Unravelling Metabolic Heterogeneity of Chinese Baijiu Fermentation in Age-Gradient Vessels
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
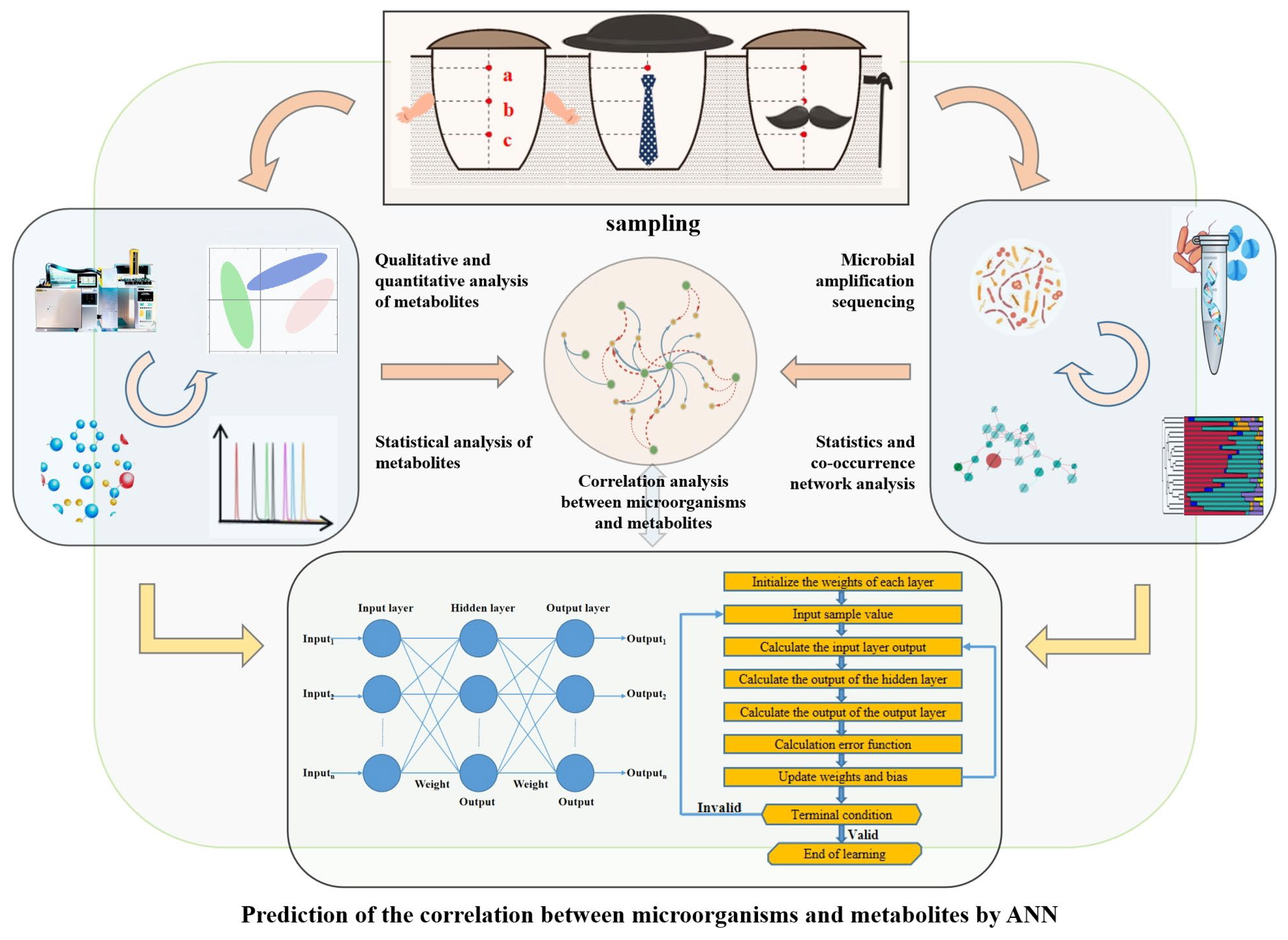
2.1. Sample Collection
2.2. DNA Extraction, Amplification, and Sequence Processing
2.3. Metabolites Analysis
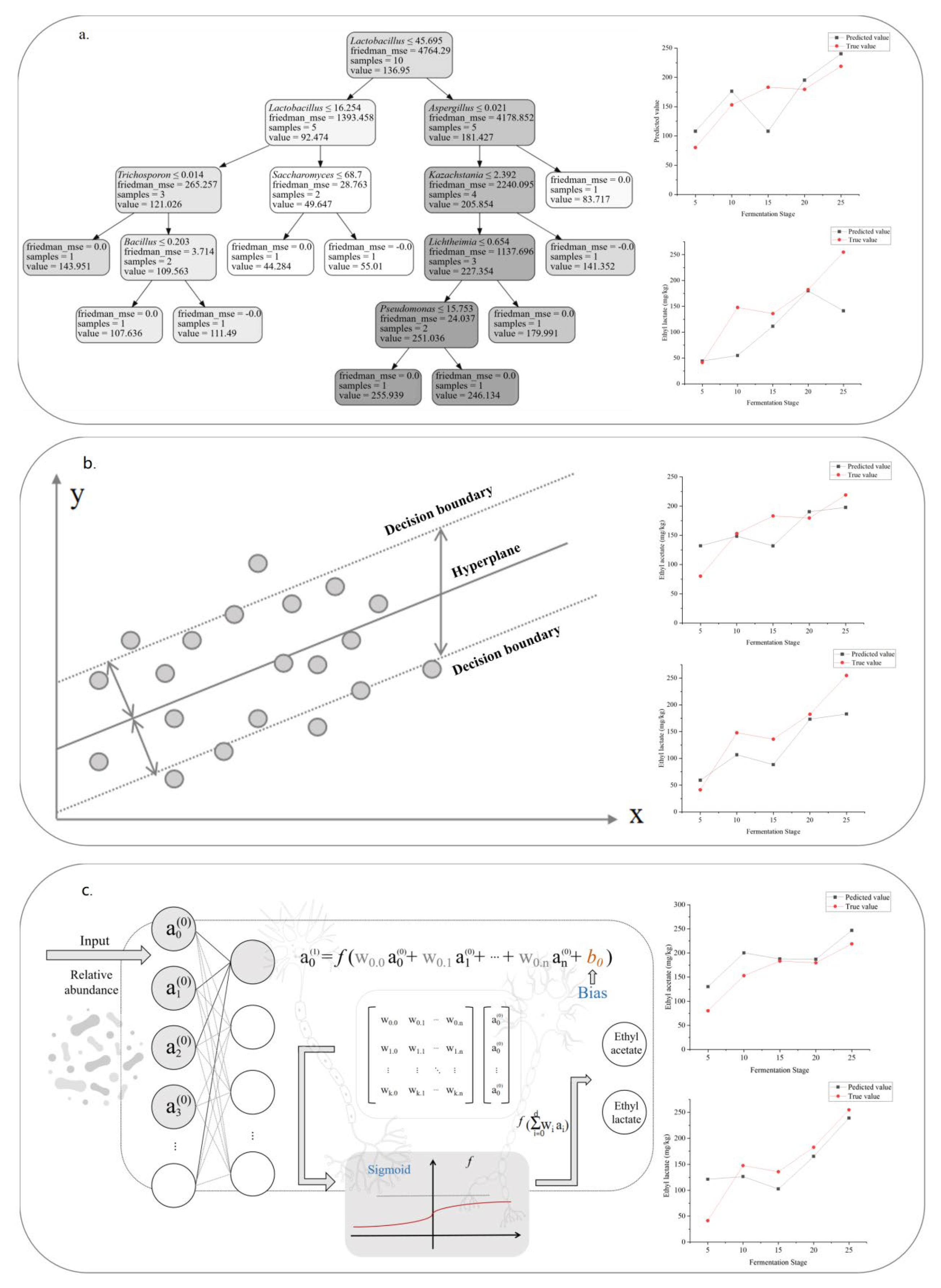
2.4. Establishment of Predictive Models
2.5. Olfactory Sensory Analysis
2.6. Data Analysis and Availability
3. Results
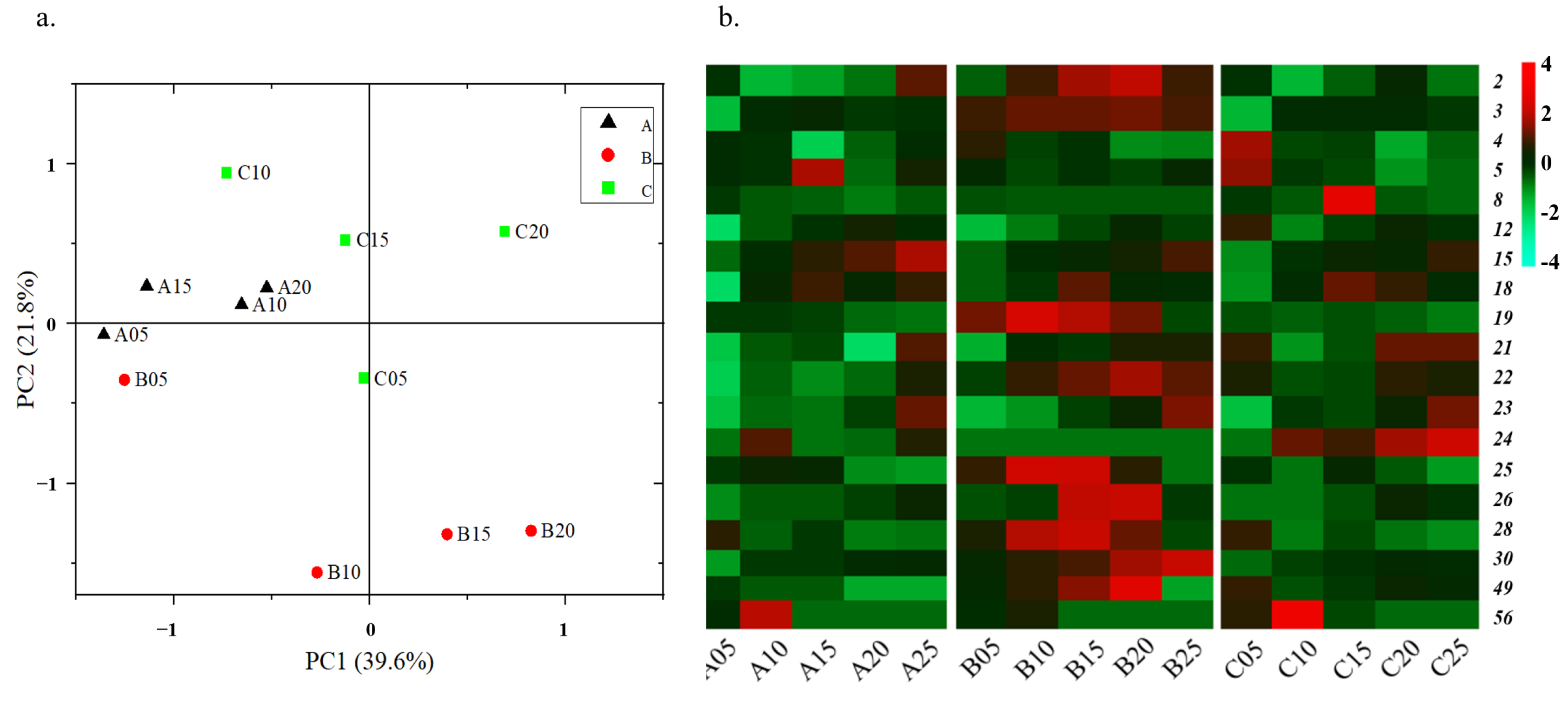
3.1. Dynamic of Metabolites among Age-Gradient Vessels for Baijiu Fermentation
3.1.1. Dynamic of Esters
3.1.2. Dynamic of Volatile Organic Acids
3.1.3. Dynamic of Alcohols
3.1.4. Dynamic of Phenols
3.2. Aroma Profile Analysis of Metabolites in Three Digangs
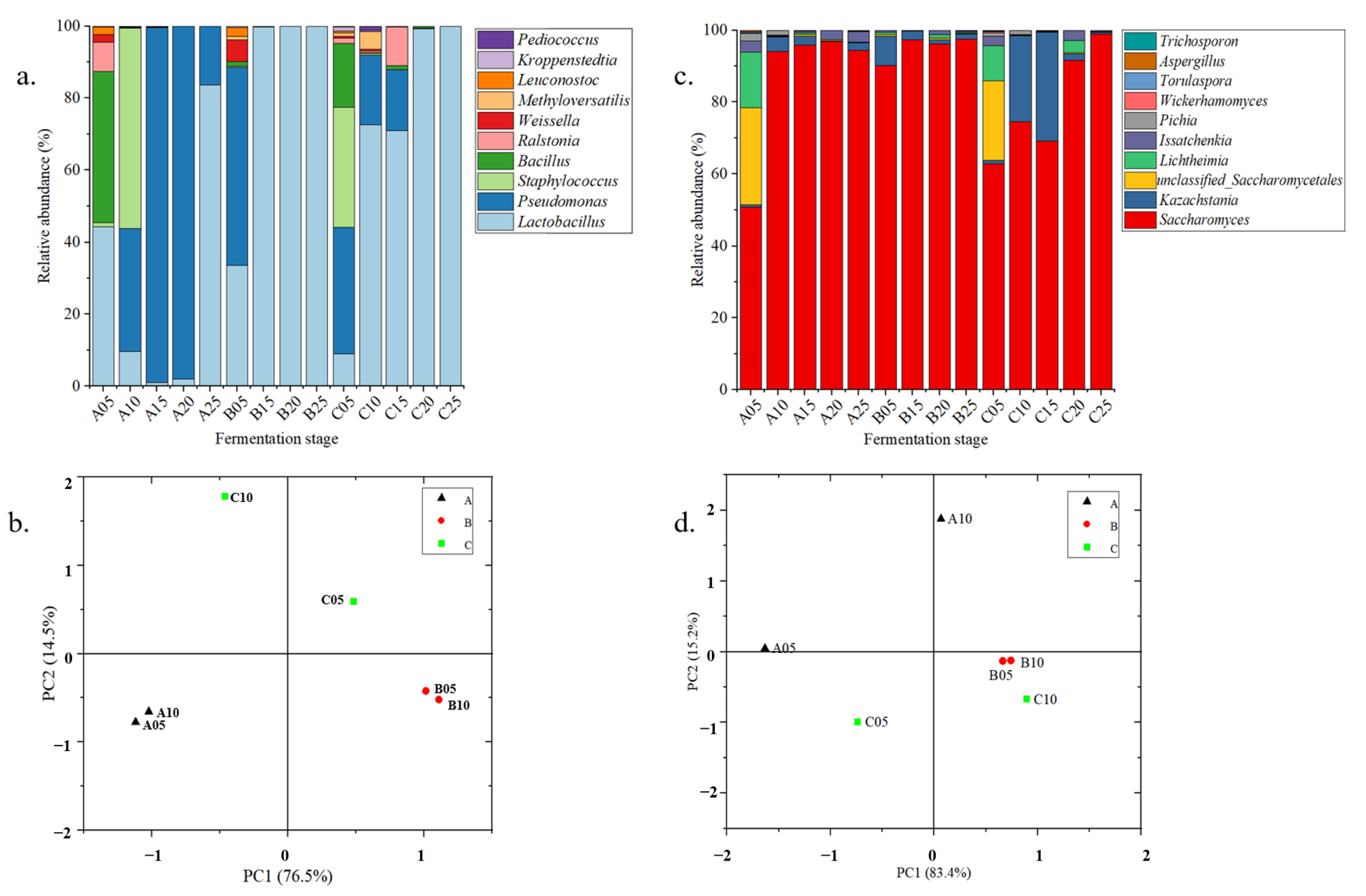
3.3. Microbial Successions in the Fermentation of Three Digangs
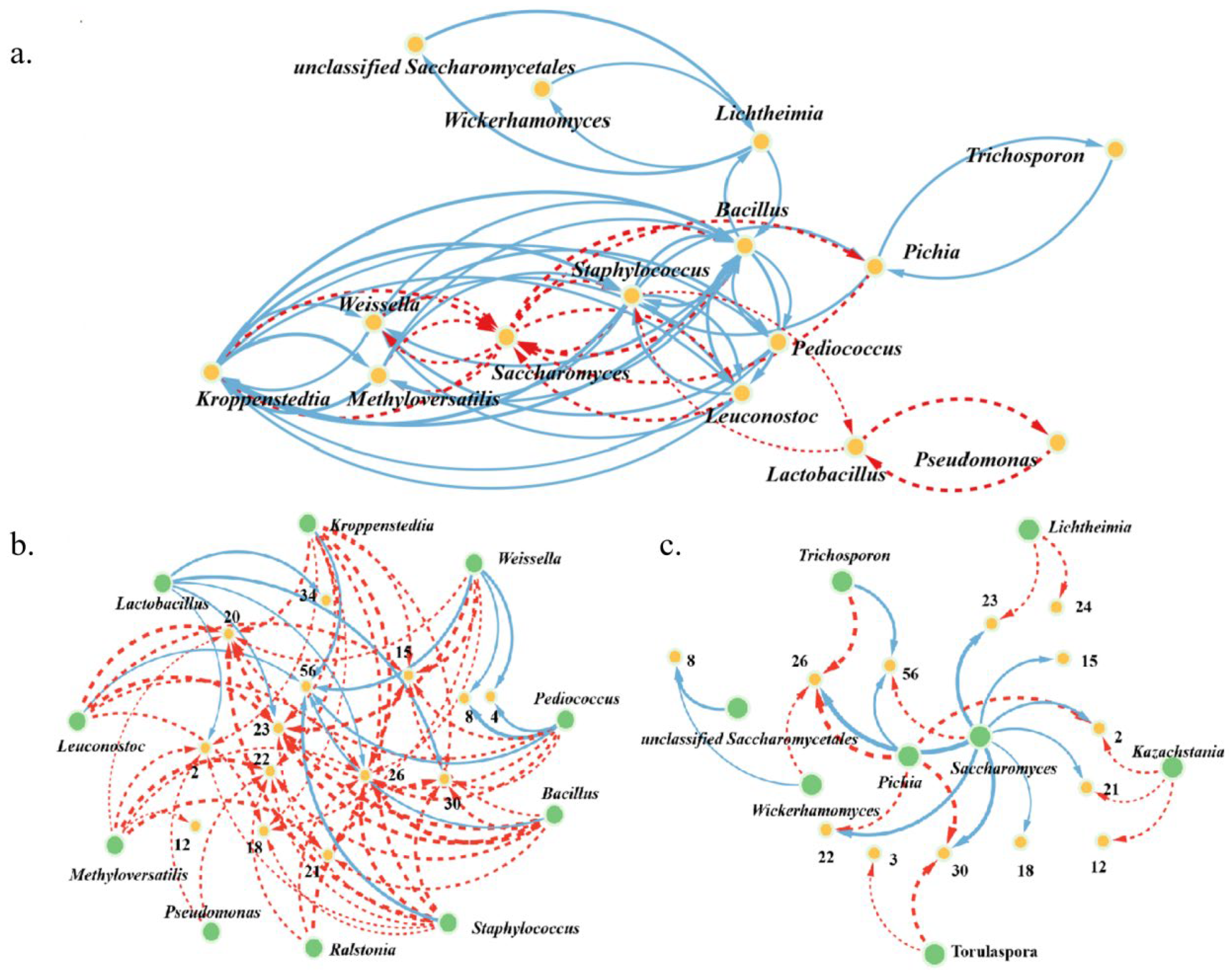
3.4. Correlations between Metabolites and Microbial Communities during the Fermentation of Three Digangs
4. Multi-Algorithm Prediction Aided Verification of Metabolic Correlation
4.1. Establishment of Neural Network Model
4.2. Evaluation of Neural Network Model
4.3. Construction and Evaluation of Other Predicting Models
4.3.1. Construction and Evaluation of Decision Tree Model
4.3.2. Construction and Evaluation of Support Vector Regression Model
4.4. Comparison of Different Predicting Models
5. Discussion
5.1. Microbial Succession Drove Metabolite Shifts in Age-Gradient Vessels
5.2. Ethyl Lactate and Ethyl Acetate Are Indicators of the Fermentation Process
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wolfe, B.E.; Dutton, R.J. Fermented foods as experimentally tractable microbial ecosystems. Cell 2015, 161, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Filippis, F.; Genovese, A.; Ferranti, P.; Gilbert, J.A.; Ercolini, D. Metatranscriptomics reveals temperature-driven functional changes in microbiome impacting cheese maturation rate. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 21871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenzini, E.C.; Lazzari, B.; Tartaglia, G.M.; Farronato, G.; Lanteri, V.; Botti, S.; Biscarini, F.; Cozzi, P.; Stella, A. Oral ecological environment modifications by hard-cheese: From pH to microbiome: A prospective cohort study based on 16s rRNA metabarcoding approach. J. Transl. Med. 2022, 20, 312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, Y.; Du, H.; Zhang, H.; Fang, C.; Jin, G.; Chen, S.; Wu, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, M.; Xu, Y. Geographically associated fungus-bacterium interactions contribute to the formation of geography-dependent flavor during high-complexity spontaneous fermentation. Microbiol. Spectr. 2022, 10, e1822–e1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Du, H.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, Y. Environmental microbiota drives microbial succession and metabolic profiles during chinese liquor fermentation. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2018, 84, e2317–e2369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, M.; Liu, X.; Shi, K.; Peng, F.; Xiao, Y. Effects of Root Zone Aeration on Soil Microbes Species in a Peach Tree Rhizosphere and Root Growth. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 1879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Lu, Z.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Z.; Yu, Y.; Shi, J.; Xu, Z. Metagenomics reveals flavour metabolic network of cereal vinegar microbiota. Food Microbiol. 2017, 62, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, W.; Cao, X.; Cheng, J.; Li, L.; Zhang, T.; Wu, Q.; Xiang, P.; Shen, C.; Li, Q. Chinese baijiu: The perfect works of microorganisms. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 919044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X. Microbial Community Structure and Microbial Source Tracking of Chinese Light-Flavor Liquor Fermentation in Different Environments. Ph.D. Thesis, Jiangnan University, Wuxi, China, 2018. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Gil I Cortiella, M.; Ubeda, C.; Covarrubias, J.I.; Laurie, V.F.; Peña-Neira, Á. Chemical and physical implications of the use of alternative vessels to oak barrels during the production of white wines. Molecules 2021, 26, 554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Fan, W.; Xu, Y. Volatile compounds sorption during the aging of Chinese Liquor (Baijiu) using pottery powder. Food Chem. 2021, 345, 128705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, S.; Hudagula, H.; Minami, N.; Maeno, N.; Yoshida, K.; Onodera, S.; Takeda, Y.; Tobiyama, T.; Nakamura, T.; Hanai, J.; et al. A model study for contributing factors of the fermentation of qvevri wine. Food Control 2023, 148, 109668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Q.; Lin, B.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; He, X.; Yang, P.; Zhou, J.; Guan, X.; Huang, X. Proteomic and high-throughput analysis of protein expression and microbial diversity of microbes from 30- and 300-year pit muds of Chinese Luzhou-flavor liquor. Food Res. Int. 2015, 75, 305–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, Y.; Huang, J.; Zhou, R.; Mao, F.; Pan, Q.; Chen, S.; Lu, Z.; Du, L.; Xie, F. Exploring the response patterns of strong-flavor baijiu brewing microecosystem to fortified Daqu under different pit ages. Food Res. Int. 2022, 155, 111062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Chen, Q.; Wang, Q.; Li, C.; Leng, Y.; Li, S.; Zhou, X.; Han, W.; Li, J.; Zhang, X.; et al. Long-term batch brewing accumulates adaptive microbes, which comprehensively produce more flavorful Chinese liquors. Food Res. Int. 2014, 62, 894–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avershina, E.; Frisli, T.; Rudi, K. De novo semi-alignment of 16s rrna gene sequences for deep phylogenetic characterization of next generation sequencing data. Microbes Environ. 2013, 28, 211–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, G.; Uhl, P.; Zhu, Y.; Wijffels, R.H.; Xu, Y.; Rinzema, A. Modeling of industrial-scale anaerobic solid-state fermentation for Chinese liquor production. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 394, 124942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, L.N. Cyclical learning rates for training neural networks. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV), Santa Rosa, CA, USA, 24–31 March 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Pedregosa, F.; Varoquaux, G.; Gramfort, A.; Michel, V.; Thirion, B.; Grisel, O.; Blondel, M.; Prettenhofer, P.; Weiss, R.; Dubourg, V.; et al. Scikit-learn: Machine learning in python. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2011, 12, 2825–2830. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, Q.; Wang, X.; Zhao, Y.; Zheng, F.; Li, H.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, F. Characterization of key aroma compounds in Laobaigan Chinese Baijiu by GC×GC-TOF/MS and means of molecular sensory science. Flavour Frag. J. 2019, 34, 514–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wu, Z.; Tong, R.; Xu, M.; Ma, H.; Liao, Y. HS-SPME-GC-MS analysis of trace volatile components in fermented grains from liquor production. Food Sci. 2013, 34, 118–124. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhong, M.; Lu, H.; Tang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Pan, C. Research status of potential risk factors identification in Baijiu producting process. J. Food Saf. Food Qual. 2022, 13, 4566–4574. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Moore, B.S. Natural Product Reports 35 years on. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2018, 35, 6–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Averill, C.; Werbin, Z.R.; Atherton, K.F.; Bhatnagar, J.M.; Dietze, M.C. Soil microbiome predictability increases with spatial and taxonomic scale. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2021, 5, 747–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.A.; Zhang, M.; Bhandari, B.; Yang, P.Q. Intelligent detection of flavor changes in ginger during microwave vacuum drying based on LF-NMR. Food Res. Int. 2019, 119, 417–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saber, W.; Al-Askar, A.A.; Ghoneem, K.M. Exclusive biosynthesis of pullulan using taguchi’s approach and decision tree learning algorithm by a novel endophytic Aureobasidium pullulans strain. Polymers 2023, 15, 1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varra, M.O.; Husakova, L.; Patocka, J.; Ghidini, S.; Zanardi, E. Classification of transformed anchovy products based on the use of element patterns and decision trees to assess traceability and country of origin labelling. Food Chem. 2021, 360, 129790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rokach, L. Decision forest: Twenty years of research. Inf. Fusion 2016, 27, 111–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thampi, A.; Hitchman, S.; Coen, S.; Vanholsbeeck, F. Towards real time assessment of intramuscular fat content in meat using optical fiber-based optical coherence tomography. Meat Sci. 2021, 181, 108411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santamaría-Bonfil, G.; Reyes-Ballesteros, A.; Gershenson, C. Wind speed forecasting for wind farms: A method based on support vector regression. Renew. Energy 2016, 85, 790–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, L.; Fu, G.; Liu, T.; Chen, Y.; Wu, S.; Cai, W.; Xie, Z.; Wan, Y. Functional microbial agents enhance ethanol contents and regulate the volatile compounds in Chinese Baijiu. Food Biosci. 2021, 44, 101411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, Z.; Hao, H.; Yan, R.; Wang, X.; Wang, B.; Sun, J.; Li, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, B. Individualization of Chinese alcoholic beverages: Feasibility towards a regulation of organic acids. LWT 2022, 172, 114168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Zhou, J.; He, G. Effect of microbial interaction on flavor quality in Chinese Baijiu fermentation. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 960712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carbonetto, B.; Nidelet, T.; Guezenec, S.; Perez, M.; Segond, D.; Sicard, D. Interactions between kazachstania humilis yeast species and lactic acid bacteria in sourdough. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Xiong, Y.; Xie, Y.; Zhang, H.; Jiang, K.; Pang, X.; Huang, M. Metabolic characteristics of lactic acid bacteria and interaction with yeast isolated from light-flavor Baijiu fermentation. Food Biosci. 2022, 50, 102102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Wang, P.; Fu, X.; Dong, S.; Li, X.; Xiao, D. Increase ethyl acetate production in saccharomyces cerevisiae by genetic engineering of ethyl acetate metabolic pathway. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2019, 46, 801–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, Y.; Li, J.; Wang, L.; Chen, J. Lactic acid biosynthesis pathways and important genes of Lactobacillus panis L7 isolated from the Chinese liquor brewing microbiome. Food Biosci. 2020, 36, 100627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhang, X.; Jian, H.; Xu, X.; Xi, Y. 2019. Biocycle Fermentation Based on Lactic Acid Bacteria and Yeast for the Production of Natural Ethyl Lactate. ACS Omega 2019, 4, 16009–16015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, M.; Geng, Y. Screening and identification of a 4-ethyl guaiacol producing strain in soy sauce fermentation. Food Ferment. Ind. 2021, 47, 18–23. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Bi, J. Effect of dissolved oxygen on the saccharifying enzyme fermentation. China Brew. 2015, 34, 97–100. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, L.; Yang, Q.; Jiang, W.; Li, Q.; Lin, B.; Tang, J.; Chen, S. Mold communities and enzyme activity characteristics in light-flavor Xiaoqu Baijiu. Food Ferment. Ind. 2022, 48, 70–77. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Wang, B.; Sun, Z.; Tan, W.; Zheng, J.; Zhu, W. Effects of modernized fermentation on the microbial community succession and ethyl lactate metabolism in Chinese Baijiu fermentation. Food Res. Int. 2022, 159, 111566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Wang, L.; Wang, H.; Yang, F.; Chen, L.; Hao, F.; Lv, X.; Du, H.; Xu, Y. Effects of initial temperature on microbial community succession rate and volatile flavors during baijiu fermentation process. Food Res. Int. 2021, 141, 109887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, J.; Zhao, D.; Sun, B. Research Progress on the Profile of Trace Components in Baijiu. Food Rev. Int. 2021, 39, 1666–1693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Miao, Z.; Bai, Y.; Wang, X.; Han, C.; Wang, B.; Li, Z.; Sun, J.; Zheng, F.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, B. Unravelling Metabolic Heterogeneity of Chinese Baijiu Fermentation in Age-Gradient Vessels. Foods 2023, 12, 3425. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12183425
Miao Z, Bai Y, Wang X, Han C, Wang B, Li Z, Sun J, Zheng F, Zhang Y, Sun B. Unravelling Metabolic Heterogeneity of Chinese Baijiu Fermentation in Age-Gradient Vessels. Foods. 2023; 12(18):3425. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12183425
Chicago/Turabian StyleMiao, Zijian, Yu Bai, Xinlei Wang, Chao Han, Bowen Wang, Zexia Li, Jinyuan Sun, Fuping Zheng, Yuhang Zhang, and Baoguo Sun. 2023. "Unravelling Metabolic Heterogeneity of Chinese Baijiu Fermentation in Age-Gradient Vessels" Foods 12, no. 18: 3425. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12183425
APA StyleMiao, Z., Bai, Y., Wang, X., Han, C., Wang, B., Li, Z., Sun, J., Zheng, F., Zhang, Y., & Sun, B. (2023). Unravelling Metabolic Heterogeneity of Chinese Baijiu Fermentation in Age-Gradient Vessels. Foods, 12(18), 3425. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12183425




