Modification of Ginseng Insoluble Dietary Fiber by Enzymatic Method: Structural, Rheological, Thermal and Functional Properties
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Procurement
2.2. Preparation of Ginseng Residue
2.3. Extraction of Ginseng IDF
2.4. Preparation and Modification of Ginseng IDF
2.5. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
2.6. Fourier Transform Infrared (FT-IR) Spectroscopy
2.7. X-ray Diffraction (XRD)
2.8. Thermal Properties
2.9. Rheological Properties
2.9.1. Solution Preparation
2.9.2. Rheological Measurements
2.10. Hydration Properties
2.11. Nitrite Adsorption Capacity (NAC)
2.12. Bile Acid Adsorption Capacity (BAC)
2.13. Cholesterol Adsorption Capacity (CAC)
2.14. Glucose Adsorption Capacity (GAC)
2.15. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Structural Analysis of Enzymatically Modified Ginseng Residue Dietary Fiber
3.1.1. SEM Microstructure
3.1.2. FTIR Analysis
3.1.3. XRD Analysis
3.2. Thermal Properties of G-IDF and G-MIDF
3.3. Viscosity of G-IDF and G-MIDF
3.4. Hydration and Functional Properties of G-IDF and G-MIDF
3.4.1. WHC
3.4.2. ORC
3.4.3. WSC
3.4.4. Nitrite Ion Adsorption Capacity (NAC)
3.4.5. Bile Acid Binding Capacity (BAC)
3.4.6. Cholesterol Absorption Capacity (CAC)
3.4.7. Glucose Absorption Capacity (GAC)
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jiang, G.; Wu, Z.; Ameer, K.; Li, S.; Ramachandraiah, K. Particle size of ginseng (Panax ginseng Meyer) insoluble dietary fiber and its effect on physicochemical properties and antioxidant activities. Appl. Biol. Chem. 2020, 63, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.-Y.; Lee, H.-N.; Hong, S.-J.; Kang, H.-J.; Cho, J.Y.; Kim, D.; Ameer, K.; Kim, Y.-M. Enhanced biotransformation of the minor ginsenosides in red ginseng extract by Penicillium decumbens β-glucosidase. Enzyme Microb. Technol. 2022, 153, 109941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, G.; Bai, X.; Wu, Z.; Li, S.; Zhao, C.; Ramachandraiah, K. Modification of ginseng insoluble dietary fiber through alkaline hydrogen peroxide treatment and its impact on structure, physicochemical and functional properties. LWT—Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 150, 111956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Ameer, K.; Jiang, G. Effects of superfine grinding on the physicochemical properties and antioxidant activities of Sanchi (Panax notoginseng) flower powders. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 58, 62–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saba, E.; Irfan, M.; Jeong, D.; Ameer, K.; Lee, Y.Y.; Park, C.-K.; Hong, S.-B.; Rhee, M.H. Mediation of antiinflammatory effects of Rg3-enriched red ginseng extract from Korean Red Ginseng via retinoid X receptor α–peroxisome-proliferating receptor γ nuclear receptors. J. Ginseng Res. 2019, 43, 442–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, G.; Wu, Z.; Ramachandra, K.; Zhao, C.; Ameer, K. Changes in structural and chemical composition of insoluble dietary fibers bound phenolic complexes from grape pomace by alkaline hydrolysis treatment. Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 42, e50921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, G.; Ameer, K.; Eun, J.-B. Encapsulation of hot air-dried asian pear powders using rice bran dietary fiber. Food Biosci. 2020, 38, 100742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, G.; Feng, X.; Zhao, C.; Ameer, K.; Wu, Z. Development of biscuits supplemented with papaya seed and peel: Effects on physicochemical properties, bioactive compounds, in vitro absorption capacities and starch digestibility. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 59, 1341–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Ameer, K.; Ramachandraiah, K.; Wu, Z.; Huo, N.; Bai, X.; Nie, W.; Jiang, G. Effects of papaya (Carica papaya L.) seed supplementation on quality attributes, adsorption capacities, and in vitro starch digestibility of wheat bread. J. Food Measur. Charac. 2022, 16, 3226–3239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, M.; Liu, Z.; Sha, J.; Li, S.; Dong, L.; Sun, Y. Effects of ginseng soluble dietary fiber on serum antioxidant status, immune factor levels and cecal health in healthy rats. Food Chem. 2021, 365, 130641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hua, M.; Fan, M.; Li, Z.; Sha, J.; Li, S.; Sun, Y. Ginseng soluble dietary fiber can regulate the intestinal flora structure, promote colon health, affect appetite and glucolipid metabolism in rats. J. Funct. Food 2021, 83, 104534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, C.; Rupasinghe, H.V.; Ayanbadejo, T.; Martos, P.; Schooley, J. Assessment of Ontario-grown ginseng (Panax quinquefolius L.) for nutritional quality and food safety. In Proceedings of the XXVI International Horticultural Congress: The Future for Medicinal and Aromatic Plants 629, Toronto, ON, Canada, 11–17 August 2002; pp. 115–121. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, H.-Y.; Rhim, D.-B.; Kim, S.-K.; Ban, O.-H.; Oh, S.-K.; Seo, J.; Hong, S.-K. Growth promotion effect of red ginseng dietary fiber to probiotics and transcriptome analysis of Lactiplantibacillus plantarum. J. Ginseng Res. 2023, 47, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, H.J.; You, S.-H.; Nam, E.H.; Truong, V.-L.; Bang, J.-H.; Bae, Y.-J.; Rarison, R.H.; Kim, S.-K.; Jeong, W.-S.; Jung, Y.H. Red ginseng dietary fiber promotes probiotic properties of Lactiplantibacillus plantarum and alters bacterial metabolism. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1139386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Y.; Xue, P.; Chen, Y.; Xie, J.; Peng, G.; Tian, S.; Chang, X.; Yu, Q. Effect of soluble dietary fiber of navel orange peel prepared by mixed solid-state fermentation on the quality of jelly. Foods 2023, 12, 1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.I.; Ameer, K.; Chung, Y.B.; Min, S.G.; Eun, J.B. Optimization of spray drying process for recovery of onion–stevia leaf hot water extract powder using response surface methodology. Food Sci. Nutr. 2023, 11, 1770–1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurek, M.A.; Karp, S.; Wyrwisz, J.; Niu, Y. Physicochemical properties of dietary fibers extracted from gluten-free sources: Quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa), amaranth (Amaranthus caudatus) and millet (Panicum miliaceum). Food Hydrocoll. 2018, 85, 321–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Q.; Ma, Z.; Wang, W.; Mu, J.; Liu, Y.; Wang, J.; Stipkovits, L.; Hui, X.; Wu, G.; Sun, J. The effects of enzymatic modification on the functional ingredient—Dietary fiber extracted from potato residue. LWT—Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 153, 112511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Liu, F.; Xiao, Y.; Cao, J.; Wang, M.; Duan, X. Alterations in physicochemical and functional properties of buckwheat straw insoluble dietary fiber by alkaline hydrogen peroxide treatment. Food Chem. X 2019, 3, 100029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Wang, Q.; Zheng, B.; Lin, L.; Chen, B.; Zheng, Y.; Xiao, J. Hydration properties and binding capacities of dietary fibers from bamboo shoot shell and its hypolipidemic effects in mice. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2017, 109, 1003–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spence, J.D.; Jenkins, D.J.; Davignon, J. Dietary cholesterol and egg yolks: Not for patients at risk of vascular disease. Canad. J. Cardiol. 2010, 26, e336–e339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hua, M.; Lu, J.; Qu, D.; Liu, C.; Zhang, L.; Li, S.; Chen, J.; Sun, Y. Structure, physicochemical properties and adsorption function of insoluble dietary fiber from ginseng residue: A potential functional ingredient. Food Chem. 2019, 286, 522–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, B.Y.; Prudencio, S.H. Alkaline hydrogen peroxide improves physical, chemical, and techno-functional properties of okara. Food Chem. 2020, 323, 126776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, G.; Ramachandraiah, K.; Murtaza, M.A.; Wang, L.; Li, S.; Ameer, K. Synergistic effects of black ginseng and aged garlic extracts for the amelioration of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) in mice. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 9, 3091–3099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, G.; Ramachandraiah, K.; Wu, Z.; Ameer, K. The influence of different extraction methods on the structure, rheological, thermal and functional properties of soluble dietary fiber from Sanchi (Panax notoginseng) flower. Foods 2022, 11, 1995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alba, K.; Macnaughtan, W.; Laws, A.; Foster, T.J.; Campbell, G.; Kontogiorgos, V. Fractionation and characterisation of dietary fibre from blackcurrant pomace. Food Hydrocoll. 2018, 81, 398–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hua, M.; Sun, Y.; Shao, Z.; Lu, J.; Lu, Y.; Liu, Z. Functional soluble dietary fiber from ginseng residue: Polysaccharide characterization, structure, antioxidant, and enzyme inhibitory activity. J. Food Biochem. 2020, 44, e13524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, J.; Yokoyama, W.; Masamba, K.G.; Majeed, H.; Zhong, F.; Li, Y. Structural and physico-chemical properties of insoluble rice bran fiber: Effect of acid–base induced modifications. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 79915–79923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Zeng, G.; Pan, Y.; Chen, W.; Huang, W.; Chen, H.; Li, Y. Properties of soluble dietary fiber-polysaccharide from papaya peel obtained through alkaline or ultrasound-assisted alkaline extraction. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 172, 102–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandra, J.; George, N.; Narayanankutty, S.K. Isolation and characterization of cellulose nanofibrils from arecanut husk fibre. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 142, 158–166. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, Y.; Wu, Y.; Qian, Y.; Ouyang, X.; Yang, D.; Qiu, X. Adsorption and desorption behaviors of lignosulfonate during the self-assembly of multilayers. BioResources 2010, 5, 1178–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, C.H.; Yan, Z.M.; Wang, P.L.; Alkhatib, A.; Zhu, J.Y.; Zou, H.C.; Sun, D.Y.; Zhu, X.D.; Gao, F.; Shi, W.T. Effect of high pressure homogenization treatment on the rheological properties of citrus peel fiber/corn oil emulsion. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2020, 100, 3658–3665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raza, H.; Liang, Q.; Ameer, K.; Ma, H.; Ren, X. Dual-frequency power ultrasound effects on the complexing index, physicochemical properties, and digestion mechanism of arrowhead starch-lipid complexes. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2022, 84, 105978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Song, R.; Wei, S.; Wang, W.; Li, F.; Tang, X.; Li, N. Modification of insoluble dietary fiber from ginger residue through enzymatic treatments to improve its bioactive properties. LWT—Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 125, 109220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sang, J.; Li, L.; Wen, J.; Liu, H.; Wu, J.; Yu, Y.; Xu, Y.; Gu, Q.; Fu, M.; Lin, X. Chemical composition, structural and functional properties of insoluble dietary fiber obtained from the Shatian pomelo peel sponge layer using different modification methods. LWT—Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 165, 113737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Jiao, Q.; Yuan, F.; Gao, Y. In vitro binding capacities and physicochemical properties of soluble fiber prepared by microfluidization pretreatment and cellulase hydrolysis of peach pomace. LWT—Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 63, 677–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Huang, C.; Ou, S. In vitro binding capacities of three dietary fibers and their mixture for four toxic elements, cholesterol, and bile acid. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 186, 236–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
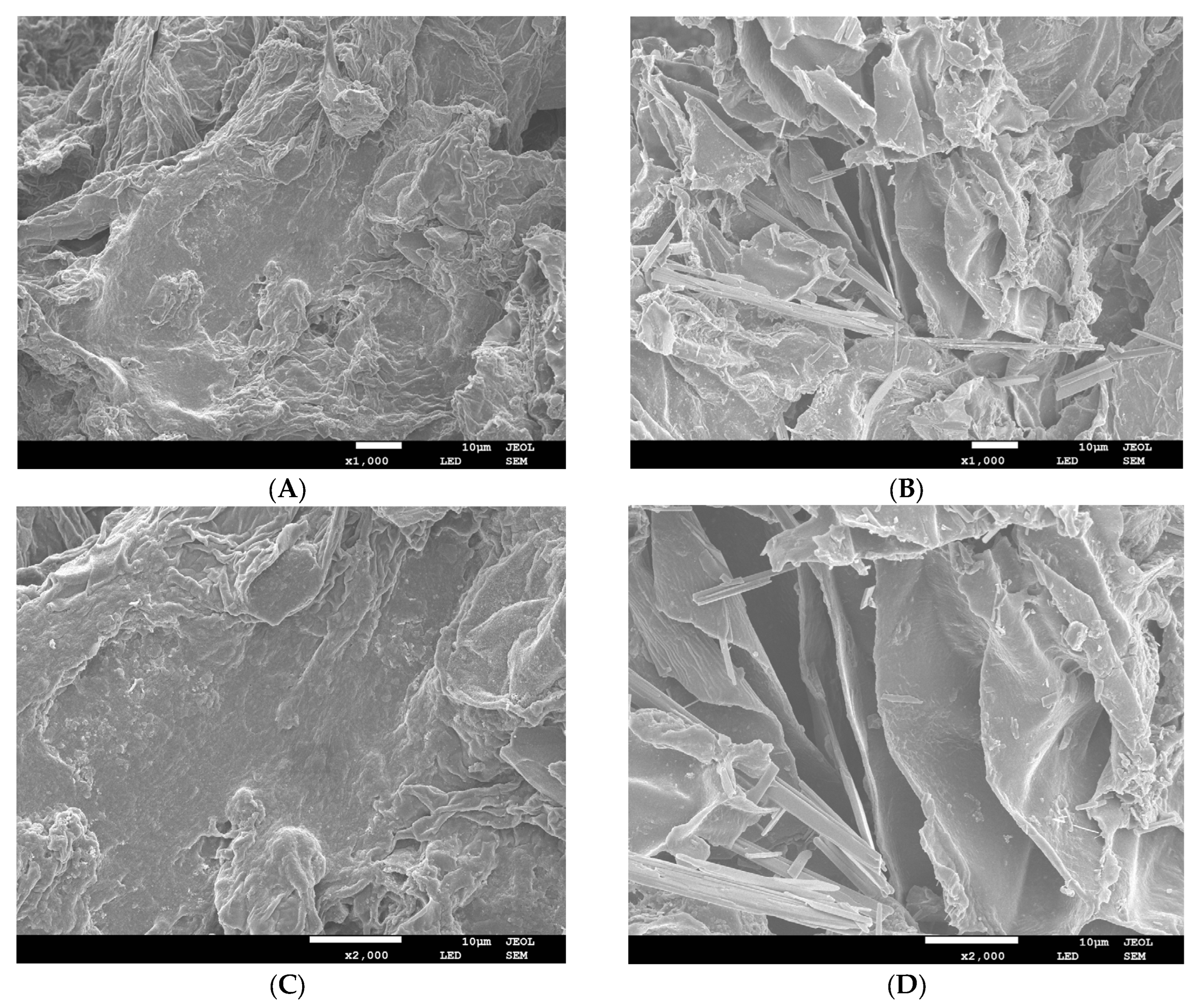


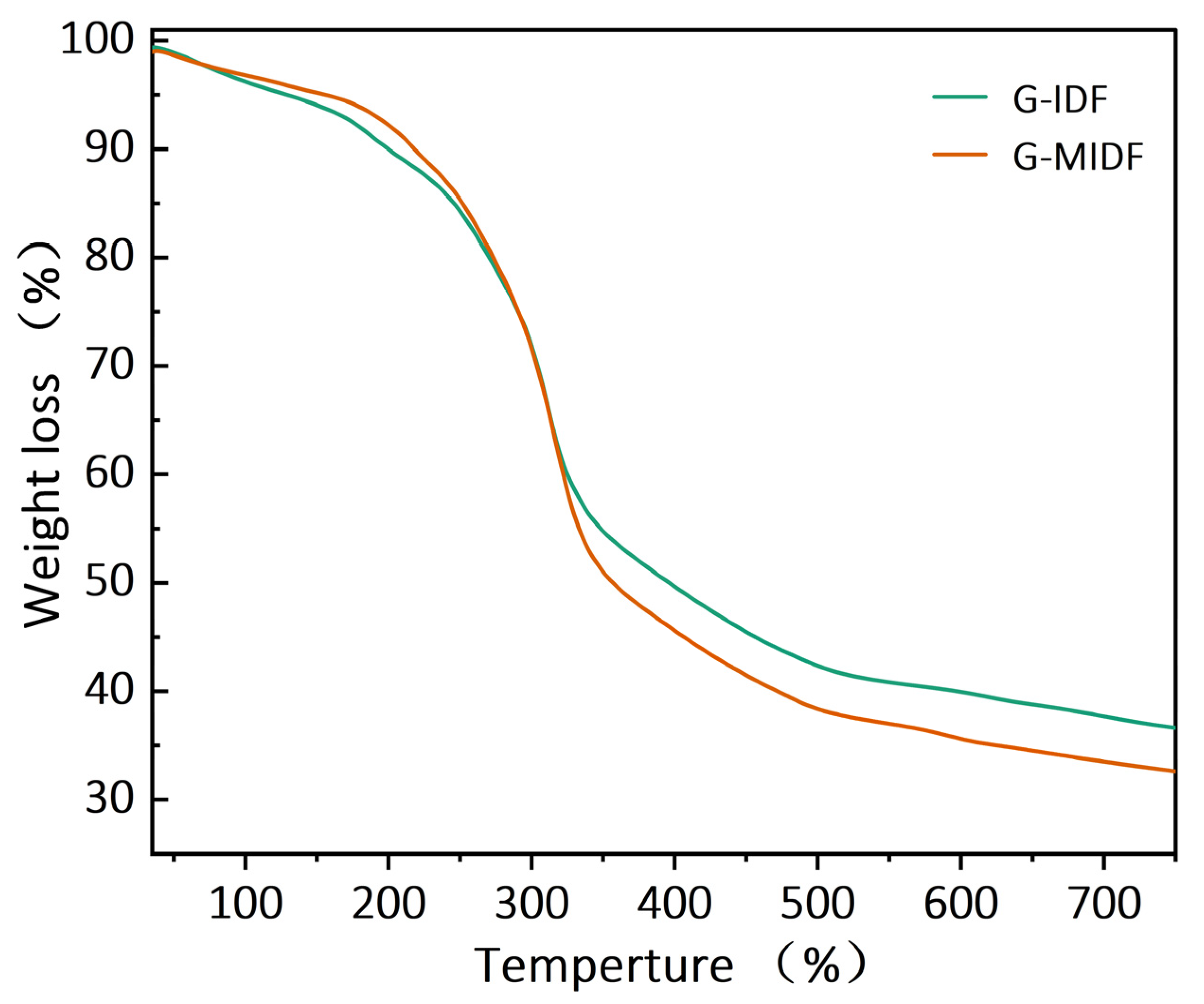
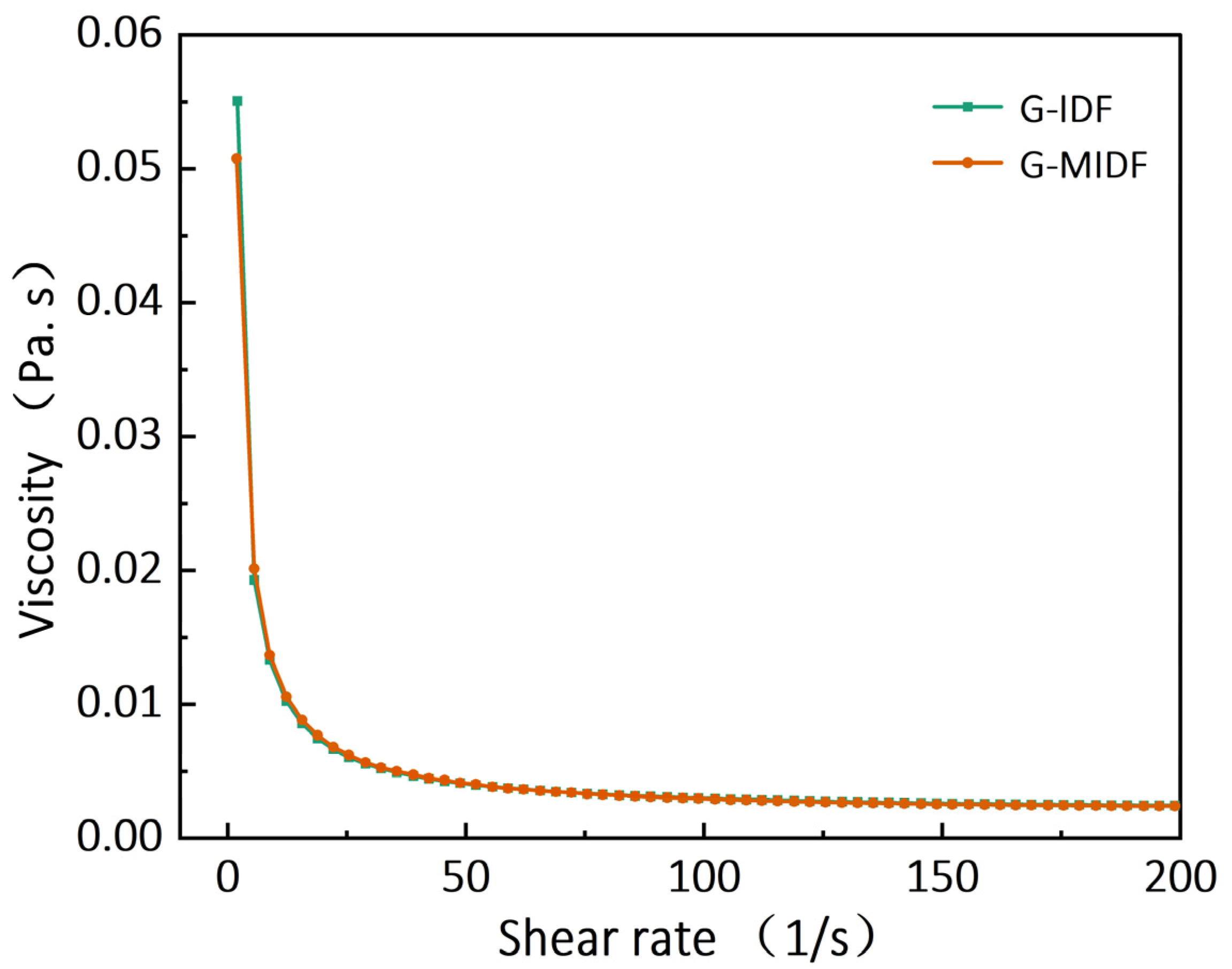
| Parameter | G-IDF | G-MIDF |
|---|---|---|
| Apparent viscosity 25 1/s (, mPa·s) | 6.06 ± 0.10 a | 6.22 ± 0.04 a |
| Consistency coefficient (K, mPa·s) | 67 ± 1.24 a | 59 ± 1.75 b |
| Flow behaviour index (n, -) | 0.40 ± 0.002 b | 0.43 ± 0.012 a |
| Property | G-IDF | G-MIDF |
|---|---|---|
| WHC (g/g) | 5.30 ± 0.09 b | 6.36 ± 0.10 a |
| ORC (g/g) | 2.91 ± 0.25 b | 4.52 ± 0.06 a |
| WSC (g/g) | 6.17 ± 0.06 b | 7.90 ± 0.17 a |
| Fiber Type | NAC (μg/g) | BAC (mg/g) | CAC (mg/g) | GAC (mg/g) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH 2.0 | pH 7.0 | 50 mmol/L | 100 mmol/L | 150 mmol/L | |||
| G-IDF | 119.92 ± 0.22 b | 117.17 ± 0.38 b | 90.60 ± 0.23 b | 8.86 ± 0.04 b | 16.49 ± 0.25 b | 31.97 ± 0.07 b | 50.16 ± 0.04 b |
| G-MIDF | 124.28 ± 0.15 a | 122.29 ± 0.30 a | 93.34 ± 0.33 a | 10.85 ± 0.07 a | 17.34 ± 0.19 a | 35.31 ± 0.12 a | 52.62 ± 0.06 a |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jiang, G.; Ramachandraiah, K.; Tan, C.; Cai, N.; Ameer, K.; Feng, X. Modification of Ginseng Insoluble Dietary Fiber by Enzymatic Method: Structural, Rheological, Thermal and Functional Properties. Foods 2023, 12, 2809. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12142809
Jiang G, Ramachandraiah K, Tan C, Cai N, Ameer K, Feng X. Modification of Ginseng Insoluble Dietary Fiber by Enzymatic Method: Structural, Rheological, Thermal and Functional Properties. Foods. 2023; 12(14):2809. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12142809
Chicago/Turabian StyleJiang, Guihun, Karna Ramachandraiah, Chaoyi Tan, Nanjie Cai, Kashif Ameer, and Xiaoyu Feng. 2023. "Modification of Ginseng Insoluble Dietary Fiber by Enzymatic Method: Structural, Rheological, Thermal and Functional Properties" Foods 12, no. 14: 2809. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12142809
APA StyleJiang, G., Ramachandraiah, K., Tan, C., Cai, N., Ameer, K., & Feng, X. (2023). Modification of Ginseng Insoluble Dietary Fiber by Enzymatic Method: Structural, Rheological, Thermal and Functional Properties. Foods, 12(14), 2809. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12142809







