Determination of Oxygen Heterocyclic Compounds in Foods Using Supercritical Fluid Chromatography–Tandem Mass Spectrometry
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Samples and Sample Preparation
2.3. Instrumental and Analytical Conditions
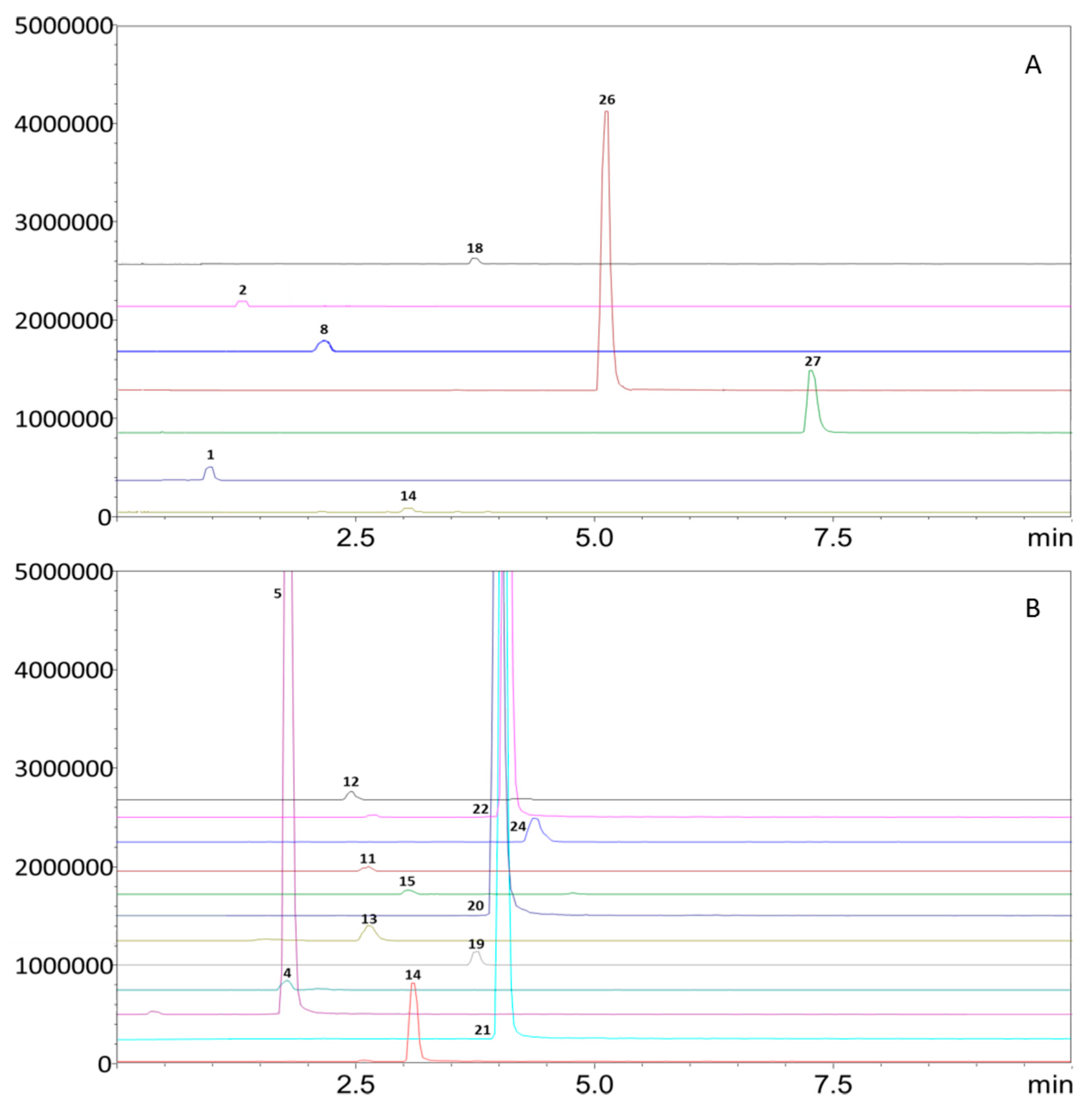
3. Results
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ganzera, M.; Zwerger, M. Analysis of natural products by SFC—Applications from 2015 to 2021. Trends Anal. Chem. 2021, 145, 116463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, M.; Rigano, F.; Arigò, A.; Dugo, P.; Mondello, L. Coumarins, psoralens and polymethoxyfavones in cold-pressed Citrus essential oils: A review. J. Essent. Oil Res. 2021, 33, 221–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, D.-W.; Zhang, Y.; Duan, X.-Y.; Zhou, Y.; Li, G.-H.; Feng, X.-S. Progress in pretreatment and analytical methods of coumarins: An update since 2012—A review. Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2021, 51, 503–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melough, M.M.; Lee, S.G.; Cho, E.; Kim, K.; Provatas, A.A.; Perkins, C.; Park, M.K.; Qureshi, A.; Chun, O.K. Identification and quantitation of furocoumarins in popularly consumed foods in the U.S. using QuEChERS extraction coupled with UPLC-MS/MS analysis. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 5049–5055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lončar, M.; Jakovljević, M.; Šubarić, D.; Pavlić, M.; Buzjak Služek, V.; Cindrić, I.; Molnar, M. Coumarins in foods and methods for their determination. Foods 2020, 9, 645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, C.T.; Pan, M.H.; Lai, C.S.; Li, S. Polymethoxyflavones as Food Factors for the Management of Inflammatory Diseases. J. Food Drug Anal. 2012, 20, 337–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, T.; Yang, S.; Cao, J.; Li, X.; Wang, L.S.; Sun, C. Beneficial Regulatory Effects of Polymethoxyflavone—Rich Fraction from Ougan (Citrus reticulata cv. Suavissima) Fruit on Gut Microbiota and Identification of Its Intestinal Metabolites in Mice. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lake, B.G. Coumarin metabolism, toxicity and carcinogenicity: Relevance for human risk assessment. Food Chem. Toxicol. 1999, 37, 423–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fotland, T.; Paulsen, J.E.; Sanner, T.; Alexander, J.; Husøy, T. Risk assessment of coumarin using the bench mark dose (BMD) approach: Children in Norway which regularly eat oatmeal porridge with cinnamon may exceed the TDI for coumarin with several folds. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2012, 50, 903–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Food Safety Authority (EFSA). Coumarin in flavourings and other food ingredients with flavouring properties—Scientific opinion of the panel on food additives, flavourings, processing aids and materials in contact with food (AFC). EFSA J. 2004, 6. Available online: https://www.efsa.europa.eu/en/efsajournal/pub/793 (accessed on 14 June 2023).
- European Commission. Regulation (EC) No 1334/2008 on flavourings and certain food ingredients. Off. J. Eur. Union 2008. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/LexUriServ/LexUriServ.do?uri=OJ:L:2008:354:0034:0050:en:PDF (accessed on 14 June 2023).
- Macmaster, A.P.; Owen, N.; Brussaux, S.; Brevardc, H.; Hiserodt, R.; Leijs, H.; Bast, N.; Weber, B.; Loesinge, G.; Sherlockf, A.; et al. Quantification of selected furocoumarins by high-performance liquid chromatography and UV-detection Capabilities and limits. J. Chromatogr. A 2012, 1257, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raters, M.; Matissek, R. Analysis of coumarin in various foods using liquid chromatography with tandem mass spectrometric detection. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2008, 227, 637–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jungen, M.; Lotz, P.; Patz, C.-D.; Steingass, C.B.; Schweiggert, R. Coumarins, psoralens, and quantitative 1H-NMR spectroscopy for authentication of lemon (Citrus limon [L.] Burm.f.) and Persian lime (Citrus × latifolia [Yu.Tanaka] Tanaka) juices. Food Chem. 2021, 359, 129804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jungen, M.; Dragicevic, N.; Rodriguez-Werner, M.; Schmidt, S.; Dinis, K.; Tsamba, L.; Jamin, E.; Fiedler, T.; Fischbach, N.; Steingass, C.B.; et al. A pragmatic authenticity assessment of lemon (Citrus limon [L.] Burm.f.) juices by its profile of coumarins, psoralens, and polymethoxyflavones. Food Control 2023, 146, 109529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sproll, C.; Ruge, W.; Andlauer, C.; Godelmann, R.; Lachenmeier, D.W. HPLC analysis and safety assessment of coumarin in foods. Food Chem. 2008, 109, 462–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Rouseff, R.; Cheng, Y.; Zhou, Q.; Wu, H. Comprehensive identification and distribution pattern of 37 oxygenated heterocyclic compounds in commercially important citrus juices. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 152, 112351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dugo, P.; Piperno, A.; Romeo, R.; Cambria, M.; Russo, M.; Carnovale, C.; Mondello, L. Determination of Oxygen Heterocyclic Components in Citrus Products by HPLC with UV Detection. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 6543–6551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arigò, A.; Rigano, F.; Russo, M.; Trovato, E.; Dugo, P.; Mondello, L. Dietary Intake of Coumarins and Furocoumarins through Citrus Beverages: A detailed estimation by a HPLC-MS/MS method combined with the Linear Retention Index system. Foods 2021, 10, 1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trovato, E.; Arigò, A.; Vento, F.; Micalizzi, G.; Dugo, P.; Mondello, L. Influence of Citrus Flavor Addition in Brewing Process: Characterization of the Volatile and Non-Volatile Profile to Prevent Frauds and Adulterations. Separations 2021, 8, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trovato, E.; Russo, M.; Cucinotta, L.; El Majdoub, Y.O.; Testa Camillo, M.R.; De Grazia, G.; Arigò, A.; Sciarrone, D.; Mondello, L.; Dugo, P. Quality evaluation of flavoured extra-virgin olive oils according to their chemical composition. Food Anal. Methods 2023, 16, 1313–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salerno, T.M.G.; Trovato, E.; Cafeo, G.; Vento, F.; Zoccali, M.; Donato, P.; Dugo, P.; Mondello, L. Hidden threat lurking in extensive hand hygiene during the Covid-19 pandemic: Investigation of sensitizing molecules in gel products by hyphenated chromatography techniques. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2023, 415, 3327–3340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zoccali, M.; Donato, P.; Mondello, L. Recent advances in the coupling of carbon dioxide-based extraction and separation techniques. Trends Anal. Chem. 2019, 16, 158–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arigò, A.; Russo, M.; Testa Camillo, M.R.; Dugo, P.; Mondello, L.; Zoccali, M. Supercritical fluid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry of oxygen heterocyclic compounds in Citrus essential oils. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2022, 414, 4821–4836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Testa Camillo, M.R.; Russo, M.; Trozzi, A.; Mondello, L.; Dugo, P. Quantification of coumarins, furocoumarins and polymethoxyflavones in hydroalcoholic fragrances by supercritical fluid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J. Essent. Oil Res. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desmortreux, C.; Rothaupt, M.; West, C.; Lesellie, E. Improved separation of furocoumarins of essential oils by supercritical fluid chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2009, 1216, 7088–7095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morin, P.; Gallois, A.; Richard, H.; Gaydou, E. Fast separation of polymethoxylated flavones by carbon dioxide supercritical fluid chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 1991, 586, 171–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winderl, B.; Schwaiger, S.; Ganzera, A. Fast and improved separation of major coumarins in Ammi visnaga (L.) Lam. by supercritical fluid chromatography. J. Sep. Sci. 2016, 39, 4042–4048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfeifer, I.; Murauer, A.; Ganzera, A. Determination of coumarins in the roots of Angelica dahurica by supercritical fluid chromatography. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2016, 129, 246–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.Y.; Li, X.K.; Yang, Z.L.; Qiu, D.; Feng, N.; Zhang, X.Z.; Li, B.Q. An accurate and reliable analytical strategy for simultaneous determination of target furanocoumarins and flavonoids in cosmetic and pharmaceutical samples by ultra-high performance supercritical fluid chromatography. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2023, 225, 115221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EURACHEM Guide. The Fitness for Purpose of Analytical Methods: A Laboratory Guide to Method Validation and Related Topics; EURACHEM Working Group LGC: Teddington, UK, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- EFSA Panel on Dietetic Products, Nutrition and Allergies (NDA). Scientific Opinion on the substantiation of health claims related to polyphenols in olive and protection of LDL particles from oxidative damage (ID 1333, 1638, 1639, 1696, 2865), maintenance of normal blood HDL-cholesterol concentrations (ID 1639), maintenance of normal blood pressure (ID 3781), “anti-inflammatory properties” (ID 1882), “contributes to the upper respiratory tract health” (ID 3468), “can help to maintain a normal function of gastrointestinal tract” (3779), and “contributes to body defences against external agents” (ID 3467) pursuant to Article 13(1) of Regulation (EC) No 1924/2006. EFSA J. 2011, 9, 2033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Samples | Description (Label) |
|---|---|
| Juices | |
| Lemon (Citrus limon [L.] Burm.) | Lab-made Citrus juice |
| Lime (Citrus aurantifolia [Christm.] Swing.) | Lab-made Citrus juice |
| Bergamot (Citrus bergamia, Risso) | Lab-made Citrus juice |
| Citron (Citrus medica, L.) | Lab-made Citrus juice |
| Sweet orange (Citrus sinensis [L.] Osb.) | Lab-made Citrus juice |
| Bitter orange (Citrus aurantium L.) | Lab-made Citrus juice |
| Mandarin (Citrus deliciosa Ten.) | Lab-made Citrus juice |
| Pink grapefruit (Citrus paradise McF.) | Lab-made Citrus juice |
| Commercial beverages | |
| Limoncello | Lemon peels 7% |
| Bergamino | Bergamot peels 8% |
| Cinnamon liquor | Cinnamon infusion 20% |
| Cocoa, sweet orange and cinnamon infusion | Sweet orange peel, bark Cinnamomum zeylanicum blume |
| Citrus-flavoured nonalcoholic beverage | Bergamot essential oil 0.2%, lemon infusion 0.2% |
| Bergamot-flavoured nonalcoholic beverage | Bergamot juice 13% |
| Green-mandarin-flavoured nonalcoholic beverage | Mandarin essential oil 1%, mandarin infusion 4% |
| Jams | |
| Lemon | Calabrian Lemon fruits |
| Bergamot | Bergamot pulp and peel |
| Orange | Orange pulp and peel |
| Orange and cinnamon | Organic orange 40%, powder cinnamon 0.1% |
| Citrus fruits and ginger | Organic Citrus fruits 40% (orange 48%, lemon 47%, mandarin 5%), organic ginger 0.9% |
| Bakery products | |
| Lemon-flavoured snack | Lemon flavour 1% |
| Lemon-flavoured biscuits | Lemon flavour 2.5% |
| Lemon- and almond-flavoured biscuits | Candied peel lemon 6.5%, lemon juice 0.4% |
| Mandarin- and almond-flavoured biscuits | Candied peel mandarin lemon 6.5%, mandarin juice 2% |
| Bergamot-flavoured biscuits | Bergamot 5% |
| Bergamot-flavoured dessert biscuits | Bergamot 5% |
| Compound | Lemon | Lime | Bergamot | Citron | Sweet Orange | Bitter Orange | Mandarin | Pink Grapefruit |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Isomeranzin (2) § | <LoD | <LoD | <LoD | <LoD | <LoD | 0.40 ± 0.012 | <LoD | 1.80 ± 0.062 |
| Herniarin (3) § | <LoD | 3.24 ± 0.001 | <LoD | <LoD | <LoD | <LoD | <LoD | <LoD |
| Oxypeucedanin (4) * | 0.01 ± 0.000 | 0.58 ± 0.014 | <LoD | 0.06 ± 0.003 | <LoD | <LoD | <LoD | <LoD |
| 8-geranyloxypsoralen (5) * | 0.38 ± 0.023 | <LoQ | <LoD | <LoQ | <LoQ | <LoQ | <LoQ | <LoQ |
| Aurapten (7) § | <LoD | <LoD | <LoD | <LoD | <LoD | <LoD | <LoD | 0.26 ± 0.013 |
| Meranzin (8) § | <LoD | <LoD | <LoD | <LoD | <LoD | 0.95 ± 0.008 | <LoD | 1.27 ± 0.009 |
| Epoxyaurapten (10) § | <LoD | <LoD | <LoD | <LoD | <LoD | <LoD | <LoD | 0.25 ± 0.002 |
| Phellopterin (12) * | <LoD | 0.05 ± 0.002 | <LoD | <LoD | <LoD | <LoD | <LoD | <LoD |
| Byakangelicol (13) * | 0.02 ± 0.005 | 0.16 ± 0.005 | <LoD | 0.09 ± 0.005 | <LoD | <LoD | <LoD | <LoD |
| Citropten (14) § | 0.07 ± 0.015 | 1.03 ± 0.020 | <LoQ | 0.02 ± 0.000 | <LoQ | <LoQ | <LoQ | <LoQ |
| Cnidilin (15) * | <LoD | 0.01 ± 0.000 | <LoD | <LoD | <LoD | <LoD | <LoD | <LoD |
| Isopimpinellin (16) * | <LoD | 1.65 ± 0.086 | <LoD | <LoD | <LoD | <LoD | <LoD | <LoD |
| Bergapten (18) * | <LoD | 0.50 ± 0.006 | 7.02 ± 0.062 | <LoD | <LoD | 0.37 ± 0.007 | <LoD | 0.01 ± 0.001 |
| Isoimperatorin (19) * | <LoD | 0.01 ± 0.000 | <LoD | <LoD | <LoD | <LoD | <LoD | <LoD |
| Oxypeucedanin hydrate (20) * | 0.09 ± 0.006 | 4.40 ± 0.121 | <LoD | 0.15 ± 0.007 | <LoD | <LoD | <LoD | <LoD |
| 5-geranyloxy-7-methoxycoumarin (21) § | <LoQ | 5.16 ± 0.018 | 0.05 ± 0.001 | <LoQ | <LoQ | <LoQ | <LoD | <LoQ |
| Bergamottin (22) * | <LoQ | 5.96 ± 0.338 | 15.81 ± 0.056 | <LoQ | <LoQ | <LoQ | <LoQ | 0.59 ± 0.036 |
| Epoxybergamottin (23) * | <LoD | <LoD | <LoD | <LoD | <LoD | <LoD | <LoQ | 0.84 ± 0.036 |
| Byakangelicin (24) * | 0.04 ± 0.001 | 5.37± 0.020 | <LoD | 0.20 ± 0.015 | <LoD | <LoD | <LoQ | <LoD |
| Tangeretin (25) + | <LoD | <LoD | <LoD | <LoD | 0.05 ± 0.002 | 0.15 ± 0.002 | 7.31 ± 0.069 | 0.07 ± 0.005 |
| Nobiletin (26) + | <LoD | <LoD | 0.01 ± 0.001 | <LoD | 0.78 ± 0.016 | 0.46 ± 0.019 | 18.79 ± 0.469 | 0.64 ± 0.028 |
| Tetra-O-methylscutellarein (27) + | <LoD | <LoD | 0.01 ± 0.000 | <LoD | <LoD | <LoD | 0.40 ± 0.018 | <LoD |
| Sinensetin (28) + | <LoD | <LoD | <LoD | <LoD | <LoD | <LoD | 84.10 ± 1.844 | <LoD |
| TOT | 1.26 ± 0.050 | 27.92 ± 0.631 | 22.90 ± 0.120 | 0.47 ± 0.030 | 0.83 ± 0.018 | 2.36 ± 0.48 | 110.54 ± 2.40 | 5.69 ± 0.192 |
| Compound | Alcoholic Beverages | Nonalcoholic Beverages | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Limoncello | Bergamino | Cinnamon Liquor | Bergamot | Green Mandarin | Citrus | Infusion | |
| Coumarin (1) § | <LoD | <LoD | 3.55 ± 0.075 | <LoD | <LoD | <LoD | 0.22 ± 0.006 |
| Herniarin (3) § | <LoD | 0.10 ± 0.002 | <LoD | 0.05 ± 0.001 | <LoD | <LoD | <LoD |
| Oxypeucedanin (4) * | 0.33 ± 0.002 | <LoD | <LoD | <LoD | <LoD | <LoD | <LoD |
| 8-geranyloxypsoralen (5) * | 7.39 ± 0.567 | <LoQ | <LoQ | <LoD | <LoQ | <LoQ | <LoQ |
| Cnidicin (11) * | 0.06 ± 0.003 | <LoD | <LoD | <LoD | <LoD | <LoD | <LoD |
| Phellopterin (12) * | 0.12 ± 0.004 | <LoD | <LoD | <LoD | <LoD | <LoD | <LoD |
| Byakangelicol (13) * | 0.80 ± 0.027 | <LoD | <LoD | <LoD | <LoD | <LoD | <LoD |
| Citropten (14) § | 1.92 ± 0.067 | 6.00 ± 0.094 | <LoQ | 0.65 ± 0.031 | <LoQ | 0.01 ± 0.001 | <LoQ |
| Cnidilin (15) * | 0.04 ± 0.003 | <LoD | <LoD | <LoD | <LoD | <LoD | <LoD |
| Isopimpinellin (16) * | <LoD | <LoD | <LoD | 0.01 ± 0.002 | <LoD | <LoD | <LoD |
| Bergapten (18) * | <LoD | 3.08 ± 0.007 | <LoD | 3.09 ± 0.011 | <LoD | <LoD | <LoD |
| Isoimperatorin (19) * | 0.10 ± 0.003 | <LoD | <LoD | <LoD | <LoD | <LoD | <LoD |
| Oxypeucedanin hydrate (20) * | 4.00 ± 0.005 | <LoD | <LoD | 0.06 0.001 | <LoD | 0.02 ± 0.001 | <LoD |
| 5-geranyloxy-7-methoxycoumarin (21) § | 2.40 ± 0.053 | 2.09 ± 0.115 | <LoQ | 0.06 ± 0.002 | <LoQ | <LoQ | <LoQ |
| Bergamottin (22) * | 3.22 ± 0.144 | 12.69 0.059 | <LoQ | 0.20 ± 0.008 | <LoQ | <LoQ | <LoQ |
| Byakangelicin (24) * | 1.68 ± 0.089 | <LoD | <LoD | <LoD | <LoD | <LoD | <LoQ |
| Tangeretin (25) + | <LoD | <LoD | <LoD | <LoD | 1.34 ± 0.054 | <LoD | <LoQ |
| Nobiletin (26) + | <LoD | 0.07 ± 0.009 | <LoD | 0.12 ± 0.002 | 4.36 ± 0.132 | <LoD | 0.11 ± 0.002 |
| Tetra-O-methylscutellarein (27) + | <LoD | <LoD | <LoD | <LoD | <LoD | <LoD | 0.04 ± 0.001 |
| Sinensetin (28) + | <LoD | <LoD | <LoD | <LoD | 10.86 0.599 | <LoD | <LoQ |
| TOT | 22.07 ± 0.967 | 24.03 ± 0.286 | 3.55 ± 0.075 | 4.72 ± 0.058 | 16.52 ± 0.785 | 0.03 ± 0.002 | 0.37 ± 0.009 |
| Compound | Jams | Bakery Products | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lemon | Bergamot | Orange | Orange Cinnamon | Citrus Ginger | Lemon Snack | Lemon Biscuits | Lemon Almond Biscuits | Mandarin Almond Biscuits | Bergamot Biscuits | Bergamot Dessert Biscuits | |
| 1 § | <LoD | <LoD | <LoD | 1.16 0.073 | <LoD | <LoD | <LoD | <LoD | <LoD | <LoD | <LoD |
| 2 § | <LoD | <LoD | <LoD | 0.05 0.002 | <LoD | 0.03 0.002 | <LoD | <LoD | <LoD | <LoD | <LoD |
| 3 § | <LoD | 0.01 0.001 | <LoD | <LoD | <LoD | <LoD | <LoD | <LoD | <LoD | <LoD | <LoD |
| 4 * | 0.07 0.003 | <LoD | <LoD | <LoD | 0.07 0.002 | <LoD | <LoD | <LoD | <LoD | <LoD | <LoD |
| 5 * | 6.78 0.128 | <LoQ | <LoQ | <LoQ | <LoQ | 0.47 0.021 | 0.45 0.067 | 0.34 0.038 | <LoD | <LoQ | <LoQ |
| 8 § | <LoD | <LoD | <LoD | 0.95 0.008 | <LoD | 0.04 0.001 | <LoD | <LoD | <LoD | <LoD | <LoD |
| 13 * | 0.14 0.012 | <LoD | <LoD | <LoD | 0.06 0.001 | <LoD | <LoD | <LoD | <LoD | <LoD | <LoD |
| 14 § | 5.40 2.814 | 3.92 0.045 | <LoQ | 0.02 0.000 | 0.22 0.002 | 0.01 0.000 | 0.04 0.002 | 0.09 0.002 | <LoD | 2.59 0.079 | 0.03 0.001 |
| 18 * | <LoD | <LoD | <LoD | 0.04 0.001 | <LoD | <LoD | <LoD | <LoD | <LoD | 2.29 0.091 | 0.03 0.000 |
| 19 * | <LoD | <LoD | <LoD | <LoD | <LoD | <LoD | <LoD | 0.01 0.000 | <LoD | <LoD | <LoD |
| 20 * | 3.61 0.004 | <LoD | <LoD | <LoD | 0.20 0.010 | 0.01 0.000 | 0.01 0.000 | 0.02 0.001 | <LoD | <LoD | <LoD |
| 21 § | 1.07 0.001 | 1.08 0.012 | <LoQ | <LoQ | 0.09 0.001 | 0.02 0.001 | 0.09 0.003 | 0.37 0.003 | <LoQ | 2.30 0.091 | 0.04 0.005 |
| 22 * | 1.03 0.000 | 10.96 0.100 | <LoQ | <LoQ | 0.08 0.000 | 0.04 0.000 | 0.07 0.006 | 0.34 0.001 | <LoD | 11.18 0.027 | 0.55 0.008 |
| 24 * | 2.31 0.001 | <LoD | <LoD | <LoD | 0.14 0.005 | <LoD | <LoD | <LoD | <LoD | <LoD | <LoD |
| 25 + | <LoD | <LoD | <LoD | <LoD | <LoD | <LoD | <LoD | <LoD | 1.00 0.009 | <LoD | <LoD |
| 26 + | <LoD | <LoD | 2.00 0.018 | 6.95 0.036 | 4.59 0.270 | <LoD | <LoD | <LoD | 1.26 0.028 | <LoD | <LoD |
| 27 + | <LoD | 0.07 0.006 | 0.76 0.019 | 2.62 0.032 | 1.63 0.040 | <LoD | <LoD | <LoD | 0.28 0.007 | 0.04 0.001 | <LoD |
| TOT | 20.41 ± 2.963 | 16.02 ± 0.164 | 2.76 ± 0.037 | 12.19 ± 0.152 | 7.38 ± 0.330 | 0.62 ± 0.025 | 0.66 ± 0.078 | 1.26 ± 0.045 | 4.50 ± 0.044 | 18.38 ± 0.198 | 0.63 ± 0.014 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cafeo, G.; Satira, A.; Russo, M.; Mondello, M.; Dugo, P. Determination of Oxygen Heterocyclic Compounds in Foods Using Supercritical Fluid Chromatography–Tandem Mass Spectrometry. Foods 2023, 12, 3408. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12183408
Cafeo G, Satira A, Russo M, Mondello M, Dugo P. Determination of Oxygen Heterocyclic Compounds in Foods Using Supercritical Fluid Chromatography–Tandem Mass Spectrometry. Foods. 2023; 12(18):3408. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12183408
Chicago/Turabian StyleCafeo, Giovanna, Antonella Satira, Marina Russo, Monica Mondello, and Paola Dugo. 2023. "Determination of Oxygen Heterocyclic Compounds in Foods Using Supercritical Fluid Chromatography–Tandem Mass Spectrometry" Foods 12, no. 18: 3408. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12183408
APA StyleCafeo, G., Satira, A., Russo, M., Mondello, M., & Dugo, P. (2023). Determination of Oxygen Heterocyclic Compounds in Foods Using Supercritical Fluid Chromatography–Tandem Mass Spectrometry. Foods, 12(18), 3408. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12183408






