Bioavailability Assessment of an Iron Formulation Using Differentiated Human Intestinal Caco-2 Cells
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Merocyanine 540 (MC540) Labeling
2.3. Caco-2 Cell Culture and Differentiation
2.4. 3-(4,5-Dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium Bromide (MTT) Assay
2.5. Cell Monolayers Integrity Evaluation
2.6. Trans-Epithelial Transport Experiments
2.7. Determination of Trans-Epithelial Transported Iron
2.7.1. Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy Analysis
2.7.2. Fluorescence Quantification of Absorbed Labeled FS
2.7.3. Morphological Studies
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
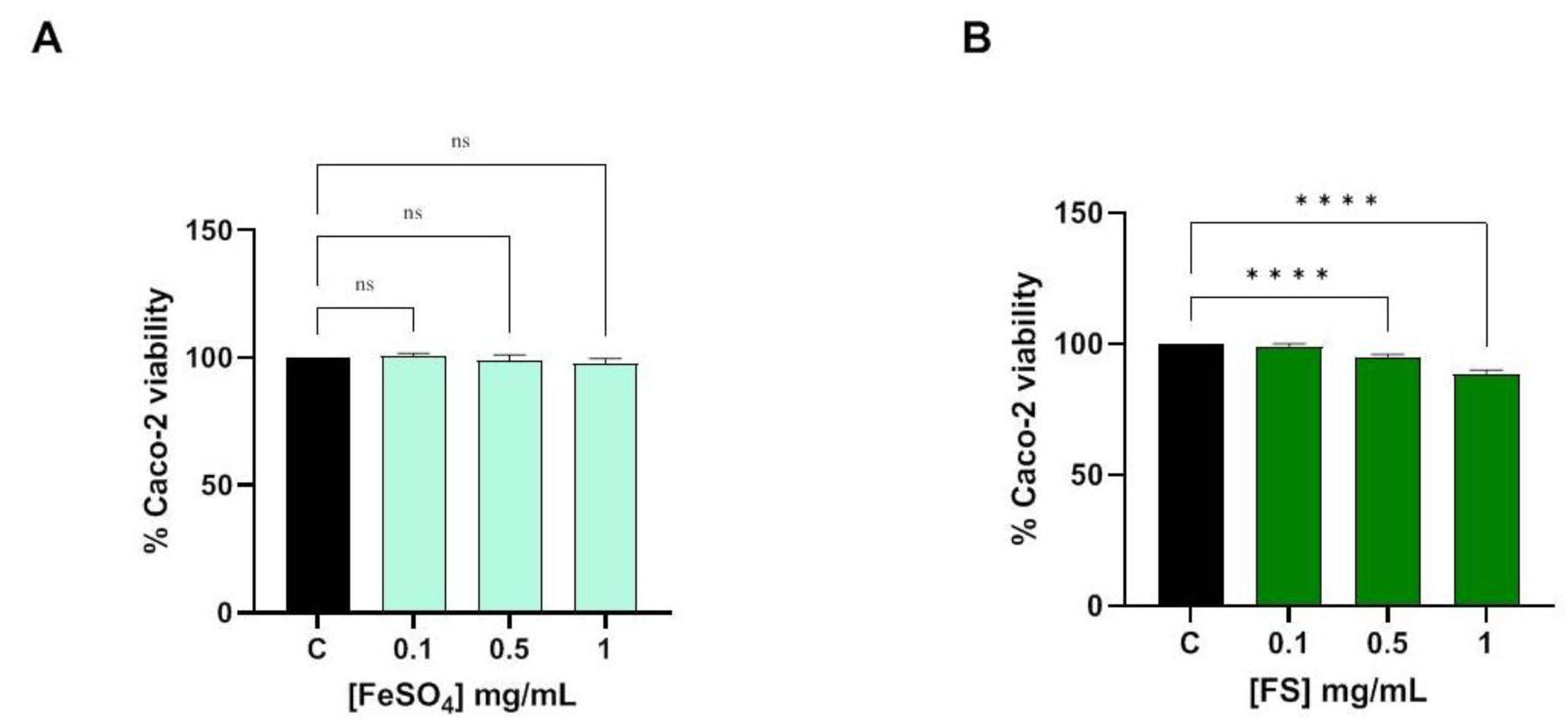
3.1. Evaluation of Caco-2 Cells Viability
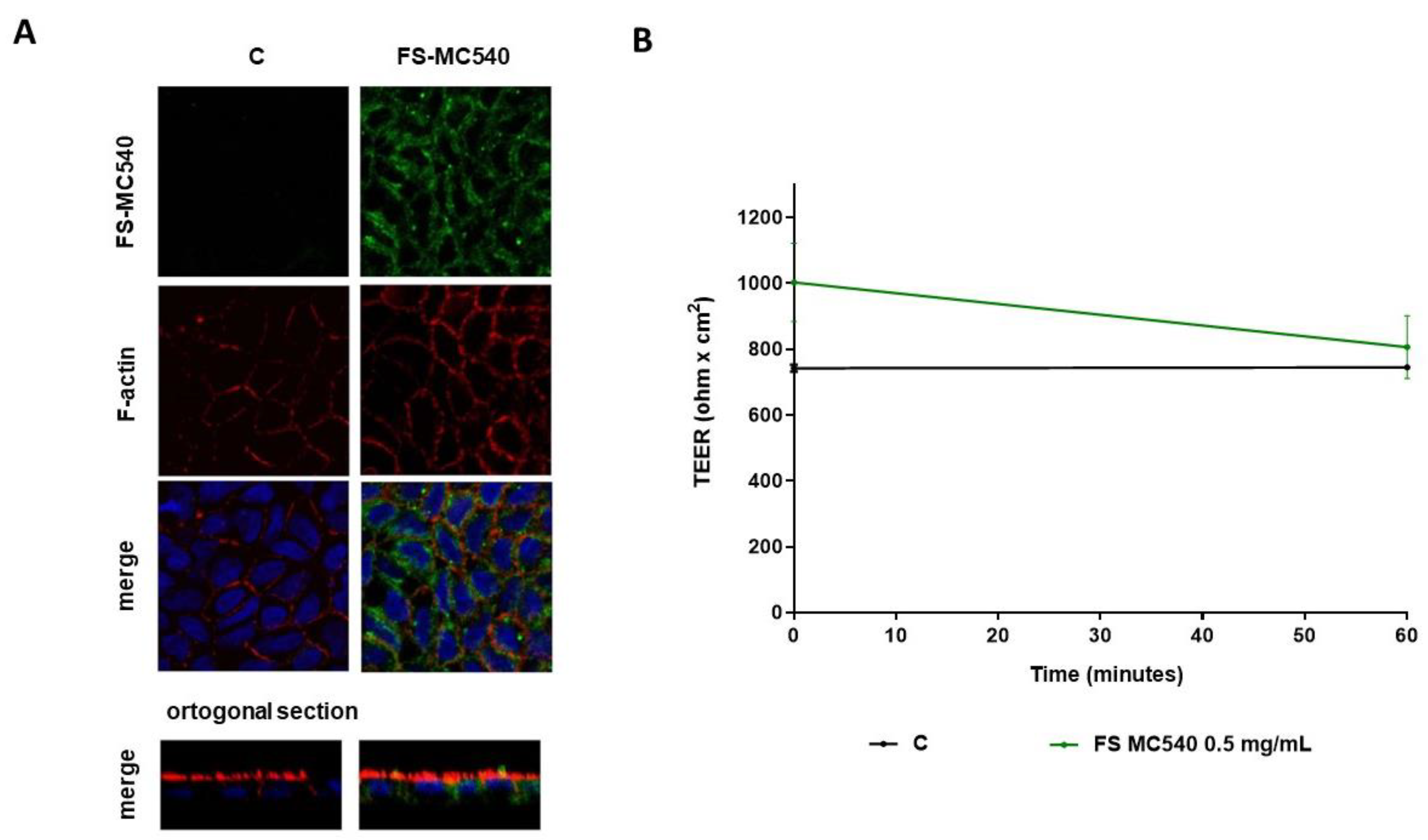
3.2. Caco-2 Cell Monolayers Integrity Evaluation after FeSO4 and FS Treatment
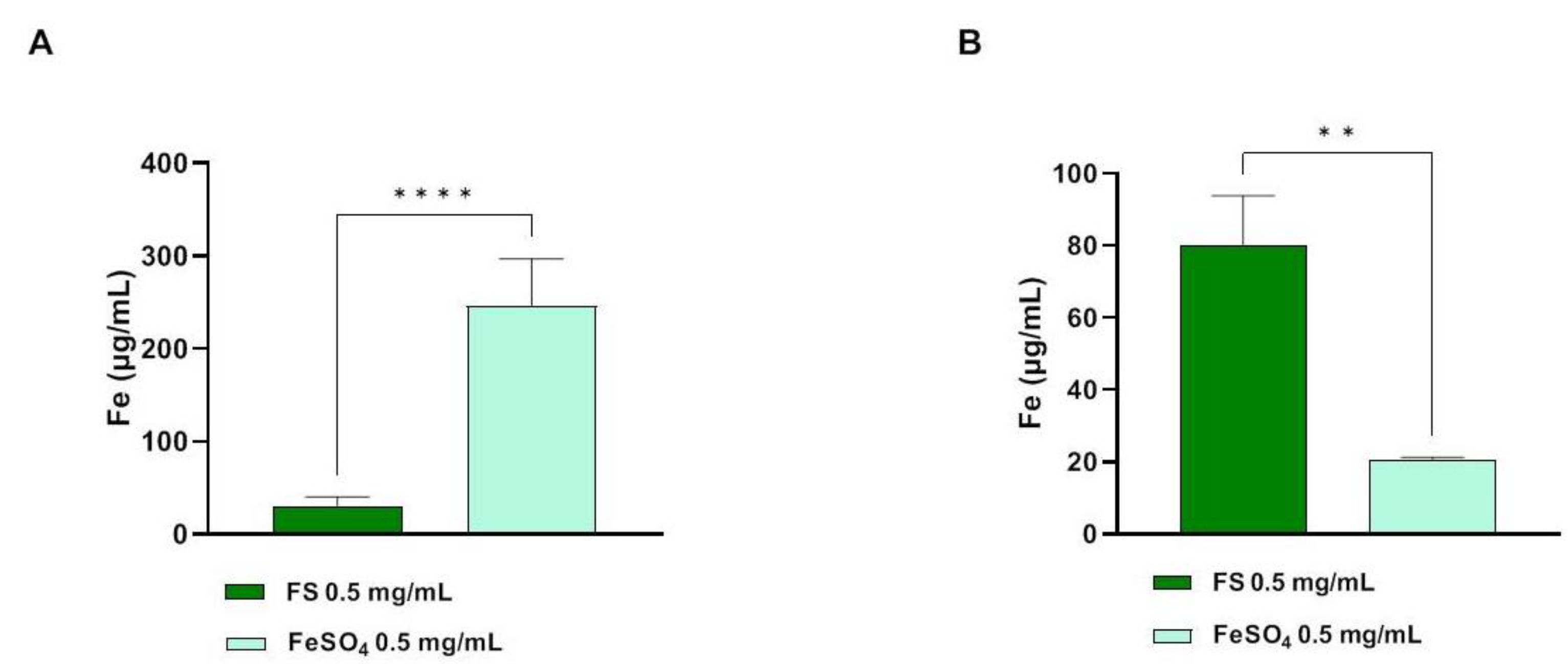
3.3. Determination of Trans-Epithelial Transported Iron through Atomic Absorption Spectrometer Analysis
3.4. Fluorescent Evaluation of FS Absorption in Caco-2 Cells
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Maladkar, M.; Sankar, S.; Yadav, A. A Novel Approach for Iron Deficiency Anaemia with Liposomal Iron: Concept to Clinic. J. Biosci. Med. 2020, 8, 27–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbaspour, N.; Hurrell, R.; Kelishadi, R. Review on Iron and Its Importance for Human Health. J. Res. Med. Sci. 2014, 19, 164–174. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bresson, J.L.; Burlingame, B.; Dean, T.; Fairweather-Tait, S.; Heinonen, M.; Hirsch-Ernst, K.I.; Mangelsdorf, I.; McArdle, H.; Naska, A.; Neuhäuser-Berthold, M.; et al. Scientific Opinion on Dietary Reference Values for Iron. EFSA J. 2015, 13, 4254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, A.S.; Enns, C.A. Iron Homeostasis: Recently Identified Proteins Provide Insight into Novel Control Mechanisms. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 711–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hunt, J.R.; Zito, C.A.; Johnson, L.A.K. Body Iron Excretion by Healthy Men and Women. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2009, 89, 1792–1798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hooda, J.; Shah, A.; Zhang, L. Heme, an Essential Nutrient from Dietary Proteins, Critically Impacts Diverse Physiological and Pathological Processes. Nutrients 2014, 6, 1080–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Friling, M.; García-Muñoz, A.M.; Perrinjaquet-Moccetti, T.; Victoria-Montesinos, D.; Pérez-Piñero, S.; Abellán-Ruiz, M.S.; Luque-Rubia, A.J.; García-Guillén, A.I.; Cánovas, F.; Ivanir, E. Tolerability of Oral Supplementation with Microencapsulated Ferric Saccharate Compared to Ferrous Sulphate in Healthy Premenopausal Woman: A Crossover, Randomized, Double-Blind Clinical Trial. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 12282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Micheletto, M.; Gaio, E.; Tedesco, E.; Di Maira, G.; Mantovan, E.; Zanella, M.; Pastore, P.; Roverso, M.; Favaro, G.; Benetti, F. Intestinal Absorption Study of a Granular Form of Ferric Pyrophosphate. Metabolites 2022, 12, 463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Zhang, X.; Xu, T.; Luo, J.; Luo, Y.; An, P. Comparative Effects between Oral Lactoferrin and Ferrous Sulfate Supplementation on Iron-Deficiency Anemia: A Comprehensive Review and Meta-Analysis of Clinical Trials. Nutrients 2022, 14, 543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgieff, M.K.; Krebs, N.F.; Cusick, S.E. The Benefits and Risks of Iron Supplementation in Pregnancy and Childhood. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 2019, 39, 121–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeLoughery, T.G. Iron Deficiency Anemia. Med. Clin. N. Am. 2017, 372, 1832–1843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hurrell, R.F. Preventing Iron Deficiency through Food Fortification. Nutr. Rev. 1997, 55, 210–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Christides, T.; Wray, D.; McBride, R.; Fairweather, R.; Sharp, P. Iron Bioavailability from Commercially Available Iron Supplements. Eur. J. Nutr. 2015, 54, 1345–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Piskin, E.; Cianciosi, D.; Gulec, S.; Tomas, M.; Capanoglu, E. Iron Absorption: Factors, Limitations, and Improvement Methods. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 20441–20456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolkien, Z.; Stecher, L.; Mander, A.P.; Pereira, D.I.A.; Powell, J.J. Ferrous Sulfate Supplementation Causes Significant Gastrointestinal Side-Effects in Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0117383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bloor, S.R.; Schutte, R.; Hobson, A.R. Oral Iron Supplementation—Gastrointestinal Side Effects and the Impact on the Gut Microbiota. Microbiol. Res. 2021, 12, 491–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oral Liposomal Iron: A Treatment Proposal for Anemia. World J. Anemia 2018, 2, 1–6. [CrossRef]
- Siddiqui, A.S.; Ashraf, T.; Imran, U. Palatability of Micro-Encapsulated Iron Pyrophosphate (Ferfer®). Int. J. Clin. Trials 2018, 5, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donnarumma, M.; Marasca, C.; Palma, M.; Vastarella, M.; Annunziata, M.C.; Fabbrocini, G. An Oral Supplementation Based on Myo-Inositol, Folic Acid and Liposomal Magnesium May Act Synergistically with Antibiotic Therapy and Can Improve Metabolic Profile in Patients Affected by Hidradenitis Suppurativa: Our Experience. G. Ital. Dermatol. Venereol. 2020, 155, 749–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, P.-P.; Chang, Y.-Z. Iron Liposome: A More Effective Iron Supplement for Sports Anemia and Anemia of Inflammation. J. Pharm. Care Health Syst. 2015, 84, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ferruzza, S.; Rossi, C.; Scarino, M.L.; Sambuy, Y. A Protocol for Differentiation of Human Intestinal Caco-2 Cells in Asymmetric Serum-Containing Medium. Toxicol. Vitr. 2012, 26, 1252–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moretti, D.; Goede, J.S.; Zeder, C.; Jiskra, M.; Chatzinakou, V.; Tjalsma, H.; Melse-Boonstra, A.; Brittenham, G.; Swinkels, D.W.; Zimmermann, M.B. Oral Iron Supplements Increase Hepcidin and Decrease Iron Absorption from Daily or Twice-Daily Doses in Iron-Depleted Young Women. Blood 2015, 126, 1981–1989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Global, Regional, and National Incidence, Prevalence, and Years Lived with Disability for 328 Diseases and Injuries for 195 Countries, 1990–2016: A Systematic Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. Lancet 2017, 390, e38.
- Cancelo-Hidalgo, M.J.; Castelo-Branco, C.; Palacios, S.; Haya-Palazuelos, J.; Ciria-Recasens, M.; Manasanch, J.; Pérez-Edo, L. Tolerability of Different Oral Iron Supplements: A Systematic Review. Curr. Med. Res. Opin. 2013, 29, 291–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awortwe, C.; Fasinu, P.S.; Rosenkranz, B. Application of Caco-2 Cell Line in Herb-Drug Interaction Studies: Current Approaches and Challenges. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2014, 17, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Foglieni, C.; Cavarelli, M.; Piscopiello, M.; Fulgenzi, A.; Ferrero, M. Mn Bioavailability by Polarized Caco-2 Cells: Comparison between Mn Gluconate and Mn Oxyprolinate. Nutr. J. 2011, 10, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheers, N.M.; Almgren, A.B.; Sandberg, A.S. Proposing a Caco-2/HepG2 Cell Model for in Vitro Iron Absorption Studies. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2014, 25, 710–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sambuy, Y.; De Angelis, I.; Ranaldi, G.; Scarino, M.L.; Stammati, A.; Zucco, F. The Caco-2 Cell Line as a Model of the Intestinal Barrier: Influence of Cell and Culture-Related Factors on Caco-2 Cell Functional Characteristics. Cell Biol. Toxicol. 2005, 21, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamiloglu, S.; Capanoglu, E.; Grootaert, C.; van Camp, J. Anthocyanin Absorption and Metabolism by Human Intestinal Caco-2 Cells—A Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 21555–21574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Uberti, F.; Morsanuto, V.; Ghirlanda, S.; Molinari, C. Iron Absorption from Three Commercially Available Supplements in Gastrointestinal Cell Lines. Nutrients 2017, 9, 1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ko, J.; Yoo, C.; Xing, D.; Gonzalez, D.E.; Jenkins, V.; Dickerson, B.; Leonard, M.; Nottingham, K.; Kendra, J.; Sowinski, R.; et al. Pharmacokinetic Analyses of Liposomal and Non-Liposomal Multivitamin/Mineral Formulations. Nutrients 2023, 15, 3073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Ferro Supremo | % |
|---|---|
| Iron | 6.5 |
| Vitamin C | 13 |
| Copper | 0.2 |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.3 |
| Sample | Solution/Time | Fluorescence (RFU) | Fluorescence (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| FS-MC540 | AP t0 | 44,532.0 ± 809.60 | 100.00 ± 0.00 |
| AP t60 | 8768.0 ± 508.80 | 19.69 ± 1.14 | |
| BL t60 | 105.03 ± 10.31 | 0.24 ± 0.023 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fanzaga, M.; Bollati, C.; Ranaldi, G.; Sucato, S.; Fustinoni, S.; Roda, G.; Lammi, C. Bioavailability Assessment of an Iron Formulation Using Differentiated Human Intestinal Caco-2 Cells. Foods 2023, 12, 3016. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12163016
Fanzaga M, Bollati C, Ranaldi G, Sucato S, Fustinoni S, Roda G, Lammi C. Bioavailability Assessment of an Iron Formulation Using Differentiated Human Intestinal Caco-2 Cells. Foods. 2023; 12(16):3016. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12163016
Chicago/Turabian StyleFanzaga, Melissa, Carlotta Bollati, Giulia Ranaldi, Sabrina Sucato, Silvia Fustinoni, Gabriella Roda, and Carmen Lammi. 2023. "Bioavailability Assessment of an Iron Formulation Using Differentiated Human Intestinal Caco-2 Cells" Foods 12, no. 16: 3016. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12163016
APA StyleFanzaga, M., Bollati, C., Ranaldi, G., Sucato, S., Fustinoni, S., Roda, G., & Lammi, C. (2023). Bioavailability Assessment of an Iron Formulation Using Differentiated Human Intestinal Caco-2 Cells. Foods, 12(16), 3016. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12163016









