The Nutritional and Functional Properties of Protein Isolates from Defatted Chia Flour Using Different Extraction pH
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Chemicals
2.2. Preparation of Chia Protein Isolate
2.3. Nutritional Properties of Chia Protein Isolate
2.3.1. Proximate Composition, Extraction, and Protein Recovery Yield
2.3.2. Protein Fractions
2.3.3. Amino Acid Profile
2.4. Functional Properties
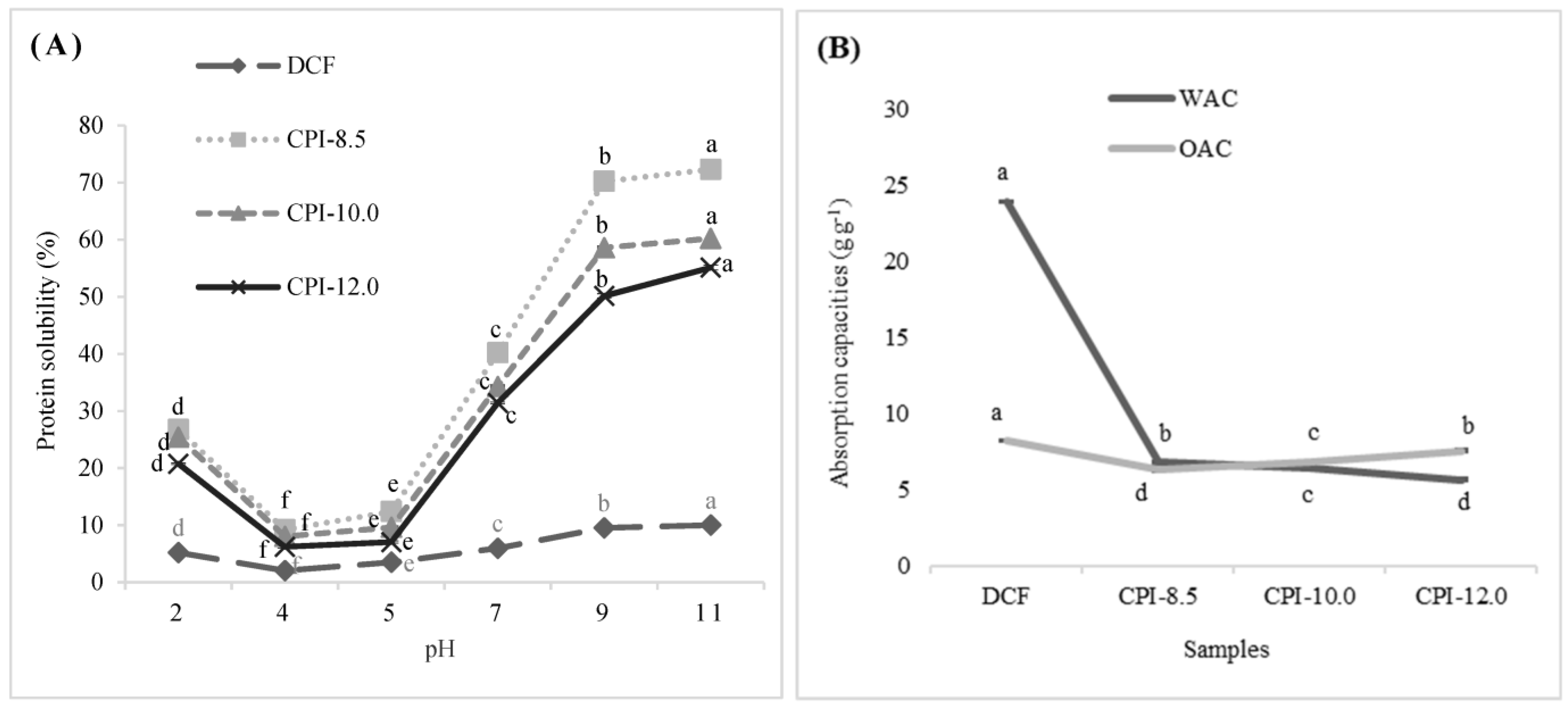
2.4.1. Protein Solubility
2.4.2. Water and Oil Absorption Capacities
2.4.3. Emulsifying Properties
2.4.4. Foaming Properties
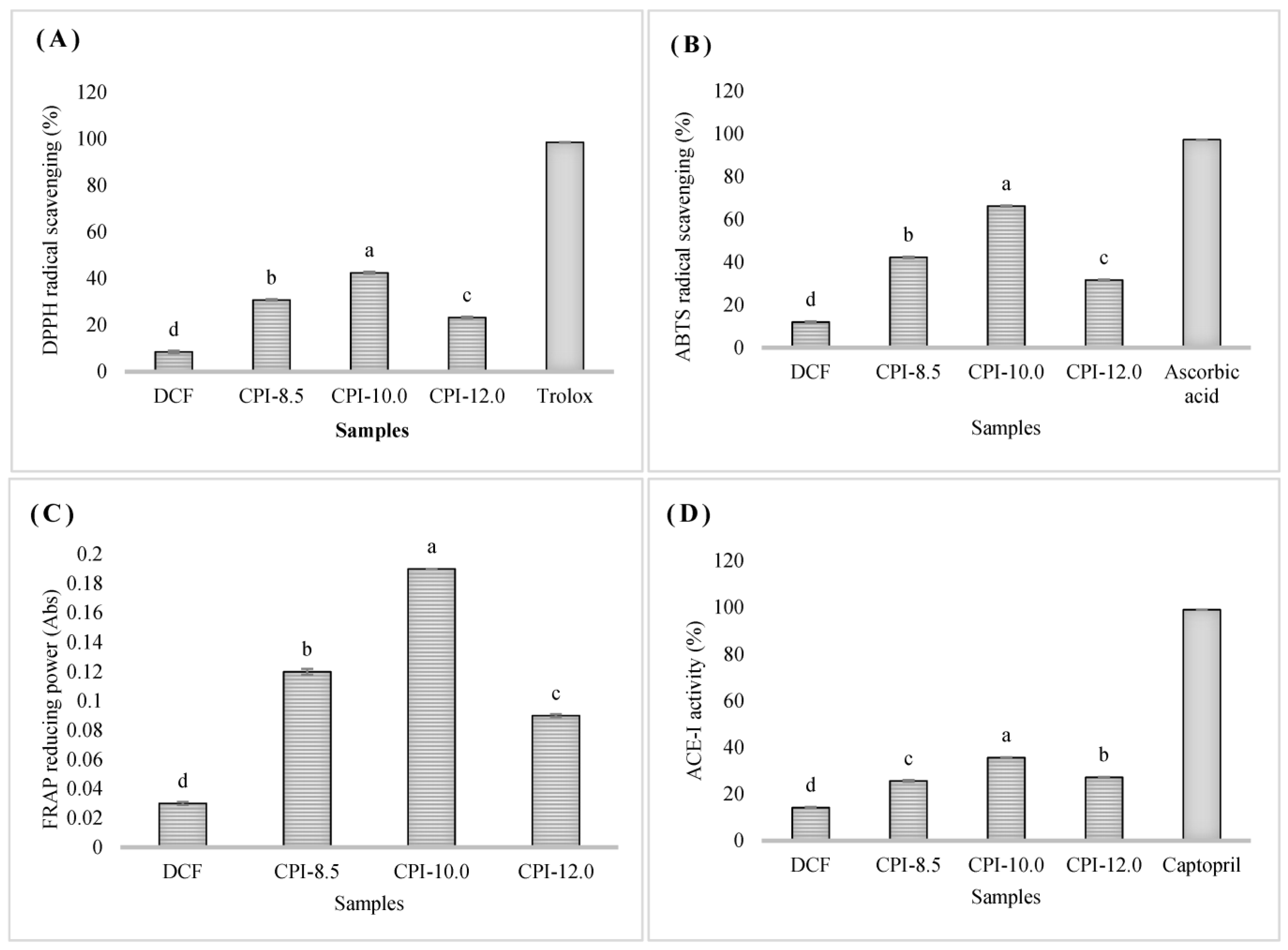
2.4.5. Antioxidant Properties
- DPPH radical scavenging assay
- ABTS radical scavenging assay
- Ferric reducing antioxidant power (FRAP) assay
2.4.6. Antihypertension Properties
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Proximate Compositions, Protein Yield, and Fractions
3.2. Amino Acids Profiles
3.3. Protein Solubility
3.4. Emulsifying Properties
3.5. Foaming Properties
3.6. Antioxidant and Antihypertensive Properties
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Razak, A.M.; Zakaria, S.N.A.; Abdul Sani, N.F.; Ab Rani, N.; Hakimi, N.H.; Mohd Said, M.; Tan, J.K.; Gan, H.K.; Mad Nordin, M.F.; Makpol, S. A subcritical water extract of soil grown Zingiber officinale Roscoe: Comparative analysis of antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects and evaluation of bioactive metabolites. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1006265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rabail, R.; Khan, M.R.; Mehwish, H.M.; Rajoka, M.S.R.; Lorenzo, J.M.; Kieiszek, M.; Khalid, A.R.; Shabbir, M.A.; Aadil, R.M. An overview of chia seed (Salvia hispanica L.) bioactive peptides’ derivation and utilization as an emerging nutraceutical food. Front. Biosci. 2021, 26, 643–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azlan, A.; Sultana, S.; Huei, C.S.; Razman, M.R. Antioxidant, anti-obesity, nutritional and other beneficial effects of different chili pepper: A review. Molecules 2022, 27, 898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ismail, B.P.; Senaratne-Lenagala, L.; Stube, A.; Brackenridge, A. Protein demand: Review of plant and animal protein used in alternative protein product development and production. Anim. Front. 2020, 10, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdul Rahim, R.; Jayusman, P.A.; Lim, V.; Ahmad, N.H.; Abdul Hamid, Z.A.; Mohamed, S.; Muhammad, N.; Ahmad, F.; Mokhtar, N.; Mohamed, N.; et al. Phytochemical analysis, antioxidant and bone anabolic effects of Blainvillea acmella (L.) Philipson. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 12, 796509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, A.C.Y.; Can Karaca, A.; Tyler, R.T.; Nickerson, M.T. Pea protein isolates: Structure, extraction, and functionality. Food Rev. Int. 2018, 34, 126–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masood, M.A. Chia seeds as potential nutritional and functional ingredients: A review of their applications for various food industries. J. Nut. Food Sci. Tech. 2022, 5, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Marcinek, P.; Krejpcio, Z. Chia seed (Salvia hispanica): Health promoting properties and the therapeutic applications—A review. Rocz. Panstw. Zakl. Hig. 2017, 68, 123–129. [Google Scholar]
- Sandoval-Oliveros, M.R.; Paredez-Lopez, O. Isolation and characterization of proteins from chia seeds (Salvia hispanica L.). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed Osama, B.R.; Bekhet Mona, H.H.; Abd El-Razek Amal, M.; Moharram Yehia, G. Evaluation of chia (Salvia hispanica L.) seeds meal as a source of bioactive ingredients. Alex. Sci. Exch. J. 2019, 40, 177–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khursheed, T.; Fatima, T.; Qadri, T.; Rafiq, A.; Malik, A.; Naseer, B.; Hussain, S.Y. Biochemical nutraceutical and phytochemical characterization of chia and basil seeds: A comparative study. Int. J. Food. Prop. 2023, 26, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, R.; Nadeen, M.; Khalique, A.; Imran, M.; Mehmood, S.; Javid, J.; Hussain, J. Nutritional and therapeutic perspectives of Chia (Salvia hispanica L.): A review. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 53, 1750–1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Olivos-Lugo, B.I.; Valdivia-Lopez, M.A.; Tecante, A. Thermal and physicochemical properties and nutritional value of the protein fraction of Mexican chia seed (Salvia hispanica L.). Food Sci. Technol. Int. 2010, 16, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nwachukwu, I.D.; Aluko, R.E. Chapter 1: Food Protein Structures, Functionality and Product Development. In Food Proteins and Peptides: Emerging Biofunctions, Food and Biomaterial Applications, 1st ed.; The Royal Society of Chemistry: London, UK, 2021; pp. 1–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.; Shen, P.; Lan, Y.; Cui, L.; Ohm, J.B.; Chen, B.; Rao, J. Effect of alkaline extraction pH on structure properties, solubility and beany flavor of yellow pea protein isolate. Food Res. Int. 2020, 131, 109045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez, D.N.; Ingrassia, R.; Busti, P.; Bonino, J.; Delgado, J.F.; Wagner, J.; Boeris, V.; Spenzini, D. Structural characterization of protein isolates obtained from chia (Salvia hispanica L.) seeds. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 90, 396–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kalaydzhiev, H.; Georgiev, R.; Ivanova, P.; Stoyanova, M.; Silma, C.L.M.; Chalova, V.I. Enhance solubility of rapeseed meal protein isolates prepared by sequential isoelectric precipitation. Foods 2020, 9, 703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valenzuela, C.; Abugoch, L.; Tapia, C.; Gamboa, A. Effect of alkaline extraction on the structure of the protein of quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa Willd.) and its influence on film formation. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2013, 48, 843–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khushairay, E.S.I.; Ghani, M.A.; Babji, A.S. Assessment of total phenolic content, antioxidative activities and amino acids profiles of low molecular weight chia hydrolysates fractions and identification of the potential antioxidative peptides sequences. Biosci. Res. 2021, 18, 8–25. [Google Scholar]
- Lan, Y.; Chen, B.; Rao, J. Pea protein isolate-high methoxyl pectin soluble complexes for improving pea protein functionality: Effect pH, biopolymer ratio and concentrations. Food Hydrocoll. 2018, 80, 245–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, E.S.K.; Ghani, M.A. The effect of enzymatic hydrolysis on the antioxidant activities and amino acid profiles of defatted chia (Salvia hispanica L.) flour. Food Res. 2020, 4 (Suppl. S4), 38–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AOAC. Official Methods of Analysis, 21st ed.; Association of Official Analytical Chemists: Washington, DC, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Vazquez-Ovando, J.A.; Rosado-Rubio, J.G.; Chel-Guerrero, L.A.; Betancur-Ancona, D. Dry processing of chia (Salvia hispanica L.) flour: Chemical characterization of fiber and protein. CYTA J. Food 2010, 2, 117–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abdul Manan, M.; Samat, N.; Kasran, M.; Hassan, H. Proximate and amino acids composition of Monascus fermented products with potential as functional feed ingredients. Cogent. Food. Agric. 2017, 3, 1295767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ninshanti, M.; Chandrapala, J.; Vasiljevic, T. Impact of storage conditions on solubility, heat stability and emulsifying properties of selected spray dried whey protein concentrates. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 92, 16–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piornos, J.A.; Burgos-Díaz, C.; Ogura, T.; Morales, E.; Rubilar, M.; Maureira-Butler, I.; Salvo-Garrido, H. Functional and physicochemical properties of a protein isolate from AluProt-CGNA: A novel protein-rich lupin variety (Lupinus luteus). Food Res. Int. 2015, 76, 719–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drozlowska, E.; Weronis, M.; Bartkowiak, A. The influence of thermal hydrolysis process on emulsifying properties of potato protein isolate. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 57, 1131–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sha, X.-M.; Hu, Z.-Z.; Tu, Z.-C.; Zhang, L.-Z.; Duan, D.-L.; Huang, T.; Xiao, H. Influence of dynamic high pressure microfluidization on functional properties and structure of gelatin from bighead carp (Hypophthalmichthys nobilis) scale. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2018, 42, e13607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, L.L.; Xu, J.; Shi, M.J.; Wang, X.L.; Li, Y.T.; Kong, L.M.; Zhou, T. Preparation, antioxidant and antimicrobial evaluation of hydroxamated degraded polysaccharides from Enteromorpha prolifera. Food Chem. 2017, 237, 481–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zielinska, E.; BaRaniak, B.; Karas, M. Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities of hydrolysates and peptide fractions obtained by enzymatic hydrolysis of selected heat-treated edible insects. Nutrients 2017, 9, 970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wootton-Beard, P.C.; Moran, A.; Ryan, L. Stability of the total antioxidant capacity and total polyphenol content of 23 commercially available vegetable juices before and after in vitro digestion measured by FRAP, DPPH, ABTS and Folin–Ciocalteu methods. Food Res. Int. 2011, 44, 217–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Pan, K.; Zhong, Q. Physical, chemical and biochemical properties of casein hydrolyzed by three proteases: Partial characterizations. Food Chem. 2014, 155, 146–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, G.A.; Xiao, W.; Boekel, M.V.; Minor, M.; Stieger, M. Effect of extraction pH on heat-induced aggregation, gelation and microstructure of protein isolate from quinoa (Chenapodium quinoa Willd). Food Chem. 2016, 209, 203–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Segura-campos, M.R. Isolation and functional characterization of chia (Salvia hispanica) proteins. Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 40, 334–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Coelho, M.S.; Salas-Mellado, M.M. How extraction method affects the physicochemical and functional properties of chia proteins. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 96, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villanueva-Lazo, A.; Montserrat-de la Paz, S.; Grao-Cruces, E.; Pedroche, J.; Toscano, R.; Millan, F.; Millan-Linares, M.C. Antioxidant and immunomodulatory properties of chia protein hydrolysates in primary human monocytes-macrophage plasticity. Foods 2022, 11, 623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nitrayova, S.; Brestensky, M.; Heger, J.; Patras, P.; Rafay, J.; Sirotkin, A. Amino acids and fatty acids profile of chia (Salvia hispanica L.) and flax (Linum usitatissimum L.) seed. Potravinarstvo 2014, 8, 72–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, K.-X.; Zhou, H.-M.; Qian, H.-F. Proteins extracted from defatted wheat germ: Nutritional and structural properties. Cereal Chem. 2006, 83, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO; FAO; UNU. Protein and Amino Acid Requirements in Human Nutrition. Report of a Joint WHO/FAO/UNU Expert Consultation; WHO Technical Report Series no. 935; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2007; Available online: https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/43411 (accessed on 23 April 2023).
- Fasuan, T.O.; Gbadamosi, S.O.; Omobujowo, T.O. Characterization of protein isolate from Sesamum indicum seed: In vitro protein digestibility, amino acid profile, and some functional properties. Food Sci. Nutr. 2018, 6, 1715–1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bashir, S.; Sharif, M.K.; Butt, M.S.; Shahid, M. Functional properties and amino acid profile of Spirulina platensis protein isolates. Pak. J. Sci. Ind. Res. B Biol. Sci. 2016, 59, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi-Shen, Z.; Shuai, S.; FitzGerald, R. Mung bean proteins and peptides: Nutritional, functional and bioactive properties. Food Nutr. Res. 2018, 62, 1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ulloa, J.A.; Barbosa, M.C.V.; Vazquez, J.A.R.; Ulloa, P.R.; Ramirez, J.C.R.; Carillo, Y.S.; Torres, L.G. Production, physico-chemical and functional characterization of protein isolate from jackfruit (Actocarpus heterophyllus) seeds. CYTA J. Food 2017, 15, 497–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, W.-Y.; Zhang, J.-T.; Miyakawa, T.; Li, G.-M.; Gu, R.-Z.; Tanokura, M. Antioxidant properties and inhibition of angiotensin-converting enzyme by highly active peptides from wheat gluten. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 5206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, R.Z.; Liu, W.-Y.; Lin, F.; Jin, Z.-T.; Chen, L.; Yi, W.-X.; Lu, J.; Cai, M.-Y. Antioxidant and angiotensin I-converting enzyme inhibitory properties of oligopeptides derived from black-bone silky fowl (Gallus gallus domesticus Brisson) muscle. Food Res. Int. 2012, 49, 326–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heredia-Leza, G.L.; Martínez, L.M.; Chuck-Hernandez, C. Impact of hydrolysis, acetylation or succinylation on functional properties of plant-based proteins: Patents, regulations, and future trends. Process 2022, 10, 283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Xing, T.; Xu, X.; Zhou, G. Influence of extreme alkaline pH induced unfolding and aggregation of PSE-like chicken protein edible film formation. Food Chem. 2020, 319, 126574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez, D.N.; Ingrassia, R.; Busti, P.; Wagner, J.; Boeris, V.; Spelzini, D. Effects of extraction pH of chia protein isolates on functional properties. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 97, 523–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shanthakumar, P.; Klepacka, J.; Bains, A.; Chawla, P.; Dhull, S.B.; Nadja, N. The current situation of pea protein and its application in the food industry. Molecules 2022, 27, 5354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shilpashree, B.G.; Arora, S.; Chawla, P.; Tomar, S.K. Effect of succinylation on physicochemical and functional properties of milk protein concentrated. Food Res. Int. 2015, 72, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishinari, K.; Fang, Y.; Guo, S.; Philips, G.O. Soy proteins: A review on composition, aggregation, and emulsification. Food Hydrocoll. 2014, 39, 301–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Mu, T.; Zhang, M.; Goffin, D.; Sun, H.; Ma, M.; Liu, X.; Zhang, D. Structure, physicochemical, and functional properties of protein isolates and major fractions from cumin (Cuminum cyminum) seeds. Int. J. Food Prop. 2018, 21, 685–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Du, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Zhu, X.; Xiong, H.; Shi, S.; Hu, J.; Peng, H.; Zhou, Q.; Sun, W. Physicochemical and functional properties of the protein isolate, and major fractions prepared from Akebia Trifoliata Var. Australis Seed. Food Chem. 2012, 133, 923–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Huang, L.; Zhang, C.; Xie, P.; Cheng, J.; Wang, X.; Li, S. Physicochemical and functional properties of Chinese quince seed protein isolate. Food Chem. 2019, 283, 539–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngo, N.T.T.; Shahidi, F. Functional properties of protein isolates from camelina (Camelina sativa L. crants) and flixweed (Sophia, Decurainis sophia L.) seed meals. Food Prod. Process. Nutr. 2021, 3, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunathilake, T.; Wansapala, J.; Herath, T. Comparison of nutritional and functional properties of mung bean (Vigna radiate) and cowpeas (Vignaunguiculata) protein isolates processed by isoelectric precipitation. Int. J. Innov. Res. Technol. 2016, 3, 139–148. [Google Scholar]
- Thakur, R.; Nimbalkar, R. Quinoa and chia seed: Protein isolates, properties, nutrition and health benefits. Int. J. Sci. Res. 2018, 9, 607–617. [Google Scholar]
- Martinez-Flores, H.; Barrera, E.S.; Romo, M.G.G.; Penagos, C.J.C.; Saavedra, J.P.; Macazaga-Alvarez, R. Functional characteristics of protein flaxseed concentrate obtained applying a response surface methodology. J. Food Sci. 2006, 71, C495–C498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celik, M.; Giizel, M.; Yildirim, M. Effect of pH on protein extraction from sour cherry kernels and functional properties of resulting protein concentrate. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 56, 3023–3032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghribi, A.M.; Gafsi, I.M.; Blecker, C.; Danthine, S.; Attia, H.; Besbes, S. Effect of drying methods on physico-chemical and functional properties of chickpea protein concentrates. J. Food. Eng. 2015, 165, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, M.; Xie, J.; Gong, B.; Xu, X.; Tang, W.; Li, X.; Li, C.; Xie, M. Extraction, physicochemical characteristics and functional properties of mung bean protein. Food Hydrocoll. 2018, 76, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tontul, I.; Gunel, A.K.; Asik, S.; Atbakan, T.; Topus, A. Functional properties of chickpea protein isolates dried by refractance window drying. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 109, 1253–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chavan, U.D.; McKenzie, D.B.; Shahidi, F. Functional properties of protein isolates from beach pea (Lathyrus maritimus L). Food Chem. 2001, 61, 429–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Li, L.; Lan, Q.; Li, M.; Wu, D.; Chen, H.; Liu, Y.; Lin, D.; Qin, Q.; Zhang, Z.; et al. Protein glycosylation: A promising way to modify the functional properties and extend the application in food system. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2018, 59, 2506–2533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benelhadj, S.; Gharsallaoui, A.; Degraeve, P.; Attia, H.; Ghorbel, D. Effect of pH on the functional properties of Arthrospira (Spirulina) plantesis protein isolate. Food Chem. 2016, 194, 1056–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aluko, R.; Yada, R.Y. Structure-function relationships of cowpea (Vigna unguiculata) globulin isolate: Influence of pH and NaCl on physicochemical and functional properties. Food Chem. 1995, 53, 259–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, T.-B.; He, T.-P.; Le, H.-B.; Tang, H.-W.; Xia, E.-Q. The structure-activity relationship of antioxidant peptides from natural proteins. Molecules 2016, 21, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ghanbari, R.; Zarei, M.; Ebrahimpour, A.; Abdul-Hamid, A.; Ismail, A.; Saari, N. Angiotensin-I converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitory and antioxidant activities of sea cucumber (Actinopyga lecanora) hydrolysates. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 28870–28885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rajapakse, N.; Mendis, E.; Byun, H.-G.; Kim, S.-K. Purification and in vitro antioxidative effects of giant squid muscle peptides on free radical-mediated oxidative systems. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2005, 16, 562–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, K.; Goto-Yamamoto, N.; Kitayama, M.; Hashizume, K. Loss of anthocyanins in red-wine grape under high temperature. J. Exp. Bot. 2007, 58, 1935–1945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, D.O.; Jeong, S.W.; Lee, C.Y. Antioxidant capacity of phenolic phytochemicals from various cultivars of plums. Food Chem. 2003, 81, 321–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Liu, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Zhu, X.; Yu, R.; Dong, S.; Wu, H. Novel natural angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE)-inhibitory peptides derived from sea cucumber-modified hydrolysates by adding exogenous proline and a study of their structure–activity relationship. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oh, J.-Y.; Je, J.-G.; Lee, H.-G.; Kim, E.-A.; Kang, S.I.; Lee, J.-S.; Jeon, Y.-J. Antihypertensive activity of novel peptides identifies from olive flounder (Parelichthys olivaceus) surimi. Foods 2020, 9, 647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.Y.; Hur, S.J. Antihypertensive peptides from animal products, marine organisms, and plants. Food Chem. 2017, 228, 506–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yea, C.S.; Ebrahimpour, A.; Hamid, A.A.; Bakar, J.; Muhammad, K.; Saari, N. Winged bean [Psophorcarpus tetragonolobus (L.) DC] seeds as an underutilized plant source of bifunctional proteolysate and biopeptides. Food Funct. 2014, 5, 1007–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| DCF | CPI-8.5 | CPI-10.0 | CPI-12.0 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Extraction yield and protein recovery (%) | |||||
| Extraction yield | 15.29 ± 0.09 c | 16.87 ± 0.16 b | 19.10 ± 0.11 a | ||
| Protein recovery yield | 44.29 ± 0.17 c | 52.31 ± 0.20 b | 59.63 ± 0.15 a | ||
| Proximate composition (%) | |||||
| Crude protein | 37.89 ± 0.25 d | 69.75 ± 0.23 c | 73.10 ± 0.17 b | 74.53 ± 0.21 a | |
| Protein fractions | Glutelin | 44.79 ± 0.19 d | 79.16 ± 0.22 b | 78.89 ± 0.26 c | 79.95 ± 0.22 a |
| Globulin | 26.32 ± 0.11 a | 5.65 ± 0.15 c | 6.04 ± 0.09 b | 6.15 ± 0.12 b | |
| Albumin | 25.22 ± 0.09 a | 6.89 ± 0.31 b | 6.58 ± 0.12 b | 6.72 ± 0.20 b | |
| Prolamin | 3.67 ± 0.13 c | 7.80 ± 0.17 b | 8.49 ± 0.12 a | 7.68 ± 0.21 b | |
| Lipid | 15.12 ± 0.23 a | 0.79 ± 0.17 b | 0.71 ± 0.15 b | 0.69 ± 0.19 b | |
| Moisture | 7.43 ± 0.11 a | 4.39 ± 0.10 b | 4.42 ± 0.11 b | 4.54 ± 0.15 b | |
| Ash | 5.21 ± 0.14 c | 6.22 ± 0.09 b | 6.41 ± 0.10 a | 6.44 ± 0.12 a | |
| Crude Fibre | 20.17 ± 0.12 a | 0.30 ± 0.02 b | 0.31 ± 0.04 b | 0.29 ± 0.04 b | |
| Nitrogen-free extract (NFE) | 14.18± 0.17 c | 18.55 ± 0.14 a | 15.05 ± 0.14 b | 13.51 ± 0.15 d | |
| Amino Acids | DCF | CPI-8.5 | CPI-10.0 | CPI-12.0 | 1 FAO/WHO/UNU (Adult) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Essential amino acids (EAA) | |||||
| Ile | 1.69 ± 0.08 c | 1.72 ± 0.05 c | 1.88 ± 0.05 b | 1.97 ± 0.04 a | 2.0 |
| Leu | 4.01 ± 0.05 c | 3.99 ± 0.07 c | 4.15 + 0.02 b | 4.29 ± 0.03 a | 3.9 |
| Lys | 4.64 ± 0.05 a | 4.59 ± 0.09 a | 4.45 ± 0.12 b | 4.39 ± 0.08 b | 3.0 |
| Met | 4.48 ± 0.04 d | 4.57 ± 0.07 c | 4.87 ± 0.06 b | 5.29 ± 0.05 a | 1.5 |
| Phe | 5.94 ± 0.06 d | 6.08 ± 0.05 c | 6.33 ± 0.04 b | 6.63 ± 0.06 a | 2.5 |
| Thr | 5.43 ± 0.09 a | 4.90 ± 0.11 b | 4.55 ± 0.06 c | 4.50 ± 0.09 c | 1.5 |
| Val | 4.00 ± 0.10 d | 4.23 ± 0.09 c | 4.41 ± 0.05 b | 4.60 ± 0.07 a | 2.6 |
| His | 3.52 ± 0.05 c | 3.61 ± 0.03 b | 3.77 ± 0.04 a | 3.80 ± 0.04 a | 1.0 |
| Trp | 1.05 ± 0.04 d | 1.19 ± 0.03 c | 1.28 ± 0.05 b | 1.40 ± 0.01 a | 0.4 |
| Non-essential amino acids (NEAA) | |||||
| Ala | 3.33 ± 0.06 a | 3.21 ± 0.04 b | 3.25 ± 0.10 b | 3.24 ± 0.05 b | |
| Arg | 12.69 ± 0.07 b | 12.93 ± 0.04 a | 12.97 ± 0.04 a | 12.02 ± 0.03 c | |
| Asp | 9.72 ± 0.08 a | 9.55 ± 0.06 b | 9.40 ± 0.06 c | 9.12 ± 0.05 d | |
| Cys | 0.88 ± 0.01 b | 0.93 ± 0.02 a | 0.90 ± 0.01 a | 0.94 ± 0.04 a | |
| Glu | 18.46 ± 0.07 a | 18.22 ± 0.06 b | 18.21 ± 0.10 b | 18.07 ± 0.09 c | |
| Gly | 5.58 ± 0.05 a | 5.51 ± 0.03 b | 5.19 ± 0.06 c | 5.09 ± 0.04 d | |
| Ser | 7.40 ± 0.03 a | 7.42 ± 0.05 a | 7.01 ± 0.05 b | 6.86 ± 0.04 c | |
| Tyr | 3.46 ± 0.07 c | 3.54 ± 0.05 b | 3.59 ± 0.03 b | 3.70 ± 0.03 a | |
| Pro | 3.72 ± 0.05 c | 3.81 ±0.04 b | 3.79 ± 0.05 b | 4.09 ± 0.07 a | |
| Total EAA | 34.76 ± 0.06 d | 34.88 ± 0.07 c | 35.69 ± 0.05 b | 36.87 ± 0.05 a | 18.4 |
| Total 2 AAH | 30.63 ± 0.06 d | 31.15 ± 0.06 c | 32.27 ± 0.05 b | 33.81 ± 0.05 a | |
| Total 3 AAR | 13.97 ± 0.06 d | 14.42 ± 0.04 c | 14.97 ± 0.04 b | 15.54 ± 0.03 a | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Khushairay, E.S.I.; Ghani, M.A.; Babji, A.S.; Yusop, S.M. The Nutritional and Functional Properties of Protein Isolates from Defatted Chia Flour Using Different Extraction pH. Foods 2023, 12, 3046. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12163046
Khushairay ESI, Ghani MA, Babji AS, Yusop SM. The Nutritional and Functional Properties of Protein Isolates from Defatted Chia Flour Using Different Extraction pH. Foods. 2023; 12(16):3046. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12163046
Chicago/Turabian StyleKhushairay, Etty Syarmila Ibrahim, Ma’aruf Abd Ghani, Abdul Salam Babji, and Salma Mohamad Yusop. 2023. "The Nutritional and Functional Properties of Protein Isolates from Defatted Chia Flour Using Different Extraction pH" Foods 12, no. 16: 3046. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12163046
APA StyleKhushairay, E. S. I., Ghani, M. A., Babji, A. S., & Yusop, S. M. (2023). The Nutritional and Functional Properties of Protein Isolates from Defatted Chia Flour Using Different Extraction pH. Foods, 12(16), 3046. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12163046