Effects of Key Components on the Antioxidant Activity of Black Tea
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Experimental Materials
2.2. Black Tea Processing and Samplings
2.3. Samples Preparation and Extraction
2.4. Determination of Total Antioxidant Activity (FRAP Method)
2.5. Determination of Total Polyphenols (TP)
2.6. Determination of Catechins, TSA, GA and CAF
2.7. Determination of Theaflavins
2.8. Determination of Free Amino Acids
2.9. Determination of Total Sugar [18]
2.10. Determination of Flavonoids
2.11. Determination of Thearubigins (TRs) and Theabrownins (TBs) [18]
2.12. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Variable Coefficient Analysis of Antioxidant Activity and Chemical Compounds of Black Tea
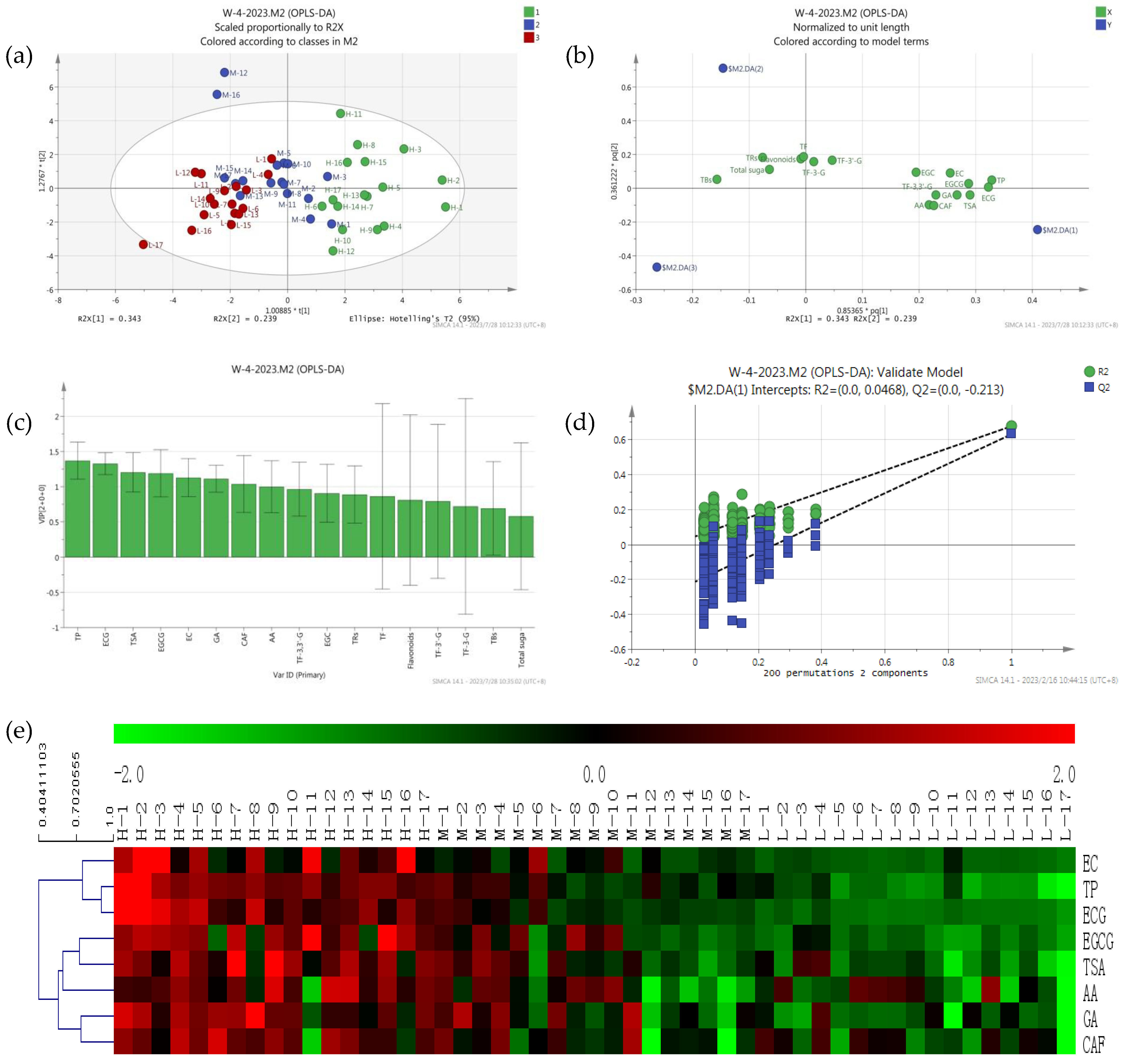
3.2. Differential Compounds Analysis of Black Tea with Different Antioxidant Activity
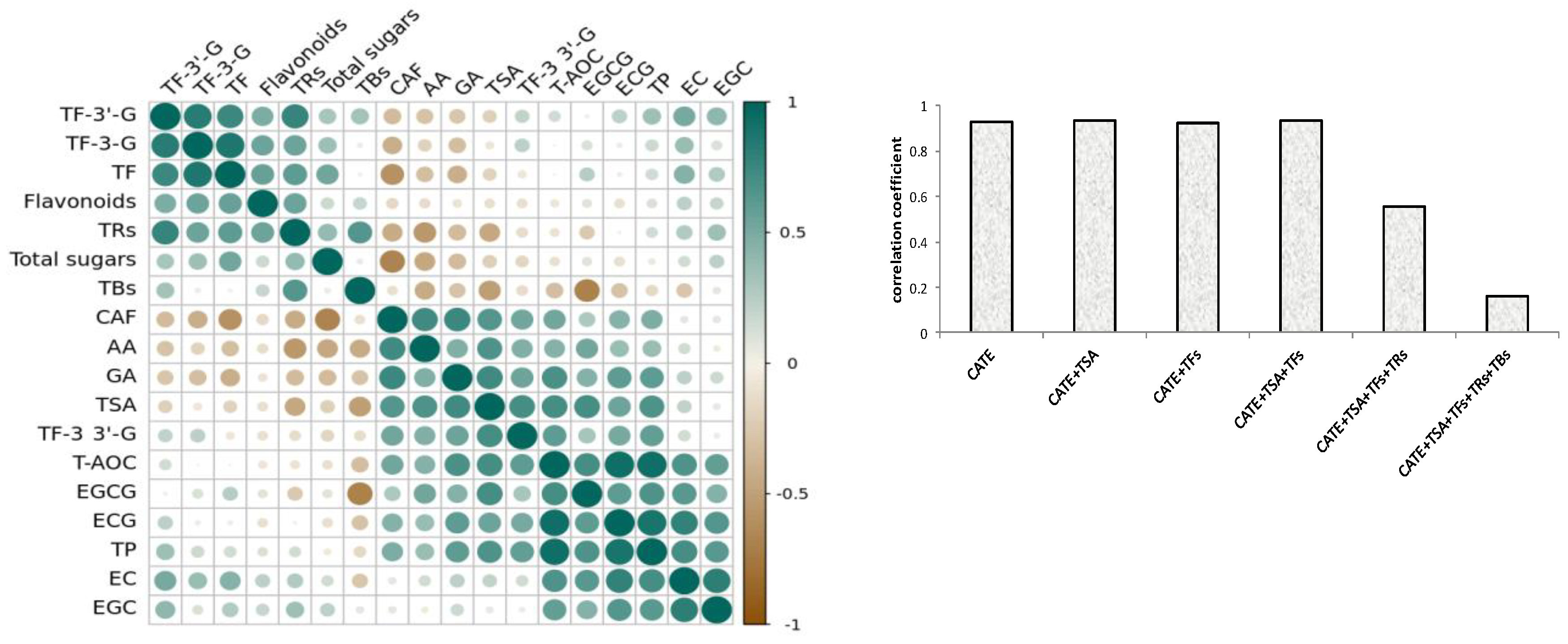
3.3. Correlation Analysis of Antioxidant Activity and Chemical Compounds of Different Black Teas
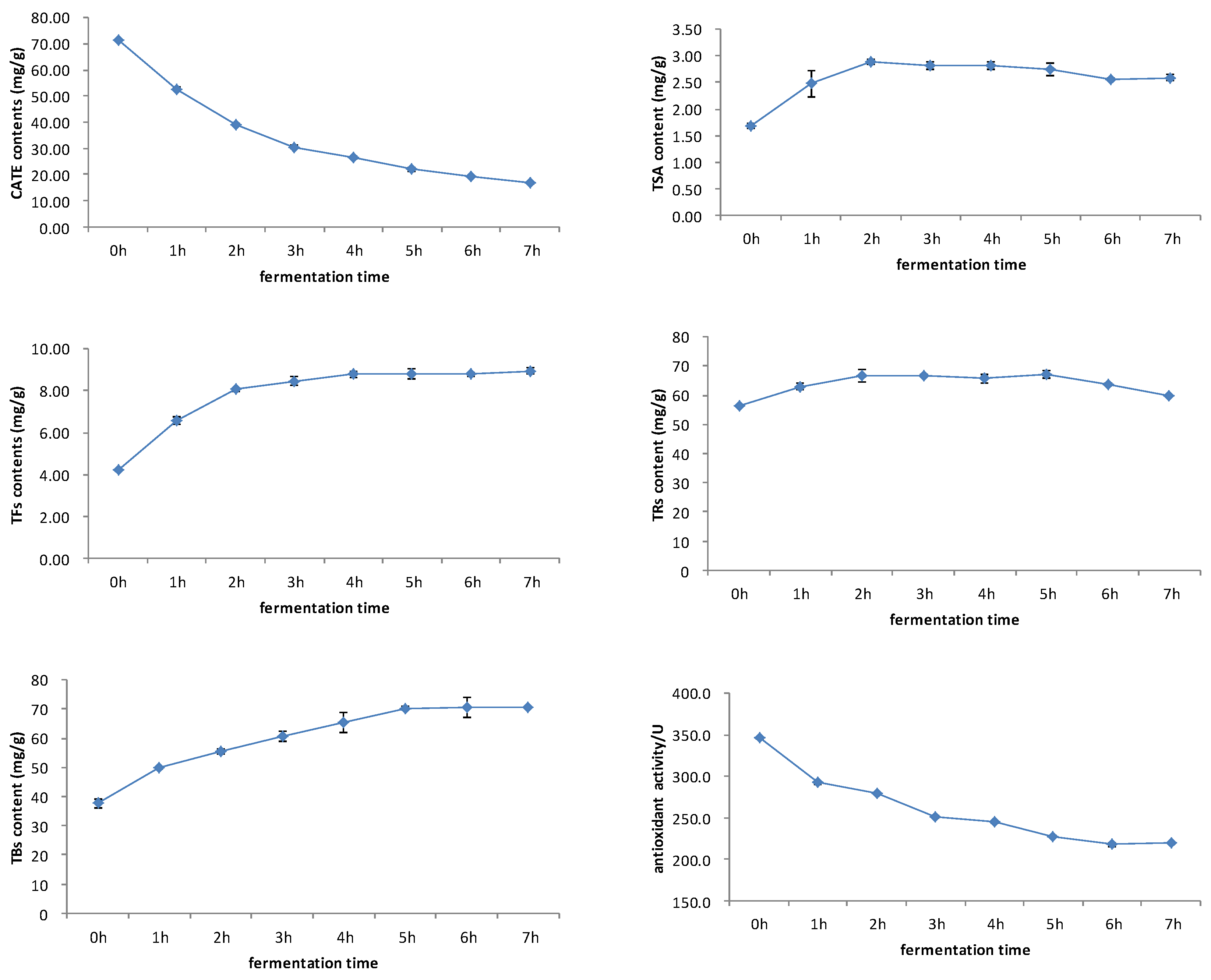
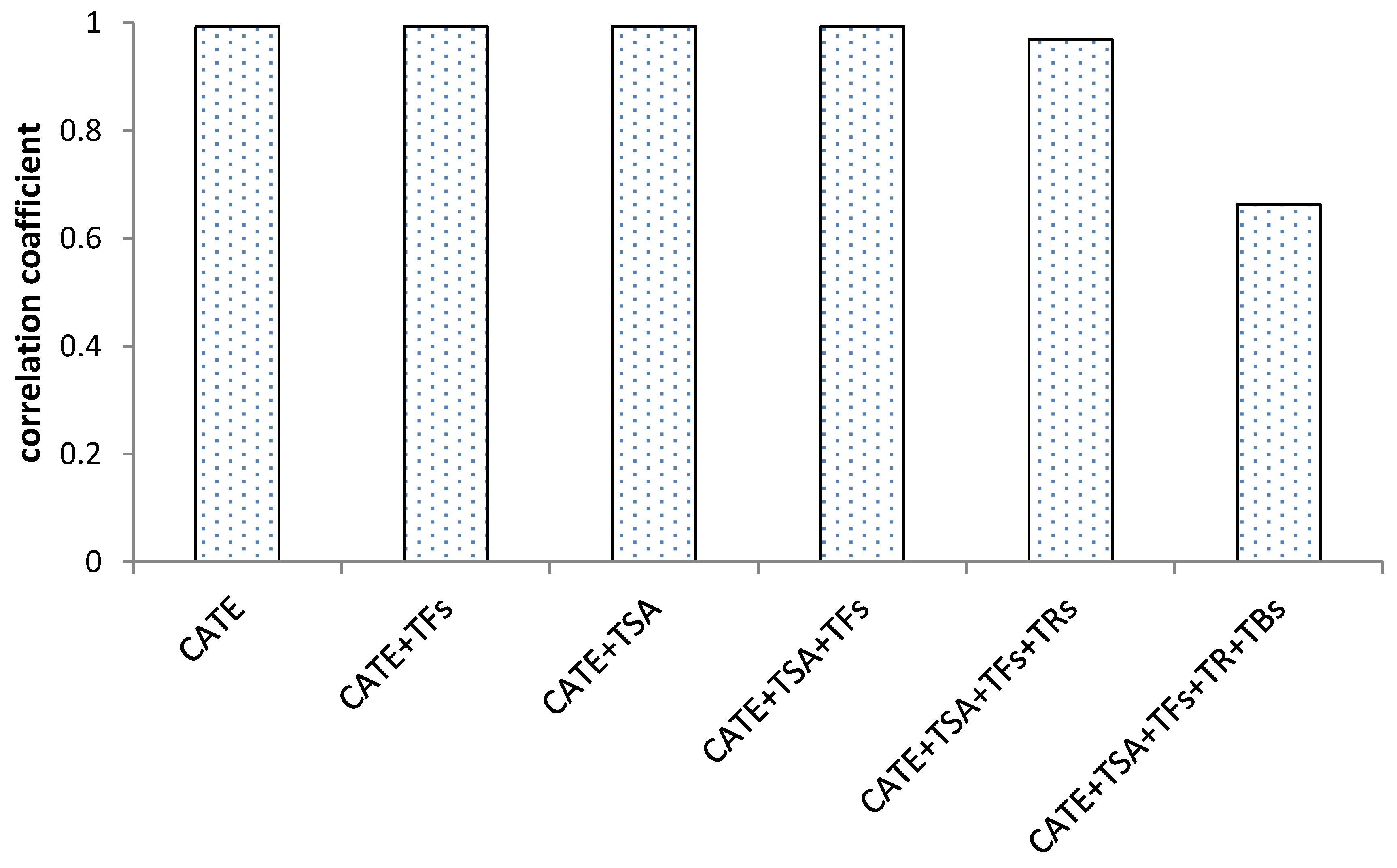
3.4. Correlation Analysis of Antioxidant Activity and Chemical Compounds during Black Tea Fermentation
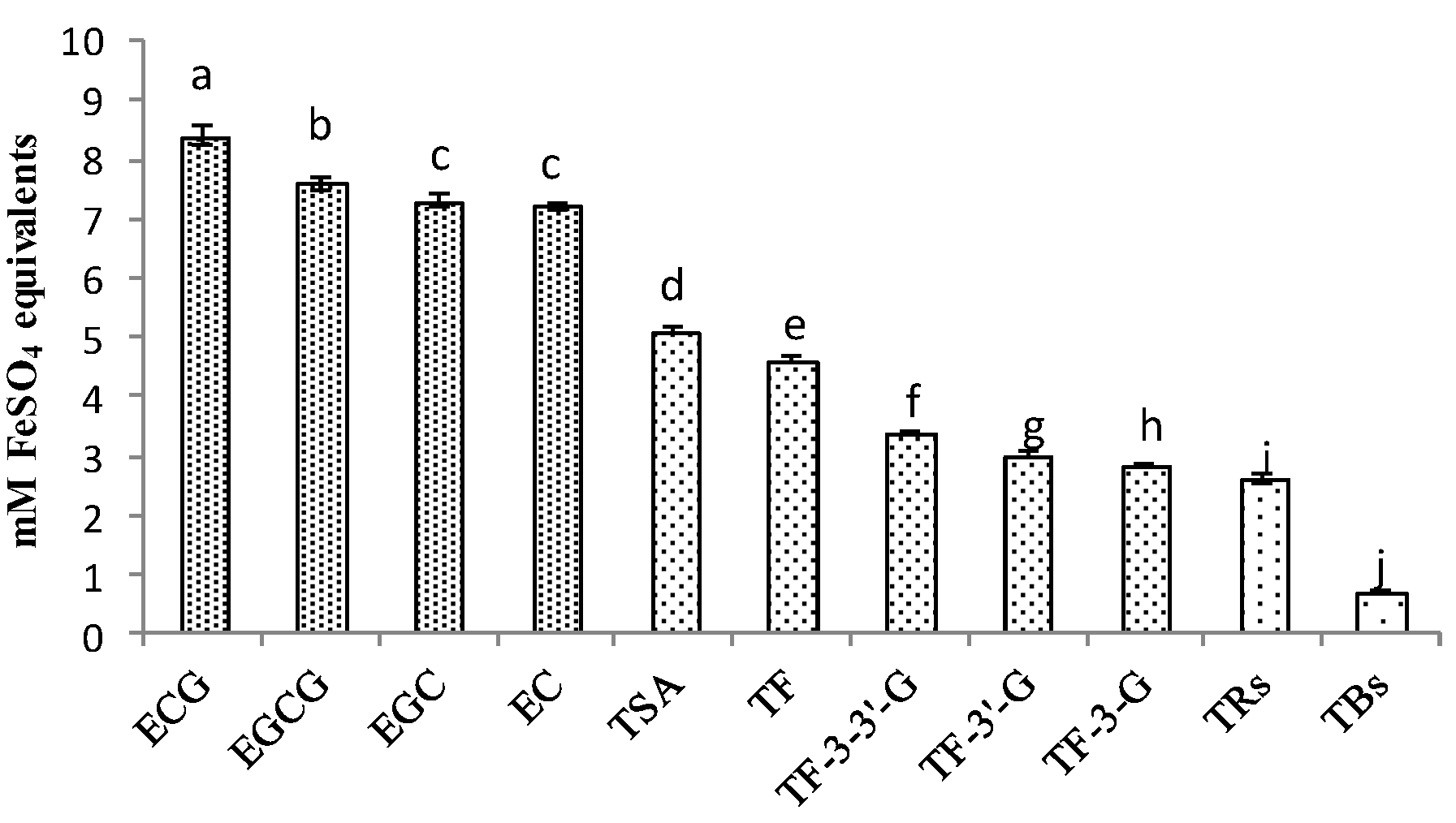
3.5. Comparison of Antioxidant Activities of Catechins and Their Oxidation Products
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ray, D.; Ferreira, M.; Braunger, M.; Riul, A., Jr.; Thomas, J.; Barbin, D. Exploration of an impedimetric electronic tongue and chemometrics for characterization of black tea from different origins. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2023, 123, 105535. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.-J.; Shen, S.; Wang, J.-J.; Jiang, Y.-W.; Li, J.; Yang, Y.-Q.; Hua, J.-J.; Yuan, H.-B. Novel insight into the effect of fermentation time on quality of Yunnan Congou black tea. LWT 2022, 155, 112939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaufmann, J.-A.; Bickford, P.-C.; Taglialatela, G. Free radical-dependent changes in constitutive nuclear factor kappa B in the aged hippocampus. Neuroreport 2002, 13, 1917–1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Qi, R.-L.; Mine, Y. The impact of oolong and black tea polyphenols on human health. Food Biosci. 2019, 29, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Suen, C.; Yang, C.; Quek, S. Antioxidant capacity and major polyphenol composition of teas as affected by geographical location, plantation elevation and leaf grade. Food Chem. 2018, 244, 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, P.; Changarath, J.; Damodaran, A.; Joshi, M. Compositional variation among black tea across geographies and their potential influence on endothelial nitric oxide and antioxidant activity. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 6655–6668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Santos, J.-S.; Cruz, T.-M.; Marques, M.-B.; Carmo, M.; Azevedo, L.; Wang, Y.-J.; Granato, D. Multivariate effects of Chinese keemun black tea grades (Camellia sinensis var. sinensis) on the phenolic composition, antioxidant, antihemolytic and cytotoxic/cytoprotection activities. Food Res. Int. 2019, 125, 108516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.-N.; Tang, G.-Y.; Cao, S.-Y.; Xu, X.-Y.; Gan, R.-Y.; Liu, Q.; Mao, Q.-Q.; Shang, A.; Li, H.-B. Phenolic profiles and antioxidant activities of 30 tea infusions from green, black, oolong, white, yellow and dark teas. Antioxidants 2019, 8, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.-Q.; Gao, Y.; Granato, D. Effects of epigallocatechin gallate, epigallocatechin and epicatechin gallate on the chemical and cell-based antioxidant activity, sensory properties, and cytotoxicity of a catechin-free model beverage. Food Chem. 2021, 339, 128060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grzesik, M.; Naparlo, K.; Bartosz, G.; Sadowska-Bartosz, I. Antioxidant properties of catechins: Comparison with other antioxidants. Food Chem. 2018, 241, 480–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, N.; Phan, H.; Chikae, M.; Takamura, Y.; Vestergaard, M. Black tea polyphenol theaflavin as promising antioxidant and potential copper chelator. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2020, 100, 3126–3135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yen, G.; Duh, P.; Tsai, H. Antioxidant and pro-oxidant properties of ascorbic acid and gallic acid. Food Chem. 2002, 79, 307–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, K.; Ouyang, J.; Huang, J.-N.; Liu, Z.-H. Research progress of black tea thearubigins: A review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. 2020, 1080, 1762161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Wang, H.-J.; Ye, Y.; Wang, Y.-F.; Xu, P. Structural insight into polyphenol oxidation during black tea fermentation. Food Chem. 2023, 17, 100615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozdemir, F.-Z.; Nadeem, H.-A.; Akdogan, A.; Dincer, C.; Topuz, A. Effect of altitude, shooting period, and tea grade on the catechins, caffeine, theaflavin, and thearubigin of Turkish black tea. Turk. J. Agric. For. 2018, 42, 334–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karori, S.-M.; Wachira, F.-N.; Wanyoko, J.-K.; Ngure, R.-M. Antioxidant capacity of different types of tea products. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2007, 6, 2287–2296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.-L.; Lai, W.-Y.; Xu, A.; Jin, J.; Wang, Y.-F.; Xu, P. Characterizing relationships among chemicals, sensory attributes and in vitro bioactivities of black tea made from an anthocyanins-enriched tea cultivar. LWT 2020, 132, 109814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, J.-J.; Xu, Q.; Yuan, H.-B.; Wang, J.-J.; Wu, Z.-Q.; Li, X.-T.; Jiang, Y.-W. Effects of novel fermentation method on the biochemical components change and quality formation of congou black tea. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2021, 96, 103751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.-R.; Lu, J.-L.; Zhang, L.Y.; Wu, S.; Wu, Y. Stimation of black tea quality by analysis of chemical composition and colour difference of tea infusions. Food Chem. 2003, 80, 283–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, G.-Y.; Zhao, C.-N.; Xu, X.-Y.; Gan, R.-Y.; Cao, S.-Y.; Liu, Q.; Shang, A.; Mao, Q.-Q.; Li, H.-B. Phytochemical Composition and Antioxidant Capacity of 30 Chinese Teas. Antioxidants 2019, 8, 180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatima, M.; Kesharwani, R.; Misra, K.; Rizvi, S. Protective effect of theaflavin on erythrocytes subjected to in vitro oxidative stress. Biochem. Res. Int. 2013, 2013, 649759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.-D.; Liu, E.-H.; Mau, J.-L. Effect of different brewing methods on antioxidant properties of steaming green tea. LWT 2008, 41, 1616–1623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fei, T.-Y.; Fei, J.; Huang, F.; Xie, T.-P.; Xu, J.-F.; Zhou, Y.; Yang, P. The anti-aging and anti-oxidation effects of tea water extract in Caenorhabditis elegans. Exp. Gerontol. 2017, 97, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, Z.-M.; Zhong, Y.-Z.; Duan, Y.-H.; Chen, Q.-H.; Li, F.-N. Antioxidant mechanism of tea polyphenols and its impact on health benefits. Anim. Nutr. 2020, 6, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camargo, L.; Pedroso, L.; Vendrame, S.; Mainardes, R.; Khalil, N. Antioxidant and antifungal activities of Camellia sinensis (L.) Kuntze leaves obtained by different forms of production. Braz. J. Biol. 2016, 76, 428–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jhoo, J.; Lo, C.; Li, S.; Sang, C.; Ang, C.; Heinze, T.; Ho, C. Stability of Black Tea Polyphenol, Theaflavin, and Identification of Theanaphthoquinone as Its Major Radical Reaction Product. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 6146–6150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.-S.; Lin, Y.; Li, Q.-S.; Gu, Y.-X. The contribution ratio of various characteristic tea compounds in antioxidant capacity by dpph assay. J. Food Biochem. 2020, 3, 13270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shabani, S.; Rabiei, Z.; Amini-khoie, H. Exploring the multifaceted neuroprotective actions of gallic acid: A review. Int. J. Food Prop. 2020, 1, 736–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, N.; Han, B.-S.; Fan, X.-W.; Cai, F.; Ren, F.-D.; Xu, M.-L.; Zhong, J.-Y.; Zhang, Y.; Ren, D.-B.; Yi, L.-Z. Uncovering the antioxidant characteristics of black tea by coupling in vitro free radical scavenging assay with uhplc–hrms analysis. J. Chromatogr. B 2020, 1145, 122092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; Zhao, B.-L.; Shen, S.-R.; Hou, J.-W.; Hu, J.-G.; Xin, W.-J. ESR study on the structure-antioxidant activity relationship of tea catechins and their epimers. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1999, 1427, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anitha, S.; Krishnan, S.; Senthilkumar, K.; Sasirekha, V. A comparative investigation on the scavenging of 2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl radical by the natural antioxidants (+) catechin and (−) epicatechin. J. Mol. Struct. 2021, 1242, 130805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aalman, S.; Oz, G.; Felek, R.; Haznedar, A.; Turna, T. Effects of fermentation time on phenolic composition, antioxidant and antimicrobial activities of green, oolong, and black teas. Food Biochem. 2022, 49, 101884. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y.-Y.; Li, W.; Yi, X.; Jin, E.; Tu, Y.-Y. Evaluation of the antioxidant effects of four main theaflavin derivatives through chemiluminescence and DNA damage analyses. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B 2011, 9, 744–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, Y.-L.; Leung, L.-K.; Huang, Y.; Chen, Z.-Y. Stability of tea theaflavins and catechins. Food Chem. 2003, 83, 189–195. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, J.-F.; Dai, W.-D.; Lu, M.-L.; Lv, H.-P.; Guo, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Peng, Q.-H.; Lin, Z. Study of dynamic changes in the non-volatile chemical constituents of black tea during fermentation processing by a non-targeted metabolomics approach. Food Res. Int. 2016, 79, 106–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, L.; Su, Y.; Chen, L.; Zhang, Z.; Huang, Y.; Chen, Z.-Y. Theaflavins in black tea and catechins in green tea are equally effective antioxidants. J. Nutr. 2001, 131, 2248–2251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Di, T.-M.; Wang, W.-W.; Jiang, H.Y. EGCG, GCG, TFDG, or TSA inhibiting melanin synthesis by downregulating MC1Rexpression. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 11017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Compounds | Minimum Content | Maximum Content | Average Content | Variable Coefficient |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EC | 0.07 | 5.19 | 1.22 ± 1.17 | 0.96 |
| EGC | 0.21 | 5.85 | 1.43 ± 1.17 | 0.82 |
| ECG | 0.16 | 25.66 | 6.47 ± 5.90 | 0.80 |
| EGCG | 1.40 | 15.89 | 7.35 ± 3.82 | 0.59 |
| TF | 0.21 | 2.65 | 0.74 ± 0.49 | 0.66 |
| TF-3-G | 0.62 | 2.72 | 1.51 ± 0.53 | 0.35 |
| TF-3′-G | 0.40 | 2.57 | 1.03 ± 0.38 | 0.37 |
| TF-3,3′-G | 0.98 | 5.27 | 3.08 ± 0.96 | 0.31 |
| TSA | 0.27 | 4.70 | 2.27 ± 1.02 | 0.45 |
| TP | 52.70 | 162.31 | 109.23 ± 21.39 | 0.20 |
| AA | 24.23 | 46.52 | 36.63 ± 5.66 | 0.15 |
| CAF | 14.81 | 36.22 | 28.89 ± 4.30 | 0.15 |
| GA | 0.54 | 3.44 | 2.06 ± 0.64 | 0.31 |
| Flavonoids | 2.73 | 20.09 | 13.03 ± 3.20 | 0.25 |
| Total sugars | 124.17 | 347.73 | 179.63 ± 45.80 | 0.26 |
| TRs | 25.92 | 92.29 | 46.08 ± 14.67 | 0.32 |
| TBs | 43.23 | 122.14 | 68.65 ± 19.17 | 0.28 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, W.; Le, T.; Wang, W.; Yu, L.; Yang, L.; Jiang, H. Effects of Key Components on the Antioxidant Activity of Black Tea. Foods 2023, 12, 3134. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12163134
Wang W, Le T, Wang W, Yu L, Yang L, Jiang H. Effects of Key Components on the Antioxidant Activity of Black Tea. Foods. 2023; 12(16):3134. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12163134
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Weiwei, Ting Le, Wei Wang, Luting Yu, Lijuan Yang, and Heyuan Jiang. 2023. "Effects of Key Components on the Antioxidant Activity of Black Tea" Foods 12, no. 16: 3134. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12163134
APA StyleWang, W., Le, T., Wang, W., Yu, L., Yang, L., & Jiang, H. (2023). Effects of Key Components on the Antioxidant Activity of Black Tea. Foods, 12(16), 3134. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12163134






