1–6 | 1.3 (1.5) | 1.0 (1.9) | -- | 0.85 | -- | -- |
| NHANES 2015–2016 c | 1–5 | -- | 0.76 | -- | 0.69 | 1.1 | 1.9 |
| NHANES 2017–2018 c | 1–5 | -- | 0.67 | -- | 0.62 | 1.1 | 1.9 |
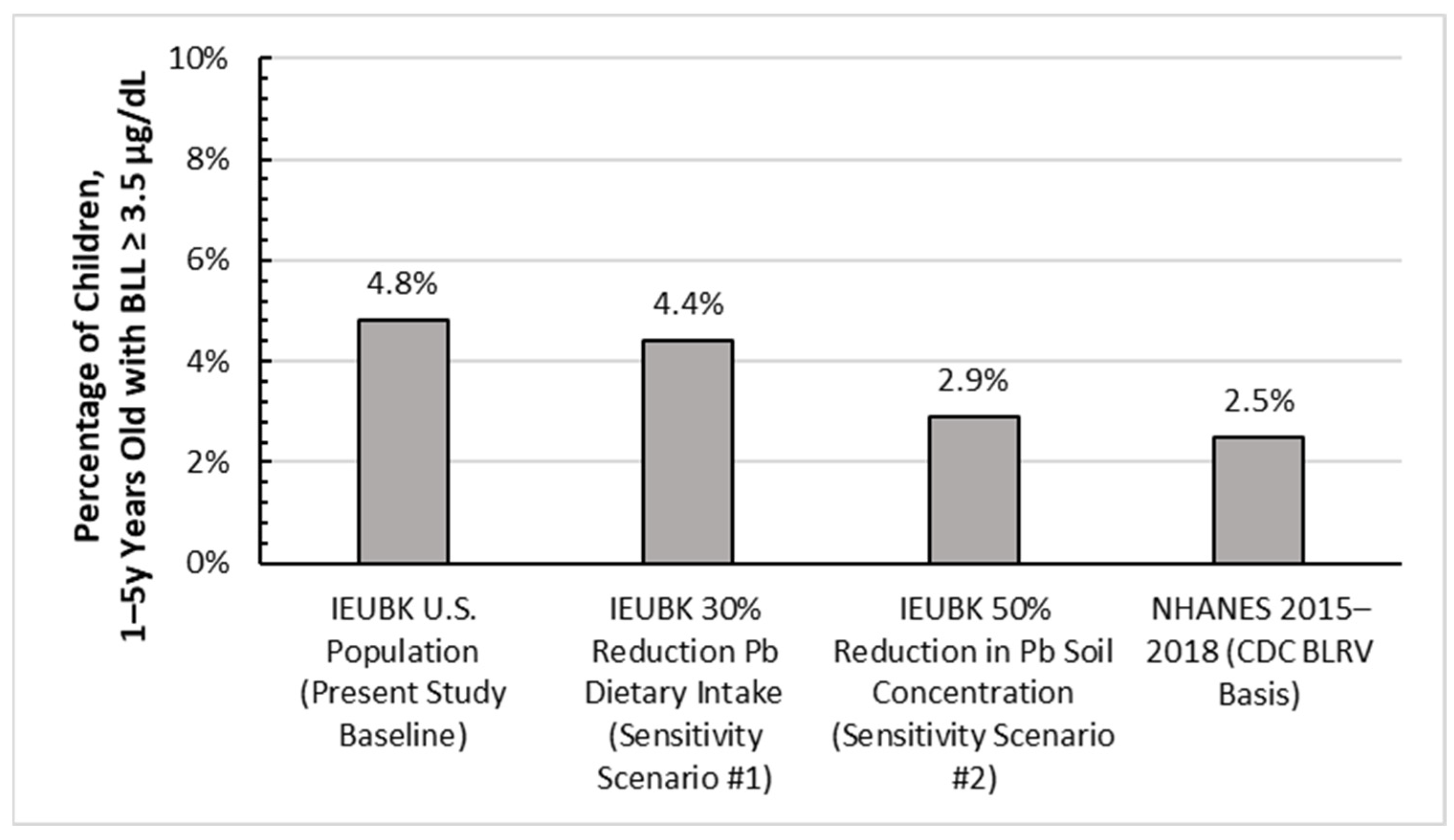
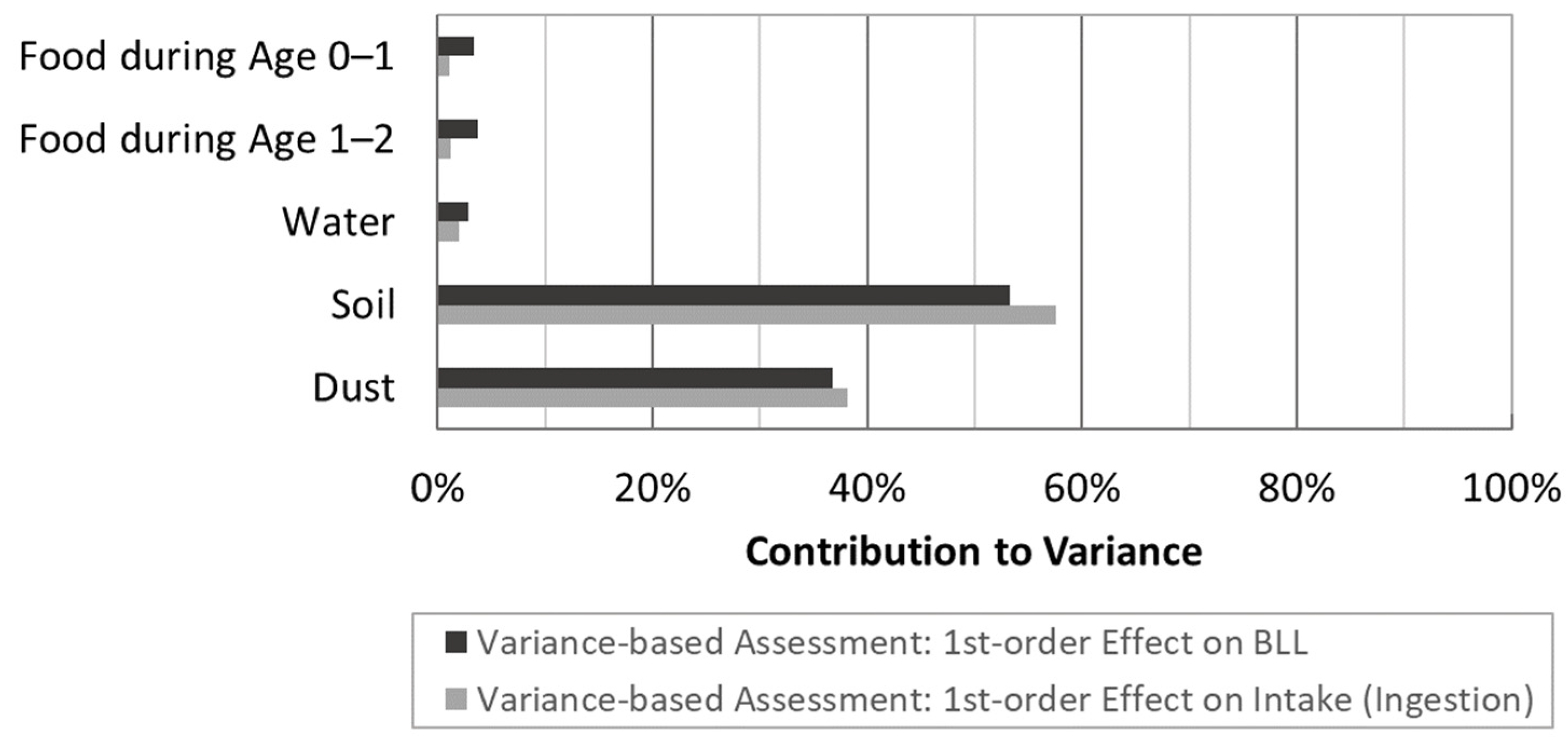
3.4. Sensitivity Analysis for IEUBK Exposure Pathways
4. Discussion
4.1. Dietary Conversion Factor
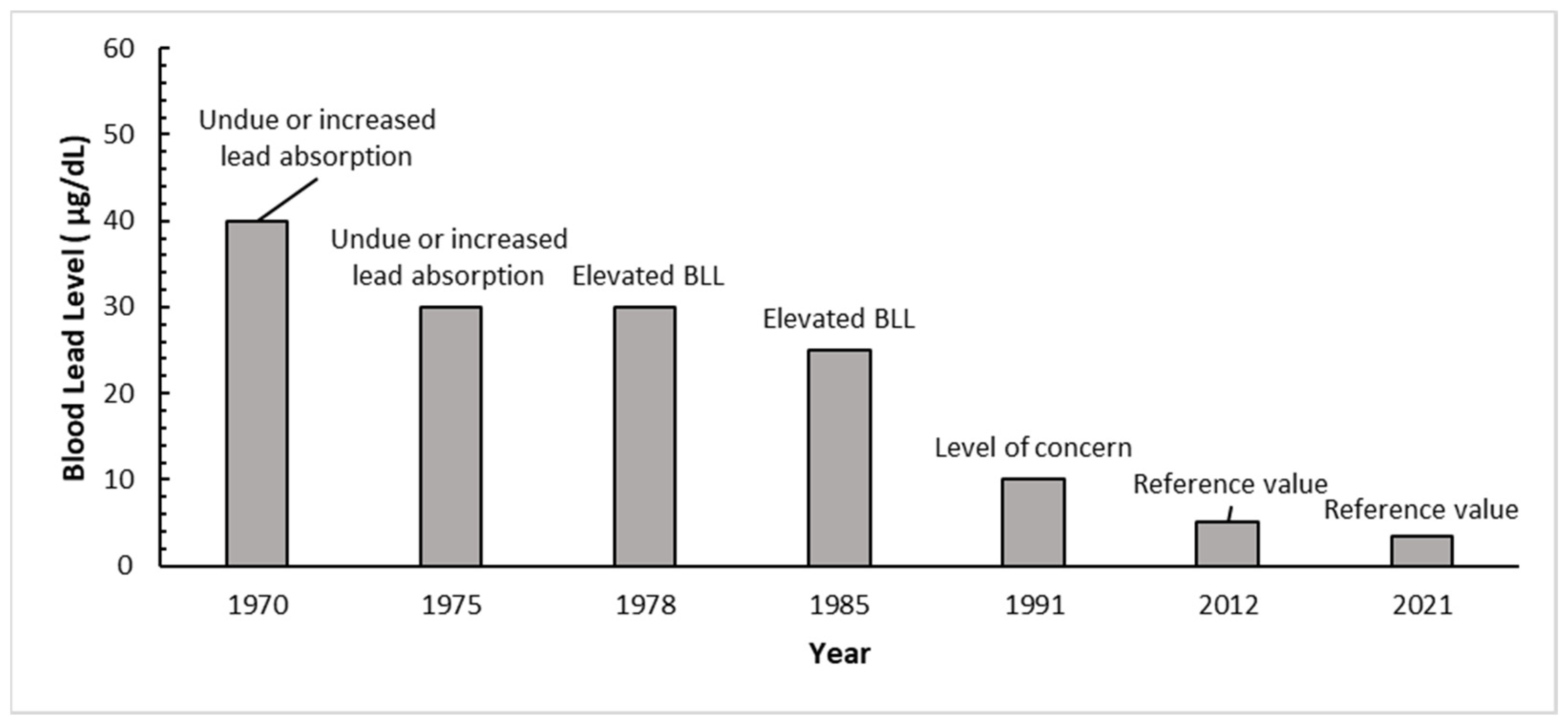
4.2. Lead Absorption Considerations
4.3. Model Comparison and Evaluation
4.4. IEUBK Probabilistic Assessment
4.5. Source Variance Contributions
4.6. Strengths and Limitations
4.7. Future Research
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bair, E.C. A narrative review of toxic heavy metal content of infant and toddler foods and evaluation of united states policy. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 919913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gardener, H.; Bowen, J.; Callan, S.P. Lead and cadmium contamination in a large sample of United States infant formulas and baby foods. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 651, 822–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gray, P.J. A survey of toxic elements in ready to eat baby foods in the US market 2021. Food Addit. Contam. Part B 2023, 16, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- USHR. Baby Foods Are Tainted with Dangerous Levels of Arsenic, Lead, Cadmium, and Mercury; Staff Report; USHR: Washington, DC, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Sanders, T.; Liu, Y.; Buchner, V.; Tchounwou, P.B. Neurotoxic effects and biomarkers of lead exposure: A review. Rev. Environ. Health 2009, 24, 15–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alexander, F.W. The uptake of lead by children in differing environments. Environ. Health Perspect. 1974, 7, 155–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mushak, P. Gastro-intestinal absorption of lead in children and adults: Overview of biological and biophysico-chemical aspects. Chem. Speciat. Bioavailab. 1991, 3, 87–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hou, S.; Yuan, L.; Jin, P.; Ding, B.; Qin, N.; Li, L.; Liu, X.; Wu, Z.; Zhao, G.; Deng, Y. A clinical study of the effects of lead poisoning on the intelligence and neurobehavioral abilities of children. Theor. Biol. Med. Model. 2013, 10, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- USFDA. Action Levels for Lead in Food Intended for Babies and Young Children: Draft Guidance for Industry. Draft Guidance; USFDA: Silver Spring, MD, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Flannery, B.M.; Middleton, K.B. Updated interim reference levels for dietary lead to support FDA’s Closer to Zero action plan. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2022, 133, 105202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, J.E.; Ziegler, E.E.; Nelson, S.E.; Fomon, S.J. Dietary intake of lead and blood lead concentration in early infancy. Am. J. Dis. Child. 1983, 137, 886–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flannery, B.M.; Dolan, L.C.; Hoffman-Pennesi, D.; Gavelek, A.; Jones, O.E.; Kanwal, R.; Wolpert, B.; Gensheimer, K.; Dennis, S.; Fitzpatrick, S.U.S. Food and Drug Administration’s interim reference levels for dietary lead exposure in children and women of childbearing age. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2020, 110, 104516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- USEPA. Air Quality Criteria for Lead; EPA-600/8-83/028cF; USEPA: Washington, DC, USA, 1986; Volume III of IV. [Google Scholar]
- Spungen, J.H. Children’s exposures to lead and cadmium: FDA total diet study 2014-16. Food Addit. Contam. Part A Chem. Anal. Control Expo. Risk Assess. 2019, 36, 893–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabinowitz, M. Historical perspective on lead biokinetic models. Environ. Health Perspect. 1998, 106 (Suppl. S6), 1461–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- White, P.D.; Van Leeuwen, P.; Davis, B.D.; Maddaloni, M.; Hogan, K.A.; Marcus, A.H.; Elias, R.W. The conceptual structure of the integrated exposure uptake biokinetic model for lead in children. Environ. Health Perspect. 1998, 106 (Suppl. S6), 1513–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pounds, J.G.; Leggett, R.W. The ICRP age-specific biokinetic model for lead: Validations, empirical comparisons, and explorations. Environ. Health Perspect. 1998, 106 (Suppl. S6), 1505–1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lakind, J.S. Comparison of three models for predicting blood lead levels in children: Episodic exposures to lead. J. Expo. Anal. Environ. Epidemiol. 1998, 8, 399–406. [Google Scholar]
- Roy, S.; Edwards, M.A. Are there excess fetal deaths attributable to waterborne lead exposure during the Flint Water Crisis? Evidence from bio-kinetic model predictions and Vital Records. J. Expo. Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 2022, 32, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- USEPA. Risk Assessment Forum White Paper: Probabilistic Risk Assessment Methods and Case Studies; EPA/100/R-14/004; USEPA: Washington, DC, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Hogan, K.; Marcus, A.; Smith, R.; White, P. Integrated exposure uptake biokinetic model for lead in children: Empirical comparisons with epidemiologic data. Environ. Health Perspect. 1998, 106 (Suppl. S6), 1557–1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zartarian, V.; Xue, J.; Tornero-Velez, R.; Brown, J. Children’s lead exposure: A multimedia modeling analysis to guide public health decision-making. Environ. Health Perspect. 2017, 125, 097009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- HUD. American Healthy Homes Survey, American Healthy Homes Survey Lead and Arsenic Findings (Lead Concentration Data Provided in 2016 from Policy and Standards Division, Office of Lead Hazard Control and Healthy Homes, U.S. Department of Housing and Urban Development); HUD: Washington, DC, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- USFDA. Total Diet Study Data 2007–2013. FDA-CSFAN Data. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/downloads/Food/FoodScienceResearch/TotalDietStudy/UCM184301.pdf (accessed on 4 April 2023).
- Bradham, K.D.; Nelson, C.M.; Sowers, T.D.; Lytle, D.A.; Tully, J.; Schock, M.R.; Li, K.; Blackmon, M.D.; Kovalcik, K.; Cox, D.; et al. A national survey of lead and other metal(loids) in residential drinking water in the United States. J. Expo. Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 2023, 33, 160–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CDC. American Healthy Homes Survey II Lead Findings Final Report 29 October 2021 U.S. Department of Housing and Urban Development Office of Lead Hazard Control and Healthy Homes. Available online: https://www.hud.gov/sites/dfiles/HH/documents/AHHS_II_Lead_Findings_Report_Final_29oct21.pdf (accessed on 4 April 2023).
- Pizzol, M.; Thomsen, M.; Andersen, M.S. Long-term human exposure to lead from different media and intake pathways. Sci. Total Environ. 2010, 408, 5478–5488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitzmaurice, G.M.; Laird, N.M.; Ware, J.H. Applied Longitudinal Analysis; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Plischke, E. How to compute variance-based sensitivity indicators with your spreadsheet software. Environ. Model. Softw. 2012, 35, 188–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radomyski, A.; Giubilato, E.; Ciffroy, P.; Critto, A.; Brochot, C.; Marcomini, A. Modelling ecological and human exposure to POPs in Venice lagoon—Part II: Quantitative uncertainty and sensitivity analysis in coupled exposure models. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 569–570, 1635–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, X.; Zhang, J.; Zhan, C.; Xuan, Y.; Ye, M.; Xu, C. Global sensitivity analysis in hydrological modeling: Review of concepts, methods, theoretical framework, and applications. J. Hydrol. 2015, 523, 739–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhan, C.-S.; Song, X.-M.; Xia, J.; Tong, C. An efficient integrated approach for global sensitivity analysis of hydrological model parameters. Environ. Model. Softw. 2013, 41, 39–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- USEPA. Research and Development: Technical Support Document on Lead. First Draft; ECAO-CIN-757; USEPA: Washington, DC, USA, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- USEPA. Guidance Manual for the Integrated Exposure Uptake Biokinetic Model for Lead in Children; EPA 540-R-93-081; USEPA: Washington, DC, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Leggett, R.W. An age-specific kinetic model of lead metabolism in humans. Environ. Health Perspect. 1993, 101, 598–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- USEPA. Overview of Changes from IEUBKwin Version 1 Build 264 to IEUBKwin Version 1.1; USEPA: Washington, DC, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- USEPA. Overview of Changes in IEUBK Model Software from IEUBKwin Version 1.1 Build 11 to IEUBKwin Version 2.0 Build 1.63; USEPA: Washington, DC, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- USEPA. AALM. For Users Guide. Users Guide for the FORTRAN Version of the All Ages Lead Model—Excel User Interface and FORTRAN Model Executable; USEPA: Washington, DC, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Fitzmaurice, G.M.; Laird, N.M.; Ware, J.H. Longitudinal data: Basic concepts. In Applied Longitudinal Analysis; Balding, D.J., Cressie, N.A., Fisher, N.I., Johnstone, I.M., Kadane, J.B., Molenberghs, G., Ryan, L.M., Scott, D.W., Smith, A.F.M., Teugels, J.L., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2004; Volume 1, pp. 19–45. [Google Scholar]
- U.S. Census Bureau. 2017–2021 American Community Survey 5-Year Estimates. Available online: https://data.census.gov/table?tid=ACSDP5Y2021.DP04&hidePreview=true (accessed on 18 May 2023).
- Egan, K.B.; Cornwell, C.R.; Courtney, J.G.; Ettinger, A.S. Blood lead levels in U.S. children ages 1–11 Years, 1976–2016. Environ. Health Perspect. 2021, 129, 37003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CDC. National Report on Human Exposure to Environmental Chemicals: Biomonitoring Data Tables for Environmental Chemicals. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/exposurereport/data_tables.html (accessed on 24 March 2022).
- Ruckart, P.Z.; Jones, R.L.; Courtney, J.G.; LeBlanc, T.T.; Jackson, W.; Karwowski, M.P.; Cheng, P.Y.; Allwood, P.; Svendsen, E.R.; Breysse, P.N. Update of the blood lead reference value—United States, 2021. MMWR Morb. Mortal Wkly. Rep. 2021, 70, 1509–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CDC. Blood Lead Reference Value. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/nceh/lead/data/blood-lead-reference-value.htm (accessed on 3 May 2023).
- Bowers, T.S.; Beck, B.D.; Karam, H.S. Assessing the relationship between environmental lead concentrations and adult blood lead levels. Risk Anal. 1994, 14, 183–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abadin, H.G.; Wheeler, J.S.; Jones, D.E.; Derosa, C.T. A framework to guide public health assessment decisions at lead sites. J. Clean Technol. Environ. Sci. 1997, 6, 225–237. [Google Scholar]
- USEPA. User’s Guide for the Integrated Exposure Uptake Biokinetic Model for Lead in Children (IEUBK) Version 2.0; USEPA: Washington, DC, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Fullmer, C.S.; Edelstein, S.; Wasserman, R.H. Lead-binding properties of intestinal calcium-binding proteins. J. Biol. Chem. 1985, 260, 6816–6819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- USEPA. Approach for Estimating Exposures and Incremental Health Effects from Lead Due to Renovation, Repair, and Painting Activities in Public and Commercial Buildings; USEPA: Washington, DC, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- USEPA. Technical Support Document for the All-Ages Lead Model (AALM), Version 2.0 (External Review Draft, 2019); EPA/600/R-19/011; U.S. Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, J.S.; Spalinger, S.M.; Weppner, S.G.; Hicks, K.J.W.; Thorhaug, M.; Thayer, W.C.; Follansbee, M.H.; Diamond, G.L. Evaluation of the integrated exposure uptake biokinetic (IEUBK) model for lead in children. J. Expo. Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 2023, 33, 187–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tebby, C.; Caudeville, J.; Fernandez, Y.; Brochot, C. Mapping blood lead levels in French children due to environmental contamination using a modeling approach. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 808, 152149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hahn, D.; Vogel, N.; Hora, C.; Kampfe, A.; Schmied-Tobies, M.; Goen, T.; Greiner, A.; Aigner, A.; Kolossa-Gehring, M. The role of dietary factors on blood lead concentration in children and adolescents—Results from the nationally representative German Environmental Survey 2014–2017 (GerES V). Environ. Pollut. 2022, 299, 118699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pantic, I.; Tamayo-Ortiz, M.; Rosa-Parra, A.; Bautista-Arredondo, L.; Wright, R.O.; Peterson, K.E.; Schnaas, L.; Rothenberg, S.J.; Hu, H.; Tellez-Rojo, M.M. Children’s blood lead concentrations from 1988 to 2015 in Mexico City: The contribution of lead in air and traditional lead-glazed ceramics. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 2153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zaragoza, L.; Hogan, K. The integrated exposure uptake biokinetic model for lead in children: Independent validation and verification. Environ. Health Perspect. 1998, 106 (Suppl. S6), 1551–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Frank, J.J.; Poulakos, A.G.; Tornero-Velez, R.; Xue, J. Systematic review and meta-analyses of lead (Pb) concentrations in environmental media (soil, dust, water, food, and air) reported in the United States from 1996 to 2016. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 694, 133489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parker, G.H.; Gillie, C.E.; Miller, J.V.; Badger, D.E.; Kreider, M.L. Human health risk assessment of arsenic, cadmium, lead, and mercury ingestion from baby foods. Toxicol. Rep. 2022, 9, 238–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Triantafyllidou, S.; Gallagher, D.; Edwards, M. Assessing risk with increasingly stringent public health goals: The case of water lead and blood lead in children. J. Water Health 2014, 12, 57–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanek, L.W.; Xue, J.; Lay, C.R.; Helm, E.C.; Schock, M.; Lytle, D.A.; Speth, T.F.; Zartarian, V.G. Modeled impacts of drinking water Pb reduction scenarios on children’s exposures and blood lead levels. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 9474–9482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandelova, M.; Lopez, W.L.; Michalke, B.; Schramm, K.-W. Ca, Cd, Cu, Fe, Hg, Mn, Ni, Pb, Se, and Zn contents in baby foods from the EU market: Comparison of assessed infant intakes with the present safety limits for minerals and trace elements. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2012, 27, 120–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Price, S.A.; Maddaloni, M.A.; Finley, B.L.; Thornton, S.A.; Unice, K.M. Extending Regulatory Biokinetic Lead Models towards Food Safety: Evaluation of Consumer Baby Food Contribution to Infant Blood Lead Levels and Variability. Foods 2023, 12, 2732. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12142732
Price SA, Maddaloni MA, Finley BL, Thornton SA, Unice KM. Extending Regulatory Biokinetic Lead Models towards Food Safety: Evaluation of Consumer Baby Food Contribution to Infant Blood Lead Levels and Variability. Foods. 2023; 12(14):2732. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12142732
Chicago/Turabian StylePrice, Skyler A., Mark A. Maddaloni, Brent L. Finley, Stephanie A. Thornton, and Ken M. Unice. 2023. "Extending Regulatory Biokinetic Lead Models towards Food Safety: Evaluation of Consumer Baby Food Contribution to Infant Blood Lead Levels and Variability" Foods 12, no. 14: 2732. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12142732
APA StylePrice, S. A., Maddaloni, M. A., Finley, B. L., Thornton, S. A., & Unice, K. M. (2023). Extending Regulatory Biokinetic Lead Models towards Food Safety: Evaluation of Consumer Baby Food Contribution to Infant Blood Lead Levels and Variability. Foods, 12(14), 2732. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12142732






