Nutritional Profiles of Yoom Noon Rice from Royal Initiative of Southern Thailand: A Comparison of White Rice, Brown Rice, and Germinated Brown Rice
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. White Rice, Brown Rice, and Germinated Brown Rice Samples
2.3. Analyses
2.3.1. Proximate Composition and Amylose
2.3.2. Mineral and Vitamin
2.3.3. GABA, Total Extractable Flavonoid (TEF), and Phytic Acid (PA)
2.3.4. Rapidly Available Glucose (RAG) and Slowly Available Glucose (SAG)
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Proximate Composition and Amylose Content
3.2. Mineral Profiles
3.3. Vitamin Profiles, GABA, TEF, and PA
3.4. RAG and SAG
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ye, L.; Zhou, S.; Liu, L.; Liu, L.; Waters, D.L.; Zhong, K.; Zhou, X.; Ma, X.; Liu, X. Phenolic compounds and antioxidant capacity of brown rice in China. Int. J. Food Eng. 2016, 12, 537–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaijan, M.; Panpipat, W. Nutritional composition and bioactivity of germinated Thai indigenous rice extracts: A feasibility study. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0237844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reddy, C.K.; Kimi, L.; Haripriya, S.; Kang, N. Effects of polishing on proximate composition, physico-chemical characteristics, mineral composition and antioxidant properties of pigmented rice. Rice Sci. 2017, 24, 241–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oppong, D.; Panpipat, W.; Chaijan, M. Chemical, physical, and functional properties of Thai indigenous brown rice flours. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0255694. [Google Scholar]
- Chumsri, P.; Chaijan, M.; Panpipat, W. A comparison of nutritional values, physicochemical features and in vitro bioactivities of Southern Thai short-grain brown rice with commercial long-grain varieties. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 56, 6515–6526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Summpunn, P.; Panpipat, W.; Manurakchinakorn, S.; Bhoopong, P.; Cheong, L.Z.; Chaijan, M. Comparative analysis of antioxidant compounds and antioxidative properties of Thai indigenous rice: Effects of rice variety and processing condition. Molecules 2022, 27, 5180. [Google Scholar]
- Ofoedu, C.E.; Akosim, C.Q.; Iwouno, J.O.; Obi, C.D.; Shorstkii, I.; Okpala, C.O.R. Characteristic changes in malt, wort, and beer produced from different Nigerian rice varieties as influenced by varying malting conditions. PeerJ 2021, 9, e10968. [Google Scholar]
- Saleh, A.S.; Wang, P.; Wang, N.; Yang, L.; Xiao, Z. Brown rice versus white rice: Nutritional quality, potential health benefits, development of food products, and preservation technologies. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2019, 18, 1070–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, N.N.; Li, H.H.; Tan, B.; Zhang, M.; Xiao, Z.G.; Tian, X.H.; Zhai, X.; Liu, M.; Liu, Y.; Wang, L.; et al. Free and bound phenolic profiles of the bran from different rice varieties and their antioxidant activity and inhibitory effects on α-amylose and α-glucosidase. J. Cereal Sci. 2018, 82, 206–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, D.K.; Srivastav, P.P. Proximate composition, mineral content and fatty acids analyses of aromatic and non-aromatic Indian rice. Rice Sci. 2017, 24, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumczynski, D.; Kotásková, E.; Družbíková, H.; Mlček, J. Determination of contents and antioxidant activity of free and bound phenolics compounds and in vitro digestibility of commercial black and red rice (Oryza sativa L.) varieties. Food Chem. 2016, 211, 339–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, T.; Zhou, Y.; Wu, D.; Chen, Q.; Shu, X. Germinated high-resistant starch rice: A potential novel functional food. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 57, 5439–5449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Xiang, J.; Zhang, L.; Zhu, X.; Evers, J.; van der Werf, W.; Duan, L. Optimizing soaking and germination conditions to improve gamma-aminobutyric acid content in japonica and indica germinated brown rice. J. Funct. Foods. 2014, 10, 283–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paiva, F.F.; Vanier, N.L.; Berrios, J.D.J.; Pan, J.; de Almeida Villanova, F.; Takeoka, G.; Elias, M.C. Physicochemical and nutritional properties of pigmented rice subjected to different degrees of milling. J. Food Compost. Anal. 2014, 35, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deb, D. Rice cultures of Bengal. Gastron. J. Food Cult. 2021, 21, 91–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandumula, N. Rice production in Asia: Key to global food security. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. India Sect. B Biol. Sci. 2018, 88, 1323–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swiderska, K.; Argumedo, A.; Wekesa, C.; Ndalilo, L.; Song, Y.; Rastogi, A.; Ryan, P. Indigenous peoples’ food systems and biocultural heritage: Addressing indigenous priorities using decolonial and interdisciplinary research approaches. Sustainability 2022, 14, 11311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thrupp, L.A. Linking agricultural biodiversity and food security: The valuable role of agrobiodiversity for sustainable agriculture. Int. Aff. 2000, 76, 265–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jitpakdee, R.; Wongsawat, S. Thep of rice farmer at Pakpanang Basin in maintaining identity of native rice. Area Based Dev. Res. 2016, 8, 56–75. [Google Scholar]
- AOAC. Official Methods of Analysis, 16th ed.; Association of Official Analytical Chemists: Washington, DC, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Saelee, N. Effects of soil salinity on nutritional compositions of fresh Jak (Nypa fruticans) sap. J. Food Compost. Anal. 2022, 114, 104767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sungpud, C.; Panpipat, W.; Sae-Yoon, A.; Chaijan, M. Tuning of virgin coconut oil and propylene glycol ratios for maximizing the polyphenol recovery and in vitro bioactivities of mangosteen (Garcinia mangostana L.) pericarp. Process Biochem. 2019, 87, 179–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, F.; Wang, J.; Zhang, S.; Xu, Z.; Zhang, G. Genotypic and environmental variation in phytic acid content and its relation to protein content and malt quality in barley. Food Chem. 2007, 105, 606–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Englyst, K.N.; Hudson, G.J.; Englyst, H.N. Starch analysis in food. In Encyclopaedia of Analytical Chemistry; Meyers, R.A., Ed.; Wiley & Sons: Chichester, UK, 2000; pp. 4246–4262. [Google Scholar]
- Englyst, K.N.; Vinoy, S.; Englyst, H.N.; Lang, V. Glycaemic index of cereal products explained by their content of rapidly and slowly available glucose. Br. J. Nutr. 2003, 89, 329–340. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, R.; Wu, X.; Liu, J.; Howitt, C.A.; Bird, A.R.; Liu, C.M.; Larkin, P.J. Rice with multilayer aleurone: A larger sink for multiple micronutrients. Rice 2021, 14, 102. [Google Scholar]
- Alhendi, A.S.; Al-Rawi, S.H.; Jasim, A.M. Effect of moisture content of two paddy varieties on the physical and cooked properties of produced rice. Braz. J. Food Technol. 2019, 22, e2018184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Klerk, G.J.; Smulders, R. Protein synthesis in embryos of dormant and germinating Agrostemma githago L. seeds. Plant Physiol. 1984, 75, 929–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Rathna Priya, T.S.; Eliazer Nelson, A.R.L.; Ravichandran, K.; Antony, U. Nutritional and functional properties of coloured rice varieties of South India: A review. J. Ethn. Foods 2019, 6, 11. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, H.Y.; Hwang, I.G.; Kim, T.M.; Woo, K.S.; Park, D.S.; Kim, J.H.; Jeong, H.S. Chemical and functional components in different parts of rough rice (Oryza sativa L.) before and after germination. Food Chem. 2012, 134, 288–293. [Google Scholar]
- Collins, H.M.; Burton, R.A.; Topping, D.L.; Liao, M.L.; Bacic, A.; Fincher, G.B. Variability in fine structures of noncellulosic cell wall polysaccharides from cereal grains: Potential importance in human health and nutrition. Cereal Chem. 2010, 87, 272–282. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, L.; Tian, S.; Liao, H.; Zhang, J.; Yang, X.; Labavitch, J.M.; Chen, W. Analysis of metal element distributions in rice (Oryza sativa L.) seeds and relocation during germination based on X-ray fluorescence imaging of Zn, Fe, K., Ca, and Mn. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e57360. [Google Scholar]
- Kranner, I.; Colville, L. Metals and seeds: Biochemical and molecular implications and their significance for seed germination. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2011, 72, 93–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, E.L.; Waters, B.M. The role of transition metal homeostasis in plant seed development. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2011, 14, 318–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, M.; Nozoye, T.; Kitajima, N.; Fukuda, N.; Hokura, A.; Terada, Y.; Nishizawa, N. In vivo analysis of metal distribution and expression of metal transporters in rice seed during germination process by microarray and X-ray Fluorescence Imaging of Fe, Zn, Mn, and Cu. Plant Soil. 2009, 325, 39–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.R.; Liang, Z.; Xiong, F.; Zhong, W. Structural and histochemical characterization of developing rice caryopsis. Rice Sci. 2014, 21, 142–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srisawas, W.; Jindal, V.K. Sensory evaluation of cooked rice in relation to water-to-rice ratio and physicochemical properties. J. Texture Stud. 2007, 38, 21–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.; Yang, N.; Chen, H.; Jin, Z.; Xu, X. Effect of germination on flavor volatiles of cooked brown rice. Cereal Chem. 2011, 88, 497–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Spiegelman, D.; van Dam, R.M.; Holmes, M.D.; Malik, V.S.; Willett, W.C.; Hu, F.B. White rice, brown rice, and risk of type 2 diabetes in US men and women. Arch. Intern. Med. 2010, 170, 961–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brand-Miller, J.; McMillan-Price, J.; Steinbeck, K.; Caterson, I. Dietary glycemic index: Health implications. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 2009, 28 (Suppl. S4), 446S–449S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, L.; Das, P. Study on amylose content of ten rice varieties recommended for Assam. Int. J. Pure Appl. Biosci. 2018, 6, 1230–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.; Chen, H.; Yang, N.; Wang, J.; Duan, X.; Jin, Z.; Xu, X. Effect of germination time on physicochemical properties of brown rice flour and starch from different rice cultivars. J. Cereal Sci. 2013, 58, 263–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.M.; He, R.G.; Huang, X.; Zheng, L.; Hu, Q.L.; Hua, P. Effects of germination on composition of carbohydrate and activity of relevant enzymes in different varieties of brown rice. Cereal Feed Ind. 2006, 5, 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Yenrina, R.; Anggraini, T.; Chania, N.E. The effects of various way of processing black glutinous rice (Oryza sativa L.) on digestibility and energy value of the products. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2019, 327, 012013. [Google Scholar]
- Muhammad, Z.; Farooq, A.; Shaukat, A.; Tahira, I. Proximate composition and minerals profile of selected rice (Oryza sativa L.) varieties of Pakistan. Asian J. Chem. 2012, 24, 417–421. [Google Scholar]
- Sangha, J.K.; Sachdeva, R. Mineral and trace element composition of some rice varities. J. Dairy Foods Home Sci. 1999, 18, 130–132. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, S.; Wang, P.; Yamaji, N.; Ma, J.F. Plant nutrition for human nutrition: Hints from rice research and future perspectives. Mol. Plant 2020, 13, 825–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, L.; Zhang, C.; Zuo, F.; Zheng, L.; Li, D.; Zhang, A.; Zhang, D. Effects of fertilizers and pesticides on the mineral elements used for the geographical origin traceability of rice. J. Food Compost. Anal. 2019, 83, 103276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.M.; Wu, J.G.; Li, G.; Yang, Z.W.; Shi, C.H. Distribution of phytic acid and mineral elements in three indica rice (Oryza sativa L.) cultivars. J. Cereal Sci. 2011, 54, 116–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamberts, L.; De Bie, E.; Vandeputte, G.E.; Veraverbeke, W.S.; Derycke, V.; De Man, W.; Delcour, J.A. Effect of milling on colour and nutritional properties of rice. Food Chem. 2007, 100, 1496–1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, A.N.F.; Asfar, M.; Suwandi, N.; Amir, M.R.R. The effect of grain germination to improve rice quality. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2019, 355, 012110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- do Nascimento, L.Á.; Abhilasha, A.; Singh, J.; Elias, M.C.; Colussi, R. Rice germination and its impact on technological and nutritional properties: A review. Rice Sci. 2022, 29, 201–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhari, P.R.; Tamrakar, N.; Singh, L.; Tandon, A.; Sharma, D. Rice nutritional and medicinal properties: A review article. J. Pharmacogn. Phytochem. 2018, 7, 150–156. [Google Scholar]
- Jeong, B.G.; Moon, H.G.; Chun, J. Water-soluble vitamin and GABA contents of brown rice affected by germination. J. Korean Soc. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 48, 1359–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibata, K.; Fukuwatari, T.; Kawamura, T. Conversion percentage of tryptophan to nicotinamide is higher in rice protein diet than in wheat protein diet in rats. Int. J. Tryptophan Res. 2015, 8, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.F.; Tsai, Y.S.; Lin, M.L.; Ou, A.S.M. Comparison of bioactive components in GABA tea and green tea produced in Taiwan. Food Chem. 2006, 96, 648–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komatsuzaki, N.; Tsukahara, K.; Toyoshima, H.; Suzuki, T.; Shimizu, N.; Kimura, T. Effect of soaking and gaseous treatment on GABA content in germinated brown rice. J. Food Eng. 2007, 78, 556–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moongngarm, A.; Saetung, N. Comparison of chemical compositions and bioactive compounds of germinated rough rice and brown rice. Food Chem. 2010, 122, 782–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goufo, P.; Trindade, H. Rice antioxidants: Phenolic acids, flavonoids, anthocyanins, proanthocyanidins, tocopherols, tocotrienols, γ-oryzanol, and phytic acid. Food Sci. Nutr. 2014, 2, 75–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagchi, T.B.; Chattopadhyay, K.; Sivashankari, M.; Roy, S.; Kumar, A.; Biswas, T.; Pal, S. Effect of different processing technologies on phenolic acids, flavonoids and other antioxidants content in pigmented rice. J. Cereal Sci. 2021, 100, 103263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Febles, C.I.; Arias, A.; Hardisson, A.; Rodrıguez-Alvarez, C.; Sierra, A. Phytic acid level in wheat flours. J. Cereal Sci. 2002, 36, 19–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lott, J.N.; Ockenden, I.; Raboy, V.; Batten, G.D. Phytic acid and phosphorus in crop seeds and fruits: A global estimate. Seed Sci. Res. 2000, 10, 11–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perlas, L.A.; Gibson, R.S. Use of soaking to enhance the bioavailability of iron and zinc from rice-based complementary foods used in the Philippines. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2002, 82, 1115–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azeke, M.A.; Egielewa, S.J.; Eigbogbo, M.U.; Ihimire, I.G. Effect of germination on the phytase activity, phytate and total phosphorus contents of rice (Oryza sativa), maize (Zea mays), millet (Panicum miliaceum), sorghum (Sorghum bicolor) and wheat (Triticum aestivum). J. Food Sci. Technol. 2011, 48, 724–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Liu, J.; Li, D.; Liu, C.M. Rice caryopsis development II: Dynamic changes in the endosperm. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2016, 58, 786–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, T.H.; Lombi, E.; Fitzgerald, M.; Laursen, K.H.; Frydenvang, J.; Husted, S.; Boualaphanh, P.; Resurreccion, A.; Howard, D.L.; de Jonge, M.D.; et al. Losses of essential mineral nutrients by polishing of rice differ among genotypes due to contrasting grain hardness and mineral distribution. J. Cereal Sci. 2012, 56, 307–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Z.; Qiao, D.; Zhao, S.; Zhang, B.; Lin, Q.; Xie, F. Whole grain rice: Updated understanding of starch digestibility and the regulation of glucose and lipid metabolism. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2022, 21, 3244–3273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Englyst, H.N.; Kingman, S.M.; Cummings, J.H. Classification and measurement of nutritionally important starch fractions. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 1992, 46, S33–S50. [Google Scholar]
- Englyst, K.N.; Englyst, H.N.; Hudson, G.J.; Cole, T.J.; Cummings, J.H. Rapidly available glucose in foods: An in vitro measurement that reflects the glycemic response. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1999, 69, 448–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saka, S.O.; Salisu, Y.Y.; Sahabi, H.U.M.; Sanusi, K.O.; Ibrahim, K.G.; Abubakar, M.B.; Imam, M.U. Nutrigenomic effects of white rice and brown rice on the pathogenesis of metabolic disorders in a fruit fly model. Molecules 2023, 28, 532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abubakar, B.; Yakasai, H.M.; Zawawi, N.; Ismail, M. Compositional analyses of white, brown and germinated forms of popular Malaysian rice to offer insight into the growing diet-related diseases. J. Food Drug Anal. 2018, 26, 706–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imam, M.U.; Musa, S.N.A.; Azmi, N.H.; Ismail, M. Effects of white rice, brown rice and germinated brown rice on antioxidant status of type 2 diabetic rats. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 13, 12952–12969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, Y.; Mizukuchi, A.; Kise, M.; Aoto, H.; Yamamoto, S.; Yoshihara, R.; Yokoyama, J. Postprandial blood glucose and insulin responses to pre-germinated brown rice in healthy subjects. J. Med. Investig. 2005, 52, 159–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nyambe-Silavwe, H.; Villa-Rodriguez, J.A.; Ifie, I.; Holmes, M.; Aydin, E.; Jensen, J.M.; Williamson, G. Inhibition of human α-amylase by dietary polyphenols. J. Funct. Foods 2015, 19, 723–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

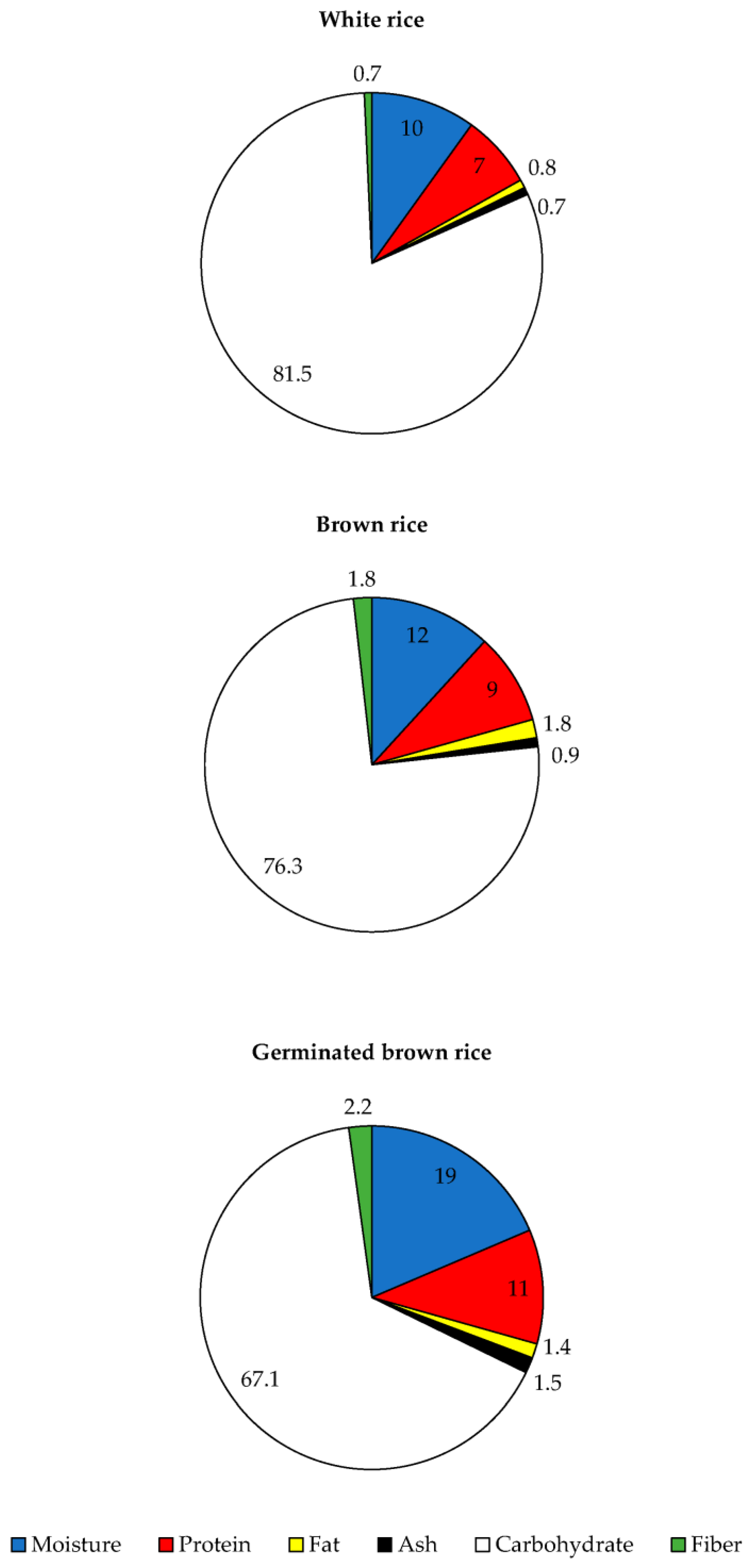
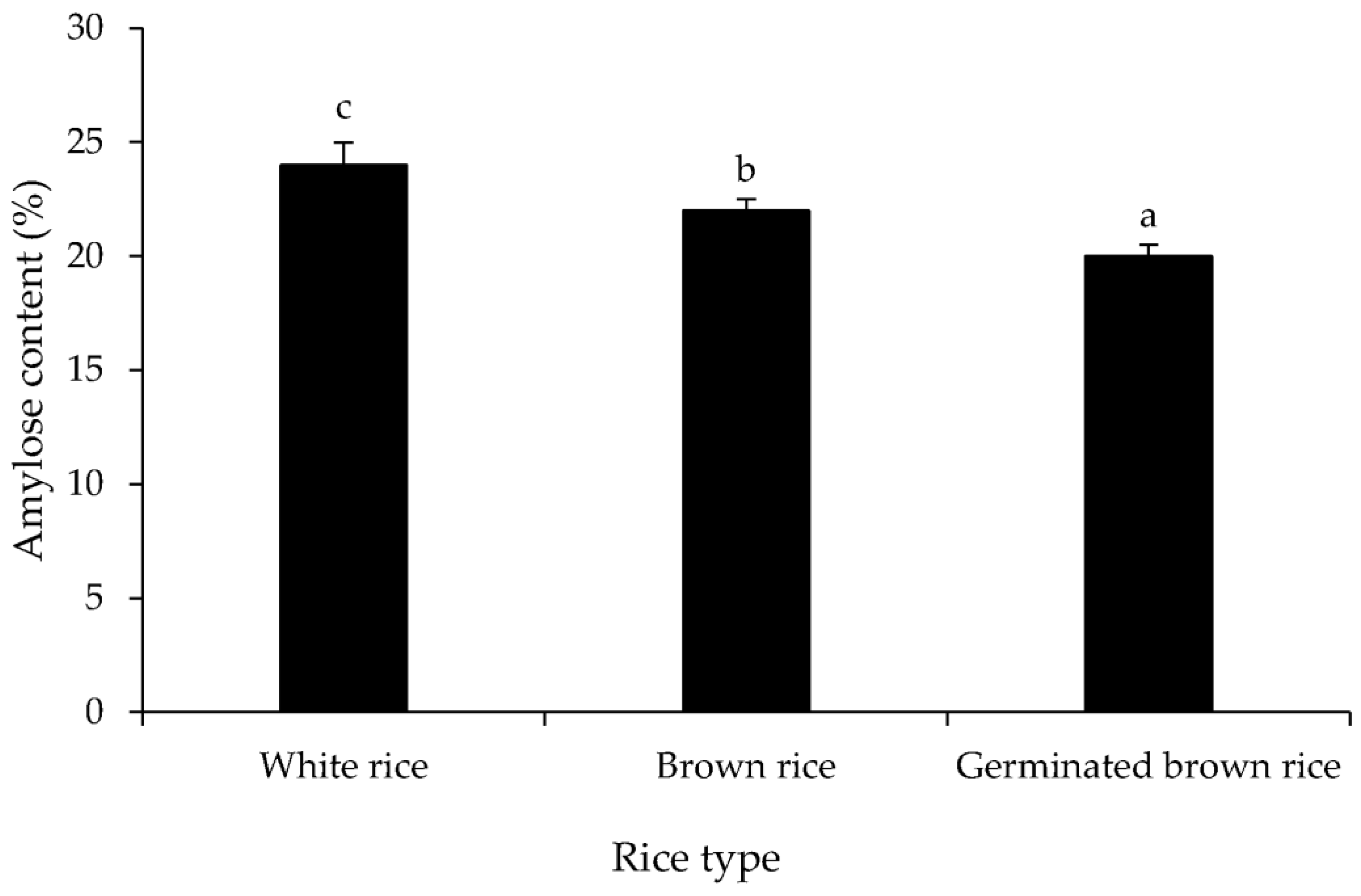
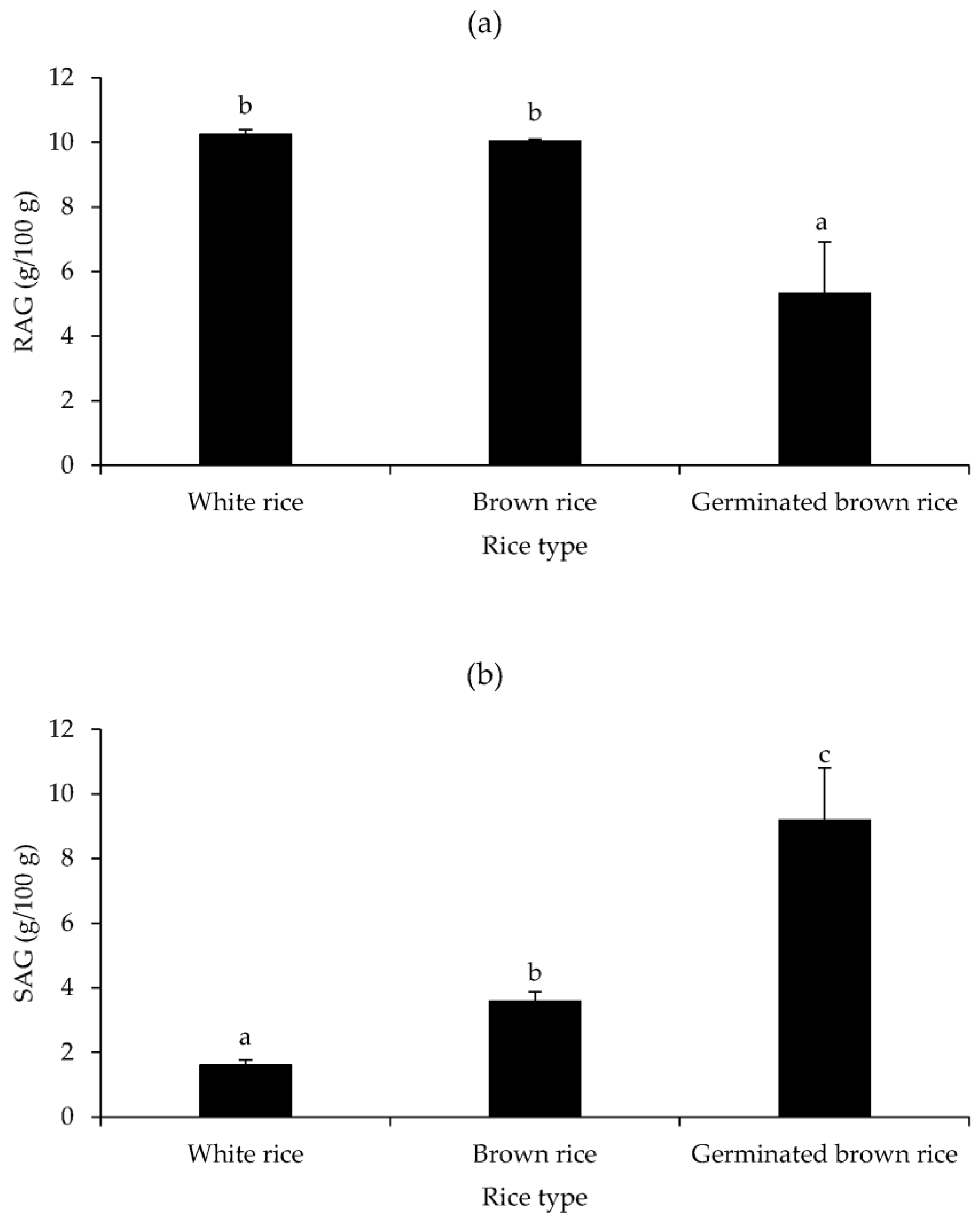
| Mineral (mg/100 g) | White Rice | Brown Rice | Germinated Brown Rice |
|---|---|---|---|
| Magnesium | 6.59 ± 0.50 a | 10.59 ± 0.71 c | 9.00 ± 0.50 b |
| Zinc | 5.98 ± 0.05 b | 6.18 ± 0.10 c | 4.10 ± 0.10 a |
| Iron | 3.60 ± 0.10 b | 4.92 ± 0.12 c | 3.45 ± 0.05 a |
| Potassium | 3.40 ± 0.05 b | 3.81 ± 0.21 c | 2.61 ± 0.11 a |
| Calcium | 1.45 ± 0.40 b | 1.66 ± 0.31 c | 1.14 ± 0.05 a |
| Manganese | 1.20 ± 0.05 a | 2.48 ± 0.10 c | 1.75 ± 0.21 b |
| Copper | 0.17 ± 0.02 a | 0.23 ± 0.01 b | 0.16 ± 0.00 a |
| Selenium | ND | ND | ND |
| Compositions | White Rice | Brown Rice | Germinated Brown Rice |
|---|---|---|---|
| Vitamin | |||
| Thiamin (mg/100 g) | 56 ± 2 a | 65 ± 4 b | 85 ± 4 c |
| Nicotinamide (μg/100 g) | 4 ± 0 a | 45 ± 1 d | 31 ± 1 b |
| Pyridoxin (μg/100 g) | 18 ± 1 a | 44 ± 1 c | 21 ± 1 b |
| Riboflavin | ND | ND | ND |
| GABA (mg/kg) | ND | 197 ± 2 a | 585 ± 1 b |
| TEF (mg RE/100 g) | ND | 495 ± 5 b | 232 ± 4 a |
| Phytic acid (mg/100 g) | ND | 11.2 ± 0.4 b | 9.6 ± 0.5 a |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Summpunn, P.; Deh-ae, N.; Panpipat, W.; Manurakchinakorn, S.; Bhoopong, P.; Donlao, N.; Rawdkuen, S.; Shetty, K.; Chaijan, M. Nutritional Profiles of Yoom Noon Rice from Royal Initiative of Southern Thailand: A Comparison of White Rice, Brown Rice, and Germinated Brown Rice. Foods 2023, 12, 2952. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12152952
Summpunn P, Deh-ae N, Panpipat W, Manurakchinakorn S, Bhoopong P, Donlao N, Rawdkuen S, Shetty K, Chaijan M. Nutritional Profiles of Yoom Noon Rice from Royal Initiative of Southern Thailand: A Comparison of White Rice, Brown Rice, and Germinated Brown Rice. Foods. 2023; 12(15):2952. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12152952
Chicago/Turabian StyleSummpunn, Pijug, Nattharika Deh-ae, Worawan Panpipat, Supranee Manurakchinakorn, Phuangthip Bhoopong, Natthawuddhi Donlao, Saroat Rawdkuen, Kalidas Shetty, and Manat Chaijan. 2023. "Nutritional Profiles of Yoom Noon Rice from Royal Initiative of Southern Thailand: A Comparison of White Rice, Brown Rice, and Germinated Brown Rice" Foods 12, no. 15: 2952. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12152952
APA StyleSummpunn, P., Deh-ae, N., Panpipat, W., Manurakchinakorn, S., Bhoopong, P., Donlao, N., Rawdkuen, S., Shetty, K., & Chaijan, M. (2023). Nutritional Profiles of Yoom Noon Rice from Royal Initiative of Southern Thailand: A Comparison of White Rice, Brown Rice, and Germinated Brown Rice. Foods, 12(15), 2952. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12152952









